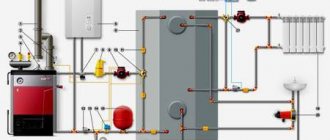
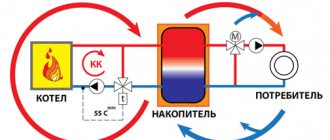
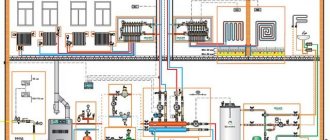
How does this system work?
The movement of water in a steam heating line can occur without the use of a circulation pump, in accordance with basic physical laws. Knowledge of the basics of such processes makes it possible to correctly calculate the heating system for all occasions.
The main quality of a liquid is a decrease in the density coefficient as the number of degrees increases. The hotter the water, the lower its density. A voltage differentiation is generated between the cold and heated fluid. The first flows spontaneously to the heat exchanger, while displacing flammable water, it moves along the main line.
With this circulation, there are differences in pressure between different fluids. Any such circuit can be differentiated by blocks:
- The water rises, heating the pipes.
- It moves down through cold pipes.
The delimiting element is the extreme points of the general contour (top and bottom).
When creating a system with a simple circulation, the problem of achieving differentiation between water that has different temperatures is solved.
One of the basic blocks in such systems is the basic riser - this is a perpendicularly fixed pipe that conducts water upward from the heat exchange block. The acceleration manifold has an elevated temperature; it is “wrapped” in insulation especially carefully if water is supplied bypassing several floors.
As a rule, the system is created so that the highest point of the collector corresponds to the highest point of the entire highway. An outlet to the tank is installed there; it is also possible to install a valve that will control the removal of excess air.
It should be taken into account that the block with the high temperature of the circuit itself does not come into contact with the elements along which the cooled water moves. The lower point of the line comes into contact with the heat exchanger and is installed in the heating unit.
On calculating the parameters of a heating system with natural circulation for a one-story house
Due to the absence of additional mechanisms in the gravity heating systems of a one-story building that provide consistently high pressure, any possible violation during the installation of the pipeline can result in problems with the heat supply. Such violations include:
- neglecting the need to maintain inclination angles;
- incorrect choice of pipes;
- excess turns when installing the system.
The level of slope when installing a heating pipeline in a private house is regulated by the provisions of SNiPs. In accordance with them, for each linear meter a slope of 1 cm is required. This ensures normal movement of the coolant through the pipeline. If this standard is violated, the system may become air-filled and the overall level of its efficiency may decrease.
About calculating pressure and heating power
Based on the provisions of SNiP, each kW of thermal power is intended to heat an area of 10 square meters of the house. When calculating power levels for regions with hot or cold climates, special coefficients should be used. In the first case it will be from 0.7 to 0.9, in the second - from 1.5 to 2.
However, a calculation method that neglects the height of ceilings is not always ideal. Therefore, there is another option - based on the volume of the room. In this case, the calculations are based on thermal power indicators (40 watts) for each cubic meter. In this case, the presence of windows increases the resulting number by 100 watts (for each window), and doors - by 200 watts (for each). In this case, for one-story private houses a coefficient of 1.5 is applied.
Actually, the standard amount of power included in the design of private one-story buildings requires a heating power of at least 50 watts per 1 sq.m.
Calculation of pipe diameter in a system with natural circulation
The diameter of pipes in gravity systems is calculated based on:
- building needs for thermal energy (+20%);
- determining the required type of pipe material (for example, the diameter of a steel pipe must be at least 0.5 cm);
- SNiP data regarding the ratio of power and internal diameter of the pipe.
It is worth considering that when choosing pipes with an unreasonably large cross-section, heating costs may increase while heat transfer decreases. Calculating the diameter of pipes for systems with self-circulation involves following another simple rule, which involves narrowing the diameter of the pipe by a size after each branch.
Advantages of a gravity system
A heating system with natural circulation has a number of advantages, of which we should highlight:
- Complete system energy independence. If you experience constant interruptions in light, you may want to look towards natural circulation heating
- Lack of complex systems in the form of a pump, safety valves, etc.;
- Ideal system for solid fuel boilers
- The simplest possible boiler room wiring
- Affordable
During installation, it is necessary to carefully calculate all the indicators and choose the circuit diagram correctly.
Where to put
It is recommended to install a circulation pump after the boiler, before the first branch, but on the supply or return pipeline it doesn’t matter. Modern units are made from materials that can withstand temperatures up to 100-115°C. There are few heating systems that work with a hotter coolant, so considerations of a more “comfortable” temperature are untenable, but if you feel safer, put it in the return line.
Can be installed in the return or direct pipeline after/before the boiler up to the first branch
There is no difference in hydraulics - the boiler, and the rest of the system; it makes absolutely no difference whether there is a pump in the supply or return branch. What matters is the correct installation, in terms of strapping, and the correct orientation of the rotor in space
Nothing else matters
There is one important point regarding the installation location. If the heating system has two separate branches - on the right and left wings of the house or on the first and second floor - it makes sense to install a separate unit on each, and not one common one - directly after the boiler. Moreover, the same rule remains on these branches: immediately after the boiler, before the first branch in this heating circuit. This will make it possible to set the required thermal conditions in each part of the house independently of the other, and also in two-story houses to save on heating. How? Due to the fact that the second floor is usually much warmer than the first floor and much less heat is required there. If there are two pumps in the branch that goes up, the speed of movement of the coolant is set much lower, and this allows you to burn less fuel, without compromising the comfort of living.
There are two types of heating systems - forced and natural circulation. Systems with forced circulation cannot work without a pump; systems with natural circulation work, but in this mode they have lower heat transfer. However, less heat is still much better than no heat at all, so in areas where electricity is often cut off, the system is designed as hydraulic (with natural circulation), and then a pump is installed into it. This gives high heating efficiency and reliability. It is clear that the installation of a circulation pump in these systems is different.

All heating systems with heated floors are forced - without a pump, the coolant will not pass through such large circuits
Forced circulation
Since a forced circulation heating system without a pump is inoperative, it is installed directly into the gap in the supply or return pipe (of your choice).
Most problems with the circulation pump arise due to the presence of mechanical impurities (sand, other abrasive particles) in the coolant. They can jam the impeller and stop the motor. Therefore, a mesh dirt filter must be placed in front of the unit.

Installing a circulation pump in a forced circulation system
It is also advisable to install ball valves on both sides. They will make it possible to replace or repair the device without draining the coolant from the system. Turn off the taps and remove the unit. Only that part of the water that was directly in this piece of the system is drained.
Natural circulation
The piping of the circulation pump in gravity systems has one significant difference - a bypass is required. This is a jumper that makes the system operational when the pump is not working. One ball shut-off valve is installed on the bypass, which is closed the entire time the pumping is running. In this mode, the system operates as forced.
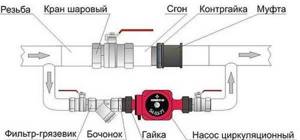
Installation diagram of a circulation pump in a system with natural circulation
When the electricity goes out or the unit fails, the valve on the jumper is opened, the valve leading to the pump is closed, and the system operates as a gravity system.
Installation features
There is one important point, without which the installation of the circulation pump will require rework: it is necessary to rotate the rotor so that it is directed horizontally. The second point is the direction of flow. There is an arrow on the body indicating which direction the coolant should flow. This is how you turn the unit so that the direction of movement of the coolant is “in the direction of the arrow”.
The pump itself can be installed both horizontally and vertically, just when selecting a model, make sure that it can work in both positions. And one more thing: with a vertical arrangement, the power (pressure created) drops by about 30%. This must be taken into account when choosing a model.
Leningradka

"Leningradka" has a basic drawback: there are large heat losses on the main lines, which specialists always take into account when designing heating. The advantages of this system: using valves, the heating can be turned off while performing preventative repairs. “Leningradka” is often used in apartments; the pipes look aesthetically pleasing and do not attract attention.
The difficulty lies in the fact that turning off one of the sections leads to a stop in the coolant circulation throughout the entire circuit. The method of installing a “bypass” is often used, when the batteries can be “bypassed” using side branches that have ball valves (2 pcs.).
For two-story objects (and one-story ones), schemes with one pipe and perpendicular risers are used. Under such circumstances, the liquid is distributed more evenly. Vertical pipes look more aesthetically pleasing and are easy to disguise in corner niches.
Pipe selection
Also, the choice of material is greatly influenced by the boiler, since in the case of solid fuel, preference should be given to steel, galvanized pipes or stainless steel products, due to the high temperature of the working fluid.
However, metal-plastic and reinforced pipes require the use of fittings, which significantly narrows the clearance; reinforced polypropylene pipes will be an ideal option at an operating temperature of 70C and a peak temperature of 95C.
Products made from special PPS plastic have an operating temperature of 95C, and a peak temperature of up to 110C, which allows use in an open system.
Spider

The wiring in which water is supplied to each battery individually with natural coolant circulation is called a spider.
With this scheme, the container is located in the attic, exactly in the center of the building’s perimeter. Risers of a certain cross-section (from batteries, radiators) are connected to it. The water, which has already cooled, flows in the usual way and enters the horizontal line.
The principle is simple:
- The water is heated in the boiler.
- Rises into the tank.
- Then it disperses by gravity through pipes of smaller diameter.
This scheme is ideal for a property with a small number of floors
The advantages of the “spider” are uniform and simple distribution of the coolant; there is also no horizontal distribution to different rooms.
There is only a large riser at the supply; it leads from the boiler to the tank. Pipes can be up to 25 mm in diameter. PVC or metal-plastic pipes are often used for branches.
Among the disadvantages of this natural circulation system, we can recall:
- The presence of a large number of joints.
- Many pipes of different diameters are used.
- Requires a lot of insulation.
- The building must have an attic space.
Slope
For the proper operation of a heating system with natural circulation, the slope of the pipes is of great importance. According to accepted building codes, this parameter should be within 1% (1 centimeter of excess per meter of pipe length), and the slope is set according to the movement of water. In this case, the rising energy of the coolant will be able to overcome friction, which will facilitate the efficient movement of liquid through the pipes of the heating system.
Note! The height of the ceiling and the level of the finished floor may differ in different rooms of the same country house, therefore, to correctly determine the slope of the pipes, it is necessary to use a building level or hydraulic level.
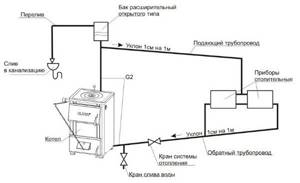
For the normal functioning of the heating system, the slope of the pipes is required.
In one- or two-pipe heating systems, in which the coolant is moved using a circulation pump, it is not necessary to maintain a slope. Such pipelines are installed in a horizontal position or with a minimal slope towards the drain. In such a case, the home owner can quickly drain the water to prevent the system from defrosting in the winter.
What pipe diameters are needed?
When calculating the system, special attention is paid to the location of the heating element, tank and radiators. The diameter of the pipes is also very important; there must be a pressure that will allow the entire heating system to function effectively.
Criteria for choosing the diameter of pipes for heating with natural circulation:
- Can it be used for hot water?
- Is it difficult to install?
- Terms of use.
- Manufacturer's warranty.
When installing a natural water circulation, pipes with a large cross-section are used. To heat an object with a total area of 220 sq. meters, the cross-section of the pipe at the return entrance to the heat exchanger is approximately two inches.
This is due to the fact that the fluid speed decreases, which can raise the following questions:
- Decrease in heat transfer for a certain unit of time.
- The occurrence of air jams.
Therefore, it is important when installing the circuit that no air gets into it, otherwise traffic jams will occur.
The inner walls of pipes can significantly reduce fluid movement. Also, the presence of a large number of narrowings and locking blocks can significantly slow down the movement of water. All of these factors come into play when it comes to choosing pipes. Metal-plastic pipes are not used very often, because they are fixed using fittings, and they have a small diameter.
Types of gravity systems
When planning to install the heating of a private house with natural circulation with your own hands, the schemes are selected in accordance with the planned performance of the system and the characteristics of the building.

Heating circuits with gravity flow of coolant are divided into types according to different parameters:
- according to the characteristics of the expansion tank (open and closed);
- according to the principle of connecting heating radiators (one-pipe and two-pipe).
To determine the best option, it is necessary to make hydraulic calculations taking into account the location and diameter of the pipes, take into account the characteristics of the boiler unit and the thermal needs of the premises. It is better to entrust the calculation to professionals, since even small inaccuracies will negatively affect the efficiency of heating the house.
Basic restrictions
The main limitations of natural circulation systems are the risk of air locks. One such plug can destroy the entire system. SNIP 41-02-2004 states that pipelines cannot be laid if the water in them moves at a speed of less than 25 cm per second. During installation, special attention is paid to the angle of inclination of the lines, then air (if it gets into the system) will be removed. The angle of inclination is about three millimeters per linear meter. In apartments this figure reaches 5.5 mm per linear meter.
There are also restrictions on the installation of radiators. The main disadvantage of the Leningradka scheme, for example, is the low acceleration of the liquid when flowing into the radiators, which inevitably leads to a decrease in efficiency. The number of batteries is supplied in limited quantities, while the “long-distance” batteries have a significantly lower temperature.
How to embed a pump
To facilitate the process of installing the pump in the heating system, it is necessary to buy a pump with a detachable thread. To perform the work efficiently, we will need the following equipment:
- Ball valves selected according to the diameter of the pipeline;
- Keys of the required size;
- Sealant;
- Fasteners, connecting elements;
- Automatic valves.
After selecting all the necessary equipment, we proceed to selecting a site for installing the circulation pump. If previously pumps were installed in the return pipeline, which made it possible to extend the service life of the device in question, now this equipment is made with water-resistant parts. In this regard, the pump can be installed both on the supply and return pipelines.
Note! In order to increase the pressure in the system, the pump is installed on the supply pipe in close proximity to the expansion tank. In the “Warm Floor” system, to prevent the formation of air accumulations, the pump is mounted in the area where the heated coolant is supplied.
When installing the pump in the heating system, you need to pay attention to one important detail. The device in question may fail after exhausting its service life, therefore, for quick replacement without draining water from the heating system, ball valves are mounted on both sides of the installation. To protect the pump from destruction, a mesh filter is installed in front of the entrance, which will trap abrasive particles present in the water.
To release accumulated gases, a manual or automatic valve is installed at the top of the bypass. The pump terminals should be oriented upward, which will prevent the possibility of a short circuit when water drains from the device. This phenomenon often happens when the pump breaks down. Each connection is coated with sealant, and special rubber gaskets are installed at the threaded connections.
Main disadvantages
This type of heating also has significant disadvantages:
- There is a large temperature difference between points.
- All pipes are open in the rooms, which looks unsightly.
- The circuit must be replenished from time to time during operation.
- Pipes with a cross-section of up to 50 mm are not cheap (usually PVC or steel is used to save money). Radiators are used whose resistance coefficient is minimal (cast iron, bimetal, aluminum alloys).
- The impossibility of room-by-room temperature control, which greatly affects heating costs.
- Unbalanced system. It is impossible to make all radiators heat approximately equally
Heat supply due to the natural circulation of the coolant may be suitable for objects that have 65 sq. meters, while the length of the pipes should not exceed 32 meters. It is also important to consider: how many floors the object has, the design of the accelerating block depends on this. In regions where there are severe winters, such a facility heating scheme is not suitable; there will be no required operating pressure in the circuit.
Heating system wiring diagram
To correctly calculate the resistance of the pipeline, and, consequently, its diameter, the wiring diagram of the heating system should be taken into account. Options:
- two-pipe vertical;
- two-pipe horizontal;
- single-pipe.
A two-pipe system with a vertical riser can be with upper and lower placement of lines. A single-pipe system, due to the economical use of the length of the lines, is suitable for heating with natural circulation; a two-pipe system, due to a double set of pipes, will require inclusion in the pump circuit.
Horizontal wiring provides 3 types:
- dead end;
- with associated (parallel) movement of water;
- collector (or beam).
In a single-pipe wiring diagram, you can provide a bypass pipe, which will serve as a backup line for liquid circulation when several or all radiators are turned off. Shut-off valves are installed on each radiator, allowing you to shut off the water supply when necessary.
Knowing the layout of the heating system, you can easily calculate the total length, possible delays in the coolant flow in the main (at bends, turns, at connections), and as a result, obtain a numerical value of the system resistance. Based on the calculated loss value, you can select the diameter of the heating lines using the method discussed below.