Features of the heat insulator
The production of penoplex for wall insulation includes the following technological operations:
- Granules of the material are loaded into an extruder, where they are heated to 130-140°C;
- Foaming agents – porophores – are added to the portion;
- The thickened mass is squeezed out of the extruder onto a conveyor belt, after which it is cut into dimensional slabs;
The mixture of semi-finished penoplex for external wall insulation consists not only of polystyrene foam and foaming agents - it also contains antioxidants designed to prevent thermal oxidation during processing and damage to the integrity of the insulation during operation, fire retardants to increase fire resistance, as well as antistatic, light-stabilizing and modifying additives that protect thermal insulation material from the influence of external factors.
The main positive parameters of the material:
- Low moisture absorption of expanded polystyrene is the main advantage;
- The minimum coefficient of thermal conductivity, which allows, when calculating the thickness, to choose thin slabs;
- High vapor permeability of penoplex: a 20 mm thick slab replaces one layer of roofing material, but at the same time also insulates the working surface;
- High compressive strength and other mechanical loads. The extrusion method in the production of thermal insulation allows the cells of the material to be evenly distributed, improving the quality of density and strength;
- Easy and quick installation of insulation due to its low weight and good density;
- Long service life of extruded foam – up to 50 years;
- Excellent sound insulation and minimal chemical activity.
Features of penoplex
Penoplex size range:
- Slab length – from 120 to 240 cm;
- Slab width – 60 cm;
- Thickness – from 2.0 to 12.0 cm.
Disadvantages of extruded foam:
- Flammability of groups G3-G4, formation of toxic smoke during fire;
- Polymer additives in the composition of the material can evaporate toxic substances when exposed to sunlight. Therefore, the optimal use of penoplex is external, for example, insulation of brickwork;
- Petroleum products and some organic substances can deform penoplex, the thickness of which can be any. These are substances such as: formaldehyde and formalin, acetone and methyl ethyl ketone; liquids containing ethyl, benzene components, polyester resins, synthetic paints and fuels and lubricants.
Thermal conductivity properties determine the quality of insulation with penoplex. The higher the thermal conductivity coefficient, the fewer centimeters the layer of insulating material will be. Laying the insulator from the inside or outside depends on the characteristics of vapor permeability and strength (density). You can compare the parameters of popular materials for insulating floors and other surfaces by studying the data in the table:

Comparison of thermal insulators
From the table it is clear that foam plastic thermal insulation has an average thermal conductivity value, which is slightly less than that of polyurethane foam, mastics and roll materials. But you can choose penoplex only because the layer of such liquid insulation does not have joints and seams, like slab insulation, no matter how many layers are applied to the surface.
What is foam plastic
For the first time, the production of foamed organic substance styrene was established by the American concern BASF in 1951. The material called “styrofoam” consisted of 98% air filling the cells of the foam base, which gave it low thermal conductivity, water absorption and vapor permeability.

The technology was improved, and extruded polystyrene foam appeared - self-extinguishing foam. Also, the current insulation material contains antifungal additives.
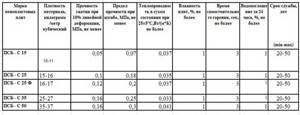
The quality and technical characteristics of foam plastics in Russia are declared by GOST 15588–2014 “Heat-insulating polystyrene foam boards. Technical conditions". Instead of the usual PSB markings and corresponding markings, the Russian Federation now has EPS markings, and expanded polystyrene itself is divided into cut (P), cut graphite-containing (RG) and thermoformed (T). Boards intended for use in insulating facades using plasters are additionally marked with the letter F.
According to this document, the technical characteristics of slabs for facade work are as follows:
| Indicator name | The value of the indicator for brand slabs | ||
| PPS16F R | PPS15F RG | PPS20 F RG | |
| Density, kg/mcub., not less | 16 | 15 | 20 |
| Compressive strength kPa | 100 | 70 | 100 |
| Bending strength, kPa, not less | 180 | 140 | 250 |
| Tensile strength kPa, not less | 100 | 100 | 150 |
| Thermal conductivity in dry condition, condition A, °C (283 K), W/(m×K), no more | 0,036 | 0,032 | 0,031 |
| Thermal conductivity in dry condition, condition B, °C (298 K), W/(m×K), no more | 0,038 | 0,034 | 0,033 |
| Humidity,% no more | 2,0 | 2 | 2 |
| Water absorption in 24 hours, % of volume, no more | 1,0 | 4 | 3 |
| Self-combustion time, s, no more | 1 | 1 | 1 |
PLEASE NOTE: façade insulation should only be done with slabs marked F.
Calculations
To achieve high-quality and effective heat retention and complete protection from the cold, you need to know how to calculate the thickness of the insulation. Such calculation of insulation thickness is carried out using existing formulas, which take into account:
- thermal conductivity;
- heat transfer resistance of the load-bearing wall;
- coefficient of thermal conductivity;
- coefficient of thermal homogeneity.
The listed characteristics are no less important at the moment when the foam thickness is calculated.
When determining the dimensions of the selected slab made from a particular material, it is worth considering that the thickness of each product allows the use of laying in 2 layers. After calculating the thermal insulation, you can be convinced that it is most convenient and profitable to use mineral wool slabs as insulation, and the thickness of such insulation should be from 10 to 14 cm.
Calculations are carried out using a specially created formula, and to obtain accurate data characterizing the heat insulator used, you need to take into account:
thermal conductivity coefficient of the load-bearing wall; if the wall is multi-layered, then it is important to take into account the thickness of its individual layer; thermal homogeneity coefficient; we are talking about the differences between brickwork and plaster; It is important to know the thickness of the load-bearing wall.
By multiplying the sum of all indicators by the thermal conductivity coefficient of the selected insulation, you can calculate the thickness of the heat insulator.
The choice of products sold on the construction market is based on these data.
It is equally important to decide on:
- where exactly the insulation will be placed; it can be the inner surface of the walls or the facade of the building;
- what material will be used as cladding; the façade of the building can be finished with facing bricks or decorative slabs;
- how many layers of thermal insulation will be used in the construction of the structure.
When choosing the thickness of the insulation, it is important to take into account the characteristics of the region in which the building is located. In the coldest regions, you will need material whose thickness reaches 14 cm, and in warm regions it is enough to install slabs 8-10 cm thick
The video shows the procedure for determining the thickness of the insulation:
Based on the results of the calculations, you can easily select the most suitable thermal insulation material, retain heat in the house and protect the walls of the building from destruction under the influence of negative, low temperatures.
Until the second half of the 20th century, few people were interested in environmental problems; only the energy crisis that broke out in the West in the 70s raised the question: how to save heat in the house without heating the street and without overpaying for energy.
There is a solution: insulating the walls, but how to determine what thickness of insulation for the walls should be so that the structure meets modern requirements for heat transfer resistance?
The effectiveness of insulation depends on the characteristics of the insulation and the method of insulation. There are several different methods that have their own advantages:
- Monolithic structure, can be made of wood or aerated concrete.
- A multilayer structure in which the insulation occupies an intermediate position between the outer and inner parts of the wall; in this case, at the construction stage, ring masonry is performed with simultaneous insulation.
- External insulation using a wet (plaster system) or dry (ventilated facade) method.
- Internal insulation, which is performed when it is impossible to insulate the wall from the outside for some reason.
To insulate already constructed and operating buildings, external insulation is used as the most effective way to reduce heat loss.
Application area
When insulating a house from the inside, it is necessary to increase the thermal insulation of the following structures:
- in the construction of the basement floor on the ground, if the underground floor is heated;
- in the floor pie of the first floor when installing a cold basement or underground;
- exterior walls;
- ceiling above the top floor when installing a cold attic;
- covering when installing a warm attic;
- attic roof.
Of all these parts, polystyrene foam for home insulation is best used in wall construction. In floors, foam plastic should only be used in conjunction with joists, which will take the main load from the floor, furniture, etc. The thing is that the density of polystyrene foam does not allow it to withstand high compressive loads.
Floors with foam plastic without joists can be used for technical purposes - attic floors, etc. Therefore, if you want to efficiently insulate the floor under the screed, the best insulation option is extruded polystyrene foam. The insulation on top should cover a layer of cement-sand screed 50 mm thick with additional reinforcement. For reinforcement, a mesh of reinforcement with a diameter of 3-4 mm is used.
Another area of application of foam plastic is the production of permanent formwork for concreting. This insulation is used in the construction of strip foundations. Allows you to reduce the number of stages of work on pouring a monolith at home and at the same time perform thermal insulation of the structure. Reliable waterproofing must be provided on top of polystyrene foam.
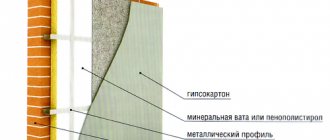
How to insulate aerated concrete, mineral wool or polystyrene foam
Mineral (stone) wool and polystyrene foam are the main insulation materials for aerated concrete houses. Low-density aerated concrete (D200) and sprayed polyurethane foam are used much less frequently.
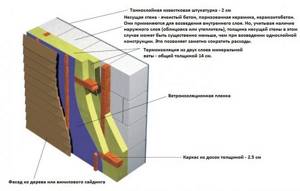
Insulation should be carried out only from the outside of the building so that the dew point is closer to the outer layer of the wall.
Dew point is a place in the wall with zero temperature. In this zone, a zone of increased condensation (moisture) is formed; the wall in this place constantly freezes and thaws.
If we compare polystyrene foam and mineral wool, then wool is a more expensive and correct solution for aerated concrete walls; it’s all about vapor permeability. Cotton wool has excellent vapor permeability, which ensures that moisture is removed from the wall to the outside of the house. Thus, the interior will be drier and more comfortable. The thickness of mineral wool insulation can be made to any thickness, but it is more economically feasible - from 100 mm.

Polystyrene foam does not allow steam to pass through well, trapping it in the wall and creating increased humidity in the house. Moreover, aerated concrete walls need to be insulated with foam plastic with a thickness of 100 mm or more in order to guarantee that the dew point will shift from the wall to the insulation. Otherwise, at the boundary between the foam plastic and the wall, moisture will constantly freeze and thaw, reducing the service life of the wall.

In general, we recommend using mineral wool or foam plastic with a thickness of 100 mm or more, but it is better to give preference to mineral wool.
Thermal insulation method
The effectiveness of insulation depends on the characteristics of the insulation and the method of insulation. There are several different methods that have their own advantages:
- Monolithic structure, can be made of wood or aerated concrete.
- A multilayer structure in which the insulation occupies an intermediate position between the outer and inner parts of the wall; in this case, at the construction stage, ring masonry is performed with simultaneous insulation.
- External insulation using a wet (plaster system) or dry (ventilated facade) method.
- Internal insulation, which is performed when it is impossible to insulate the wall from the outside for some reason.
To insulate already constructed and operating buildings, external insulation is used as the most effective way to reduce heat loss.
Foam density: which one to choose for external wall insulation
The article briefly and clearly describes what density of polystyrene foam is best suited for external wall insulation.
Important recommendation : read about the harm polystyrene foam can cause, and also visit the page where reviews of this material are collected from people who have already used it for their own purposes. You might be surprised.
So, earlier on the pages of Vyborstm.ru we talked about choosing the thickness of polystyrene foam for insulating walls outside. Today we’ll talk about choosing the density of foam.
As you know, today many people strive to make their home warmer, more comfortable, and insulated. And this is understandable - less money will be needed for heating in winter and for cooling air in summer.
In fact, there are many different insulation materials on the market that solve this problem. However, from an economic point of view and for some other reasons, many still prefer polystyrene foam.
And here the question arises:
Standard length, width and thickness of bricks
Since bricks have their own standard dimensions (6.5 x 12 x 25), the thickness of the brick wall will have several standard dimensions, taking into account the thickness of the seam between adjacent bricks.
There are other sizes, but they mainly differ in height, and the height of the brick does not affect the thickness of the wall.
Standard dimensions of a brick wall
| Number of bricks, pcs | Wall thickness, cm |
| 0,5 | 12 |
| 1 | 25 |
| 1,5 | 38 |
| 2 | 51 |
| 2,5 | 64 |
In addition to the thickness of 65 mm, there are brick thicknesses of 88 mm - one-and-a-half bricks and 138 mm - double bricks. Those. sizes 8.8x12x25 and 13.8x12x25. In general, the thickness (height) of the brick does not in any way affect the thickness of the brickwork.
The main criterion when choosing the thickness of a brick wall is the purpose and location of the wall itself.
Securely connect the insulation to the wall
Often foam plastic is attached only with glue, and this is enough, but I recommend additionally connecting the insulation to the wall using disc dowels. It definitely won’t be superfluous - it’s better to spend a little more time and money, but be sure that nothing will happen to the insulation.
Of course, the length of such dowels can be different, so for your case you need to calculate it, taking into account the thickness of the insulation, glue, spacer part of the dowel and another two to three cm “for reserve”. They can be attached directly to the block - in the corners and in the center, or at the seams. Both methods are effective.

The slabs can be additionally fixed using disc dowels
First I drilled holes for the dowels, then installed them using a drill. Sometimes these dowels simply become clogged, depending on which ones you purchased.
Then the insulation must be reinforced, otherwise the material may simply deteriorate and stop “working” as it should. You need to prepare a plaster-adhesive mixture, apply a thin layer, press the reinforcing wall and smooth it on top. It is better to start with windows and doors, and then “process” all the walls in parts. Additionally, I used a drip profile.
It is very important to take into account that if you have several pieces of mesh, they should be laid with an overlap of at least 10 cm.

Installation of reinforcing mesh
Then I leveled the surface and putty it. That's all! You can “decorate” the walls outside, but this deserves a separate post.

At the end the wall needs to be puttied
Calculate the thickness of the insulation
Thermal insulation of the outer wall reduces heat loss by two or more times. For a country, most of whose territory belongs to a continental and sharply continental climate with a long period of low negative temperatures, like Russia, thermal insulation of enclosing structures provides a huge economic effect.
Whether the thickness of the heat insulator for external walls is correctly calculated determines the durability of the structure and the microclimate in the room: if the thickness of the heat insulator is insufficient, the dew point is located inside the wall material or on its inner surface, which causes the formation of condensation, high humidity, and then the formation of mold and fungal infection.
The method for calculating the thickness of insulation is prescribed in the Code of Rules “SP 50. 13330. 2012 SNiP 23–02–2003. Thermal protection of buildings."
Factors influencing the calculation:
- Characteristics of the wall material - thickness, design, thermal conductivity, density.
- Climatic characteristics of the building area - the air temperature of the coldest five-day period.
- Characteristics of materials of additional layers (cladding or plaster of the inner surface of the wall).
The insulation layer that meets regulatory requirements is calculated using the formula:

In the “ventilated facade” insulation system, the thermal resistance of the curtain wall material and the ventilated gap is not taken into account in the calculation.
Preparing the wall surface
The wall surface must meet the following requirements:
- No loose plaster.
- No old paint.
- The surface of the wall should be stable and not crumble when you run your hand over it.
- The plane of the wall must be flat, the maximum difference is 1-2 cm. Deeper depressions must be plastered or sealed.
If necessary, the wall is plastered or coated with a deep penetration primer (if it is very crumbling).

Surface preparation
Example of calculating wall thickness
The thickness of the insulation of a frame house for permanent residence using the example of the Moscow region (this calculation was given above) was 150 mm when using mineral wool with a density of 50 kg/m3. Since most manufacturers produce this insulation in thicknesses of 50 and 100 mm, you will have to put insulation in either three layers of 50 mm thickness, or two layers of 100 and 50 mm. This will not change the thermal conductivity coefficient.
OSB with a thickness of 12 mm with an air gap of 50 mm and plaster of 5 mm was chosen as the external cladding.
The interior is lined with 13 mm plasterboard.
Total: 150 + 12 + 50 + 5 + 13 = 230 (mm).
Now, based on these data, you can now calculate the foundation, but you need to understand that this is just a mathematical calculation and it does not take into account problems that may arise during installation of the structure.
To make sure that there is no draft anywhere in the house, the structure is checked with a thermal imager
Working scheme for insulating walls with foam plastic from the outside
Compliance with technology when insulating walls with foam plastic is important, because inaccuracy in calculations, incorrect processing and installation sequence can lead to destruction of the heat-protective coating. The optimal scheme can be called the following:
- Preparatory work - leveling the surfaces on which the foam boards will be attached. Convexities and concavities can cause the material to break, so you need to pay attention to the walls. The maximum permissible size of irregularities is up to 1.5 cm.
- Cleaning the walls - all grease and rust stains, stains, paint and plaster residues are destroyed. If there are nails or remnants of reinforcement, they are ideally removed; if this is not possible, they are treated with an anti-corrosion compound. After this, the surface is primed.
- Installation of a metal strip (base profile) along the bottom of the walls - the first row of insulation boards is inserted into it. It is recommended to achieve maximum effect when insulating walls with foam plastic from the outside. It will not allow the insulation to move down under its weight and will serve as additional protection against rodents.
- External processing of insulation boards. Most sold foam boards have a smooth surface. They are pleasant to hold in your hands, but their adhesion to walls is poor. You can slightly disturb the structure of the surface - grooves are cut with a knife, holes are made with a needle roller or an iron brush. This ensures a stronger adhesion of the plates to each other and to the surface.
- Installation of sills and insulation of window slopes. It will protect the walls from rainwater and provide additional thermal insulation.
- Fixing foam boards. They are glued to the wall according to the following scheme: After drying, the sheets are additionally fixed with umbrella dowels. If the thickness of the foam is 50 mm, then the length of the umbrella will be 110 mm (50 mm + 10 mm + 50 mm), the hole for the dowel will be 130 mm (110 mm + 20 mm).
- Sealing gaps and seams. You can place strips of insulation in large gaps, and foam in small ones. All excess foam or material that stands out above the surface is cut off, and the joints are sealed with putty.
- Finishing the walls. There are no strict recommendations here. It all depends on personal preferences and the final cost of insulating the facade with foam plastic, which you go out and focus on. This could be siding, lining, decorative brick cladding, etc.
Penoplex thickness for insulation
Penoplex is a derivative of the extrusion of polystyrene foam, a higher quality type of foam, to which improvers are added when pressed through a mold. There are quite a few brands of penoplex, and the choice of a suitable material for insulating a house outside or inside depends not only on the properties of a particular class of penoplex - the functional purpose of the room, the thickness of the penoplex, installation parameters, and many other factors will play a role here. To navigate the properties of this insulation, you should study its characteristics.

Penoplex production
Classification of façade foam plastic by production method

Foam or expanded polystyrene (EPS) is a rigid insulating material produced in the form of slabs of various densities and thicknesses. The raw materials for its production are polystyrene granules, and the foaming agents are low-boiling hydrocarbons and gas-forming agents. When heated, the granules increase in volume by 10-30 times. Carbon dioxide, isopentane or other reagents foam polystyrene. As a result, in the finished product the polymer occupies only 2% of the volume, and the rest is occupied by gas.
According to the production method, PPP is divided into two types:
- Produced by the sintering method, when, when heated, the granules are sintered together with the simultaneous formation of the product.
- Obtained by foaming from a granular mass to which a gas-forming agent is added.
Various production methods make it possible to obtain a material similar in composition, but differing in structure (open or closed) and cell density.
How to calculate the thickness of insulation
- The required total thermal resistance (R) is 5.28.
- R of aerated concrete wall 400 mm from D500 – 2.6.
- R of the insulation should be: 5.28-2.6 = 2.68
Now you need to use a table that shows the thermal conductivity of insulation materials, in our case mineral wool.
AGB – autoclaved aerated concrete
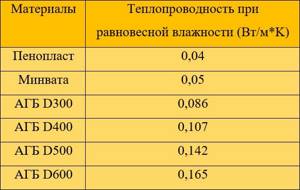
The thermal conductivity of mineral wool at equilibrium humidity is 0.05.
The thickness of the insulation is determined quite simply: the required thermal resistance of the insulation is multiplied by its thermal conductivity, that is
2.68 x 0.05 = 0.134 meters.
Conclusion: we need mineral wool with a thickness of 134 mm. But mineral wool slabs are sold in multiples of 50 mm, which means the insulation layer will be 150 mm.
Important! The economically justified thickness of mineral wool for wet facades is from 100 mm. Since when installing insulation (wet facade) it is necessary to use several layers of plaster, mesh, facade umbrellas, and other fasteners, there will not be much savings between insulation thicknesses of 50 and 100 mm
And the cost of work and consumables when installing insulation of different thicknesses is almost the same
Since when installing insulation (wet facade) it is necessary to use several layers of plaster, mesh, facade umbrellas, and other fasteners, there will not be much savings between insulation thicknesses of 50 and 100 mm. And the cost of work and consumables when installing insulation of different thicknesses is almost the same.

We also note that 100 mm of insulation, in 90% of cases, shifts the dew point from the wall to the insulation. That is, moisture will never freeze in the wall, therefore, the service life of such a wall will be almost endless.
How I insulated the corners of the house with polystyrene foam
With corners you have to “suffer” a little more - on one side the slab must protrude to the thickness of the same slab that will be installed on the other wall from the corner. Also on the second wall, foam plastic should be laid according to the “opposite” principle. If there is any excess slab left, you can simply cut it off. The sides must change, that is, first the slab “sticks out” first from one wall, then from the other, then again from the first, and so on. I specifically depicted this in the photo for better understanding.
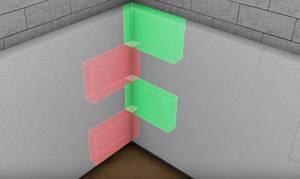
Corners are insulated according to this scheme
Very important! The part that protrudes should remain clean, that is, there is no need to apply glue to it.
If your angles are internal, then everything happens in a similar way. Of course, I marked everything out in advance - it’s better not to do anything by eye, because it’s easy to make a mistake.

We do not apply glue to the protruding part of the block.
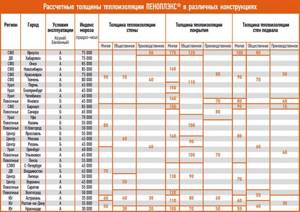
Characteristics of various materials
Table 1
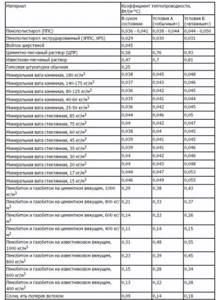
The value of the standardized heat transfer resistance of an external wall depends on the region of the Russian Federation in which the building is located.
table 2
The required layer of thermal insulation material is determined based on the following conditions:
- the external enclosing structure of the building is solid ceramic brick of plastic pressing with a thickness of 380 mm;
- interior finishing – plaster with cement-lime composition 20 mm thick;
- external finishing – a layer of polymer-cement plaster, layer thickness 0.8 cm;
- the coefficient of thermal homogeneity of the structure is 0.9;
- thermal conductivity coefficient of insulation - λA=0.040; λB=0.042.
What is penoplex
Heat loss through the walls of a building can range from ¼ to 1/3 of the total. Increasing thermal resistance due to the inclusion of special coatings in the design of external walls makes it possible to reduce its thickness and reduce the consumption of other building materials.
Wall insulation is necessary not only to prevent heat from escaping from the house in the cold season, but also to excessive heating of the room in the summer, so the correct choice of a heat insulator determines the financial costs not only during construction, but also during operation (heating, air conditioning).
Differences from other options
In the name of this insulation, you should pay attention to the word “extruded”, since a different production technology distinguishes it from ordinary polystyrene. The molten polymer is passed under high pressure through small nozzles, resulting in a dense foam board with a thickness of 20 to 100 mm as a result of solidification.
The molten polymer is passed under high pressure through small nozzles, resulting in a dense foam board with a thickness of 20 to 100 mm as a result of solidification.
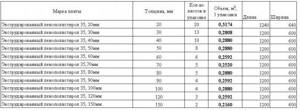
The technical characteristics of various brands of penoplex are presented in the summary table:
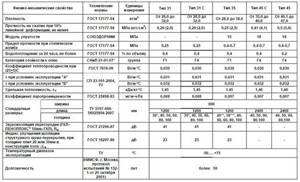
Of the presented types, only 45 are used for making road surfaces, the rest are used for insulating residential buildings.
Meaning of indicators
The fine-porous structure of penoplex (100 - 200 microns) makes it a fairly light but durable material. Its characteristic qualities are:
- resistance to mechanical loads (when laid on a flat surface);
- low vapor permeability (thickness 20 mm is comparable to 1 layer of roofing felt);
- moisture resistance allows use on the outside of walls, in bathhouses, bathrooms, basement levels without heating;
- the insignificant coefficient of thermal conductivity expands the possibilities of use in thin partitions created with your own hands: balcony railings, veranda walls, extensions or garages;
- low weight does not lead to a significant increase in the load on the base when covering already designed structures (insulation of individual apartments in a multi-storey building);
- the density of the polymer allows the use of conventional cutting tools to adjust sheets to size when performing work;
- chemical resistance to most compounds used in construction (exceptions: gasoline, diesel fuel, acetone, enamels, oil paints, formaldehyde, acetate-based solvents). For more information about the qualities of the material, watch this video:
What to compare with
The listed characteristics classify penoplex among modern achievements in the line of traditional insulation and polymer counterparts.
The ratio of technical characteristics can be seen in the reference tables of materials:
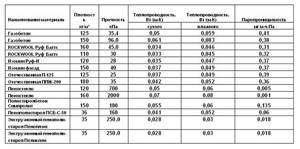
Types of polystyrene foam for home insulation

To understand what kind of polystyrene foam is needed for specific types of work, it is worth carefully studying the types of material. Classification of heat insulators for walls and floors of a house is carried out according to the following criteria:
- raw materials for manufacturing;
- density;
- sizes.
Depending on the raw materials used, there are such types of foam as polyurethane, polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and polyethylene. The first has high elasticity and is a foam rubber that is actively used in the furniture industry. In construction, polyurethane foam is made from such foam.
Polyethylene foam is produced in the form of sheets and is used for packaging fragile items. The usual construction foam is PVC. Expanded polystyrene of this type is suitable as insulation for a house inside and out.
The density of the foam is an important indicator. The area of use of the material depends on it (whether it can be used in the construction of walls, floors, foundations, etc.). Before buying foam insulation for your home, it is better to familiarize yourself with what it is, depending on the feature in question:
- PSB 50 is a high-density material. It is rarely found in construction due to the desire of customers to reduce financial costs. This material is suitable as insulation from the outside and from the inside. Such material can be laid as part of the floor of premises with constant occupancy of people, furniture and equipment.
- PSB 35 is suitable for insulating the walls of a house from the outside and inside. This type of insulation can also be laid in the attic floor pie, provided there is a strong concrete screed. The density of expanded polystyrene 35 is the most common.
- PSB 25. The density of the material allows it to be used as wall insulation on the room side. When laying, it is necessary to ensure a gap between the heat insulator and the finishing material. It is strongly not recommended to use it for floors and external insulation.
- PSB 15 is the minimum density used in construction. This type is best suited for thermal insulation of temporary structures (for example, cabins), containers and wagons.
The sizes of foam sheets are typical. If necessary, it is easy to cut the required shape from the material. Dimensions are determined depending on the area of the insulated surface, its length and height.
The following sizes are sold on the construction market:
- 2000x1000 mm.
- 1000x1000 mm;
- 1000x500 mm.
The most common sizes are 1000x1000 mm. Such sheets will not cause problems during transportation, at the same time they have a fairly large area and allow you to increase the speed of work. The standard size 1200x600 mm is also very popular - it fits perfectly with the spacing of racks or sheathing for external insulation.
Dimensions of foam boards
Variety and features of insulation
Modern manufacturers offer a wide range of materials used as insulation and meeting all existing requirements and standards:
- Styrofoam;
- basalt or stone mineral wool;
- penoplex;
Before making your final choice, you need to familiarize yourself in detail with the features and advantages of each of them. Having studied the technical characteristics of various materials, we can safely say that the leaders in their main qualities are slabs of mineral wool or basalt insulation, as well as slabs for wall insulation.
The basis for the choice is data on the thermal conductivity, thickness and density of each material:
- stone wool - from 130 to 145 kg/m³;
- expanded polystyrene - from 15 to 25 kg/m³;
- penoplex - from 25 to 35 kg/m³.
The density of basalt wool reaches 100 kg/m³, which makes basalt insulation one of the most popular and popular. This does not mean that consumers should abandon the use of mineral wool as an insulating material used during finishing work before facing the façade walls of a building made of brick.
Thermal insulation material is selected based on the most significant characteristics of each. Having decided to choose polystyrene foam as a reliable and effective heat insulator, it is necessary to clarify the dimensions of the slab, its density, weight, vapor permeability, and resistance to moisture. Despite many positive qualities, this wall insulation also has some negative features:
- susceptible to destruction by rodents;
- high degree of flammability.
This forces consumers to select other materials, among which mineral wool is the most popular for wall insulation. It is characterized by high density, low weight, and low thermal conductivity. Its vapor permeability allows you to ensure a normal level of humidity. In addition, mineral wool is one of the fire-resistant materials.
Extruded polystyrene foam is in demand among consumers. These plates are characterized by a high degree of resistance to mechanical damage. EPS is not susceptible to rotting, the formation of fungus and mold, and is resistant to moisture. It is used to insulate the basement and load-bearing walls. In the latter case, slabs are installed whose density is 35 kg/m³.
Main brands of foam plastic
After foaming the polystyrene, the raw materials for the finished products are loaded into a container. Steam is injected into it under pressure. The granules foam and become saturated with air. At the next stage, the finished granules are dried from moisture; hot air is used for this.

When drying, the granules are shaken periodically. The finished granules are placed in bins that are calibrated according to foam grades. Molding occurs under pressure. When molding, the following types of foam are obtained, which differ in density:
- PSB-S-15;
- PSB-S-25;
- PSB-S-35;
- PSB-S-50.
The last number in the marking determines the density of the foam for insulation. Many developers do not know what the specific gravity of foam is. Density (specific gravity) is the mass of a product in its volume. The density of polystyrene grade PSB-S-15 is 15 kg/m³. Accordingly, one cubic meter of PSB-S-15 polystyrene boards weighs 15 kg.

The question arises of how to independently determine the density of foam plastic without special equipment. This is easy to do: you need to calculate the cubic capacity of the finished product and weigh it on the scales. To make a claim, the store must have in hand a state verification certificate of the scales. Weighing can be carried out directly in the store or at the construction warehouse of the materials supplier. This technical calculation of foam density will be the most optimal.
Frame house projects
- 1 room
- 1 bathroom
- 42² Total area
- 6 x 7m Construction area
- 1 room
- 1 bathroom
- 28² Total area
- 5 x 4m Building area
- 4 rooms
- 2 bathrooms
- 170² Total area
- 11 x 8m Construction area
- 3 rooms
- 2 bathrooms
- 127² Total area
- 10 x 7m Construction area
- 4 rooms
- 2 bathrooms
- 200² Total area
- 9 x 13m Construction area
- 4 rooms
- 2 bathrooms
- 140² Total area
- 12 x 9m Construction area
- 3 rooms
- 2 bathrooms
- 127² Total area
- 9 x 8m Construction area
- 4 rooms
- 2 bathrooms
- 130² Total area
- 10 x 10m Construction area
- 3 rooms
- 1 bathroom
- 83² Total area
- 10 x 9m Construction area
- 1 room
- 1 bathroom
- 30² Total area
- 7 x 6m Building area
- 3 rooms
- 2 bathrooms
- 156² Total area
- 11 x 9m Construction area
- 4 rooms
- 2 bathrooms
- 140² Total area
- 8 x 9m Construction area
- 4 rooms
- 2 bathrooms
- 120² Total area
- 8 x 10m Construction area
- 1 room
- 1 bathroom
- 35² Total area
- 5 x 9m Construction area
- 2 rooms
- 1 bathroom
- 42² Total area
- 6 x 9m Construction area
- 2 rooms
- 1 bathroom
- 72² Total area
- 12 x 6m Construction area
- 2 rooms
- 1 bathroom
- 74² Total area
- 7 x 6m Building area
- 3 rooms
- 1 bathroom
- 110² Total area
- 13 x 9m Construction area
- 3 rooms
- 1 bathroom
- 75² Total area
- 9 x 7m Construction area
- 1 room
- 1 bathroom
- 45² Total area
- 6 x 9m Construction area
At a fairly low price, the quality of materials used in frame housing construction is growing every year. It is not surprising that this type of building is becoming increasingly widespread in all regions of Russia. And depending on the climate zone, the same project will have different requirements for heat conservation, therefore, what the thickness of the walls of a frame house should be must be determined in each case separately.
There are several subtypes of frame technology - if the general principle of building houses is the same, then the nuances, including the thickness of the walls, may differ
Foam plastic - advantages and disadvantages

Polystyrene foam is a leader among insulating materials, combining the most successful qualities:
- Low thermal conductivity . Polystyrene foam consists of 98% air and only 2% polystyrene, so its heat-saving qualities are very high.
- Light weight . Among all materials, foam is the lightest; it does not create unnecessary loads on the walls.
- No consequences from the action of water . The material consists of many sealed granules filled with gas bubbles into which water simply cannot penetrate.
- Sufficient rigidity . The foam sheet is convenient for installation, it does not bend and holds its shape well, and is easy to cut.
- Convenient format and sheet thickness . Standard sheet sizes have convenient linear dimensions and thickness, allowing you to use the optimal option.
- Good adhesion - adhesion of the foam surface to primers or compositions for plastering walls.
- Fire safety . Manufacturers claim that ball foam does not burn at all. This is not entirely true, it burns, but its ignition temperature is twice as high as, for example, that of wood. Therefore, it cannot be a source of danger.
- The price of polystyrene foam is the lowest of all types of insulation.

Difference in thickness with the same thermal insulation
Such properties characterize the material from a very positive side.
However, there are also disadvantages:
- Polystyrene foam does not tolerate contact with solvents such as acetone or gasoline.
- The fragility of the material is quite high; it crumbles when cut and does not allow bending.
- Foam boards are impermeable to air, unlike mineral wool.
- There is a possibility of rodents living in the thickness of the material.
All shortcomings can be compensated in a certain way if you know about their existence and take the necessary measures.
What materials are used for insulation?
Mineral wool is one of the most common insulation materials, which is characterized by good thermal insulation, but has a significant drawback: high moisture absorption. In this case, it is recommended to protect the wool with hydro- and vapor barrier.
Fiberglass is a good heat insulator. The material is resistant to high temperatures and does not rot. Mineral wool can be used not only for insulating the external walls of a brick house, but also for thermal insulation of a chimney in a boiler room or bathhouse.
Cellulose wool is used mostly for interior work. The material has good characteristics, with the exception of a high degree of moisture absorption and low resistance to mechanical loads. Note that this heat insulator is environmentally friendly.
A good option for insulating brick walls from the outside or inside is polyurethane foam, which is characterized by resistance to mold and is not susceptible to rotting. The material can be used without any problems when insulating a brick house with your own hands.
Insulation such as expanded polystyrene (foam plastic), which is characterized by low cost and high thermal insulation, is also widely used. It is necessary to take into account that the material does not absorb moisture, but is also highly flammable. It is not recommended to use it in residential buildings; however, internal insulation of brick walls is often carried out using polystyrene foam.
Extruded polystyrene foam has similar characteristics. Among the positive features, it is worth highlighting the low vapor permeability and high strength index. The characteristics of the material are maintained even at high humidity levels. It can be used not only for insulating a brick house from the inside or outside, but also in the construction of an insulated blind area, since this design has a longer service life.
Insulation technology
Once it has been decided what material is required to complete the work, it is important to familiarize yourself with the nuances of the technology for carrying out the work. When fastening, it is necessary to take into account such thermal insulation features as:
- low strength;
- destruction when exposed to moisture and cold (high-quality waterproofing and vapor barrier will be required);
- instability to fire;
- low vapor permeability, creating a greenhouse effect in the house (a forced ventilation device is required).
The material can be attached from the cold air side or from the inside. Insulation with foam plastic from the outside will be more effective. Insulation of walls with foam plastic from the inside can only be done if there is justification (it is not possible to disassemble the finishing of a house, insulation of one apartment in an apartment building).
Why is it necessary to calculate the thickness of insulation?
Comfortable living in the house involves maintaining optimal indoor temperature, especially in winter. When constructing a building, you should remember about thermal insulation; you should correctly select and calculate the thickness of insulation for the walls, roof, floor and attic. Any material - brick, wood, foam block or mineral wool - has its own value of thermal conductivity and thermal resistance.
A warm home is every owner’s dream
Thermal conductivity is the ability of a material to conduct heat. This value is determined in laboratory conditions, and the obtained data is provided by the manufacturer on the packaging or. Thermal resistance of a material is the reciprocal value of thermal conductivity. A material that conducts heat well has low heat resistance and requires insulation.
When constructing a building, you should remember about high-quality thermal insulation. If mistakes were made in the walls of the house or in other structures during construction, then cold bridges may appear - areas through which heat quickly escapes from the house. In these places, condensation may appear, and subsequently the formation of mold, if insulation measures are not taken during the process.