XPS is an abbreviation that stands for extruded polystyrene foam (extruded polystyrene foam). In simple words, this is a thermal insulation material used in the construction of civil and industrial buildings. But what exactly is it, and what are the characteristic advantages and disadvantages of EPS? We provide detailed explanations in the description and technical characteristics, as well as recommendations on the appropriateness of application and selection for a specific case of insulation.
Characteristics
EPPS is manufactured in the same way as polystyrene foam - a lightweight foamed polymer that is produced in a vacuum under pressure. But ordinary polystyrene foam is easily deformed and broken, and crumbs can crumble when rubbed on your fingers. EPPS is produced using foam technology, but has greater plasticity and strength due to extrusion - pressing through diffusers - extruders. In Europe, the material is labeled with the abbreviation XPS.
In construction, the material is used in the form of:
- Slab.
- Canvases and substrates.
- Segments for pipe insulation.
- Elements of complex geometry.
| Name | Dimension | 31С | 31 | 35 | 45C | 45 |
| Density | kg/m³ | 28,0-30,5 | 25,0-30,5 | 28,0-37,0 | 35,0-40,0 | 38,1-45,0 |
| Compressive strength at 10% linear deformation, not less | MPa (kgf/cm²; t/m²) | 0,20 (2; 20) | 0,20 (2; 20) | 0,25 (2,5; 25) | 0,41 (4,1; 41) | 0,50 (5; 50) |
| Ultimate strength during static bending, not less | MPa | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,4 | 0,4 | 0,4-0,7 |
| Elastic modulus | MPa | 15 | 15 | 15 | 18 | 18 |
| Water absorption in 24 hours, no more | % by volume | 0,4 | 0,4 | 0,4 | 0,4 | 0,2 |
| Water absorption in 30 days | % by volume | 0,5 | 0,5 | 0,5 | 0,5 | 0,4 |
| Fire resistance category | group | G4 | G1 | G1 | G4 | G4 |
| Thermal conductivity coefficient at (25±5)°С | W/(m°K) | 0,030 | 0,030 | 0,030 | 0,030 | 0,030 |
| Calculated thermal conductivity coefficient under operating conditions “A“ | W/(m°K) | 0,031 | 0,031 | 0,031 | 0,031 | 0,031 |
| Calculated thermal conductivity coefficient under operating conditions “B” | 0,032 | 0,032 | 0,032 | 0,032 | 0,032 | |
| Heat absorption under conditions “A” (with a period of 24 hours) | 0,32 | 0,32 | 0,33 | 0,35 | 0,35 | |
| Heat absorption under conditions “B” (with a period of 24 hours) | 0,33 | 0,33 | 0,34 | 0,36 | 0,36 | |
| Vapor permeability coefficient | mg/(m h Pa) | 0,008 | 0,008 | 0,007 | 0,007 | 0,007 |
| Specific heat capacity, s | kJ/(kg °K) | 1,45 | 1,45 | 1,45 | 1,40 | 1,40 |
| Sound insulation of partition (GKL-PENOPLEX 50 mm-GKL), Rw | dB | 41 | 41 | 41 | — | — |
| Improvement index for structural noise insulation in floor construction | dB | 23 | 23 | 23 | — | — |
Technical characteristics of EPPS
Temperature range of application -50- +75 degrees.
The most popular form of release is polymer boards, which facilitate the installation of the heat-insulating layer. The range of slabs includes a large list of modifications: smooth, corrugated, thin-layer, thick, butt and overlap, as well as individual production.
Eps board size
Standard sizes of XPS boards:
- 600 x 1200 mm, thickness: 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 80, 100 (mm);
- 600 x 2400 mm, thickness: 40, 50, 60, 80, 100 (mm);
The service life of EPS (extruded polystyrene foam), according to manufacturers, ranges from 20 to 50 years. But in reality, depending on the place of application, the period is 15-20 years.
Difference from polystyrene foam

Extruded polystyrene is the same plastic, characterized by a more uniform structure, in which there are many closed cells - their size is about 0.1–0.2 mm.
As a result of mixing all the necessary components and passing them through the extruder, smooth, colorless or colored sheets are obtained. After complete drying, these materials can be used for their intended purpose.
Extruded polystyrene foam has quite a lot in common with polystyrene foam. These products have a similar chemical composition, the main component of which is polystyrene.
As for the functional component, there is no comparison between EPS and polystyrene foam. During production, foam does not pass through an extruder, but for expanded polystyrene this is a standard procedure.
In this case, extrusion gives this material a completely different transformation, and therefore completely different performance characteristics.
Production technology
EPS is produced using foam plastic manufacturing technology, but instead of vacuum pressing, extrusion is used - pressing under pressure into a mold through special diffuser holes. Passing through holes allows the mold to be filled with a polymer structure in a “suspended state.”
The production of EPS (XPS) is regulated by the interstate standard GOST 32310-2012 (EN 13164:2008) Thermal insulation products made from extruded polystyrene foam XPS, industrial production, used in construction.
Technological stages
Production is carried out in the following sequence:
- Polystyrene is crushed and granulated. Afterwards it is mixed with “additives” that increase elasticity. The entire mass is subject to melting.
- The molten mass is foamed with oxygen or CO2. In this case, the mass must be mixed.
- The foamed substance is fed under pressure into the extruder and extruded into the mold.
Advantages and disadvantages
All advantages are associated with the unique production technology of modified foam and polystyrene raw materials. The most characteristic advantage is the texture of the material - light and rich in airy pores.
Important! It is known that the best insulator of heat is atmospheric air.
In addition to textural advantages, EPS has the following positive properties:

Water absorption of XPS
- The material is completely inert to water, it flows over the surface and is not absorbed into the pores.
- The air in the pores provides thermal insulation properties.
- Not susceptible to rotting and mold.
- Durability. Since the material does not absorb moisture, the internal structure is not subject to deformation when moisture freezes and expands.
Important! Even if the surface of the slab is damaged, moisture will penetrate only into the damaged area without being absorbed further.
- Laying EPS boards will eliminate the need for additional vapor barrier installation. The extruded foam itself is capable of insulating vapor fumes.
- The plates are resistant to compression. The denser the slab, the greater the resistance.
- When heated, the pores do not expand.
- It has a small mass, which, even when installing large volumes, does not increase the load on the walls and foundation of the house.
- Ease of processing – easy cutting of slabs, adjustment and installation.
Flaws
The material is very often in demand due to the low cost of the slabs, but it also has some disadvantages:
- Inappropriate for use in insulating wooden walls. Moisture from steam condensation does not penetrate the insulating board, but remains on the surface of the wooden wall. The wall may become moldy and begin to rot.

EPS is very toxic when heated
- If the material is heated above 70 degrees, it begins to evaporate toxic substances into the atmosphere that are harmful to health.
Important! In order to stop harmful fumes, fire retardant additives and antifreeze are added to EPS.
Why is extruded polystyrene foam dangerous for human health?
- Styrene – 0.05%. This figure is tens of times less than what is allowed by sanitary standards for residential premises in the Russian Federation. At the same time, the maximum permissible concentration of styrene in the EU countries is at the level of 0.002 mg/m3. But, do not forget that styrene tends to accumulate in the body. It demonstrates a cumulative effect (concentration increases 600 times over 20 years). And styrene is released already at a temperature of 25°C.
- The damage to polystyrene foam when exposed to high temperatures is another important aspect. In this case, toxic substances are released: fumes of styrene, benzene , carbon monoxide , carbon dioxide and soot . In this case, the combustion temperature of styrene is 1100°C. At this temperature, even metal melts, which leads to the destruction of the building.
- Time is another indicator. The decomposition period of expanded polystyrene is more than a century. During intensive use (20-25 years), its harm to health increases. After all, during this time, about 60% of the decomposed styrene is released.
- Oxygen, upon interaction with which formaldehyde and benzaldehyde .
The main features of high-quality extruded polystyrene foam
The main parameters that indicate product quality are regulated by GOST 15588-2014. They can only be fully tested in laboratory conditions.
Meanwhile, some indicators, and, first of all, the structure, can be assessed independently. To do this, you need to cut a piece of slab with a sharp knife and carefully examine the cut.
High-quality material has a uniform fine-cell structure.
Non-compliance with the requirements of the standard is indicated by the presence of pores and cells that are visible to the naked eye. Such a stove will not last more than three years.
You can also check the strength properties without special equipment. It is enough to press your finger firmly on the sample.
If the material is defective, you will hear a cracking noise made by collapsing cells. High-quality material can easily withstand such a load without damage.
To assess the level of water absorption, two samples should be placed in water for a day. After this time, you need to place the products on a napkin and press on each of them. A puddle will form around defective polystyrene foam, while quality polystyrene will only slightly moisten the fabric.
Scope of application of EPPS

The most effective use of polystyrene boards is found in construction for the manufacture of thermal insulation. They are insulated with:
- Facades.
- Foundation.
- Floor and ceilings.
- Plinths and basements.
- Roofing.
The slabs are laid as an intermediate layer between the main wall and the sheathing for external decoration. There are models of slabs that have a textured surface - they themselves are fragments of external decoration.
Important! It is not advisable to decorate the inside of a house with polystyrene foam boards, since they are not permeable to steam. This means that moisture will not be removed from the premises - additional ventilation of the internal space will be required.

In addition to indoor walls, polystyrene boards are used for thermal insulation of any technological pipelines, wells, septic drains, cellars and greenhouses.
It is enough to simply wrap it around the rough surface or secure the slabs with various adhesives.
Criteria for choosing EPS
The basis for selecting XPS slabs is the choice according to their configuration and properties: weight, density, dimensions, filler properties.
Technical specifications
Density of expanded polystyrene . The higher the density, the stronger the texture of the slab. This property allowed the slabs to be used in the construction of road surfaces. The most common density value ranges from 20 to 43 kg/m3. The specific value is indicated on the product packaging, where recommendations for use are also given.
Important! A low density is relevant for use on the roof, and the highest value is advisable to use for laying thermal insulation in basements.
How to choose EPS?
The technological properties of a product are greatly influenced by its quality. In order to purchase products that meet all the necessary functional requirements, you must buy XPS only in certified stores, always in original packaging. Otherwise, the slabs may be saturated with toxic substances. Also, simple polystyrene foam can be sold under the guise of EPS.
Important! As already mentioned, EPS granules are much smaller than foam “balls”. In order to ensure that the product meets the quality and manufacturing parameters, you can break off a small corner from the slab or inspect any break point. If the granules are barely noticeable, then this is an extruded polypropylene board.
Manufacturers
We recommend purchasing products from the following manufacturers, as their products are proven for quality, reasonable prices and a huge range of types.
Knauf

Thermal insulation is available in three modifications: Compack - for universal use in construction, Wall - for walls only, Flor - for insulating floors and plinths, Roof Light - for laying an insulating layer of the roof and attic, 5 in 1 - for foundations and structures that are subject to weight loads.
Penoplex

Domestic insulator, which is marked for specific areas of application: walls, roofing, foundation. The Penoplex Comfort modification is used as slabs for universal use, and Penoplex 45 is used for slabs with an increased fracture limit.
Technoplex

The domestically produced TechnoNIKOL brand is characterized by the properties of strength and lightness. Scope of application: construction of structures, buildings and roads. The most popular are: Carbon Prof, Carbon Solid, Carbon Fas, Carbon Sand. They have high strength, thermal conductivity and plasticity, which is realized in the manufacture of sandwich panels, road surfaces, walls, foundations and roofs.
What it is?
Photo:

Today, the range of various finishing materials is so large that you can simply get lost in its richness.
Thus, one of the most popular coatings, which has many positive qualities, is extruded polystyrene.
This product is a special material of synthetic origin, which was first released in the USA in 1941. Currently, polystyrene is used for a variety of purposes.
It is this raw material that is used for thermal insulation of structures such as foundations and roofs. In addition, extruded polystyrene has good contact with facade plaster.
Installation features
In order to effectively use EPS for laying a thermal insulation layer, it is necessary to understand in detail the nuances of installation. Further specific recommendations will be given for each area of application.
On the floor

To insulate floors, EPS is used depending on what the surface of the subfloor is:
- Slabs of various types with a smooth surface do not require additional structures. To install XPS boards, simply lay them end-to-end for subsequent finishing.
- Installation on wooden logs or under parquet requires the manufacture of a special sheathing made of thin timber. In this case, the extrusion panels are secured with dowel-nails.
On the walls
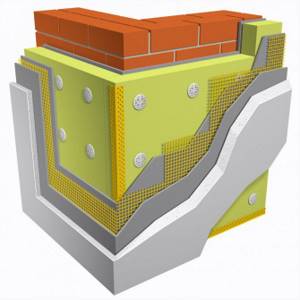
Stages of installation of EPS on walls:
- The first task should be to putty the walls with a solution on which the insulation itself will lie. The overlay layer should be dense and continuous. You can also take a special adhesive for installation, on which you can put a reinforced mesh.
- Expanded polystyrene sheets are mounted as closely as possible to each other. The resulting cracks are processed and filled with foam cuttings.
- Next, the glue is diluted as indicated on the manufacturer’s packaging. The resulting solution is applied in an even layer using a spatula with notches 8 cm wide. First, zigzag lines are made in the center, and then in the corners. The adhesive on the tile should occupy up to 40% of the area. Fastening the thermal insulation material In the strip that runs across the entire area of the tile, it is necessary to leave small gaps through which air will subsequently pass. After the glue is applied, you need to wait for it to dry for 10-15 minutes. During this period, the XPS board must already be installed.
- When all the plates are installed, and the fastening of the polystyrene foam to the wall is also completed, they are secured with special fasteners with mushroom caps. They are attached first in the center and in all corners. A total of 5 pieces per sheet of insulation. To insert a dowel into a sheet, you need to drill a hole in it using a drill. Our dowel is inserted into the finished hole.
- You need to add the reinforced mesh to the polystyrene foam layer when all the fasteners are installed and the adhesive layer has dried. Another layer of glue is placed on top of the reinforced mesh with a special roller to completely embed it inside. This is the final layer for insulation.
- When the glue dries, you can treat the surface with decorative plasters, primers, or level the layer.
- The last step will be painting it.
How can you attach EPS?
All slabs are attached to walls or sheathing using various types of fasteners. Sometimes special cells are made in the sheathing for laying slabs. But mainly the following two methods are used
Glue

For installation, you can use either a ready-made composition or prepare it yourself. Glue is sold in any hardware store and all manufacturers, in essence, produce products with the same properties.
The advantages of using glue are as follows:
- Installation is greatly simplified.
- Allows a tight fit to the concrete surface.
Flaws:
- Application is only suitable for insulating brick, stone and concrete slabs.
- Additional surface grinding is required before applying the composition.
Dowels
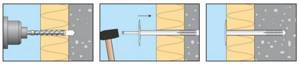
The use of dowels is possible for any surface. First, the surface is drilled and then attached to a dowel.
Such fasteners allow point installation in certain areas, for example, on thin laths. The main disadvantage is the wear of the slab, as well as possible loose fit and swelling of the slab.
Combined fastener
In order to avoid swelling of the slabs during installation, it is best to use a universal fastening method - the combined use of adhesive and dowels.
How to cut EPS
The texture of EPPS is divided into products with high and low density. Therefore, some modifications of insulation allow cutting only with a grinder. Products with low density can be processed using a clerical knife, but slabs with such a density are not used in industrial and civil construction.
How to cut EPS
For industrial cutting of EPS, special devices are used - electric torch knives, which cut the slab with a thin beam of electricity with a temperature above 100 degrees.
Important! This method can be used in private construction by periodically heating the cutting edge of a knife. This method is used for final forming of slabs.
Each method has its own advantages, but they all require increased attention and safety precautions.
Reflective type thermal insulation
Insulation materials, called reflective or reflective, work on the principle of slowing down the movement of heat. After all, every building material is capable of absorbing this heat and then radiating it. As is known, heat loss occurs mainly due to the exit of infrared rays from the building. They easily penetrate even materials with low thermal conductivity.
But there are other substances - their surface is capable of reflecting from 97 to 99 percent of the heat reaching it. These are, for example, silver, gold and polished aluminum without impurities. By taking one of these materials and constructing a thermal barrier using polyethylene film, you can get an excellent thermal insulator. Moreover, it will also serve as a vapor barrier. Therefore, it is ideal for insulating a bathhouse or sauna.
Today's reflective insulation is polished aluminum (one or two layers) plus polyethylene foam (one layer). This material is thin, but gives a tangible result. So, with a thickness of such insulation from 1 to 2.5 centimeters, the effect will be the same as when using a fibrous heat insulator from 10 to 27 centimeters thick. As an example, let's name Armofol, Ecofol, Porilex, Penofol.

One of the types of reflective thermal insulation.
So, we have listed all types of insulation and their characteristics. When choosing one of them, pay attention to the possibility of its complex use. It’s not bad if this material not only insulates your home, but also protects it from noise and gusts of wind.











