In cars there is an insignificant, at first glance, but integral and very necessary element of the liquid cooling system - this is the expansion tank. It works as a compensator for fluctuations in coolant volumes when temperature conditions change. Depending on the complexity of the cooling system design, it can be either a regular reservoir for excess liquid or a device that regulates the pressure in the cooling system.
Purpose of the expansion tank
Coolants based on an aqueous solution of propylene or ethylene glycol have a higher coefficient of thermal expansion than distilled water. If you fill the radiator to capacity with such a cooler, then when the engine starts, the liquid will expand significantly under the influence of high temperatures, forming excess. Next, it will begin to be squeezed out of the radiator through the safety valve and will fall into that very simple expansion tank, which serves as a reservoir for the accumulation of excess antifreeze.
When the engine is turned off and cools down, the volume of coolant in the radiator will return to normal, and a vacuum will arise in the cooling system.
The radiator cap valve will work and suck in air, thus there is a high probability of air clots appearing in the cooling jackets. This will entail more global disturbances in the heat exchange process and overheating of the power unit. That is why there was a need to install an additional container for excess liquid, which would prevent air from entering the radiator, filling the free space with antifreeze. The expansion tank became such an element.
Today, there are systems in which a valve similar to the bypass on the radiator cap is present on the cap of the expansion tank. Its purpose is to release excess steam and even overheated antifreeze. In this case, the expansion tank is assigned the function of a kind of upper part of the radiator, which gives it every right to be considered an important element of the cooling system.
Expansion tank location
This device is located close to the radiator and is attached directly to the car body. The expansion tank protrudes above the radiator by half its size. This is necessary for the effect of communicating vessels to take place. They are connected to each other using a hose. It is attached to the bottom of the expansion tank on one side, and to the radiator filler neck on the other.
Thanks to this design solution, excess heated coolant enters the expansion tank, and when the engine cools down, the volume of coolant in the system is compensated from the contents of the expansion tank. With this process, air cannot enter and accumulate in the radiator.
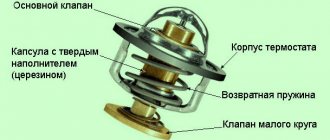
Expansion tank design
The design of this element is extremely simple. It looks like a plastic container in which a special sensor is mounted, which reacts to changes in the normal level of coolant. The tank is hermetically sealed with a lid with a pressure regulating valve, which is activated when there is excess pressure in the system above the nominal one.
Frame
Expansion tanks are mostly made of translucent plastic. There is a special scale on the side wall with which you can monitor the level of coolant in the system. The bottom mark shows how much coolant is required at a minimum. The maximum coolant level when the engine has cooled should not exceed three centimeters above the top mark of the scale marked on the side of the expansion tank.
We recommend: Steering rod - design and malfunctions
Expansion tank cap
The cover of the expansion tank of the power unit cooling system contains only three elements: a rubber mount, a spring ring and a top. The last element is the only block of air inlet and steam outlet valves.
When the engine begins to heat up, the coolant pressure in the cooling system, as well as in the expansion tank, accordingly, gradually begins to increase. When the pressure reaches a maximum of 120 kPa, the outlet valve opens. If the pressure drops below 83.4 kPa, it closes. If the pressure in the system increases excessively, it can cause damage to the hoses and even the radiator itself. The release valve of the expansion tank plug prevents the pressure in the cooling system from increasing to a critical level.
When the ignition is turned off and the engine cools down, the pressure in the system begins to decrease and a vacuum occurs. When the system pressure drops below 3 kPa, the inlet valve of the expansion tank opens and air enters it. The pressure begins to gradually normalize due to compensation of the coolant volume from the contents of the tank.
Possible faults
Considering the simplest design of the expansion tank, it cannot even occur to you that there is something in it that could break. This is just a container with a rubber lid, but it is precisely this that is not a simple element. This is a pressure relief valve, as we said earlier. The normal functioning of the engine cooling system depends on its correct operation. Also, the most common failures can fairly be considered leakage and rupture of the RB.
Expansion tank rupture
If the expansion tank ruptures, the volume of coolant that is necessary for the normal functioning of the engine cooling system is significantly reduced, and this leads to its inevitable failure. If the RB bursts, it is strictly forbidden to continue moving. A burst expansion tank must be replaced immediately and the nominal volume of coolant must be filled. Adding coolant is strictly prohibited, as this can lead to damage to the cylinder head. This is a significant breakdown and will seriously affect the operation of your car.
Expansion tank leak
It begins to leak due to a violation of the integrity of the housing as a result of any mechanical damage, a defect in the connecting hose, or a broken or simply loose cover.
Broken expansion tank cap valves
If the expansion tank cap is worn out, corroded or the valves are broken, the engine cooling system depressurizes. As a result, it is filled with excess air, which increases pressure and damages the elements of the system. This, of course, leads to inevitable overheating of the power unit. Also, excess air provokes “thrombus formation” in the cooling system, as a result of which the stove stops working.
If the lid valves become clogged, then their functions are also impaired. Again, excess air does not leave the system, it depressurizes, the pipes are damaged, and the engine is damaged. If the cap is slightly clogged, but the valves do not have time to draw in air and release it in a timely manner, then this has a detrimental effect on the radiator, it begins to leak. The thermostat and pump also break.
Subscribe to our feeds on social networks such as Facebook, Vkontakte, Instagram, Pinterest, Yandex Zen, Twitter and Telegram: all the most interesting automotive events collected in one place.
Purpose of expansion tank
The cooling systems of various cars contain from 5 to 20 or more liters of non-freezing liquid - antifreeze (antifreeze). During operation, the engine, and along with it the antifreeze, heats up from low temperatures in winter to high temperatures in summer.
The temperature difference can reach 100 °C or more. For example, when operating a car in northern regions, where engine warm-up starts at minus 20 °C and ends at an operating temperature of 90 °C, this difference will be 110 °C.
During engine operation, a pressure of about 1 bar arises in the expansion tank
Since any liquid expands in volume when heated, excess is formed in the cooling circuit of the car, which needs to be directed somewhere. Antifreeze is an incompressible medium, so when it expands, it will create high pressure in the system, which can rupture the pipes and radiator honeycombs. Conversely, when cooled, the liquid will decrease in volume and create a vacuum (vacuum), which acts with the same force.
To ensure normal operation of the power unit cooling system and avoid pressure surges, an expansion tank is integrated into it. Its functions are as follows:

Large expansion tanks are used on trucks
Antifreeze, which is a mixture of distilled water with ethylene glycol (sometimes propylene glycol), adds about 5% in volume when heated from zero to 100 °C. In a circuit designed for 10 liters of antifreeze, after complete warming up, as much as 500 ml is formed, which goes into the expansion tank.
Video: why do you need an expansion tank?
A little theory
During operation, a pressure is created in the cooling system that is significantly higher than atmospheric pressure. It is created due to the fact that the coolant heats up along with the engine, as a result of which it increases in volume. As a result, the pressure increases, and due to the lack of contact with the environment, there is nowhere for it to escape.
This is where the same expansion tank cap comes to the rescue, through which the pressure in the cooling system is regulated.
At normal atmospheric pressure, water boils at 100°C, antifreeze at 110°C, antifreeze at 120°C. And modern cars have operating temperatures very close to these values.
In some cases, a short-term increased temperature is created, which will have little effect on the engine, but will create even more pressure in the cooling system. For example, in cars of the VAZ family, the coolant can heat up to a temperature of 125°C. Which is even higher than the boiling point of antifreeze. But from physics you can remember (or learn