Water supply in an apartment building, private house or country cottage is a common occurrence; water should be available at any time of the year. However, temperature fluctuations can make significant adjustments to the water supply process.
Insulation of external water supply in a private house
Apartment owners think little about how the water supply is organized, and owners of private houses are forced to take steps on their own to ensure that the water in the pipes does not freeze in winter. At the same time, we note that frost does not spare either steel or plastic pipes. The only way to keep water in liquid form and prevent damage to the water supply system is to fully insulate the water pipes. After all, unlike a heating pipe system, there is no warm medium.
Due to the fact that thermal insulation is carried out on your own site, we are not talking about an industrial scale of work, which means it makes sense to study how to insulate water pipes with your own hands.
Do underground water pipes need to be insulated?
If the pipes are laid below the soil freezing level - no, if above - yes.
The depth of the water pipeline is regulated by SNiP 2.04.02-84.
Depth of water supply SNiP 2.04.02-84 and SP 40-102-2000, MSP 4.01-101-2000
Let’s make a reservation right away that laying pipes at the correct depth neutralizes the effects of low temperatures; the material in this article is focused on those cases where, for certain reasons, the water supply system was buried at a shallow depth.
The need for insulation of external pipelines
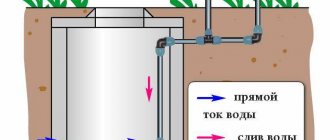
Connection diagram for water supply system with insulation
According to SNiP standards, to guarantee protection of water pipes from frost, they should be buried in the ground 0.5 meters deeper than the freezing level of the soil in the area.
But in private households, laying highways at such a depth is difficult and costly. And shallow pipes will lead to their freezing and failure. Therefore, in addition to a small layer of earth, it is necessary to provide additional protection for the pipeline during the cold season.
At country dachas, subject to periodic residence, insulation of local water supply pipes is required not only on the site, but also in the underground of the house.
Methods for insulating water pipes outdoors (in the ground)
- increasing pressure in the water supply system;
- cable for heating a water pipe;
- thermal insulation for water supply pipes.
Creating high pressure in the water supply system
The water pipe will not freeze because the water will move at high speed. To implement this method, a pump is used to increase the pressure in the water supply system or a receiver that cuts into the pipe directly next to the pump.
Heating cable for water supply
Cable power 10-15 W (average price – 15 USD/m.p.). Excellent for heating pipes in the ground when they are placed at a shallow depth. According to the rules, it is not advisable to place any communications in the soil below the soil freezing level. There are situations in which this requirement is ignored. In this case, simple insulation of pipes will not give the desired result, because... the pipeline will in fact be located in water (in a humid environment that freezes in winter). Most of the insulation materials are not suitable for this mode of operation and do not provide proper thermal insulation.
Using a cable to heat the water supply makes it possible to lay pipes at a depth of up to 500 mm.
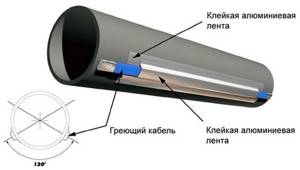
Heating cable for water pipe
The heating cable for insulating water pipes is wound along the pipe or around it with a given pitch. The pitch is determined by the power of the cable. The lower the power, the smaller the step. Methods for laying the heating cable are shown in the diagram.
Wiring diagram for installing a cable for heating a water pipe
Craftsmen and users note that insulating a water supply system by heating the pipe with a cable is the most reliable method for protecting pipes laid in the ground freezing zone.
Cable heating makes it possible to avoid freezing of water in the pipe, and, equally important, to quickly defrost frozen pipes. Such a need may arise at a dacha if it is intended for seasonal living. In this case, you can quickly prepare the pipeline for operation, because under natural conditions you can wait until May for complete defrosting (when laying pipes at the level of soil freezing). The cable is located both inside and outside the water supply pipe.
Note. Installing temperature sensors along the cable route will make it possible to monitor the cable temperature and regulate it manually or automatically.
Application of thermal insulation materials for pipes
This is the most cost-effective and easiest insulation method from the point of view of independent implementation. Let's look at it in more detail. Let's start with the best way to insulate a water supply system, what materials can be better used depending on specific conditions.
Factors affecting heating pipes in the ground
A heating pipe buried in the ground is subject to the same influences as an external pipeline, plus factors caused by burial:
- internal pressure of the coolant, causing circumferential and longitudinal tensile stresses in the pipe section;
- coolant temperature is a factor, in addition to thermal effects, also causing pipeline stress;
- soil temperature - in winter, taking this factor into account is especially important;
- soil deformations - the pipe is affected by any of its displacements (settlement, shear, etc.);
- pre-bending stress of the pipeline - the trench profile often follows the terrain;
- vertical load - the effect of the weight of the trench backfill layer;
- the resistive action of the soil on the walls and bottom of the pipeline - counteracting the vertical load;
- vibration loads - from passing vehicles, excavation work in the neighborhood, etc.;
- moisture – precipitation and groundwater;
- exposure to chemicals - compounds in the soil and coolant;
- biological factor - bacteria, decomposition.
Thus, laying a pipeline in the ground should be done taking into account all of the above factors and solving the question of how to insulate heating pipes in the ground.
Thermal insulation for water supply pipes
It is not difficult to get confused in the wide range of thermal insulation materials. To choose the best option, you need, at a minimum, to know the main types and types, key characteristics and features.
Thermal insulation of water pipes is carried out with various insulation materials, which are grouped below (in the form of a classification) according to the principle of unity of insulation technology.
Materials for insulating water pipes
Types, types, varieties and rules for choosing pipe insulation.
Rigid insulation
This category includes polystyrene foam, polystyrene foam (2560-3200 rubles/cube) and Penoplex (3500-5000 rubles/cube), thermal insulation properties and price depend on density.
Polystyrene foam is an excellent insulator and has a relatively low cost (compared to other materials). However, it is quite difficult to insulate a round pipe with a rigid insulation board. To insulate pipes, special shells (hard boxes) are used - shells in which pipes are placed, and the space is filled with soft insulation.

Laying water pipes in a foam box
Roll insulation
This segment includes: polyethylene (as an additional material), foil penofol (50-56 rubles/sq.m.), mineral wool (70-75 rubles/sq.m.) and glass wool (110-125 rubles/sq.m.) ), furniture foam rubber (250-850 rubles/sq.m. depending on thickness).
Insulating water supply pipes with rolled thermal insulation is also fraught with difficulties, which lie in the hygroscopicity of the material. Those. insulation loses its properties when exposed to moisture, which means it has a narrower scope of application, or needs additional protection. Plus, you need to think about how to attach the insulation to the pipe.

Basalt heat-insulating mats and foam rubber for insulation of water pipes
Segmental (shell) insulation
Pipe insulation casing is the most progressive option for pipeline thermal insulation. The shell for insulating the water pipe ensures maximum tightness and, as a result, creates a reliable thermal insulation layer.
There are types of segmental insulation:

Polystyrene foam shells for insulating water pipes are rigid (thermal insulating casing for pipes is a shell made of polystyrene foam (PPU) or foam plastic. Price from 190 rubles/m.p., depends on the thickness and diameter of the cylinder);

Pipe insulation made of foamed polyethylene for insulation of soft water pipes (pipe insulation made of foamed polyethylene, cost from 28 rubles/m.p. with a thickness of 13 mm); Material prepared for the site www.moydomik.net

Basalt cylinders for insulation of water pipes, basalt cylinders for pipes (from 15 rubles/m.p. with a thickness of 30 mm. (from 70 rubles/m.p. for foil-coated basalt cylinders).
Sprayed insulation (PPU)
The peculiarity of insulation by spraying polyurethane foam is that thermal insulation is applied to the surface of the pipe, ensuring 100% tightness (the cost of components for polyurethane foam filling starts from 3.5 euros per kg). The number of components is determined by the thickness of the fill; work is paid additionally). On average, the cost of insulation with sprayed polyurethane foam is 15-20 dollars/m.p.
Sprayed insulation also includes heat-insulating paint for pipes. You can apply it yourself, because... Thermal paint is sold in aerosol cans. A layer of paint of 20 mm. replaces 50 mm of basalt wool insulation. In addition, this is the only material that is not susceptible to damage from rodents.

Insulation of water pipes by spraying polyurethane foam (PPU)

Water pipe insulated with polyurethane foam (PPU)
When choosing thermal insulation material for insulating water supply pipes, you need to take into account the following factors:
- pipeline installation location. Insulation of pipes laid on the ground and located underground is carried out in different ways, even when using the same materials (it is also important to take into account whether the pipes are laid before or below the freezing level);
- frequency of pipeline operation. For example, in a country house that is not intended for permanent residence, it is enough to simply avoid a pipe rupture. To do this, a receiver is installed or the water supply is insulated with a cable. But in a private house it is necessary to ensure a year-round water supply. Here you need to approach the choice of insulation more carefully;
- thermal conductivity indicator of pipes (plastic, metal);
- resistance to moisture, combustion, biological activity, ultraviolet radiation, etc. determines the need to protect the insulation from these factors;
- ease of installation;
- price;
- life time.
Protection of insulation from negative factors
Protection against freezing of a water supply system located in the ground has its own specifics. The material should not completely or partially lose its thermal insulation properties under the influence of external factors.
Re-insulating or repairing the outer layers requires expensive and time-consuming excavation work, so immediate care must be taken to maintain the integrity of the protective structure.
Destructive effects of earth and water
The underground water supply system experiences soil pressure, so the material used for insulation may be crushed. This can significantly increase its thermal conductivity. To prevent such developments, it is necessary to create a hard outer shell using larger diameter pipes or special trays.

Mineral wool is hygroscopic and can be crushed with a little finger effort, so the layer of earth will compress the material and it will lose its low thermal conductivity property
In the case of using hygroscopic materials as thermal insulation of pipelines, it is necessary to prevent the possibility of influence of groundwater on them, which is always located in the ground, regardless of the degree of water saturation of the soil.
To protect mineral and glass wool, additional means of protection are used - plastic pipes larger than water pipes, which at the same time solves the problem of insulation collapse.
You can also use the following materials to create a waterproofing shell:
- rolled aluminum foil;
- reinforced (plumbing) tape;
- roofing felt;
- high density polyethylene film.
Polystyrene foam and extruded polystyrene foam weakly absorb moisture, but over time they also become unusable with constant defrosting. Foam glass, polyurethane foam, and heat-insulating paint are completely unaffected by wrinkles and moisture.

Protecting objects located in the ground from moisture using roofing felt is a long-used, but not the most practical option.
Solving the problem of insects and rodents
Another cause of damage to the insulation of the water supply system can be rodents and insects. Ants gnaw numerous passages in the thermal insulation that is attractive to them, and mice use it to build a nest. These actions expose parts of the pipes, which negatively affects the quality of insulation.
Neither insects nor mice can spoil polyurethane foam or foam glass, but they do an excellent job with basalt wool. It and similar materials for external insulation of water supply pipes must be protected from rodents if they are located at a depth of less than 2 meters. Earth ants do not penetrate below 1 meter, while forest ants build a large anthill, the above-ground part of which is impossible not to notice.
To protect against rodents, you can wrap the insulation with a fine-mesh metal mesh. To prevent access not only to mice, but also to ants, it is necessary to wrap the material with aluminum foil, reinforced tape, or use plastic pipes or trays of any shape as the outer shell.

A shell made of polyurethane foam or foam glass can withstand soil pressure, exposure to moisture in the ground, and cannot be damaged by rodents and insects
How to insulate a water pipe with your own hands
The location of the pipes is another important factor that must be taken into account when choosing insulation. Indeed, depending on where the pipes are located (in the ground, basement, cold attic, unheated room), the temperature and humidity conditions are determined, as well as the ease of installation of the insulation and the need for its additional protection.
Insulation of water pipes on the street
Water pipes are rarely laid by air or on the soil surface. Rather, in this case, the part of the pipeline that runs directly under the house or at the junction of the pipe with the pump, meter, or inside the distribution well needs insulation.
The specificity of insulation in this case is such that the pipe is insulated with any insulation that is capable of ensuring a sufficient tightness of the fit and is not exposed to moisture. As a rule, the thickness of the insulation intended for above-ground insulation of pipes is higher than for underground insulation. At this stage, it is important not only to insulate the pipe, but also to ensure protection of the thermal insulation material, in particular from getting wet.
Note. The most dangerous place from the point of view of freezing is the pipe exiting to the surface. To insulate this unit, it is necessary to use materials with greater thermal insulation capacity or lay it in two or three layers.
Insulation of water pipes in the ground
Such insulation will be needed only if the pipes are laid above the soil freezing level. To insulate a pipeline in the ground, you can use any material, including rigid insulation.
It is worth noting that the insulation of external water supply does not end with the installation of insulation. It is important to protect the insulation from getting wet. To do this, a film, roofing material is wound over the main thermal insulation material, or a plastic box is installed.
Thermal insulation materials for underground water supply and their features
In the construction industry, a variety of insulation materials are used, which are produced in rolls or sheets; it is clear that shells shaped like their surface are better suited for insulating pipes. Almost all materials used for thermal insulation are produced in the form of pipe shells, some of them have built-in channels for laying electric heating cables.

Foam pipe casing
Styrofoam
Expanded polystyrene EPS (foam plastic), due to its physical parameters and rigidity, is the most suitable option for thermal insulation of underground pipelines; its distinctive qualities are:
- One of the lowest thermal conductivity coefficients with an average value of about 0.04 W/m °C.
- High rigidity (depending on the brand) makes the material indispensable when used in environments with high loads on the shell; its density reaches 50 kg/m3.
- Polystyrene foam does not transmit or absorb water; water absorption depends on the density of the material and on average does not exceed 2%.
- Low cost, thanks to which polystyrene foam is available to a wide range of consumers.
- The service life of a foam shell underground is up to 40 years.
- The temperature range for using polystyrene foam is from -50 to +70 °C.
- Expanded polystyrene is resistant to chemical and biological effects of the underground environment, does not decompose under the influence of mold, bacteria, microbes and other microorganisms.
- The foam shell is lightweight and can be easily installed by one person in a short time without additional assistance.
An analogue of expanded polystyrene is the extruded variety (Orange Penoplex), which has higher strength characteristics, density, low water absorption of about 0.2% and thermal conductivity of about 0.3 W/m °C. Shells for thermal insulation of pipelines are also made from extruded polystyrene foam; it costs a little more than regular polystyrene foam.

Pipe polyurethane foam
Polyurethane foam
PPU polyurethane foam is the leader among all insulation materials in terms of thermal conductivity; thanks to this quality, it is widely used in the industrial production of insulated pipes with a zinc or polymer outer shell. The construction market offers polyurethane foam shells of various diameters and their characteristic features:
- Higher price compared to foam.
- Thermal conductivity coefficient is 0.025 W/m°C.
- Temperature range of use from -160 to +150 °C.
- Polyurethane foam has high rigidity and strength, its density reaches 250 kg/m3.
- The material is resistant to chemical and biological influences, does not allow water to pass through, its water absorption is 1 - 2%.
Polyethylene foam
Shells and foamed polyethylene PPE (Penoplex, Energoflex) are widely used for thermal insulation of external pipelines in individual houses; they can be used outdoors to seal open sections of pipes located in a caisson well or entering a house on stilts.

Polyethylene foam tubes
Due to their low rigidity, polyethylene foam tubes crumple when used underground without a hard shell and, due to a decrease in thickness, significantly lose their heat-insulating qualities, the main parameters of polyethylene foam:
- Thermal conductivity 0.31 - 0.55 W/m °C (depending on the brand, the figure is lower for products made using cross-linking technology).
- Temperature range -60 - +75 °C.
- Density from 25 to 100 kg/m3.
- Polyethylene foam does not allow moisture to pass through or absorb moisture, its water absorption coefficient does not exceed 1%.
Mineral wool
Insulation materials made from glass and basalt wool are widely popular among consumers due to their affordability and environmental friendliness, allowing their use inside residential premises. Glass wool has low rigidity and easily wrinkles, basalt-based material is stiffer, but due to the main disadvantage - high moisture absorption, shells made of quartz and basalt are not laid underground. Like other soft materials, mineral wool is used to insulate external water supply in coffered wells and supply points to the house.

Mineral wool shells
Mineral wool has the following characteristics:
- Thermal conductivity coefficient is 0.033 - 0.05 W/m °C.
- Water absorption is about 10%.
- Temperature range from -60 to +450 °C for glass wool and -100 - +700 °C for basalt (depending on manufacturing technology).
- Density 30 - 225 kg/m3.
- Mineral wool is resistant to most chemicals, non-flammable and does not support combustion.
- The cost of mineral wool is 2 times higher than that of expanded polystyrene.
Thermal insulation paints
This type of heat insulator is classified as a high-tech product; the acrylic-based paint contains perlite, foam glass particles, quartz fibers and microscopic granules containing a vacuum inside the shell. Thermal paint is applied to the surface to be treated with a brush or spray in several layers up to 4 mm thick; it is mainly used for treating surface pipelines and containers in the national economy; in everyday life, the use of this product is not economically feasible due to its high cost.

Application of heat-insulating paints
In addition, many experts are not confident in the veracity of the information provided by the manufacturer about the thermal conductivity of paint below that of air (0.0012 W/m °K versus 0.022 - 0.025 W/m °K), and indicate other data in independent calculations - 0. 07 W/(m·°K.) - this is lower than the values of any of the standard heat insulators.
Sprayed heat insulators
In industry, liquid polyurethane or polystyrene is often sprayed onto insulated surfaces, the two components are mixed and the composition is applied to the pipe shell with a spray gun. After spraying, the substance increases in volume and provides reliable thermal insulation of the object without cold bridges with high tightness.
Due to its high cost, the technology is rarely used in everyday life by individual homeowners, but theoretically, this installation can be used to coat HDPE pipes if you agree on a price with its owners.

Spraying polyurethane foam
How to install a heating cable for heating pipes
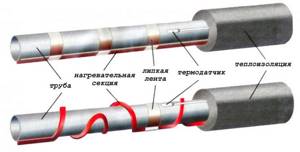
For installation, prepare: foil tape, thermal insulation material, heating cable (power 20 W per linear meter).
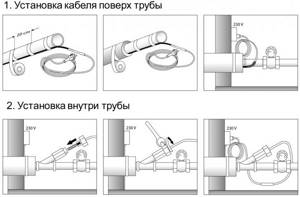
Installing a heating cable on top and inside a water pipe
Technology for insulating water pipes with cable:
- the pipe along its entire length (from the well/well to the house) is glued with foil tape;
- The heating cable is laid in a convenient way with the same pitch. For a 20 W cable, a pitch of 100-150 mm will be optimal. For a less powerful cable, the pitch is reduced. The most convenient way to lay the cable is to wrap the pipe in a spiral;
- the cable is fixed with foil tape;
- Insulation is installed on the pipe. Pipes made of foamed polymers, basalt cylinders or polyurethane foam shells are placed on the pipe. In this case, it is necessary to ensure that the diameter of the pipe corresponds to the internal diameter of the segmental insulation. Before starting work, roll insulation is cut into strips, which are wrapped around the pipe and secured with clamps or wire. Their task is to hold the insulation in a given position.
Note. The main thing when installing insulation is to minimize the number of joints that form cold bridges. Laying the heat insulator in two layers with an offset helps to completely eliminate them.
- the insulation is fixed to the pipe with tape (plumbing tape). The tape is wrapped very tightly. The main task of the winding is waterproofing, i.e. prevent groundwater from entering the insulation;
- additionally insulate the pipe at the point where it reaches the soil surface. The following options are offered: additional winding with insulation or arrangement of a box in which the insulation will be placed.
Advice. To avoid the risk of freezing of the water supply at the entrance to the house, it is advisable to wind the heating cable until it exits the wall in the house.
Installation of cable for heating pipes - video
Heating of external water supply systems
If we consider any system, then insulation is just a way to increase the time for its temperature to decrease to a value corresponding to the environment. Therefore, sometimes you have to resort to another option to prevent water pipes from freezing - heating.
The water supply is heated using external energy sources, and there are several ways to organize this process.
Organization of water circulation
The simplest source of additional thermal energy is water, the temperature of which is higher than in the insulated section of the water supply system. If warmer water constantly replaces cooler water, the system does not freeze. For this reason, the “half-open tap” method works, when a slow but constant movement of liquid through the pipes is organized.
For cold water supply to individual housing, it is possible to periodically replace the water in the outer branch with a warmer one. In the case of supply from the main water supply, it is necessary to drain frequently in small portions to ensure replacement of the liquid.
For this purpose, it is rational to use a special container located in the house, which also performs the functions of a sump, from which to subsequently draw water for your needs.

Draining water to prevent freezing can be done at times when it is not needed. The storage tank will allow you to use it later
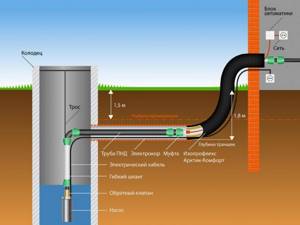
If the supply is organized from wells in which the water temperature is usually from 7 to 10 degrees Celsius, then it is necessary to turn on the pump more often. You can also use a regular storage tank or hydraulic tank to store water.
You can use a second pipe and a three-way valve to organize the circulation of the liquid and drain it back into the well. At one time, it is enough to pump 1.5 - 2 volumes of a section of water supply located in the ground between the head of the well and the entrance to the house.
In the case of drawing water from a well, there is also the option of draining it back by gravity after stopping the pump. This method is not advisable to use in the case of metal elements of the water supply system. Constant change of liquid and air leads to intense corrosion of the inner surface of pipes and deterioration of water quality.
In autonomous water supply systems based on wells, insulation of the water source is required in the same way as thermal insulation of the pipeline itself. We recommend that you read the article on methods of thermal insulation of water wells.
If there is a possibility of long-term idle water and, as a result, its freezing, then despite insulation, it is necessary to use other heating methods.
Using the Electrical Cable
Most often, electric cables are used as an additional heat source for individual water supply systems located in the ground. They can be placed both inside the pipe supplying water and on its external surface. The principle of heating is to convert electrical energy into thermal energy.

The electric cable heats the water supply elements, the heat from which is transferred to the water. External insulation prevents heat from escaping into the ground
Cables located inside the system have a higher efficiency than external ones due to direct heating of the liquid.
The disadvantages of this cable arrangement include:
- higher price per linear meter due to compliance with environmental requirements;
- the difficulty, and sometimes the impossibility, of passing through curved sections of the water supply system;
- specialists strongly recommend that the connection be made through an RCD, despite certificates of compliance with increased electrical protection requirements.
Installation of both options is approximately equal in complexity. The cable running inside the pipe is sold complete with a special termination coupling. Its connection is made through a standard tee. The outer cable is secured with aluminum tape, and an insulating shell must be placed on top so that the energy does not go into the ground.
Image gallery
Photo from
Installation of heating cable outside the pipe
Specifics of cable installation inside the pipe
Insulation of water supply in open areas
Laying pipes with cable in the ground
Complete with a resistive cable that produces a constant amount of heat, to save energy it is better to use a thermostat to automatically turn the heating on and off. When using a self-regulating cable option, it is necessary to select its parameters correctly, then there is no need to use a temperature regulating device.
There are ready-made complex solutions that, in addition to a water pipe, insulation and a rigid waterproof shell, have an embedded heating cable. Such kits significantly reduce the installation time of the system, but purchasing all the elements separately will be much cheaper.

Ready-made solutions for underground water pipes may contain a heating cable, which virtually eliminates the possibility of the system freezing
The heating cable can be used to heat both part of the system and the entire outer section of the pipeline, making it unnecessary to lay the pipeline below the seasonal freezing mark of the soil.
Application of warm air
Another effective way to protect a water pipe laid in the ground from freezing is to heat it with warm air from the house. There are two options - with natural and forced air circulation, and both require the installation of an additional closed tray or pipe of a larger diameter.
In the case of natural air circulation, a pipe is placed on the water supply and insulated from the outside. It has access to a warm room and, therefore, there is a slow circulation of air enveloping the water supply system with the transfer of heat from the basement or first floor of the house.
In the second case, two channels (U-shaped profiles) are attached along the entire length of the water pipeline, through which air passes. They are wrapped with insulation and covered with an outer pipe to prevent the insulation and profiles from being compressed by the earth.
At the end of the heated section, these profiles are connected, thus obtaining a closed system with input and output indoors. The air supply is forced using a hair dryer.
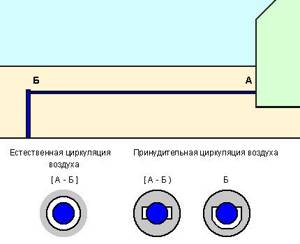
Schematic representation of the insulated structure of an underground water supply system in the case of heating it with warm air from the room. The forced circulation option involves using a hair dryer to direct a stream of air into one of the profiles
Useful tips
I told you all the methods that I once used. I think this is enough to insulate pipes in your dacha or country house. To ensure that the work is carried out as efficiently as possible, I will give you some tips:
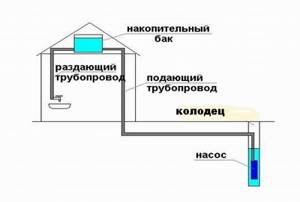
After laying utility lines, I recommend drawing up a diagram of their location.
- When burying pipes in the ground, do not be lazy to draw up an accurate diagram of the engineering system. Particular attention should be paid to the location of the connecting elements. It is at these points that pipes often fail when the water inside freezes.
- It is necessary to insulate both internal and external communications at the same time. As a last resort, if you need to insulate a short section of the system (50-70 centimeters), cut out a piece of pipe from the sewer, put it on the water supply and fill it with construction foam. Suitable as a temporary option.
Why do you need to insulate communications?
Perhaps someone may wonder why insulate something that is already hot. Indeed, the heating circuit is always warm, since heated coolant circulates in it. Do not forget that all insulation for heating pipes has excellent thermal insulation properties.
It is especially important to use insulation for heating pipes if the heating main runs through the air or underground from the place where the water is heated to the heated room. Let’s assume that the pipe is not insulated; this is extremely negative for heating. In this case, the boiler, or a set of heaters, raises the temperature of the water in the system and directs the working fluid to the place where it should give up its heat. Such places are heated residential and non-residential areas. The coolant interacts with the walls of the circuit and heats them. And they, in turn, interact with the environment. As a result, the water in the system becomes colder and, accordingly, the temperature in the heated room will also be lower.
It turns out that a certain amount of fuel was spent to heat the water. And since significant heat loss occurs from the place where the coolant is heated to the destination point, the efficiency of the heater becomes lower. A lot of fuel was burned, and the temperature in the heated rooms was low. Therefore, to reduce fuel consumption and increase efficiency, the pipe must be insulated. Various materials are used for heating in private homes and for large highways.
Criteria for choosing insulation
There are quite a lot of selection criteria, but they are all determined by significant factors. Let's go through the points so that everyone can choose insulation for a specific situation.
- Price. Yes, the first point is always the price. The question is not so much about the cheapness of the design, but about the specific insulation budget. A specific amount must be allocated that must be met, and only then the remaining parameters come. The cheapest option would be to fill it with expanded clay, but you need to install a separate box under it, which is extremely inconvenient, but cheap.
- Thermal loads. You need to know the temperature of the coolant in the supply line. The insulation must withstand this temperature without any kind of deformation.
- Impact of pests. If you are firmly convinced that you do not have pests, then you don’t have to look back at this point. If they are, you will have to treat the insulation with an antiseptic or use mineral wool. Remember, any modern insulation must be biologically inert. This means that despite any impact, bacteria or fungi will not grow in the insulation.
- Hygroscopicity. Insulation that absorbs water is not the best option. It will have to be covered with additional covers to protect it from moisture. But, if there are no other options, you can also use hygroscopic insulation.
- Shrinkability. Good insulation should not “shrink” over time. In practice, shrinkage means that after a certain period of time the insulation will have to be replaced. The absence of shrinkage extends the service life of the insulation.
- Easy to install. The easier it is to install the insulation, the better. But among other indicators, this one ranks last. If, after you have gone through all the points, there are still a few options left, you can think about ease of installation.
Stages of insulation at home
After calculating the insulation area, you can begin the procedure for calculating the thermal insulation material. Having chosen mineral wool as an insulating agent and purchased it, installation begins.
The installation diagram consists of the following steps:
- Rewinding the pipe with tape with a foil surface or foil, which acts as a heat reflector.
- Place the insulation over the surface of the pipe. The segmented casing is put on the channel, and the rolled casing must be cut into sections corresponding to the cross-section.
- Inspect the treated surface and eliminate any defects;
- Secure the material with metallized or plumbing tape.
- When the channels are in humid conditions, waterproofing should be done using roofing felt, iron, or fiberglass.
If the material contains a foil coating, which serves as an additional thermal insulation layer, then the effectiveness of insulation procedures increases. But such a coating does not resist mechanical stress.
Polyurethane foam
If you want to insulate with polyurethane foam, you need to spend quite a bit of money. The technology when using cylinders consists of the following stages:
- Spray the composition on the surface.
- After hardening, check for gaps and eliminate them.
- Provide protection from sunlight to prevent crumbling of the composition.
Please note: during the hardening process, polyurethane foam increases its volume by 2-3 times. If there are blanks in the form of half-cylinders, then put them on the pipe
They are usually equipped with a UV protection layer
If there are blanks in the form of half-cylinders, then put them on the pipe. They are usually equipped with a UV protection layer.
Expanded polystyrene
It is easier to install with ready-made shells than to cut sheets of polystyrene foam into pieces. It is worth considering that the upper limit temperature point corresponds to 75ºС. Therefore, the material is preferably used for insulating cold water supply pipes.
If a private house is heated using a coolant whose temperature does not exceed this value of 50-60 ºС, then it is allowed for use.
Shell installation diagram:
- Tape the abutting areas of the half-cylinders with double-sided tape.
- Place the shells on the pipes using the offset method at a distance of 10-20 cm to achieve solidity.
- Secure with single-sided tape.
- Apply a light-proof coating (fiberglass, foil insulation, glassine).
In the store you can purchase galvanized sheets for external closure, prepared for a specific shell size.
Having sheets of polystyrene foam available, you need to cut the blanks. Secure them with tape when applying them to the pipe. You should also use a light-proof coating if exposure to sunlight is possible.
Penoizol
It is used for insulating heating lines with special installations. Therefore, home use is excluded.
Foamed polyethylene and rubber
When purchasing rolled material, you need to wind it onto the pipeline and secure it with tape. If there is a cylindrical insulation, pull it over the pipeline like a stocking. If the pipes are already installed, then you can cut the cylinder lengthwise.
Widely used for insulating hot water, hot water and heating systems pipelines due to the material’s resistance to high and low temperatures.
Thermal insulation paint
The material is available in cans and aerosol cans. It can be applied by spraying or using a roller (brush). The layer is calculated based on climatic conditions and the properties of the fluid being moved. If severe frosts are observed, the layer becomes thicker.
After a section of the pipeline is insulated, you can think about the presence of a sealant. Pipe sealing tape is used if the pipe is laid underground. In this case, it is necessary to protect the insulating material from excess moisture.