Volume of water in a heating radiator - aluminum, cast iron, bimetallic
There are many reasons why you may need to know the volume of water in a heating radiator. The easiest way is to look at the specifications, instructions or other documentation for the product. But what to do if it is not there?
From this article you will learn how many liters of water are in one section of a heating radiator, depending on its model and dimensions. We will also tell you how to calculate this indicator for non-standard models.
How much water is in one section of a cast iron radiator?
Cast iron batteries differ in section height, depth, power and weight. For example, the MC 140-500 model has a height of 50 mm and a depth of 140 mm. Basically, the volume of water in the cast iron section of the radiator is affected by its height.
The most common is the MS series. Depending on the manufacturer, the volume of coolant may vary, so there is a slight scatter.
Volume of one section of the MS brand (in liters)
- MS 140-300 – 0.8-1.3;
- MS 140-500 – 1.3-1.8;
- MS-140 – 1.1-1.4;
- MS 90-500 – 0.9-1.2;
- MS 100-500 – 0.9-1.2;
- MS 110-500 – 1-1.4.
Cast iron batteries of the ChM series are very popular. The model marking indicates the number of channels, height and depth of the section.
For example, ChM2-100-300 has a height of 300 mm, a depth of 100 mm, and water circulates in it through two channels.
Volume of water in one section of the ChM brand (in liters)
- World Championship 1-70-300 – 0.66;
- World Championship1-70-500 – 0.9;
- World Championship2-100-300 – 0.7;
- World Championship2-100-500 – 0.95;
- ChM3-120-300 – 0.95;
- World Championship3-120-500 – 1.38.
The data below is consistent with other manufacturers' specifications. To play it safe, you can use them by adding a 20 percent safety margin.
Water volume in one section of an aluminum radiator
There are dozens of manufacturers of aluminum heating radiators, the products of each of them differ in the design and size of the internal channels. Therefore, we can only approximately say how much water is in one section of an aluminum radiator.
The main difference between the models is in height, so here is a list of the most common sizes (data are given in liters):
- 350 mm – 0.2-0.3;
- 500 mm – 0.35-0.45;
- 600 mm – 0.4-0.5;
- 900 mm – 0.6-0.8;
- 1200 mm – 0.8-1.
For non-standard sizes, you can use the formula (V – volume in liters, h – height in meters):
V = hx 0.8
The result will be approximate, but if you don’t have the equipment specifications at hand, you can use the obtained value. This way you can determine how much water is in one fin of an aluminum battery with an error of no more than 20%.
Please note that the capacity of an aluminum heating radiator may decrease over time due to corrosion. It is formed due to water with poor alkalinity or acidity. Also, the volume of liquid in an aluminum radiator may be reduced due to silting.
As with aluminum, there are many options for manufacturers and brands of bimetallic radiators. Their structure, appearance, and channel diameters differ in the same way.
The volume of water in a bimetallic radiator depends on its height and is (in liters):
- 35 cm – 0.1-0.15;
- 50 cm – 0.2-0.3;
- 60 cm – 0.25-0.35;
- 90 cm – 0.3-0.5;
- 120 cm – 0.4-0.6.
To calculate the volume of a section of a bimetallic radiator of non-standard height, use the formula (V – volume in liters, h – height in meters):
V = hx 0.35
This will give you an approximate value, which may vary within 20%.
Water volume in the heating radiator table
Radiator typeHeight (mm) / modelMinimum section volume (l)Maximum section volume (l)
| Aluminum | 350 | 0,2 | 0,3 |
| 500 | 0,35 | 0,45 | |
| 600 | 0,4 | 0,5 | |
| 900 | 0,6 | 0,8 | |
| 1200 | 0,8 | 1 | |
| Bimetallic | 350 | 0,1 | 0,15 |
| 500 | 0,2 | 0,3 | |
| 600 | 0,25 | 0,35 | |
| 900 | 0,3 | 0,5 | |
| 1200 | 0,4 | 0,6 | |
| Cast iron | MS 140-300 | 0,8 | 1,3 |
| MS 140-500 | 1,3 | 1,8 | |
| MS-140 | 1,1 | 1,4 | |
| MS 90-500 | 0,9 | 1,2 | |
| MS 100-500 | 0,9 | 0,2 | |
| MS 110-500 | 1 | 1,4 |
We hope that we were able to help you determine the volume of water in one section of the battery. Let us remind you: if you are going to make any manipulations with the heating system, it is better not to take risks.
When working with non-standard models, calculate their volume with a small margin of 10-20%. This will not complicate the task, but will help avoid trouble. Don't forget to share the article with your friends!
Technical aspects of aluminum batteries
To install an autonomous heating system, it is necessary not only to carry out installation work in accordance with current regulations, but also to choose the right aluminum radiators. This can only be done after a thorough study and analysis of their properties, design features, and technical characteristics.
Classification and design features
Manufacturers of modern heating equipment make sections of aluminum radiators not from pure aluminum, but from its alloy with silicon additives. This allows the products to be corrosion resistant, more durable and extend their service life.
Today, the retail chain offers a wide range of aluminum radiators, differing in appearance, represented by such products as:
- panel;
- tubular.
According to the constructive solution of a single section, which are:
- Solid or cast.
- Extruded or composed of three separate elements, internally secured to each other with bolts with foam rubber or silicone gaskets.
Batteries are also differentiated by size.
Standard sizes with a width of 40 cm and a height of 58 cm.
Low, up to 15 cm high, which makes it possible to install them in very limited spaces. Recently, manufacturers have been producing aluminum radiators of this series of “plinth” design with a height of 2 to 4 cm.
Tall or vertical. With a small width, such radiators can reach a height of up to two or three meters. This working height arrangement helps to heat large volumes of air in the room quite effectively. In addition, this original design of radiators also performs a decorative function.
The service life of modern aluminum radiators is determined by the quality of the source material and does not depend on the number of its constituent elements, their sizes and internal volume . The manufacturer guarantees their stable operation with proper use for up to 20 years.
Main performance characteristics
Comparative characteristics
Technical characteristics and design solutions of aluminum radiators are developed to ensure convenient and reliable heating of rooms. The main components characterizing their technical properties and operational capabilities are the following factors.
Operating pressure. Modern aluminum radiators are designed for coolant pressure in the heating system from 6 to 25 atmospheres. To guarantee these indicators, in the factory, each battery is tested at a pressure of 30 atmospheres. This fact makes it possible to install this heating equipment in any heating system where the possibility of water hammer formation is excluded.
Power. This indicator characterizes the thermodynamic process of heat transfer from the surface of the heating battery to the environment. It indicates how much heat in watts the device can produce per unit time.
By the way, heat transfer from aluminum radiators occurs by convection and thermal radiation in a ratio of 50 to 50. The numerical value of the heat transfer parameter of each section is indicated in the device passport.
When calculating the number of batteries required for installation, their power plays a primary role. The maximum heat transfer of one section of an aluminum heating radiator is quite high and reaches 230 Watts. This impressive figure is explained by the high heat transfer ability of aluminum.
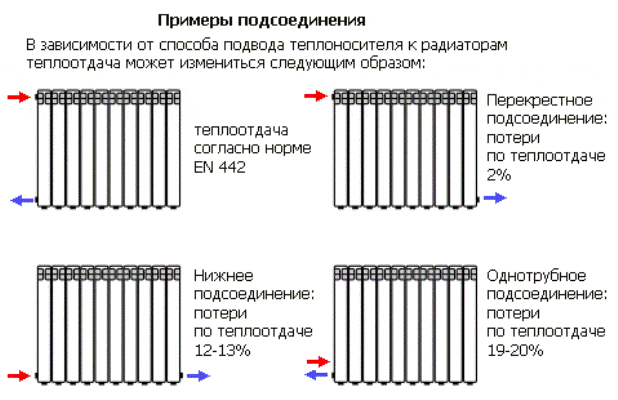
Effect of connection on heat transfer
Section volume. This indicator characterizes the amount of coolant that is present in the radiator section in working condition. It depends on the overall dimensions of the radiator and its internal design. For each type and type of radiators, this value is different.
The volume of the section is an important technical characteristic of an aluminum radiator and must be indicated in the accompanying passport for each product from the manufacturer.
Due to the design features, to fill an aluminum radiator it is necessary to use a smaller volume of coolant compared to a cast iron device of the same power.
This means that it requires less energy to heat it than its cast iron counterpart.
The temperature range for heating the coolant in aluminum batteries exceeds 100 degrees.
As a reference, a standard section of an aluminum radiator with a height of 350–1000 mm, a depth of 110–140 mm, with a wall thickness of 2 to 3 mm, has a coolant volume of 0.35–0.5 liters, and is capable of heating an area of 0.4– 0.6 square meters.
How much water is in one section of an aluminum radiator: methods for calculating volume
Nowadays, replacing old cast-iron batteries with new models has become not a tribute to fashion, but a vital necessity.
Concern for the safety of the heating system and attempts to reduce the cost of utilities have led to more and more consumers choosing aluminum radiators, which differ from other types of heaters in both technical characteristics and price. One of the important parameters is the volume of the heating radiator.
Calculation of the volume of an aluminum radiator
There are two ways to determine the capacity of a heating battery:
- Using calculations. To do this, you will need a table that indicates how much water can be held in an aluminum heating radiator. Such information must be present in the product documents or available from the seller. It indicates not only the center distance, but also the mass and volume of the device. For example, an aluminum radiator with a distance of 350 mm between the upper and lower manifold will require 0.19 liters of water for one section.
- The most universal way is to measure the volume of the radiator by filling it with water. To do this you will need:
- Place plugs on the lower holes and begin to draw water.
- When the liquid begins to pour out of the upper hole, a plug is placed on it.
- Pour water into the filler hole until the radiator is completely filled.
- Calculate how many liters of liquid were poured into the battery.
This, although a very labor-intensive method, is the most reliable and accurate, since manufacturers can overestimate or underestimate the parameters of their products in the technical documentation.
When choosing the type of radiator, you should pay attention to the difference in the parameters of domestic and foreign manufacturers. Some indicators may look very attractive, but are not suitable for the centralized Soviet heating system. You also need to think in advance which coolant in the network will be used, and make calculations indicating its viscosity.
To summarize, we can say that the volume of an aluminum radiator is an important parameter that must be taken into account in order for the system to work truly efficiently in the future.
Section volume and coolant flow
Today, not all autonomous heating systems are filled with water . This is due to two factors.
Section size
- A situation arises when the owners need to leave the house without heating for a long time, since due to a long absence there is no need to heat the premises.
- Water tends to freeze even at zero temperatures. When water freezes, it expands and turns into ice, that is, it changes from one physical state to another. During this process, the intermolecular bonds of water are released and changed, resulting in a huge force that breaks radiators and pipes made of any metal.
To prevent such situations from occurring, instead of water, another coolant is used to fill the heating system, which does not have the problem of freezing. These can be household antifreezes such as:
- ethylene glycol;
- saline solution;
- glycerin composition;
- food alcohol;
- petroleum oil.
Thanks to special additives that are introduced into these components, coolant compositions retain their state of aggregation in liquid form even at subzero temperatures.
Coolant calculation
Determining the volume of coolant flow required for an autonomous heating system requires accurate calculation. For a simple way to find out how much antifreeze is needed to fill the heating system, there are various calculation tables.
Water volume in one section
For basic calculations, you can use the information presented in thematic reference books:
- A standard aluminum battery section contains 0.45 liters of coolant.
- A linear meter of a 15 mm pipe contains 0.177 liters, and a pipe with a diameter of 32 mm contains 0.8 liters of coolant.
Information about the characteristics of the charging pump and expansion tank can be taken from the passport data of this equipment.
The total volume of the heating system will be equal to the total volume of all heating devices:
- radiators;
- pipelines;
- boiler heat exchanger;
- expansion tank.
The refined formula for the main calculation is adjusted taking into account the expansion coefficient of the coolant. For water it is 4%, for ethylene glycol ─ 4.4%.
What is the volume of water in an aluminum radiator?
In pursuit of performance and practicality, aluminum heating batteries for a private home or apartment appeared on the shelves of rafter stores and in the catalogs of global manufacturers.
Excellent thermal conductivity and heat transfer, along with lightness and attractive appearance, have earned aluminum radiators popularity and distribution.
However, you should take a closer look at these heat exchangers and understand the details, what are their strengths, and where are the obvious disadvantages, which should not be kept silent when choosing radiators for your heating system.
Types of aluminum radiators
In turn, aluminum heating radiators are divided into two types, depending on the technology used in their production:
Cast
To make them, all sections of the device are cast from a special alloy based on aluminum with the addition of silicon, which gives the material special strength under high pressure conditions. The individual parts of the radiator structure are connected to each other by welding in an inert gas environment.
Their strengths:
- Strength and tightness of connections, guaranteeing high quality and efficiency of products.
- Possibility of creating radiators of various lengths and power by changing the number of sections.
Flaws:
- High cost compared to extrusion-type radiators.
Extrusion
In the production of radiators of this type, parts are not cast, but extruded under high pressure conditions, and then pressed with upper and lower manifolds, manufactured by casting. In some cases, composite-type adhesive is used to mount individual parts of the battery, which makes these products even cheaper.
Their advantages:
- Slightly higher heat dissipation compared to molded batteries.
- Smaller volume of sections, due to which they require less coolant.
- Less weight of the radiator due to the small thickness of the fins.
- Low cost.
Flaws:
- Impossibility of repairing and disassembling the radiator.
- The likelihood of a leak occurring in the area where the collector connects to the section. This may be due to insufficient quality of the adhesive composition or wear of the rubber or Teflon sealing rings.
- The presence of crackling sounds arising from temperature differences during operation of the devices.
Helpful advice - when choosing aluminum radiators, it is better to opt for options made by casting. They have thicker walls and better withstand high operating pressure in the system.
If the light weight and cost of these products are of decisive importance when purchasing, then it makes sense to choose extruded aluminum heating radiators, the price per section of which is significantly lower than injection molded batteries.
How to calculate the volume of water in a heating radiator - basics and calculation rules
The efficient operation of the heating system depends on the correct selection of all its component elements, from the storage boiler to the circulation pump. In order to navigate this diversity, you need to make a correct calculation of the volume of water in the heating system, including in radiators.
In what cases is the coolant volume calculated?
The liquid in the water circuit of the heating system performs the most important function - it is a heat carrier. Many elements of the heating system are selected relative to the volume of coolant being distilled.
Therefore, preliminary calculations will allow you to complete the heat supply most efficiently.
It is easy to calculate the total volume of coolant, given that the amount of liquid in radiators is 10-12 percent of the total amount of liquid being distilled.
Calculation of water in the heating system must be done in the following cases:
- before installing heating, determine the amount of coolant that will be distilled by a boiler of a certain power;
- when non-freezing liquid is poured into the system, it is necessary to maintain a certain proportion in relation to the entire distilled liquid;
- the size of the expansion tank depends on the amount of coolant;
- you need to know the required volume of water in the heating system of country or private houses where the water supply is not centralized.
In addition, in order to properly mount the batteries on the wall, you need to know their weight. For example, just one section of a cast iron radiator, already heavy, holds 1.5 liters of liquid. That is, the seven-section cast-iron battery becomes more than ten kilograms heavier when the system starts.
What situations can be avoided if you correctly calculate the volume of coolant
Many people install a heating system, relying on the advice of experts, friends or their own intuition. Choose a more powerful boiler and increase the number of radiator sections “just in case.” But the result is the opposite picture: instead of the expected heat, the batteries do not warm up evenly, the boiler “winds” fuel idle.
You can avoid the following unpleasant situations if you know how to calculate the amount of water in the heating system:
- uneven heating of the water circuit in the rooms;
- increased fuel consumption;
- emergency situations (broken connections, leaks in radiators).
All these “surprises” are quite predictable if the volume of coolant is incorrectly calculated.
Attention! Antifreeze should not be used in a heating system that uses galvanized pipes or other elements.
What can you take from the documentation?
Technical data sheets for devices, if available, will help you find out how much water will circulate in the heating radiator and boiler during operation of the heating system.
If you need to choose a radiator based on coolant volume, you can compare different options:
- aluminum and bimetallic with a height of 300 and 500 mm hold 0.3 and 0.39 l/m, respectively;
- cast iron MS-140 with a height of 300 and 500 mm. holds 3 and 4 l/m respectively;
- an imported cast iron radiator with a height of 300 and 500 mm will include 0.5 and 0.6 l/m.
Thus, the volume of a bimetallic radiator is the same as that of an aluminum radiator.
Another “cheat sheet” will help when selecting cast iron radiators of different models (the amount of coolant per section is indicated):
- MS 140 – 1.11–1.45 l
- World Cup 1 – 0.66–0.9 l s;
- World Cup 2 – 0.7–0.95 l;
- World Cup 3 – 0.155–0.246 l;
As for pipes, the calculations are as follows.
Based on the internal diameter of the pipes, in the documentation you can find out the amount of liquid they contain per linear meter:
- 13.2 mm - 0.137 l;
- 16.4 mm - 0.216 l;
- 21.2 mm - 0.353 l;
- 26.6 mm - 0.556 l;
- 42 mm - 0.139 l;
- 50 mm - 0.876 l.
The calculations are simple. So, for example, a 5-meter pipe with an internal diameter of 50 mm will hold 4.4 liters of water: 5x0.876 = 4.4
Attention! If you compare how many liters of water are in heating radiators of different models, you can choose the appropriate option that matches the power of the boiler.
How to calculate the amount of coolant in radiators yourself
Sometimes you have to face a situation where it is impossible to determine whether radiators belong to a certain model. Documents for radiators may be lost, the model name is not visible. There is an easy way to find out how many liters are in a heating radiator without resorting to documentation or tables from the Internet.
Proceed as follows:
- close one side of the radiator with a plug;
- pour liquid to the top;
- pour the liquid into a measuring container.
Attention! There are two options for calculating the volume of water in a heating radiator: immediately note the amount of liquid poured in, or after draining it.
In this simple way you can calculate the amount of liquid that enters a radiator of any complexity or model.
Critical stage: calculating the capacity of the expansion tank
In order to have a clear idea of the displacement of the entire heating system, you need to know how much water is placed in the boiler heat exchanger.
You can take averages. So, on average, a wall-mounted heating boiler contains 3-6 liters of water, while a floor or parapet boiler contains 10-30 liters.
Now you can calculate the capacity of the expansion tank, which performs an important function. It compensates for the excess pressure that occurs when the coolant expands when heated.
Depending on the type of heating system, tanks are:
For small rooms, the open type is suitable, but in large two-story cottages, closed expansion joints (membrane) are increasingly being installed.
If the tank capacity is smaller than required, the valve will release pressure too often. In this case, you have to change it, or install an additional tank in parallel.
For the formula for calculating the capacity of the expansion tank, the following indicators are needed:
- V(c) is the volume of coolant in the system;
- K is the coefficient of water expansion (the value is taken as 1.04, based on the water expansion rate of 4%);
- D is the expansion efficiency of the tank, which is calculated by the formula: (Pmax – Pb)/(Pmax+1)=D, where Pmax is the maximum permissible pressure in the system, and Pb is the pre-pumping pressure of the compensator air chamber (parameters are indicated in the documentation for the tank );
- V(b) - expansion tank capacity.
So, (V(c) x K)/D = V(b)
Results
If you take into account the required volume of coolant when installing a heating system, then you can forget about cold pipes and radiators. Calculations are performed both empirically and using tables and indicators, which are given in the documentation for the structural elements of the system.
Coolant volumes will be needed for scheduled or emergency repairs.
Correct calculation
You also need to take into account the fact that the heat exchanger of the heating boiler also holds a certain amount of coolant. The heat exchanger of a wall-mounted heating boiler can hold from 3 to 6 liters of water, and floor heating devices can hold from 9 to 30 liters.
Having determined for certain the internal volume of all heating radiators, pipelines and heat exchanger, you can proceed to selecting an expansion tank. This element of the heating system is very important, since maintaining optimal pressure in the heating circuit depends on it.