Here you will learn:
- Advantages of a forced circulation heating system
- What is a circulation pump and why is it needed?
- Selecting the right unit
- Choosing a location for installation
- Installation rules
- Installation diagrams in various heating systems
- Tools and Supplies
- Circulation pump installation steps
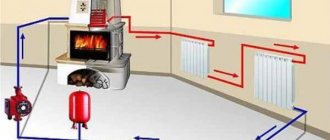
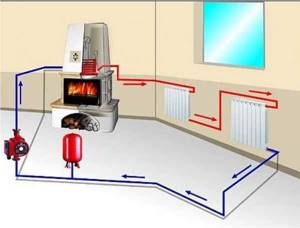
Installation of the heating pump is carried out after preliminary selection of the location and installation diagram. First, a direct insertion is made into the pipe - metal or plastic. Then install ball valves, a pump and connect it to the power supply.
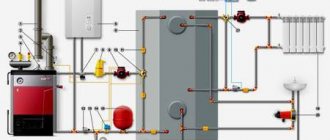
Connecting an electric boiler to the heating system
piping of an electric heating boiler Electric heating convectors: how to choose - little tricks
To reduce the amount of electricity consumed, it is advisable to resort to the following scheme:
- install a heated floor system that distributes heat evenly throughout the room;
- install a heat accumulator - a heat-insulated storage tank. In it, the water will be heated at night, when a lower electricity tariff is in effect, and during the day it will slowly cool, releasing heat into the room (more details: “Correct heating scheme with a heat accumulator”).
Connecting an electric boiler to the heating system: instructions
Types of circulation pumps
A pump with a “wet” rotor is made of stainless steel, cast iron, bronze or aluminum. Inside there is a ceramic or steel motor
To understand how this device works, you need to know the differences between the two types of circulation pumping equipment. Although the fundamental design of a heating system based on a heat pump does not change, the two types of such units differ in their operating features:
- A pump with a “wet” rotor is made of stainless steel, cast iron, bronze or aluminum. Inside there is a ceramic or steel motor. The technopolymer impeller is mounted on the rotor shaft. When the impeller blades rotate, the water in the system is set in motion. This water simultaneously functions as an engine cooler and a lubricant for the working elements of the device. Since the “wet” device circuit does not provide for the use of a fan, the operation of the unit is almost silent. Such equipment only works in a horizontal position, otherwise the device will simply overheat and fail. The main advantages of a wet pump are that it does not require maintenance and also has excellent maintainability. However, the efficiency of the device is only 45%, which is a minor drawback. But for domestic use this unit is perfect.
- A pump with a “dry” rotor differs from its counterpart in that its motor does not come into contact with the liquid. As a result, the unit has less durability. If the device operates “dry,” then the risk of overheating and failure is low, but there is a risk of leakage due to abrasion of the seal. Since the efficiency of a dry circulation pump is 70%, it is advisable to use it to solve utility and industrial problems. To cool the engine, the device circuit provides for the use of a fan, which causes an increase in the noise level during operation, which is a disadvantage of this type of pump. Since in this unit water does not serve as a lubricant for working elements, during operation of the unit it is necessary to periodically carry out technical inspection and lubricate parts.
In turn, “dry” circulation units are divided into several types according to the type of installation and connection to the engine:
- Console. In these devices, the engine and housing have their own place. They are separated and firmly fixed on it. The drive and working shafts of such a pump are connected by a coupling. To install this type of device, you will need to build a foundation, and maintaining this unit is quite expensive.
- Monoblock pumps can be used for three years. The body and engine are located separately, but are combined by a monoblock. The wheel in such a device is installed on the rotor shaft.
- Vertical. The service life of these devices reaches up to five years. These are sealed advanced units with a seal on the end side made of two polished rings. For the manufacture of seals, graphite, ceramics, stainless steel, and aluminum are used. When the device is running, these rings rotate relative to each other.
There are also more powerful devices on sale that have two rotors. This dual circuit allows you to increase the performance of the device at maximum load. If one of the rotors fails, the second can take over its functions. This allows not only to enhance the operation of the unit, but also to save energy, because with a decrease in heat requirements, only one rotor works.
Equipment selection
An important parameter when purchasing a water pump is its power. An unsuccessful selection will lead to excessive energy consumption and severe noise interference during operation. The complex architecture of the heating system will also require the intervention of a heating engineer.

To calculate the required power, the owner of a private house can use the diagram presented below. The technical parameters of the installed devices must exceed the calculated values by 10-15%.
Search for power
The heating requirements provided by the pump depend on the cross-section of the conducting pipe. They are greatly influenced by the maximum pressure indicator, the volume of coolant, its temperature and density.

The amount of working fluid passing through a random section of the water circuit is calculated similar to the volumes of water that the boiler used. Consumption values are equal to power parameters.
In practice, using a 20 kW boiler will mean that it will pass 20 liters of liquid through it per minute.
Calculation formula
A similar principle applies to radiators. When choosing the location where the circulation pump will be installed, you need to take into account the fluid flow of each ring of the heating network. This indicator will also be affected by the cross-section of the pipeline and its length.

Each ten-meter section of the heating system will require 0.6 m of pressure from the working pump. For hundred-meter-long communications installed in a private house, you will need a device with a pressure of 6 m.
Types of pumping units
Stimulating the movement of liquid in pipes involves the use of one of two qualitatively different methods. A “dry” type unit can be installed in the system, the rotor of which will not come into contact with water inside the circuit. The connection diagram for a “wet” pump, on the contrary, requires immersing its working part in a coolant liquid.
Hermetically insulated flywheels of devices of the first type are used in the construction of high-rise buildings or large shopping centers. The air turbulence that accompanies their rotation causes loud noise and makes them inconvenient for installation in private buildings.
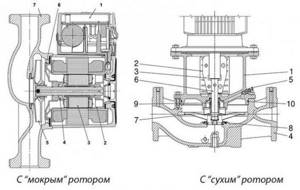
The housings of “wet” pumps are made of brass or bronze, and ceramic or steel parts are placed inside them. Water flowing through them acts as a lubricant and extends the service life.
Water heating systems
Water heating is a method of heating rooms using a liquid coolant (water or water-based antifreeze). Heat is transferred to the premises using heating devices (radiators, convectors, pipe registers, etc.).
Unlike steam heating, water is in a liquid state, which means it has a lower temperature. This makes water heating safer. Radiators for water heating have larger dimensions than for steam heating. In addition, when heat is transferred over a long distance using water, the temperature drops significantly. Therefore, they often make a combined heating system: from the boiler room, with the help of steam, heat enters the building, where it heats the water in a heat exchanger, which is already supplied to the radiators.
In water heating systems, water circulation can be either natural or artificial. Systems with natural circulation of water are simple and relatively reliable, but have low efficiency (this depends on the correct design of the system).
A disadvantage of water heating is also air pockets, which can form after draining the water during heating repairs and after severe cold snaps, when the temperature in the boiler rooms is increased and part of the air dissolved in it is released from it. To combat them, special release valves are installed. Before the start of the heating season, air is released using these valves due to excess water pressure.
Heating systems are distinguished according to many characteristics, for example: - according to the method of wiring - with upper, lower, combined, horizontal, vertical wiring; - according to the design of the risers - single-pipe and double-pipe;
— along the flow of the coolant in the main pipelines — dead-end and associated; - according to hydraulic modes - with constant and variable hydraulic modes; - according to the communication with the atmosphere - open and closed.
Tools and Supplies
Correctly connecting the pump involves preliminary preparation of the necessary equipment. To work you will need:
- 2 water pipes or 2 Swedish wrenches of the appropriate diameter;
- fum tape 10 mm;
- 3 ball valves;
- 2 tees.

The basic set may vary depending on the type of pipes used.
For efficient heat distribution, it is better to connect the circulation pump before the start of the heating season. In this case, you can immediately check how effectively it works.
Power determination
When choosing a pump, you need to consider factors such as:
- power of heating radiators;
- coolant movement speed;
- total pipeline length;
- flow section of pipelines;
- boiler power.
Calculations
To more accurately determine the pump power, you can use the rule of 1 kW of power per 1 liter of pumped water. Thus, a 25 kW pump can circulate a maximum of 25 liters of coolant.
Sometimes a simplified selection scheme is used, based on the area of the heated room:
- to heat buildings with an area of up to 250 m2, buy a pump with a capacity of 3.5 cubic meters of water per hour and a pressure force of 0.4 atmospheres;
- from 250 to 350 m2 - with a capacity of 4.5 cubic meters per hour and a pressure force of 0.6 atmospheres;
- from 350 m2 - with a capacity of 11 cubic meters per hour and a pressure force of 0.8 atmospheres.
European calculation method
When choosing equipment, you can use another method - standard housing improvement projects developed in the European Union. So, per 1 m2 of space there should be a pump power of 97 Watt, provided that the air temperature outside is 25C° (minus), or 101 Watt if the temperature drops to 30C° (minus).
This norm applies to buildings with a height of three floors or more. When arranging a private house up to two floors high, the pump power per 1 m2 of area should be 173 Watts at street temperatures up to 25C° below zero and 177 Watts – below 25C°.
General information.
The fact that the heating scheme of a one-story house with natural circulation has practically no moving elements allows it to be operated without major repairs for a long time. If the CO distribution is carried out using galvanized or polymer pipes, then the terms can reach fifty years.
EC automatically implies a low pressure difference between the inlet and outlet. Naturally, the coolant experiences a certain resistance to its movement as it passes through heating devices and pipes. Taking this into account, the optimal radius for normal operation of the SO with the EC was determined to be thirty meters. But we must understand that the figure is quite arbitrary and may fluctuate.
Due to the design features, the heating system with natural circulation of a one-story house has high inertia. From the moment the boiler is ignited until the temperature in the premises of the building stabilizes, at least several hours pass. The reason is simple. First, the boiler heat exchanger warms up and only then the slow movement of the coolant begins.
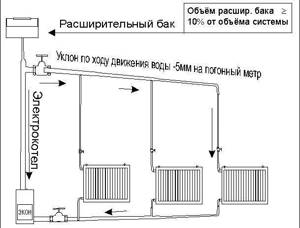
House heating scheme with natural circulation
It is important that in those places where CO pipes are laid horizontally, they must have a mandatory slope in the direction of coolant flow. This achieves the movement of water in the system without stagnation and the automatic removal of air from the system to its highest point, which is located in the expansion tank
It is made in one of three options: open, with a built-in air vent, or sealed.
Recommendations for installing pumps
In order to ensure normal circulation of fluid in the heating system, you need to make the right choice of the place where the pump will be installed. A location in the water suction area should be identified where excess hydraulic pressure is always present.
Most often, the highest point of the pipeline is selected, from which the expansion tank rises to a height of approximately 80 cm. The use of this method is possible in a room with a high altitude. It is usually practiced to install an expansion tank in the attic, provided that it is insulated for the winter.
In the second case, the tube is transferred from the expansion tank and cuts into the return pipe instead of the supply pipe. The suction pipe of the pump is located near this place, so the most favorable conditions are created for forced circulation.
The third installation option is to insert the pump into the supply line, directly behind the point at which water flows from the expansion tank. The use of such a connection is possible if a particular model is resistant to high water temperatures.
How to install a pump in a gas boiler: can you do it yourself?
A pump unit with the necessary fittings is already integrated into the design of many gas boilers. However, the unit’s performance may not be enough to “pull through” an extensive heating system. This, as well as the lack of a pump in the kit, forces homeowners to install additional “circulators” outside the heater.
You can install the pump unit yourself if no changes are made to the design of the gas boiler. Otherwise, you need to entrust the work to specialists. Before installing the pump unit, it is necessary to check whether it can be used in an existing or planned heating system. To do this, calculate the required performance and pressure, which will ensure efficient operation and heating. Based on the obtained parameters, a pump is selected, choosing a standard size with a larger nominal value.
Where to put
It is recommended to install a circulation pump after the boiler, before the first branch, but on the supply or return pipeline it doesn’t matter. Modern units are made from materials that can withstand temperatures up to 100-115°C. There are few heating systems that work with a hotter coolant, so considerations of a more “comfortable” temperature are untenable, but if you feel safer, put it in the return line.
Can be installed in the return or direct pipeline after/before the boiler up to the first branch
There is no difference in hydraulics - the boiler, and the rest of the system; it makes absolutely no difference whether there is a pump in the supply or return branch. What matters is the correct installation, in terms of strapping, and the correct orientation of the rotor in space
Nothing else matters
There is one important point regarding the installation location. If the heating system has two separate branches - on the right and left wings of the house or on the first and second floor - it makes sense to install a separate unit on each, and not one common one - directly after the boiler. Moreover, the same rule remains on these branches: immediately after the boiler, before the first branch in this heating circuit. This will make it possible to set the required thermal conditions in each part of the house independently of the other, and also in two-story houses to save on heating. How? Due to the fact that the second floor is usually much warmer than the first floor and much less heat is required there. If there are two pumps in the branch that goes up, the speed of movement of the coolant is set much lower, and this allows you to burn less fuel, without compromising the comfort of living.
There are two types of heating systems - forced and natural circulation. Systems with forced circulation cannot work without a pump; systems with natural circulation work, but in this mode they have lower heat transfer. However, less heat is still much better than no heat at all, so in areas where electricity is often cut off, the system is designed as hydraulic (with natural circulation), and then a pump is installed into it. This gives high heating efficiency and reliability. It is clear that the installation of a circulation pump in these systems is different.

All heating systems with heated floors are forced - without a pump, the coolant will not pass through such large circuits
Forced circulation
Since a forced circulation heating system without a pump is inoperative, it is installed directly into the gap in the supply or return pipe (of your choice).
Most problems with the circulation pump arise due to the presence of mechanical impurities (sand, other abrasive particles) in the coolant. They can jam the impeller and stop the motor. Therefore, a mesh dirt filter must be placed in front of the unit.

Installing a circulation pump in a forced circulation system
It is also advisable to install ball valves on both sides. They will make it possible to replace or repair the device without draining the coolant from the system. Turn off the taps and remove the unit. Only that part of the water that was directly in this piece of the system is drained.
Natural circulation
The piping of the circulation pump in gravity systems has one significant difference - a bypass is required. This is a jumper that makes the system operational when the pump is not working. One ball shut-off valve is installed on the bypass, which is closed the entire time the pumping is running. In this mode, the system operates as forced.
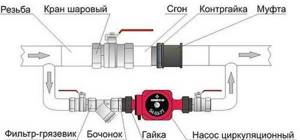
Installation diagram of a circulation pump in a system with natural circulation
When the electricity goes out or the unit fails, the valve on the jumper is opened, the valve leading to the pump is closed, and the system operates as a gravity system.
Installation features
There is one important point, without which the installation of the circulation pump will require rework: it is necessary to rotate the rotor so that it is directed horizontally. The second point is the direction of flow. There is an arrow on the body indicating which direction the coolant should flow. This is how you turn the unit so that the direction of movement of the coolant is “in the direction of the arrow”.
The pump itself can be installed both horizontally and vertically, just when selecting a model, make sure that it can work in both positions. And one more thing: with a vertical arrangement, the power (pressure created) drops by about 30%. This must be taken into account when choosing a model.
Where should the pump be mounted - supply or return?
Users are always tormented by the question: is it possible to put the circulation pump on supply? Despite the large amount of different information on the Internet, it is difficult to understand where to correctly install the heating pump so that there is forced circulation of water in the house.
p, blockquote 9,0,0,0,0 —>
Information regarding this issue is very contradictory. Many people say that the device should only be installed on the return pipeline, arguing that:
p, blockquote 10,0,0,0,0 —>
- the temperature of the coolant in the supply is much higher than in the return, and therefore the pump will not operate for long;
- The density of hot water in the supply line is lower, so it is difficult to pump;
- The static pressure in the return line is higher, making the pump easier to operate.
Sometimes a person happens to get into a boiler room, which provides central heating for apartments, and sees that the devices used there are embedded in the return line. Based on this, he concludes that this decision is correct, without taking into account the fact that in other boiler houses the pumps can also be installed on the supply pipe.
Experts respond to the statements described as follows:
p, blockquote 12,1,0,0,0 —>
- Household circulation pumps are designed to operate at a maximum coolant temperature of 110°C. In heating systems in a house, the coolant rarely heats up above 70°C, and the boiler heats water to no more than 90°C.
- The density of water at 50°C is 988 kg/m³, and at 70°C - 977.8 kg/m³. For a device that develops a pressure of 4-6 m of water column and has the ability to pump about a ton of coolant per hour, a difference in the density of the transported medium of 10 kg/m³ will not play any role.
- In practice, the difference in static pressure of the coolant in the supply and return lines also does not have any significant effect.
The conclusion is simple: circulation pumps for heating can be embedded in both the return and supply pipelines of the heating system of a private house. This factor will not in any way affect the performance of the device or the efficiency of heat supply to the building.
p, blockquote 13,0,0,0,0 —>

Position of the circulation pump during installation
As an exception, we can highlight cheap solid fuel direct combustion boilers, which are not equipped with automation. If the coolant overheats, it will simply begin to boil, because... burning wood cannot be extinguished at once. If the circulation pump is on supply, then the emerging steam, mixed with water, will begin to flow into the housing with the impeller. The process will then look like this:
p, blockquote 14,0,0,0,0 —>
- The impeller of the pumping device is unsuitable for moving gases. That is why the performance of the unit decreases sharply, and the coolant will move at a lower speed.
- Less cooling water enters the boiler tank, causing overheating to increase and the amount of steam to increase even more.
- An increase in steam velocity and its entry into the impeller leads to a complete stop of the coolant movement in the system. This becomes the cause of an emergency and, as a result of an increase in pressure, the safety valve is activated, which releases steam directly into the boiler room.
- If no measures are taken to extinguish the firewood, the valve simply cannot cope with the pressure release and an explosion will occur with the destruction of the boiler shell.
Two-pipe system with top wiring
The supply pipeline is laid under the ceiling, the return pipeline is laid along the floor. This explains the constantly high pressure in the system and allows the use of pipes of the same diameter even when forming a gravity-type structure. The expansion tank must be installed in the attic, making sure to insulate it, or placed between the ceiling - the lower part remains in the heated room, the upper part in the attic.
Experts recommend installing the upper line above the level of the window openings. In this case, it is possible to place the expansion tank under the ceiling, provided that the riser height is sufficient to ensure pressure in the system. The return pipe is laid out on the floor or lowered under it.
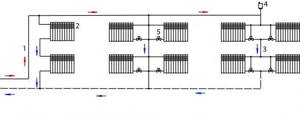
In the case of overhead wiring, the upper pipes remain visible, which does not improve the appearance of the room; also, some of the heat remains at the top and is not used to warm the rooms. You can run the pipes of the passing main under the radiators, and to ensure normal circulation, install a pump, which allows you to use small-diameter pipes.
In two-story private buildings, overhead wiring is considered effective and helps to achieve good heating of all rooms. The expansion tank is placed at the highest point, the boiler in the basement. This difference in height guarantees the efficiency of transportation of the coolant, the availability of connecting a tank to provide hot water supply - water circulation will ensure a constant flow of hot water to all appliances.
If you install a gas or non-volatile boiler in your house, the circuit becomes autonomous. To reduce costs, you should consider the option of combining a one- and two-pipe heating system. For example, make a warm (single-circuit) floor on the second floor, and equip a double-circuit structure on the first.
The advantages of the scheme are:
- coolant movement speed;
- maximum and even heating of rooms;
- eliminating the risk of air pockets.
The disadvantages include high consumption of components, insufficient energy to heat large rooms and difficulties with placing the expansion tank.
Pipeline options
There are two types of two-pipe wiring: vertical and horizontal. Pipelines are usually installed vertically in multi-storey buildings. This scheme makes it possible to provide heating to each apartment, but at the same time there is a large consumption of materials.
Upper and lower wiring
The coolant is distributed according to the upper or lower principle. With top wiring, the supply pipeline passes under the ceiling and goes down to the radiator. The return pipe runs along the floor.
With this design, natural circulation of the coolant occurs well; thanks to the difference in heights, it manages to gain speed. But such wiring has not been widely used due to its external unattractiveness.
The diagram of a two-pipe heating system with bottom wiring is much more common. In it, the pipes are located at the bottom, but the supply, as a rule, passes slightly above the return. Moreover, pipelines are sometimes laid under the floor or in the basement, which is a big advantage of such a system.
This arrangement is suitable for schemes with forced movement of coolant, since with natural circulation the boiler must be at least 0.5 m below the radiators. Therefore, it is very difficult to install.
Counter and parallel movement of coolant
A two-pipe heating scheme in which hot water moves in different directions is called counter or dead-end. When the coolant moves through both pipelines in the same direction, it is called a passing system.
In such heating, when installing pipes, they often resort to the telescope principle, which makes adjustment easier. That is, when assembling a pipeline, sections of pipes are laid sequentially, gradually reducing their diameter. When the coolant moves in the opposite direction, thermal valves and needle valves are required for adjustment.
Fan connection diagram
A fan or beam circuit is used in multi-storey buildings to connect each apartment with the possibility of installing meters. To do this, a collector is installed on each floor with a pipe exiting to each apartment.
Moreover, only whole sections of pipes are used for wiring, that is, those without joints. Thermal metering devices are installed on pipelines. This allows each owner to control their heat energy consumption. When constructing a private house, this scheme is used for floor-by-floor piping.
To do this, a comb is installed in the boiler piping, from which each radiator is connected separately. This allows you to evenly distribute the coolant between the devices and reduce its losses from the heating system.
Where to install the pump for a solid fuel boiler?
If such a device overheats, then it is impossible to turn it off quickly, since it is not possible to make the wood burn faster. If the pump in this system is mounted on the supply side, then when the boiler boils, steam is formed, which penetrates the pump with the impeller and the following happens:
- The pump is not intended for pumping gases, due to this the device stops working and the directional speed drops.
- A small amount of cooled liquid begins to flow into the boiler tank, which causes overheating and the amount of steam increases very quickly.
- When a significant amount of steam penetrates the impeller, the movement in the system stops. This situation is emergency; a safety valve is activated, which releases steam directly into the room.
- If the firewood is not extinguished in this case, it may happen that the valve will not be able to cope with the pressure and an explosion will occur.
If the pump is installed on the return line, then:
- Under no circumstances will he meet couples;
- And even if steam penetrates the system, it is pushed into the heating device, where it is converted back into liquid.
Moreover, the difference in the permissible explosion in both cases is 25 minutes, this time is, in principle, enough to approach the boiler, extinguish the firewood there and prevent an explosion.
Due to this, in solid fuel boilers, especially those in which there is little or no automation, it is necessary to install a pump on the return line. Moreover, it is correct that it be installed in the following order: tap - non-flush filter - pump - tap. If the system is hybrid, it will work quite well on its own, but when this cannot be done, a pump is installed. In this branching system, the main thing is to install a tap. But the most common mistake that everyone makes is installing a check valve. be installed , as it will push the gravity flow to stop. The tap can be opened when the system does not stop working on its own and closed when the pump turns on.
It is extremely important to treat the heating system with special care, because not only home warmth, but its safety may depend on it. Thanks to this, when installing on your own, first of all follow the instructions without any deviations. Well, if you have doubts about your own capabilities, then it is best to use the services of professionals who will do everything according to the rules and correctly.
Where is the circulation pump installed?
Options for piping in the system
The efficiency, economy and aesthetics of the heat supply system depend on the layout of heating devices and connecting pipes. The choice of wiring is determined based on the design features and area of the house.
Specifics of one-pipe and two-pipe schemes
Heated water flows to the radiators and back to the boiler in different ways. In a single-circuit system, the coolant is supplied through one large-diameter pipeline. The pipeline runs through all radiators.
Advantages of a single-pipe self-circulation system:
- minimal consumption of materials;
- ease of installation;
- limited number of pipes inside the living space.
The main disadvantage of a scheme with one pipe performing supply and return duties is the uneven heating of the heating radiators. The heating intensity and heat transfer of the batteries decreases as they move away from the boiler.
With a long wiring chain and a large number of radiators, the last battery may turn out to be completely ineffective. “Hot” heating devices are recommended to be installed in north-facing rooms, children’s rooms and bedrooms
The two-pipe heating scheme is confidently gaining ground. Radiators connect the return and supply pipelines. Local rings form between the batteries and the heat source.
- all heating devices heat up evenly;
- the ability to adjust the heating of each radiator separately;
- reliability of operation of the circuit.
A dual-circuit system requires large investments and labor costs. It will be more difficult to install two lines of communications along building structures.
The two-pipe system is easily balanced, ensuring the supply of coolant at the same temperature to all heating devices. Rooms are heated evenly
Upper and lower coolant supply
Depending on the location of the main line supplying hot coolant, a distinction is made between upper and lower connections.
In open heating systems with overhead wiring, there is no need to use air exhaust devices. Its excess is discharged through the surface of the expansion tank communicating with the atmosphere
With overhead distribution, warm water rises through the main riser and is transferred through distribution pipelines to the radiators. The installation of such a heating system is advisable in one- and two-story cottages and private houses.
A heat supply system with bottom wiring is quite practical. The supply pipe is located at the bottom, next to the return pipe. Coolant movement in the direction from bottom to top. The water, having passed through the radiators, is directed through the return pipeline to the heating boiler. The batteries are equipped with Mayevsky valves to remove air from the line.
In heating systems with bottom wiring, it becomes necessary to use air exhaust devices, the simplest of which is the Mayevsky tap
Vertical and horizontal risers
Based on the type of position of the main risers, a distinction is made between vertical and horizontal pipeline routing methods. In the first option, radiators on all floors are connected to vertical risers.
Vertical wiring is used when arranging houses of two, three or more floors with an attic space, within which a pipeline can be laid and insulated
Features of “vertical” systems:
- no air pockets;
- suitable for heating high-rise buildings;
- floor connection to the riser;
- difficulties in installing apartment heat meters in multi-storey buildings.
Horizontal wiring involves connecting radiators on one floor to a single riser. The advantage of the scheme is that the device uses fewer pipes and installation costs are lower.
Horizontal risers are usually used in one- and two-story premises. The arrangement of the system is relevant in panel-frame houses and residential buildings without walls
Advantages
A system equipped with a circulation pump does not have these disadvantages. It is perfect for heating rooms ranging from 200 to 800 m2. Its advantages include:
- no requirements for the configuration of the heating circuit - for coolant circulation there is no need to create narrow places in the pipeline, install pipes at an angle and use other technical techniques;
- rapid acceleration of the liquid - circulation of heated water in the circuit begins immediately after turning on the pump. As a result, the rooms of a private house warm up to the desired temperature in just a few minutes;
- high efficiency - thanks to the rapid circulation of the coolant, heat losses are reduced. The problem is solved when one of the rooms warms up more than the others. Due to this, fuel is consumed more economically;
- reliability of operation - the simple design of the pump eliminates the occurrence of accidental breakdowns.
If you plan to equip a system with natural circulation with a pump, its design remains virtually unchanged.
All you need to do is install the pump itself, and also move the expansion tank from the water supply circuit to the circuit through which it returns to the boiler.
Open and closed heating system
If an open type expansion tank is installed, then the system is called open. In its simplest form, it is some kind of container (saucepan, small plastic barrel, etc.) to which the following elements are connected:
- small diameter connecting pipe;
- a level control device (float), which opens/closes the make-up valve when the amount of coolant drops below a critical level (in the figure below it works on the principle of a toilet flush cistern);
- air release device (if the tank without a lid is not necessary);
- drain hose or circuit for removing excess coolant if its level exceeds the maximum.
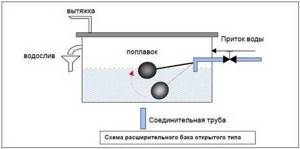
One of the open type expansion tanks
Today, open systems are made less and less often, and all because a large amount of oxygen is constantly present in it, which is an active oxidizer and accelerates corrosion processes. When using this type, heat exchangers fail much faster, pipes, pumps and other elements are destroyed. In addition, due to evaporation, you have to constantly monitor the coolant level and periodically add it. Another drawback is that it is not recommended to use antifreeze in open systems due to the fact that they evaporate, that is, they harm the environment, and also change their composition (the concentration increases). That’s why closed systems are becoming more and more popular - they exclude the supply of oxygen, and the oxidation of elements occurs much slower because they are considered better.
A membrane-type tank is installed in closed heating systems
In closed systems, membrane-type tanks are installed. In them, the sealed container is divided into two parts by an elastic membrane. At the bottom there is a coolant, and the upper part is filled with gas - ordinary air or nitrogen. When the pressure is low, the tank is either empty or contains a small amount of liquid. As the pressure increases, an increasing amount of coolant is forced into it, which compresses the gas contained in the upper part. To prevent the device from bursting if the threshold value is exceeded, an air valve is installed in the upper part of the tank, which is activated at a certain pressure, releasing part of the gas and equalizing the pressure.
Where is it usually recommended to install the pump?
Often on the Internet you can find information that it is best to put the pump on the return line and, of course, there are specific explanations for this:
- If you install a pump on the supply, the pump will break down faster, due to the fact that the temperature here is higher, and if you install on the return, the device will last for several years;
- At the supply level, the density of water is less and it is difficult to pump;
- The return pressure is higher, and this makes it easier for the pump to work.
But all the above arguments are considered not very correct and we will try to figure out why.
- First of all, the possible temperature for pumps is considered to be +110 - +115 degrees, however, in a heating system, in most cases the temperature can reach 80 o and sometimes 90 o. Thanks to this, it does not at all affect the moment where to install the pump
on the return or supply. - The density of water also does not work, because the difference between this parameter at a temperature of 50 o and 80 o is so small that it will not be reflected at all in the operation of the unit.
- The pressure difference between the value in the thermal media and the line is also small, so there is no point in calculating it.
Based on this, we draw the only conclusion that we should put
Circular pumps can be used for both supply and return. And where it will be placed will not at all affect its performance and durability. The main requirement that must be met during installation of the boiler is ease of maintenance.