In Europe and the USA, alternative energy sources have long been used. In some cases, they are a good substitute for gas, as well as solid fuel materials. In particular, “heat pumps”, which extract energy from water, air and earth, have become widespread. All these installations have their own specifics and features that affect the efficiency of their operation. Experts note that the air-to-water heat pump is easy to install and operate. In addition, it has a long service life and high reliability. Many people choose air-to-water heat pumps for use in a country house or country house. This material will discuss the principle of operation, operation, installation, as well as the choice of an air-to-water heat pump.
Operating principle of an air-to-water heat pump
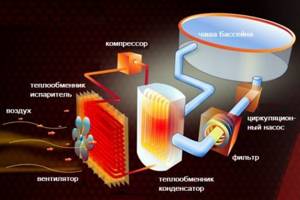
A heat pump is a type of space heating equipment that takes dissipated heat from the surrounding air and concentrates it into thermal energy. This energy is used to heat water, which is then used to heat the room. The operating principle of an air-to-water heat pump is similar to that of an air conditioner, but uses a reverse Carnot cycle. Modern climate control equipment uses a similar principle. Air conditioners designed to cool a room can operate for heating until the ambient temperature drops below minus five Celsius.
Operating principle of an air-to-water heat pump
Air-to-water heat pumps differ from climate control equipment in improved parameters. They can work to heat the room until the outside air temperature drops to 15-25 degrees below zero.
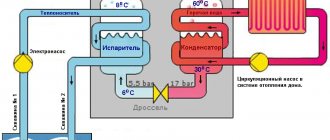
The installation includes a circuit where freon circulates, as well as a compressor, evaporator and condenser. In the evaporator, freon is converted into a gaseous state, absorbing heat from the OS. In the compressor under high pressure, the gas heats up to 120-125 degrees and enters the condenser. There it turns into a liquid, the heat of which is used to heat water in the heating circuit.
This operating principle is almost the same for all types of heat pumps. The only difference is what medium is used to extract heat. This can be water, earth, air and other sources. The outside temperature has a significant impact on the performance of heat pumps. Therefore, the use of air-to-water heat pumps is possible in the south of Russia and in the middle zone. In the north, where frosts persist for a long time, their use is problematic.
The coolant, which is water, is heated with freon to approximately 55-65 degrees. The temperature is quite enough to organize hot water supply, heating system, and heated floors. The operating principle is based on the use of low-grade thermal energy. This is what limits the use of a heat pump to environmental factors. The optimal operating mode is down to minus 10 degrees Celsius. If the temperature “overboard” decreases, then the efficiency of the air-water installation is greatly reduced.
External heat pump unit
To eliminate this problem, experts have developed a scheme for the operation of the air-water system along with other heat sources.
Here the scheme of work is as follows. When the outside temperature drops, the pump begins to work with increasing load. When the load increases to a certain limit value, an additional heat source is connected to the operation. This can be an electric or gas boiler. When the temperature outside the window increases and the heat pump copes with the load, the boiler automatically turns off. As experts say, it is better to use an electric boiler as a backup. In any case, installing an air-to-water pump is impractical in northern latitudes, where there are severe frosts for a long time.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The following video will introduce you to the principle of operation and design of a heat pump that processes wind energy:
A homemade air-to-water heat pump is one of the effective and inexpensive devices for additional home heating. Anyone can make and install this system.
Please write comments in the block below. Perhaps you have interesting information and photos on the topic of the article? Ask questions, share your own opinions and tips that are useful for site visitors.
Power calculation
Before you buy a heat pump or make it yourself, you should make an approximate calculation of the power. After all, if the power is insufficient for the area of your home, then heating will not be carried out to the fullest extent. If you choose an overly powerful pump, this will lead to unnecessary costs. Specialists who manufacture and install air-to-water heat pumps use special software to calculate power. They allow you to calculate the various elements of such a system, down to the area of the coil. Those who make a heat pump with their own hands use special calculators. They are available on websites related to construction and heating. The calculators use input data about the area of the house, region, ceiling height, and the state of thermal insulation in the house. As a result of calculations, the estimated power of an air-to-water heat pump or another type is derived. If the building is well insulated and has a small area, less heat pump power will be needed. So, experts recommend doing thermal insulation before buying a heat pump.
Below you can see a table of the approximate dependence of the power of the heat pump depending on the area of the heated room.
| Room area, sq. m. | 100 | 150 | 200 | 250 | 300 | 350 |
| power, kWt | 5 | 8 | 12 | 16 | 21 | 28 |
Prices for drilling wells for heat pumps
Cost of installation of the first geothermal heating circuit
| 1 | Drilling wells in soft rocks | 1 p.m. | 600 |
| 2 | Drilling wells through hard rocks (limestones) | 1 p.m. | 900 |
| 3 | Installation (lowering) of a geothermal probe) | 1 p.m. | 100 |
| 4 | Crimping and filling the external contour | 1 p.m. | 50 |
| 5 | Well filling to improve heat transfer (granite screening) | 1 p.m. | 50 |
Why did I choose a heat pump for my home heating and water supply system?
So, I bought a plot to build a house without gas. The prospect of gas supply is in 4 years. We had to decide how to survive until that time.
The following options were considered:
- 1) gas tank 2) diesel fuel 3) pellets
The costs for all these types of heating are proportionate, so I decided to make a detailed calculation using the example of a gas tank. The considerations were as follows: 4 years on imported liquefied gas, then replacement of the nozzle in the boiler, supply of main gas and a minimum of costs for rework. The result is:
- for a house of 250 m2, the cost of a boiler and gas tank is about 500,000 rubles
- the whole area needs to be dug up
- availability of convenient access for the refueler in the future
- maintenance is about 100,000 rubles per year:
- the house will have heating + hot water
- at a temperature of -150°C and below costs 15-20,000 rubles per month).
Total:
- gas holder + boiler – 500,000 rub.
- operation 4 years – 400,000 rub.
- supply of a main gas pipe to the site – RUB 350,000
- nozzle replacement, boiler maintenance – RUB 40,000
In total - 1,250,000 rubles and a lot of fuss around the issue of heating in the next 4 years! Personal time in terms of money is also a decent amount.
Therefore, my choice fell on a heat pump with commensurate costs for drilling 3 wells of 85 meters and purchasing it with installation. The Buderus 14 kW heat pump has been in operation for 2 years. A year ago I installed a separate meter for it: 12,000 kW hours per year!!! In terms of money: 2400 rubles per month! (Monthly gas payment would be higher) Heating, hot water and free air conditioning in the summer!
Air conditioning works by raising coolant at a temperature of +6-8°C from wells, which is used to cool rooms through conventional fan coil units (a radiator with a fan and a temperature sensor).
Conventional air conditioners are also very energy-intensive - at least 3 kW for each room. That is 9-12 kW for the whole house! This difference must also be taken into account in the payback of the heat pump.
So a payback of 5-10 years is a myth for those who are sitting on a gas pipe, the rest are welcome to join the club of “Green” energy consumers.
Features of installation and operation
The air-to-water heat pump and the heating equipment associated with it are complex technical devices. Therefore, ordering and installation should be ordered from specialized organizations. You should only undertake self-installation if you have a clear idea of what needs to be done.
Installation of a heat pump usually includes the following steps:
- preparatory work;
- installation of the outdoor unit;
- Installation of the indoor unit and home heating system;
- Commissioning works.
It should also be noted some features when installing a heat pump. They are valid both for air-to-water installations and for others.
- The external unit is installed next to the building (2─10 meters);
- A canopy should be made over the external unit to protect it from dust, rain and snow;
- In addition, it must be located at a distance from sources of fire;
- The installation itself must be mounted on a metal base;
- Connections in the heat pump circuit where freon circulates must be rolled;
- Installation as a whole should be carried out with the expectation that the coolant temperature will not be high.
A number of experts say that if an air-to-water pump is used in a heating system, the optimal type of room heating is heated floors.
Air-water thermal installation
It is also worth mentioning some important points when operating heat pumps. Their work is regulated automatically and does not require constant monitoring. But at least once a year you should conduct an inspection for faulty system elements to identify various problems. This will avoid major repairs and high costs.
Here are some points to pay attention to when operating an air-to-water heat pump:
- Checking filters. Their timely cleaning and replacement;
- Monitoring the oil temperature in the compressor. The oil should be warm;
- Cleaning debris from the external heat exchanger;
- Cleaning temperature sensors;
- Checking wiring integrity;
- Inspection of pipes, hoses, as well as their connections for damage and leaks;
- If necessary, lubricate the moving parts of the fan and motor;
- Before starting the pump, you need to turn on the compressor and leave it for several hours to warm up the oil. If you run it on cold oil, its service life will be shortened.
Making a heat generator with your own hands
List of parts and accessories for creating a heat generator:
- to measure the pressure at the inlet and outlet of the working chamber, two pressure gauges are needed;
- thermometer for measuring the temperature of inlet and outlet fluid;
- valve for removing air pockets from the heating system;
- inlet and outlet pipes with taps;
- thermometer sleeves.
Selecting a circulation pump
To do this, you need to determine the required device parameters. The first characteristic is the ability of the pump to operate with high-temperature liquids. If this condition is neglected, the pump will quickly fail.
Next you need to select the operating pressure that the pump can create.
For a heat generator, it is enough that a pressure of 4 atmospheres is reported when the liquid enters; this figure can be raised to 12 atmospheres, which will increase the heating rate of the liquid.
The performance of the pump will not have a significant impact on the heating rate, since during operation the liquid passes through a relatively narrow diameter of the nozzle. Typically up to 3–5 cubic meters of water per hour is transported. The coefficient of conversion of electricity into thermal energy will have a much greater impact on the operation of the heat generator.
Manufacturing of a cavitation chamber
But in this case, the flow of water will be reduced, which will lead to its mixing with cold masses. The small opening of the nozzle also works to increase the number of air bubbles, which increases the noise effect of the operation and can lead to bubbles starting to form already in the pump chamber. This will reduce its service life. As practice has shown, the most acceptable diameter is 9–16 mm.
The shape and profile of the nozzles are cylindrical, conical and rounded. It is impossible to say for sure which choice will be more effective; it all depends on the other installation parameters. The main thing is that the vortex process arises already at the stage of the initial entry of the liquid into the nozzle.
Choice: prices and manufacturers
The problem of heating residential and industrial premises can be solved by choosing the right air-to-water heat pump. What you need to take into account and not make a mistake when choosing. The first thing you should think about after calculating the power is the design of the case. Manufacturers offer two options.

Low temperature monoblock heat pump
There are low temperature monoblock heat pumps.
In this case, no additional installation is installed in the room. All elements of the heat pump are located outside the building or in the utility room, and only the pipeline with the coolant passes into the house or industrial premises. The second version is the well-known split system. Most often, this option is used in domestic premises. The external unit is located on the street, and the main line from the storage device goes to it. Freon heats the condenser and heat is transferred to the liquid that circulates in the heating circuit.
Based on functionality and purpose, manufactured heat pump models can also be divided into 2 groups. Some air-to-water units are designed for heating only, while others can provide hot water in addition to heating. In terms of ambient air temperature, air-water installations, as a rule, operate in the range from plus 45 to minus 15 C. Some models can operate at outdoor temperatures of minus 25-32 C. The efficiency of air-water heat pumps directly depends on the ambient temperature .

Viessmann air-to-water heat pump
Over the past 10-15 years, many models of different heat pumps have appeared on the market.
These products are produced by manufacturers from Germany, Japan, China, Russia and other countries. Their products are similar in design, but often differ in effectiveness. The following well-known companies in this market can be named:
- Stiebel Eltron (Germany). The models are in high demand on the Russian market. Among the advantages, it is worth noting a large wide range of models, developed functionality, and the possibility of individual production. In general, Stiebel Eltron heat pumps are economical and have a high COP;
- The company produces high-performance air-water units. They are used for heating domestic and industrial facilities. All models are adapted for use in Russian conditions. Most Buderus heat pumps offered are designed to heat rooms larger than 500 square meters;
- The company has been producing heat pumps for several decades. The model range is constantly changing, the wishes of the owners of heating installations are taken into account, and new technologies are constantly being mastered. Viessmann often use innovative automation in their products. With its help, the air-water installation provides fully automatic heating of the room depending on weather conditions;
- Heliotherm (Austria). The company produces models of heat pumps with the best COP indicators. The company has its own representative office in Russia. Thanks to this, warranty obligations, installation and support of equipment are provided.
The cost of modern heat pumps ranges from 160 thousand to 1.2 million rubles. The cost may vary depending on the manufacturer. The Chinese produce models that are cheaper, but they have a lower COP and service life. A common practice is when the installation of air-to-water heat pumps is included in the price of the equipment. Many companies offer free project estimates. There are also examples where services for further maintenance of installations are offered.
Calculation of a horizontal heat pump collector
The efficiency of a horizontal collector depends on the temperature of the medium in which it is immersed, its thermal conductivity, and the area of contact with the surface of the pipe. The calculation method is quite complex, so in most cases averaged data is used.

- 10 W – when buried in dry sandy or rocky soil;
- 20 W – in dry clay soil;
- 25 W – in wet clay soil;
- 35 W – in very damp clay soil.
Thus, to calculate the length of the collector (L), the required thermal power (Q) should be divided by the calorific value of the soil (p):
L = Q/p.
The values given can only be considered valid if the following conditions are met:
- The area of land above the sewer is not developed, shaded or planted with trees or bushes.
- The distance between adjacent turns of the spiral or sections of the “snake” is at least 0.7 m.
When calculating the collector, it should be taken into account that the soil temperature after the first year of operation drops by several degrees.
Feasibility of installing an air-to-water heat pump
The efficiency of using air-water heating systems is determined by the COP coefficient. It is used to compare electricity costs when generating heat (in our case, by a heat pump). The main consumption of electricity goes to powering the compressor that builds up pressure. The COP value shows how much thermal energy was obtained when a certain amount of electricity was consumed. For example, COP is 5. This means that an air-to-water heat pump, consuming 1 kilowatt of electricity, produces 3 kilowatts of heat.
But when assessing the efficiency of air-water installations, one more important factor should be taken into account, without which the assessment will be incorrect. This is dependent on the ambient temperature. When the outside air temperature drops, operating efficiency is greatly reduced. Therefore, the efficiency of the same pump in the north and in central Russia will differ significantly. This dependence on the OS temperature is the main disadvantage of air-water installations. Therefore, before purchasing such equipment, you should read reviews about its performance from people in your climate zone. It’s even better to see everything with your own eyes, if possible.
Tips for purchasing and installing a heat pump heating system
Based on the disadvantages of a heat pump, it is ideal for regions with moderate winters and is ineffective in cool and northern climate zones. But do not be upset if in winter in your area there are cold temperatures below -7C. In this situation, there are the following solutions:
- Inclusion of a buffer tank in the heating system, which will accumulate the resulting heat. One tank (small, apartment size) with the source turned off can evenly distribute heat throughout the system for up to a day. This is a convenient option for areas where severe frosts usually do not last long.
- Installation of an auxiliary heat source: gas or electric boiler. When a cheap heat pump cannot work, a less economical “backup” will replace it.
- Combination of the two previous techniques.
Attention! As with any heating system, before installation it is important to carefully check the heat loss of your home and, if possible, insulate it. The warmer the house, the less power you will need the device.
Specifics of application and operation
The heat pump operates productively exclusively in the temperature range from -5 to +7 degrees. At an air temperature of +7, the system will generate more heat than necessary, and at temperatures below -5, it will not be enough for heating. This is due to the fact that the concentrated freon contained in the structure boils at a temperature of -55 degrees.
- When installing an air-water heat pump, a small, neat device will appear on the facade of the house.
- Like any heat pump, the air-water system consists of two interconnected parts: external and internal.
- A unit of equipment located inside the house processes energy borrowed from the air, heating water for heating and hot water circuits.
- If it is necessary to increase the system performance, the external complex is supplemented with the required number of modules.
- Air-to-water heat pumps do an excellent job of heating water used in heating systems.
- Air-water heating units will provide warm water to bathrooms and kitchens of private houses with autonomous engineering systems.
- One of the most common energy consumers of air-to-water heat pumps is water heated floors.
- Low-temperature circuits are connected to the heat pump as an energy source.
Theoretically, the system can generate heat even in 30-degree frost, but it will not be enough for heating, because the heating capacity directly depends on the difference between the boiling point of the refrigerant and the air temperature.
Therefore, this system will not be suitable for residents of the Northern regions, where cold weather sets in earlier, but in houses in the Southern regions it can effectively serve for several cold months.
If standard batteries are installed in the room, the heat pump will work less efficiently. The air-to-water device is best combined with convectors and other radiators with a large area, as well as with water-type “warm floor” and “warm wall” systems.
Also, the room itself must be well insulated from the outside, have built-in multi-chamber windows that provide better thermal insulation than conventional wooden or plastic ones.

The heat pump interacts best with a water-based “warm floor” system, which does not require heating the coolant above 40 - 45º C
A homemade heat pump can effectively heat houses up to 100 square meters. m and is guaranteed to produce a power of 5 kW. It should be understood that it is impossible to fill freon with sufficient quality into a structure created in domestic conditions, so you should count on its boiling point of up to -22 degrees.
The home-assembled device is ideal for supplying heat to a garage, greenhouse, utility room, small private pool, etc. The system is usually used as additional heating.
An electric boiler or other traditional equipment for the heating season will be required in any case. During severe frosts (-15-30 degrees), it is recommended to turn off the heat pump to avoid wasting electricity, because during this period its efficiency is no more than 10%.
Heat pumps supply sufficient energy to heat water in indoor private swimming pools (+)
Drilling wells for a heat pump system
It is better to entrust the construction of a well to a professional installation organization. It is optimal for representatives of the company selling the heat pump to do this. Thus, it is possible to take into account all the nuances of drilling and the location of probes from the structure, and fulfill other requirements.
A specialized organization will assist in obtaining permission to drill a well for probes for a ground source heat pump. According to the law, the use of groundwater for economic purposes is prohibited. We are talking about using water located below the first aquifer for any purpose.
As a rule, the procedure for drilling vertical systems must be agreed upon with government authorities. Lack of permits leads to penalties.
After receiving all the necessary documents, installation work begins according to the following procedure:
- Drilling points and probe locations on the site are determined, taking into account the distance from the building, landscape features, the presence of groundwater, etc. Maintain a minimum gap between the wells and the house of at least 3 m.
- Equipment for drilling, as well as equipment necessary for performing landscaping work, is imported. A drill and a breaker are required for vertical and horizontal installation. To drill the soil at an angle, drilling rigs with a fan circuit are used. The most widely used model is the one that operates on crawler tracks. Probes are placed in the resulting wells and the gaps are filled with special solutions.

Drilling wells for heat pumps (with the exception of cluster wiring) is allowed at a distance from the building of at least 3 m. The maximum distance to the house should not exceed 100 m. The project is carried out based on these standards.
What depth should the well be
The depth is calculated based on several factors:
- Dependence of efficiency on well depth - there is such a thing as an annual decrease in heat transfer. If the well is very deep, and in some cases it is necessary to make a channel up to 150 m, the heat received will decrease every year, and over time the process will stabilize. Making a well of maximum depth is not the best solution. Usually several vertical channels are made, spaced apart from each other. The distance between wells is 1-1.5 m.
- Calculation of the depth of drilling a well for probes is carried out taking into account the following: the total area of the local area, the presence of groundwater and artesian wells, the total heated area. So, for example, the depth of drilling wells with high groundwater is sharply reduced compared to making wells in sandy soil.
Creating geothermal wells is a complex technical process. All work, from design documentation to commissioning of the heat pump, must be carried out exclusively by specialists.
To calculate the approximate cost of work, use online calculators. The programs help to calculate the volume of water in the well (affects the amount of propylene glycol required), its depth and perform other calculations.
How to fill a well
The choice of materials often falls entirely on the owners themselves.
The contractor may advise you to pay attention to the type of pipe and recommend a composition for filling the well, but the final decision will have to be made independently. What are the options?
- Pipes used for wells use plastic and metal contours. As practice has shown, the second option is more acceptable. The service life of a metal pipe is at least 50-70 years; the metal walls have good thermal conductivity, which increases the efficiency of the collector. Plastic is easier to install, so construction organizations often offer it.
- Material for filling gaps between pipe and soil. Well plugging is a mandatory rule. If the space between the pipe and the soil is not filled, shrinkage will occur over time, which can damage the integrity of the circuit. The gaps are filled with any building material with good thermal conductivity and elasticity, such as Betonite. Filling the well for the heat pump should not interfere with the normal circulation of heat from the ground to the collector. The work is done slowly so as not to leave any voids.

Even if drilling and positioning of probes from the structure and from each other are done correctly, after a year additional work will be required due to shrinkage of the collector.