It is believed that a well-planned stove can solve most of the problems associated with heating and supplying the required amount of boiling water to the steam room and sink. This is in theory. In practice, the amount of heat emitted by the walls of a classic brick or cast iron firebox is not enough to warm up the entire bathhouse. For a small bathhouse there is still enough heat; for buildings with a normal steam room, sink and rest room, one brick stove is not enough. Therefore, it is better not to build at random, but to immediately plan a stove for a bath with a water circuit. And the heating will be soft, and the bathhouse will dry from accumulated moisture in a matter of hours.
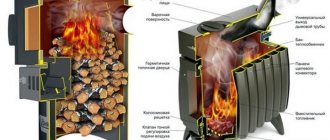
Classic sauna stove with built-in water circuit
How does the water circuit work in a sauna stove?
There is nothing new in using an additional heat sink embedded in the structure of a heater or brick stove. With the help of a homemade cast-iron, or less often copper, samovar tank, the most savvy bathhouse attendants managed to get boiling water back in the century before last. Since then, the principle of the built-in water circuit has not changed at all, the technology has become more advanced, and it has become possible to make a sauna stove with a heating circuit, both efficiently and safely.
In a modern bathhouse, two types of water circuit construction are used:
- Direct heat extraction from the furnace using a built-in heat exchanger. Most often this is a twisted pipe, a disk tank or a register system in the form of a grill made of heat-resistant stainless steel. Water is often supplied to the inlet by gravity from a tank suspended above the stove at least 1-1.5 m. The output is boiling water, which is sent through pipes to the sink or to the bathhouse heating system;
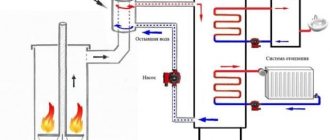
- Double-circuit furnace diagram. Heat is taken from combustion products, as in the case of the direct scheme, but hot boiling water is not supplied to the heating system or to a tank with a tap, but accumulates and circulates in an intermediate boiler-tank.
With the help of additional heat exchangers built into the tank, it is possible to pump, heat and send slightly colder, but still hot water to the heating system of the bathhouse or to its washing compartment.
Direct flow heating system
The first or direct heating scheme is used in low-power metal furnaces; due to the absence of an intermediate tank, the bath heating system is more economical. But in this case, you have to use steel heating pipes, aluminum or cast iron radiators. There can be no talk of any built-in water-heated floor in the bathhouse.
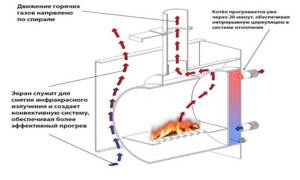
Oven with flat built-in water circuit

Diaphragm tank
Due to the difficulties that arise with adjusting the degree of water heating, subheated water or boiling water may enter the heating system. And the greater the power of the stove in the bathhouse, the more difficult it is to ensure the stability of its operation. You can get burns, but the main thing is that a sauna stove with a direct heating water circuit can easily fail if the movement of water through the pipes suddenly stops or the flow stops. Perhaps there will be no explosion, but the stove in the bathhouse will completely fail.
Advantages of dual-circuit heat extraction
For a heating system with a double circuit for heat selection and distribution, the problems listed above do not exist. In principle, there are no restrictions on power and pipe layout; you can create a warm floor, a heated pool, and there will still be energy left to dry the room after the stove has been extinguished. Moreover, a bath boiler with a double-acting water circuit is often used as the main heat source for heating a residential building built nearby.
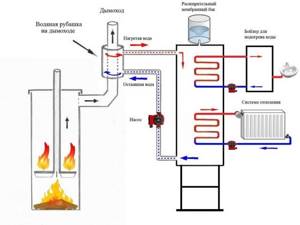
Double water furnace
The main advantages of a dual-circuit system are as follows:
- Water moves through the first hot circuit at a constant speed. The coolant is pumped by a circulation pump, so the heat exchanger inside the firebox and the furnace itself do not experience thermal and hydraulic shocks, which means they will last much longer than with a direct-flow scheme;
- Due to the high flow rate, it is possible to remove 5-6 times more energy from the heat exchanger. A huge tank of water will store boiling water for 6-12 hours after the stove in the bathhouse has been extinguished;
- Instead of water, you can and should use synthetic coolants specially designed for use in double-circuit heating systems. You can take car antifreeze, but its service life will be limited to one or two years.
Important! Using synthetics instead of water significantly increases the life of the circulation pump. If with purified water the service life is on average 5 years, then with a special brand of antifreeze it is 15 years.
Another advantage is that such a bath heating system can be left over the winter without draining the coolant. In addition, the collector system, couplings and pipe distribution do not rot or corrode, as is often the case when using water.
Installation requirements
The thickness of the water layer in the heat exchanger should exceed 4 cm, since with a smaller thickness the water will boil.
The walls of the coil must be at least 5 mm, and if coal is used, even thicker. Failure to comply with the thickness can lead to burning of the walls.

Furnace construction process
Under no circumstances should the heat exchanger be mounted close to the firebox wall. Leave at least 2 cm. This space is necessary for thermal expansion of the coil.
Particular attention must be paid to the fire safety of the system. There must certainly be air gaps between the stove and the wooden partitions, since overheating of wooden structures is the first cause of fires
It is best to line it with brick or other fire-resistant materials.
Heating a bath using water circuits
Before planning the heating of a room using a sauna stove with a water circuit, it is necessary to correctly select the main components and parts of the system. The efficiency of heating a bath largely depends on how well the main element was chosen - the main hot heat exchanger. After installation on the stove in the bathhouse, replacing or redoing it will be expensive and difficult. The remaining elements of the double-circuit heating system can be changed, modified, repaired and improved without restrictions.
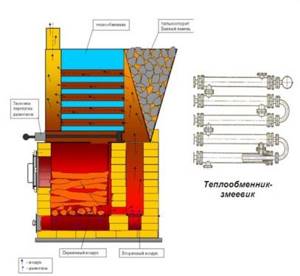
Option for a water circuit built into the oven - a coil
Heat exchanger
There are three ways to extract heat:
- A mounting tank mounted on one of the walls of the furnace;
- A radiator or twisted heat exchanger built into the furnace firebox;
- Use a tank or spiral radiator installed on the sauna chimney.
A hinged or mounted tank can also be used for heating the interior of a bathhouse, but very small ones, for example, to heat the sink or changing room of a small bathhouse. A huge disadvantage of a built-in tank as a heat exchanger is that heat enters the water through two walls - the lining inside the firebox and the wall of the tank itself. As a result, the heat flow is quite weak. The external temperature of the furnace wall is 150-160°C, so the water heats up very slowly.
The most effective is considered to be a heat exchanger mounted into the wall of the firebox. High temperatures provide at least 6-8 kW/h of thermal energy. This means that a 100 liter boiler, through which water circulates in the primary circuit, will heat up to the required 80°C in 20-25 minutes. The only disadvantage of such a heat exchanger is that it is not easy to make with your own hands. Most often this is a pipe or flat tank made of stainless steel with welded fittings. The heat exchanger is difficult to repair and maintain in a bathhouse, especially if it is a homemade device. The best option would be to purchase a ready-made factory-made membrane tank.
It is quite possible to make the third type of heat exchangers for heating a bathhouse with your own hands. Most often, for a double-circuit sauna stove, the same coil is used, but from a copper pipe. If the power of the stove is large enough, then instead of a spiral water circuit, you can use the classic version of a coaxial tank mounted on the chimney of the bathhouse.
Copper coil installed on a metal chimney
Heat exchangers and water circuits built into a brick chimney can work just as well. The only negative is that heat can be removed for the bathhouse heating system no earlier than the chimney has warmed up. Otherwise, there will be no draft, and it will take a very long time to heat the bathhouse.
Pipes and radiators
Ideally, a bathhouse heating system should be built from four units, each of which has a different heat load. The main stove of the bathhouse, installed in the steam room. A primary circuit with a heat exchanger, steel pipes and a circulation pump is mounted inside the firebox or on the chimney. Pipes must be metal. It is allowed to supply and drain water to the heat exchanger of the furnace using plastic and metal-plastic, but no closer than 120 cm to the hot surface.
A boiler, a heat exchanger mounted in it and water supply pipes to the washing compartment. Water supply and heating can be carried out either by gravity or by an additional circulation pump. The heat exchanger material is copper, pipes are made of heat-resistant polypropylene.
For the heating system of the bathhouse, another secondary circuit is allocated. It includes:
- Copper heat exchanger built into the boiler. The pipe diameter is usually twice as large as for the hot water supply circuit for a sink;
- Heating system using wall-mounted aluminum radiators. Pipes with a cross-section of ½ inch made of heat-resistant polypropylene with foil reinforcement;
- Distribution manifold with fittings for connecting plastic polyethylene pipes built into the heated floor.
In addition to the above, a circuit with a built-in flow-through electric heater can be connected to the water heating system of the bath. This scheme is used in heating winter saunas and baths located in areas with severe frosts.
Important! The electric heater built into the heating circuit very quickly warms up the air in the bathhouse at the initial stage. This creates minimal comfortable conditions, and most importantly, warm air ensures stable draft in the chimney and reliable ignition of the furnace firebox.
Water floor
The heating floor base made of pipes is no different in its design from the classic water floor used in apartments and residential buildings. In the relaxation room and steam room, plastic pipes are laid in a spiral; in the sink and locker room, the layout of the heating water circuit can be simplified to several parallel threads.
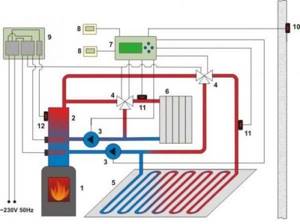
Due to the specifics of the design and operation of the sauna, it is not recommended to build the heating of the bath only on the basis of a heated floor. It is extremely important to include several, at least two, wall-mounted radiators in the water circuit. One of which should be located in the washing compartment, and another one in the rest room. By manually adjusting the water flow through the wall radiators using a tap, it is possible to select the optimal temperature regime for the main rooms of the bathhouse. You can, of course, install an automatic electronic thermostat, but such a device is more suitable for electric heating. There are also models for the water circuit, but their cost is too high for use in a bathhouse.
Circulating water pump
A dual-circuit heating system uses as many as three electric pumps. The main water pump with a power of 150-200 W is used to pump hot water from the heating circuit on the stove to the boiler. Moreover, such a pump operates constantly while the wood is burning in the furnace firebox. To avoid accidents, the main circulation pump is equipped with automatic control of temperature and water flow. Often a separate backup power supply is connected to it.
Advice! If the primary circuit heat exchanger is installed on a chimney, then the control automation can be replaced with only one thermostat or pressure sensor. Even if the pump fails, hot water will flow into the boiler by gravity for at least another 15-20 minutes. This is enough to detect and eliminate the problem in the water heating of the bath.

The remaining two circulation pumps with a power of 100-120 W are switched on periodically as needed at the command of the sensor. For a shower or sink, this could be a pressure drop sensor that turns on the pump when a hot water tap is opened.
For heated floors and circuits with wall radiators, a temperature sensor built into the pipe is used. Many customers of water heating refuse automatic adjustment of the heating level and frequency of pump activation, preferring to constantly run the motor at low speeds throughout the entire stay in the bathhouse. In this case, the heating level is adjusted manually using a return valve.
There is nothing complicated in the adjustment procedure with a tap, especially since you only have to select the required heating level once, and then adjust the air temperature in the bathhouse using the speed controller on the circulation pump.
Heat exchanger power calculations
All calculations and diagrams of double-circuit heating are meaningless if you do not make at least an approximate calculation of a double-circuit sauna stove. This will help to avoid the most serious mistakes when arranging the first heating circuit.
We determine the total need for thermal energy for the auxiliary premises of the bathhouse
In the calculation process, you need to determine two values, the first is the required amount of heat for heating the sink, locker room and rest room. The second is the amount of energy required for hot water in the shower.
For the first point, we obtain the total heat consumption by multiplying the area in square meters of heated premises by 0.2 kW.
For your information! Typically, when calculating water heating, a heat load of 0.1 kW/h per m2 is assumed. This is exactly how much heat should be released from the surface.
As an example, the area of the rest room and locker room is 2.5 x 3 m = 7.5 m2, the amount of thermal energy released through the heated floor and wall radiators must be at least 7.5 x 0.2 = 1.5 kW/h. For the steam room and sink, the total area is 2.5x2+1.5x2=8m2, respectively. Since the air temperature in the steam room and shower should be higher, we take the flow rate at 0.3 kW/h, resulting in 8x0.3=2.4 kW/h. In total, at least 3.7 kW/h of heat should be allocated for heating the bathhouse on the secondary water circuit.
Another 1-1.5 kW/h will be required to heat the water in the washing compartment. The total demand will be 4.7 kW/h. This means that the first water circuit must take at least 5 kW/h in thermal equivalent from the furnace firebox. The difference of 300 W will go to losses during the redistribution of thermal energy in the second heating circuit.
For your information! A sauna stove with a water circuit should produce approximately 3.3-3.7 times more energy in operating mode than is required to heat the sauna. Otherwise, the steam room will be damp and cold.
How to determine the characteristics of the primary water circuit heat exchanger
After receiving approximate data on the required amount of energy for heating the bath, you can begin to calculate the scheme for extracting heat from the furnace. It is assumed that the stove with a chimney and all the necessary attributes has already been installed and is working properly in the steam room of the bathhouse.
First, you need to decide on the design of the primary circuit heat exchanger. You can use a tank that fits onto the chimney, or a twisted copper coil that fits onto the chimney. It is better to choose a twisted heat exchanger; the tank is suitable at best for obtaining a small amount of boiling water for washing, and often becomes the cause of breakdowns and leaks.
Preparation for calculation
Knowing the need for heat, which is 5 kW/h, you can calculate the characteristics using a ready-made program. But most software systems are either difficult to master on your own, or do not always give the desired result for a specific bath and the power of the water circuit.
Therefore, the parameters will be determined experimentally:
- We buy copper pipes for installing air conditioners. For all heat exchangers we use a pipe with a diameter of 12 mm;
- We bend a coil with 10 turns on a metal blank; the inner diameter of the heat exchanger should be 1-1.2 mm less than the outer size of the stove chimney. There should be a supply of pipe at the ends so that additional turns can be added;
- We install the coil on the pipe, connect one flexible metal corrugated hose to the inlet and outlet holes;
- We connect the inlet to the heat exchanger with the outlet of the circulation pump, and send the outlet from the coil into a metal barrel with a capacity of 70-100 liters.
Next, you need to connect the circulation pump to a water supply or a container with warm water.
Circuit tests
To determine whether 10 turns will be enough for the primary circuit water heat exchanger, you need to test the assembled circuit in operation. We heat the steam room of the bath, the chimney should warm up to operating temperature, and start the circulation pump at minimum output.
We note the time, fill the barrel with 50 liters of hot water and turn off the system. We measure the water temperature with a thermometer. Next, we calculate the amount of heat removed from the heat exchanger by the water flow through the chimney of the bathhouse. It is still necessary to determine how hot the water flow is. All that remains is to multiply the weight of water - 50 kg by its heat capacity and the difference in temperature. Knowing the heating time of water in the primary circuit and the amount of heat, you can calculate the thermal power of the heating part of the sauna chimney. By adding and decreasing the number of turns of the heat exchanger, you can adjust the characteristic to the required value of 5 kW/h. On average, 20-25 turns of 12 mm copper pipe are laid on the chimney of a bathhouse.

Heat exchanger of the first water circuit
You can also go the opposite way - wind the maximum amount of copper pipe and, after installation on the stove and practical testing in the water heating system of the bathhouse, cut off several turns to reduce the amount of heat taken from the furnace firebox.

Small water circuit, with its help heat will be removed from the boiler to provide the washing department of the bathhouse with hot water
Several alternative options
Despite the fact that the options described above are the most popular and considered optimal, I decided to briefly mention some alternatives. In fact, they are varieties of stove heating, but have their own characteristics.
For example, if you have such capabilities, then you can install a diesel fuel boiler in your bathhouse. But this option requires a separate room (diesel fuel does not smell much), and you need to think about fuel storage.
There are also pyrolysis heating boilers. The undoubted advantage of such a boiler can be considered a very long, almost complete combustion of fuel. The disadvantage is the high cost and difficulty of operation (for example, raw wood does not burn in it).
It is also possible to use long-term combustion boilers, capable of burning a separate batch of fuel for up to 5 days, maintaining the desired temperature. There are even options for high-quality graded coal. But this is rather an “industrial” option, which is not suitable for a good traditional bath.
How to make a water circuit in a bathhouse
The first step is to choose a place to install the storage boiler. For reliable operation of the heating system, you will need a tank with a capacity of at least 100 liters. You can use the body from an electric boiler, but for your own bath it is best to weld a cylindrical stainless steel tank.

Tank assembly
We manufacture a water storage tank and install secondary circuit heat exchangers:
- We order the tank body from a welder. The stainless steel will need to be pre-bent onto a cylindrical blank with a diameter of 40-50 cm and secured with soft wire. The central seam is welded using a semi-automatic welding machine. The bottoms are welded at the end;
- To extract heat from the tank, two heat exchangers are required. The first one is made by winding a copper pipe on a steel billet. We drill holes in the body, insert the coil inside and spread the coils on holders - spacers made of plastic;
- We make a coil for the washing compartment in a similar way. It will be enough to make 5-7 turns on a blank with a diameter of 50-60 mm. It is attached to the housing at the bottom of the tank;
- We weld a feed pipe and two fittings into the body for supplying and discharging hot water flow from the primary circuit on the stove chimney.
After welding the bottom and lid, the tank must be checked for leaks, fill it with water and leave it in the bathhouse for several hours. If there are no problems, you can proceed to installation. Usually the tank is mounted on the wall in the washing compartment.

The most powerful circuit should be made for the stove
Assembling a water heating system
The first step is to lay pipes from the bath’s water heating system into the washing compartment. An existing bathhouse probably already has running water. From the water pipe we make a branch to the central storage tank. We install a feed tap, a pressure gauge and an expansion tank.
We install the tank next to the stove
We connect another branch of the water supply pipe to a small heat exchanger. The connection can be made directly or through a circulation pump and damping tank. If the water pressure in the water supply is at least 1.5 At, then you can install only one tap.
Next, you need to punch holes in the wall and lay a straight or top pipe that supplies water flow to the heating radiators and underfloor heating system. The return to the furnace is also connected through a tap and a damper tank. We install a circulation pump into the supply line.
We install water heating radiators and a heated floor system in a bathhouse according to the same scheme as for residential premises.
Making a potbelly stove
Initially, it is necessary to draw up a drawing diagram indicating all the dimensions of the parts and prepare the necessary tools for performing metal work (welding, grinder, pliers) and materials.
After cutting the metal, the following actions are performed:
The main elements are welded at right angles: the bottom and walls. Except for the front.
It is important to know! It is recommended to install the bottom of the heating structure at a distance of at least 30 cm from the floor level. Installed metal legs will help reduce the strong temperature effect on the floor covering
The furnace space is subject to zoning, namely, a grate or a sheet of metal is welded between the firebox and the ash pit, in which backlashes are drilled to remove ash.
- It is necessary to make an opening on the front wall to mount the doors. Now the front part can be welded to the remaining elements.
- Hinged hinges are added to the sides, after which the doors can be installed according to the location diagram.
A chimney pipe must be welded at the top of the stove structure. After completion of the work, all seams are cleaned and checked for defects. The next stage is the installation of the water jacket.