Here you will learn:
- Operating principle of a water-to-water heat pump
- Heat pump device
- Advantages of water heat pumps
- Calculation of equipment power: implementation rules
- Recommendations for choosing a model
- How to make such a device yourself
- Assembling a pump from an old refrigerator
- Which is cheaper for heating: electricity, gas or heat pump
- Features of operation of such a heat pump
A water-to-water heat pump converts a heat source from a well and groundwater for heating and hot water supply systems in a private home. You can make it yourself or buy ready-made.
Operating principle of a water-to-water heat pump
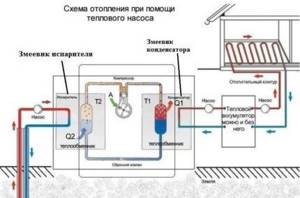
The heat pump embodies the principle of the Carnot cycle. It lies in the fact that a substance moving through a closed system and changing its state of aggregation from liquid to gaseous under the influence of chemical, physical or thermal factors releases and absorbs a huge amount of thermal energy.
The working substance is a heat carrier - water from a well or reservoir.
Even in winter, natural springs at a certain depth maintain a positive temperature, so thermal energy can be extracted from them all year round. The only drawback of the installation is the high power consumption and the need to purchase additional equipment.
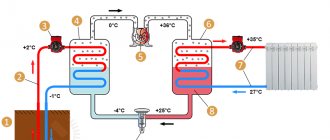
The diagram shows the circulation path of water and refrigerant. The system allows you to receive thermal energy, regardless of the season
The main elements of a water-to-water heat pump:
- compressor;
- evaporator;
- capacitor;
- expansion induction valve;
- automatic system that monitors indicators;
- multiple lines of copper pipes;
- working substance (refrigerant).
Using a special pump, water flows through tubes from the source to the heating unit, after which it interacts with gas (freon), which boils at a temperature of +2-3 degrees. Freon absorbs some of the heat from the water and is sucked into the compressor, where its temperature rises during compression.
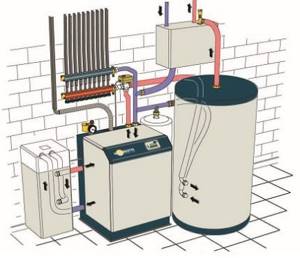
Heat pump equipment takes up a lot of space, but provides an opportunity to get rid of utility dependence
Next, the refrigerant enters the condenser, after which the hot substance heats the water to a given temperature (from +40 to +80 degrees), which is transported through the pipes of the heating system.
Cooled water enters the evaporator and then drains into the receiving well. After passing through the condenser, the refrigerant becomes liquid and collects at the bottom of the element, then returns through the throttle to its original location. Then the cycle repeats.
By design, a heat pump is an inverted refrigerator. Only its evaporator is immersed in water, and the heated part is on the ground and produces heat.
The operation of the internal block of the water-water geosystem is aimed at heating the coolant for heating circuits and water for hot water supply.
Heat pumps manufactured for low-rise buildings are pleasing with their small dimensions. They use water from open reservoirs, wells and antifreeze from closed systems laid in the ground.
Depending on the design and technical equipment, heat pumps consume from 5 to 25% of energy, the rest of the energy goes to providing engineering systems.
Preparatory work before operation
Preparation for assembly, connection and commissioning of a heat pump from the water-to-water series includes a number of standard steps, which we will get acquainted with later.
Choosing the optimal water source
It should be noted that not every open source or water well is suitable for the uninterrupted operation of a heat pump. Water quality plays an important role, but filters will help solve the problem of contamination.
It is permissible to use a reservoir or pond located within a radius of 100 meters from the building. If there is no such source, then the need to drill wells arises.
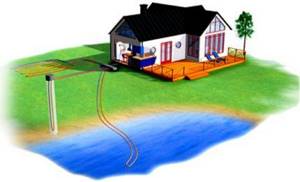
The choice of source for a heat pump should be based on ease of use and cost of use. If there is a nearby open reservoir, it is wiser to use it
The behavior of an open source is more predictable than groundwater, so if possible, it is better to give preference to reservoirs.
Image gallery
Photo from
Geothermal well for heat pump
Inexpensive heat pump evaporator option
Connecting the evaporator pipes to the heat exchanger
Evaporator pipes are prepared for inspection
Installation of a thermal system using a well
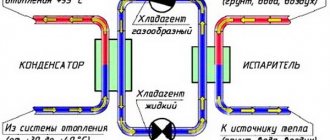
To install a system using a heat pump, you will need two wells. One of the wells is usually called debit. It is into this that a special pump is immersed, with the help of which water is taken for subsequent processing in the system. The second well is a receiving well. Cooled water is drained into it.
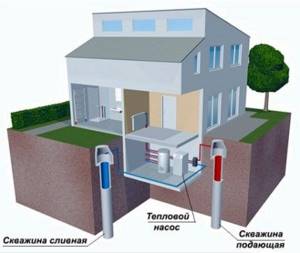
The drain and supply wells must be located at least 15 meters apart from each other.
The depth of the debit well should not exceed 50 meters. The deeper the water source is, the more powerful the pump required to supply it, which will increase the amount of energy consumed.
Construction of a debit well
Before starting to operate a debit well, it is important to find out how much water it can produce and how much liquid is needed to provide heat to the entire room. The higher the water temperature, the less it will be needed for heating.
It is important to pre-calculate the volume V that needs to be pumped out of the well within an hour to heat the room. Let's say there is a pump whose heat output is equal to a certain number Q kW, and the power consumption is equal to a number P kW. You will also need to find out the temperature of the groundwater ( t1 ) and its temperature after temperature exchange ( t2 ).
Then the formula for calculating the volume of the required amount of water per hour looks like this:
V = (QP)/(t1-t2).
It is analytically impossible to determine the ability of a debit well to produce the required volume of water, so it is tested. For 3 days, the pump uninterruptedly pumps water from the well. In this way, the receiving well is also checked for its ability to receive the required amount of water under high load.
It is important to understand that groundwater behaves unpredictably, so the amount of water from a debit well may become less over time. For example, in spring there are high tides, but in winter, on the contrary, the water decreases. If there is not enough water in the well, the system automatically turns off and heating does not occur.
Features of the receiving well
The receiving tube well is located downstream of the groundwater. It is analytically impossible to determine in which direction the water is moving. Therefore, in practice, an arbitrary well is selected as a debit well and a submersible pump is launched into it.
If the water level does not drop during operation of the system, then the choice was made correctly. If the level has dropped and the water temperature has dropped, then it is necessary to swap the wells - move the submersible pump to another hole.
The drain pipe into the receiving well must be immersed a few centimeters in water, without reaching the bottom. If you dump waste liquid from above, it will lead to waterlogging. The tube well may stop receiving water and become clogged.
The result threatens overflow, and in winter, possible icing. The best options for a receiving source are a river or pond. If these objects are not nearby, then there is a need to drill one or more receiving wells in order to insure against overflow.

The figure shows an example of using one well as a receiving and debiting well
It is impossible to find out whether a well will receive water either analytically or by testing. Practice shows that a drain well can uninterruptedly absorb water for many years, or it can completely fail in one season.
There are technologies that allow you to use one well as a debit and a receiving well, but this method is not effective - operation will be accompanied by difficulties, a decrease in water temperature, waterlogging and a number of other problems are possible.
Design of a system using a reservoir
The selected pond must be deep enough so that the lower layers of water do not freeze during severe frosts. In the Southern regions, the optimal depth will be approximately 1 meter; in the Northern regions, a source with a depth of 3 meters will be required. Also, the pond must be stable - fluctuations in the water level and its decrease are unacceptable.
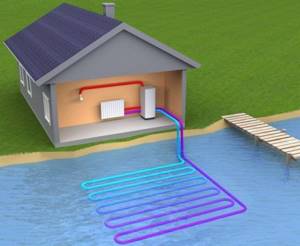
There are two pipelines to the reservoir - debit and receiving. A submersible pump is installed in the receiving area
It is recommended to use HDPE models as pipes, which are characterized by durability and reliability. It is important to protect pipes from freezing by additionally insulating them, and from breakthroughs.
Preparing your home for a heat pump installation
To interact with a water-to-water heat pump, the house must be equipped with a water-based heating system, presented in the form of pipes and radiator batteries. For better insulation, it is also permissible to install heating pipes in the floor and walls.
If the equipment will be used to supply hot water, then the house must have a collection system. To operate the pump, you need to be connected to an electrical network with unlimited power.
Without additional measures for thermal insulation of the house (insulation from the outside, installation of double-chamber windows, etc.), operating a heat pump makes no sense.
Experts recommend additionally installing a supply-type ventilation system with an air heating mechanism. The freon used in the equipment is harmful to humans. If micro-ruptures occur in the system circuit, the gas will be released and thereby displace air from the room. The refrigerant can cause exacerbation of lung diseases and asthma attacks in humans.
A heat pump is heavy equipment, its weight can reach a ton (depending on the power and size), so in some cases its installation requires the construction of its own foundation, not connected to the foundation of the cottage.
Before installing the equipment, you need to take into account the permissible dimensions of the room and maintain the distance to the walls specified in the product passport.
Heat pump device
The principle of operation has long been known. There are three closed, sealed circuits - internal, compressor, external.
Main components:
- Heating system. It is optimal to use warm floors. An additional option is hot water supply.
- Capacitor. Transfers energy collected externally from the refrigerant (usually freon) to the heating fluid (water).
- Evaporator. Collects thermal energy from the coolant (for example, ethylene glycol) circulating in the external circuit.
- Compressor. Pumps refrigerant from the evaporator, converting it from gaseous to liquid, increasing pressure and cooling it in the condenser.
- Expansion valve. Installed by evaporator. Regulates the flow of refrigerant.
- External contour. Placed on the bottom of a reservoir or lowered into wells.
- Internal and external circuit pumps.
- Automation. Controls the system according to a given amount of room heating and changes in outside air temperature.
In the evaporator, the coolant of the external circuit is cooled, giving off heat to the refrigerant, and then pumped through the external circuit by a pump. There it heats up and the cycle repeats again.
The external contour in the pond near the building looks like this.
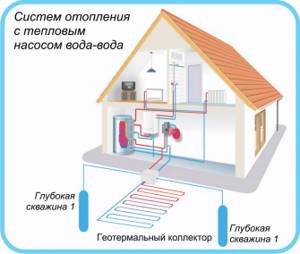
The collector is effective all year round. In winter, at a depth of more than 3 meters, the water temperature is sufficient for heating.
After the evaporator, the refrigerant passes through the compressor, where its pressure and temperature increase. Then the condenser transfers heat to the heating system.
The refrigerant then passes through the choke, where the pressure drops sharply due to expansion. When it transforms into a gaseous state, the temperature of the refrigerant decreases greatly almost instantly. This process can be experienced in practice when refilling a gas lighter from a can of liquefied gas. A significant temperature difference contributes to the effective absorption of heat by the refrigerant from the external circuit.
There is an option with an open collector. Possible when the water is of good quality. Then the system and the pump are not threatened by siltation, deposition of hardness salts, or accelerated corrosion.

Such heat generators found practical use only after the energy crises of the 70s of the last century.
Until then, their development was hampered by the relative cheapness of energy resources - oil, gas, etc. In addition, the imperfection of technology hampered the mass introduction of innovation.
Types of soil water collector
The ground source heat pump collector can be of two types (Fig. 2):
- Vertical;
- Horizontal.

2 Types of collectors for soil pumps: vertical and horizontal A vertical collector is a long pipeline lowered into a well, the length of which is from 40 to 150 m. This type of heat exchanger is better than horizontal ones in that at such a depth the temperature is higher. If the well is very deep, then the heat exchanger is also equipped with a protective casing pipe, but if the depth is relatively shallow, then this is not necessary. But a significant disadvantage of this method of reservoir placement is the high cost of such a well.
Of course, experts recommend drilling the well deeper. But if technology or soil does not allow, then several wells can be made. For example, you can make one well 80 m deep, or you can make 4 wells 20 m deep. The main thing is that the total result is sufficient to heat the house. There may be rocky soil, which is quite difficult to work with; wells can be drilled in it no more than 15-20 meters.
Horizontal collector (Fig. 3) - this type of soil collector for a ground-water pump looks like a pipeline that is laid out horizontally to a certain depth, under a layer of earth. This manifold is easy to install.

Rice. 3 External circuit of the ground-water pump
The area on which the earth heat pump collector is installed is quite large, in contrast to the vertical version, which requires a small piece of land. As a rule, a horizontal heat exchanger occupies from 25 to 50 m2, and maybe more, depending on the heated area. The negative factor of this option is that the area with this collector can only be used for a lawn.
Depending on various circumstances, the heat exchanger can be laid in a zigzag, loops, snake, etc.
It is very important what the thermal conductivity of the soil in which the heat exchanger is installed is. It depends on the quality of the soil, for example, if the soil is wet, then the thermal conductivity is greater, and if the soil is sandy, then the thermal conductivity is small
If there are many loops in the heat exchanger, then the package must include a circulation pump.
Advantages of water heat pumps
Compared to ground and air heat pumps, water-to-water heat pumps have the following advantages:
- open and closed reservoirs are used as a heat source for water heat pumps;
- reservoirs have a positive temperature even in winter;
- a water-to-water heat pump has a shorter external circuit - therefore, the energy conversion coefficient is higher;
- water-to-water heat pumps require less time and costs for preparatory work;
- the water heat pump circuit does not interfere with any activity (with a ground circuit, construction is prohibited and farming is limited).
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The video will introduce you to the principle of operation and features of the device:
As a result, we can conclude that a water-to-water heat pump is considered an effective environmentally friendly equipment designed to heat houses up to 150 square meters. Arranging a larger area may require quite complex engineering surveys.
If you have any questions while reading the information provided, please ask them in the block below. We are waiting for your comments, questions on the topic, stories and photos about the construction of a mini-hydroelectric power station with your own hands. We are interested in your opinion.
Calculation of equipment power: implementation rules
Before you begin choosing a specific heat pump model, you need to develop a design for the heating system that such equipment will serve, as well as calculate its power. Such calculations are necessary in order to determine the actual thermal energy demand of a building with certain parameters. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the heat losses in such a building, as well as the presence of a hot water supply circuit in it.
For a water-to-water heat pump, power calculation is performed using the following method.
- First, determine the total area of the building for heating which the purchased heat pump will be used.
- Having determined the area of the building, you can calculate the power of the heat pump capable of providing heating. When performing this calculation, they adhere to the following rule: for 10 sq. m of building area requires 0.7 kilowatts of heat pump power.
- If the heat pump will also be used to ensure the functioning of the domestic hot water system, then 15–20% is added to the obtained value of its power.
Calculation of heat pump power, carried out according to the above described method, is relevant for buildings in which the ceiling height does not exceed 2.7 meters. More accurate calculations that take into account all the features of buildings that are to be heated using a heat pump are performed by employees of specialized organizations.
Optional equipment
Selecting additional equipment for a heat pump is a responsible task, the solution of which largely determines the long-term service life of the heating system as a whole and the absence of operational problems.
Submersible pump for wells and reservoirs
If the system uses a heat pump to supply hot water, then a device with low power can reduce the pressure in the taps. A powerful pump will solve this problem, but it consumes more energy. The minimum permissible power when operating a GSV is 1 kW.
There are many different modifications of submersible pumps. The choice is made taking into account three criteria, these are:
- The amount of liquid used for pumping (the more water has to be transported, the higher the pump power must be).
- Well depth (the deeper the well, the greater the equipment power should be);
- Well diameter (traditionally, preference is given to 4-inch shafts, since the largest number of pumps have been created for them, as opposed to 3-inch ones).
To determine the depth of the well, it is necessary to attach a weight to a rope and lower it into the shaft. The wet part of the rope will indicate the full depth of the well, the dry part will determine the distance from the beginning of the water to the surface.

The pump is immersed in the wellbore to a depth specified by the device manufacturer. Usually the technical passport indicates how many meters there should be between the water surface and the pump, the bottom of the excavation and the pump
Both universal pumps and equipment specifically designed for wells can be suitable for mines. If the mine was developed by professionals, then it is less clogged with sand, so you can safely use a universal pump.
Pumps designed specifically for wells are more expensive, but they cope well with sand and dirt and become less clogged. Universal ones are sensitive to high organic content; they must be regularly cleaned of dirt, as a result of which their service life is reduced.
Preference should be given to pumps with automation, since if the motor overheats, there is excessive blockage or there is no water in the well, they turn off on their own, as a result of which the motor does not overheat and fail.
Based on the principle of operation, there are 2 types of submersible pumps:
- Centrifugal.
- Vibrating.
For work in wells producing water in limestone, centrifugal deep models are preferable. They are sensitive to water with grains of sand and clay suspension.
If the heat pump will be connected to an open reservoir, it is better to use surface pumping equipment designed for pumping dirty water, or an inexpensive vibration device.
Heat pump intermediate heat exchanger
In heat pumps, the freon may not be cooled well enough during circulation, causing the compressor to overheat due to excessive discharge temperatures. Therefore, it is important to improve the cooling of the substance, thereby reducing the pressure in the circuits.
There is another problem that is common to all heat pumps - the refrigerant can mix with water vapor. If liquid gets into the compressor, water hammer may occur. In this case, repair or replacement of the part will be necessary. Also, water can get into the oil, and it is difficult to remove it from there.
All the problems described above are solved by installing an intermediate heat exchanger. There are three types of heat exchangers - open type, shell-and-tube and coil.
The open type modification neutralizes the liquid that gets into the freon during circulation, which minimizes the likelihood of compressor water hammer. The device features high performance with minimal power consumption.

When installing an open-type heat exchanger, it is important to select the correct size of the liquid pipeline to ensure minimal pressure compression
Properly selected pipes will neutralize the possibility of boiling liquid. In this case, the valve must have sufficient throughput so that liquid can penetrate into the device at a low pressure difference.
The shell-and-tube heat exchanger is presented in the form of a closed structure. Heat exchange occurs through the walls of the pipes, and the liquid and refrigerant in it do not mix, unlike open ones, which provides high pressure for the circulation of steam and air.
The coil heat exchanger is distinguished by the presence of a flow regulator that controls the flow of liquid freon. The size of the device directly depends on the power of the heat pump. It is necessary to select a product taking into account the functionality and the amount available. It is advisable to give preference to collapsible models.
Heat pump filters
Water from wells or reservoirs does not come in pure form. It may contain sand, dirt, various trace elements - iron, hydrogen sulfide, manganese, chlorine, ammonia, etc. Before entering the heat pump, the water must be filtered.
First of all, it is necessary to eliminate large substances - stones, sand, dirt, silt. To remove them from the water, it is necessary to install a hydrocyclone.

A hydrocyclone is a device required for rough water purification. It must be selected taking into account the pump power
Next, it is important to install filters that eliminate iron, hydrogen sulfide, manganese, and ammonia. These microelements shorten the life of the equipment and expose it to corrosion.
You can use reverse osmosis filters, softeners, iron removers and their modifications. To provide drinking hot water, you should additionally equip it with carbon filters and a UV sterilizer that destroys bacteria and viruses.
Electric generator for backup power
Heat pumps operate from the electrical network, so if there is a power outage, the house will be left without heating. It is advisable to additionally purchase an electric generator that runs on flammable substances.

It is important that the electric generator can generate the necessary power to operate the pump compressor
Recommendations for choosing a model
In order for the heat pump, the operation scheme of which is described above, to demonstrate high efficiency, you should know how to choose the right equipment. It is highly advisable that the selection of a water-to-water heat pump (as well as “air-to-water” and “earth-to-water”) is carried out with the participation of a qualified and experienced specialist.
When choosing a heat pump for water heating, the following parameters of such equipment are taken into account:
- productivity, which determines the area of the building the heating of which the pump can provide;
- the brand under which the equipment was manufactured (this parameter must be taken into account because serious companies, whose products have already been appreciated by many consumers, pay serious attention to both the reliability and functionality of the models they produce);
- the cost of both the selected equipment and its installation.

Equipping a boiler room with a heat pump
When choosing heat pumps water-to-water, air-to-water, earth-to-water, it is recommended to pay attention to the availability of additional options for such equipment. This includes, in particular, the following opportunities:
- control the operation of equipment in automatic mode (heat pumps operating in this mode due to a special controller allow you to create comfortable living conditions in the building they serve; changing operating parameters and other actions to control heat pumps that are equipped with a controller can be performed using a mobile device or remote control );
- using equipment for heating water in a hot water supply system (pay attention to this option because in some (especially old) models of heat pumps, the collector of which is installed in open reservoirs, it is not available).
What to look for when arranging such heating?
There are a large number of different modifications of heat pumps designed for premises of any purpose and size, as well as operating in different conditions. The equipment is intended for heating houses with a total area of 50 to 150 square meters.
Guideline No. 1 – water hardness
The water quality of a well or reservoir plays an important role when choosing equipment. Not all models are able to work on hard water containing large amounts of manganese and iron.
A high concentration of these elements harms the system - corrosion forms on the pipes faster, which leads to a decrease in the efficiency of the equipment and its service life.
Therefore, before purchasing a heat pump, they take a water sample and analyze it for the presence of these and other microelements - hydrogen sulfide, ammonia, chlorine, etc. Usually, if the temperature in the pond exceeds +13 degrees, then there is a high probability that there are a lot of iron and manganese ions in the water.
Thus, the water-to-water heat pump is selected taking into account the water hardness. There are systems whose elements are maximally protected from corrosion, but they are more expensive.
Guideline No. 2 – operating mode
The heat pump can be used as the sole heat source or in conjunction with other systems. Therefore, before choosing a model, it is important to determine in which mode the device will operate.
There are two types of system operation:
- Monovalent. The devices have great power and are suitable for heating a home.
- Bivalent. Less efficient devices complement the main heating equipment.
To build an autonomous system with a main water-to-water heating unit, you need a monovalent type.
Guideline No. 3 – pump power
Power is an important indicator when choosing a heat pump, since the performance of the system depends on it. The higher the power, the higher the efficiency of the equipment, but the higher the energy consumption.
The performance of the water-to-water heat pump is selected based on real needs
If you choose a device with insufficient power, the efficiency of the system will decrease if the heat loss in the house exceeds the amount of energy supplied by the system. The heat pump can operate around the clock, but it will have no effect due to the drop in water temperature.
When the heat loss of a building is lower than the heat transfer of the system, the pump usually automatically starts for a few minutes, heats the water to the set temperature, and transports it through the system. Then it turns off until the temperature drops a few degrees. Then the cycle repeats.
Guideline No. 4 – functionality of a specific model
Heat pumps may have additional functions, these are:
- An automatic control system that will allow you to adjust the microclimate of the room to your taste. Control is usually carried out using a remote control.
- Water heating function for hot water supply.
- Soundproof housing.
- Possibility of connection to other heating systems, solar collectors, which will make the heating equipment completely autonomous.
The service life of water-to-water heat pumps usually exceeds 30 years.
Equally important when choosing equipment is the cost of installation and assembly.
How to make such a device yourself
A homemade water-to-water heat pump is a set of ready-made units that must be connected in the correct sequence. It looks simple, but in practice the whole thing can be ruined due to the lack of competent calculations. They are necessary to find out the optimal compressor power, the diameter of the heat exchanger pipe, as well as other system parameters. Non-specialists have several options for solving this problem:
- use special software (for example, CoolPack 1.46 and Copeland programs);
- use online calculators that are offered on the websites of manufacturers of such equipment;
- invite a specialist who will help you calculate everything for a fee or out of the kindness of your heart.
So, now about each detail in more detail.
Part #1 - compressor
The easiest way to get a suitable compressor is to remove it from an air conditioner, for example, from an LG split system. The seven-watt compressor has a power of 9.7 kW for heat production and 7.5 kW for cooling. An additional advantage of such compressors is their low noise level during operation.

The compressor for a water-to-water heat pump can be removed from an old air conditioner. It is preferable to choose a model that is suitable for power and operates silently
Many compressors use R22 freon, whose boiling point is -10 and condensing temperature is +55. In 2030, this refrigerant will be banned from use. A “younger” R422 freon may be a worthy alternative. However, you can change the refrigerant not only when creating a heat pump, but also at any suitable time.
Part #2 - capacitor
To make a condenser, you can use a stainless steel tank of approximately 120 liters. It is cut in half, a copper coil is mounted inside, connections with two-inch threads are welded, then the halves of the tank are connected by welding. The area of the coil through which the refrigerant will circulate is calculated by the formula:
PZ = MT/0.8RT, where:
- PZ - coil area;
- MT — Heat power generated by the system, kW;
- 0.8 - thermal conductivity coefficient during the interaction of water and copper;
- RT is the difference in water temperature at the entrance to the system and at the exit from it, degrees Celsius.
To make a coil, a half-inch copper pipe, a special refrigeration pipe or clean plumbing pipe, is suitable. The recommended pipe wall thickness is 1-1.2 mm. To turn a piece of pipe of the required length into a coil, it is enough to wind it on any suitable cylinder, for example, on a gas cylinder. The ends of the coil are brought out using plumbing adapters. To ensure a tight connection, use flax and a clamping nut.

To make a coil for a water-to-water heat pump condenser, you need to carefully wrap the copper pipe around the cylinder. A metal strip will help fix the pitch of the turns.
Please note that the freon inlet should be located at the top of the condenser to prevent bubbles from forming.
Part #3 - evaporator
A plastic barrel with a volume of 127 liters is suitable for the role of an evaporator. It is more convenient if it has a wide neck. The evaporator is calculated in the same way as the condenser. A copper pipe can be twisted with copper wire, without any insulation.

A homemade evaporator for a water-to-water heat pump can be made from a plastic barrel with a wide neck. The coil can be placed in a smaller container, but it is more convenient to work with a barrel with a volume of more than 120 liters
Experts recommend using “flooded” type evaporators for homemade heat pumps, in which the liquefied refrigerant enters the water from below and evaporates at the top. Adapters can be made from the necks of ordinary plastic bottles, which are fixed with flax and sealant. Standard sewer pipes are suitable for supplying and draining water. When installing a thermostatic valve, before soldering the equalization line pipe, you should wrap it with a damp cloth, since this element cannot be heated to more than 100 degrees.
Assembly and refilling with freon
To assemble the prepared devices into a single system, you will need a welding machine. It is recommended to make a filling valve at the entrance to the compressor, which will be useful in the future. Then, using a special vacuum pump, you should check the system for vacuum.
To charge the system with freon, you will need a cylinder containing at least 2 kg of refrigerant. After refueling, it is recommended to wait several days while checking the pressure in the system. If it remains constant, then there are no leaks. If the pressure decreases, you can determine the location of leaks in the simplest way: using soap foam. For inexperienced technicians, it is better to contact a specialist who will refuel the equipment professionally and reliably.
To automatically regulate the operation of the system, it is recommended to use a 40A single-phase starting relay, a 16A fuse, an electrical panel and a DIN rail. You will need two capillary temperature sensors: at the outlet of the system (recommended maximum temperature value is 40 degrees) and at the outlet of the evaporator (shutdown temperature is 0 degrees to prevent the system from freezing). If a controller is used to take into account the readings of both temperature sensors, you should remember that its settings may be lost if there is a power outage.

This is what one of the options for a homemade water-to-water heat pump looks like. The top of the device is covered with a metal casing on which the control panel is mounted
After the system is ready and its elements are placed in convenient places, two separate wells should be built for collecting and discharging groundwater and connecting the external circuit to the system. In areas where drilling wells is associated with certain problems, this issue should be addressed first. If wells cannot be drilled, you may have to choose another heat pump option, such as ground-to-water.
Useful tips
At all stages of building a house, starting from the design stage, we must remember that the HP is an inertial system. It can be compared to a massive Russian stove, which was usually heated once a day during cooking. Then the accumulated heat warmed the home until the next morning.
Walls made of heavy logs have a fairly high degree of thermal inertia. Simply put, they cool down slowly when it gets colder at night. Good thermal inertia for thick stone walls, as well as for heavy concrete or brick.
Polystyrene foam and foam concrete have good thermal insulation properties. But due to their low specific gravity they have low thermal inertia. A heater in a building with walls made of such materials, when the outside air temperature sharply drops, will not always be able to “pump” enough heat from outside into the “warm floor” heating system.
Other factors must also be taken into account:
- To reduce heat loss or avoid freezing of pipes in the main between the house and the wells or collector, it is necessary to lay them to a depth below the freezing level. In Crimea - 0.75 meters is enough, and at the latitude of Moscow - at least 1.5.
- The greatest heat loss is usually through windows. Therefore, triple glazing is not a luxury at all, but an economically sound construction solution. The ideal option is to use glass that can reflect infrared rays.
- In the case of using the option of 2 wells for collecting and draining water, the distance between them must be at least 20 meters.
- It is better to try a homemade TN first in a utility room or garage. Installing heated floors in a residential area will require additional costs.
Assembling a pump from an old refrigerator
There are two ways to make a heat pump from an old refrigerator.
In the first case, the refrigerator must be located indoors, and 2 air ducts must be laid outside and cut into the front door. Air enters the freezer through the upper one, the air is cooled, and through the lower air duct it leaves the refrigerator. The room is heated by a heat exchanger located on the rear wall.
Using the second method, making a heat pump with your own hands is also quite simple. To do this, you will need an old refrigerator; it just needs to be built outside the heated room.
Such a heater can operate at outside temperatures down to minus 5 ºС.

Technology for creating wells for heat pumps
The process of creating wells for heat pumps involves the use of specialized drilling rigs. However, before using them, you need to carefully calculate the parameters of the well itself. The most important of them are its depth and the materials used in installation.
Required well depth for heat pumps
The depth of wells for heat pumps is calculated taking into account several factors. These include the area of the house, and, accordingly, the amount of heat required for heating it. In addition, the already mentioned types of soil and the area available for the location of wells play a role. In the event that there are no area restrictions, it is better to make several medium-depth wells, about 30 meters deep. The equipment allows drilling to 100 meters or more. However, it is better not to do this, since it is much easier to maintain wells and monitor their condition at shallower depths.
Which is cheaper for heating: electricity, gas or heat pump
We present the costs of connecting each type of heating. To present the general picture, let’s take the Moscow region. Prices may differ in regions, but the price ratio will remain the same. In the calculations we assume that the site is “bare” - without gas or electricity.
Connection costs
Heat pump. Laying a horizontal contour at MO prices - 10,000 rubles per shift of an excavator with a bucket bucket (removes up to 1,000 m³ of soil in 8 hours). A system for a house of 100 m² will be buried in 2 days (true for loam, on which you can remove up to 30 W of thermal energy from 1 square meter of circuit). About 5,000 rubles will be required to prepare the circuit for operation. As a result, the horizontal option for placing the primary circuit will cost 25,000.
The well will be more expensive (1,000 rubles per linear meter, taking into account the installation of probes, piping them into one line, filling with coolant and pressure testing), but it will be much more profitable for future operation. With a smaller occupied area of the site, the output increases (for a 50 m well - at least 50 W per meter). The pump's needs are covered and additional potential appears. Therefore, the entire system will not work for wear, but with some reserve power. Place 350 meters of contour in vertical wells – 350,000 rubles.
A gas boiler. In the Moscow region, for connection to the gas network, work on the site and installation of the boiler, Mosoblgaz requests from 260,000 rubles.
Electric boiler. Connecting a three-phase network will cost 10,000 rubles: 550 for local electrical networks, the rest for the distribution board, meter and other contents.
Consumption
To operate a HP with a thermal power of 9 kW, 2.7 kW/h of electricity is required - 9 rubles. 53 kopecks at one o'clock,
The specific heat during combustion of 1 m³ of gas is the same 9 kW. Household gas for Moscow region is priced at 5 rubles. 14 kopecks per cubic meter
An electric boiler consumes 9 kW/h = 31 rubles. 77 kop. at one o'clock. The difference with TN is almost 3.5 times.
Exploitation
- If gas is supplied, then the most cost-effective option for heating is a gas boiler. The equipment (9 kW) costs at least 26,000 rubles, the monthly payment for gas (12 hours per day) will be 1,850 rubles.
- Powerful electrical equipment is more profitable from the point of view of organizing a three-phase network and purchasing the equipment itself (boilers - from 10,000 rubles). A warm house will cost 11,437 rubles per month.
- Taking into account the initial investment in alternative heating (equipment 275,000 and installation of a horizontal circuit 25,000), a heat pump that consumes electricity at 3,430 rubles/month will pay for itself no earlier than in 3 years.
Comparing all heating options, provided that the system is created from scratch, it becomes obvious: gas will not be much more profitable than a geothermal heat pump, and heating with electricity in the next 3 years is hopelessly inferior to both of these options.
Detailed calculations in favor of operating a heat pump can be found by watching a video from the manufacturer:
Some additions and experience of effective operation are highlighted in this video:
How to analyze climatic conditions and select the bivalence point
How efficient the operation of an air source heat pump will be directly depends on what air temperature is maintained outside the room. It is logical to assume that the higher it is, the more productive the air-to-water equipment demonstrates itself. If we consider it from the point of view of financial savings, then a powerful air source heat pump may not be profitable if installed in order to cover the heat load by 100%. It is much more rational to use similar equipment that can provide up to 90% of the heat demand, while during periods of peak loads it is better to additionally connect a heat generator of a different type, which can be a spare boiler or electric heater. Such a solution will ensure minimal costs for operating the equipment. Specialists in this field call the moment of transition to additional heating the point of bivalence. For Kyiv and surrounding regions, this parameter will be -7 °C, even though the air-to-water heat pump can easily cope with the load at -25 °C.
It turns out that it is enough to correctly calculate the necessary parameters just once before purchasing such a system in order to ultimately obtain a rational solution that ideally performs its functions and is not expensive in terms of cost. An air-to-water heat pump, which is not inexpensive, is still the most profitable type of heating and air conditioning, since it pays for itself very quickly and serves the owner for many years.
Features of operation of such a heat pump
Once a year, it is necessary to conduct an independent visual inspection of the pump components, follow the recommendations for maintenance - lubricate the parts in a timely manner, monitor the correct operation of the device when pumping water.
Some types of equipment require regular inspection (usually 1-2 times a year) by service center specialists. During the inspection, the following is revealed:
- engine oil leaks through cracks in the circuit;
- quality of fastenings and connections;
- pressure level in tanks and circuits;
- malfunctions in the power wiring.
The installation of a water-to-water heat pump should be carried out by trained specialists. The ineffectiveness of the system is most often due to its incorrect installation. Thermal equipment is suitable for use by both residents of the Southern and Northern regions.
What to buy - top 5 best pumps
Purchasing a heat pump is an important and responsible procedure. It is possible to give any recommendations in this area only if you have specific information about the size of the house, the material of the walls, the degree of insulation, the configuration of the premises, the type of heating system, etc. Without this data, it is pointless to talk about the best pumps. However, we can consider the most well-known manufacturers who supply high-quality equipment to the market and are leaders in this field:
ALTAL GRUP
The company is based in Ukraine, Russia and Moldova. Equipment production is focused on the conditions of Russian regions and can be used in harsh conditions
NIBE Industry AB
The Swedish company has been on the market since 1949 and is rightfully a leader in its field. Production is carried out according to the most advanced developments, the best materials and components are used
Viessmann Group
One of the oldest European companies - the company's foundation dates back to 1928. German specialists have gained extensive experience and achieved the highest quality of their products
OCHSNER
An Austrian company that was one of the first to begin serial production of heat pumps and has received recognition from users due to the quality, reliability and durability of the equipment
Heliotherm
Another Austrian company producing heat pumps and other equipment. Products are sold in Europe, high quality, reliability and wide functionality of heating systems are noted
Installation technology
Assembly of equipment of this type is carried out in several stages:
- a project is drawn up;
- collector communications are collected;
- a heat pump is installed in the system;
- equipment is installed inside the house;
- coolant is being filled.
Next, we’ll look at how to install a turnkey heat pump with your own hands step by step.
How to create a project
Before you begin assembling communications of this type, of course, you should make all the necessary calculations. The work of the external part of the system must be fully consistent with the work of the internal part. Calculations are made depending on the selected type of equipment. For horizontal collectors they are performed as follows:
- The amount of antifreeze required is determined. In this case, the formula is used: Vs = Qo 3600 / (1.05 3.7 t), where Qo is the thermal power of the source, t is the temperature difference between the supply and return lines. The Qo parameter is calculated as the difference between the pump power and the electrical power spent on heating the refrigerant.
- The required length of the collector is determined. The calculation formula in this case looks like this: L = Qo/q, where q is the specific heat removal. The value of the last indicator depends on the type of soil on the site. For clay, for example, it is 20 W per linear meter, for sand - 10 W, etc.
- The area required for laying the collector is determined. In this case, the calculation is carried out using the formula A = L·da, where da is the pipe laying pitch.
The power of the heat pump is determined approximately at the rate of 70 W of heat per 1 m2 with a ceiling height of 2.7 m. The collector pipes are usually laid at a distance of 0.8 m from each other or a little more.
How to assemble a heat pump
Equipment of this type is quite expensive. The design of a heat pump is relatively simple. Therefore, you can try to make it yourself. The procedure goes something like this:
- A compressor is purchased (air conditioning equipment will do).
- The capacitor housing is manufactured. To do this, a 100 liter stainless steel tank is cut in half.
- The coil is being manufactured. The gas or oxygen cylinder is wrapped with a copper tube from the refrigerator. The latter can be fixed using aluminum perforated corners.
- The coil is installed in the housing, after which the latter is sealed.
- An evaporator is made from an 80 liter plastic container. A coil made of ¾-inch pipe is mounted into it.
- Water pipes are connected to the evaporator to deliver and drain water.
- The system is filled with refrigerant. This operation should be entrusted to a specialist. If you do it ineptly, you can not only damage the assembled equipment, but also get injured.
Installation of collector communications
The technology for installing the external circuit of the heating system also depends on its type. For a vertical collector, wells 20-100 m deep are drilled. Under the horizontal collector, trenches 1.5 m deep are dug. At the next stage, pipes are laid. Trees should not grow near the horizontal collector, as their roots can damage the mains. To assemble the latter, you can use low-pressure polyethylene pipes.
Equipment installation
This operation is performed in the usual way. That is, heating radiators are installed in the premises, lines are laid and they are connected to the boiler. An expansion tank, a filter and a circulation pump on the bypass are mounted on the return pipe. You can also assemble and connect a “warm floor” system to the heat pump. At the final stage, the selected type of coolant is poured into the external and internal circuits.
As you can see, you can install the heat pump and collector yourself. Technologically, the procedure is not particularly complicated. However, unlike other types of similar equipment, assembling such a system, even of a horizontal type, is a physically quite labor-intensive operation. Drilling vertical wells on your own without special equipment is generally almost impossible. Therefore, it may still be worth hiring specialists to perform calculations and work on assembling the system. Today there are companies on the market that install equipment such as heat pumps on a turnkey basis.