Long gone are the days of ceramic plugs that were screwed into home electrical panels. Currently, various types of circuit breakers that perform protective functions are widely used. These devices are very effective against short circuits and overloads. Many consumers have not yet fully mastered these devices, so the question often arises which machine should be installed at 15 kW. The reliable and durable operation of electrical networks, appliances and equipment in a house or apartment completely depends on the choice of machine.
Purpose
The circuit breaker for the electric boiler protects the power cable from thermal overload. The cause of insulation melting is prolonged overheating of the wires caused by excess current. This may cause a short circuit.
As a rule, the fuse is installed on the meter, on the wire leading to the protected equipment.
To correctly select a pass-through switch with an automatic circuit breaker, you need to select the wire cross-section, calculate the rated current of the electric boiler and take into account the nature of use of the connected equipment.
The wire
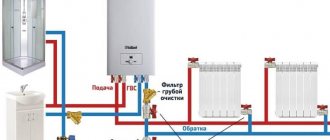
To connect an electric boiler, you need to lay a dedicated cable. Even if the boiler has a power of up to 3 kW at 220 V, you should not plug it into the network through a regular outlet - you will load the internal wires of the electrical wiring unnecessarily.
It is recommended to connect electrical equipment and partitions with a power of over 1.5 kW via a copper wire. Copper wires are more durable than aluminum, and for the same load you will need a smaller cross-sectional diameter.
The cross-section of the current-carrying wire is selected based on the rated power of the connected equipment and the network voltage.
The power section of the wire for 220 V will be thicker than for a voltage of 380 V with the same power of an electric boiler.
You can calculate the wire cross-section yourself. To simplify the task, we offer a final table of cross-sections of aluminum and copper conductors.
Nuances of choice
Today it is necessary to take into account the fact that the number of convenient household appliances is limited, and every person tries to acquire new devices, thereby making their life easier. This means that by increasing the number of equipment, we increase the load on the network. Therefore, experts recommend using a multiplying factor when calculating the power of the machine.
Let's return to our example. Imagine that the owner of the apartment purchased a 1.5 kW coffee machine. Accordingly, the total power indicator will be equal to 4.6 kW. Of course, this is more power than the circuit breaker we selected (16A). And if all the devices are turned on at the same time (plus the coffee machine), the machine will immediately reset and disconnect the circuit.
You can recalculate all the indicators, buy a new machine and reinstall it. In principle, this is all easy. But it will be optimal if you foresee this situation in advance, especially since it is standard these days. It is difficult to predict exactly what additional household appliances can be installed. Therefore, the simplest option is to increase the total calculated indicator by 50%. That is, use a multiplying factor of 1.5. Let's go back to our example again, where the end result will be like this:
3.1x1.5=4.65 kW. Let's return to one of the methods for determining the current load, in which it will be shown that for such an indicator you will need a 25 ampere machine.
For some cases, a reduction factor can be used. For example, there is not enough sockets for all devices to work simultaneously. This could be one socket for an electric kettle and a coffee machine. That is, it is not possible to turn on these two devices at the same time.
Attention! When it comes to increasing the current load on a network section, it is necessary to change not only the machine, but also check whether the electrical wiring can withstand the load, for which the cross-section of the laid wires is considered. If the cross-section does not meet the standards, then it is better to change the wiring.
Rated current of circuit breaker
The rated current of a fuse characterizes the limit value of the electric current in amperes, exceeding which will cause the circuit breaker to trip. There are exact formulas for calculating the rated current that specialists use. But, as a rule, approximate calculations are enough to select the right fuse.
Simplified formulas for calculating rated current
- For 220 V network: I nom. = P/224 (A)
- For 380 V network: I nom. = P/624 (A)
Once you have your circuit's current rating, select the closest value from the standardized range of circuit breaker ratings: 6, 10, 16, 20, 25, 32, 40, 50, or 63 A.
Table of wire cross-section and fuse current for electric boilers by power
How to choose a circuit breaker and wire for an electric boiler
admin Date: 02/04/2019
To protect electric boilers from overload, circuit breakers are used. How to correctly calculate the parameters and choose a circuit breaker for an electric boiler.
The circuit breaker for the electric boiler protects the power cable from thermal overload. The cause of insulation melting is prolonged overheating of the wires caused by excess current. This may cause a short circuit.
As a rule, the fuse is installed on the meter, on the wire leading to the protected equipment.
To correctly select a pass-through switch with an automatic circuit breaker, you need to select the wire cross-section, calculate the rated current of the electric boiler and take into account the nature of use of the connected equipment.
The wire
To connect an electric boiler, you need to lay a dedicated cable. Even if the boiler has a power of up to 3 kW at 220 V, you should not plug it into the network through a regular outlet - you will load the internal wires of the electrical wiring unnecessarily.
It is recommended to connect electrical equipment and partitions with a power of over 1.5 kW via a copper wire. Copper wires are more durable than aluminum, and for the same load you will need a smaller cross-sectional diameter.
The cross-section of the current-carrying wire is selected based on the rated power of the connected equipment and the network voltage.
The power section of the wire for 220 V will be thicker than for a voltage of 380 V with the same power of an electric boiler.
You can calculate the wire cross-section yourself. To simplify the task, we offer a final table of cross-sections of aluminum and copper conductors.
Wire cross-section table
Table of wire cross-sections for connecting electrical equipment
| Core cross-sectional area, mm2 | Copper wire | Aluminum wire | ||||||
| Single-phase network 220 V | Three-phase network 380 V | Single-phase network 220 V | Three-phase network 380 V | |||||
| Rated current, A | power, kWt | Rated current, A | power, kWt | Rated current, A | power, kWt | Rated current, A | power, kWt | |
| 1,5 | 19 | 4,3 | 16 | 10,0 | — | — | — | — |
| 2,5 | 27 | 6,0 | 25 | 16,6 | 20 | 4,5 | 19 | 11,9 |
| 4 | 38 | 8,5 | 30 | 18,7 | 28 | 6,3 | 23 | 14,6 |
| 6 | 46 | 10,3 | 40 | 25,0 | 36 | 8,1 | 30 | 18,7 |
| 10 | 70 | 15,7 | 50 | 31,2 | 50 | 11,2 | 39 | 24,3 |
| 16 | 85 | 19,0 | 75 | 46,8 | 60 | 13,4 | 55 | 34,3 |
| 25 | 115 | 25,8 | 90 | 56,2 | 85 | 19,0 | 70 | 43,7 |
| 35 | 135 | 30,2 | 115 | 71,8 | 100 | 22,4 | 85 | 53,0 |
| 50 | 175 | 39,2 | 145 | 90,5 | 135 | 30,2 | 110 | 68,6 |
| 70 | 215 | 48,2 | 180 | 112,3 | 165 | 37,0 | 140 | 87,4 |
| 95 | 260 | 58,2 | 220 | 13,7 | 200 | 48,0 | 170 | 106,1 |
The rated current of a fuse characterizes the limit value of the electric current in amperes, exceeding which will cause the circuit breaker to trip. There are exact formulas for calculating the rated current that specialists use. But, as a rule, approximate calculations are enough to select the right fuse.
Simplified formulas for calculating rated current
- For 220 V network: I nom. = P/224 (A)
- For 380 V network: I nom. = P/624 (A)
Once you have your circuit's current rating, select the closest value from the standardized range of circuit breaker ratings: 6, 10, 16, 20, 25, 32, 40, 50, or 63 A.
Table of wire cross-section and fuse current for electric boilers by power
| Electric boiler power, kW | Power supply 220 V | Power supply 380 V | ||||
| Cross section of copper wire, mm2 | Rated current, A | Fuse current, A | Cross section of copper wire, mm2 | Rated current, A | Fuse current, A | |
| 3,0 | 2 × 1,5 | 13,9 | 16 | 4 × 1,5 | 4,38 | 6 |
| 4,5 | 2 × 2,5 | 20,1 | 25 | 4 × 1,5 | 7,2 | 10 |
| 6,0 | 2 × 4,0 | 26,8 | 32 | 4 × 2,5 | 9,6 | 10 |
| 7,5 | 2 × 6,0 | 33,5 | 40 | 4 × 2,5 | 12,0 | 16 |
| 9,0 | 2 × 6,0 | 40,2 | 50 | 4 × 4,0 | 14,4 | 16 |
| 10,5 | — | — | — | 4 × 4,0 | 16,9 | 20 |
| 12,0 | — | — | — | 4 × 6,0 | 19,2 | 20 |
| 15,0 | — | — | — | 4 × 10 | 24,0 | 25 |
| 18,0 | — | — | — | 4 × 10 | 28,8 | 32 |
| 21,0 | — | — | — | 4 × 10 | 33,7 | 40 |
| 24,0 | — | — | — | 4 × 10 | 38,5 | 40 |
| 30,0 | — | — | — | 4 × 16 | 48,1 | 50 |
| 36,0 | — | — | — | 4 × 16 | 57,7 | 63 |
Time-current characteristics of circuit breakers
Within a few milliseconds when starting an electric boiler, the starting current exceeds the rated current by 4.5 times (for 220 V) or 1.5 times for a 380 V network. This time is not enough to damage the circuit wiring, so such an excess does not pose a threat. To prevent the machine from tripping at this time, you need to select the desired time-current characteristic.
of type C is most often chosen (from 5 to 10 nominal current values), less often type B (from 3 to 5 nominal values).
Polarity of circuit breakers
For a network with a rated power of 220 V, single-pole or double-pole designs are installed.
For a three-phase 380 V network - three-pole or four-pole circuit breakers.
In electrical networks of the old traditional type, single- and three-pole circuit breakers are used.
Two- and four-pole circuit breakers are used in modern networks with separated wires for neutral (N) and ground (PE).
Diagrams for connecting wires to circuit breakers with different numbers of poles
When purchasing an electric boiler in the EcoSystem online store, we carry out accurate calculations and give recommendations on the selection of related equipment for the correct installation and connection of electric boilers.
Time-current characteristics of circuit breakers
Within a few milliseconds when starting an electric boiler, the starting current exceeds the rated current by 4.5 times (for 220 V) or 1.5 times for a 380 V network. This time is not enough to damage the circuit wiring, so such an excess does not pose a threat. To prevent the machine from tripping at this time, you need to select the desired time-current characteristic.
of type C is most often chosen (from 5 to 10 nominal current values), less often type B (from 3 to 5 nominal values).
Which cable to connect a 6 and 9 kW electric boiler
Content
According to PUE-7, the permissible load on a standard outlet should not exceed 3 kW. That is, an electric boiler with a power of 3 kW seems to be able to be connected via an outlet. However, it is strictly not recommended to do this, since the electric boiler must have its own cable, and always through a separate circuit breaker.
Many people also argue about whether it is possible to connect electric boilers with an aluminum cable. In fact, it is possible, although it is recommended, to connect electrical equipment with a power of 1.5 kW or more through copper conductors. In any case, it won't get any worse.
Selection methods
Let’s say right away that there are several ways. But no matter which one you choose, first of all you need to determine the total load on the network. How to calculate this indicator? To do this, you will have to deal with all the household appliances that are installed on the power supply section. In order not to be unfounded, we will give an example of a network into which a large number of household appliances are usually connected. It's a kitchen.
So, in the kitchen there is usually:
- Refrigerator with power consumption of 500 W.
- Microwave oven – 1 kW.
- Electric kettle – 1.5 kW.
- Hood – 100 W.
This is almost a standard set, which can be a little larger or a little smaller. Adding up all these indicators, we get the total power of the site, which is equal to 3.1 kW. And now here are the methods for determining the load and the choice of machine itself.
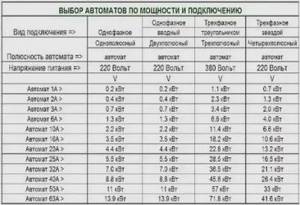
Tabular method
This is the easiest option to choose the right circuit breaker. To do this, you will need a table in which you can select a machine (single- or three-phase) based on the total indicator. Here's the selection table below:
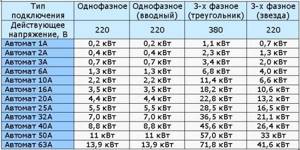
Everything is quite simple here. Most importantly, you need to understand that the calculated total power may not be the same as in the table. Therefore, the calculated indicator will have to be increased to the tabular one. From our example it can be seen that the power consumption of the site is 3.1 kW. There is no such indicator in the table, so we take the nearest larger one. And this is 3.5 kW, which corresponds to a 16-amp machine.
Graphic method
This is practically the same as the tabular one. Only instead of a table, a graph is used here. They are also freely available on the Internet. As an example, we give one of these.
On the graph, circuit breakers with current load indicator are located horizontally, and the power consumption of the network section is located vertically. To determine the power of the circuit breaker, you must first find the calculated power consumption on the vertical axis, and then draw a horizontal line from it to the green column that determines the rated current of the machine. You can do this yourself with our example, which shows that our calculation and selection was done correctly. That is, this power corresponds to a machine with a load of 16A.
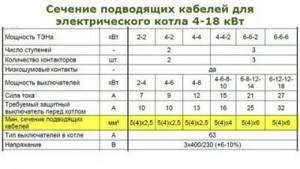
Which power cable should be used to connect a 6 and 9 kW electric boiler?
To know which cable to connect a 6 or 9 kW electric boiler, you can use the table below. In any case, you need to understand that the cable must withstand the rated power of the electric boiler, and even be a little large in reserve.
You should also know that to connect electric boilers to a 220 Volt network, the cable cross-section must be larger than to connect to a three-phase 380 Volt network. It is important to understand that aluminum cable can withstand less load than copper cable.
So, to connect a 6 kW electric boiler you will need a copper wire with a cross-section of at least 4 mm². If you connect an electric boiler with such power through a 2.5 mm² cable, it will not withstand the load and will burn out. More detailed information on calculating cable loads can be found here: https://elektriksam.ru/raschet-nagruzki-na-kabel.html
To connect a 9 kW electric boiler, the conductor cross-section must be larger, but not less than 6 mm². However, you should know that electric boilers with a power of over 6 kW are not recommended to be connected to a single-phase 220 Volt network.
Therefore, if the boiler is connected to 380 Volts, then the cross-section of the conductor can be reduced (divided into 3 phases). To connect a 9 kW electric boiler to a three-phase 380 Volt network, a four-core cable with a cross-section of 4 mm² (with copper conductors) will be sufficient.
What machines should be installed on an electric boiler?
It was said above that an electric boiler, even 3 kW, is best connected with a separate wire and through a circuit breaker. To calculate the rating of the machine, it is enough to know what current the cable can withstand.
A cable with a cross section of 4 mm² can withstand a current of 27 Amps. Therefore, you need to install the closest 32 Ampere circuit breaker, since a 25 Ampere circuit breaker can trip as a result of overloads. As for a cable with a cross-section of 6 mm², it can withstand a current of 40 Amps. Therefore, the circuit breaker must be selected with an appropriate value, no less than 40 Amperes.
So, let's summarize:
- Although they say, it is better to connect electric boilers with a power of up to 3.5 kW through a separate cable and a separate automatic circuit breaker; it is also possible with an RCD;
- Electric boilers with a power of 7-10 kW must be connected through a separate automatic device and, if possible, with an RCD;
- To connect electric boilers with a power of more than 10 kW, permission is most often required.
Power cable for an electric heating boiler: selection of cross-section and brand
Let me remind you of the general rules for connecting electric boilers:
- Boilers up to 3.5 kW can be connected to the power supply via an outlet.
- Boilers up to 7 kW must be connected only through a separate circuit breaker with the installation of an RCD.
- Boilers 7–10 kW must be connected from 380 Volts, only through a separate circuit breaker.
- Boilers over 10 kW require a separate installation permit.
No wires, just cables?
The first question, which usually remains “behind the scenes,” is why you need to use a cable and not separate wires to connect an electric boiler?
In the theory of electrical installations and regulations, there are no prohibitions on using wires selected according to the cross-section and protected according to all rules to power electrical installations.
Another thing is that doing electrical wiring with wires is more difficult, or rather more inconvenient, than with a cable. Wires cannot be laid without protection. To lay them, it is imperative to use metal or electrical plastic pipes. Tightening wires into pipes requires some skills and special tools.
Selecting a machine by power
Everyone knows that electricity is not something to joke about. Incorrect calculation of the power supply circuit can lead to at least two unpleasant consequences. The first is when, when several energy-intensive electrical appliances (for example, a washing machine, electric kettle and iron) are turned on, the circuit breakers trip and the network is de-energized. Unpleasant, but not fatal. The second is when, when you turn on the same devices, the automatic devices will not work, and the electrical wiring will begin to melt and smoke. And this is already a mortal danger: there is only one step to a fire. That is why choosing a machine based on load power is of paramount importance.

Automatic single-pole switch Schneider BA63 1P 25A C for 25 amperes.
A little theory
It is known from the physics course that there is a relationship between electrical power, current strength and voltage in the electrical network. In a simplified form, this relationship is expressed by the following formula for a single-phase network:
where W is the current power in watts (W);
I – current strength in amperes (A);
V – voltage in volts (V).
In this case, we will be interested in the current strength, since the circuit breaker and electrical wiring characteristics are often selected based on this parameter. For convenience, we transform the above formula into the expression:
As an example, let’s calculate the current strength for the load that the energy-intensive consumers mentioned above provide to the power grid. Their total power will be about 6 kW, and at a voltage of 220 V we get the current in the circuit:
I = 6000 W / 220 V = 27.3 A
For a three-phase connection diagram, formula (2) will take the following form:
This change is caused by the fact that with an equal load and uniform distribution of power across phases, the current in a three-phase network will be three times less. Thus, with the same total power of 6 kW, but at a voltage of 380 V, the current in the circuit will be equal to:
I = 6000 W / (1.73 x 380 V) = 9.1 A
Having received this indicator, you can begin to select a circuit breaker that provides network overload protection.
Selection of circuit breaker rating for current and load power
To select a suitable machine, it is convenient to calculate the current per kilowatt of load power and draw up the corresponding table. Applying formula (2) and a power factor of 0.95 for a voltage of 220 V, we obtain:
1000 W / (220 V x 0.95) = 4.78 A
Considering that the voltage in our electrical networks often does not reach the required 220 V, it is quite correct to take the value of 5 A per 1 kW of power. Then the table of current versus load will look like this in Table 1:
| power, kWt | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 16 |
| Current strength, A | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 70 | 80 |
This table gives an approximate estimate of the strength of alternating current flowing through a single-phase electrical network when household electrical appliances are turned on. It should be remembered that this refers to peak power consumption, not average. This information can be found in the documentation supplied with the electrical product. In practice, it is more convenient to use the table of maximum loads, which takes into account the fact that machines are produced with a certain current rating (Table 2):
Three-phase automatic machine: selection according to power and load, connection in a single-phase network
To prevent short circuits and overload of the electrical network, a three-phase circuit breaker is used. The switching device can be used for direct and alternating current lines. The design of the standard model is represented by expanders with switching depending on the frequency of the circuit.
Which machine is suitable for 15 kW
The purpose of a three-phase circuit breaker is overload protection
The purpose of a 3-phase machine is protection against overcurrents and overloads. The 15 kW modification operates on a network with a voltage of 380 V, that is, you will need a 25 A device for input. When choosing, you need to take into account that in conditions of short circuits, the current strength increases and can cause a fire in the electrical wiring.
When selecting a 15 kW machine model for a three-phase load, you will need to take into account the parameters of the permissible voltage and current during a short circuit. It is worth focusing on the calculated current indicators of the cable with the minimum cross-section that protects the switch and the rated current of the receiver.
When calculating the input switching machine according to power parameters in a 380 V network, the following are taken into account:
- electrical power – actual and additional;
- cable loading intensity;
- availability of free capacity in the design indicator of a residential building;
- remoteness of outbuildings and non-residential premises from the cable entry point.
In a 15 kilowatt network with additional power, an ASU device is installed.
Functions of three-phase machines
A three-phase unit simultaneously serves several single-phase circuit zones
Before choosing an automatic switch, you should understand its functionality. Users are often mistaken into thinking that the device protects household appliances. The machine does not respond to its electrical indicators, only triggering in the event of a short circuit or overload. The three-phase functions include:
- simultaneous maintenance of several single-phase circuit zones;
- preventing the formation of overcurrents on the line;
- joint work with AC rectifiers;
- protection of high-power equipment;
- increased power due to the installation of a special converter;
- fast response in short circuit mode on a line with a large number of consumers;
- the ability to turn off manually using a switch or switch;
- Compatible with optional safety terminals.
Without a automatic device, the risk of cable fire increases.
Operating principle and purpose of the circuit breaker
Circuit breaker characteristics
The three-phase circuit breaker is activated in case of a line fault using an electromagnetic switch. The principle of operation of the element is to heat the bimetallic plate at the moment the current rating increases and the voltage is turned off.
The fuse prevents short circuits and overcurrents with values higher than the calculated values from affecting the wiring. Without it, the cable cores heat up to the melting point, which leads to the ignition of the insulating layer. For this reason, it is important to know whether the network can handle the voltage.
Correspondence of wires to load
The problem is typical for old buildings, in which new machines, a meter, and an RCD are installed on the existing line. The machines are selected according to the overall power of the equipment, but sometimes they do not work - the cable smokes or burns.
For example, the cores of an old cable with a cross-section of 1.5 mm2 have a current limit of 19 A. If equipment with a total current of 22.7 A is turned on at a time, only a 25 Ampere modification will provide protection.
The wires will heat up, but the switch will remain turned on until the insulation melts. A fire can be prevented by completely replacing the wiring with a copper cable with a cross-section of 2.5 mm2.
Protecting the weakest section of cable wiring
Based on clause 3.1.4 of the PUE, the task of the automatic device is to prevent overload on the weakest link of the electrical circuit. Its rated current is selected based on the current of the connected household appliances.
If the machine is selected incorrectly, the unprotected area will cause a fire.
Principles for calculating the machine according to the cable cross-section
Calculations for a 3-phase automatic circuit breaker are carried out based on the cable cross-section. For a 25 A model, you will need to refer to the table.
| Wire cross-section, mm2 | Permissible load current based on cable material | |
| Copper | Aluminum | |
| 0,75 | 11 | 8 |
| 1 | 15 | 11 |
| 1,5 | 17 | 13 |
| 2,5 | 25 | 19 |
| 4 | 35 | 28 |
The 25 Ampere modification can be used to protect wiring or installed at the input.
For example, a copper wire with a cross-section of 1.5 mm2 with a permissible load current of 19 A is used for wiring. To prevent the cable from heating up, you will need to select a lower value - 16 A.
Determination of the dependence of power on the cross section using the formula
Table for selecting cable cross-section depending on power
If the cable cross-section is unknown, you can use the formula:
Icalc=P/Unom, where:
- Icalc – calculated current,
- P – power of devices,
- Unom – voltage rating.
As an example, we can calculate the machine that will need to be installed on a boiler with a load of 3 kW and a network voltage of 220 V:
- Convert 3 kW to Watts – 3x1000=3000.
- Divide the value by the voltage: 3000/220=13.636.
- Round the calculated current to 14 A.
Depending on the environmental conditions and the method of laying the cable, you need to take into account the correction factor for the 220 V network. The average value is 5 A. It will need to be added to the calculated current indicator Icalc = 14 +5 = 19 A. Next, the cross-section of the copper wire is selected from the PUE table.
| Section, mm2 | Load current, A | |||||
| Single core cable | Two-core cable | Three-core cable | ||||
| Single wire | 2 wires together | 3 wires together | 4 wires together | Single installation | Single installation | |
| 1 | 17 | 16 | 15 | 14 | 15 | 14 |
| 1,5 | 23 | 19 | 17 | 16 | 18 | 15 |
| 2,5 | 30 | 27 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 21 |
| 4 | 41 | 38 | 35 | 30 | 32 | 27 |
| 6 | 50 | 46 | 42 | 40 | 40 | 34 |
Selection of automatic switch by power
Table of power of electrical appliances in the kitchen
Calculating the total power of household appliances will help you select a protective switch. You will need to look at the value in the device passport. For example, in the kitchen the following are plugged into the socket:
- coffee maker – 1000 W;
- electric oven – 2000 W;
- microwave oven – 2000 W;
- electric kettle – 1000 W;
- refrigerator – 500 W.
Summing up the indicators, we get 6500 W or 6.5 kilowatts. Next, you will need to refer to the table of machines depending on the connection power.
| Single-phase connection 220 V | Three-phase connection | Machine power | |
| Delta circuit 380 V | Star circuit, 220 V | ||
| 3.5 kW | 18.2 kW | 10.6 kW | 16 A |
| 4.4 kW | 22.8 kW | 13.2 kW | 20 A |
| 5.5 kW | 28.5 kW | 16.5 kW | 25 A |
| 7 kW | 36.5 kW | 21.1 kW | 32 A |
| 8.8 kW | 45.6 kW | 26.4 kW | 40 A |
Based on the standard voltage wiring table, you can select a 32 A device that is suitable for a total power of 7 kW.
If you plan to connect additional equipment, an increase factor is used. The average value of 1.5 is multiplied by the power obtained from the calculations. A reduction factor is applied if it is impossible to operate several electrical appliances at the same time. It is equal to 1 or minus 1.