Advantages
Chiller fan coil differs from similar systems in that it:
- Easy to maintain
. Filters are easy to clean and can be changed quickly - It is possible to serve a large number of consumers, that is, premises in which fan coil units are installed. Their number is determined by the power of the unit, chiller.
- A device that heats or cools the coolant, a chiller, is installed in one place. This means that you don’t need a lot of space to place it
. - If the pipes have high-quality thermal insulation, and the coolant has a high heat capacity, then the distance from the chiller to the rooms in which air conditioning is carried out does not matter. It can be installed at a considerable distance
. If gas is used, this advantage disappears. - Low cost of installation work
. It is due to the use of conventional pipes, standard shut-off valves, and simple automation in the system. - Environmentally friendly
. The coolant is water or ethylene glycol mixed with water. The latter, although toxic, can only be poisoned by prolonged inhalation of its vapors. But the first time it enters the body, it causes a painful cough and forces you to leave the room. The refrigerant, which poses a certain danger, circulates only in the chiller. And it is mounted either in the attic, or, if the device is made in the form of a monoblock, on the roof. - The system can be used in conjunction with ventilation
, preferably supply and exhaust type, and with heating. - Relatively low cost
of the system itself.
Fan coil design
The English name of the device fan coil literally means “coil fan” and indicates a structural similarity with the long-known AVO heaters (air heating units). In appearance and design, fan coil units also resemble the internal units of a split system, only instead of freon, water or antifreeze is used.
Reference. The working fluid in industrial air conditioning systems is traditionally toxic antifreeze ethylene glycol. A safe analogue - propylene glycol - is 30-50% more expensive, therefore it is used less often.
The fan coil consists of the following elements:
- a housing equipped with air grilles or pipes;
- heat exchanger - a coil made of a copper tube with numerous plates;
- fan, usually centrifugal;
- coarse air filter;
- solenoid valve – regulator of fluid flow through the heat exchange radiator;
- manual air release valve;
- electronic control board.
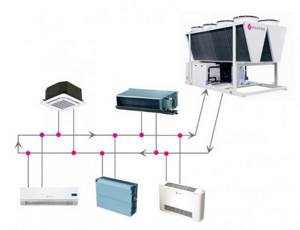
Chiller-fan coil system design
Simplified, this air conditioning system looks like this: its external unit is a water-cooling machine, called a chiller, connected by a pipeline to an internal heat exchanger - a fan coil unit, which is blown by a fan.
Such a system is easy to operate and can effectively cool or heat the air in a large room or in several rooms at once. It does not have the same restrictions as freon. The length of the coolant line is limited only by the power of the booster pumps.
In addition, this air conditioning option can operate at any ambient temperature, unlike freon air conditioning, which must be stopped already at -10C° to avoid breakdown. To move the coolant, you can use ordinary water pipes, both metal and PVC, which significantly reduces the cost of the entire system. Design of chillers
The chiller is an ordinary powerful refrigeration machine in which the evaporative heat exchanger discharges the accumulated cold not into the air, as in an air conditioner, but into water, which, when cooled, flows through the piping system to the fan coil units. There are two main types of chillers - absorption and vapor compression. Absorption ones are quite expensive, bulky and have a rather narrow application. The most common are vapor compression chillers, which come in several types:

- Air-cooled chillers for outdoor installation. In such installations, the heat exchanger-condenser is cooled using axial fans.
- Air-cooled devices for indoor installation. In them, air is taken in for cooling and the hot air flow is released through air ducts, for the movement of which a centrifugal pump is used.
- Refrigeration units with water-cooled heat exchanger. Most often they are installed in places where it is possible to cool the condenser with running water from natural reservoirs.
- Chillers are reversible. They allow you to both cool the air and heat it, so they can be used in air conditioning systems without installing additional water heating equipment.
Fan coil installation
Fan coil units are the so-called internal units of the chiller-fan coil air conditioning system, which are also called closers. Their device consists of a heat exchanger and a powerful fan that blows it. In addition, they are equipped with easily removable air filters and a control unit. More modern models provide wireless device control panels. There are several types of this equipment:
- Cassette fan coils are designed for cooling or heating air in large rooms, the design of which includes suspended ceilings. It is in them that these devices are mounted. They can distribute air flow to two or four sides.
- Duct fan coil units are installed in separate rooms. Air is taken in through separate air ducts, and air is discharged into the premises through air ducts located behind suspended ceilings.

By the way, many companies produce universal devices that can be mounted both on the wall and on the ceiling. Additional equipment In order for the equipment to operate uninterruptedly and year-round, various devices and accessories are used that significantly expand the functions of this air conditioning system.
- To be able to regulate the air temperature in each room, in front of each indoor unit - fan coil unit, special devices are installed that allow you to regulate the coolant flow.
- Additionally, to heat the air, a hot water gas boiler is installed, which operates in the cold season instead of a chiller.
- It is also equipped with a storage and expansion tank to compensate for the expansion of the coolant when heated.
Chiller fan coil or air conditioners?
Split and multi-split are traditional air conditioning systems for small rooms and buildings. There are small capacity chiller-fan coil systems that can replace an 18,000 BTU air conditioner. More information about chiller models and prices can be found in this online store. What are their differences and advantages?
Any number of fan coil units corresponding to its capacity can be connected to the chiller. An analogue of such a system are multi-zone (multi-split) air conditioners.
The main chiller unit can be placed on the roof or in the basement, where it is easily accessible for maintenance and repair and hidden from public view. The outdoor unit of the air conditioner is installed on the facade of the building, access to it is difficult.
Air conditioners require frequent diagnostics, prevention and repair. They fail more often, are less wear-resistant and have lower energy efficiency.
The temperature range of air conditioners is lower, which affects energy consumption when operating for heating in winter and cooling in summer.
To operate a chiller-fan coil system, longer lines are required than for air conditioners. The cost of installation work is increasing.
If one outdoor air conditioner unit breaks down, one or more rooms will be left without cooling or heating, and not the entire building.
For the operation of air conditioners, a freon line is laid between the outdoor and indoor units. If it breaks, the refrigerant evaporates and requires refilling. If the pipelines leading to the fan coil units are damaged, it is enough to replenish the water supply in the storage tank.
Chillers have a longer service life than air conditioners; high quality parts are used in the configuration; distributors and manufacturers provide a long warranty period.

Chillers on the roof of a building in the vicinity of Buckingham Palace.
Types of fan coil units
Like conventional air conditioners, there are several types of equipment, depending on the intended installation location. The wide range allows you to place the equipment almost anywhere.
Duct fan coil
The positive aspects include the possibility of providing a completely hidden installation: all communications, including equipment, are sewn under the rough ceiling.
An example of installation of duct blocks. First stage.
Stage two, renovation completed. Ceiling version of gratings.
Wall-mounted option for supplying air through grilles.
Indoor unit with air ducts: installation
Completion of installation of duct systems
Upon completion of the work associated with the installation of a duct fan coil, only decorative grilles are visible, to which rectangular or round air ducts are connected for distributing cooled or heated (depending on the type and operating mode) air. Increasingly, new residential complexes are installing this type of equipment. The only negative is the need to additionally lower the finishing ceiling in the places where the fan coil itself is installed and throughout the laying of communications.
Wall mounted fan coil
It is installed where it is not possible to place a duct type, and is often installed due to savings: when the developer delivers a residential complex to the apartment, communications for the supply of coolant have already been installed, all that remains is to connect it. There is no need to lay additional communications such as air ducts, noise mufflers, mixing chambers, etc. Just choose a place to install the indoor unit. Yes, it will be visible and much simpler than a regular freon air conditioner for an apartment, but it will be cheaper.
The lines from the chiller are brought into the apartment
Laying the pipeline to the indoor units
An example of connecting a pipeline to a fan coil
The result of installing fan coil units in an apartment
Cassette fan coil
office premises central system
- increase efficiency through modern engineering solutions for cooling and heating;
- avoid the “Shanghai” of “birdhouses” of external blocks on the façade of the building installed by tenants.
This type is becoming increasingly popular. Distribution in four independent directions makes air exchange more comfortable, without the formation of drafts, ease of maintenance, and hidden installation (like a duct type) - only the decorative panel is visible. But, like duct fan coils, cassette units also need free space under the ceiling.
Below are several examples of installation of cassette fan coils and air conditioners at our facilities:
Connection and piping of cassette fan coil unit.
Installation of equipment at the repair stage.
Fan coils and ventilation in the office.
Cassette type in a country house.
But, we must pay tribute, this is still a more commercial type of equipment: 97% of objects on “cassettes” are commercial real estate, offices, and government agencies.
Horizontal installation - also known as sub-ceiling - is used more in retail and general purpose premises, where it is not possible to lower the finished ceiling and in which there are no special requirements for interior design.
Fan coil
Quite a simple design, externally reminiscent of the internal unit of a household split. Inside there is a heat exchange radiator, through which cooled water and an aqueous ethylene glycol solution are driven by a hydraulic pump. There is also a fan here that promotes air circulation through the radiator. This is how the cooling of the premises occurs. It performs its function only in interaction with the chiller. A fan coil unit cannot produce cold on its own. It only transfers and delivers coolant to its destination.
The chiller supplies liquid at a certain temperature, the same for all rooms. Individual temperature parameters depend on the fan coil unit.
Installing the indoor module is similar to installing a similar split unit. At the same time, the communications supplying the coolant have more joints, which must be sealed and thermally insulated. Installation of shut-off valves is required.
Structurally, fan coil units are classified:
- cabinet (floor-ceiling, wall);
- unframed (for hidden installation, for example, duct).
By installation method:
- wall-mounted (mounted on the wall);
- cassette (installed in the suspended ceiling in place of one of the panels. Air supply in four directions);
- duct (mounted under the ceiling. Air supply through air ducts leading to all rooms);
- floor-ceiling (installation options: on the floor or on the ceiling).
High-precision precision air conditioners >>>>
For air cooling
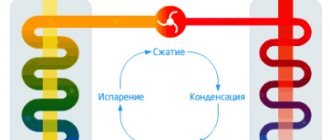
Chiller-fan coil system
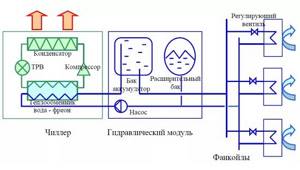
- a centralized, multi-zone air conditioning system, in which the coolant between the central cooling machine (chiller) and local heat exchangers (air cooling units, fan coils) is a cooled liquid circulating under relatively low pressure - ordinary water (in tropical climates) or an aqueous solution of ethylene glycol ( in temperate and cold climates). In addition to the chiller(s) and fan coil units, the system includes piping between them, a pumping station (hydraulic module) and an automatic control subsystem.
Terminology
There is no translation for the English “chiller” in GOST 22270-76 “Equipment for air conditioning, ventilation and heating”. For the term “fan coil unit” GOST gives the translation “fan coil unit” (a closer that, using a built-in fan, carries out local recirculation and supplies a mixture of internal air with external air into the room, which has previously been processed in a central air conditioner, as well as heating and/or cooling air).
Differences
Compared to VRV/VRF systems, in which gas refrigerant circulates between the refrigeration machine and local units, chiller-fan coil systems have differences:
Twice the maximum distance between the chiller and fan coils. The length of the routes can reach hundreds of meters, since with a high heat capacity of the liquid coolant, the specific losses per linear meter of the route are lower than in systems with a gas refrigerant.
Wiring cost. To connect chillers and fan coils, ordinary water pipes, shut-off valves, etc. are used. Balancing water pipes, that is, equalizing the pressure and flow rate of water between individual fan coils, is much simpler and cheaper than in gas-filled systems.
Safety. Potentially volatile gases (gas refrigerant) are concentrated in the chiller, which is usually installed outdoors (on the roof or directly on the ground). Piping failures within a building are limited by the risk of flooding, which can be reduced by automatic shut-off valves.
Flaws
Chiller-fan coil systems are more economical in terms of electricity consumption than rooftop systems, but they are certainly less economical than systems with variable refrigerant flow ( VRF)
).
However, the maximum performance VRF
systems is limited (the volume of cooled rooms is up to several thousand cubic meters).
Malfunctions
- Freon leak. Freon leakage can occur as a result of a leaky connection in the freon circuit.
- Compressor failure. In a compressor, the stator winding usually burns out or the valves (piston group) are destroyed.
- Moisture in the refrigeration circuit. Moisture (water) can enter the refrigeration circuit as a result of a leak in the evaporator, resulting in mixing of two freon-water circuits.
Basic liquid cooling schemes
- Direct cooling..
The most common option. Cooling of the liquid occurs in the liquid/freon heat exchanger. The temperature difference between inlet/outlet is no more than 7°C. Standard air conditioning mode +7/12°С. - Cooling using an intermediate coolant.
This type of circuit is used when the difference in liquid temperature at the inlet and outlet of the chiller is more than 7°C.
Connecting the air conditioning system
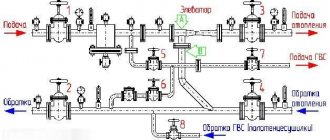
The key elements of the circuit are the fan coil, chiller and hydraulic module. The chiller and fan coil are connected to each other through pipelines, and the hydraulic module – the pumping station – is tasked with creating a circulating fluid flow.
In addition to the pump, the station includes:
- valves;
- expansion tank - here the change in coolant volume caused by a change in temperature conditions is compensated;
- protection and control elements;
- storage tank, through which the volume and heat capacity of the carrier are increased. This component is necessary to protect the compressor from premature wear.
To facilitate the procedure for connecting the bundle, a generalized overview of all working units that together form the conditioning technique under consideration should be given:
- heat exchanger - fan coil - it looks like a grill, liquid circulates in it through thin tubes;
- a fan that directs air to the grille with tubes;
- electronic controls that coordinate the operation of the fan coil unit, for example, setting the fan speed and refrigerant supply intensity;
- remote control, which allows you to set settings regarding the above processes;
- a route made up of standard plumbing pipes;
- chiller - it is responsible for cooling and maintaining the set temperature of the working medium, which is sent to the fan coil units along the pipeline route;
- a boiler in which the liquid is heated;
- a pump that circulates fluid.
In accordance with this, connecting equipment can be reduced to several manipulations:
- Installation of units.
- Making a binding knot.
- Formation of the route, installation of thermal insulation.
- Introduction of air ducts with full measures for their sound insulation.
- Arrangement of a drainage system.
- Supplying batteries to the equipment.
- Checking the tightness of connections.
- Trial run of the scheme.
The chiller-fan coil system is a complex device; it is better to entrust its installation and configuration to highly specialized specialists. Professionals will make the necessary calculations, taking into account the specifics of the premises and the potential functional load, and select the most effective points for installing the units.
Water or glycol mixtures
The main disadvantage of water is its high freezing point. Under normal conditions (i.e. at atmospheric pressure), as soon as the temperature drops below zero, the water will freeze, and if it freezes in the pipes, the system will defrost. This happens because the density of ice is less than the density of water, i.e. the volume of ice is greater, and the ice literally breaks the pipelines.
There is only one way out - to use a coolant whose freezing point is lower than the temperatures characteristic of the winter period for this particular region. And, taking into account the excellent physical properties of water, they simply began to add other substances to it in order to achieve the required freezing temperature of the mixture.
The most widely used are aqueous solutions of glycols: ethylene glycol and propylene glycol. The first is more favorable in its thermodynamic properties and its cost is lower, while the second is safe and environmentally friendly.
You should also keep in mind that ethylene glycol is poisonous. When using it, the issue inevitably arises of complicating maintenance work and subsequent disposal. Moreover, its use is prohibited in some facilities with permanent presence of people.
However, you should always consider both options and make your own informed choice on a case-by-case basis.
Installation benefits
We have already talked above about the advantages of the system itself. We especially note once again that it is not difficult to install.
The cost of components is low. It is easy to maintain and repair. In addition, it can be designed for any type of building.
Application area
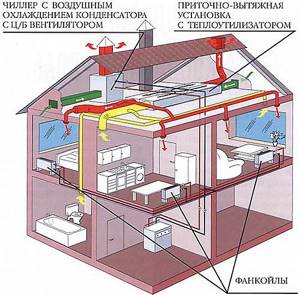
Devices of this type are mainly used in:
- In office premises.
- Hospitals.
- Supermarkets and other retail outlets.
- Hotel complexes.
Price
The price of the product depends on the cost of components, that is, the chiller and fan coil.
As an example, let's give the cost of two products.
TRUST series fan coil
– 12678 rubles.
Homo series
– 15609.
The devices were selected randomly. At the same time, the first unit has higher productivity and serves a larger area of the room, but its price is lower than that of the second.
Hence the conclusion: the main factor shaping the price of the unit is the manufacturer.
Features of operation
The main feature of servicing this type of unit is to charge the device with refrigerant.
In this case, you must strictly follow the instructions set out in the technical documentation of the device. In all other respects, the system is maintained in the same way as similar units.
February 2019
What are chiller fan coils and how do they differ?
First of all, different system models differ in the size and power of chillers and pumps. These are the key elements that influence how and where the system can be used. There are small pumps and small chillers for individual heating of private houses, but even more often large pumping stations and large chillers are produced for heating and cooling large premises.

Chillers also differ in functionality. Some chillers can only cool water, others can also heat it. The condenser inside the fan coil can be cooled by both air and liquid.
Fan coil units differ in the installation method: there are wall, floor and ceiling units. In addition, fan coil units come in two-pipe and four-pipe types - for cooling or for cooling and heating rooms, respectively.
The role of the fan coil in the air conditioning system
Fan coil is an important element of a centralized air conditioning system. The second name is fan coil. If the term fan-coil is translated from English literally, it sounds like a fan-heat exchanger, which most accurately conveys the principle of its operation.
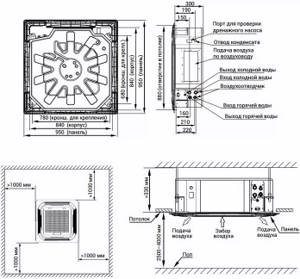
The design of the fan coil unit includes a network module that provides connection to the central control device. The durable case hides the structural elements and protects them from damage. A panel is installed outside, evenly distributing air flows in different directions.
The purpose of the device is to receive low-temperature media. The list of its functions also includes both recirculation and cooling of air in the room where it is installed, without the intake of air from outside. The main elements of the fan-coil are located in its body.
These include:
- centrifugal or diametrical fan;
- heat exchanger in the form of a coil, consisting of a copper tube and aluminum fins mounted on it;
- dust filter;
- Control block.
In addition to the main components and parts, the design of the fan coil unit includes a tray for collecting condensate, a pump for pumping out the latter, an electric motor, through which the air dampers are rotated.

The photo shows a Trane duct fan coil. The productivity of double-row heat exchangers is 1.5 – 4.9 kW. The unit is equipped with a low-noise fan and a compact housing. It fits perfectly behind false panels or behind a suspended ceiling structure
Depending on the installation method, there are ceiling fan coils, duct units, mounted in ducts through which air flows, unframed units, where all elements are mounted on a frame, wall-mounted or console units.
Ceiling devices are the most popular and have 2 versions: cassette and duct. The first ones are installed in large rooms with suspended ceilings. The housing is located behind the suspended structure. The bottom panel remains visible. They can disperse air flow on two or all four sides.
If the system is planned to be used exclusively for cooling, then the best place for it is the ceiling. If the structure is intended for heating, the device is placed on the wall in its lower part
The need for cooling does not always exist, therefore, as can be seen in the diagram depicting the operating principle of the chiller-fincoil system, a container is built into the hydraulic module that acts as an accumulator for the refrigerant. The thermal expansion of water is compensated by an expansion tank connected to the supply pipeline.
They control fan coils in both manual and automatic modes. If the fan coil operates for heating, then the cold water supply is manually cut off. When it is working for cooling, the hot water is shut off and the path is opened for the flow of cooling working fluid.

Remote control for controlling both 2-pipe and 4-pipe fan coil units. The module is connected directly to the device and placed near it. The control panel and wires for its power are connected from it.
To operate in automatic mode, the panel sets the temperature required for a specific room. The set parameter is maintained by means of thermostats that adjust the circulation of coolants - cold and hot.

The advantage of a fan coil unit is expressed not only in the use of a safe and cheap coolant, but also in the quick elimination of problems in the form of water leaks. This makes their service cheaper. The use of these devices is the most energy-efficient way to create a favorable microclimate in a building
Since any large building has zones with different temperature requirements, each of them must be served by a separate fan coil unit or a group of them with identical settings.
The number of units is determined at the system design stage by calculation. The cost of individual components of the chiller-fan coil system is quite high, therefore both the calculation and design of the system must be performed as accurately as possible.
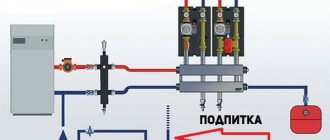
Chiller-fan coil operation diagrams
In this section we will look at connection diagrams for a chiller with a remote and built-in condenser. On them you will see the ability to connect additional systems.
Since the chiller is a universal refrigeration machine, it can be used for different purposes. For example, connect warm floors or radiator heating to it.
The circuit for a chiller with a built-in capacitor looked exactly the same, but points 1 and 2 would be combined. Sometimes a cooling tower is included in the system for greater energy efficiency.
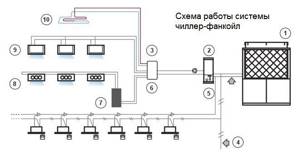
Diagram of operation of a chiller-fan coil system with a remote condenser
- Capacitor;
- Chiller with water heat exchanger;
- Buffer capacity;
- Controllers;
- Refrigerant line;
- Line for water or antifreeze;
- Air treatment unit;
- Forced ventilation;
- Fan coil units;
- Warm floor.
Why should you install an air conditioner?
An air conditioner is a device that creates the most comfortable temperature in a room and then maintains it. The mechanism of operation of the air conditioner is based on the transformation of the state of aggregation of the refrigerant. The changes depend on the temperature and pressure in the closed system. The design of the air conditioner consists of the following elements: ventilation system, compressor, condenser, condenser fan, dryer, expansion valve.
Schematic representation of the operation of the air conditioner:
Classification of air conditioners by purpose, type and area of use:
Offices, cottages, rooms in residential premises.
Premises ranging from 50 to 300 m². Trading areas, household premises, production areas.
Premises with an area of over 300 m².
Administrative buildings, sports complexes, specialized premises.
Fan coil and its features
Fan coil unit includes the following elements:
- heat exchanger;
- fan;
- air filter;
- automatic control subsystem.
The mechanism of operation of the fan coil consists of the following stages:
- The chiller transports cold water through the pipes to the fan coil heat exchanger;
- Meanwhile, the fan provides air flow;
- This causes cool water from the water to enter the building.
The functionality of a fan coil unit also includes heating the room. A special feature is that this mechanism can both air condition the room and heat it at the same time. Remote control comes to the rescue here, thanks to which you can set the desired temperature.
Fan coil operating diagram:

The scope of application of fan coil units is extensive. They are perfect for bars, restaurants, public institutions, hostels, and industrial buildings.
Main classes of chillers
The conditional division of chillers into classes occurs depending on the type of refrigeration cycle. Based on this feature, all chillers can be conditionally classified into two classes - absorption and steam compressor.
The structure of the absorption unit
An absorption chiller or ABCM uses a binary solution with water and lithium bromide present in it - an absorber. The principle of operation is the absorption of heat by the refrigerant in the phase of converting steam into a liquid state.
Such units use the heat generated during the operation of industrial equipment. In this case, an absorbent absorber with a boiling point significantly higher than the corresponding parameter of the refrigerant dissolves the latter well.
The operating diagram of a chiller of this class is as follows:
- Heat from an external source is supplied to a generator, where it heats a mixture of lithium bromide and water. When the working mixture boils, the refrigerant (water) completely evaporates.
- The steam is transferred to the condenser and becomes a liquid.
- The refrigerant enters the throttle in liquid form. Here it cools and the pressure drops.
- The liquid enters the evaporator, where water evaporates and its vapors are absorbed by a lithium bromide solution - an absorber. The air in the room is cooled.
- The diluted absorbent is reheated in the generator and the cycle starts again.
Such an air conditioning system has not yet become widespread, but it is fully in tune with modern trends regarding energy saving, and therefore has good prospects.
Design of vapor compression units
Most refrigeration units operate on the basis of compression cooling. Cooling occurs due to continuous circulation, boiling at low temperatures, pressure and condensation of the coolant in a closed-type system.
The design of a chiller of this class includes:
- compressor;
- evaporator;
- capacitor;
- pipelines;
- flow regulator.
The refrigerant circulates in a closed system. This process is controlled by a compressor, in which a gaseous substance with a low temperature (-5⁰) and a pressure of 7 atm is compressed when the temperature is raised to 80⁰.
Dry saturated steam in a compressed state goes into the condenser, where it is cooled to 45⁰ at a constant pressure and converted into liquid.
The next point on the movement path is the throttle (reducing valve). At this stage, the pressure decreases from the value corresponding to condensation to the limit at which evaporation occurs. At the same time, the temperature drops to approximately 0⁰. The liquid partially evaporates and wet steam is formed.
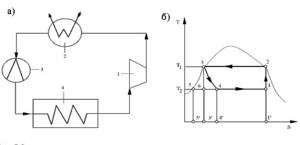
The diagram shows a closed cycle according to which a vapor compression unit operates. In the compressor (1), wet saturated steam is compressed until it reaches pressure p1. In the compressor (2), the steam gives off heat and is transformed into liquid. In the throttle (3), both pressure (p3 - p4) and temperature (T1-T2) decrease. In the heat exchanger (4), pressure (p2) and temperature (T2) remain unchanged
Having entered the heat exchanger - evaporator, the working substance, a mixture of steam and liquid, gives off cold to the coolant and takes heat from the refrigerant, drying at the same time. The process occurs at constant pressure and temperature. Pumps supply low temperature liquid to the fan coil units. Having passed this path, the refrigerant returns to the compressor to repeat the entire vapor compression cycle again.
Specifics of a vapor compression chiller
In cold weather, the chiller can operate in natural cooling mode - this is called free cooling. At the same time, the coolant cools the street air. Theoretically, free cooling can be used at an external temperature of less than 7⁰C. In practice, the optimal temperature for this is 0⁰.
When configured in “heat pump” mode, the chiller operates for heating. The cycle undergoes changes, in particular, the condenser and evaporator exchange their functions. In this case, the coolant must be heated rather than cooled.
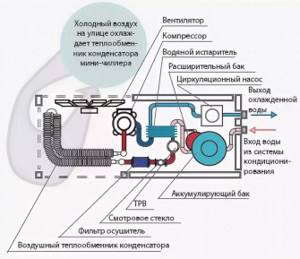
The simplest are monoblock chillers. They compactly combine all the elements into one. They go on sale 100% complete, right down to the refrigerant charge.
This mode is most often used in large offices, public buildings, warehouses. The chiller is a refrigeration unit that produces 3 times more cold than it consumes. Its efficiency as a heater is even higher - it consumes 4 times less electricity than it produces heat.
What is the operation of this system based on?
As mentioned above, the most common chillers are vapor compression devices. The operating principle of this type of chiller is quite simple:
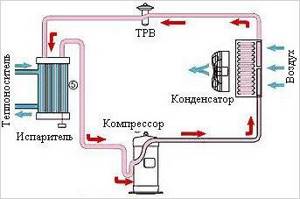
Fan coil units can have one or two heat exchangers, respectively, the chiller-fan coil system can be two-pipe or four-pipe. In the first option, two pipes extend from the heat exchanger, through which only cold and hot working fluid circulates, and in the second, for supplying coolant from the chiller to the fan coil and supplying hot water from the heating to the second heat exchanger.
Advantages and disadvantages
The main disadvantage of this air conditioning option is the complexity and therefore high cost of installation. Also a very important aspect in its effective operation is the choice of location for installing the equipment. In addition, there are other disadvantages:
- Noisy operation of the system.
- High price of devices.
- Low energy efficiency.
The main advantage of the chiller-fan coil system is that there are no restrictions on the length of communications between fan coils. There is another significant advantage - you can add the required number of indoor units to an already operating system as the building is put into operation. Very often this property is decisive when choosing a particular air conditioning system. In addition, the advantages include the following:
- Safety and environmental friendliness, due to the absence of freon and other volatile gases in its lines.
- It does not require the presence of several external blocks, which significantly spoil the appearance of the building.
We love it when the temperature at home is comfortable, even if it’s hot or cold outside. In summer, air conditioners save us. But can one air conditioner cope with a large private house? But what if you need to cool an office or an entire shopping center?
Many people believe that air conditioners are limited. Of course, this type is the most common, but there are other types that are no less effective. One of them is a chiller-fan coil air conditioning system. The word is complex, but from it it is not difficult to guess what this system consists of. Let's try to disassemble each part of the system - fan coil and chiller - and understand what its advantages are.
Pros and cons of the chiller-fan coil refrigeration system
This solution is one of the most popular due to the following advantages:
- the possibility of creating pipelines of any length, their length depends only on the power of the chiller. Even remote elements of hundreds of meters will not cause a deterioration in performance and efficiency;
- compactness of the outdoor unit. When installed, the chiller takes up minimal space and will not disturb the aesthetics of the building’s façade;
- affordable cost of components. The cooled liquid circulates through conventional pipes, rather than copper pipes, as is the case with split systems, which significantly reduces the installation budget;
- volatile gases do not leave the chiller, the use of such equipment does not pose a risk to human health;
- flexibility and adaptability. Users can create custom settings and change them interactively.
Among the disadvantages, one should highlight the high cost of external and internal units, the complexity of installation, the high noise level that accompanies the operation of the equipment, and the significant energy consumption of the bundle.
Principle of operation
The chiller, which is an air conditioner, heats or cools the coolant entering it. It can be water or other non-freezing liquid. Then, using pumps, the liquid is pumped into the system and transferred through pipes to the fan coil units.
This device receives air from the room, which is mixed using a fan with the air inside the unit, already heated or cooled.
After this operation, the air mixture is released into the external environment. This is how room conditioning occurs using a chiller-fan coil unit.
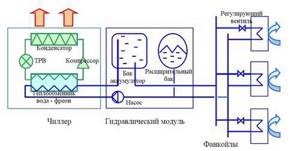
Unit diagram
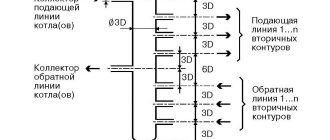
The chiller heat exchanger is connected to the pump and storage tank. The expansion tank is also connected to the pump. The coolant is supplied through a pipeline through a system of control valves to the fan coil units.
Design features
The main feature of the system is that a chiller-fan coil project is developed individually for each building. For example, the design of one building does not allow the chiller to be placed anywhere other than on the roof. And the other is built in such a way that the main device of the system can only be located in the attic.
In addition, the development takes into account the requirements for the microclimate created in the premises, their purpose, and the infrastructure around the building.
The chiller, its type and modification, is selected in accordance with the specified requirements, the number of fan coils is also determined, how the system will be used, the intensity of its operation, what its mode will be, whether the air will be cooled or, conversely, heated, or both , and more together.
Organization of system operation
Chiller-fan coil is a complex system. In practice, this means that individual elements of the system (chiller, pump, fan coils) are selected based on the tasks for which they will be used.
Fan coil units are selected, firstly, based on the function they will perform (only cooling, or also heating - two-pipe or four-pipe), as well as based on design considerations (installation method - wall, floor, ceiling).
Chiller-fan coil is a system that can only be installed according to an individual project. Typically, the purchase of all necessary equipment, installation and further maintenance of the system is carried out by specialized companies. They also help organize the operation of the system from an engineering and design point of view.
There are many models of fan coils, chillers, and pumps, which is why they are selected individually for each case. It is impossible to simply purchase equipment and install it, since this will also require work with communications inside the building.
Installation features
Taking into account the complexity of fan coil-chiller systems, its installation and configuration should be carried out by highly professional specialists. Only they will be able to perform high-quality installation of fan coil units by performing competent:
- installation of the unit in the place where its operation will be most efficient;
- assembly of piping units, installing the necessary taps, valves, temperature and pressure control devices;
- laying and thermal insulation of pipes;
- installation of a condensate drainage system;
- work on connecting devices to the electrical network;
- pressure testing the system and checking its tightness;
- supply of carrier (water).
They will also make all the necessary calculations before starting work, taking into account what functional load a particular fan coil unit will perform, as well as the characteristics of each room in the structure.
Thus, you were able to see not only that fan coil-chiller systems are very efficient, economical and reliable, but also that they require complex installation and commissioning operations. And for this it is necessary to attract employees of organizations specializing in the creation of such turnkey systems.
The multi-zone chiller-fan coil climate system is designed to create comfortable conditions inside a large building. It works constantly - it supplies cold in the summer, and heat in the winter, warming the air to the set temperature. It’s worth getting to know her device, don’t you agree?
The article we propose describes in detail the design and components of the climate system. Methods for connecting equipment are given and discussed in detail. We will tell you how this thermoregulation system works and functions.
The role of the cooling device is assigned to the chiller - an external unit that produces and supplies cold through pipelines with water or ethylene glycol circulating through them. This is what distinguishes it from other split systems, where freon is pumped in as a coolant.
For the movement and transmission of freon, a refrigerant, expensive copper pipes are needed. Here, water pipes with thermal insulation cope well with this task. Its operation is not affected by the outside air temperature, while split systems with freon lose their functionality already at -10⁰. The internal heat exchange unit is a fan coil.
It receives liquid at a low temperature, then transfers the cold into the room air, and the heated liquid is returned back to the chiller. Fan coil units are installed in all rooms. Each of them works according to an individual program.
The main elements of the system are a pumping station, a chiller, a fan coil. The fan coil can be installed at a great distance from the chiller. It all depends on how much power the pump has. The number of fan coil units is proportional to the chiller power
Typically, such systems are used in hypermarkets, shopping malls, structures built underground, and hotels. Sometimes they are used as heating. Then heated water is supplied to the fan coils through the second circuit or the system is switched to the heating boiler.
Areas of application of chiller fan coil
The main advantage of the technology under consideration is the ability to provide an independent, stable microclimate in several rooms at once. Therefore, the equipment is extremely in demand when arranging the following types of objects:
- large warehouses and production sites (including those with special sanitary requirements);
- shopping, administrative, entertainment and hotel complexes;
- social buildings divided into a large number of rooms, for example, recreational facilities, clinics;
- multi-storey business centers, complexes;
- supermarkets.
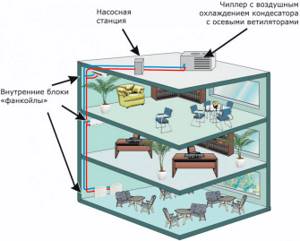
Despite the complexity of implementation, a chiller-fan coil helps to rationalize temperature and humidity parameters without reference to external conditions, which is very important, given the variability of the domestic climate.