Types of pressure
The pressure in the heating system in private and multi-storey buildings is determined by three factors:
- Dynamic pressure. When the coolant moves through pipelines, the indicator characterizes the pressure on the elements of the heating system.
- Static pressure. This indicator indicates strength. The coolant with this force acts on the elements of the heating system at different heights. When calculating, the level of liquid pressure on the surface is assumed to be zero.
- Permissible pressure is an indicator of the pressure on pipes and radiators. When under pressure, they must work without interruption.
Types of pressure gauges
We list the types of pressure gauges used:
- A liquid pressure gauge shows the change in pressure level using a column of liquid applied as a balancing force;
- Diaphragm pressure gauges display pressure using a special diaphragm box that facilitates volume measurement and movement of the needle along a built-in scale;
- Electrical contact devices are installed in automatic control mechanisms. After a pressure drop, a short circuit occurs in the electrical network;
- The functional characteristics of various types of devices are combined in differential pressure gauges;
- The most popular are devices with spring mechanisms.
Since such pressure gauges are endowed with certain advantages, they are most often installed in home heating systems.
Causes of pressure drop
The operating pressure level of the system is not always at the required level and may fall or increase.
The main reasons for its decline:
- leaks . Leaks can appear in all elements of the heating circuit - in pipes, radiators, and are usually associated with defects in their manufacture.
Leaks at joints are often caused by loose fasteners or damage to the joint during assembly.
- Wear of the structure. Usually caused by improper installation of the circuit or violations of operating standards - too high pressure or significant changes in it, increased water temperature or high “hardness”. Individual elements of the system, including the circulation pump, have a warranty period, and after its expiration they may reduce performance, requiring their adjustment or replacement.
- Scale . It appears when water heats up to too high temperatures. Scale is solid deposits of salts that form on the heating surfaces of a heat exchanger. Accumulating in the heat exchanger, scale blocks the flow of water and lowers the operating pressure.
Important! Too “hard” water contains an increased amount of oxygen, chemical impurities and salts that form rust deposits. Hard water may be present in the system due to frequent replenishment of it with fresh water , including due to coolant leaks.
What does the pressure gauge on a gas boiler show?

A pressure gauge is a device for monitoring gas or water pressure in a closed system. This device is mandatory if you are installing independent heating. Together with the safety valve, it protects the system from critical pressure deviations. To measure fluctuations in this value, you need to find a reliable and simple pressure gauge. You can install it yourself. The article will help you with the choice, as well as with installing the device yourself.
Why is it important to control the pressure in the system?
Individual heating is a closed system with water as the coolant. The liquid is in a static state when the boiler and pump are turned off. As soon as you light the burner, the water becomes mobile and hydrodynamic pressure appears in the system. It can be of 3 types:
- Natural circulation. When the boiler is turned on and the pump is turned off, water still moves in the pipes, because it has different temperatures in different places in the system.
- Forced circulation. The pump “drives” water in a circle.
- Expansion of a liquid due to heat, which in the process displaces air and occupies the vacated space.
All these types of pressure, which add up to one indicator, are what the pressure gauge is designed to measure. Together with the automatic air vent and emergency safety valve, it is the key to the safety of your system, since going out of range means your heating is not working properly. This could even cause the equipment to explode.
The installation of these 3 elements (they are also called the safety group) is required only for solid fuel boilers (wood, coal). If the device is purchased complete with a boiler, then it is compatible with it, but you can assemble the group separately. Installation of a pressure gauge, emergency valve and air vent is not necessary for a closed system with a gas or electric boiler, because they can stop heating themselves if an extremely high pressure or temperature develops. However, in this case, the pressure gauge and its “assistants” are recommended for convenience and additional protection. Moreover, the devices and their components are inexpensive.
Main characteristics and principles of operation of the pressure gauge
There are devices for different pressure levels. For convenience, buy a device with an intuitive scale that will not require additional calculations. Usually there are two arrows on it: red and black. Red controls the permissible level. For home boilers, manufacturers recommend 2 atmospheres (the exact value is indicated in the passport). If the black one “runs” behind the red one, something is broken. A decrease in value by 0.02 MPa (0.2 atm) means that you need to look for a coolant leak or check for a sufficient pressure level in the expansion tank.
The pressure gauge usually has two scales: pressure in atmospheres and bars. Sometimes the device is combined with a thermometer, so it also has a temperature scale. The operating principle of pressure gauges is based on balancing the desired pressure with another force. According to this characteristic, devices are divided into:
- liquid;
- spring;
- membrane;
- electrical contact (ECM);
- differential.
Advice. Since the pressure in a conventional closed heating system fluctuates between 2-3 atm, choose a pressure gauge with a scale of up to 4 atm. If the upper value of the pressure gauge is, for example, 50 atm, the divisions will be small. You will not record a small pressure drop, which can become critical for the system.
It is not advisable to install the device when:
- there is no seal or other verification mark on it;
- the pressure gauge verification period has expired;
- it has visual damage, such as a crack in the glass;
- after disconnecting, the arrow does not return to “0”.
Types of pressure gauges: what to choose
- In a liquid pressure gauge, the pressure difference is calculated using a column of liquid, which is used as a balancing force (communicating vessel principle). They are used either in laboratory research or in industrial settings.
- In a membrane pressure gauge, the measured pressure is recorded by a pair of welded membranes (membrane box), which change the volume and thereby move the needle along the scale.
- An electric contact pressure gauge is used in automatic control, alarm or regulation systems. The pressure difference causes a short circuit in the electrical circuit.
- Differential devices combine the properties of different types of pressure gauges.
- The most popular devices are those with a spring mechanism. Among other things, they are most often used in heating systems, as they have a number of advantages:
- simplest in design;
- can have a wide measurement range;
- the most reliable.
Source: https://ostwest.su/instrumenty/chto-pokazyvaet-manometr-na-gazovom-kotle.php/
Reasons for the increase and decrease in pressure in the system
One of the most common causes of pressure drop in a heating system is a coolant leak. The “weak” links most often become the joints of individual parts. Although pipes can burst if they are already very worn out or defective. The presence of a leak in the pipeline is indicated by a drop in the level of static pressure measured with the circulation pumps turned off.
If the static pressure is normal, then the fault must be looked for in the pumps themselves. To make it easier to find the location of the leak, you need to turn off different sections one by one, monitoring the pressure level. Having identified the damaged area, it is cut off from the system, repaired, sealing all connections and replacing parts with visible defects.

Elimination of visible coolant leaks after they are detected during an inspection of the heating system circuit of a private house or apartment
If the coolant pressure drops and the leak cannot be found, then specialists are called. Using professional equipment, experienced craftsmen pump air into the system, which has previously been freed of water, as well as cut off from the boiler and radiators. The whistling air escaping through microcracks and loose connections makes it easy to detect leaks. If pressure losses in the heating system are not confirmed, then proceed to checking the serviceability of the boiler equipment.

Use of professional equipment when searching for hidden leaks. Excess moisture detection scanner allows you to accurately identify a crack in a pipe
The reasons leading to a decrease in pressure in the system due to a malfunction of boiler equipment include:
- accumulation of scale in the heat exchanger (typical for areas with hard tap water);
- the appearance of microcracks in the heat exchanger caused by physical wear and tear of equipment, preventive flushing, and manufacturing defects;
- destruction of the bithermic heat exchanger that occurred during a water hammer;
- damage to the expansion tank chamber of the heating boiler.
In each case the problem is solved differently. Water hardness is reduced using special additives. The damaged heat exchanger is sealed or replaced. The tank built into the boiler is plugged, replacing it with an external device that has suitable parameters. Boiler maintenance must be carried out by a suitably qualified engineer.
Reasons for the increase in pressure in the system:
- the movement of the coolant along the circuit is stopped (check the heating regulator);
- constant replenishment of the system, occurring due to human fault or as a result of automation failure;
- shutting off the tap or valve in the direction of the coolant flow;
- formation of an air lock;
- clogged filter or sump.
Purpose of the pump for heating
Previously, circulation pumps were used only in centralized heating systems, and for private housing construction the natural movement of the coolant caused by temperature differences was the norm.
Now forced circulation is used everywhere thanks to the emergence of compact and inexpensive models designed to service the heating networks of small houses and cottages.

Due to the increase in the speed of movement of the coolant in the pipeline, thermal energy flows faster to the heating radiators, and accordingly, the rooms are warmed up faster. The load on the boiler has decreased because the water is also heated faster.
The need to install bulky and inconvenient large-diameter pipelines has disappeared; contours have become easier to camouflage under floor coverings or be buried in walls.
The main disadvantage of pumps for heating systems is their dependence on electricity. If the power supply is intermittent or there is a risk of a complete power outage for some period, it is necessary to install a backup power generator or at least an uninterruptible power supply.
The remaining disadvantages relate to the designs and functionality of various types of devices. For example, monoblock units and devices with a dry rotor are noisier and require constant maintenance, while a pump with a wet rotor is demanding on the quality of the coolant and has a pressure limitation.
Security group device
The safety group is quite simple and consists of three devices installed on a common manifold.
The manifold itself is made of brass or stainless steel and has three seats in the form of threaded holes. At the bottom of the collector is equipped with a threaded coupling, which is used for connection to the heating system. Screwed on top of it are: a pressure gauge, an automatic air vent, and a relief safety valve. The listed devices provide the security group with three functions, which it performs.
Safety group pressure gauge
It is best if the safety group pressure gauge is equipped with two arrows: black and red. The black arrow shows the operating pressure in the heating system, and the red one controls the movement of the black arrow in one direction or another. This is important because you will know in advance what is happening with the pressure in the system and will be able to take the necessary measures to prevent an emergency shutdown of the boiler. The red arrow is set manually when setting the system pressure.
Safety group air vent
The safety group air vent, also called an automatic air vent valve, together with other devices is attached at the highest point so that air can easily escape.
The operating principle of the air vent is similar to the operation of the Mayevsky crane. The only difference is that the air is removed from it automatically when the critical pressure is exceeded. The importance of this operation of the air vent is that you practically do not see when and how air leaves the heating system. This is especially important in cases of emergency situations when, in the absence of a proper response from the thermostat, the coolant may boil.
The connection of the air vent to the manifold must be sealed, so brass or steel, stainless steel fittings are used for this.
Safety group safety valve
The safety group safety valve protects the heating system from increased pressure in the pipes, even if the expansion tank is configured and operating correctly.
The valve is an emergency device and, in the absence of a proper response from the expansion tank to a critical increase in pressure, will release excess coolant.
The safety valve of the safety group is available in different designs. The most commonly used are valves with a spring-type mechanism. However, on heating pipelines with pipe diameters ≥ 200 mm, valves with a lever-weight mechanism work better. The safety valve requires a clear response to critical moments in the heating system, given its inertia. So for pipes that can withstand pressure ≤ 0.25 MPa, the inertia should be 15%, and for pressure ≥ 0.25 MPa - 10%.
The diameter of the safety group safety valve must be equal to the diameter of the inlet pipe. The valve should operate instantly if the expansion tank is broken or can no longer compensate for the volume of coolant that increases when heated. According to regulations, the safety valve must cut into the pipeline at the outlet of the boiler. In this case, the pressure gauge is installed parallel to the valve.
In order to check the operation of the safety valve, there is a red handle in its upper part. By turning the knob in the direction of the arrow, you can visually check the operation of the device. If the safety valve does not operate or does not hold the coolant well enough, it must be replaced. Depending on the system it operates in, the safety valve may be designed for different pressures. Therefore, when choosing a safety valve for the safety group of your heating system, you must know its pressure parameters, usually indicated on the boiler jacket.
For reference, I will say that in most boiler installations the upper pressure threshold is 3 bar, although there are systems with a maximum operating pressure from 1.6 to 2 bar.
Selecting and installing a pressure gauge
The device for measuring excess pressure must be selected according to the maximum atmosphere indicated in the documents for the boiler. To select a suitable pressure gauge, the following aspects must be considered:
- compliance of the device with the design documentation of your heating system;
- type of heating equipment;
- technical parameters of heating radiators;
- volume of the system to be filled.
Installation of a pressure gauge and a safety group in a heating system is accessible to a person without specific skills who has a regular plumbing kit.
There are such ways:
- Installation on the “original” fitting coming out of the heat generator.
- Insertion into the supply line at the outlet of the boiler.
Calculate the place for tapping into the system so that there is the minimum possible distance from the pressure gauge to the boiler. Ideally, right next to the boiler. In this case, there should be no additional fittings or other devices connected via a tee (taps, valves, etc.).
Selecting a pressure gauge is an important component of installing a heating system. If the device and its “assistants” are installed incorrectly, you may even be denied warranty service for the boiler. Take care of monitoring the pressure in your heating pipes, because prevention is always cheaper than repairs and eliminating negative consequences.
Pressure drops in the heating system: causes and consequences
A closed heating circuit, like any closed system, obeys the laws of thermodynamics. Namely: when the temperature of the medium in a closed container with a constant volume increases, the pressure inevitably increases. In fact, it does not matter what static pressure was in the system before heating the coolant; the pressure parameters when starting coolant circulation and reaching the design capacity are much more important.
Pressure drops caused by isochoric phenomena have both positive and negative effects on the system. The positive thing is an increase in efficiency, and the negative thing is an increase in the load on the boiler, batteries, pipes and docking units, and it is much more pronounced than the positive one.

To minimize the negative impact of high pressure, membrane-type expansion tanks are installed in closed heating systems. They accept the volume of coolant that has increased as a result of heating, as a result of which the increasing pressure is partially compensated.
Pressure drops in heating systems can be caused not only by isochoric processes. They can also be caused by depressurization of wiring elements, connecting nodes and any other components of the system. In this case, the pressure can not only increase, but also fall.
The process of increasing and decreasing pressure can be controlled and spontaneous. In the first case, it is initiated by a special valve, which releases excess coolant to the outside to stabilize the pressure. After the indicators return to normal, it will independently restore the tightness of the heating circuit.
In the second case, the reason for the decrease in pressure may be a crack in the distribution pipe or a leak in the tank, radiator or any connecting unit. This kind of problem needs to be eliminated immediately.
Classification of pressure gauges according to operating principle
Nowadays, devices operating under pressure are used in almost all spheres of human activity. Consequently, pressure gauges are also used with them, providing accurate information about pressure indicators. In this case, measuring instruments may differ from each other in design and principle of operation. The devices available on the market are divided into the following types:

- Piston pressure gauges - their device includes a cylinder with a piston inside. During operation, one part of the piston pump is acted upon by a working medium - gas or liquid, and on the other - a load pressure of a certain value. Together with the movement of the slider, the arrow on the instrument scale is activated;
- Liquid pressure gauges - their design includes a tube, inside of which there is a liquid and a movable plug. When using a liquid pressure gauge, the working fluid acts on the plug, causing the liquid level inside the tube to change. At this moment, the instrument needle begins to move;
- Deformation pressure gauges - inside such devices there is a membrane, the deformation of which activates the index arrow above the device scale.
- Stationary - such devices are mounted and used only on a specific unit without the possibility of dismantling the measuring device. Often, the unit used also uses a water pressure regulator with a pressure gauge;
- Portable - these measuring instruments can be dismantled and used to work with different units and in different systems. The portable device has smaller dimensions.
Modern pressure gauges are also divided into mechanical and electronic devices. A mechanical pressure gauge for a pump or water supply system has a simple design, but cannot accurately measure pressure. The design of the electronic device includes a contact unit that more accurately measures the pressure of the working medium.
According to the method of use, pressure gauges are divided into the following types:

What are the safety groups for heating?
Security blocks come in different configurations, for example:
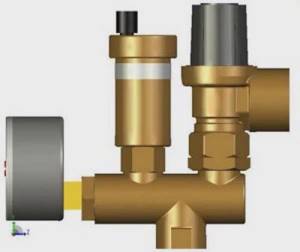
Heating safety group
Or enclosed in one building:
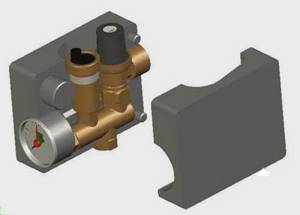
Security group enclosed in one building

Well, many different others can be found on sale, but appearance is not important, because all safety units work the same way, and you need to choose, as mentioned above, according to the pressure for which the safety valve and pressure gauge are designed.
Installation of homemade automation
High-quality products from well-known manufacturers are quite expensive. For example, the cost of a safety group for boilers of the Italian brand Icma is 40-43 USD. e. If you buy components from the same manufacturer and assemble the safety automatics yourself, the price will be significantly lower:
- safety valve – 6 cu. e.;
- pressure gauge - 10 cu. e.;
- automatic air vent – 5 cu. e.;
- brass crosspiece DN 15 as a collector – 2.2 cu. e.
The total amount for a security group assembled with your own hands is 23.2 USD. That is, the benefit is obvious.
When choosing components, be sure to take into account the advice of our expert, based on many years of practice:
- Do not go for absolute cheapness when purchasing safety valves. Chinese products begin to leak after the first actuation or do not release pressure at all.
- Pressure gauges “originally” from the Middle Kingdom often lie. If, when filling the system with coolant, the device underestimates the readings, then after heating the pressure in the network will jump to critical and an accident will occur.

Assembling a homemade block
- Select a safety valve according to the boiler operating pressure specified in the technical data sheet.
- Do not buy an angular type air vent, only a straight one. The first creates increased resistance to the outgoing air.
- The crosspiece should be made of high-quality thick-walled brass. When choosing, compare the weight of a cheap and expensive part in the palm of your hand and feel the difference.
For reference. The vast majority of gas and wood heat generators operate with a maximum water pressure of 3 bar. The exception is Stropuva long-burning cylindrical heaters (max - 2 Bar) and completely cheap boilers with thin walls (max - 1.5 Bar).
Setting up a homemade security group is quite simple. Screw the air vent into the upper terminal of the cross, and install a pressure gauge and safety valve on the side terminals in any order. Cut the finished element into the main line next to the boiler according to the diagram (see the previous section).
If you want to maximize the safety of your solid fuel heating unit, pay attention to thermal relief valves. They work in tandem with the main group and, in case of overheating, release the coolant from the water jacket of the boiler, running cold water from the water supply inside. Product types and connection diagrams are described in our earlier publication.
Why do you need a pressure gauge in a heating system?

What does the pressure in the heating system of a private home depend on? What should it be like? How to protect the heating system from destruction? What equipment is used for these purposes? How a security group protects the heating system from ruptures and a private home from damage.
This article explains and describes everything perfectly, answering all these questions.
Pressure in the heating system of a private house.
Many homeowners almost never think about what pressure should be in the heating system. This is primarily due to the fact that modern heating systems in private houses are equipped with all the necessary protective equipment that operates automatically and does not require user intervention.
Despite these realities, the coolant pressure in the heating system of a private home is the basis for the efficiency of the entire heating system as a whole. Let's look at how the coolant pressure in the heating system affects the heating of rooms. From physics we know that heat is always transferred from warm to cold. Consequently, the cold air in the room takes heat from the heated radiators, which in turn take heat from the hot water circulating through the heating system.
Next, what determines the heating temperature of heating radiators? It depends on two factors: 1 The temperature of the coolant, that is, the water in the heating system 2 The speed at which hot water is supplied to the radiator
The higher the temperature of the water and the speed of its movement through the heating system, the higher the heating of the radiators. Therefore, you can control the temperature in the room both by increasing the heating temperature of the water and by increasing the speed of its flow. The speed of water flow in a closed heating system depends on the pressure created by the transfer pump. The higher the pressure in the heating system, the more the radiators heat, the lower the pressure, the colder it is.
Stationary pressure gauges

To do this, they are connected to the heating system using a thread or bracket. Over time, the accuracy of a stationary pressure gauge decreases, but it can be replaced. When choosing a device, it is important that its scale is intuitive. It is enough to mark two zones - red and black or blue: red indicates exceeding safe values. Sometimes the device records the value in bars and atmospheres, or adds a temperature scale.
Optimal pressure levels in the system largely determine its thermal efficiency and significantly extend its service life. A drop or increase in values by 0.2 atmospheres from the working norm of 1.5-2 atmospheres is sufficient reason to look for its cause.
This allows you to notice and eliminate the malfunction in a timely manner and bring the system to an optimal operating mode without the development of emergency situations and unplanned repairs.
Automatic system recharge
The second unit that ensures the maintenance of excess pressure in the system is an automatic replenishment device. Of course, you can pump water into the system manually, but this is inconvenient to do with large volumes of leakage. For example, if the system has many fittings or there are gaps through which microscopic doses of coolant regularly leak. Also, automatic replenishment is practically irreplaceable for closed systems with a special coolant - without a pressure pump it simply will not be possible to provide a sufficiently high pressure.
The first type of automatic replenishment devices operates on the principle of a compressor automation group. High and low pressure switches turn the make-up on and off if the pressure in the system is lower or, respectively, higher than the set threshold. Such devices are the simplest and cheapest, but have a main drawback - they do not take into account the temperature of the liquid and the degree of its expansion.

Let's say that during system operation the pressure drops 20–30% below operating pressure, but does not reach the minimum threshold to which the relay is set. This is not surprising, because the relay calibration occurs in a cold state of the system. Another special case: when the relay is triggered, make-up is turned on, adding a portion of cold, that is, not yet expanded, liquid to the system. If the expansion tank has insufficient capacity, eventually the expansion of the coolant will cause the safety valve to operate, part of the coolant will be discharged, the pressure will drop again, the make-up will turn on again, and so on in a circle.

The described nuance is important for heating systems that contain over 300 liters of water. In such cases, it is optimal to use digital make-up dispensers, which are equipped with most advanced boiler equipment. The controller will make the necessary adjustments and add a strictly defined amount of coolant to the system, taking into account its temperature and expansion ability. Like conventional mechanical make-up valves, it is better to connect the electronic dispenser to the supply line immediately after inserting the bypass tube into it in order to avoid temperature shock of the heat exchanger. It is recommended to install a dirt or cartridge filter on the inlet pipe for the coolant; the injection unit is connected through a ball valve.
Boiler - which one to choose
Since the closed heating system of a private house can operate autonomously, it makes sense to install a heating boiler with automation. In this case, having configured the parameters, you do not need to return to this. All modes are supported without human intervention.
The most convenient gas boilers in this regard. They have the ability to connect a room thermostat. The temperature set on it is maintained with an accuracy of one degree. It dropped by a degree, the boiler turned on, heating the house. As soon as the thermostat is activated (the temperature is reached), the operation stops. Comfortable, convenient, economical.
Some models have the ability to connect weather-dependent automation - these are external sensors. Based on their readings, the boiler adjusts the power of the burners. Gas boilers in closed heating systems are good equipment that can provide comfort. The only pity is that gas is not available everywhere.
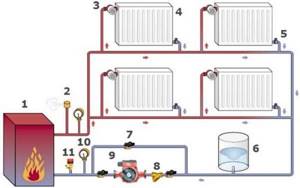
Two-pipe closed heating system in a house on two floors (diagram)
Electric boilers can provide a no less degree of automation. In addition to traditional units, induction and electrode units have recently appeared on heating elements. They are distinguished by their compact size and low inertia. Many believe that they are more economical than boilers using heating elements. But even this type of heating unit cannot be used everywhere, since power outages in winter are a common occurrence in many regions of our country. And provide the boiler with electricity. 8-12 kW from the generator is a very difficult matter.
Solid or liquid fuel boilers are more versatile and independent in this regard. An important point: to install a liquid fuel boiler, a separate room is required - this is a requirement of the fire service. Solid fuel boilers can be installed in the house, but this is inconvenient, since a lot of debris falls from the fuel during combustion.
Modern solid fuel boilers, although they remain periodic equipment (they warm up during combustion and cool down when the fuel burns out), but they also have automation that allows you to maintain a given temperature in the system, regulating the intensity of combustion. Although the degree of automation is not as high as that of gas or electric boilers, it is there.
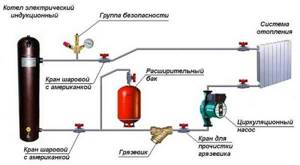
Example of a closed heating system with an induction boiler
Pellet boilers are not very common in our country. In fact, this is also solid fuel, but boilers of this type operate in continuous mode. Pellets are automatically fed into the firebox (until the stock in the burner is finished). If the fuel quality is good, ash cleaning is required once every few weeks, and all operating parameters are controlled automatically. The only thing holding back the spread of this equipment is its high price: the manufacturers are mainly European, and their prices are corresponding.
A little about calculating boiler power for closed-type heating systems. It is determined according to the general principle: per 10 sq. meters of area with normal insulation take 1 kW of boiler power. It’s just not recommended to take it “back to back”. First, there are unusually cold periods during which you may not have enough rated power. Secondly, working at the power limit leads to rapid wear of the equipment. Therefore, it is advisable to take the boiler power for the system with a margin of 30-50%.
Closed heating system - what is it?
As you know, any heating system in a private home has an expansion tank. This is a container that contains some coolant removal. This tank is necessary to compensate for thermal expansion under various operating conditions. By design, expansion tanks are of open and closed type, respectively, and heating systems are called open and closed.
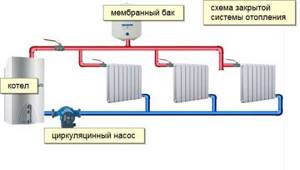
Closed two-pipe heating system
In recent years, a closed heating scheme has become increasingly popular. Firstly, it is automated and works without human intervention for a long time. Secondly, it can use any type of coolant, including antifreeze (it evaporates from open tanks). Thirdly, the pressure is maintained constant, which allows the use of any household appliances in a private home. There are several more advantages that relate to wiring and operation:
- There is no direct contact of the coolant with air, therefore, there is no (or almost no) unbound oxygen, which is a powerful oxidizing agent. This means that the heating elements will not oxidize, which will increase their service life.
- A closed-type expansion tank is placed anywhere, usually close to the boiler (wall-mounted gas boilers come immediately with expansion tanks). An open-type tank should be located in the attic, and this means additional pipes, as well as insulation measures so that heat does not “leak” through the roof.
- The closed type system has automatic air vents, so there is no airing.
In general, a closed heating system is considered more convenient. Its main drawback is its energy dependence. The movement of the coolant is ensured by a circulation pump (forced circulation), and it does not work without electricity. It is possible to organize natural circulation in closed systems, but it is difficult - it requires regulating the flow using the thickness of the pipes. This is a rather complicated calculation, which is why it is often believed that a closed heating system only works with a pump.
To reduce energy dependence and increase heating reliability, install uninterruptible power supplies with batteries and/or small generators that will provide emergency power supply.
Rules for constructing closed contours
For open-type hydraulic systems, the issue of pressure regulation is irrelevant: there are simply no adequate ways to do this. In turn, closed heating systems can be configured more flexibly, including in relation to coolant pressure. However, first you need to provide the system with measuring instruments - pressure gauges, which are installed through three-way valves at the following points:
- in the security group collector;
- on branching and collecting collectors;
- directly next to the expansion tank;
- on mixing and dispensing devices;
- at the outlet of circulation pumps;
- at the mud filter (to control clogging).
Not every position is absolutely mandatory; much depends on the power, complexity and degree of automation of the system. Quite often, the boiler room piping is arranged in such a way that the parts important from the point of view of control converge in one node, where the measuring device is installed. Thus, one pressure gauge at the pump inlet can also serve to monitor the condition of the filter.

Why do you need to monitor pressure at different points? The reason is simple: pressure in the heating system is a collective term, which in itself can only indicate the tightness of the system. The concept of a worker includes static pressure, formed by the effect of gravity on the coolant, and dynamic pressure—oscillations that accompany changes in operating modes of the system and appear in areas with different hydraulic resistance. Thus, pressure can change significantly when:
- heating the coolant;
- circulation disorders;
- turning on the make-up;
- clogging of pipelines;
- the appearance of air jams.
It is the installation of control pressure gauges at different points in the circuit that allows you to quickly and accurately determine the cause of failures and begin to eliminate them. However, before considering this issue, you should study: what devices exist to maintain operating pressure at the desired level.
Setup and Troubleshooting

It is impossible to maintain pressure in the heating system without following the rules for filling it. This must be done at minimum pressure and with open valves to bleed air in the radiator network. The underfloor heating loops are filled one at a time, otherwise due to the difference in length, air will certainly be displaced into longer coils. After the system is filled, it is pressurized with double working pressure and the pressure gauge readings are monitored for a certain time. Usually, the pressure of the water supply system is sufficient for pressure testing; otherwise, you have to use a manual plunger hydraulic pump. After checking, the pressure is reduced to the minimum, the system is heated to the maximum operating temperature, and upon completion of warming up the entire volume of the coolant, the pressure is measured: it should be 20–30% less than the limit.

A decrease in pressure over time is common for systems filled with fresh water. Dissolved oxygen is released from it, and accordingly, over time, the total volume of the coolant decreases. You just need to periodically recharge the system until the effect disappears on its own. An increase in pressure is a clear sign of an incorrect calculation of the expansion tank; its volume needs to be increased. Small differences within 10–15% of the operating pressure are considered quite normal, this is due to the linear expansion of the pipes. If pressure surges during heating and cooling of the system go beyond 30% of the nominal value, this indicates either damage to the membrane in the tank or the presence of air pockets in the system.
A pressure gauge is a device for monitoring gas or water pressure in a closed system. This device is mandatory if you are installing independent heating. Together with the safety valve, it protects the system from critical pressure deviations. To measure fluctuations in this value, you need to find a reliable and simple pressure gauge. You can install it yourself. The article will help you with the choice, as well as with installing the device yourself.
Direct installation method
They are installed in those places indicated in the design documentation, for example, before and after valves. An adapter must be installed in the place where the pressure gauge is installed. It is either welded, sometimes they are screwed in. Welding is the most affordable way to fix adapters.
The direct method is used for installing devices that operate in a stable environment without any pressure surges and frequent replacement of the measuring sensor.