Builders widely use foam plastic for heat and sound insulation of private houses, apartments in multi-storey buildings, and large construction projects. They insulate facades, soundproof the walls and ceilings of apartments and houses from the inside, and simultaneously insulate them.
The editors of the StroyGuru portal decided to find out how effective it is to use polystyrene foam for insulation and sound insulation, how to choose the right insulation, what materials and tools are required when carrying out thermal insulation work.
Characteristics
It is difficult to find a person who, at the everyday level, would not come across foam plastic: light white sheets of polystyrene foam foamed using a non-press method (another name is polystyrene).
The material was first obtained in the middle of the twentieth century by polymerizing styropor with the simultaneous introduction of a foaming agent into the molten mixture. The result was a material consisting of 98% air chambers formed by thin polystyrene walls.
Gas, as is known, transfers heat only by convection, which is not the case in foam cells. And along the walls of the chambers, heat transfer is insignificant due to their small thickness. Therefore, the resulting material turned out to be an excellent insulation material.
To identify types of foam, sets of letters and numbers are used. The marking is as follows: PSB-S-25 F, where PSB indicates that this is pressless polystyrene, C is self-extinguishing, 25 is density in kg/m3, F is façade. Instead of the letter “F” or next to it there may be:
- A - regular geometric shape with a smooth edge;
- B - edge with an L-shaped cut;
- R - sheets were cut with a hot string;
- N - can be used for outdoor work.
Polystyrene with printed markings.
During the production process, it is possible to achieve different densities of foam plastic with different indicators of mechanical strength, rigidity, and resistance to various types of impact. Depending on the mass of the material per unit volume (kg/m3), the following grades of insulation are distinguished: PSB-15, PSB-25, PSB-35. Sometimes you can find PSB-50 on sale. But it is used mainly for installing permanent formwork in monolithic construction.
Having different densities, polystyrene foam has different physical and technical characteristics. For clarity, the main characteristics are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1. Main indicators of foam grades.
| Foam grade / Indicators | PSB-S-15 | PSB-S-25 | PSB-S-35 |
| Thermal conductivity, W/(m×°K) | 0.043 | 0.039 | 0.037 |
| Density, kg/m3 | 8,0-15,0 | 15,0-25,0 | 25,0-35,0 |
| Compressive strength, mPa | 0,04-0,05 | 0,08-0,10 | 0.16 |
| Bending resistance, mPa | 0,06-0,07 | 0.18 | 0.25 |
| Flammability class | G3 | G3 | G3 |
| Vapor permeability coefficient, mg/(m*h*Pa) | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| Self-extinguishing time after contact with an open flame, sec | 4 | 1 | 1 |
| Water absorption when immersed in water for 24 hours, % | 4 | 3 | 2 |
In terms of thickness, manufacturers offer sheets from 10 to 100 mm in increments of 10 mm. If necessary, it is possible to obtain foam insulation up to 500 mm thick at any production facility at the same price per 1 m3. The most popular thicknesses among buyers are 40 and 50 mm.
This is explained by the fact that a foam plastic board 5 cm thick has the same heat-saving properties as wood 27 cm thick, brickwork 75 cm thick, or a concrete wall 150 cm thick. This is enough to insulate housing in central Russia. For regions of the Far North, thicker insulation is needed - 10 cm.
There are two standards for length and width: 500 x 1000 and 1000 x 1000. Sometimes you can find a size of 1000 x 2000.
What if you use heated floors?
Recently, builders have begun to insulate building floors not only with cotton wool, but also with polystyrene foam. A foam block mounted on the floor will retain heat, it will become an excellent sound insulator, and will help reduce the sound of footsteps and the creaking of moving furniture, which is very important in multi-story construction.
To insulate floors, foam plastic with a thickness of 5 cm or more is used. Foam plastic sheets are mounted directly on the waterproofing. The resulting seams are sealed with sealant, and then a rough screed is applied to the floor.
Advantages and disadvantages
Polystyrene foam has both strengths and weaknesses. The advantages are obvious:
- low thermal conductivity - 0.037-0.041 W/(m K), comparable to mineral wool, which makes it possible to effectively insulate building structures made of brick, concrete, expanded clay concrete, gas silicate blocks, etc.;
- ability to maintain performance properties over a wide temperature range: from -50oC to +75oC (if there is no contact with an open flame, it begins to deteriorate at +160oC);
- low cost - refers to the budget type of materials;
- simple installation - there is no need to install the sheathing, as it is fixed with adhesive;
- does not require work experience or special tools when carrying out thermal insulation;
- low specific gravity - does not create a load on the structural elements of the building;
- does not serve as a base for the proliferation of mold and mildew;
- exhibits inertness to the components of cement-sand mortar, gypsum, and weak acids.
disadvantages , but consumers pay little attention to them. Among the disadvantages:
- flammability - class G3 (normally flammable). Clarification is necessary here: manufacturers claim that the insulation is self-extinguishing due to special additives - fire retardants, as indicated by the marking with the letter “C” (see photo above). However, this property is demonstrated during experiments only by products of well-known brands: Nova Chemicals, BASF, Polimeri Europa and Styrochem. Russian manufacturers also introduce fire retardants into the composition, but do not achieve a self-extinguishing effect: the products burn well;

The foam with the cladding is burning.
- release of toxic substances during combustion (hydrocyanic acid, phosgene, hydrogen bromide, etc.), as a result of which a person quickly loses consciousness and dies during a fire;
- transition to a fluid phase during the combustion process - spreads across the floor, increasing the area of the fire;
- release of styrene, which is harmful to health, when the temperature rises above +30oC;
Attention: is polystyrene foam harmful as insulation indoors? In the absence of extreme (high temperature) or force majeure circumstances (fire), foam insulation is absolutely harmless to humans, which cannot be said in the event of an emergency situation.
- short service life - 5-7 years, during which the original thermal conductivity values are maintained, although manufacturers claim the opposite, talking about 30 years or more. Laboratory tests, during which a foam plastic slab that had served for 9 years was removed from the wall, showed that due to destructive processes (the appearance of shells, cavities, increased density and decreased volume), the thermal conductivity coefficient increased almost 8 times;
- amplifies (resonates) indoor noise. Explanations are also needed here, since on the Internet, including Wikipedia, it is stated that polystyrene foam has good soundproofing properties. But this is a myth. The insulation has a closed cell structure and is light weight. Therefore, it cannot reflect sound waves - there is no mass and absorb noise - the material does not allow air to pass through. On the contrary, the high rigidity of the plate and low mass lead to the occurrence of resonance in the region of 500 Hz, i.e. in the very center of household noise;
- instability to most paint solvents - melts instantly;
- ages intensively under ultraviolet radiation (sun rays), which is intensely hushed up by manufacturers and sellers;
- lack of vapor permeability, although all reference books provide digital values that refute this statement. The problem is solved either by the correct choice of material thickness, which requires complex calculations, or by installing a ventilated facade and roof;
- low mechanical strength - easily damaged during transportation, installation and operation.

The foam was damaged by a falling branch.
Particular attention should be paid to the relationship between the insulation and mice - if they are found in the house, then first of all the damage will be caused to the foam plastic.

The mice did their best.
Basic properties of the material
The basic technical characteristics of insulation based on foamed polystyrene are as follows:

- low thermal conductivity in the range of 0.036 – 0.042 W/mK;
- ability to absorb and dampen sounds;
- chemical inertness;
- non-biodegradable;
- minimal thermal deformation and resistance to low temperatures;
- low permeability to air and water vapor.
Resistance to various influences
Styrene polymers have a stable structure, so they can withstand the effects of acids, alkalis, solvents and other aggressive environments. Polystyrene foam is no exception.

Its chemical inertness ensures the durability of the insulation regardless of operating conditions.
Foamed polystyrene is not subject to biological corrosion. The material does not contain a nutrient medium for microorganisms, therefore it does not rot or form mold on the surface.
Flaws
The main disadvantages of polystyrene foam include:
- high flammability of insulation;
- low strength of the material;
- the need for additional protection against rodents.

Despite its inedibility, polystyrene foam is often attacked by rodents, who use the thickness of the insulation to create their burrows and nests. Often mice and rats simply take away the material. Therefore, if you do not protect the insulation, then in a couple of years its layer will decrease significantly.
In addition, the material perfectly supports combustion, which significantly reduces the safety of the building.

Polystyrene foam as insulation is often subjected to additional protection by covering it on top with special plaster compositions based on mineral binders. This protection increases the fire resistance of the foam and prevents it from being damaged by rodents.
Which is better - polystyrene foam or polystyrene foam?
Among specialists and home craftsmen, disputes often arise about what is better to use for insulation: polystyrene foam or expanded polystyrene. Advanced portal visitors will say that these are one and the same. And they will be right. Indeed, from the point of view of a chemist, expanded polystyrene (aka styrofoam) is not only a classic representative of foam plastics, but also the founder of the class of foamed plastics.
At the household level, not everything is so simple, since expanded polystyrene is associated with materials such as Penoplex, TechnoNIKOL, Styrofoam, URSA, which in structure are almost indistinguishable from polystyrene foam, but are made from extruded polystyrene foam. It’s easy to figure out where the foam insulation is and where the extruded polystyrene foam is: the first is always white, the second is colored (painted). Moreover, each manufacturer uses its own color scheme: TechnoNIKOL (yellow), Penoplex (orange), Styrofoam (blue), etc.
When it comes to their performance characteristics, there are differences, but they are minor:
- Polystyrene foam has a higher thermal conductivity, which requires a thicker layer of thermal insulation. And this is the loss of usable area of the room when insulating from the inside;
- extruded polystyrene foam has higher strength and rigidity;
- polystyrene foam costs much less (approximately 2,000 rubles/m3 versus 4,500 rubles/m3).
Foundation thermal insulation
Insulating the foundation with polystyrene foam requires enhanced protection, since not only does soil pressure occur, but also the load on the foam plastic increases in winter during soil heaving, and this occurs during freezing. Strong reinforcement is required; for this, brickwork is done or concrete is poured.

Insulation of the foundation with polystyrene foam. Photo – plaforamaconstruye.com
Application area
Foam insulation can be found in various sectors of the national economy. They are used, for example, for thermal insulation of freezers, refrigerators, isothermal vans, etc. In construction they use for insulation:
- facades, which allows you to solve several problems at the same time: create effective thermal insulation of the building; protect walls from rain, wind, sunlight and temperature changes; remove the “dew point” from the thickness of the wall, preventing it from freezing (very important for brick and ceramics);
- floors - used for insulation using the “floating screed” method;
- roofs (roofs) - laid on the back side of the roof (“Ventilated roof”) and on top (“Non-ventilated roof”);
- foundations;
- ceiling (interfloor ceiling);
- walls from the inside of the premises, balconies, loggias, garages, workshops and other utility or utility rooms;
- pipelines.
Foam plastic is also increasingly used in the installation of permanent formwork during the construction of monolithic buildings.
Thermal insulation of engineering systems
Foam plastic has become very often used for thermal insulation of engineering systems. For example, for thermal insulation of water and sewer pipes during winter freezing, the use of polystyrene foam will be simply irreplaceable, as it will help to avoid the catastrophe of pipe breakage in the winter. Foam plastic is also used for thermal insulation of cold water supply pipes. Ventilation ducts, telephone lines and recessed ducts are also insulated with foam.
If you notice an error, a non-working video or link, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter .
0
Manufacturers and prices
Construction foam is produced in all regions of Russia, since it is very expensive to deliver outside the region or region. Therefore, there is no point in talking about specific supplier companies. Prices for 1 m3 vary within 1790 rubles. for PSB-S-15 insulation up to 3900 rubles. for PSB-S-50.
A number of foreign enterprises also supply their products to Russian markets. Some from their factories outside the Russian Federation, some from production facilities located in Russia. Among them:
- BASF is a German company with branches in Russia;
- Polimeri Europa (Dunastyr) (Italy);
- "Styrochem" (Finland), etc.
Prices for products from foreign companies are 10-85% higher with the same performance characteristics, with the exception of flammability. Imported polystyrene foam does not burn and goes out, but Russian foam does not burn.
Insulation technology
Any novice craftsman who is familiar with the basics of thermal insulation work can insulate a house with polystyrene foam. To work, you will need to purchase materials and assemble a set of tools.
Tools and materials
Consumables you need to buy:
- Styrofoam;
- cement or synthetic based adhesive;
- special mushrooms for attaching foam plastic, the length exceeding the thickness of the slabs by 4-5 cm - needed when insulating vertical and inclined surfaces;
- reinforcing mesh;
- polyurethane foam.
The toolkit includes:
- level;
- plumb line;
- roulette;
- a knife with a replaceable blade or a hacksaw;
- electric drill;
- glue container;
- mixer attachment for mixing glue.
A universal set of tools for all structural elements of the house. Technologies for insulating roofs, floors and walls from the outside and inside have their own nuances. Therefore, we will consider separately.
façade
Insulation of the wall outside the building is carried out in several steps.
Step 1. The wall is dust-free.
Step 2: Apply a layer of penetrating primer;
Step 3. At the junction of the wall with the foundation or at a height of 50 cm from the ground along the perimeter of the building, a profile for insulation is attached - it serves as a support for the bottom sheets of foam plastic.
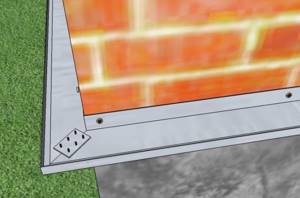
Scheme of fastening the profile to the wall and in the corners of the building.
Step 4. Mix the glue with a drill and mixer.
Step 5. The adhesive mixture is applied to the insulation boards. There are several methods of application: in a continuous layer, in 5 points (in the corners and in the middle), in stripes around the perimeter and in the center, in stripes or dots.

Glue is applied.
Step 6. The foam sheet is placed on the profile and then pressed against the wall surface. In the pressed position, you need to fix the insulation for a few seconds for the glue to set. Excess glue that appears is removed with a spatula.
Step 7. 2 rows of insulation are attached.

The next row is attached.
Step 8. Holes for fungi are drilled in the wall using a drill (perforator). There are five for each sheet: in the corners and in the center.
Step 9. Additional fastening of foam sheets to the wall is carried out. First, fungi are inserted into the holes, then they are fixed with plastic dowels.

Fungi are inserted into the holes.

The fungus is fixed with a dowel.
Step 10. Reinforcing mesh is glued.

The surface of the heat-insulating layer is reinforced with reinforcing mesh.
The further progress of work is determined by the type of finishing. Decorative plaster is applied to the reinforcing mesh. The sheathing is placed under the siding.
Paula
Floor insulation is carried out under the screed and along the joists. Thermal insulation under the screed is carried out in several stages:
- the base of the floor is being prepared. Full information about the technology for preparing the subfloor is given in the work “Preparing the floor for pouring screed”;
- waterproofing work is being carried out;
- Foam boards are laid tightly next to each other. Adjacent rows are mounted staggered, “staggered” - the transverse seams should not coincide. Here you need to pay attention to several points: the sheets are fixed with glue, there should be a technological gap of 1-2 cm between the wall and the insulation, the joints between the plates are glued with tape, the cracks are sealed with adhesive putty;

Floor insulation.
- the insulating layer is reinforced;
- the screed is poured.
The algorithm for floor insulation on joists is as follows:
- the floor base is being prepared;
- The subfloor is being waterproofed - details can be found in the material “Waterproofing a wooden floor”;
- logs are attached;
- foam is laid;
- the gaps between the joists and the insulation are foamed with polyurethane foam;
- the thermal insulation layer is covered with a vapor barrier film;
- plywood or OSB sheets are attached to the joists;
- finishing floor is installed.
Walls from the inside
You can insulate walls from the inside using 2 technologies:
- for glue for decorative plaster, painting or “liquid” wallpaper;
- using lathing, if the finishing is ceramic tiles or PVC panels.
Attention: builders have recently abandoned lathing altogether, replacing gypsum plaster with gypsum plaster for wallpaper and paint.
In the second case, the foam is glued to the wall between the vertical posts. The gaps between the insulation boards and the frame are foamed. On top of the insulation, sheets of plasterboard are attached under ceramic tiles or a counter-lattice is placed under PVC panels.
Roofs
The roof is insulated with foam plastic in 2 ways, depending on the type of roof.
- A horizontal (flat) roof is covered with insulation boards 7-10 cm thick on top, after which it is filled with bitumen and glued with two layers of roofing felt.
- The pitched roof is insulated from the rear side, in relation to the attic space. The slabs, 10 cm thick, are attached to the lathing, mounted on the flooring under the foam. Here it is important to properly perform a vapor barrier and create a ventilation gap between the roof and the insulation to avoid the formation of condensation.
Wall finishing with insulation
As soon as the leveling layer of plaster has dried, you can begin finishing the exterior of the house facade. Most often, decorative plaster, painting or siding are used for this purpose.

Financial possibilities play a role: it is easier to purchase an acrylic mixture, but a mineral one will cost more. All finishing mixtures can be purchased ready-made in containers of different sizes.

Plaster will protect the heat insulator from the negative influences of the street environment, at the same time giving the house a decorative, dignified appearance.
The nuance of finishing for siding
Siding can be installed at any time, but the vinyl version must still be installed at temperatures above -10°C - frost will make the material brittle and contribute to its breakage during installation work.
To install siding on insulation, you will first need to mount the sheathing on brick or stone, which will eliminate problems with uneven walls.

The insulation is installed on the frame, and a diffuse membrane and siding are laid on top of it, screwing it onto the sheathing.
Vertical siding must be mounted on a horizontal sheathing, and vice versa, horizontal siding must be mounted on a vertical one.











