Home / Heating /
For 9 years, at almost every project a builder always appears who, with a smart look, convinces the Customer to save on radiators and heat the house with heated floors. The customer has doubts and is right. At first glance, warm floors are more comfortable, but is it convenient for heating? Let's figure it out.
Good afternoon My name is Alexey Goltsov . I am a design engineer, author of articles. Heating is my main specialty. I carry out projects for country houses, shops and restaurants. 20 projects for country houses a year
I mainly design for Moscow and the region. I'm leaving for the site.
You can order a heating project from me on the “Services” .
Why did this question arise?
No matter how funny it may sound: global warming and the view of Western countries are to blame.
The design temperature for heating in Moscow is –25°C for 5 days. This temperature has not been seen for many years, and customers of private houses began to share the opinion that radiators do not work, and therefore are not needed.
Warm floors cost 3 times more than radiators. Therefore, this opinion was picked up by builders and for the last 5-7 years they have been confidently advocating to abandon radiators completely.
But there are 2 nuances in this issue that they do not take into account:
How many years are you building the house for?
My Customers often say that their neighbor’s underfloor heating works successfully. But neither the Customer nor the neighbor takes into account the period of time.
If we are talking about the short term of 3-5 years, then radiators are really not needed in this case. But the house is being built for a longer period.
In building codes, heating is considered efficient if it heats the house for 50 years. For Moscow, the minimum temperature for 30-50 years is -25°C. And even if there has not been such a temperature over the past 5 years, this does not mean that it will not happen in the coming decades.
Therefore, as a specialist, I design a combined system of radiators and heated floors. We are obliged to provide radiators as a reserve so that the house does not freeze in the cold winter.
We don't need to "heat the house"
Heating a house is an incorrect term.
The whole nuance is that we must maintain a different temperature in each room. We need to heat each room separately. In the boiler room, garage, storeroom, it is enough to maintain +15°C. In the bedroom +23°C, in the bathrooms and bathrooms +25°C.
Indeed, if we calculate the house as a single space, a warm floor for heating is quite enough, but in practice we only need to heat those rooms that border on external walls and windows.
For example, internal corridors, halls and storage rooms in a 250 m2 house are often about 50 m2, but they do not need to be heated at all.
Heating with diesel fuel
For heating with diesel fuel, you will also need a tank, and the costs of its installation will be comparable to the costs of autonomous gasification at home. At the same time, unlike propane-butane, diesel fuel cannot be called cheap.
High price. Diesel fuel is the most expensive source of energy used for autonomous heating of a private home. A kilowatt-hour of diesel fuel costs 4.75 rubles. Even electricity is a little cheaper. It may not be easy to spend more on heating.
Unpleasant smell. This is an inevitable property of diesel fuel. A strong smell will follow the unfortunate owner of a diesel fuel tank everywhere. The house will smell like a garage, and the area will smell like a running tractor, and nothing can be done about it.
Problems when using low-quality fuel. The use of low-quality diesel fuel can lead to serious damage to heating equipment. Those who use liquefied gas and DESIGN PRESTIGE gas tanks do not have such a problem: the quality of propane-butane does not affect its consumer properties.
Disadvantages of heating with diesel fuel
- High price.
- Sometimes you have to clear snow for winter delivery.
- Strong odor in the house and area.
- Use of storage space.
Is it possible to abandon radiators and heat the house only with heated floors?
From the legal side
Answer: No, you can't. If you contact a large construction company with such an idea, they will refuse you. There are 3 reasons for this:
1) The heating system is designed for the lowest temperature. For Moscow this is –25°C for 5 days. If the average temperature stays at -25°C for 5 days, no heated floors will cope. More details: SP60.13330.2016 clause 5.13.
Minimum winter temperatures in Moscow
2) The temperature of the floor surface should be no more than 26°C, and for children's institutions 23°C. This is too low a temperature to heat a room. Radiators heat up to 80°C. I will tell you further what overheating of the surface leads to. More details: SP60.13330.2016 clause 6.4.8
3) Cold convection currents always come from the window. Radiators cover 50% of the window width, which helps reduce the cold air flow from the window. More details: SP60.13330.2016 clause 6.4.4.
From a practical point of view
Answer: Yes, it is possible, but is it convenient? Unfortunately, neither customers nor builders see all the consequences. The customer relies on the experience of the builder. The builder relies on the experience of past projects. That’s why there are so many speculations and fantasies on the topic of heated floors.
I will share these consequences with you.
Popular types of heating radiators
| Photo | Name | Rating | Price | |
| #1 |
| Aluminum | ⭐ 99 / 100 | More details |
| #2 |
| Bimetallic | ⭐ 98 / 100 | More details |
| #3 |
| Steel | ⭐ 97 / 100 | More details |
Aluminum
pros
- the most energy efficient type;
- low susceptibility to coolant;
- low susceptibility to corrosion;
- a light weight.
Minuses
- Suitable only for individual heating systems.
Heating radiator Global
Bimetallic
pros
- high heat transfer;
- increased strength;
- a light weight;
- neutrality to the chemical composition of the coolant.
Minuses
- high price.
Heating radiator Rifar
Steel
pros
- average energy efficiency;
- varied performance;
- fast warm-up;
- affordable price.
Minuses
- susceptibility to corrosion.
Heating radiator Purmo
What problems do you have to face when heating underfloor heating?
The house will not warm up before your arrival
Warm floors without radiators respond very slowly to any commands and changes. His inertia is too high.
First, the system will receive a command from the boiler, then it will warm up 45 mm of concrete screed, 20 mm of floor covering, and only then it will begin to slowly release heat into the room. The floor temperature is 35°C. Therefore, to heat the house from the standby temperature of 15°C to a comfortable 23°C, the heated floor will need approximately 11 hours.
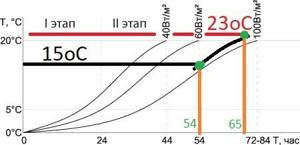
Heated floor heating rate graph
If you do not plan to live in the house 24/7, underfloor heating will be uneconomical. When you are not at home, you will have to maintain not 15°C, but 20°C, otherwise the house simply will not have time to warm up before your arrival. Radiators will heat a house from 15°C to 23°C in an average of 3 hours.
No reserve in case of extreme cold
In a combined system, radiators turn on at an outside temperature of -12°C and work together with the heated floor.
Warm floors are needed for comfort. That is why it is “warm” and not “hot”. Heating a house with underfloor heating will not work in extreme cold.
If you decide not to install radiators, you are deprived of a reserve that is guaranteed to heat the house in extreme cold. In this case, you will have to overheat the floors and run across the floor. Overheated surfaces will emit odor.
According to calculations: an overheated floor can heat a room down to -16°C. At lower temperatures, the floors will not cope and the room will be cold.
Floor covering - tiles or porcelain stoneware
Underfloor heating imposes its own limitations on the coating material. Even small carpets on the floor will have to be eliminated throughout the house, because they completely block the heat flow.
Heat transfer from the floor surface directly depends on the coating material. You won't be able to afford parquet, laminate, PVC or cork. all this is not suitable for underfloor heating systems. Laminate and parquet transfer heat 7 times worse than tiles.
Important nuance : the internal composition of the material is not so important as the surface itself! Matte and ribbed surfaces of the same porcelain stoneware transfer heat 30% worse than smooth ones.
No floor-to-ceiling stained glass windows
Stained glass windows in rooms create large heat losses. About 50% larger than ordinary windows, so heated floors are not suitable for heating a house with stained glass windows. You will have to give up façade and stained glass windows in all living rooms.
It is permissible to heat underfloor heating in rooms with 1 or 2 regular windows. If the windows are stained glass, the warm floor will not cope.
A warm floor in a room with stained glass windows can heat the room at an outside temperature of at least -12°C, which is why in Europe warm floors are used as the main heating system. This is unacceptable in Russia.
Local hot spots or furniture with legs
With underfloor heating, the only source of heat is the floor surface. In bedrooms, furniture usually consumes 40% of the space. Sofas, wardrobes and beds completely block the heat flow from the floor to the air, so heat exchange does not occur and the room is not heated.
Therefore, there are 2 options for solving this problem: – sofas, wardrobes and beds must have legs; – local overheating zones along the windows.
Local overheating zones are the area of the floor around walls and windows in which underfloor heating pipes are laid close to each other, with a reduced laying pitch, which results in an increase in heat flow.
Usually in bedrooms, the local overheating zone exactly falls on the area around the bed, so when you wake up on a frosty winter morning and get out of bed, you will definitely hit the hot zone of the heated floor with a temperature of 38-42 ° C, while without radiators the air temperature in the room will be about 18 ° C .
Connection diagrams for heating radiators
There are only 3 such schemes, each of them has its own characteristics, pros and cons.
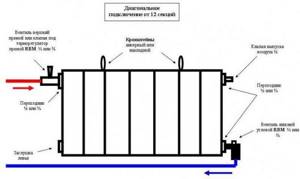
Diagonal connection from 12 radiator sections
Option #1. Single-pipe
Here the radiators are connected in series, making installation much easier and requiring much less consumables. A pipe running under the radiators goes from the boiler through all the rooms and returns to it. The radiators are connected via lower pipes. The liquid fills the sections of the batteries, giving them heat, falls and goes through another pipe into the same pipe.
Video - Advantages of single-pipe heating systems
As for the disadvantages of the scheme, these include, first of all, rather low heat transfer, because the coolant in this case enters each battery after it has already cooled down. As a result, the further the room is from the boiler, the colder it will be.
Option #2. Two-pipe
There are 2 pipe circuits here at once - through one the coolant is supplied to the radiators, and through the other it is removed, due to which the thermal energy is distributed evenly throughout the house.
Note! This scheme has many advantages, since each individual room can provide its own temperature regime. And if repairs are required, there is no need to turn off the entire heating system. In a word, the scheme is much better than the one described above.
Video - Connecting radiators in a two-pipe system
About methods of connecting pipes to radiators
How effective such heating will be largely depends on the way the batteries are connected to the pipeline. There are several of these methods; let’s look at the features of each of them.
Table. How batteries are connected to heating pipes.
| Connection method | Short description |
| Lateral | The supply and return are connected on one side of the heating device (top and bottom, respectively; you can swap them, but the heating efficiency in this case will decrease by approximately 7 percent). |
| Lower | Can be used in both one- and two-pipe systems. Experts believe that this is the most ineffective method. |
| Diagonal | The supply is connected from above on one side, and the “return” from below on the other. The best method if we consider it from the point of view of heat transfer efficiency. |
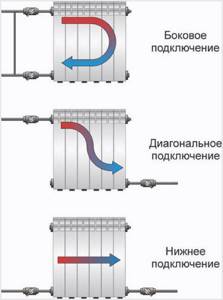
How to connect a radiator to pipes
A few more words about radiator heating
Due to the fact that heated air rises upward due to the laws of physics, the air temperature near the ceiling and next to the radiators can be quite high. In other words, heating will occur in areas that do not really need to be heated. But the floor temperature in this case will be only 16-17 degrees, that is, not the most comfortable for the feet. We conclude: with radiator heating, heat is distributed irrationally.
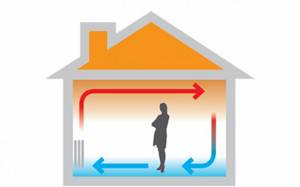
Operating principle of radiator heating
The air that passes through the batteries is warmed up and distributed throughout the room. Simply put, it circulates, and dust rises with it.
On a note! For radiator heating, it is very important to correctly calculate the number of sections for each device. After all, each section can heat only a limited area and the efficiency of the entire system depends on the number of sections in the batteries.
Video - Arrangement of a radiator heating system
When can you heat a house without radiators?
For this article, I analyzed the heating calculations of 20 cottages. For Moscow, the heating system is calculated according to standards for –25°C, St. Petersburg –24°C, Kazan –31°C, and only in the Krasnodar and Stavropol Territories, Rostov-on-Don and Crimea can it be heated with heated floors without radiators.
You can heat your house with underfloor heating when the outside temperature is not lower than -18°C.
Special construction region. Krasnodar region, Stavropol region, Rostov-on-Don and Crimea.
You do not plan to live in the house in winter. In the fall, you drain the water supply system and heated floors and close the house until spring.
Additional heat sources. Do you have a fireplace, stove or electric heaters?
Building with temporary use. Garage, covered gazebo, separate bathhouse. There is no point in maintaining a temperature of +23°C. In the most extreme cold, you will not be in the building, and the standby temperature of +15°C is sufficient. Warm floors will do.
Heat pump. Heating with heated floors is recommended by sellers of heat pumps. The heat pump does not prepare water at 80 °C - as needed for heating, but only 55 °C, which is optimal for a heated floor system. Radiators on water at 55°C will turn out to be huge.
Conditions for installation as the only heat source
Heated floors are considered a more economically advantageous heating system than radiator heating. But to make it effective, you will need to make careful calculations and take into account all the key parameters. In addition, the technical feasibility of implementing a particular type of heating should be determined in advance.
Among the important conditions for installing heated floors as basic heating are the following:
- The power of the heating elements should be sufficient to maintain the room temperature at 20-24 ° C even in the cold months.
- When calculating the heating of an apartment, heat loss through walls, doors and windows must be taken into account. For a private house, losses through the roof are also taken into account.
- The walls of the building not only transfer heat to the outside, but also let cold in, so when designing the system it is necessary to increase the heating of the room along the walls.
- Installing a water floor in an apartment building requires special permission. Even if it is available, installation will be difficult from a technical point of view.
- Installation of electric floors is possible for any type of room, but their connection requires properly functioning electrical wiring. In addition, heating a home using such a system increases energy consumption.
- All types of heated floors, except film ones, are laid under a concrete screed, which reduces the height of the room by 6-10 cm.
How much underfloor heating is needed for heating?
The issue of heating a house only with warm floors needs to be worked out at the stage of the architectural project. Rooms with stained glass windows cannot be heated with underfloor heating alone; radiators are required. But rooms with conventional glazing are quite suitable for underfloor heating.
To heat rooms only with heated floors, you need to deliberately increase the free area of such rooms.
We know that 40% of the area is occupied by furniture, so we need to compensate for the missing space by combining rooms with adjacent rooms: combining a bedroom with a dressing room, moving the door to the corridor.
The formula for any type of house looks like this:
Spom – room area in m2 For a room with 1 window and a window sill Spom x 0.69 (69% of the floor) For a room with 2 windows on different facades Spom x 0.79 (79% of the floor)
For example , for a bedroom of 21 m2 with 2 windows, the required heated floor area is 21 × 0.79 = 16.6 m2. Furniture occupies 40% of the area, which is 0.4 x 21 = 8.4 m2. To heat such a bedroom with a warm floor, we need to increase the floor area by 16.6 - (21-8.4) = 4 m2. As a result, we need to expand the room by 1 m2 and add a dressing room of 3 m2.
Using this formula, you must first calculate the total area of all bedrooms, and only then adjust the area of the remaining rooms.
Which is better: heated floors or radiators?
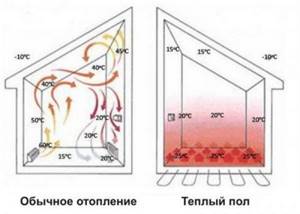
For heating in autumn and spring - warm floor. In winter - radiators. Warm floors are a low-temperature system and respond slowly to weather changes.
In spring and autumn, the temperature difference between inside and outside the house is not as significant as in winter. Therefore, warm floors during this period, despite their slowness, are much better than radiators.
But in winter the picture is the opposite. In the house +23°C, outside -15°C. The temperature difference is huge. The cold flow from windows and stained glass penetrates into the room much more intensely than in autumn or spring. We need to stop these flows. Nothing can be better than radiators or convectors built into the floor.
Heating with gas convectors
The devices mentioned above are powered by gas supply. Their positive features:
Gas convectors are an ideal choice for installation in an apartment or country house. The device serves not only as the main one, but also as a backup temperature controller (the temperature can rise to 38 °C).
The system is powered by natural as well as liquefied hydrocarbon gas. The fuel change occurs due to the settings of the gas valve.
The device is usually mounted on a window sill. The kit includes pipe routing and temperature sensors. This device significantly minimizes heat loss, which is an important advantage.
A flaw in the system is manifested in the construction of holes in the walls to provide chimney channels.
Analysis of misconceptions
Uniform heating with heated floors. The temperature in the legs is higher, above the head – lower, and this is good, because... evenly and physiologically. Complete nonsense! Our task is to ensure not uniform, but rather local heating of the room in the areas of windows, external walls, corners, and street doors. We need to stop the cold currents from these surfaces.
Cost-effectiveness of heated floors?! How can a system that responds slowly to change be economical? The room became hot - and the warm floor will reduce power only after a couple of hours. Where are the savings?
Warm floors for allergy sufferers are complete nonsense! The phenomenon of “dry sublimation of dust” begins at temperatures above 90°C. The smell of dust from radiators comes only because they generally forget to wash them. In this case it has nothing to do with temperature.
Warm floors retain moisture. In winter, the air outside is dry by itself: 0.39 g/kg. In summer – wet – 10g/kg. Air humidity does not depend on the temperature of heated floors or radiators.
If there are misconceptions that I missed, write to me, we’ll discuss them and add them to the article.
Specifications
Water system
Main technical characteristics of water heated floors:
- Heat dissipation. The average heat transfer of a water heated floor is 50 W/sq. m. This value was determined from many calculated values of different projects and was recognized as the most correct for average conditions. The value is 2 times less than the accepted average value of the required heat transfer for radiator systems, equal to 0.1 kW/sq. m., which indicates greater efficiency of the system and lower losses.
- Maximum coolant temperature. In this case, the value of the initial temperature is not so important, since the operating temperature of the pipes is achieved by mixing the cooled return into the direct flow. The operating temperature of the coolant is always lower than in the direct flow of the main line, otherwise the room will be very hot. The usual temperature of the mixture is around 50 degrees, due to which the temperature of the warm water floor, taking into account losses and cooling in the circuits, allows you to obtain comfortable conditions in the room.
- Working and maximum working pressure. The optimal operating pressure is considered to be 1.5-2 atm, pressure testing - 4-5 atm. It should be taken into account that the pressure test is created only in the circuit system, since its own boiler is rarely designed for pressure above 3 atm.
- Thermal power of a water heated floor. Determined by dividing the amount of heat loss by the area of the room. The problem is that the area is easy to determine, but heat loss is difficult, this involves the method of installing a heated floor, the type of coating, the type of construction, and the material of the pipes. The easiest way is to use an online calculator, which determines the thermal power using its own algorithms; you just need to enter your own data - area, pipe material, laying pitch, etc.
Radiators

Main technical characteristics of heating radiators:
- Heat dissipation. Depending on the material of the device, the amount of heat transfer varies. For example, cast iron radiators have 4 times less heat transfer than aluminum radiators and 6 times less than bimetallic radiators. Therefore, it is impossible to indicate exact numbers without reference to the size of the device, room and coolant temperature. There is an average value - 0.1 kW/sq. m., which serves to determine the required heating heat transfer for certain rooms. It is used to roughly determine the power of the device when choosing. Each device has its own heat transfer value indicated in the passport. The main thing is to clarify whether this means the general value, or for one section.
- Maximum coolant temperature. If the power is supplied from the central heating network, then established standards apply that link the temperature of the coolant with the air temperature outside. For example, at -15 degrees, the water temperature in the central heating main is 105 degrees. During transportation, it drops by some amount, but in any case, the water must withstand return transportation to avoid freezing of pipes along the route. Based on comfort considerations, the temperature of the radiators should ensure 18-20 degrees in the room (this is the established norm, for some it is cool), which depends on the size of the room, as well as the size of the radiator. At the same time, the calculated values of the maximum coolant temperatures are much higher, for example, for cast iron radiators it is assumed to be 150 degrees, for bimetallic radiators - 130 degrees, steel ones have a limit of 110-120 degrees.
- Working and maximum working pressure. The values differ slightly for devices made of different materials, on average the working pressure is 8-11 atm, the pressure test pressure is 14-16 atm. These are declared passport values, which in reality do not always correspond to such values. In the network, the operating pressure is often reduced and is about 6-7 atm, while the pressure test reaches 15 atm. It must be remembered that when powered by a central heating system, you have to use the pressure provided by the network, which requires monitoring and regulation. If the operating parameters of the radiators do not correspond to the existing values, reduction gears or diaphragms should be used.
- Thermal power. The thermal power of a heating radiator is equal to the coolant flow rate. More complex methods of determination can only confuse and complicate all calculations; it is much easier to use either passport data or the amount of coolant flow. Another option is to calculate based on the volume of the room. The heating requirement of a room is calculated by multiplying the volume of the room by 41 W (the amount of energy per 1 cubic meter of volume). That is, knowing the estimated power of the heater, you can select the appropriate one according to the parameters.
Advantages of radiators
1. Installed under the windows . Windows are a source of rapid heat loss. The temperature outside changes all the time, which leads either to an increase in the cold flow from the window or to its decrease. The radiator smoothes out these flows.
2. No requirements for premises. Over the years, you can replace tiles with parquet, lay carpets, install monolithic furniture and not depend on the requirements for heated floors.
3. No overheating areas that are uncomfortable to walk on.
4. No odors from furniture or carpets. Warm floors heat up the furniture. There is a smell coming from the furniture.
Conclusion
Each house is too individual to promise anything without calculations. It is possible to heat a house with underfloor heating, but this issue needs to be discussed at the stage of the architectural project.
Combine bedrooms with a dressing room, increase the area of the rooms due to corridors and moving doors. Conceptually, you need to think through each room separately.
A house without a project is just “savings”.
If you find a company that easily answers this question, I advise you to doubt the competence of these people. The issue is complex and requires a thoughtful approach.
If you don’t have time to experiment with the heating system, or don’t have extra money for constant improvements, I recommend calculating the heat loss of the building, or better yet, designing a heating system and heated floors.
You can order a project from me in the “Services” . Based on calculations, we will be able to select the right radiators, pipes and find out the exact cost of equipment and installation work. We will be able to understand which rooms can be heated with underfloor heating and what architectural modifications are needed for this.
Preliminary project cost calculator
Thanks for reading! For the design of engineering systems, please call or email [email protected]
You might be interested in:
How to choose a design company? Guide for the Customer What is included in the design cost? 10 reasons to work with us
Comments
- Leonid:
06/01/2020 at 17:23In practice, 3 houses are fully heated with underfloor heating, everyone is happy. You have too many pros and cons.
Answer
- Goltsov Alexey:
02.06.2020 at 15:57
Leonid, Good afternoon. Thank you for your attention. An excellent phrase: “In practice, 3 houses are completely heated with underfloor heating.”
1) What do you mean heated? At what temperature? At -10°C - is it “heated”? and at -25°C? Professionals don't talk like that. According to the standards, “houses are heated” at -25°C for 5 days for Moscow. This temperature has not been seen for a long time. I suspect that you are misleading me.
2) What does completely mean? — My sofa is near the window, the guests are sitting with their backs to the window. In the morning they complain - “the back is blown.” Is it complete or not complete? or is the guest to blame? or is the owner a fool? And the Code of Rules SP 60.13330.2016 - are we violating because we come up with our own rules? Is that how it works?
3) The house will be warmed up with warm floors from 12 degrees to 23 for 11 hours. This is a minus that outweighs all the pluses.
Answer
- Alexander:
01/18/2021 at 10:06
I will be very surprised if my post gets approval)) But the author must be able to admit his mistakes.
Answer
- Goltsov Alexey:
01/18/2021 at 14:38
Alexander, Good afternoon. There is no need to treat people as idiots. I really won't post your messages with an advertising link.
You are involved in heat pumps. Radiators don't work with a heat pump, so you're left with underfloor heating. Your income and the well-being of you and your family depend on it.
For my readers: - Alexander wrote that heated floors are 20-30% cheaper than radiators. — Local overheating zones are not dangerous. I didn’t specify what exactly is not scary. — Stained glass windows and heated floors are combined within reasonable limits. He did not specify where reasonable limits begin and end. — Sent the video to my resource
Answer
- Ulvi:
04/25/2021 at 21:00
I don’t even know what to say, but I was working in such an office, sitting all day in a huge room of 150 square meters, even more, and there was only a warm floor. It was very hot, even stuffy in winter. But in our street the maximum temperature is -2
Answer
- Goltsov Alexey:
04/26/2021 at 13:23
Ulvi, the floor area of an office space is much larger than the area of the external walls and windows; if you have a single room of 150 m2, then underfloor heating is possible. My article about underfloor heating for private homes.
Answer
How can I do it?
Below is a schematic diagram of the heating system of a two-story house without radiators.
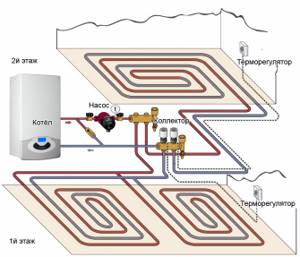
There are no fundamental differences in the design of the heated floor itself from the combined system with batteries. All the same components are used, and the floor “pie” is laid in the same way. The number of circuits will correspond to the number of rooms. But if the room area is large and the maximum loop length is exceeded, then the loop is split into two.
When heating a house without batteries, the main issue will be calculating the heat loss of the building, insulation of the walls and foundation. Therefore, the choice of a heated floor as the only source of heat must be approached at the stage of designing a house, when the material and thickness of the walls are determined. Even then you can understand whether the warm floor is enough to heat the house.
We hope that the article was useful to you. Leave your questions and comments in the comments below.