When carrying out construction work, the question often arises as to which brand of insulation is best to use to create a layer of thermal insulation before finishing the facade. Most professional builders give their preference to domestic insulation TechnoNIKOL. From this article you will learn how to choose the right option and method of insulation, as well as the advantages of thermal insulation material of the specified brand.
- 3.1 "Wet" method
Insulating composition of rolled waterproofing materials
The main ingredients for such materials can be bitumen compositions, bitumen-polymer compositions and membrane waterproofing.
Bitumen waterproofing composition is bitumen resin mixed with crushed basalt-shale chips. This combination is used in the production of roofing felt, construction roofing felt and glass roofing felt.
The bitumen-polymer composition is obtained by adding special additives to bitumen designed to increase its elasticity and heat resistance. Plastic modifiers in such compositions are artificial rubber (or plastic). Such modifying additives are needed to increase the resistance of the bitumen component to temperature changes and ultraviolet radiation, which makes it possible to use this type of coating in areas with hot climates.
Membrane insulation belongs to a new generation of high-tech materials. It is made of high or low density polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride or polyophepine and is a thin film with a thickness of 0.2 - 2 mm. For some types of membrane waterproofing coating, a layer of corrugation is applied for more effective adhesion to the solution.
The advantages of waterproofing membranes are their mechanical strength, resistance to damage, long service life (up to 50 years), environmental friendliness, resistance to rotting and decomposition, as well as a wide temperature range from -40 to +50 degrees Celsius.
The brand's roll waterproofing is one of the main leaders among waterproofing building materials in this segment of the international market. The reason for such a high popularity of this type of TechnoNIKOL product is:
- their high level of reliability and effectiveness of protection against moisture penetration and the formation of condensate accumulations;
- biological and chemical stability;
- the ability to maintain flexibility and elasticity at low temperatures;
- the ability to withstand significant tensile loads;
- long-term (about 35 years) service life;
- efficiency;
- ease of installation.
Why choose TechnoNikol products
TechnoNikol basalt insulation is very popular among builders, as it has the following advantages:
- Low thermal conductivity.
The finest interwoven fibers, representing the structure of the material, hold a large volume of air, which remains in a stationary state. As a result, the resistance to heat transfer increases significantly, so in the cold season the room is warm, and in the heat it is cool.
- Long service life.
Stone wool is able to perform its function throughout the entire service life of the building without losing its original properties.
- Protection from aggressive environments.
The insulation does not interact chemically with other materials and many compounds.
- Resistance to biological factors.
Basalt wool does not rot, does not serve as a favorable environment for the development of fungi, and is not food or shelter for rodents.
- Manufacturability.
The material can be easily processed with hand-held cutting tools and is easy to install.
- Environmentally friendly.
All components of the heat insulator are safe for human health and the environment. Production waste is reused.
- Vapor permeability.
Air easily penetrates through the fibrous structure of the insulation, so moisture does not accumulate in it, and a comfortable microclimate is created in the room.
- Non-flammability.
The insulation is based on rocks with a melting point above 1000℃.
- High sound insulation characteristics.
Sound waves are effectively absorbed by the fine-porous structure, which allows the insulation to be used as a sound insulator.
- Hydrophobicity.
The use of special water-repellent additives during production makes the material water-repellent. This has a positive effect on its ability to retain heat.
Classification of offers from TechnoNIKOL
Manufacturer TechnoNIKOL divides its products into different classes, depending on the specific tasks and roofs for which they will be used.
Let's look at them in more detail, so that you don't overpay just for the big name, and it turns out that for the flat roof of your house you could have originally chosen a simpler material.
As you may have guessed from the subtitle, this type of roofing is applied to the most significant facilities in the country. The material is designed to solve a number of problems at once, the main of which is high reliability and guarantees.
Buyers of such roofing are usually provided with full technical and information support. In a word, any plant contacted a TechnoNIKOL representative, and the roofing was done, without searching for additional contractors and without any worries about quality.
These are brands of the Technoelast series, which were specially developed to solve specific problems, such as installation features, heat resistance and fire safety requirements.
These materials are designed to be easy to work with and the quality remains high. Business class roofing is considered the most popular in the modern construction world, and TechnoNIKOL also has a support service for its sales.
If you initially selected a built-up roof for your garage, then the economy class is just what you need. They cope with the main function quite well. And to lay such a roof you do not need expensive or special equipment.
Detailed description
Foundation waterproofing TechnoNIKOL is a self-adhesive waterproofing baseless bitumen-polymer material. The upper side of the material consists of a high-strength polymer film that protects the waterproofing layer from mechanical damage. The underside of the material is covered with a protective polyethylene film, which must be removed at the installation stage.
Designed for waterproofing shallow foundations (up to 3 m) with low groundwater levels. The upper side of the material not only protects the waterproofing from mechanical damage, but also from exposure to a chemically aggressive environment. The material is laid in 1 layer. Quick and simple installation (installation can be carried out by 1 person without professional skills or additional equipment) Laying is possible on a flammable base
Installation features
Builders practice two methods of facade insulation - wet and dry. Let's look at them in more detail.
"Wet" method
When finishing a facade using this method, moisture-containing materials (plaster, adhesive solutions, etc.) are used. The method involves the use of insulation with a low level of water absorption. The technology of the “wet” method is as follows: the insulation is fixed to the surface using glue, after which it is additionally secured with umbrella dowels (five or more pieces per square meter) or anchors. A layer of waterproofing solution is applied on top. Then the surface is reinforced with a metal mesh, which is also covered with a waterproof layer. The soil is applied next. The final stage is applying plaster and painting the surface.
This method prevents the insulation from deforming during operation and reliably fixes its position. In addition, it is characterized by low cost and ease of installation. However, it cannot be used at air temperatures below 5 °C.
"Dry" method

During the insulation process, the insulating material is attached to the wall and covered with a hydro- and windproof membrane layer, which protects the insulation from getting wet. Then, using a special metal frame (aluminum or stainless steel), a free space of up to 50 mm wide is created between the cladding and the insulation layer. Finishing is carried out using siding, porcelain stoneware or plastic panels and other ready-made facing materials. This system provides good ventilation and evaporation of condensate, which guarantees its strength and long service life. Using a frame allows you to hide the imperfections of the walls, since it does not require cleaning and leveling them before insulation. In addition, the finishing procedure using this method can be carried out in any weather conditions, regardless of the time of year.
Insulation of a house is necessary for comfortable living in it. The use of thermal insulation will ensure that the room maintains a warm and dry environment, and will also increase the level of noise absorption. However, for this you need to be confident in the quality of the material used and the professionalism of the builders who install it.
Waterproofing for wooden flat roofs
Unlike pitched structures, water or snow can accumulate on a flat surface, so it is necessary that the waterproofing be sealed.

Welded waterproofing will allow you to thoroughly cover the roof surface from moisture penetration Source thesamaritancounselingcenter.org
The wooden roof itself consists of rafter legs located at some distance from each other. A sparse sheathing is mounted perpendicular to them. Then the wooden flooring is laid. Since TechnoNIKOL roof waterproofing is installed without the use of open fire, it can be successfully used for wooden structures.
The presence of self-adhesive edges makes it possible to achieve complete tightness of the laid waterproofing as simply as possible.
Variety of TechnoNIKOL insulation materials
Thermal insulation of domestic manufacturers is represented by two main classes of insulation: mineral wool and extruded polystyrene foam .
TechnoNIKOL mineral wool consists of the finest threads of rocks. Between the weaves of basalt there are air cells. This combination provides excellent performance. Stone threads are responsible for the strength and fire resistance of the material, and many air cells give basalt slabs the necessary heat capacity .
Extruded polystyrene foam (EPS) is produced by combining styrene with special foaming additives. All components are mixed under high heat and pressure. The prepared mass is passed through an extruder - the output is slabs with a smooth surface .
Competitive advantages of EPS: light weight, ease of installation and rigidity . Excellent strength characteristics make it possible to use polystyrene foam in areas where a soft thermal insulator is not suitable. The disadvantages of EPS are flammability and the release of acrid smoke when burning.
Purpose of TechnoNIKOL roll insulation for foundations
The manufacturer in question is one of the leaders in the Russian market in the production of roll-type moisture protection (4 mm), which is mounted both externally and internally. Let's take a closer look at film 1 for finishing the base of the house:
- High-quality surface protection from water (TechnoNIKOL aquamast bitumen mastic).
- Cut-off insulation that does not allow small moisture vapors to pass through (TechnoNIKOL 600, providing reliable protection of structures).
- Bipole EPP 3 allows the surface of the structure to breathe and does not allow moisture to pass through, which is why fungus does not appear.
As a rule, the foundation is constantly exposed to groundwater, which is why it can quickly collapse. To avoid such a problem, roll insulation is used, which reliably protects the structure.
Among most manufacturers, this particular brand stands out, since its products have an optimal price-quality ratio, thanks to which even corporate developers are often the company’s clients.

Installation of insulation
Each type of insulation has its own installation technology. At the same time, it can vary depending on what kind of building structure is insulated. The standard insulation scheme looks like this:
- calculation of the necessary materials is carried out (insulation, vapor barrier film, timber for sheathing, fasteners, etc.);
- a set of tools and devices is prepared, materials are purchased;
- preparatory work is being carried out;
- insulation is attached;
- if necessary, vapor barrier work is carried out;
- The finishing of the walls is carried out outside and inside, and the ceiling from the inside.
A detailed description of each type of thermal insulation work using TechnoNIKOL insulation can be found on our website Stroy.Guru.Com:
- insulation of roof structures:
- “Is it possible to insulate a roof with foam plastic and how?” – the instructions for insulation are the same for EPS and PIR boards;
- “Insulation of a polyurethane foam roof with your own hands”;
- “Insulating the roof of a private house with mineral wool.”
- ceiling:
- "Ceiling insulation with mineral wool."
- facade:
- “Do-it-yourself insulation of walls with mineral wool”;
- “Do-it-yourself insulation of polyurethane foam walls”;
- “Technology for insulating walls with basalt wool”;
- “How to insulate internal and external walls with foam plastic” - the technology is suitable for extruded polystyrene foam and PIR boards.
- gender:
- “Insulation of polyurethane foam floors with your own hands”;
- “Floor insulation with mineral wool”;
- “How to insulate a floor with foam plastic.”
Foundation insulation
In addition to insulating from moisture, it is better to immediately insulate the foundation. Almost certainly, after the first winter, the owners will decide to cover the base with insulation - heat losses are at least 10% in the absence of a coating.

TechnoNIKOL insulation materials
TechnoNIKOL brand insulation is frost-resistant insulation with minimal hygroscopicity, steam absorption, and resistance to mechanical loads.
Products made from polystyrene foam and polyurethane foam are suitable for external cladding. The latter type of thermal insulation is recommended due to the peculiarities of the structure: foam material is sprayed onto the base, so seams and cold bridges are eliminated.
Characteristics
Each type of insulation has its own technical and operational characteristics.
Basalt wool
TechnoNIKOL basalt insulation has performance indicators that are attractive to consumers:
- thermal conductivity - 0.048-0.077 W/(m K);
- density - 28-210 kg/m3. The value of the indicator depends on the purpose of the insulation. So, for inclined surfaces the most optimal density will be 35-40 kg/m3, for a facade - 80-100 kg/m3, and for a screed on the floor or on a flat roof - 150-210 kg/m3;
- vapor permeability - 0.25-0.35 mg/m2*h*Pa;
- strength:
- for compression - 8-60 kPa;
- separation of horizontal layers from each other - 80 kPa;
- bending - 0.15 MPa.
- durability - more than 50 years;
- operating temperature: from -170oC to +1000oC.

In addition, cotton wool does not burn (flammability class NG) and does not absorb moisture—hygroscopicity is completely absent (water absorption is only 0.095% after 24 hours of soaking). More details about the performance of basalt mats can be found in the work “Basalt Slab”.
Extruded polystyrene foam
A feature of extruded polystyrene foam produced at the enterprises of the TechnoNIKOL concern is the inclusion of carbon in the form of nanoparticles in the insulation composition. This significantly changed all technical parameters of the material: thermal conductivity, service life and physical and mechanical properties. Therefore, the digital values given below may differ significantly from the generally accepted ones (data taken from the official website of the company www.tn.ru):
- thermal conductivity coefficient - 0.029-0.035 W/(m K);
- density - 26-36 kg/m3;
- bending strength - 0.025-1.0 MPa;
- vapor permeability - 0.005-0.011 mg/m2*h*Pa;
- flammability class - G3-G4 (note that the company honestly indicates the flammability class);
- durability - more than 50 years.
Liquid polyurethane foam
One-component polyurethane foam has open cells, and therefore its technical characteristics differ significantly from those of two-component polyurethane foam:
- thermal conductivity coefficient - 0.025-0.045 W/(m×°K);
- vapor permeability - 0.07-0.17 mg/(m*h*Pa);
- density - 8-18 kg/m3;
- moisture absorption - 10.0-60.0%;
- compressive strength - about 1.02 kgf/cm2;
- bending strength - about 17.0 kgf/cm2.
PIR thermal insulation boards
PPU slabs have the best technical and operational indicators among all insulation products on the market. Among them:
- thermal conductivity - 0.028-0.030 W/(m×°K). The manufacturer indicates a value of 0.021 W/(m×°K), which raises reasonable doubts. The work “PUF Slabs” explains in detail why;
- density - 40-160 kg/m3;
- vapor permeability - 0.02-0.05 mg/(m*h*Pa);
- strength:
- when compressed to failure - 200 kPa or more;
- bending for fracture - not less than 300 kPa.
- water absorption when immersed in water for a day is 1-1.5%.
Symbols for roll waterproofing brands
In addition to the name of the model of waterproofing material, the name contains letter markings. Each of the letters denotes a specific feature inherent in this brand of waterproofing agent, based on the use of a specific base and the characteristics of the protective layer.
| Characteristic feature | Explanation of markings |
| Base used | E – polyester fiber |
| O – natural (organic) base – cardboard | |
| C – soft fiberglass | |
| X – fiberglass | |
| T – fiberglass frame | |
| Top protective layer | P – film |
| K – coarse crumbs | |
| M – fine-grained crumbs | |
| bottom layer | C – self-adhesive layer |
| M - fine-grained crumbs (sand) | |
| B – layer with VENT channel |
Thus, the roll insulation of the Uniflex HPP model stands for a material with a fiberglass base, covered with a protective film on both sides.
Criteria for choosing stone wool

- If you are going to insulate a roof that is built with a slope, then buy a heat insulator that has a thickness of 15 centimeters and a density of up to 40 kilograms per cubic meter. Otherwise, over time the insulation risks sagging.
- To insulate interior partitions, use stone wool with a density of up to 50 kg/m3. This indicator will provide the necessary noise insulation.
- It is recommended to insulate load-bearing walls from the outside. This way you will move the dew point, where condensation will appear, outside. It is advisable to use stone wool with a thickness of about 10 centimeters and a density of at least 80 kilograms per cubic meter.
- To insulate a ventilated façade, choose cotton wool that consists of two layers, or lay the material in two layers. Moreover, each will have a different density: loose - near the walls, dense - outside.
Rocklight

It is a lightweight basalt wool slab with a low content of phenolic additives. Distinctive features:
- environmental friendliness and relatively low strength;
- does not absorb moisture, retains heat well and provides sound insulation;
- universal for use in the construction of private houses - suitable for attics, frame walls, walls with light finishing (siding), flooring and partitions.
Heatroll

Supplied in rolls, the fabric of which is a very light mat based on basalt wool fibers. Its key characteristics:
- low content of harmful substances and extremely low density;
- non-flammable and moisture-permeable;
- from the point of view of insulating characteristics - Heatroll is universal. However, it should be used where the insulation layer will not absorb external loads - when arranging attics and ceilings. Suitable for insulating floors if they are leveled on joists and not on slabs.
How to make your bedroom warm and cozy
Technoacoustic

Plates with a special arrangement of mineral fibers, providing a high level of sound absorption. In addition to non-flammability and moisture resistance, the following should be noted:
- the main scope of application is the arrangement of sound insulation of frame partitions, suspended ceilings and ceilings between floors with laying on joists, without load;
- can be used both in apartments and office premises;
- the material has a low compressibility index, which allows it to work without shrinkage as part of vertical structures for 50 years or more.
Technoblock

More dense and incompressible (compared to those listed) mineral wool slabs with a low phenol content in the binder.
- similar to Technoacoustic slabs, they provide both thermal insulation and noise protection;
- can be used to construct layered wall masonry (unlike expanded polystyrene, these boards are vapor-permeable), both with and without an air gap, as well as frame walls.
Mineral wool used for external heat and sound insulation of brick and concrete walls under plaster.

Technoflor
The material is intended for insulation of floors subject to severe weight and vibration loads. Indispensable for arranging gyms, production workshops and warehouses. The cement screed is poured over the mineral slabs. The material has low moisture absorption and is often used in combination with a “warm floor” system.
Techno T
The material has a narrow specialization and is used for thermal insulation of technological equipment. The slabs have increased hardness and high heat resistance, allowing the mineral wool to easily withstand temperatures from minus 180 to plus 750 degrees. This allows you to isolate gas ducts, electric precipitators and other engineering systems.

Technovent
A non-shrinking board of increased rigidity, used for insulation of ventilated external systems, and also used as an intermediate layer in plastered facades.

Technoruf
High-density mineral wool designed for insulation of reinforced concrete floors and metal roofing. Sometimes used to insulate floors that are not equipped with a concrete screed. The slabs have a slight slope, necessary to drain moisture to the drainage areas, and are covered with fiberglass.

Types of insulating materials

During construction and finishing work, the following thermal insulation options are used:
- Styrofoam. Its advantages are availability, ease of use and low price. However, such insulation is not highly durable and is also highly flammable.
- Fiberglass. Due to its structure, which includes many long, parallel fibers, it is characterized by good ductility. In addition, such an insulating layer is practically incapable of ignition.
- Expanded polystyrene. It is often used when finishing lower floors and basements, as well as saunas and baths, since it practically does not absorb water and is impenetrable to steam.
- Slabs made of basalt and other minerals. Due to their composition, they are resistant to mechanical stress and also insulate heat well.
- Foam glass. This material, obtained by melting glass, is durable, resistant to mechanical damage and at the same time non-flammable.
TechnoNIKOL insulation has various forms of release, due to which it is widely used in a variety of areas of construction. It is especially often used for insulating building facades.
Characteristics of Technoelast ALPHA

This roll waterproofing "TechnoNIKOL" is a material made from polyester. During the production process, the latter is combined with an aluminum screen that is capable of retaining gas. On both sides, insulation is carried out by applying a bitumen-polymer binder layer. The presence of a metal screen inside the material allows it to exhibit the ability to protect underground premises from the spread of gases such as methane and radon.
The material can be used in all climatic zones and has increased waterproofing capabilities. A polymer film is used as the upper and lower protective layers. Its thickness is 4 mm, the error in both directions can be 0.1 mm. The mass of one square meter is 4.95 kg with an error of 0.25 kg. It is also worth asking about the breaking force in the transverse and longitudinal directions. These characteristics are 400 and 600 N, respectively.
On a beam with a radius of 25 mm, the flexibility temperature does not exceed -20 °C, while the heat resistance is 100 °C. The length and width of the roll are 10 and 1 m, respectively. As for vapor permeability, in this case it is 0 kg/(m.s.Pa).
Features of basalt insulation
Basalt insulation is a material made from fibers obtained at high temperatures from igneous hard rocks under special technological conditions. When solid rock melted on special equipment flows through holes of a certain diameter, threads are formed, which are then used to make insulating mats and rolls.
Basalt fiber has sizes from several units to hundreds of microns. It largely determines the rigidity of finished products, as well as their thermal insulation properties.
It can be successfully used:
- for a frame house;
- for facade;
- for the roof;
- for floor and ceiling
TOP 3 best products according to customers
Basalt wool Rockwool Acoustic Butts 1000x600x100 mm - heat-insulating, sound-absorbing.
Izovol Izobel L-25 insulation is used for heat, sound and fire insulation of non-load-bearing structures.
Insulation with membrane
When ground moisture lies high or there is a lot of it, protection is used in the form of a drainage system. When assembling drainage, membrane waterproofing is used, which is created on the basis of high-density polymers.

PVC membrane
During the work process, the foundation is partially excavated, dried, covered with a primer and waterproofing, and then a membrane is installed. The purpose of the membrane sheet is to collect excess water and redirect the liquid to the drainage pipes.
The canvas is laid so that the rounded spikes remain outside. The material is resistant to cold down to -50 degrees, durable, however, does not at all interfere with the movement of air flows. Under the shelter, neither concrete nor earth will rot - ventilation proceeds almost as usual.
Extruded polystyrene foam - application features
Expanded polystyrene insulators are combined into one series - Carbon. The materials have similar characteristics, but differ in release form. The type of execution largely determines the scope of use of EPS.
Material characteristics
The insulation is produced by extrusion. As a result, many sealed cells are formed. The composition and structure of expanded polystyrene endowed the heat insulator with the following properties:
- Low thermal conductivity. An indicator of 0.028-0.035 W/m*C puts the material among the leaders in terms of thermal efficiency.
- Hydrophobicity. EPS does not absorb moisture and retains its characteristics in a humid environment.
- Moderate combustion. The use of carbon made it possible to minimize the flammability of polystyrene foam - when the material melts, burning drops do not form .
- Insulation thickness – 20-120 mm. The choice depends on the area of use.
- The thermal insulator is resistant to fungus, mold, and pests.
- The operating temperature range is comparable to that of basalt insulation - from -50°C to +75°C.
Weaknesses of EPPS: vulnerability to gasoline, solvents, UV rays, fire.
Carbon: variety of product items
Types of extruded polystyrene foam TechnoNIKOL Carbon:
- Eco - slabs of various thicknesses (20-100 mm) for insulation of low-rise buildings and cottages.
- Drain – one side of the EPS has drainage grooves. The holes provide improved ventilation when insulating a flat roof or draining rainwater when insulating a foundation.
- Eco Fas – arrangement of house plinths, plastered facades. Milling on the outside ensures good adhesion to various surfaces.
- Eco SP – suitable for insulating foundations using the Swedish plate method. The foundation includes communications and a floor heating system. Eco SP has increased rigidity and very low thermal conductivity .
- Prof – maximum strength. Application – insulation of floors on the ground, various foundations, flat roofs.
- Prof Slope is a combination of five slabs forming a wedge-shaped insulation.
- Solid – high strength due to closed cells. Used on an industrial scale: insulation of highways, floors under load, railway tracks.
Types of insulating materials
Modern roll waterproofing is divided into classes according to different criteria:
- according to the method of attachment to the base;
- according to the base material used.
Based on the method of fastening, insulating materials are divided into welded, adhesive or mechanically fixed.
Welded waterproofing
The welded insulating material is a rot-resistant base with a layer of binder coating applied to it. The lower part of the roof insulation is a layer of polyethylene, which when heated by the burners melts and is firmly fixed to the surface.

The basis of the fused insulation can be fiberglass/fiberglass, polyester. These materials replaced the cardboard traditionally used in previous years.
The astringent component of roll waterproofing is bitumen or bitumen-polymer mastics, often with the addition of APP (atactic polypropylene), called artificial plastic or artificial rubber SBS (styrene-butadiene-styrene).
Fused roll waterproofing is the most commonly used roofing material. Its popularity is due to its high performance characteristics, easy installation and affordable price. Fused roofing can be installed at any time of the year and on any base. In addition, the fused insulation laid in accordance with the technology is a single whole; there are practically no cracks or joints in it, which enhances its waterproofing properties.
Mechanically fastened roll waterproofing
Unlike built-up waterproofing, in mechanically fixed roll roofing material the bottom layer is not a polyethylene film, but fine-grained sand. The prototype of roll waterproofing with mechanical fastening to the surface is the well-known roofing material.

Modern waterproofing is produced in rolls; the canvas is attached to the base using self-tapping screws or overhead strips. The disadvantage of using this option for fastening insulation is the laboriousness of installation and reduced effectiveness in protecting the roof/foundation from moisture penetration.
Adhesive (adhesive) waterproofing
Adhesive waterproofing, similar to built-up waterproofing, has a base made of PVC or fiberglass with an applied bitumen-polymer component and mineral topping. To install the adhesive waterproofing, mastics or glue based on epoxy resin are used. Reliable protection against moisture is achieved by installing 2-5 layers of insulating material.

Pasted waterproofing can be mounted on any base; their installation does not require special knowledge or additional tools. The main condition for flawless waterproofing using adhesive materials is a flat base surface, without protrusions or irregularities. In addition, adhesive waterproofing requires drying conditions, so installation is carried out in warm, rainy weather.
Range of insulation materials and prices
The company produces insulation with dimensions and technical characteristics for specific building structures. To make it easy for the consumer to navigate the variety of products presented, each type is given its own name.
Basalt wool
The most widely represented line of basalt mats. The manufacturer offers slabs and rolls:
- "Rocklight";
- "Technoruf";
- "Technovent";
- "Technolight";
- "Technoflor";
- "Technofas";
- "Technoblock";
- "Technoroll".
"Rocklight." Lightweight basalt fiber slabs (density 35 kg/m3) for external and internal thermal insulation of horizontal and vertical structures in private homes: attic walls and frame buildings, floors, internal partitions; ceiling from the attic, pitched roofs.

Available in two sizes:
- 120x60x5 cm at a price of 170 rubles/m2;
- 120x60x10 cm costing about 250 rubles/m2.
"Technoruf". The main purpose is to insulate facades using the “wet” method under decorative plaster or painting and flat roofs under screed. For this purpose, the company produces Tekhnoruf slabs with a density of 140 kg/m3 and high delamination strength (at least 15 kPa). In addition, we have mastered the production of wedge-shaped insulation (Tekhnoruf n prof).
The length and width dimensions are standard: 120x60 cm. The thickness can be any in the range of 20-100 mm. A slab with a thickness of 120 mm can be produced upon request. The price is high, starting from 7,000 rubles/m3.
"Technovent". Specialized insulation for walls with ventilated facades. The manufacturer also allows for use as a middle layer in the “wet” method of insulation for painting and decorative plaster with a thin solution thickness. You can buy it for 2.8-3.2 thousand rubles/m3.
"Technolight". "Technolight" is another specialized type of basalt wool - insulation for pitched roofs. According to its characteristics, it can also be used for internal insulation of balcony walls along the frame, ceilings and walls from inside the apartment along the sheathing, and wooden floors along the joists - it can only be fastened by surprise.
But when used for other purposes than its intended purpose, you need to look at how much 1 m2 of this type of mat costs, because... for profile heat insulators it may be lower. The cost of 1 m3 is about 1800 rubles.
"Technoflor". Thermal insulator with high compressive strength, withstands up to 50 kPa and a density of about 170 kg/m3 is intended for insulation of floors with increased load: sports facilities, warehouses and industrial premises. Therefore, it is practically not used in private construction (it is used for insulating flat roofs of residential buildings). It is expensive - 4,960 rubles/m3 or more.
"Technofas". The entire line of this brand of basalt mats belongs to the best facade insulation materials from TechnoNIKOL. It is used for insulation of buildings made of brick and concrete with subsequent finishing with building mixtures. The price ranges from 3,300 to 5,500 rubles/m3, which is a bit expensive for the middle class.
"Technoblock". The material was created for insulating walls using the “well” method, when the insulating layer is placed between two walls: load-bearing and decorative. It has a high density, which allows it to withstand significant loads on the edge when the mats are supported on each other. But it does not always have the same compressive strength along the plane. Therefore, it is not used for horizontal insulation. The price fluctuates around 2,180-2,470 rubles/m3.
"Technoroll". The only type of basalt insulation that is sold not in sheets in packs, but in rolls. Mat length is 4,000 mm, width - 1,000 mm, standard thickness: 50 and 100 mm. Lightweight (density 30 kg/m3), and therefore its use is possible where there are no static loads on the surface of the heat insulator: when insulating floors along joists, attics and ceilings. The price is budget.

For information: At the time of writing, the company has temporarily suspended the production of rolled material. Therefore, it is not possible to indicate a more accurate price.
Extruded polystyrene foam
For private construction, according to technical indicators, the most optimal option is extruded polystyrene foam, produced under the general name “Carbon”. The following types of insulation can be found on sale:
- XPS CARBON ECO;
- XPS CARBON ECO DRAIN;
- XPS CARBON ECO FAS;
- CARBON ECO SP;
- CARBON PROF;
- CARBON PROF SLOPE;
- CARBON SOLID;
- XPS CARBON SAND;
- C-XPS CARBON.

XPS CARBON ECO. The slabs of this series are the basic ones in the Eco line. They are used in low-rise construction to insulate foundations, floors, roofs and facades. They burn well, so they are not recommended for use for insulating walls and ceilings from the inside of rooms. A pack of 8 slabs measuring 1180x580x50 mm can be purchased for 1230-1252 rubles.
XPS CARBON ECO DRAIN. They have a distinctive feature - drainage grooves, which allows the following functions to be performed when insulating the foundation and flat roof:
- drain rain and groundwater;
- organize microventilation of the roof.

1 m3 of such a slab costs from 17,590 rubles.
XPS CARBON ECO FAS. Specialized insulation for facades under plaster. Technical characteristics allow it to be used when insulating walls using the “well” method, pitched roofs, ceilings from the attic side and floors under screed. A distinctive feature is that it has excellent adhesion to mortars and all kinds of adhesives based on cement and gypsum. Price from 215 rub./m2.
CARBON ECO SP. Rigid and very durable insulation is used for thermal insulation of shallow foundations using the “insulated Swedish slab” type. It has no analogues of Russian origin. A package of 4 slabs measuring 2360x580x100 costs RUB 2,670-2,780.

CARBON PROF. CARBON PROF slabs are the basic version of insulation for multi-storey construction. The Prof line from Eco is distinguished by:
- reduced flammability class due to the addition of fire retardants;
- the presence of a special edge to speed up installation (some Eco series also have it);
- ability to withstand significant loads during operation.
The slab is used to insulate foundations, flat roofs and floors along the ground and under the screed. Insulation costs from RUB 4,090/m3.
CARBON PROF SLOPE. The original form of insulation, patented by the company, for a pitched roof. Consists of 5 wedges of different sizes. When assembled, a slope is created to remove water from wet areas of the rafter system. 1 m3 costs more than 6,000 rubles.

CARBON SOLID. EPPS CARBON SOLID is an ideal insulation material for floors. It can also be used when laying highways and railway tracks - it does not deform under loads and does not swell in a humid environment. The price starts from 6,490 rubles/m3.
XPS CARBON SAND. The slabs are produced for companies producing sandwich panels.
C-XPS CARBON. The main purpose is laying on top of a “dry” floor screed. Can be used for thermal insulation of other building structures during renovation. Cost of 1 m2 - from 865 rubles.
Calculation nuances
It must be taken into account that the calculation of the screed is made taking into account its constituent components. The main substances are cement and sand, to which the necessary additives are mixed. The mixture is made by adding water. The final result depends on the resulting ratio.
The material consumption can also be affected by the purpose of the coating:
- Creating a surface that will be used in a technical room. This could be the floor in a utility room or garage.
- Pouring a rough coating with a thickness of 80 mm or more. For this purpose, a concrete mixture for floor screed, which includes a coarse fraction, is best suited. To obtain lower values, a cement-sand mortar also copes with the task, but subject to reinforcement.
- The finishing option, which serves as the basis for subsequent cladding with decorative materials. The coating has a thickness from 5 to 30 mm.
Specifications
Physical and mechanical characteristics determine the suitability of a particular material for the specific needs of the buyer. The slabs differ in strength, slope, thickness and cost.

Fire resistance
Most insulating materials are non-flammable. The flammability group of raw materials has its own marks. For example, “Pir” thermal insulation boards for bathhouses and balconies are marked with the G4 mark. Materials with a lining of fiberglass and foil have indicators G1 and G2.
Extrusion varieties “Eco” and professional insulation with carbon have indicators G 3 and G4. In this case, smoke generation and flammability are marked with D3 and B2. Techno stitching materials are a non-flammable type of heat-insulating material for any material thickness (from 30 to 80 mm). Options based on basalt and basalite sandwich are marked NG (non-flammable).

Thermal conductivity
The performance of each material is different. For example, the thermal conductivity level is:
- technical heat insulators – 0.037-0.041 W/mS;
- extrusion analogues in the form of plates – 0.032 W/mS;
- thermal insulation boards “Pir” – 0.021 W/mS;
- analogues based on basalt – 0.038-0.042 W/mS;
- options for shipbuilding – 0.033-0.088 W/mS.
What structural elements of a building are affected by groundwater ↑
When we talk about the need to protect the foundation from moisture, we significantly narrow the problem. In fact, the floor and walls of the basement, the walls of the basement and the house, internal partitions, windows and doors in places where they adjoin the walls, as well as the ceiling of the lower level are also subject to destructive effects.
Moisture spreads perfectly in the middle of the structure of almost any material, as well as along its surface. Therefore, in order to prevent the occurrence of the above problems, it is necessary to create a continuous waterproofing layer on the side where the building is exposed to hydrostatic pressure, and also to suppress capillary rise of water. First of all, you need to protect the foundation.
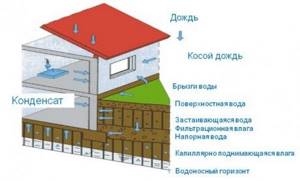
Types and sources of water and moisture
Penoplex floor insulation technology under screed
As mentioned above, the insulation technology will directly depend on the base surface on which the entire floor structure with screed will be laid. Therefore, it is worth considering various options.
Insulated floor on concrete base
If we talk about the insulation of concrete floors in apartments, then there is a difference in the technologies for thermal insulation of the floors of the first floor and all subsequent ones.
In apartments located above the basement, the floors are always colder. In addition, there is a risk of dampness and mold, so it is recommended to carry out thermal insulation work before moving into a new home. In such rooms, more layers of different materials are used, which will prevent the room from cooling down and also protect it from moisture penetration.
The first thing that needs to be done before moving on to the main work is to thoroughly prepare the surface. It is carried out the same way for concrete floors of apartments, regardless of the floor.
You may be interested in information on how to install a heated floor on a balcony with your own hands
Surface preparation
Although this stage of work is not considered the main one, it is extremely important, and the process must be taken seriously.
- The first step is to clean the surface from the old floor covering, the remains of the glue on which it was laid, or “blots” of concrete mortar that have hardened in certain areas of the floor.

Cleaning the floor surface from large irregularities
It is very important to thoroughly clean the entire surface, otherwise concrete build-up will interfere with the installation of insulating material.
- Then, all debris is removed from the floor, and dust from the surface is swept out to clean concrete.

Cleaning the surface from debris and dust
- Next, all holes and recesses are sealed - this work can be done using special repair putties. It will be more profitable to seal deep flaws with polyurethane foam.

Repairing large defects with polyurethane foam
After the foam has hardened, the protruding excess is cut off flush with the floor surface.

As it hardens, excess foam is cut off
- Next, the entire floor surface must be carefully primed with a special deep penetration compound.

It is better to apply the primer in several layers
The primer on the surface should dry well. In the case of obvious rapid absorption of the soil, it is applied in several layers, each time after the previous one has completely dried.

The lower part of the walls around the entire perimeter of the room must also be primed.
The walls also need to be primed to a height of 150 ÷ 200 mm, since a damper tape for screed or waterproofing material will be attached to this part of their surface.
- After the surface has completely dried, it must be leveled with a self-leveling compound. If the surface is mostly flat and only in some places there are depressions and differences, then leveling is carried out precisely in these areas of the floor.
It is advisable to fill large uneven areas with a self-leveling compound.
- If insulation will be carried out in a ground floor apartment, it is recommended to waterproof the floor and the lower part of the walls. To do this, it is best to use roofing felt, which is laid on mastic using a hot method or on “cold” bitumen mastic (mastic). The waterproofing material should extend onto the walls by 120 ÷ 150 mm.
Floor surface after high-quality waterproofing
On the ground floor this process is mandatory, but on the upper floors waterproofing can also be carried out - it will reduce the likelihood of possible flooding of the apartment below in the event of a water supply accident.

A damper tape must be glued along the perimeter at the junction of the floor and walls
- Next, a damper tape is glued along the entire perimeter of the room, at the junction of the floor and the wall. You can buy it ready-made or cut it yourself from foamed polyethylene with a thickness of 7 ÷ 80 mm. The glued tape should be 50 ÷ 70 mm higher than the future screed. Damper tape is necessary to compensate for expansion of the screed during temperature changes and prevent deformation of the coating.
Floor insulation process
Since laying insulation on a waterproofing material differs from installing it on an open, prepared concrete floor, some stages of the work will vary.
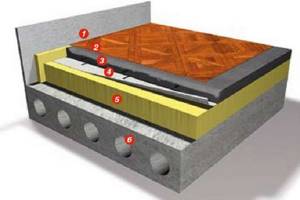
Diagram of an insulated floor on a concrete floor slab
This diagram clearly shows what sequence the layers of a concrete floor insulated with Penoplex should have.
1 - flooring - it can be linoleum, parquet boards, laminate or ceramic tiles.
2 – layer of concrete screed.
3 – reinforcing mesh.
4 – waterproofing layer.
5 – insulation layer “Penoplex”
6 – concrete floor slab.
A semi-dry screed can be laid on a base insulated with Penoplex or a regular, “wet” screed can be poured, so the sequence of layers can be slightly changed.
If a waterproofing material is applied or laid on the surface, then “penoplex” is laid on top of it. In the case when installation will be carried out on a leveled concrete surface, the heat-insulating material is laid on a bedding of purified sand.
For example, consider the process of creating an insulated floor with polystyrene foam using semi-dry screed technology:
| Illustration | Brief description of the operation performed |
| In this case, the insulation will be laid on a concrete floor. If any pipe or insulating box with wires passes along its surface, then first insulation is laid on top, and a mark is made in the width and depth at the place where the communication passes. Then, a groove is drawn and cut out in which the pipe will be placed during installation. | |
| But before finally laying the insulation in place, the concrete surface is leveled with clean sand or a sand-cement mixture, the thickness of which should be 1.5 ÷ 2 mm. It is necessary to fill in minor unevenness in the floor. | |
| Sheets of insulation are laid on top of the cement-sand mixture. They are moved lightly with pressure along the poured layer back and forth, thereby leveling the fill underneath and creating adhesion between the surfaces over the entire area of the panel. | |
| This backfill is done sequentially, on floor areas for two or three slabs. Next, heat-insulating boards are laid, and then the same backfill is applied to the next section. Work continues in the same order until the entire floor surface is covered with polystyrene foam boards. | |
| Having finished installing the insulation boards, reinforcing mesh cards with cells of 80 ÷ 100 mm are laid overlapping on top of them. | |
| The reinforcement cards are connected to each other with wire, the ends of which are tucked under the metal bars of the mesh. | |
| Next, you need to make a semi-dry mixture for the screed. It is convenient to mix the solution directly on the insulated floor, after laying sheets of plywood or thick cardboard on it. A certain amount of dry composition is poured out of the bags onto an improvised flooring, and then a depression is made in the center of the slide with a shovel. | |
| Water is poured into the recess according to the proportions indicated on the packaging. | |
| After this, using shovels, mix the solution, which should not be too dry, but also not spread over the surface. While mixing, the dry mixture around is constantly sprinkled with water to reduce the amount of rising dust. | |
| The kneaded mass, when squeezed in a fist, should not crumble, however, and should not be so wet that water oozes out of it. | |
| The next step is to spread the finished solution over the reinforced surface using a shovel. This layer should have a thickness of 10-15 mm. After filling the entire floor area with it, the mixture is trampled down or rolled with a metal roller. | |
| Next, the reinforcing mesh must be raised to the top of the poured mixture. To do this, pick up the mesh with your fingers, lift it a little and release it. Thus, the reinforcing cards on the entire floor surface are on top of the semi-dry cement mixture. | |
| After this, the entire surface is again trampled down or rolled with a roller. | |
| If it was planned to lay a heated floor cable under the main layer of the screed, then the time has come for its installation. The cable must be solid. It is carefully unwound and laid according to a pre-planned pattern with a calculated step between the loops. | |
| The cable is carefully secured to the reinforcing mesh using wire or plastic clamps. The ends of these garters are also hidden in the solution. When installing and securing an electrical cable, it is not advisable to step on it, do not bend it, and turns of the wire must be smooth. It is very important to remember that “warm floors” are not installed in places where heavy furniture will be permanently installed. | |
| In the selected location for installing the thermostat, strictly in the center of the cable loop, a corrugated tube with a temperature sensor is laid. Its second end should be located in the groove on the wall going to the thermostat installation socket | |
| After completing the installation of the cable, the entire floor surface is covered with a semi-dry mixture to the specified thickness of the screed. | |
| After backfilling, the surface must be trampled or rolled using a roller. | |
| Using a laser or regular level, the height of the future screed is marked on the walls. Using these marks on the backfill, level areas are filled using a grater, and then stripes are created that will serve as beacons for leveling the rest of the screed along them. | |
| The strips are leveled and compacted using a rule. Instead of this procedure, you can install metal beacons, but in such a way as not to damage the “warm floor” cable, that is, before the last filling of the mixture. The guides can be secured with wire to the reinforcing mesh. | |
| In this case, the master aligns the main screed with the padded beacons. The leveling process is carried out using a rule that, with slight pressure, is guided along the beacons, collecting excess mixture. If defects form on the surface, the required amount of mixture is poured onto them and they are rubbed. | |
| After leveling as a rule, the master goes over the entire surface with a construction float, lightly moistening the surface as necessary. And in order not to damage the screed, you need to wear special pads on your feet under work shoes, reminiscent of snowshoes. | |
| Next, a trowel is used to bring the surface to perfect smoothness. | |
| The levelness of the screed is checked using the building level. It is considered ideal if there is not even a small gap between the floor surface and the level. | |
| After grouting, the screed is left to dry for a day. Then the excess damper tape is cut off. | |
| After removing the protruding part of the damper tape, it is recommended to thoroughly spray the entire floor surface with water. This procedure is carried out to strengthen the screed. |
After this, the screed should be left to dry and gain strength for two weeks. If it was planned to lay ceramic tiles on top, then you must wait at least 20 days before laying. Coverings such as laminate, linoleum or parquet boards are installed only after laying additional film waterproofing and always after complete drying of not only the screed, but the entire room.
You may be interested in information on how to insulate a wooden floor with your own hands
Penoplex-insulated ground screed
Floors are also insulated with Penoplex in a private house built on a strip foundation - this method is called ground insulation.
Such insulation is possible under the following conditions:
- if the floors of the room do not bear heavy loads;
- absence of a basement or basement under the house;
- if groundwater lies at a depth of at least 4000 ÷ 5000 mm;
— presence of heating in the house, otherwise freezing of the soil can lead to deformation of the screed.
It is better to choose Penoplex slabs for this method of thermal insulation with butt grooves, since there will not be a hard and dense surface underneath them. And the interlocking connections (lamellas) will prevent cold bridges from appearing and will reliably hold the slabs together in a single plane.
For these works, in addition to insulation, it is necessary to prepare additional building materials, the quantity of which will depend on the volume of space to be filled. This is clean sand, gravel-sand mixture, crushed stone, waterproofing material (roofing felt and mastic), cement, self-leveling mixtures, damper tape and reinforcing mesh in cards or rolls.
Insulation schemes
There are several schemes according to which the process of erecting an insulated polystyrene foam floor on the ground can be carried out. First, it’s worth understanding them:

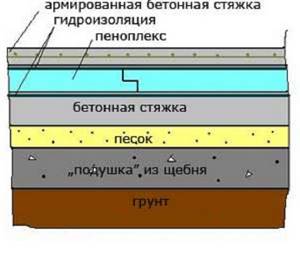
Scheme 1
- In this option, the insulation is laid on a layer of compacted sand, under which a reliable gravel and crushed stone cushion is made.
Scheme 2
- The second insulation option consists of two ties, one of which is placed inside the “pie”, between sand and insulation, and the second covers the heat-insulating material. A “warm floor” system can be installed in the top concrete layer.
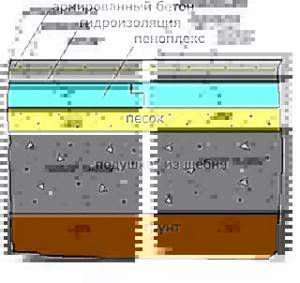
Scheme 3
- In the third option, medium-fraction crushed stone is used to backfill directly onto the ground, which is covered on top with a “cushion” of sand, on which Penoplex is then laid. Then the insulation is covered with waterproofing and reinforced screed.
You may be interested in information on how to insulate the floor in a private house
Laying an insulated floor on the ground

Installation of insulated screed on the ground
The most used scheme for laying an insulated floor on the ground is as follows:
- The soil is selected from the space where the backfill will be located, 550 ÷ 600 mm in depth.
- Next, the soil surface is well compacted so that it does not subsequently shrink, which can lead to deformation and cracking of the screed.
- Then, a layer of crushed stone or gravel is poured. Sometimes a mixture of these materials is used, which is also compacted as much as possible. The height of this layer should be at least 250 ÷ 300 mm when compacted.
- To increase the overall efficiency of thermal insulation, crushed stone is sometimes backfilled with middle fraction expanded clay. For the layer to be effective, its thickness must be at least 100 mm, and if the height of the space allows, then the entire 150 mm.

Expanded clay backfill will dramatically increase the degree of insulation of the room
- A cushion of medium-grained sand or granite screenings is placed on top of crushed stone or expanded clay. The layer is well soaked with water and rolled with a roller or compacted with a manual tamper. When compacted, the thickness of the sand layer should be at least 100 ÷ 120 mm. Its surface must be very well leveled and measured to the building level.
- The next step is to attach foamed polyethylene to the walls of the foundation tape around the entire perimeter, which will act as a damper tape. The material must have a width that will be 120 ÷ 150 mm higher than the intended screed. It should be noted that instead of foamed polyethylene, thin foam, about 15 mm thick, can be used.
- Next, Penoplex is placed on top of the sand cushion, which should fit tightly to the leveled surface. To do this, each of the plates is moved back and forth across the sand until it takes the desired position. The insulating mats are connected using the tongue-and-groove grooves or lamellas on them. The thickness of the insulation should be 100 mm - this makes the coating more dense and stable.

Laying insulation boards on a sand bed
- The joints of the plates are sometimes taped with waterproof foil tape - this will completely eliminate the appearance of cold bridges.
- Some craftsmen prefer to lay dense polyethylene on top of the insulation, which serves as waterproofing for the screed. In any case, this layer will never be superfluous.
- Next, a reinforcing metal mesh is laid on top of Penoplex or polyethylene. If several cards are stacked, they are tied together with wire.

Reinforcement of the surface before pouring the screed
- Metal guides are leveled on the grid - beacons, which are leveled and fixed with slides of mortar. At the same time, you can install the underfloor heating cable if you plan to lay it. After the beacon system has hardened, you can proceed to pouring the screed itself.

Beacon guides installed, heating cable laid
- A screed is placed on top - for this, the mixed solution is laid out on the surface. It is aligned by the rule according to the installed beacons.

Leveling the screed according to the beacons
As in the previous case, semi-dry or “classic” concrete mixture can be used.
The screed is given the time established by technology for complete maturation. It is advisable to regularly, starting from the second day, moisten the surface that is gaining strength.
- After the screed has hardened and gained its brand strength, if necessary, the floor is filled with a self-leveling mixture. It is advisable to carry out this process if linoleum or laminate will be laid on top.

You can bring the surface to the “ideal” using a self-leveling compound
- When the leveling layer also hardens, the excess damper tape is cut off. Its upper edge should be flush with the surface of the screed.
Now you can install the selected decorative coating on the surface of the floor insulated with polystyrene foam.
During the presentation, it is not for nothing that attention was focused several times on the damper tape. The construction of a floor insulated with Penoplex or other slab heat insulators using such a tape is “floating” and not connected to the walls, so it does not depend in any way on their shrinkage. The main thing is to have a reliable and stable foundation, and this is especially important when installing an insulated floor on the ground.
And in conclusion, a video tutorial from a specialist on the correct installation of insulated floors on the ground. You can find out about the long-burning double-circuit solid fuel boiler at the link.
TechnoNIKOL waterproofing classes, nomenclature
TechnoNIKOL Corporation produces a large line of roofing roll materials and all of them can be divided into classes (based on service life).
| Class name | Service life, up to years | Series name |
| SUBECONOMY | 5 | Stekloizol; rubemast; glassine; roofing felt |
| ECONOMY | 10 | Bikrost |
| STANDARD | 15 | Linocrom; Linokrom REM TKP; bipole; bicroelast |
| BUSINESS | 25 | Uniflex; ecoflex |
| PREMIUM | 30 | Vapor barrier C; technoelast |
Uniflex and technoelast have a number of modified versions that give the roof properties that improve fire safety and ventilation; variations of self-adhesive insulation of this brand are produced in different colors.
Waterproofing with a self-adhesive layer greatly simplifies its installationSource supersadovnik.ru
Range of waterproofing products from Technonikol
During construction, many important and small details are taken into account. Protecting the foundation from the action of water in the ground is one of the most serious issues. Ignoring it often leads to negative consequences:
- the foundation is destroyed faster than expected, both outside and inside;
- the basement or underground garage is constantly flooded;
- The operating time of the entire building is reduced.
The use of TechnoNIKOL foundation waterproofing can avoid damage and extend the life of the house. The company produces materials that differ in the methods of their application to the base. The following technologies are used:
- pasting;
- smearing
The products are produced in the form of rolls and mastics. Installed waterproofing membranes are also used. They are used in conjunction with other types of products. Not only the cost of the product, but also its quality and practical effectiveness depend on the components included.
You should pay attention to the markings when choosing. It should be borne in mind that the polyester fiber base is inherent in cheap, budget products
Floating floors: TN-POL Prof system
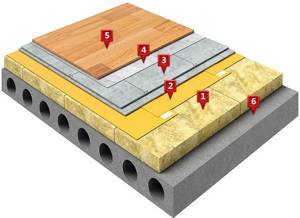
Structure:
1.
Reinforced concrete floor slab
2.
Heat and sound insulating material TECHNOFLOOR STANDARD, made of stone wool
3.
barrier PET film TechnoNIKOL
4.
Prefabricated (dry) screed made of composite, plasterboard or gypsum fiber
5.
A layer of cork or foamed polymer for the final coating
6.
Finishing floor – laminate or parquet
A floating floor is one of the most reliable and effective soundproofing systems. Its quality is ensured by the use of TECHNOFLOOR STANDARD noise reduction boards, which have high elasticity and density.
The “floating floor” technology is used in various facilities - in residential buildings, public buildings, industrial buildings, etc. The installation of floating floors is especially important where there is a consistently high level of noise (both impact and street).
Rolled waterproofing TechnoNIKOL
Rolled waterproofing, produced under the TechnoNIKOL brand, occupies a leading position in the ranking of building materials on the international market. The reason for the popularity of TechnoNIKOL brands are:
- high degree of reliability and effective protection against moisture and condensation;
- biological and chemical resistance, maintaining flexibility and elasticity at low temperatures;
- ability to withstand significant tensile load;
- long-term service life - from 35 years;
- ease of installation, cost-effective.
The strength of TechnoNIKOL waterproofing products is due to the use of a multilayer structure consisting of a polyester base, two layers of bitumen-polymer filler and a protective film. All coatings are produced in strict accordance with GOST and current building regulations.
Under the TechnoNIKOL brand, new models of roll waterproofing are being developed, taking into account different climatic conditions and the production capabilities of the consumer. Baseless self-adhesive roll coatings are widely used for waterproofing floors and foundations.
In addition to protection from moisture, waterproofing coatings from TechnoNIKOL are capable of protecting premises from noise, dust, and harmful gases.
Roofing and insulation materials are used both in the construction of new buildings and in repair and restoration work. The scope of application of waterproofing materials from TechnoNIKOL includes:
- strengthening foundations under industrial structures;
- construction of high-rise buildings;
- waterproofing of private households from the destructive effects of dampness and moisture;
- construction of tunnels, viaducts and bridges using reinforced concrete slabs.
Modern roll materials for waterproofing can effectively and reliably protect a building or structure from groundwater, freezing and precipitation. The correct choice of waterproofing material, strict adherence to the recommendations of specialists and installation technology are the basis for successful installation of roll waterproofing and the durability of the structure.
Application area
TechnoNikol thermal insulating basalt slabs are produced in several lines, each of which is designed for specific purposes and operating conditions. The material is widely used for insulation:
- floors between floors and roofs;
- internal partitions and walls;
- ventilated facades;
- attic;
- non-insulated and heated floors.
Insulation of pitched roofs
To reduce heat loss through the roof, TechnoNikol has developed special types of basalt insulation:
- Technoblock.
Effective insulation with high sound insulation characteristics. The thickness of the slabs is 50 mm.
- Rocklight.
It has increased rigidity and low thermal conductivity. The material is able to work under conditions of temperature changes and high humidity.
Insulation of facades
The operating conditions of external wall surfaces require that thermal insulation materials provide maximum protection against heat loss. In this case, it is advisable to use insulation materials such as:
- Technovent.
A special development designed for thermal insulation of ventilated facades.
- Technolight.
A universal option that is effective for insulating various building structures, including building facades.

Noise insulation
All TechnoNikol basalt insulation not only serves as a thermal barrier, but is also an excellent sound insulator. In cases where it is necessary to achieve maximum sound insulation, the following types of insulation are used:
- Technolight Optima.
Provides effective protection against noise and heat loss.
- Rocklight.
Technical characteristics are ideal for heat and sound insulation of interior walls.
- Technoacoustic.
The material is created as a sound insulator that can reduce noise levels by up to 60 dB.

Insulation of floors and flat roofs
If it is necessary to insulate the floor, it is necessary to use insulation with maximum density. The optimal solution in this case would be the following types of materials:
- Heat roll.
It is most widely used for insulating floors, but can be used for thermal insulation of flat roofs.
- Rocklight.
The material is able to withstand significant mechanical loads, therefore it is used when it is necessary to protect floors and roofs from heat loss.

Mapeplastik waterproofing
Mapeplast waterproofing is in constant demand, and this is not surprising, given its unique properties and characteristics:
- This is an elastic composition of two components based on cement and special additives, synthetic polymers, which is applied in several layers. It is able to protect the surface from any cracks, including hairline cracks, and reliably protect it from moisture;
- due to the presence of high-quality synthetic resins, Mapeplast has excellent adhesion to brick and concrete surfaces and is highly resistant to various chemical compounds, including sulfates and chlorides;
- has a wide range of applications for waterproofing hydraulic and industrial facilities, bathrooms and swimming pools, retaining walls and structures that require elastic protection due to deformation by load or are exposed to sea water or aggressive chemical compounds;
- Despite the fact that Mapeplastik waterproofing is often used to treat rooms that will be covered with ceramic tiles, artificial or natural stone, it can be used without additional protection with a surface layer.
When using the Mapeplastik composition, it is important to remember:
- it cannot be used at temperatures below 5–8 degrees Celsius;
- the composition cannot be applied in a layer thicker than two millimeters, and the recommended waiting time before re-application is 5 hours;
- it is necessary to carefully prepare the surface - moisten and wipe off dust and dirt;
- It is recommended to lay facing materials on a surface treated with Mapeplast no earlier than five days;
- Manufacturer's recommendations and instructions must be followed.
When choosing a waterproofing material, experts recommend paying attention to:
- for compliance with the features and characteristics of the object that will be processed;
- on the conditions in which construction and repair work will be carried out, because some materials have restrictions on temperature and humidity during work;
- on the technical characteristics of the material in terms of resistance to mechanical and temperature influences, resistance to ultraviolet radiation and aggressive chemical environments.
Basalt wool: properties and purpose of different types
Mineral wool insulation is in demand at different stages of thermal insulation of premises. The material is especially popular in the construction of prefabricated structures - its qualities meet all the requirements and standards of frame housing construction .
Distinctive characteristics
TechnoNIKOL stone wool is made of basalt. Processed rock, special production technology and binding components endowed the heat insulator with a number of advantages:
- fire safety – class of non-combustible materials;
- excellent thermal efficiency;
- resistance to chemical influences;
- wide operating temperature range – from -60°С to +400°С;
- vapor permeability - quality is especially important for the walls of a frame house; proper installation of mineral wool prevents the appearance of the “thermos effect”;
- moisture resistance;
- insignificant content of harmful substances – binding components no more than 2.5%;
- moderate elasticity and resilience.
TechnoNIKOL produces slabs of different sizes, the thickness of the mats is standard - 50 mm and 100 mm . The parameters of insulation depend on the density of the heat insulator and its purpose. Let us denote the average characteristics of stone wool:
- thermal conductivity – 0.035-0.039 W/m*C;
- water absorption – within 1.5-2%;
- density – 25-50 kg/m3;
- vapor permeability – 0.3 mg/(m*h*Pa);
- compressibility - up to 8-55%, the indicator depends on the density of the material.
Materials for pitched roofing
On the official website, for the convenience of customers, the manufacturer has arranged materials according to their scope of application. For pitched roofs, low-density mats are suitable , since it is assumed that the load on the roof will be small.
Solutions from TechnoNIKOL:
- Rocklight. Universal slabs for private construction. Density of TechnoNIKOL Rocklight - 30 kg/m 3, compressibility - 30%, dimensions - 120 * 60 cm. Suitable for inclined, vertical structures that do not bear external loads. The binding component is a resin with a low phenol content. This composition allows Rocklight to be used for internal thermal insulation .
- Heat roll. Long mats of stone wool insulation, wound into a roll. Density is 30 kg/m3, and compressibility is within 50%. Dimensions – 4*1 m, thickness – 50/100 mm. The material is suitable for laying on pitched roofs and other inclined surfaces.
- Technoblock Standard. The increased density (45 kg/m 3 ) allows the slabs to be used not only for insulating frame roofs, but also for thermal insulation of layered masonry, frame-type walls and facades with a ventilation gap.
- Technolight Optima. The average density is 35 kg/m3. The scope of application is limited to buildings and structures without significant loads. Can be used as the first internal layer of thermal insulation in the construction of ventilated facades .
- Technolight Extra. The slabs have a very low percentage of moisture absorption - no more than 0.5%. Density indicator – 30 kg/m3. The material perfectly resists compression and can be used as a facade heat insulator under siding .
Working with a vertical surface
It is carried out vertically along the walls of the foundation and basement and protects them from groundwater, rain or melt water.
1. Preparation:
– carry out the same manipulations as when preparing horizontal surfaces; – eliminate sharp protrusions and corners that may cause breakage or pushing through of the material; – organize transition fillets from cement-sand mortar in a size of 100 mm horizontally.
2. Priming (priming):
- treat the surface with bitumen primer using a roller, and in difficult places - a brush;
- wait for the painted areas to dry completely;
- Check the degree of drying with a regular paper napkin, similar to checking on a horizontal surface.
3. Arrangement of reinforcement layers:
pay attention to complex nodes, internal and external corners, places where communications enter, transitions from horizontal to vertical surfaces; make layers of reinforcement along the perimeter of the foundation, on sharp corners and fillets, rolling them well with a silicone roller; make sure that the layers of reinforcement are laid joint to joint, that is, without overlaps.
4. Laying the waterproofing membrane:
- lay the material from bottom to top, do not use one roll when changing the direction of laying more than twice due to the risk of material detachment from the foundation and the formation of air bubbles in problem areas. Cut the material into shorter pieces. Do not join rolls 2 in the area of fillets - smoothed internal corners of the structure, lay them on the vertical part of roll 1;
- Perform transverse overlaps on smooth (without bends or kinks, not in fillet areas) areas of the foundation slab. The size of the transverse overlap should not be less than 150 mm;
- At the top point, fix the membrane using a metal strip with a fastening pitch of 200 mm;
- leave a gap of 5-10 mm between adjacent slats, fill the space between the slats and the wall with polyurethane roofing sealant;
- Protect the waterproofing from possible mechanical damage with extruded polystyrene foam (if foundation insulation is required) or a profiled membrane.
Would you like to receive individual advice on the choice of waterproofing material and installation? Contact our support team by phone. The call is free for you.
You might be interested
Types of insulation
has mastered the production of 4 types of insulation from different raw materials:
- basalt (mineral wool insulation);
- extruded polystyrene foam;
- semi-rigid polyurethane foam (PPU);
- polyisocyanurate foam (PIR thermal insulation boards, better known among builders as PPU boards).
Basalt wool
Basalt insulation "TechnoNIKOL" is made from rocks of basalt or gabbro (rock wool). The production process begins with crushing the stone. After this, the rock is fed into the furnace, where at high temperatures (up to +1500oC) it melts to a fluid state. The liquid mass is fed into a centrifuge, where very fine fibers are formed with the help of a strong air flow.
The process continues by irrigating the shapeless mass, consisting of stone threads, with plasticizers: formaldehyde or arbolo-urea resin. During the cooling process, at a temperature of 200oC, the resin polymerizes, forming a thin protective layer on the fibers. The production process is completed on a conveyor belt, where the fibers are compressed to a given density and then cut to the required width and length.
Extruded polystyrene foam
Synthetic insulation material made from granulated polystyrene, obtained by foaming the raw material and then pressing it through a special mold (the technology is called extrusion), is called extruded polystyrene foam. Available in sheets with a thickness of 20 to 100 mm. Keeps warm perfectly. Lightweight yet durable.
It has a strong resemblance in appearance to polystyrene foam. Therefore, the company paints its products in orange and silver, with the addition of carbon fiber.
Semi-rigid polyurethane foam
The company’s line of thermal insulators also includes sprayed insulation “TechnoNIKOL” - one-component polyurethane foam. Available in tubes. It is sprayed using a special nozzle onto a mounting gun familiar to builders.
PPU forms a seamless, low thermal conductivity, thermal insulation layer with small, open pores. It adheres well to all types of building materials, with the exception of polyethylene.

Thermal insulation PIR
heat-insulating material made of polyol and isocyanate in the form of plates is positioned as an innovative product of a new generation. To enhance the impression of the new product, the insulation was called PIR thermal insulation. This misleads many consumers. Indeed, in reality, this is rigid polyurethane foam in the form of slabs, familiar to many builders. What PU foam sheets are is described in detail in the work “PPU Boards”.











