Thermostat
Purpose and design features of thermostats
The thermostat automatically maintains the required fluid temperature in the cooling system and allows you to quickly warm up a cold engine after starting.
By design, thermostats can be liquid (bellows) or with a solid filler, as well as single-valve, two-valve and two-stage. In addition, thermostats are electronically controlled by means of a tracking temperature sensor and an on-board computer, while the design of the mechanical part of such thermostats can be different.
Single-valve thermostats completely limit the fluid flow, while two-valve thermostats can distribute the fluid flow between a large circle (circulation through the radiator) and a small circle (circulation only inside the cooling jacket).
Design and operation of a bellows thermostat
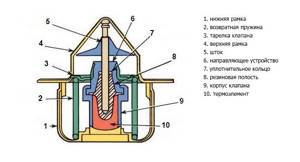
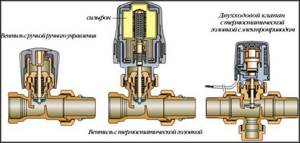
A liquid (bellows) thermostat (Fig. 1, a) consists of a housing 7 with windows, a corrugated cylinder 2 filled with an easily evaporating liquid, which is usually a mixture of 2/3 distilled water and 1/3 ethyl alcohol, as well as a valve 5. A rod 3 with a valve is soldered to the upper part of the cylinder, the lower part of the cylinder is rigidly connected to bracket 8 of the thermostat housing. The stem can move in the body guide, opening and closing the valve.
If the liquid in the bellows is cold, ethyl alcohol does not evaporate, and there is no excess pressure in the cylinder. The valve that allows coolant to flow to the radiator is closed. As the coolant warms up, the container with a mixture of water and alcohol also heats up, and the alcohol begins to evaporate intensively, raising the pressure in the container. The bellows begins to expand in length, acts on the stem and opens the valve, after which the liquid begins to circulate in a large circle through the radiator. The valve begins to open at a coolant temperature of 70...80 ˚С, and fully opens at a temperature of 85...95 ˚С.
Design and operation of a thermostat with solid filler
The bellows (cylinder) of a liquid thermostat is its weakest element - microcracks often appear on the thin corrugated shell, leading to its depressurization and failure. For this reason, modern cars often use solid-state thermostats, the main working element of which is cylindrical capsules filled with a solid filler, which is usually crystalline (granulated) petroleum wax (ceresin) mixed with copper, graphite, aluminum filings or powder. This substance can expand significantly when heated when it changes from solid to liquid. The capsule with the heat-sensitive substance is closed with a rubber buffer membrane connected to the rod that controls the thermostat valve.
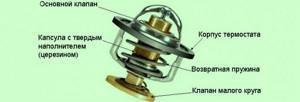
When the wax melts or similar heat-sensitive substance begins to melt, a rod is squeezed out of the capsule, opening the thermostat valve and allowing coolant to flow to the radiator. When the engine cools, for example, after stopping it, the wax returns to a solid state, decreasing in volume. In this case, the rod that controls the thermostat valve returns to its original position, closing the large circle of the cooling system.
As the coolant temperature decreases, the volume of ceresin decreases and the thermostat valve closes under the action of the return spring.
A common disadvantage of thermostats with heat-sensitive fillers is the interruption of fluid circulation through the radiator at low ambient temperatures (for example, in winter) when the engine is not yet warmed up. If the cooling system is filled with water, this can lead to freezing in the lower tank or radiator core tubes, causing it to fail. Water freezing can also occur in the lower rubber pipe - it becomes hard to the touch. In this case, the engine can quickly overheat, since the circulation of water in a small circle does not provide proper cooling of the parts. Therefore, in engine cooling systems with thermostats in the winter, it is advisable to use low-freezing liquids or insulate the radiator. If the water nevertheless freezes in the system, the car must be urgently placed in a warm garage or the frozen areas of the cooling system must be poured with boiling water.
Electronic thermostat
The most modern type of this device is an electronically controlled thermostat. Using an electronic control system, the most optimal engine cooling process is ensured, and the design can operate in both automatic and manual mode. Electronically controlled thermostats are installed on modern passenger cars equipped with an on-board computer operating under the control of a program that monitors, among other things, the thermostat.
On some engines, two thermostats may be installed. This design is often used in engines equipped with a dual cooling system, with one of the thermostats monitoring the heating of the temperature-sensitive element, the other monitoring the coolant temperature.

Source
The structure of the Cummins liquid thermostat
The liquid thermostat consists of a housing with windows, a corrugated cylinder filled with a liquid that can easily evaporate (a mixture of ethyl alcohol and distilled water) and a valve.
The lower part of the cylinder has a rigid connection with the body bracket, and a rod with a valve is soldered to the upper part. The rod moves freely in the housing guide. When the liquid in the cooling system has not yet been warmed up, the pressure in the bellows is accordingly low and the liquid is in a compressed state and the valve is closed.
When the cooling system begins to warm up, the liquid evaporates, increasing the pressure, the bellows expands and opens the valve. As soon as the valve begins to open, coolant begins to circulate through the radiator.
Liquid-type thermostats have a rather limited service life due to the fact that microscopic cracks form on the walls of the bellows and the seal is lost. Therefore, thermostats with solid filler are now used on engines.
Diagnosis of thermostat malfunctions and repair features
An internal combustion engine can only operate within a narrow temperature range. Deviation to a smaller or larger direction leads to increased wear and damage to the motor. The main purpose of the thermostat is to maintain optimal operating conditions. It helps speed up the engine warm-up process, and in the event of impending overheating, it ensures a decrease in coolant temperature. Failure of the thermostat can result in the engine boiling, which can cause significant damage to the power plant, so at the first suspicion that the device is not working properly, it is necessary to diagnose the engine cooling system.
Historical excursion
Automobile manufacturers have been serially installing a thermostat in liquid cooling systems since 1922. This was due to the advent of power plants that generate large amounts of heat, in which standard heat transfer fins no longer cope with the task assigned to them. A thermostat became necessary to prevent the consequences of overheating the engine.
The first designs did not provide high operational reliability. In the process of improving automobile thermostats, several main types of thermostats have appeared. Their design was very different; for example, the filler could be liquid or solid. Modern devices have acquired electronics that allow them to receive control signals from an electronic controller.
Types of thermostats
There are several modifications of thermostats on the market, differing in their structure and operating principle, but they all perform the same functions.
Mechanical regulator
Mechanical thermostats provide for manual adjustment of the degree of heating of radiators. They are inexpensive, reliable in operation, easy to set up and almost never fail, since all their work is based on the mechanical laws of physics. On the tap itself there is a graduation in degrees, which allows you to adjust the heating with fairly high accuracy. However, this installation is carried out experimentally - you cannot simply set the required number of degrees, which can be attributed to the disadvantage of the device.
Mechanical regulator
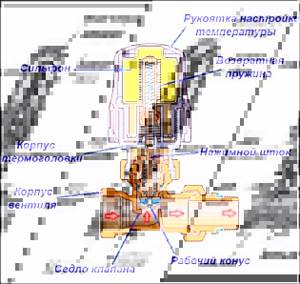
A mechanical thermostat has three main working parts - a bellows (gas or liquid), a drive and the regulator itself. The filled bellows (the substance in it) plays a decisive role in the automatic adjustment of the device. When we turn the thermostat lever, the contents flow into the spool, affecting the position of the rod.
The rod itself, when pressure is applied to it, lowers and partially blocks the passage for the coolant. Limiting its passage. The diagram below shows a more detailed structure of such a thermostat.
The structure of a mechanical thermostat
Electronic thermostat
The second type of thermostat is electronic. A microprocessor is installed inside it, which is responsible for regulating the heating of the batteries. Of course, such devices are very convenient to use, as they allow you to perform degree-by-degree adjustments.
Electronic thermostat
The thermostat is usually controlled using a button panel, which is quite reliable and convenient. Some models can simultaneously control boilers, pumps and even mixers. They cost a lot, which is not surprising.
The electronic thermostat also has a mechanical working part, which is practically no different from the option described above. The bellows in this case is cylindrical, and its walls are made in the form of corrugations. Inside the bellows there is a substance that reacts to the surrounding temperature.
The electronic thermostat looks very technologically advanced
When heated, such a substance begins to expand, and the pressure inside the device increases, affecting the position of the rod, which also regulates the volume of coolant passing through the device. When the temperature decreases, the reverse process occurs. Such a thermostat is very reliable, the bellows can easily withstand tens of thousands of compressions and expansions, its resource will last for more than 10 years, the main thing is that the electronics do not fail.
Among electronic thermostats, two different types of devices can be distinguished - closed and open. The former cannot determine the temperature automatically, so the user must make all settings independently. Its advantage over a manual device is that you can set the temperature in degrees, rather than on a graduated scale of more or less.
Open ones are complex electronic devices with programming capabilities. For example, when the temperature rises to a certain threshold, the device automatically changes its operating mode to the selected one.
Batteries are required to power the electronic part.
Such thermostats operate from replaceable batteries – batteries. It does not consume much energy, so frequent replacement is not required - you can do this 1-2 times during the entire heating season. There are also models that have a rechargeable battery installed - a charger is included with it.
Innovation Monitor
There are also semi-electronic devices. Their operating principle is also similar to mechanical ones, but there are several important differences. The bellows head is oriented to the room temperature, so it is quite large. They have a remote sensor, which is connected to the working part by a capillary tube.
Operating principle of a solid-fill thermostat
The mechanical valve is the main structural unit that distributes antifreeze flows. It is controlled by a heat-sensitive element, which is often used artificial wax, located in a sealed chamber. Its melting leads to an increase in the occupied volume. The wax compresses the rubber chamber. It, in turn, acts on the chrome-plated metal rod. The activated valve opens or closes the flow of fluid, which is the main principle of how the thermostat works.
Device and principle of operation
Regardless of the design option, the thermostat device follows one general scheme and consists of 3 main modules or blocks:
- Primary temperature sensor equipped with a temperature-sensitive element;
- tuning module;
- control module.

The primary sensor determines the heating temperature of the controlled medium: air or water. When the temperature inside the measuring sensor changes, the physical parameters of the primary element change, which are transmitted to the control unit.
Important! The output signal into which the input quantity is converted can be non-electrical or electrical. Most primary sensors are electrical, operating on voltage or EMF.
After receiving the signal, the control unit processes and transmits it to the actuator, which will accordingly adjust the volume of energy carrier to heat the environment.
The following are used as actuators in heating systems:
- electromagnetic relays;
- valve of mechanical or electrical operating principle;
- digital/analog device for subsequent signal processing.
TP is capable of maintaining a certain temperature value or a set range. This indicator is affected by the hysteresis of the primary sensor.
In the retail chain today there are quite a few models of thermostats that can be equipped with additional functions, for example, starting heating using a timer and programming the device according to a given schedule. But the operation of all these devices is based on the above-mentioned principle of operation.
Operating principle of a liquid filled thermostat
The operating principle of a thermostat with a bellows is similar to devices with a solid filler. The main difference is that the temperature-sensitive element is a mixture of distilled water and ethyl alcohol. When the engine is cold, evaporation does not occur inside the sealed cylinder and there is no excess pressure. The thermostat valve prevents coolant from circulating through the radiator.
When the engine heats up, ethyl alcohol begins to evaporate rapidly. The pressure in the cylinder increases. The bellows, which expands in length, acts on the stem and the valve opens. After this, the antifreeze enters the large circulation circle instead of the small one.
Thermostat device with liquid filler
The liquid filled thermostat consists of a body, a brass corrugated cylinder, a stem and a double valve. The corrugated cylinder is filled with a special liquid with a boiling point of 70-75 degrees Celsius. The opening temperature of the main thermostat valve is indicated on its body and may vary. For example, on engines of cars supplied to countries with hot climates, thermostats with a minimum valve opening temperature are installed.
A mercury thermostat for maintaining the temperature in an incubator for chickens was invented by the Englishman Cornelius Drebbel in 1620
As long as the engine coolant temperature is below the boiling point of the thermostat fill, the main valve is closed. At this time, the coolant circulates in a small circle, that is, through the engine itself, without entering the cooling radiator.
When the coolant is heated to 70-75 degrees, the liquid contained in the thermostat cylinder begins to boil and evaporate. The pressure in the cylinder increases, “unclipping” it. The stem moves and opens the valve. A path is created for the coolant to move in a large circle through the radiator.
The automobile gel thermostat was invented by the Frenchman Serge Vernier in 1936. Vernet continues to produce thermostats for a wide variety of cars today
When the temperature of the working fluid in the cooling system reaches 90 degrees, the thermostat valve opens completely. At the same time, its beveled edge blocks the access of liquid to the small circle.
Types of thermostats
Design options for thermostats include:
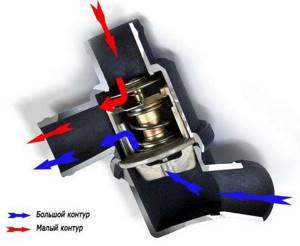
Single-valve technology has gained the most popularity. It is simple and reliable. Cars of past years predominantly had this type of thermostat. The two-stage design became a necessary measure caused by high antifreeze pressure. The thermostat valve was not able to overcome the force, resulting in small and large plates in the design. The smaller one opens first, as it is subject to slight coolant pressure. During the second stage, the main plate is added and all the antifreeze is directed into a large circle.
The two-stage implementation has only one valve. In contrast, the design of a two-valve thermostat involves the presence of two separate control devices combined in one housing. Each valve is responsible only for its own circle of coolant circulation. The most important thing in the design is the synchronization of the operation of each part of the device.
Automakers managed to achieve maximum accuracy in operation by equipping the thermostat with electronic control. The design difference with the classic model is the presence of a heating resistance. The thermostat maintains the engine temperature at 85-95°C at high loads and 95-110°C in other engine operating modes. This allows you to reduce fuel consumption and get a slight increase in power. The thermostat receives the control signal from the injector ECU. In the case of a diesel engine, the temperature ranges may be different.
Diagnostics and repair
You can answer the question whether the unit is working without the help of a specialist using the instrument panel. If the temperature outside is zero, then the engine should reach optimal operating temperature within 5-10 minutes of driving. The main thing is that the sensor is in working condition and accurately displays readings.
In the absence of such deviations, a signal of a possible breakdown will be:
- constant overheating of the motor;
- lack of operating temperature for a running internal combustion engine;
- long time to warm up the engine;
- irregular presence of the above symptoms.
If the unit malfunctions, the upper radiator pipe begins to heat up almost immediately after starting the engine. This indicates that the coolant is passing through a large circle, which means the valve is already open. In a working, serviceable CO system, the upper pipe should remain cold for some time after starting the car.
Because of this, the engine is not able to reach the required temperature. The moving elements are not lubricated to the required extent, parts wear out, and the oil thickens, losing its properties. As a result, fuel consumption and the risk of engine failure increase.
In case of intermittent malfunctions, the thermostat “sticks” is observed. To identify its presence, system diagnostics and replacement will be required to avoid more serious damage.
You can check the functionality of the device yourself. To do this, you need to remove it and place it, for example, in a pan of water. To create working conditions, just boil water. If the valve on the device opens approximately 0.2 cm and closes after cooling, the device can be operated.
Design features of thermostats
Structurally, thermostats are divided into cased and uncased. Each type has its own advantages. The leader at the moment is still a thermostat with a shell.
The case thermostat, regardless of the internal filling, has at least two outputs. Thermostats are made of brass, aluminum, and plastic. The device does not have manual control of the response temperature.
The frameless thermostat is mounted in the engine block. For these purposes, a special place is provided in the engine. The temperature characteristic of the thermostat is applied using digital markings. The appearance of the frameless regulator is shown in the image below.

Major device failures
The most dangerous failure is the thermostat getting stuck in the closed position. Overheating of the engine leads to a decrease in its service life and accelerated aging of the oil. Under unfavorable conditions, serious damage may occur after the engine boils, which can only be corrected by a major overhaul.
After the valve is stuck in the open position, the antifreeze circulates in a large circle all the time. The engine takes a long time to warm up, especially in winter. Running the engine at temperatures below normal speeds up the process of engine wear.
How to check
Without removing the thermostat from the car, you can roughly check its operation. The exception is when it is stuck in the fully open or closed position. In this case, based on the temperature of the pipes, warm-up time and temperature sensor, we can conclude that the thermostat may be malfunctioning.
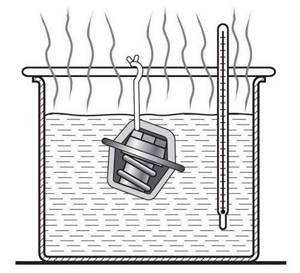
In hot water the thermostat should open
You can check the thermostat yourself by removing it from the car. To do this, either pour boiling water over it, visually observing the opening, or heat it in a container of water on an electric stove, control the temperature with a thermometer and measure the length of the extension of the rod. Both of these methods give a very inaccurate result, not allowing you to display the hysteresis loop of the thermostat and compare it with the standard one obtained in the manufacturer’s laboratory.
The thermostat can be professionally checked only at specialized diagnostic points, since its incorrect operation can be associated with other engine problems that you need to be able to distinguish. If you have no complaints about the operation of the engine, which “keeps” the thermometer needle in the normal zone in winter and does not overheat in summer, then everything is fine with your thermostat. Accurate diagnostics of the device operation requires the participation of an experienced specialist and special equipment.
Video: Thermostat - checking and principle of operation.
Thermostat diagnostics
A normally functioning thermostat does not require the attention of the car owner. Intervention into the operation of the cooling system will be required if there are signs of overheating or the engine has been warming up for too long. In this case, first of all, you need to start with diagnosing the thermostat. It is recommended to follow the following plan:
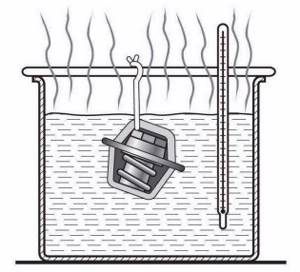
During the operation of the car, it is necessary to constantly monitor its temperature conditions. Having discovered a malfunction of the thermostat, it is necessary to diagnose and repair the cooling system as soon as possible. Otherwise, the engine may boil and subsequent expensive repairs may occur.
Source
Causes of malfunction
The main symptom of device failure is loss of valve functionality. The loss of mobility of these elements is due to the formation of scale or corrosion on the air conditioner thermostat.
Also, many car enthusiasts underestimate the importance of regular coolant replacement and in winter they increase the service life of the filled working mixture. The use of untested, cheap products in this regard also negatively affects the operation of the entire cooling system as a whole. Another option for negligent treatment of a car is when the coolant concentrate is diluted with ordinary water rather than distilled water, forgetting to clean the system before refueling.

Due to contamination of the device, the familiar “jam” may occur. The valves lose mobility and remain in one position, most often open. But the filler can also cause failure: the loss of its main physical properties will result in a decrease in its ability to expand. This means he will not be able to fully push out the bayonet. This threatens to disrupt the functioning of the valves. If the thermostat is not working, the coolant will lose the ability to maintain the desired temperature and will either “boil” or remain cold.
Automotive thermostat in an internal combustion engine liquid cooling system: design and principle of operation

The thermostat is one of the most important elements that is installed in the liquid cooling system of a gasoline or diesel power unit. In its standard version, this small device has a diameter of about five centimeters and is located between the engine and the radiator. The main task of the thermostat is to control the flow of coolant that circulates through the engine jacket and cooling radiator. The result of the device’s operation is the ability to quickly and effectively warm up the internal combustion engine during a cold start and further maintain optimal temperature balance in all operating modes and under any engine loads.
Features of models for boilers
Domestic boiler systems are considered one of the most complex units in the heating equipment category. Consequently, the thermostat must work with a wide range of operating parameters. Moreover, it is in boiler maintenance that two- and three-channel models are often used. They allow you to separately control not just different parameters, but, in fact, devices. An illustration of this approach can be a device that simultaneously controls the functions of the boiler itself in the form of a combustion chamber, and, separately, a boiler water heating installation. In addition, thermostats for heating boilers are often produced with remote sensors and programming capabilities.
Appearance and modernization of the device
One of the first thermostats is considered to be the appearance of a mercury device for maintaining optimal temperature balance in a chicken incubator, which was invented in 1620 by Mr. Cornelius Drebbel from Great Britain.
The thermostat has been actively used in the liquid cooling system of internal combustion engines since 1922, when the first and relatively powerful units with large heat release during operation appeared. Early on, there were several unsuccessful attempts to use the device in a cooling system. Further, the design was improved, engineers selected optimal manufacturing materials and achieved such characteristics and reliability that the thermostat became a widely used element in the liquid cooling system of an internal combustion engine.
There are two types of thermostats used in car cooling systems. There are solutions with solid or liquid filler. The gel thermostat for automobile liquid engine cooling systems was invented by a Frenchman named Serge Vernier in 1963. The Vernet company specializes in the production of thermostats today, and the products of this brand enjoy well-deserved authority in the auto parts market for various brands of cars around the world.
Thermostat filler
The thermostat can have various types of filler at the core of its design. We have already mentioned that there is a liquid filler and a solid filler. The operating principle and design of these solutions are almost the same. The differences lie only in the increased sealing of the liquid structure, as well as in the individual physical properties of the filler itself and its sensitivity to temperature fluctuations, depending on the composition.
Functions and location
Once the engine reaches its optimal operating temperature, it becomes necessary to maintain this indicator within strict limits until the very moment the engine stops, and in some cases, for some time after the engine stops operating. The main task of the device is to control and distribute the flow of heated cooling liquid inside the system to remove heat from the engine.
Thermostat manufacturers

The market offers enough solutions for any need, including boiler control requirements. In particular, the mechanical thermostat TDC 1 from the manufacturer Ballu has proven itself to be the best due to its functionality, reliability and high-quality assembly. True, this model has a rather narrow range of operating temperatures from 10 to 30 °C, so it may not be suitable for every boiler.
Electrolux offers wider possibilities for temperature control in its Basic ETB line. It is also worth paying attention to offers from the companies DEVI, HEAT-PRO, TIMBERK with TMS modifications, etc. But, if we discard the temperature scale, the standard Ballu mechanical thermostat will outperform its competitors due to its low price tag of 700 rubles.
Types of temperature control devices in a car
Let's talk in more detail about the different types of autothermostats, taking into account the features of their design. The engine can be equipped with various thermostat options, including:
Single valve, two valve and two stage thermostat
The single valve solution is characterized by its simplicity of design and associated reliability. Automakers around the world prefer this type of design and equip most of their cars with this type of device.
A separate type of thermostat with one valve is the two-stage design. The installation of such a solution is due to the fact that some cooling systems create very high coolant pressure during operation. It is difficult for the thermostat valve to overcome this pressure. For this reason, the design of a two-stage thermostat received a solution that implies the presence of two valve plates, which are called small and large. The first to open in the thermostat is the small plate, which requires noticeably less force to overcome the pressure created in the system. The small plate opens easier, and when it opens, it interacts with the large plate and simply pulls it along with it. Opening the large (main) thermostat plate all the way opens the coolant passage.
If in the first case the thermostat has one valve with two plates, then the two-valve regulator received two separate valves, which are located in a single housing. The first valve is the main one and serves to shut off a large circle during the movement of coolant in the system. The second valve is a bypass valve and is responsible for circulating liquid in a small circle. The operation of the valves is synchronized. When one of them blocks the coolant channel, the other opens the desired circuit. This thermostat design has found wide application in the design of passenger cars and trucks, which are products of the auto industry from the CIS countries.
Electronically controlled device
The most advanced and relatively complex in design, but at the same time the most accurate and efficient, is a thermostat equipped with electronic control. The main advantage of such a device is the provision of different temperature indicators to achieve the optimal temperature in relation to the dynamically changing operating conditions of the engine during its operation.
The design of the device resembles a conventional thermostat with a single valve, but an additional heating resistance is added to its thermocouple. The heating of the specified resistance is controlled by the electronic engine control unit (ECU). Thanks to this design, it becomes possible to implement a flexible temperature regime. The indicator is maintained at 95-110°C at light loads on the motor and 85-95°C at maximum load. The main achievement from the use of an electronic device is a noticeable reduction in fuel consumption, as well as a slight increase in power at the “lower” range due to better cooling of the intake air.
The temperature threshold in the BC region is higher and is at around 105°C. This implementation of temperature control in the cooling system has found application in the design of high-performance turbo engines and provides a resulting increase in power of the power unit due to improved air cooling.
Advantages and selection criteria for electric convectors with a mechanical thermostat
Increasingly, you can find convectors for sale in household appliance stores. This equipment is quite popular and has received good reviews from customers. In anticipation of the end of the heating season, such products are of particular interest. If you want to add warmth to your home or prepare for the onset of cold weather, then do not pass by convectors. Find out more information about them in this article.

What are convectors with a mechanical thermostat?
An electric convector is a device that is necessary to maintain heat in a living space. There are many modifications and subtypes of such devices.
What is it for and where is it used?
Basically, manufacturers divide convectors into electrical and mechanical. Each type has its own pros and cons.
Recently, less and less often buyers give preference to mechanical devices. Although, in fact, this is unfounded.
A convector with a mechanical thermostat is a device that is capable of maintaining the optimal set temperature in a room. If the device also has a built-in timer, it will be activated every time the temperature drops a couple of degrees, which is very convenient.
In tandem, these two additions provide the necessary functionality to constantly maintain the optimal temperature at home.
Such a device can be used both in everyday life, for example, for heating a house and apartment, and for industrial purposes. You can often find convectors in offices, hospitals, and shops. However, the larger the room, the more windows it has, the higher the power should be.
How it works: device and principle of operation
The operating principle of the convector is very simple. The air mass in the room is cold and heavy. The convector, which is put into operation, thanks to the fan, draws cold air masses from below into the housing.
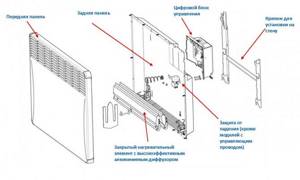
There, thanks to the heating element, the air undergoes a processing procedure. Once warm, it automatically becomes less voluminous and lighter, then rises to the top of the case and exits through the top hole.
Warm air accumulates in the upper part of the room, thereby displacing the lower cold air into the body of the device.
This procedure goes in a circle. As the upper layers cool, they fall down and fall back into the convector.
When the temperature in the room has reached the optimal set point, the device turns off automatically. But don't unplug it from the network. As soon as the thermometer detects a drop in temperature of a couple of degrees, the device will turn on automatically and continue operating until the required degree is reached.
Installation methods: wall or floor?
Convectors are also divided according to the method of fastening. There are floor-standing, wall-mounted, and combined units, which provide placement depending on your needs.

Floor-standing ones are equipped with special wheels so that they can be easily transported from place to place.
Wall convectors are supplied with mounting and fastening elements. They are needed in order to mount it on the wall without harm to the device.

Combined ones have both elements in their arsenal.
Reviews of convectors with a mechanical thermostat: pros and cons
A mechanical thermostat has its pros and cons, and this fact should not be denied. The buyer must be aware of the presence of both factors in order to make a purchasing decision.
The advantages include low cost, as well as:
- Good power.
- Ease.
- Compactness.
- Availability of various models.
- There is the necessary functionality.
- Convenient switching system.
- The device is resistant to power outages and its settings are not lost.
- Consume less electrical energy.
Unfortunately, there are a number of disadvantages that some buyers are not willing to put up with:
- This device is loud. This is due to the fact that a thermometer and timer are built into the case.
- Switching systems in the form of a dial and buttons also work with sound effects.
- The device doesn't look very modern.
Manufacturers and popular models: ranking of the best and prices
NOIROT CNX-4 2000W

A model designed for an area of 25 square meters. Operating power 2000 W. Equipped with mechanical control. There is an overheat protection function. Available in three colors: red, black and white. The cost on the market is 4,000 rubles.
Heater TIMBERK TEC.PF10N DG 1000 IN

Convector, which is designed for an area of 15 square meters. Its power is 1,000 W. There is a mechanical control and a remote control included. Waterproof housing and overheat protection. Cost 3,500 rub.
Heating device BALLU BIHP/R-1000 RED Evolution

Designed for an area of 15 square meters. Power 1000W. There is a mechanical control function. Protects against overheating and accumulates moisture. The set includes wheels for transportation on the floor. Cost 3100 rub.
Convector AEG WKL 1003 S

The device has a power of 1600 W. Designed for a room of 15 to 20 square meters. Includes remote control, mounting brackets and wheels. Overheating and moisture protection function. Cost 2,200 rub.
Heater with mechanical thermostat WWQ KM-15

Convector, which has a power of 1500 watts. Has mechanical control and overheat protection function. Made in a white case. Hangs on the wall. Can be mounted. The high cost is explained by the compactness of such a device. The surface is glossy and reflective. Designed for an area of 20 square meters. Cost 9000 rub.
RESANTA OK-2500

Heating power 500 W. There is a function of moisture protection, mechanical control and overheat protection. The model is flat, made in a white case. Hangs on the wall. Cost 5000 rub.
Convector LYNX K-2001

A device from a Russian manufacturer, which is designed for an area of up to 20 square meters. At the same time, the power is 1,500 W. The set includes a remote control, and there are also control buttons on the case. There is an overheat protection function. Cost 3,000 rub.
Which manufacturer and which type is better to choose: TOP-3
Calculation of the minimum required power
Power can be calculated using two formulas:
- The first one is quite simple.
The number of convectors in the room should be equal to the number of windows.The window is an additional source of cold. Even if it is closed and has no cracks, the glass is always cold and takes away additional heat from the room.
- As for calculating the power of the device, the formula applies here:
Multiply 50 by the number of square meters of the room and add 300.- 50 is a unit of power per 1 square meter.
- 300 is an additional power reserve in case there is a heat leak in the room, for example, an open window or door.
For example, you are the owner of a room of 20 square meters. 50 must be multiplied by 20 and added 300. As a result, we get 1.300. This amount is the minimum power indicator for your premises.
What else to consider when choosing a device?
There are several other factors that you should pay attention to when choosing a device.
- Purchase a convector only from official suppliers.
- You should not order such a device over the Internet.
- Be sure to read the reviews in advance.
- Calculate the required power for your premises.
- There is no need to plan to place a convector in a children's room.
- Study the information about the types of heating element and decide which one you need.
- Decide on the body.
- Think about the price at which you are willing to purchase such a product.
- Study information about the leaders in the convector market.
Taken together, following all these tips, you will be able to select the necessary device.
3 best models
- Pay attention to the Ballu BIH PR1500 model for 3,500 rubles. This device can be selected in the color that suits you best. In addition, it is very powerful.
- And another model that will not leave you indifferent is the Electrolux 2000 Mr. The heating power is 2000 W, which means that such a device can cope with a large room.
- RESANTA OK-2500. Floor heater that can be easily moved thanks to wheels. Cost 2,000 rub. There are all the necessary functions, as well as average power.

Price
The cost of each model consists of several factors combined.
- Materials spent on the manufacture of the device.
- A manufacturer or brand that also charges money for its name.
- Power.
- Its design.
- Shelf life and service life.
- Accessories.
- Placement method.
You can buy a convector for 2,500 rubles. However, it is far from certain that it will be able to cope with the square footage of your room. A convector of good power, which can serve an average living room, costs from 4,000 rubles.
If you purchase industrial equipment or a device with a unique design, then such a purchase will cost you 6 - 7 thousand rubles.
Where to buy a convector with a mechanical thermostat for an apartment or house?
In Moscow
- M Video. Moscow city, MKAD 24 kilometer. Phone 8 495 777 77 75.
- Bartolini. City of Moscow, Baikalskaya street, building 1. Telephone 8 499 381 18 91.
- Ecoline. Moscow city, Rumyantsevo business park, 22 km of Kievskoe highway, building 4, building 16. Telephone.
In St. Petersburg
- Heat stoves City of St. Petersburg, line 24 of Krestovsky Island, telephone.
- Ecohouse. City of St. Petersburg, Blagodatnaya street, building 2. Telephone 8.
- Warmer at home. City of St. Petersburg, Aviakonstruktorov street, building 5. Telephone.
Safety precautions and operating features
If you want the convector to serve you for a long time, you need to pay attention to studying the operating rules.
- Carry out wet cleaning of the convector once a season. To do this, you need to remove the top cover.
- Perform dry cleaning once a week, wiping dust from the body and all accessible openings.
- If the device is not working and is not in standby mode, unplug it.
- Install as stated in the instructions.
- You should not use a convector in a room that is several times higher than the declared power.
- You should not place such devices in a children's room.
- In order for the convector to work successfully, no windows or doors should be open in the room.
A mechanical thermostat is more of a plus than a minus. But not everyone knows about this. Now that you have realized that this device will only bring benefits, you can not only enjoy the purchase, but also save your money, because devices equipped with a mechanical thermostat are much cheaper.
Apr 23, 2018ventsyst
Solid-state thermostat design
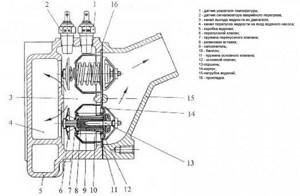
Modern internal combustion engine liquid cooling systems have received the most common version with a single valve, as well as a two-valve thermostat with a solid filler in the vast majority of cases. This element of the internal combustion engine cooling system is a heat-sensitive valve, which is enclosed in a brass frame. The valve also has a plate that is attached to the body. The body itself is a kind of cylinder. A special rod is inserted into this cylinder. The specified rod has one end resting on the upper part of the thermostat frame, and the other end rests on a rubber cavity in the device body. The body and rubber cavity are separated by a heat-sensitive element.
To put it simply, a common two-valve thermostat has a housing, two inlet pipes, an outlet pipe, a main and an additional valve, as well as a coolant temperature-sensitive element. The device is often installed in front of the point where the working fluid enters the centrifugal pump housing and is connected to it with a special outlet pipe. One inlet pipe connects the thermostat to the cylinder head, and the other makes a connection to the lower radiator tank.
The heat-sensitive coolant element consists of a copper cylinder, a rubber diaphragm and a rod. The solid filler is located between the diaphragm and the wall of the balloon. The element is a mixture of copper and granulated wax.
Wax was used in the design due to its ability to expand significantly under the influence of heat and change from solid to liquid and back. This wax or paraffin, which is used in the construction of car thermostats, is artificial and differs from the material we are used to. This wax has a number of specific properties that it acquires after undergoing the distillation process.
Principle of operation
When the engine starts, the thermostat is in a closed state at this moment and blocks the access of coolant to the large circle. The coolant circulates along a route that causes it to leave the cylinder block and return immediately. This feature of the cooling system ensures the most efficient heating of the power unit and its subsequent reaching the optimal temperature for its operation under load in the shortest possible time.
When the heating of the coolant reaches a temperature threshold of 80-90°C, then the thermostat begins to open. This happens because the solid element in the device body begins to melt at this temperature. There is a natural increase in the volume of the thermoelement. An increase in volume initiates movement of the thermostat housing along the rod. The rod itself is not capable of moving, since it is rigidly fixed structurally to the upper frame. The valve disc overcomes the force of the return spring and begins to open. This allows the coolant to pass through a fully or partially open valve and begin circulating through the radiator. The cooling efficiency of the coolant in the radiator increases significantly.
At the maximum permissible increase in coolant temperature, the thermostat is fully open, allowing the coolant to pass through the radiator in full. The thermostat opens fully at a temperature of about 95-105°C. When a car engine operates in various modes that are constantly changing, there is a constant change in the degree of opening of the thermostat.
If we consider the operating principle of a two-valve thermostat, taking into account the more familiar concepts of coolant movement in a “large” and “small” circle, then we get the following. Let's imagine that the temperature of the coolant in the system has exceeded 80 degrees Celsius. The solid filler of the thermostat begins to melt and increases in volume, then presses on the rod, which comes out of the cylinder. The balloon begins to move upward, thereby closing the additional valve of the device. The access of coolant to the small circle is closed.
What modifications of thermostats are there?
All thermostats are classified into several groups to make it easier for users to navigate when choosing them
The first group of TR is determined by the type of control:
- mechanical;
- combined electromechanical;
- electronic or digital.
Types of thermostats can also be grouped according to the following criteria:
- Location: with indoor installation - indoors and outdoors - weatherproof.
- Installation method: cabinet, wall or DIN rail.
- Functionality: wired connection from the control unit and wireless remote connection using modern communication lines via the Internet.
- Temperature measurement range, from -60 to 1200 °C.
- Number of channels: single and multi-channel with a series of standard temperature sensors.
- Type of programming: local, on one device, for example, a heating radiator, and central control of complex objects occurs from one center, the most common type in practice. In this option, special software and a computer are used for control.
Before choosing a specific model, you need to understand what a thermostat is needed for, for local control or integrated control in a general automatic system.

Mechanical
They have a simple design, in most cases they are non-volatile, that is, they do not require the use of electricity in operation. The modes are controlled by a knob with a scale on the body; in some cases there is a toggle switch for turning it on and off. The case has a simple interface with light indication.
Mechanical thermostats are used for heating and cooling systems. Design features:
- The bellows thermoelement is made in the form of a cylinder with internal corrugated walls, allowing it to stretch to a certain length.
- A valve that cuts off the movement of coolant.
- The special medium being measured, liquid or gaseous, is capable of responding to temperature fluctuations inside the room.
- A working rod that opens or closes the valve depending on the degree of heating of the room.
- Scale with instructions for setting the heating mode.
The operating principle of any mechanical thermostat is quite simple and lies in the fact that when the air in the room is heated, the working medium in a bellows-type thermoelement heats up and, expanding, straightens the cylinder, which acts on the rod, which in turn presses on the control valve, pressing it more tightly it to the coolant passage hole, thereby reducing it until it is completely closed, after which water does not flow into the battery. The air temperature in the room drops, the thermoelement contracts, the rod lowers, freeing the passage of the heating fluid into the battery, thereby starting a new heating cycle.
Mechanical TRs, despite their simplicity, have many advantages, including reliability, resistance to temperature changes, energy independence and long service life.
The disadvantages include low control accuracy, low functionality and the presence of noise effects in the form of clicks when the valve is turned on/off.
Electromechanical
Electromechanical temperature controllers are used for various heating devices, for example, electric boilers. As a rule, they can be made in 2 modifications: with a bimetallic plate connected to a group of electrical contacts and with a capillary tube.
The bimetallic plate heats up under the influence of the ambient temperature, which causes it to bend and break the contacts. At this moment, the supply of voltage to the electrical heating elements is stopped and the boiler stops. The coolant continues to circulate through the boiler, its temperature gradually decreases, the bimetallic plate returns to its original state, closing the electrical contacts and supplying voltage to the heating elements of the boiler.
A TR with a capillary tube filled with gas is placed in a container where the coolant is heated. When the set temperature of the water in the container is reached, the gas in the tube expands, thereby closing the electrical contact, the energy carrier is turned off, the water in the container cools down, the capillary tube contracts and opens the contacts. This type of regulator is installed in boilers and electric heating radiators.
Unpretentious electromechanical heat pumps have many advantages, first of all, they are budget-friendly in price; in addition, they are non-volatile, accurately support the automatic on/off mode of the heating device, while remaining sealed, without polluting the internal coolant circuit.
The downside is the rather rough settings for control limits of up to 2–3 °C.
Digital
This is a group of electronic thermostats that are installed in complex climate control equipment, for example, in automatic gas boilers, in control units for underfloor heating and split air conditioning systems.
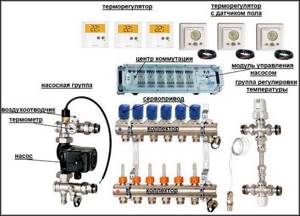
Basic design elements of digital TRs:
- Primary temperature sensor in the form of a remote device;
- controller - a command device on thermostats that controls the temperature in the room and generates “turn on” and “turn off” commands to the actuator of the heating unit;
- contact group, in the form of an electronic key.
The electronic TP controller can operate with closed and open logic. In the first case, the operating algorithm is constant, program adjustments are impossible, only the operating parameters of the heating device change. These models are used for low-power household equipment.
In the second case, the settings have a wider range, and therefore you can change the operating algorithm of the unit. Suitable for large industrial installations.
This is a modern type of thermostat that allows you to control and manage heating processes remotely using regular smartphones and the Internet. They have the widest range of regulation and can be built into any modern heat-heating devices.

Important! High control accuracy allows for efficient operation of equipment with high efficiency. Today, an innovative system of weather-controlled automation for gas boilers has been introduced on their basis; they are also part of the “smart home” system.
Common faults
The main and most common cause of device malfunction is impaired mobility of the thermostat valves. The reasons are different, but in most cases this phenomenon is a consequence of contamination of the thermostat with scale, as well as the formation of corrosion.
The thermostat fails especially quickly due to the fact that many drivers neglect to regularly replace the coolant in the system and use the coolant much longer than it should be. Many people use low-quality and cheapest products from unknown manufacturers, dilute the coolant concentrate with ordinary water instead of distilled water, skip the most important step of flushing the cooling system before the next scheduled coolant replacement, etc.
Car enthusiasts are very familiar with the expression “the thermostat is stuck.” The result of contamination of the thermostat is that the valves of the device may simply freeze in a certain position. Most often this happens in an open or slightly open position. The second common cause of thermostat failure is the loss of its most important physicochemical properties by the solid filler. If the coefficient of expansion of a solid filler decreases, this will mean that in the expanded state its final volume will also change.
Consequently, the thermostat filler will not exert the required pressure on the rod. The structure will partially or completely fail to move, one or both valves will stop functioning properly. If the thermostat malfunctions, the coolant in the system will either overheat or remain constantly cold, and intermediate temperatures deviating from the calculated norm are also possible.
Diagnosis of failure
Serious problems in the cooling system will be indicated to you by a clear deviation from the normal readings of the coolant temperature indicator on the instrument panel in the cabin. With normal operation of the internal combustion engine cooling system and the air temperature outside is about zero degrees Celsius, the power unit should reach operating temperature under load while driving in 5–10 minutes.
The only condition is the serviceability of the temperature sensor itself, the indicator on the instrument panel and the cooling system. If the tightness of the system and the functionality of other elements are not impaired, the coolant level in the expansion tank is at the required level, then obvious signs of a thermostat malfunction are:
Identifying a thermostat malfunction is quite simple. After starting a cold engine, the upper radiator hose should be cold and remain so for a certain period of time. If everything is normal, then the coolant circulates only through the “cooling jacket” of the engine (small circle) and access to the radiator during warm-up mode is blocked by the thermostat valve.
When the upper pipe warms up almost immediately, then there is impaired circulation. This means that the main valve of the device is open and the coolant immediately flows in a large circle. As a result, the internal combustion engine is not able to warm up to the optimal operating temperature. This phenomenon means that there is accelerated wear of power plant parts. The rubbing pairs of the unit do not receive adequate lubrication, since an unheated motor has thermal clearances that are different from the norm. The oil also remains too thick and loses its properties, which leads to increased fuel consumption and premature wear of the internal combustion engine.
It also happens when the thermostat valves stick only periodically. The malfunction disappears on its own, then appears again. In such cases, they say that the thermostat is “stuck.” This breakdown is more insidious, since a malfunction with such symptoms is more difficult to identify. You should check the condition of the cooling system and perform a preventative replacement of the thermostat. You shouldn't wait for the situation to worsen.
There is another way to check the functionality of the thermostat, but this solution is extremely rarely used. We are talking about dismantling and then checking the thermostat under conditions close to actual operation. To do this, place the thermostat in a container of water and begin to heat it. When the water temperature reaches the opening threshold of the thermostat valve, then a working device will respond properly. The filler will expand and open the valve approximately 20mm. If this did not happen at all, the valve opened only partially or did not return to its original state after cooling, then we can talk about a malfunction of the device.
Maintenance, prevention and repair
An important criterion when choosing a new thermostat is the temperature at which it operates and when the valve begins to open. This point must be taken into account and the thermostat must be selected in relation to a specific engine. The fact is that devices from different manufacturers have their own temperature “threshold”. If you set a thermostat that is different from the recommended threshold, then the internal combustion engine may overheat. Early operation will mean the engine is unable to reach operating temperature.
Typical thermostat malfunctions
The main cause of thermostat malfunction is deterioration in the mobility of its valves.
The reason for this may be contamination of the thermostat with scale or chemical degradation of the solid filler.
If the expansion coefficient of a solid filler has decreased, this does not mean that its volume has also changed. Therefore, there will be no expansion and the stem will not move, leaving either one or the other valve open. When the engine is running, the coolant will either not heat up enough or overheat too much.
Due to contamination of the thermostat, its valves may jam mechanically - most often this happens in the open or slightly open position.
Diagnosing such a thermostat malfunction is not difficult. When starting a cold engine, the upper radiator hose should remain cold for some time. If it immediately warms up, it means that the main thermostat valve is open and the coolant circulates in a large circle, and the engine does not warm up to the optimal operating temperature. This leads to accelerated wear of its parts and components. The rubbing parts of the engine do not receive sufficient lubrication as the oil remains too thick, which leads to increased fuel consumption.
If the thermostat valve is stuck in the closed position, then overheating and boiling of the coolant are inevitable, and overheating threatens to damage the engine.
There are situations when a thermostat malfunction only appears from time to time, when the valve either “sticks” or functions normally again. This type of thermostat failure is dangerous because it is difficult to diagnose.
If, when turned on, the engine does not warm up for a long time, if the car interior is poorly heated, if the arrow of the sensor that controls the coolant temperature is in the red zone, you should urgently check the serviceability of the thermostat. Any of these signs may indicate that it is broken.

It is impossible to imagine the modern world without cars. All kinds of mechanical engineering products are widely used in heavy industry, agriculture, the oil industry, energy, and the automotive industry.
The engine of any machine must be protected from large temperature differences (excessive overheating or cooling).
That is why each of them contains such an important element as a thermostat. Today, for production purposes for large and small cargo transportation, vehicles with diesel engines are very popular. In this regard, the thermostats at Kamens? This is a product that should definitely be given attention.