Purpose of the pump for heating
Previously, circulation pumps were used only in centralized heating systems, and for private housing construction the natural movement of the coolant caused by temperature differences was the norm.
Now forced circulation is used everywhere thanks to the emergence of compact and inexpensive models designed to service the heating networks of small houses and cottages.
Due to the increase in the speed of movement of the coolant in the pipeline, thermal energy flows faster to the heating radiators, and accordingly, the rooms are warmed up faster. The load on the boiler has decreased because the water is also heated faster.
The need to install bulky and inconvenient large-diameter pipelines has disappeared; contours have become easier to camouflage under floor coverings or be buried in walls.
The main disadvantage of pumps for heating systems is their dependence on electricity. If the power supply is intermittent or there is a risk of a complete power outage for some period, it is necessary to install a backup power generator or at least an uninterruptible power supply.
The remaining disadvantages relate to the designs and functionality of various types of devices. For example, monoblock units and devices with a dry rotor are noisier and require constant maintenance, while a pump with a wet rotor is demanding on the quality of the coolant and has a pressure limitation.
Need for use
If in city central heating lines the water pressure is regulated by special centralized substations, then when equipping an autonomous heating and hot water supply system for a country house, a circulation pump device is an absolutely irreplaceable unit. Especially if we are talking about a fairly large building. The fact is that it is capable of “accelerating” the heat supply of a closed circuit in almost any conditions and in any weather.
Without forced circulation, the heating system tends to “heat up” for a very long time. This is especially true in cases where a country house is used not every day, but from time to time. In these cases, a heating circulation heat pump is able to create an optimal microclimate in much less time. Thus, in many cases it is simply impossible to overestimate the value and importance of this unit.
Criteria for proper selection of equipment
All installation efforts will be reduced to zero if the equipment is selected incorrectly. In order not to make a mistake, it is necessary to first analyze all aspects of a particular heating system and make the necessary calculations.
Main types of pumps
According to their design features, all devices are divided into 2 categories: with a wet and dry rotor.
Wet type pumps . This option is suitable for private homes. The unit is compact, almost silent and has a modular structure that is convenient for maintenance and repair.
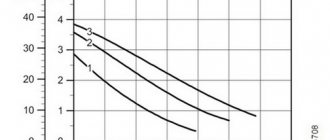
But, unfortunately, it does not have high productivity - the maximum efficiency of modern models reaches 52-54%.
Pumps with a dry rotor are productive, unpretentious to the quality of the coolant, capable of operating under high pressure and do not require a strictly horizontal position on the pipe. However, they are noisier, and their operation is accompanied by vibration. Many models are installed on a foundation or metal support frame.
For installation of console, monoblock or “In-line” models, a separate room is required - a boiler room. It is advisable to use them when a flow rate of more than 100 m³/h is required, that is, for servicing groups of cottages or apartment buildings.
Brief overview of technical characteristics
When choosing a pump, you should definitely study the technical characteristics and compare them with the requirements of the heating system.
The following indicators are important:
- pressure , which covers hydraulic losses in the circuit;
- productivity - volume of water or supply over a certain time interval;
- operating coolant temperature , max and min – for modern models on average +2 ºС… +110 ºС;
- power – taking into account hydraulic losses, mechanical power prevails over useful power.
Structural details are also important, for example, the inlet/outlet diameter of the pipes. For heating systems, the average parameters are 25 mm and 32 mm.
An example of a unit for equipping a residential heating network with an area of 100 m² is a Grundfos UPS with a 32 mm pipe connection, a capacity of 62 l/s and a weight of 3.65 kg. The compact and low-noise cast iron device is inaudible even behind a thin partition, and its power is sufficient to transport liquid to the 2nd floor.
Pumps with built-in electronics allow you to quickly switch equipment to a more convenient mode depending on changes in temperature or pressure in the network. Automatic devices are equipped with digital displays that provide maximum information on the operation of the pump: temperature, resistance, pressure, etc.
Additional information on the calculation and selection of a circulation pump for heating is presented in the articles:
Power calculation
Calculating the power of a heat pump is a rather complex process that requires not only sufficiently deep theoretical knowledge and rich practical experience, but also taking into account many aspects and nuances. Therefore, it is most advisable to entrust such calculations to highly qualified specialists. However, there are general principles on the basis of which power can be calculated. True, these calculations will be quite approximate.
There are two calculation methods:
- European. According to it, each square meter of an individual household should receive 100 W of heat, and an apartment complex – 70 W.
- Domestic. For low-rise housing (1-2 floors), it provides for the need to obtain 173 W of heat at a temperature of -25 degrees and 177 at -30. For multi-storey buildings, these indicators are set at 97 and 101 W, respectively.
Of course, in addition to power, the pressure in the system and its configuration itself are also important. That is why it is customary to entrust all calculations to experts from specialized companies. Professionally made calculations allow not only to fully satisfy heat needs, but also to avoid unjustified expenses, as well as unnecessary overloads of the system or, conversely, its idling.
Requirements for installation of a circulation pump
There are a number of standards that regulate at the legislative level the installation of a circulation pump in a heating system. Some of the rules are set out in SNiP 2.04.05 “Heating...”. For example, it talks about the priority of schemes with forced circulation in heating networks.
Almost all requirements are justified by the operating efficiency of the system as a whole and the circulation device in particular. For example, the shaft of a device with a wet rotor must be installed on the pipe strictly horizontally in level so that there are no air pockets inside and the pump parts do not wear out prematurely.
A filter for dirt and abrasive particles is needed in any case, even when installing monolithic models. Filtered coolant will cause much less damage to pump parts than liquid with sand and suspended matter.
The mudguard is installed with the plug down in the direction of water movement to reduce resistance and facilitate system maintenance.
Some rules are dictated by manufacturers. For example, it was customary to install old models of certain brands exclusively on the return line, since they could not withstand high temperatures.
Now pumps have become more versatile and can be installed in any suitable location, but subject to power parameters.
Analysis of installation technology
The installation process itself is quick; to secure the housing, you need to secure two union nuts. This is very convenient for further maintenance and repair work. But before installation, it is necessary to choose the right installation location, otherwise the pump will either work intermittently or will soon fail.
Schemes for inserting a pump into the network
When choosing one of the schemes, it is necessary to take into account the type of heating system, boiler model and ease of maintenance.
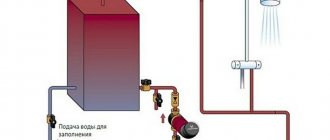
Option 1. This is the most common solution: the pump is mounted on the “return”, through which the cooled coolant returns to the boiler. Warm water does not have such an aggressive effect on the parts of the device, so it lasts longer.
Option 2 . This solution is relevant if for some reason it is not possible to install a pump on the return line. Then it is fixed at the beginning of the circuit, at the supply, but not near the boiler, but after the safety group.
Modern devices can easily withstand high temperatures, but there are still experts who reject such a scheme.
There is such a heating network option as an open system with an expansion tank installed at the highest point of the circuit.
If you install a circulation pump, you will be able to operate it in two modes: natural and forced. Natural circulation will come in handy if there are power outages.
The last scheme applies only to networks with a solid fuel boiler. The supply pump is not installed due to the risk of explosion. The fact is that with solid fuel boilers it is impossible to quickly stop the heating process, as a result of which the water boils.
Boiling water with steam gets inside the pump, it reduces productivity, the cooled water in the circuit does not have time to flow back into the boiler in the required quantity - and it heats up even more. The result of overheating is an explosion.
If you run cooled water from the circuit into a heating boiler, condensation will form. To prevent this from happening, the water is first heated in the small circuit to +55°C, and then the thermostatic valve smoothly switches to the large circuit.
As a result, cold water is mixed with already heated water and “temperature shock” does not occur for the boiler.
How piping is done
The circulation pump piping is the equipment necessary for its proper functioning, as well as for the smooth operation of the entire heating system.
First you need to finally decide how many pumps there will be. For one simple circuit, one device is enough, but with complex wiring it is possible to install two or more.
If you plan to use a “warm floor” system in your house or install an indirect heating boiler, then it is better to increase the number of appliances to two. If two boilers are installed - solid fuel and electric - you will also need a separate pump for each unit.
As mentioned above, ball valves are mandatory elements. They are mounted together with the pump, and in the event of an emergency, they will have to be used.
A check valve made of brass or cast iron is also required so that the coolant moves in one given direction. It is mounted on the pipe immediately after the pump, in the direction of water movement.
A “dirt filter” will be required to prevent solid particles from entering the device housing. Fine filters are not installed in heating circuits. If clean water is needed, it is pre-purified before being poured into the system.
There is a risk of air getting into the network, so there is a need to install an air valve. It can turn on automatically, but there are also manual models.
After installing all the devices, the pump is connected to power. A big mistake is to use an ordinary outlet without grounding. This is a safety violation and can cost lives in the event of an accident.
There are smarter ways to power power:
- via uninterruptible power supply (UPS);
- through a differential circuit breaker;
- by connecting to the boiler automation.
The easiest way is to use a circuit breaker: you will need an 8 A switch itself, contacts, and wires. But for practical use, a solution with a thermostat is very convenient.
If you plan to install a UPS, you can connect an uninterruptible power supply to both the pump and the boiler at the same time.
Step-by-step instruction
Let's start with the fact that if tie-in work is carried out in winter, that is, when uninterrupted operation of the heating system is necessary, then it is necessary to organize a so-called bypass - a temporary workaround that allows the heating system to operate in natural circulation mode.
The basic algorithm for installing the pump itself is as follows:
- It is necessary to pick up the assembled unit and point the marking arrow marked on it towards the heating boiler.
- On the right side, first the filter is screwed on, then the tap, after which a threaded angle with a tee is installed.
- On the left side, the same operations are carried out, with the exception of installing a filter - there is no need for it here.
- After which all that remains is to connect the resulting structure to the pipe, and the pump itself to the power supply.
However, pump installation looks simple and smooth only on paper. As a rule, such work requires cutting pipes, installing ball valves, connecting elements, and sometimes welding. Experienced specialists will cope with this much easier and faster.
Brief installation instructions
A common option is to install the pump on a bypass. This is due to two good reasons: it becomes possible to quickly dismantle or temporarily disconnect the device from the network, for example, if problems arise with electricity.
Various modifications of ready-made pumping units are available for sale: for welding or flange connection, with places for installing taps or valves, with a special area reserved for the pump.
But if you cannot purchase a ready-made unit or there is not enough space for its installation, you can independently organize the bypass piping and fix all the parts in the places allocated for them.
The following tools and materials are required for work:
- a set of open-end or adjustable wrenches for assembly;
- pliers:
- linen thread or tow;
- Unipak sealant.
American nuts are usually supplied with the pump, but taps, adapters or fittings will also have to be prepared. Attention should be paid to more reliable materials for making fittings and the diameter of the products.
- Assembling units with taps . Two will be located on the edges of the pump, the third will become part of a straight pipe. It is important to measure the “return” section in order to accurately weld the fragment with the tap.
- Assembling the pump loop. Tightening the nuts must be postponed until the final stage of installation, but for now they just need to be screwed on.
- Trying on the bypass loop . Mark the places where the units are welded into the pipe.
- Welding should be left to a qualified welder.
- Assembly of the lower unit is on the “return” side.
- Connecting the pump to the power supply.
As an example, install the GRUNDFOS .
Maintenance of the installed pump is carried out in operating mode. It is necessary to clean the filter more often and check the pressure gauge readings.
If the values do not correspond to the norm, the device must be removed and adjusted. It is better to do this in a specialized workshop.