Residents of modern multi-storey buildings may encounter such an unpleasant phenomenon as a weakening of water pressure in the pipes. In order to find out whether this is a personal problem or a general one, you must first visit your neighbors in the riser. If everything is in order, they will most likely need to clean the water pipes located at the level of the point of problematic water supply.
Reduced water pressure from the tap may be caused by clogged pipes.
Damage assessment
How to clean a water pipe successfully?
It's better to do the following:
- Visual inspection for plaque and rust.
- Analysis of steel performance. If there is too much plaque (corrosion), then removal may damage the already thin walls.
- Dismantling is required so that the pipes can be cleaned of rust correctly.
- Consultations in difficult situations. Plumbers and on-duty engineers will advise on problem or neglected areas.
If the work is doable, then we choose an external or internal method for our case to get rid of scale and rust. More about this.
Effective methods for external cleaning
It is not difficult to clean the surface from the outside. There are four rust removal methods to work with:
- Mechanically. Sandpaper and special attachments for power tools are suitable. Corrosion will be eliminated, after which washing and protection with a primer (paint) is required. Painting over rust is prohibited. Only after mechanical cleaning. Otherwise, high humidity (water passes under pressure through small pores and joints) will destroy any pipe in a short time.
- You can't do without using acid. Mix household ingredients (vinegar and citric acid) in different proportions. We apply the composition. In 2-3 hours there will be no trace of the raid. But for convenience, it is better to first go through step 1.
- Alkaline cleaning is carried out. Classic soda in the amount of 3 tablespoons dissolves in water. Apply to rust, then remove with vinegar. But soda will only work on a thin layer of rust; thick parts, again, are best cleaned with a tool with an attachment. It's faster that way.
- Using special chemicals (not for household use). We are talking about industrial compounds or concentrates.
Any method makes sense if you properly protect the outer surface after cleaning the surfaces with abrasives, for example. After all, steel, cleaned from the outside, will oxidize again after some time.
Let's see how to fix this below.
How to clean rust from a metal pipe

The weak point of metal pipes is their susceptibility to corrosion. Over time, pipes made of cast iron and steel inevitably rust, and this does not have the best effect on the operational characteristics of the pipeline. To ensure that the pipeline lasts longer and its condition does not negatively affect the quality of water, rust should be removed in a timely manner.
Why do you need to clean pipes from corrosive deposits?
Rust affects not only the fact that in places where plaque has formed, the pipe can simply leak, but also the quality of the transported liquid. Water in rusty pipes has an unpleasant odor and becomes suitable only for technical use.
Corrosion in heating pipes reduces heating efficiency, which inevitably increases operating costs.
Methods for cleaning rusty pipes
Corrosion can occur on both the outside and inside of the pipe. Cleaning methods depend on the location of the plaque and the degree of damage.
You should not remove rust from heavily rusted pipes - this can lead to damage, and as a result, the pipe will become unusable . Therefore, in case of severe corrosion, it is much more advisable to simply replace the damaged section of the pipeline or the entire line.
Only if the pipe is slightly damaged by rust, cleaning will be effective and will increase the life of the pipe for some time.
Cleaning the pipe outside
If the pipe is rusty on the outside, you can use the following to clean it:
- Mechanical means - sandpaper or a brush with metal bristles, you can use a cable brush with bristles arranged in a spiral, put on an angle grinder.
- Chemicals are special compounds that, as a result of a chemical reaction, convert rust into compounds that are safe for the metal surface. Rust removers contain various acids or alkalis. You can buy a ready-made product, or use proven folk methods, for example, citric acid and vinegar, mixed in equal proportions. The product is applied for 2-3 hours, after which it is washed off with soapy water. Another home remedy is a soda solution (two tablespoons per third glass of water) applied for 20 minutes, rinse off the alkaline paste with a weak vinegar solution. Chemicals are often used after mechanical cleaning. After cleaning the outer surface of the pipe, it is better to apply a primer containing corrosive deposit converters.
Note! Special rust removers should be used strictly following the instructions and dosage. They contain strong alkalis, which, if the instructions are not followed, can damage the pipes.
Cleaning the pipe from the inside
In addition to corrosion, scale and various deposits accumulate on the inner walls of pipes. To maintain the capacity of the pipe, it is necessary to regularly clean and flush it from the inside for preventive purposes.
We recommend that you read: How to make a chimney pipe box on the roof?
To do this, there are several effective methods that allow you to get rid of unwanted deposits on the inner surface:
- chemical methods;
- hydrodynamic cleaning;
- mechanical methods.
Mechanical cleaning is considered the most popular, and it can be carried out either using simple devices in the form of a cable or a plunger, or using special equipment.
Special cables whose diameter is smaller than the diameter of the pipe. The device is a spiral, hollow inside and is considered a household tool. The cable is passed into the pipe and clears blockages, acting like a mechanical brush. The kit often includes additional attachments.
These devices work on the principle of a drill; a special nozzle is installed, which, rotating, removes dirt and pushes it into the
Chemical methods
There are many chemical compounds on sale for cleaning pipes from rust and plaque. Such products cope well with minor damage and can be used independently without the involvement of specialists.
If used correctly, you can extend the life of pipes by using products not only when rust has already begun to corrode the metal surface, but also for prevention.
Cleaning pipes with chemicals helps restore their capacity. These products contain glycolic or glyoxal, as well as other chemical compounds that are safe for human health.
Hydrodynamics
This method does not require dismantling the line, but the procedure can be carried out by specialists with sufficient knowledge, qualifications and experience. Cleaning occurs by supplying a high-pressure water jet into the pipe using special equipment.
Water cleanses the inner surface of rust and other deposits of various types. Often cleaning is carried out together with mechanical treatment, thus cleaning and washing the inner walls of the pipe.
The latest technical method for cleaning pipes is carried out using pneumatic-hydropulse equipment. The device creates a pulse wave inside the pipe due to the formation of cavitation bubbles, which cause air turbulence and water bubbling, removing deposits from the walls.
Abrasives for sandblasting
The sandblasting method is used as abrasive cleaning. The principle of operation of the device is the directed spraying of an abrasive agent under high pressure. Thanks to this, the abrasive, directed at high speed to the surface to be cleaned, breaks off the layered deposits.
For internal
All methods to prevent plaque and eliminate it strictly from the inside of metal pipes. Let's consider those cases when the steel system has already worked for some time.
Water hammer
It is optimally suited, since there is no need to disassemble the rusted system.
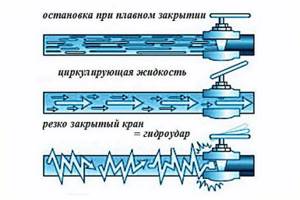
Water hammer has been practiced for several decades in a classic apartment heating system (cleaning water pipes of rust before the season). In a private water supply and heating system, you cannot do without special equipment. The blow works due to the release of compressed air, knocking down plaque from the walls of the pipes.
Sandblasting
The water supply and heating system is disassembled in advance. Sandblasting is carried out only by craftsmen who have access to the equipment. Otherwise, limbs may be injured.

The idea is simple - air with sand (or other abrasive material) is supplied under pressure into rusty pipes. There are hand sandblasters, but they are not suitable for cleaning such products. Be careful.
Chemistry
Plaque removers. A primitive, but quite effective way for independent work. It is recommended to use plumbing flushing for prevention specifically in the water supply system. But you can independently supply rust converters to the heating system only in a private modern house.

It is better to give preference to inexpensive types of chemicals. And remember that all these compounds can get into the surrounding living environment. When pumping out a septic tank, this should be taken into account.
Abrasives
With abrasive everything is simple, because it is an analogue of sandblasting. Only air is replaced by liquid during the cleaning process. The abrasive cleaning system is expensive, complex, and is performed by highly specialized craftsmen. It is necessary to create increased pressure in the system in several approaches and pump out the rust. Therefore, a preliminary assessment of the condition of the pipes is mandatory.

We conclude that it is easier to remove internal corrosion systematically using chemistry. Heating systems are most often flushed by household utilities.
What is defatting
The essence of the procedure is to remove fatty substances from the surface of the substrate, which are often present in cooling emulsions, mineral oils, preservative lubricants, and polishing compounds. Degreasing of the metal surface before painting also has to be done to remove residues from washing and etching, traces of sweat and fingers. All these contaminants can extremely negatively affect the quality of surface wetting with paints and varnishes, as well as harm film formation and other properties of the coating.
Depending on the amount of fatty impurities present per square meter, several degrees of surface contamination can be distinguished:
- Weak - up to 1 g;
- Medium - from 1 to 5 g;
- Increased - more than 5 g.
When processing fats with chemical reagents, several sequential processes occur on the surface:
- Solvent;
- Emulsifying;
- Saponifying.
Depending on the ability of fats to be destroyed under the influence of solvents, several types of contaminants are distinguished:
- Non-destructible - for example, emulsions.
- Pollinated - polishing materials, lubricant residues.
Chemical methods
The main type is organic solvents, which allow you to quickly remove grease and oily areas from metal parts. They are most widely used in individual production, although sometimes they are used in serial production, but not often due to their high explosion and fire hazard. The desired effect, namely the dissolution of oil and fat deposits, is achieved at the moment of contact of organic solvents with them.
The quality of surface degreasing is directly affected by the degree of solvent contamination, since the more fats are contained on the surface, the worse the chemical’s ability to dissolve existing deposits becomes. Most often, aliphatic and chlorinated solvents are used to remove fat and oil areas. Despite their high efficiency in metal cleaning, they have a serious drawback - these compounds are not able to remove abrasive materials and other mineral contaminants from the surface.
Aqueous solutions
As is known, water has poor purification ability, which is associated with significant surface tension and incompatibility with fats. Therefore, when it wets greasy surfaces, stable emulsions are not formed. To increase the cleaning properties of an aqueous solution, manufacturers resort to various techniques - increasing the pH acidity level, increasing the temperature regime of use to the range of 50-65 degrees Celsius, and introducing surfactants into the composition.
Alkaline degreasers
These compounds have a lot of positive properties. These include high cleaning ability, fire safety, environmental friendliness, and a wide selection of application methods. When treated with aqueous solutions of saponified fats and oils, the latter are inevitably destroyed, and unsaponifiable contaminants are emulsified. The latter case can be described as the process of detachment of fatty layers from the surface with gradual transformation into a working liquid and removal along with the working solution. The main disadvantage of these compositions is the need for anti-corrosion treatment of the surface after cleaning.
Among the components present in cleaning solutions, surfactants - surfactants - deal best with fatty and oily areas. Once on the surface, they form foam on it, simultaneously reducing interfacial and surface tension, increasing wettability and destroying solid and liquid contaminants, transforming them into a more convenient form for removal. The surfactant content in grease cleaners , as a rule, fluctuates within 10%.
If the need arises, along with degreasing, to remove thin oxide or hydroxide films, acidic solutions containing 1-3% phosphoric acid are used.
After treating surfaces with cleaning compounds, they must be washed with water. The presence of salt residues is unacceptable, since they can destroy the properties of paint films, increasing moisture permeability and accelerating the development of under-film corrosion.
Emulsion compositions
In cases where there is a need to remove oil deposits, grease, and difficult-to-remove contaminants from the surface, emulsion degreasing is used. This method is combined and has the advantages of organic solvents and aqueous alkaline solutions. These compositions contain emulsions of solvents and surfactants diluted with water. Chlorinated or aliphatic hydrocarbons can be used as solvents.
Ultrasonic and electrochemical methods
To increase the cleaning ability of detergent compositions, special baths with an ultrasonic field are used. This method is most relevant for small-sized products with a highly complex surface, for which it is important to remove contaminants with the highest quality possible. For large parts, it is not practical to use this method due to economic considerations, since there is a need to increase the output power of the device.
When preparing metal products using the electrochemical degreasing method, specially equipped baths are also used, and the process itself is carried out due to the action of gas bubbles formed on the electrodes. This makes it possible to reduce the consumption of components of chemical compositions and improve the quality of surface treatment.
How to protect clean pipes from rust
Inexpensive, fast and practical. Here are two simple options:
- External protection for a warm room.
- Protection for underground pipes (we visit hardware stores).
We protect steel inside an apartment or house
Any anti-corrosion compound is suitable. The following primers are suitable for cold systems:
- GF021
- XC068
- EP076
- FL053
- PF046
- GF032
Moisture-resistant or heat-resistant paint will also protect the steel from the outside. But before applying it, it is important to use the previously listed compositions.

But it is best to cover a fresh pipe, not yet damaged by rust, with casein glue and cement mortar. After this mixture has dried, you need to apply drying oil, then permanent oil paint. Several layers will certainly create a waterproof film.
Underground communications
Fortunately, steel pipes can be protected in several ways in the 21st century. Choose for your case:
- Petroleum bitumen. Ideal for all types of pipes laid outdoors. Before applying it, it is necessary to clean even new pipes, then mix the material with gasoline to obtain a dense primer.
- Bitumen mastic with crushed asbestos (cement or kaolin). Mix until the paint is thick and apply hot to the cleaned steel.
- Hydroisol (fiberglass).
- Polyethylene (extruded).
- Polyurethane foam. In the form of shells or a liquid composition poured between the pipe and polyethylene.
Why do pipes get clogged?
Pipes most often become clogged due to deposits on the walls. Even if you have a plastic water supply, you should look for the cause of the blockage where the connection with steel pipes begins. A large amount of rust, most of which is in the form of layers, is separated from old pipes and spreads evenly along the entire length with the flow of water.
Cleaning out an old water pipe is worthwhile, but very tedious. But for the next 10-15 years you will provide yourself with a reliable flow of water.
If the problem is not in your system, then you need to protect yourself from the invasion of rust from the outside. Moreover, it not only damages pipes, but also clogs measuring instruments, boilers, dishwashers and washing machines. In the latter, despite their own protection filters, a sufficient amount of fine rust still accumulates. Gradually, these deposits wear away pumps and points of contact with the water flow.
In order to assess the feasibility of the cleaning procedure, calculate how much money all the equipment in the house costs. Now imagine that everything that comes into contact with rusty water is under the potential threat of wear and tear.
What other causes of blockages?
It may be that the pipes are clogged with sand or other impurities. A very good and sure way is to turn off the valve that supplies the house, and then drain the entire riser into the basement. The pressure difference should clear such blockages very easily. This problem occurs because the surface of the pipes becomes rough over time. A large amount of different debris simply settles in the pipe, clinging to each other.
Completely foreign debris unrelated to water can cause a blockage. A piece of sealant or a synthetic rag can easily be removed from a seemingly potable water supply. In this case, only cleaning with a cable will help.
Is internal protection possible for steel pipes?
You cannot organize this on your own. We can only rely on the manufacturer, who happily produces and sells steel for pipelines with a cement-sand mixture on the inner walls.
This is a difficult method, since a coating device is passed inside the workpiece (in production). After which the corrosion protection is fired.
As an option for the private sector, an unassembled steel system can be dipped into heated bitumen. Yes, the process is elegant, but expensive. Requires compliance with safety regulations.










