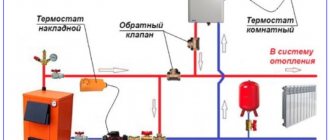
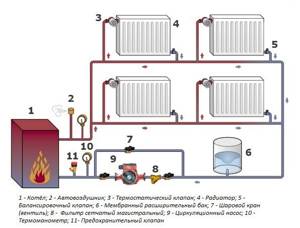
Additional requirements for the boiler room
Regardless of where you decide to install the heating boiler - in the house, in an extension or a separate building, the room must meet certain requirements.
Moreover, the requirements are also different for different types of boilers. For example, if you are building a frame house with a gas boiler room, then the area of the boiler room must be at least 15 meters with a height of 2.2 meters. However, this only applies to heating boilers with a power of no more than 30 kW. If you are using a boiler with a power of 30 to 150 kW, then the ceiling height should be at least 2.5 meters.
Also note that you cannot store a gas tank (whether cylinders or another container) in the same room as the boiler, in order to avoid fire and a terrible explosion.
For boiler rooms with solid fuel boilers, the area can be reduced to 7 square meters, and you can choose the height that seems sufficient to you.
If you are using a wall-mounted boiler, make sure that the boiler room layout includes one wall built of non-combustible material (brick or concrete). When choosing a heavier floor-standing boiler, make sure that the boiler room foundation can withstand such a significant load. Of course, the floor must have a completely non-flammable coating. When creating a heating system in an extension or outdoors, it would be better to fill the floor with concrete. If you are installing the boiler indoors, it will be enough to lay a steel sheet of sufficient thickness on the floor.
You should not skimp on components. Yes, by buying high-quality smoke detectors, bypasses, shut-off valves and other equipment in a specialized store rather than on the market, you will spend several hundred or even thousands of rubles more. However, in this case, you will be sure that each part is made of high-quality materials, and not brittle alloys that cannot withstand significant pressure and frequent temperature changes.
This means you guarantee the safety of yourself, your loved ones and your property. Isn't it worth the extra thousand rubles spent? In some cases, it is necessary to connect a sewer drain to the boiler room. Condensate that, under certain circumstances, occurs in the chimney of the heating boiler will flow there.
After all, it is important not only to correctly calculate the power of the installed boiler, but also to select suitable equipment based on the size of the premises, the thickness of the walls, the area of windows, the strength and direction of the wind in a given region, and the temperature (average in winter and extremely low). Therefore, most people prefer not to even try to draw up a plan on their own, entrusting this extremely complex and responsible work to specialists

Yes, because of this, the already expensive operation of installing a heating boiler turns into the most expensive of all installation procedures for engineering systems. But you can be sure that nothing threatens your family and you personally. And that even on the coldest winter days, when a blizzard howls outside the window, you will be warm and feel really comfortable.
A properly designed heating system for a one-story house can provide high-quality and efficient heating of the premises, but to do this you need to know how to properly implement such a system in your home. One of the most popular individual heating systems is the single-pipe natural circulation water heating system.
Most often, the installation of heating pipelines is carried out with metal-plastic pipes due to their practicality and reasonable price.
As a rule, water is used as a coolant, but it is also possible to use a non-freezing liquid that will prevent the heating system from freezing during the cold season.
How to plan a forced circulation system
First you need to decide on the power of the boiler.
This can be done again using average numbers: for 10 m 2 of area, take 1 kW of boiler power. If the ceilings are higher than 2.5m, you need to enter an increasing factor of 1.2. It is also necessary to increase power when located in the northern regions. These standards are for central Russia. If the house is located further north, add another 30-50%. A reserve is also required if the house is poorly insulated, because it is necessary to make up for heat losses that escape through the walls/floor/ceiling. So in this case, you need to take more powerful equipment. You also need to decide on the type of water preparation for domestic needs. If it will be heated by a boiler, the boiler power should also be increased for this - add 30-50% to the calculated boiler power. Read more about how to determine the power of a heating boiler here.

When calculating a home heating system, you need to decide on the power. boiler
Then we proceed to calculate the number of radiators: at least one for each window, plus one radiator for the bathroom/toilet. In the northern regions, radiators installed in the corridor/vestibule, which act as thermal curtains, have performed well to conserve heat.
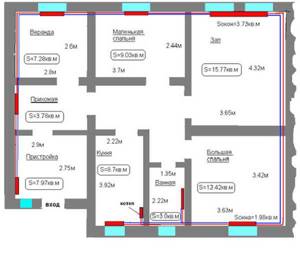
When calculating the number of radiators, we proceed from the rule: one radiator for each window
Once you have decided on the number of radiators, you need to calculate the number of sections in each. In general, they are calculated based on the area of the room: there are standards. Knowing the area of the room, divide it by the norm and get the number of sections. But this is again an average approach. Here you also need to take into account the type of wiring and the location of the radiator in the heating circuit. For example, single-pipe wiring. It is characterized by the fact that radiators located closer to the boiler receive hotter coolant and heat up to higher temperatures. The farther the radiator is located, the colder the coolant washes it. Therefore, to compensate and equalize the position in distant radiators, the number of sections is increased or they are installed with a larger area (height and power).
They do the same with a two-pipe installation, although the difference there is not so obvious: a coolant with the same temperature is supplied to the input of each radiator, it’s just that those located closer to the boiler have a higher flow rate through the radiator than those further away. To equalize the flow, thermostatic valves are installed on each radiator.

To regulate the heat transfer of the radiator and compensate the system, install thermostatic valves
But in a two-pipe heating scheme there is an option with a Tichelman loop. This heating scheme is initially compensated (if the radiators are installed the same). But it requires more pipes even compared to a conventional two-pipe.
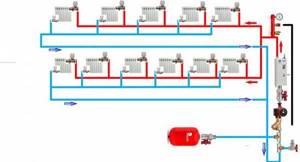
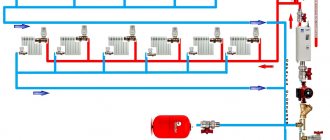
Diagram of a forced circulation system. The house is two-story. Two-pipe system with bottom supply, dead-end coolant flow pattern
The number, composition of radiators, and type of wiring have been decided. You need to decide on the type and diameter of the pipes and the type of system. What kinds of heating pipes there are and the features of their use are described here.

To bleed air from the system, install a Mayevsky valve on the radiators
When installing the system yourself, after the radiators are assembled and the pipes are connected, the entire system must be flushed. And only then connect the pump and boiler. In systems with solid fuel boilers, a safety group is required, which includes a pressure gauge, an air outlet valve and a blast valve, which is set to the operating pressure in the system and, if it is exceeded, is activated automatically.
A filter must be installed at the feed line inlet to the boiler to protect the circuit and equipment from the ingress of abrasive or contaminant particles.
The selection of a pump and expansion tank is irrelevant if you plan to install a wall-mounted gas boiler. Most models have a built-in expansion tank and pump. Then all that remains is to navigate by the volume of the system with which this modification can work. Based on this, select the diameters of the pipes and the area/power of the batteries.
Heating system installation
Installation of a water heating circuit for a home is one of the simplest. It begins with the installation of a heating boiler and subsequent laying of pipes, connecting them to heating devices (radiators, heated towel rails and others). Metal pipes are usually used, since plastic ones can contribute to overheating of the entire system and its failure. For a one-story house, it is recommended to use the following pipes:
- Supply line - pipes with diameters of one and a half to two inches (pipes of type DN 40-50);
- For the return line - two-inch pipes (less often one and a half inches).
The heating system lines are installed with a slope of one centimeter per meter of the length of the pipe itself. Heating devices must be installed centrally under the windows, with connections using three-quarter inch pipes (DN 20).
When the heating system is operating, the devices closest to the boiler heat up first. That is why so-called control taps are installed, which allow heat to spread throughout the house more evenly. It is advisable to install such taps on both sides of the heating device. This can allow repair work to be carried out easily and quickly without shutting down the entire system.
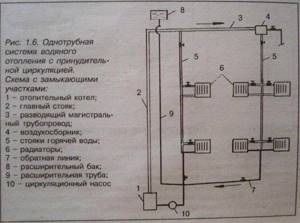
Diagram of the heating system of a two-story house
Heating radiators for such a system can be installed in a variety of different ways, with the exception of panel radiators, which clog very quickly in such a system. Therefore, it is imperative to make an insert for the outlet (drain) tap for water near the boiler (at the lowest point of the system). The drain valve will allow dirty water to exit the system when necessary.
For filling, a valve is perfect, which will allow you to evenly fill the heating system while removing air from the radiators without the risk of air locks.
When installing a home heating circuit, it is necessary to provide an overflow on the expansion tank. To do this, use a DN 15-20 pipe (half - three-quarters of an inch), which is led outside or into a sink located nearby.
With this scheme, the heating time is 30-40 minutes. The disadvantage is the need to lay large-diameter pipes and the effective operation of the system only for one-story houses or houses with a small area. The maximum length for the supply line is thirty meters.
Usually the boiler is located in the center of the house so that the heating system can be divided into two wings. The heating scheme of a one-story house in this case works more efficiently, since a two-circuit system in two halves allows heating a larger area.
The supply lines usually run under the window sills, from where outlets go to individual radiators. In the case where there is no space to install such a system, a DN 32 pipe (five-quarters of an inch) is used, which directly connects several radiators.
The main advantage of installing such systems is that they can operate without power supply. The coolant functions independently in them.
Advantages and disadvantages
Any home heating scheme has its positive and negative features.
The stove system is characterized by high consumption of solid fuel, which requires a special storage space. In addition, the maximum number of rooms that can be heated using a stove or fireplace is only two or three.
On the other hand, many stoves, in addition to the heating function, can be used for cooking. They are easy to install and use, and their fuel is relatively cheap. Such heating does not depend on the supply of electricity.
Electric heating
This system is the most effective, it does not require the installation of bulky equipment, and the heating devices themselves are lightweight and small in size, and are easy to move to another place. However, significant disadvantages are the dependence on the supply of electricity and its high cost.
The air heating scheme for your own one-story house has the following advantages: it does not require the installation of a sewer system or special heating devices. However, in terms of heat capacity, such a system is much inferior in comparison with a water system.
The water system is also not ideal, the disadvantages are: the danger of freezing of the existing water in the pipes, high metal consumption and large diameter pipes, small radius of action of one main line.
However, these systems do not lose popularity, since they are easy to install, do not depend on the supply of electricity, are durable, do not require a noisy pump, and can be self-regulating.
Comparison by installation price
Supporters of single-pipe heating networks like to remind people of the low cost of this type of wiring. The reduction in costs compared to a two-pipe scheme is justified by half the number of pipes. We claim the following: “Leningradka” will cost less than a dead-end system in one case - if you solder the heating from polypropylene.
Let's prove our statement with calculations - let's take as an example a one-story dwelling measuring 10 x 10 m = 100 m² (in plan). Let's put the "Leningrad" layout on the drawing, count the fittings with pipes, then make a similar estimate for the dead-end wiring.
So, to install one-pipe heating you will need:
- pipe DN20 to the collector (outside Ø25 mm) – 40 m;
- tr. DN25 Ø32 mm for return – 10 m;
- tr. DN10 Ø16 mm for connections – 8 m;
- tee 25 x 25 x 16 (outer size) – 16 pieces;
- tee 25 x 25 x 20 – 1 pc.
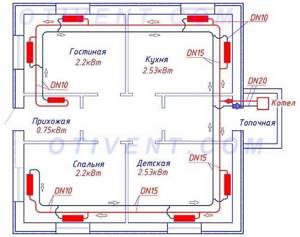
Based on the following layout, we will find out the need for pipes and fittings for a two-pipe network:
- tr. DN15 Ø20 mm – 68 meters (mains);
- tr. DN10 Ø16 mm – 22 m (radiator connections);
- tee 20 x 20 x 16 mm – 16 pcs.
Now we will find current prices for plumbing fittings and pipes made of 3 materials: reinforced polypropylene PP-R, metal-plastic PEX-AL-PEX and cross-linked polyethylene PEX from well-known manufacturers. Let's put the calculation results in the table:
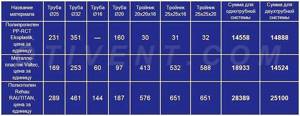
As you can see, the costs for polypropylene tees and pipes are almost the same for both schemes - the shoulder scheme turned out to be only 330 rubles more expensive. For other materials, two-pipe wiring definitely wins. The reason lies in the diameters - the prices of larger cross-section pipes increase sharply compared to the “running” sizes of 16 and 20 mm.
You can take cheaper plumbing fixtures from other manufacturers and perform the calculation - the ratio is unlikely to change. Note that we skipped the 90° elbows for pipe turns and other small items, since we do not know the exact quantity. If you carefully calculate all the materials, the cost of the Leningradka will increase even more. An expert demonstrating calculations on video came to similar conclusions:
Where is the best place to locate the boiler room?
A heating boiler, even if all required safety rules are observed, is a source of increased fire hazard. Therefore, you should approach the choice of the place where it will be installed very responsibly and seriously. It is necessary to consider not only the cost of placement and operational safety, but also ease of use. Based on this, there are three main ways to locate a boiler room.
The first is out-of-home placement. It should be said right away that this method is as expensive as it is safe.
But keep in mind that you will have to develop a separate drawing, pour an additional foundation, think about installing external utility networks and their thermal insulation.

You will have to spend a lot of money and time. And the ease of use is significantly reduced. Secondly, if the designs of houses with a boiler room were initially developed taking into account the installation of the necessary equipment, then the heating boiler can be located on the ground floor or even in the basement. Most people prefer to place it in the basement. Then you won’t have to allocate 15-16 square meters of usable space on the ground floor, which means that the freed up space can be used to greater advantage.
To install a diesel boiler or solid fuel boiler, it is necessary to provide a separate room: when coal, wood, peat or diesel fuel is burned, a large amount of smoke is released, which can cause certain problems for the inhabitants of the house. Well, even the most economical owner can allocate 15 square meters when building luxurious two-story houses with a boiler room.
two-story house
If you prefer an electric heating boiler or a not too powerful (no more than 30 kW) gas boiler, then you can install the equipment in the kitchen. Modern equipment is small in size, so it is not noticeable and does not take up extra space. If desired, you can even choose special wall-mounted boilers that take up virtually no useful space in the room.
Of course, the kitchen must have high-quality ventilation, and simply monitoring the condition of the equipment will never be superfluous.
And finally, an option that allows you to combine the advantages of the two described above and at the same time, partially get rid of their disadvantages. When designing wooden houses with a boiler room, you need to provide a small extension in advance.

wooden house
A foundation is also poured under it, which is part of the main foundation. In most cases, extensions are made from lightweight materials (frame construction), which allows you to save a considerable amount during construction. This simplifies the organization of high-quality ventilation. As a result, you get a boiler room, which is located in close proximity to the house. Thanks to this, you will not have to spend extra money on laying the pipeline.
At any time you can enter the extension both from the side of the house and from the street: in most cases, extensions are equipped with two doors. If a gas leak (carbon monoxide or explosive) occurs, the risk of serious damage to the main building is minimized. Therefore, an extension to the house dedicated to the boiler room can be called the optimal solution.
Reasons for lack of water circulation
Often users of one- or two-story houses are faced with a situation where heaters begin to work less efficiently. If there is no circulation in the heating system, there may be reasons for this.
Lack of circulation in the heating system can be caused by:
- System contamination. The batteries must be washed periodically, otherwise the structure may become clogged along its entire diameter. If this happens, you will have to change the pipes.
- The pipe diameter is too small. And the smaller the pipe diameter, the greater the hydraulic resistance. This may also be the reason that there is no circulation in the heating radiator, or there is circulation, but it is very weak.
- Airing the heater. To solve this problem, Mayevsky cranes are installed.
Very often, wet-type pumps with a power of up to 40-60 W are installed in heating systems with natural circulation. You can read more about the operation of heat pumps for heating here. This is one of the options for improving water circulation in the home heating system. In addition, pumps can help save up to 25% of costs.
- How to fill water into an open and closed heating system?
- Popular floor-standing gas boiler made in Russia
- How to properly bleed air from a heating radiator?
- Expansion tank for closed heating: device and principle of operation
- Gas double-circuit wall-mounted boiler Navien: error codes for malfunctions
Recommended reading
Steam heating: advantages and installation methods Infrared heating at home: pros and cons Independent and dependent heating system: advantages and disadvantages Autonomous heating of an apartment and private house
2016–2017 — Leading heating portal. All rights reserved and protected by law
Copying site materials is prohibited. Any copyright infringement will result in legal liability. Contacts
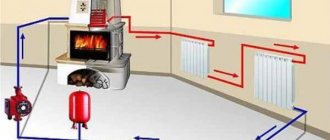
Heating scheme for a house that has natural circulation
This is the easiest way to heat your home.
Before installing equipment for this system, you must purchase:
- Heating boiler (this is the most important component in the circuit).
- The entire set of pipelines (you can calculate how many pipes are needed according to the diagram).
- Expansion tank.
- Batteries (radiators - can also be calculated according to the diagram).
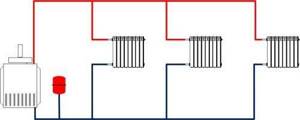
Rice. 3
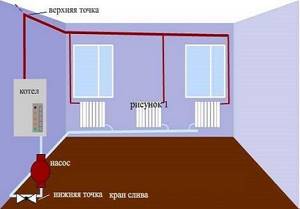
This heating system is also called gravity, since the pipes are installed at an angle, so the water flows into the heating device on its own. A boiler with natural circulation is suitable just for small private houses - that is, for those places where the smallest pressure drops are created.
The disadvantages of a system with natural circulation include the fact that it cannot be installed in a large building, and the diameter of the installed pipes is quite large, so you also need to make additional space to hide them.
Before installing a heating system, you need to think carefully about everything so that no problems occur during the operation of gas equipment. Because if it is installed incorrectly, you will soon need to call a technician and make repairs, and who needs extra expenses. So my big advice is to think 10 times and do it once.
In a country with such a harsh climate as Russia, high-quality heating of private residential buildings is a matter of not only comfort, but also safety. This is why most people who decide to move from an apartment to a private house take the issue of heat supply very seriously.
Option for planning a house with a boiler room
Of course, at the planning stage they are most interested in house designs with a boiler room. The boiler room provided for during the design usually meets a number of requirements placed on it by specialists and ordinary users. And every person who orders a project for their future home from a specialized company needs to know about them. In addition, you need to know what stages you will have to go through when designing a house with a boiler room.
It is especially difficult to comply with all the standards if you order a project for a small one-story house with a boiler room.
Since in this case it is necessary to comply with safety requirements and not take up too much space, otherwise the area of other rooms in the cottage will be reduced.
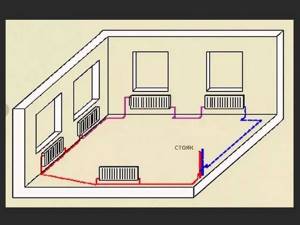
Single-pipe heating system
Only one main line is installed in the house, under or above the floor, with batteries connected in series. In such a heating circuit there is no distribution between the supply pipe and the return pipe.
Along the perimeter of a one-story building, only one round pipe with a diameter of at least 32 mm is installed, which is conventionally divided in half. The half leaving the heat generator is called the supply, and the second part of the line is called the return. Radiators/convectors are mounted into the loop using a welded or seamless pipe of small diameter.
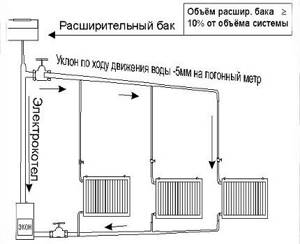
Organizing a heating system with natural circulation involves installing a supply pipeline with a slope of 4-5 mm every 2 m
The single-pipe circuit includes the following functional elements:
- heat supply source (boiler);
- heating radiators;
- expansion tank;
- pipe routing elements.
The heated liquid flows alternately into the heating radiators, each time giving off part of its heat. After this, it is already cooled and returned to the boiler for the next heating cycle. Each battery loses heat and the last element in the chain remains the coldest in comparison with the others.
There are several ways to optimize the operation of a single-pipe system. You can additionally install special thermostatic valves for heat exchangers, balancing valves with adjustable hydraulic resistance or compact ball valves. Such equipment helps normalize the heat supply to the batteries.
Installed valves make it possible to regulate the amount of heat entering each individual radiator
Another way is to increase the number of sections of each subsequent radiator in the heating circuit. You can also install a circulation pump. The pumping device is connected at the end of the return line - the place where the working fluid has the lowest temperature.
The single-pipe heating option is easy to install and put into operation. Heat loss is minimized, since absolutely all communications are located inside the living rooms of a private house.
Such a scheme can be organized in the form of a system with horizontal wiring and forced movement of the coolant or a vertical heating network with natural, forced or combined movement of the working fluid.
We also recommend reading our other material, where we examined in detail a single-pipe heating system for a private home.
Horizontal wiring method
Installation of the supply pipe in a horizontal plane is carried out with the required slope in the direction of movement of the heated water. In this case, all batteries around the perimeter of the house must be installed at the same level. To bleed air from radiators, Mayevsky taps or automatic air vent devices are used.
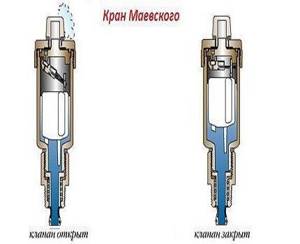
The Mayevsky tap is a special device for removing accumulated air from batteries. The shut-off valve is turned until a hissing sound is clearly audible. When the mixture of gases is removed, water will flow from the tap.
The horizontal line can be installed in the floor structure itself or mounted above it. To avoid heat loss, in the first case it is necessary to insulate the pipes.
Vertical wiring option
In such a system, the transportation of the coolant liquid is ensured by a natural circulation mode, and therefore there is no need to install an additional pump. Energy independence is the main advantage of a single-pipe vertical home heating system.
With this method of wiring, the working fluid, heated to a given temperature, moves up the riser, after which it enters the batteries through distribution pipes. The operating efficiency of a vertically located single-pipe system is achieved by installing the main line at a slope, as well as by installing large-diameter pipes.
Of course, a massive pipeline will not decorate the interior of living rooms. But this obvious drawback can be avoided by installing circulation equipment in the system.
Selecting the media circulation type
The first step in designing a heating system is choosing the type of coolant circulation: natural or forced. (See also: Heating with natural circulation)
The main advantage of gravity circulation is the energy independence of the system, due to the absence of a pump operating using electricity. However, such a heating system with forced circulation has a number of significant disadvantages: large diameter pipes, difficulty in calculations and practical compliance with pipeline slopes. In addition, such a system is difficult to regulate, it is difficult to control individual parts of the heating system, and the ability to use modern materials and technologies is difficult.
The use of circulation pumps allows you to overcome all of the above difficulties. Systems with natural circulation are considered obsolete and are becoming a thing of the past, giving way to heating with forced circulation.
The choice of type of coolant movement determines the range of heating equipment purchased and the materials from which it is made. (See also: Circular pump for heating)
Advantages and disadvantages of forced circulation heating
The big advantages of this type of heating are the following factors:
— high efficiency achieved by using a small volume of coolant;
- aesthetic appearance, since small diameter pipes are used in the construction of this system;
— the ability to hide pipes in wall cladding or under the floor;
— compactness.
The disadvantages of a forced circulation system include, first of all, energy dependence. However, this issue is especially relevant only for boilers operating using solid fuel. Gas units, even if they are energy dependent, are equipped with sensors that protect the system from overheating. In addition, technological progress that does not stand still offers options for solving this problem. In particular, there are devices that allow you to provide the heating system with electricity when it is centrally turned off. This equipment operates using external batteries.
An important element in a forced circulation system is the pump. Circulation pumps can be built into the heating boiler, or they can be purchased and installed separately. In both cases, their presence significantly speeds up the ability to achieve a comfortable temperature in the room. In addition, such a system, if a thermostatic valve and a control head are installed in it, allows you to achieve the desired temperature in the rooms. (See also: Water pumps for heating)
Heating systems in which the coolant moves using a circulation pump allow the widespread use of automation, with the help of which the building owner can program the desired temperature both depending on the season and the time of day.
Heating boilers
A forced heating scheme for a private house cannot do without heating equipment, which can be a boiler of one of the following types:
- Gas . The most common option. To install gas boilers, you need a main line, and the installation process is quite expensive. However, this is where the disadvantages end - gas-fired boilers are cheaper than all others to operate, and they do not require attention.
- Electrical . A less common and relatively inexpensive type of boiler. The biggest disadvantage of such devices is the cost of electricity and its consumption - ultimately, heating costs are prohibitively high.
- Liquid fuel . This is a fairly economical type of boiler, but it cannot be called a leader in this parameter. Diesel oil is usually used as fuel, which, on the one hand, is relatively inexpensive, but on the other hand, it will have to be topped up periodically, so it will be impossible to leave the boiler unattended.
- Solid fuel . Such boilers are inexpensive, and the cost of solid fuel (coal, firewood and pellets) is relatively low. Of course, to maintain the operating temperature, you will have to constantly add a new portion of fuel - that is, solid fuel boilers are quite inconvenient to operate.

In order for the heating scheme of a private house with forced circulation to be sufficiently effective, it is necessary to calculate the required boiler power at the design stage. It would be best to turn to specialists, but if you really want to, you can do this work yourself - for example, using an online calculator. There is also a technique that allows you to calculate the approximate value of the power, according to which, for heating every 10 sq.m. the premises require 1 kW of thermal energy.
Combination of two-pipe and single-pipe options
In private two-story (or higher) houses, both two-pipe and single-pipe vertical risers can be used, along with horizontal single-pipe distribution to rooms with a variety of ways to connect heating devices.
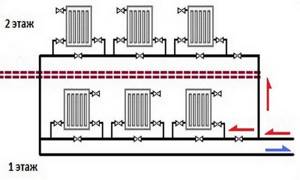
Diagram of a single-pipe heating system for a 2-story house.
The temperature difference in room radiators in this case is calculated by the formula ∆T_р=∆T⁄P, where P is the number of heating devices connected in series (in this case P=3). A horizontal single-pipe main must carry P times more liquid than through horizontal pipes with a two-pipe distribution. This will require an increase in pump power for its forced circulation and high energy costs, but the hydraulic stability of the circuit will be high.
Tips for choosing pipe diameters and connections
A single-pipe heating option can be designed and installed independently, without resorting to complex hydraulic calculations. Let’s simplify the task and give useful recommendations on the design of single-circuit systems:
- The maximum number of heating devices on one loop of a closed Leningradka is 5 pcs. To deliver the required volume of coolant to the batteries, a pipe Ø25 mm (DN20) is sufficient. We make the connections from pipes Ø16 mm.
- If, due to objective reasons, the number of radiators on 1 ring of a closed system needs to be increased, the cross-section of the main line is increased to a diameter of 32 mm (DN25), the liner - to 20 mm. It is not economically feasible to install more than 7 batteries on one pipeline; it is cheaper to lay 2 smaller lines.
- The minimum diameter of a horizontal collector with natural circulation is DN40, outer diameter is Ø48 mm. In a two-story house, the accelerating riser and the beginning of the distribution branches are made from a DN50 pipe (Ø57 mm), remote areas are reduced to a size of DN32. Vertical lines to radiators - DN20-25 depending on the thermal power of the heaters.
- To automatically regulate heat transfer, select full-bore valves with thermal heads. The hole in standard radiator valves is too small.
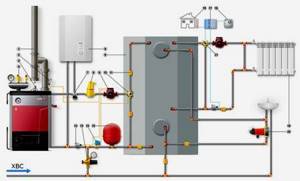
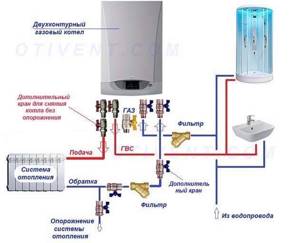
- Connection to a wall-mounted or floor-standing gas boiler is made according to the standard diagram shown in the picture below. The wiring of an electric water heating apparatus is done in a similar way.
- It is better to connect the Leningradka solid fuel boiler through a three-way mixing valve and a buffer tank. Since there is too little coolant in the system, there is a risk of overheating and boiling. Gravity distribution, holding more than 200 liters of water, can be connected directly to the TT boiler.
The listed recommendations will help you organize heating correctly if you use single-pipe wiring wisely. For an analysis of common mistakes and questions regarding the installation of the Leningradka, see the next video:
Types of heating schemes and their differences
The most popular are two schemes: one-pipe and two-pipe with different types of wiring.
Single-pipe heating scheme for a one-story house
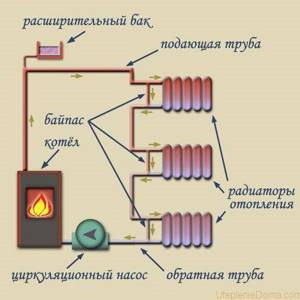
Single-pipe heating circuit
This type of scheme is the simplest and most accessible. The coolant is water, and its movement through the pipes is ensured by natural circulation. In this case, pipes with a sufficiently large diameter should be used. To improve the work result and using a more compact pipeline (in diameter), you can use a special circulation pump. This is necessary in case of real estate with a large area.
The water heated in the boiler enters the pipeline to further enter the radiators. It is here that it gradually cools down, giving up its heat, and returns the same way.
At the highest point, which in most cases is located in the attic, an expansion tank is mounted. Without exaggeration, this heating system can be considered the simplest and most economical among other types.
The disadvantages of the system include two factors:
- The temperature of the radiator battery, which is closer to the boiler, will be higher than that of distant heating devices. The water cools down on its way and gives off less heat to each subsequent battery.
- It is impossible to control the operation of a single radiator battery. If a heating element breaks down, the entire system will shut down.
This heating scheme for a one-story house has its advantages:
- Economical heating option;
- Quick and easy installation, you can do it yourself;
- All heat is spent on heating the house, its losses are excluded;
- If the pump malfunctions, circulation can occur naturally.
Two-pipe heating scheme for a one-story house
The system is quite actively used in private houses of any number of floors. Its characteristic features are separation of the coolant circuit and uniform heating of the entire area. Water or other coolant passes through the supply pipe from the boiler to radiator batteries, a “warm floor” system, or for household needs. And after cooling, it returns back to the boiler, but through a different pipe.
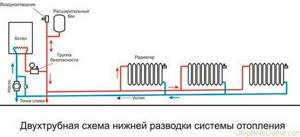
A two-pipe heating system for a one-story house has the following positive aspects:
- Ability to regulate the operation of heating elements;
- Efficiency of work in any private houses that belong to low-rise construction;
- If one radiator breaks down, there is no need to shut down the entire system;
- You can get hot water for your needs.
Among the disadvantages, it is worth highlighting the large number of pipes, which do not add aesthetics to the design, but, on the contrary, reduce it. In addition, a two-pipe heating scheme for a one-story house requires a more complex installation process and the purchase of more materials and equipment.
Which scheme should I choose?
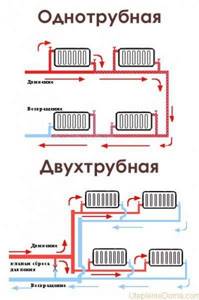
Operating principle of two-pipe and one-pipe systems
The choice of heating scheme for a private one-story house can be based on various factors that depend on each specific situation. But among the general criteria, one can highlight the living space of the house, the characteristics of the materials that were used in its construction, as well as the type of residence (permanent or seasonal). The degree of autonomy of the system plays an important role. It is necessary to take into account which external connection the entire system will operate from, the availability of communications and other factors.
It is believed that the optimal heating scheme for a one-story house is a horizontal two-pipe system. It will allow you to evenly distribute all the heat in the house and create optimal temperature indicators.
Classification of heat supply systems
In cottages, houses and just one-story buildings, autonomous heating systems are installed or those that depend on external power sources. The first ones will operate on liquefied gas, diesel and solid fuel. The latter require connection to the electrical network or main gas pipeline. Another difference between heat supply options is that a person is required to participate in the operation of the equipment.
Automated control systems do not require constant supervision or manual adjustments. Maintaining the required temperature inside the house is ensured by the operation of temperature sensors and thermostats. Such devices help to regularly monitor changes in temperature indicators, and this allows the heating system to take into account all the factors that will have a direct impact on the temperature inside the room - heat from the sun, radiation from other household devices, heating from a lighting lamp, etc.
Often, a heat supply system is installed together with boiler automation. Its main task is to achieve the highest possible efficiency, but at the same time not to go beyond acceptable parameters. Automation makes it possible to change the temperature mode at any time of the day.
When classifying heating systems, the following characteristics should be taken into account:
- Type of coolant – air, steam, water, combined.
- Type of fuel - electricity, gas, firewood, peat, pellets or coal.
- The method of movement of the coolant is natural and forced circulation.
- The movement of the coolant is dead-end and forward.
- The boiler connection method is a two-pipe and one-pipe system.
- Wiring scheme - horizontal or vertical arrangement of the distribution line, top or bottom laying, combined method.
In buildings with a large number of apartments, a vertical wiring diagram is most often used, and in one-story houses, a horizontal wiring diagram is most often used. The combined method of heat supply is used mainly in new buildings.
Local automatic temperature stabilization
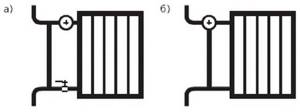
Single-pipe adjustable radiator unit with a straight-through (a) or three-way (b) thermostatic valve on the top supply.
An adjustable radiator unit for vertical single-pipe heating can be made with a straight-through (Fig. a) or three-way (Fig. b) thermostatic valve (thermostat). The piping unit branches the coolant into two flows: through the device and through the bypass. The diameters of the thermostat valve plunger and the opening for the passage of liquid are made to the maximum. The thermostat does not clog when the coolant is contaminated and ensures its free flow (when fully open). Unauthorized replacement of the radiator, accompanied by removal of the thermostat, does not lead to imbalance of the entire heating system, as in the two-pipe version.
If the room air temperature exceeds the set one, the valve will close (go to minimum mode), directing the liquid through the bypass past the radiator. Closing (minimum opening) the valves of all thermostats of a given riser increases the proportion of coolant passing through the bypasses from 80% to 90%, while simultaneously reducing the flow through the radiators, i.e. without changing the total flow rate.
Lower and upper wiring diagram
When distributing the system at the bottom, the main line is laid in the basement or basement. It is also possible to install pipes under the floor. The coolant enters the heating equipment from the bottom up.
The mixture of gases is removed through a special air line connected to the risers. In case of unforeseen emergency situations, the return and supply risers are equipped with special shut-off valves.
To implement a scheme with an upper distribution line, the expansion tank is mounted at the highest point of the pipeline. The network is branched in the same place.
It is impossible to design overhead wiring in private houses where there is no attic
Equipment selection
In order to turn any gravity heating system into a circuit with forced movement of coolant, you need to choose the right equipment. Its effectiveness and efficiency will depend on this.
The pump is the central figure in ensuring the circulation of water throughout the circuit. As a rule, centrifugal-type devices with straight impeller blades are used for household heating systems.
Pumps differ in the operating pressure that can be created in the system, productivity, power consumption, pressure height and diameter of the connecting pipes.
The required performance of the circulation pump can be calculated using the formula (Q/c*Dt)/ P, where Q is the heat loss of the house;
C – how much heat water can carry (tautical value, equal to 1.16);
DT – temperature delta;
P – density of water at nominal t°C (tabular value).
Recommended values can be used.
- For residential buildings with an area of up to 250 m2, it is recommended to use a circulation pump with the following characteristics: productivity 3 - 4 m3 / h; pressure 0.4 - 0.5 atmospheres.
- Up to 350 m 2 – 4 – 5 m 3 / h; pressure 0.6 atmospheres.
- Up to 800 m 2 – 11 – 12 m 3 / h; pressure 0.9 atmospheres.
Pump, a self-sufficient element of circulating CO. But for reliable operation of this device, proper harnessing is required, which includes:
- Ball valves on both sides of the pump.
- Sump.
In addition, it is recommended to connect the pumping group to the CO through a bypass equipped with a check valve.
The expansion tank is another one of the most important elements of CO with forced circulation. Depending on its design, there are schemes of open heating systems with forced circulation and closed ones.
In open COs, atmospheric devices are used that serve to compensate for the thermal expansion of the coolant. If the pressure in the system exceeds, part of the coolant is discharged. To replenish water in the CO, a float valve is used, which is connected directly to the water supply.
The operation of a sealed expansion tank in closed heating systems with forced circulation is very simple: a rubber membrane is installed in the body of this device. On one side of the membrane there is a coolant, on the other there is air pumped into the tank under a certain pressure.
When the pressure in the CO is exceeded, the membrane bends towards the air, and when it falls, it bends towards the coolant. Thanks to this simple technology, pressure surges in heating systems are leveled out.
Tip: the capacity of the expansion tank depends on many factors. Based on experience, expansion tanks with a capacity of 10% of the amount of coolant are used in household CO systems.
Advantages and disadvantages of heating with one pipe
Single-pipe heating (also called “Leningradka”) is characterized by the supply of liquid to the radiators and its removal from them sequentially.
It has the following advantages:
- reduction of installation time and labor intensity;
- the highway can be hidden in the walls, which improves the aesthetic properties of the room;
- there is the possibility of organizing gravity flow of coolant in buildings on 2-3 floors;
- comparatively cheap pipe laying;
- if the system is closed, then its adjustment is carried out automatically, through thermostatic radiator valves.
However, Leningrad is characterized by the following disadvantages:
- as the liquid moves to the distant batteries, it cools down, so at the end the circuit does not provide the required heating of the room;
- hydraulic instability (when the valve on one radiator is closed, others will begin to overheat, which will create an unpleasant microclimate in the rooms);
- for good movement of water with a closed type of system, the installation of full bore fittings on the branches is required;
- a single-pipe design with vertical wiring is more expensive than a two-pipe design;
- balancing the system is not easy.
If the structure is gravity-flowing, then it is necessary to ensure a large pipe diameter. Moreover, they are laid with a certain slope - up to 5 mm per 1 linear meter.