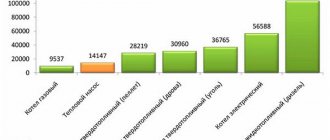
Basic requirements for raw materials for pellets
Humidity
Requirements for raw material humidity for industrial pellet granulators are from 8 to 15%. In other cases, the raw materials require drying, or, conversely, steam treatment.
Ash content
The ash content of pellets is the percentage of unburnable residues after burning a batch. For premium pellets this figure is up to 1% according to the EN Plus A-2 standard and up to 0.5-0.7% according to the EN Plus A-1 standard. High ash content of fuel can lead to clogging of the combustion chamber and chimney over time.
Content of chemical compounds in raw materials
At the moment, the European Union is tightening standards for the emission of combustion products into the atmosphere. Raw materials for pellets must contain a minimum amount of chemicals such as azor, chlorine, sulfur.
Fraction size
For granulation, the material should be crushed to a particle size of up to 3 mm in length and up to 1-2 mm in thickness.
High energy value of the material
The calorific value of raw materials - how much heat can be obtained during combustion - is the main consumer value for pellets. High-quality raw materials have a high calorie content. This parameter is influenced, among other things, by the freshness of the material. Wood that has been subjected to rotting loses part of its energy potential.
Suitability for granulation
Certain materials can be easier or more difficult to press and prepare. Moreover, less durable and dense pellets can be obtained from difficult-to-granulate raw materials. To increase the strength of granules, various additives are used.
Raw material cost
Such costs add to the cost of raw materials, which also includes procurement and transportation costs. If the total raw material costs are too high, production may not be economically feasible.
Waste briquetting device
Homemade press
If you plan to use heating briquettes for winter heating of a country house in winter or as an alternative fuel in an individual home, making them manually is quite labor-intensive.
In this case, it is advisable to make a simple machine that will speed up and facilitate the work. Today, various modifications of machines are available for sale. They differ in functionality, the number of cells in the forms, and the type of drive - manual or mechanical.
All models have one thing in common - they allow you to mechanize the most labor-intensive process - compacting the wet mass in the cells of the mold.
The simplest machine is a metal frame welded from a corner, on which a wooden tabletop painted with moisture-resistant paint is fixed. A “P”-shaped bracket is welded to the frame, between the uprights of which a swinging lever is fixed - a rocker arm, the length of which determines the compression force.
A punch is hinged on the lever, the dimensions of which are slightly smaller than the dimensions of the cells. A mold filled with briquette mass is placed on the countertop and pressed with a punch until the briquettes are given the required density. Moving the mold along the tabletop, the pressing operation is repeated for each cell.
In order for the press to last long enough, after each pressing operation it should be cleaned of adhering mass.
If the gardener has the opportunity to obtain or make a vibrating plate, then a press is not required. The sawdust-clay mass is compacted due to vibration.
Wood pellets
Most often, such granules are called “sawdust pellets,” but in fact they are obtained from various types of waste.
- Shavings, sawdust
obtained by sawing and processing raw and dried timber
- wood chips
- one of the most common waste
- Croaker, wood balance
– large wood waste, sawn or whole trunks, which for some reason are rejected for use for their main purpose (have defects, do not have the right diameter, etc.).
- Substandard wooden products
: new or recycled.
Dry sawdust and shavings are considered the ideal raw materials for producing high-quality pellets. They usually do not contain bark inclusions or soil particles that form slag upon combustion. This is why the production of sawdust pellets is so popular.
The quality of wood chips as a raw material for pellets depends on the type of wood it is obtained from - regular or debarked, as well as on the characteristics of its storage. The less bark and foreign inclusions get into the pellets, the lower their ash content, and therefore the higher their quality.
The same can be said about the processing of slab and pulpwood.
Substandard wooden products, in theory, should ensure high quality pellets, because this is pure, debarked wood without impurities. However, it is worth paying attention to what materials are used in the manufacture of the product. Various varnishes, processing agents, and glue can affect the environmental friendliness of such a material.

Granulation of different types of wood
Different types of wood as raw materials for pellets differ in the ease of granulation.
Firstly, stronger pellets are obtained from wood species with a higher content of natural lignin. Coniferous species are noticeably ahead of deciduous species in this parameter: different coniferous varieties contain 23-38% lignin, and the spread in deciduous species is 14-25%. If there is little lignin in the raw material, then the amount of screenings after granulation increases.
Secondly, wood species have different hardness. Harder wood is more difficult to press into pellets and creates higher loads on the equipment, especially on consumable parts - the matrix, press rolls. Coniferous woods are softer and more pliable for pressing, while hardwoods are always harder. However, the calorific value of hardwood pellets is higher, so a cubic meter of beech or oak pellets will weigh more than the same volume of pine pellets, and will give off more heat.
At the same time, as practice shows, it is possible to successfully mix sawdust of different species and granulate it. Such a mixed material for fuel pellets does not reduce the quality of the final product: if you mix the rocks in the right proportions, you can achieve pellet compliance with EN plus A1 or A2 certificates - suitable for heating private houses. The addition of hardwoods such as beech and oak increases the energy value of the pellet. Another thing is that some hardwood species have a dark shade of wood, and mixed pellets from different types of wood turn out coffee-colored, gray or dark. Private consumers of pellets sometimes have a prejudice against pellets of any color other than light beige, so they may reject dark oak pellets based on their type alone, despite the presence of high quality certificates. The prejudice is so strong that some German researchers create fuel from a mixture of species with the addition of about 20% oak or beech to softwood, while the final product retains an attractive light color.
Necessary equipment
Despite the relative ease of obtaining fuel, you still have to acquire some equipment. Or adapt existing ones to new needs. What you will need:
- Chopper. You can’t do without it, because the finer the raw material, the denser the finished briquette. And when making it with your own hands, materials of various fractions are used. You won’t have to spend money on purchases if your farm has a device that chops vegetation to send it to compost. Inventors with skillful hands adapt an old activator-type washing machine for a shredder - they change the activator itself with knives;
- Any container where the raw materials will be mixed before being placed in the matrix. It would be a good idea to supplement the “trough” with a miniature concrete mixer or construction mixer. In the absence of both, get ready for hard physical work of kneading raw materials;

You can make a briquetting press yourself
- Press for the production of fuel briquettes. It can be manual or hydraulic, wall or floor mounted. In general terms, a press for the production of briquettes from sawdust and other plant waste consists of a solid frame made of steel and what can be called a working part;
- Matrices with which briquettes will be formed. They can be in the form of standard bricks, but it is more convenient to use cylindrical shapes - less fuss. Although warehousing and storing will be somewhat more difficult. The matrix must have perforated walls: moisture squeezed out of the workpiece by the press will be removed through the holes.
Particular attention should be paid to the moment of pressing. Muscular effects are a waste of time and effort with low efficiency. Experienced craftsmen recommend equipping the press for the production of fuel briquettes with a hydraulic jack from a car. It should be fixed upside down on the upper frame of the press.
Press device
To mount a simple structure in the form of a piston press, you will need a cylindrical metal base, which must be removable . Then a piston press with the required diameter is selected to it. You also need to make a special lever with which the piston will be driven.
Then you need to connect all the prepared parts on a metal frame, and the sawdust pressing device is considered ready. But it is immediately worth noting that the installation will produce briquettes of low density.
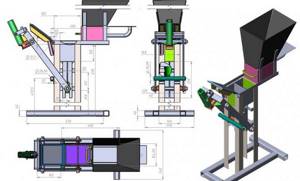
Better results can be obtained from a screw press; manufacturing such a device will also not be difficult. First you need to prepare a metal frame, and through it the screw with the piston will be rotated. A wide handle needs to be attached to the upper part; with its help, the pressure necessary for pressing will be created. This method produces higher quality briquettes.
In addition to these options, there are many other ways to make a homemade press. Each master decides for himself which model to choose, depending on the available material and skill. The main thing is that the device applies maximum pressure to the sawdust.
How to make your own abs
To make a briquette press with your own hands, you need to stock up on some materials and available tools. In addition to the main component, you will also have to buy different types of rolled steel:
- channel;
- corner measuring 100x100 mm;
- a sheet 3-6 mm thick from which you will need to cut a punch. The thickness of the workpiece is determined by the diameter of the matrix.
It is also necessary to prepare a pipe with a cross-section of 25-30 mm for the manufacture of the punch rod, a thick-walled pipe for the matrix and a larger one for the body. In the absence of such material, the drum can be created from a sheet of tin. Also, galvanized steel is prepared for the upcoming work - trays are created from it.
The machine is assembled according to the following instructions:
- Equip the base of the device. It is created from channels using a welding machine.
- Based on the angle, four 1.5 m long posts are made. They are welded vertically with the same pitch.
- Next, a drum is created from a steel pipe or sheet of tin, where the feedstock will be mixed. If you have a broken washing machine in your house, you can remove the drum from it.
- The drum structure is then welded to the racks. If possible, it is better to equip it with an engine. If the power plant creates strong vibrations during operation and its rotation speed is too high, this can be solved using a gearbox.
- A tray is installed under the drum through which the raw materials will be fed into the matrix.
- At the bottom of the matrix there is a flange to which a removable bottom is screwed. It will require a steel sheet.
- Then you need to weld or screw the matrix to the base.
- A round punch is cut from a sheet of steel. Instead, you can use a regular disk of suitable diameter.

The briquetting press is designed for the production of fuel briquettes from soft and hard wood sawdust, sunflower husks and other plant waste
Mixed pellets
According to research company Future Metrics, consumption of industrial pellets alone will almost double by 2023: it will be 21.5 million tons versus the current 12 million tons. Wood waste has become increasingly in demand; not only biofuel producers, but also chipboard factories and many other industries compete for it. Back in 2010, the European Union adopted a program to expand the range of biological waste that will be used for heating and energy supply.
Let's define the terminology:
Mixed pellets
is a fuel that is granulated from several types of raw materials, both wood and other origins.
Agro-pellets
– granules from a variety of plant materials, usually agricultural. waste.

What are alternative raw materials for pellets?
- Waste from the agro-industrial complex: legume pods, corn cobs, rice husks, buckwheat, sunflower husks, flax husks, nut shells, fruit seeds, stillage, ungerminated grain, brewer's grains.
- Plants: reeds, straw, sugar cane, as well as trees and shrubs cut down during landscaping and sanitary felling.
- Other natural flammable substances: peat, lignin.
These materials can be granulated, but compared to wood they have a number of disadvantages: the content of undesirable chemical compounds, high ash content, low melting point of ash residues, which leads to the growth of slag formations in boilers.
To find optimal pellet recipes, European researchers are conducting experiments on mixing different types of raw materials into pellets. Based on research, viable “recipes” for mixed pellets from various raw materials have been obtained, which are gentle on boilers and do not emit harmful substances during combustion. It is usually believed that a granule should not contain mineral inclusions, but scientists from the Austrian Forest Research Institute created granules from corn cobs, rapeseed and straw with the addition of kaolin, bentonite and coal ash. The resulting granules emit a minimal percentage of undesirable substances into the atmosphere; when they are burned in the firebox, slag cakes do not form.

Also, wood in pellets is combined with 10-15% coniferous needles, or mixed pellets are produced from coniferous and deciduous wood. The Russian patent is a combination of sawdust and about 20-25% charcoal; for successful granulation of this mixture, 1-3% starch is added. The potential of such pellets is up to 20-23 MJ/kg, which makes them an alternative to low-calorie coal and peat. Any type of wood is suitable for their production, including dead wood and firewood, as well as coal collected from forest fires.
The main obstacle to the spread of mixed pellets and agropellets is the tightening of standards for emissions of combustion products into the atmosphere in the European Union. Such measures may make it economically unfeasible to use such fuel, since boiler owners will need expensive filters and technologies to comply with all standards.
In the production of mixed pellets, various additives are often used for better gluing of the granules. If coniferous trees have enough of their own lignin, then for deciduous trees, as well as agricultural waste, starch is added. You can also use fish oil, soda, lime, paraffin, vegetable oils, and coffee grounds for these purposes. Such additives improve the user properties of the product: a lower percentage of dropouts, crumbling, better resistance to fracture when poured during transportation and direct use in boilers.
Wood from fruit trees – cherry, apple, etc. – is granulated in small volumes. They are usually used not for heating, but for smoking meat and fish, giving the product a pleasant aroma.

Features of use
Sunflower briquettes
Before you start recycling waste on your personal or garden plot and start production, you need to decide on the scope of use of briquetted fuel and calculate the need for the source material.
If briquettes are intended to be used as an alternative, additional fuel for combustion in a stove or fireplace in a country house, then any plant waste can be used as the starting material:
- Sawdust, shavings, wood chips, chopped small branches
left after pruning trees. - Agricultural waste
– dry plant stems, straw, seed husks. - Garden waste
that is usually burned or composted - dry grass (weeds), fallen leaves, root crop tops. - Household waste
– cardboard, paper.
Some gardeners use plastic film as an additive to plant matter. However, there are no official recommendations on this matter and the use of plastic waste is carried out at the own peril and risk of the manufacturer and consumer of briquettes.
Clay or starch is used as a binding material.
Agropellets
One of the most popular types of agricultural pellet raw materials is straw from various agricultural crops (especially wheat and rapeseed). In terms of energy potential, this material is not much inferior to wood: up to 16 MJ/kg versus up to 18.4 MJ/kg. Straw is a renewable source of fuel; burning straw does not change the balance of nitrogen dioxide in the air: during growth, it consumes the same amount of CO2 as it releases during combustion. Straw pellets are also used not only for heating, but also as bedding for animals in livestock farms and stables.

A type of raw material similar to straw is reed, while its higher calorific value is 19 MJ/kg, and its ash content is approximately 4%. Such raw materials are very cheap; they are collected using swamp harvesting and grinding machines.
Sunflower husk is one of the most promising materials for agropellets. Sunflower pellets have an ash content of 3%, and give off almost as much heat as brown coal - up to 21 MJ/kg. Ash after burning husks is a valuable fertilizer. Buckwheat husks, millet husks, and rice husks are also granulated.
Production
To produce briquetted fuel for heating a summer house or garden house, you will need crushed waste and clay. They are mixed in a ratio of 10:1, adding water little by little until a paste-like mass is obtained.
The quality of combustion will depend on how evenly the initial components are mixed, so mixing is best done using a household construction mixer (concrete mixer).
Using special equipment for the production of small batches, it is necessary to make a cellular form.
For trial batches, the mold can be put together from boards. The size of the cells is chosen arbitrarily, based on the desired form of briquettes.
Some summer residents press the mixture in old pots, boxes and other unnecessary household containers. However, a rectangular shape is preferable since rectangular fuel blocks are easier to store.
The wet mass is placed into the cells of the mold and compacted. The quality of homemade fuel depends on the degree of compaction.
To prevent the briquettes from crumbling and falling apart in your hands, it is advisable to lay several layers of newsprint on the bottom of the mold (or under the mold when using cells without a bottom).
Drying is done naturally in air. On sunny summer days, this process does not take much time. After removing the briquettes from the mold, they are placed under a canopy, in a stack with gaps, where they are dried in a draft.
Other materials
Russia has vast deposits of peat, which is suitable for granulation. Peat pellets and briquettes are made using approximately the same technology as wood. The calorific value of peat is high - up to 21 MJ/kg, however, the ash content of such granules is increased - up to 5%. This fuel is suitable for industrial and municipal boilers. In Russia, granulation and briquetting of peat has mainly 2 prospects: providing heat and electricity to non-gasified areas and exporting granules to Scandinavian countries. In Northern Europe, peat is recognized as a partially renewable raw material, and its use in the energy sector is encouraged from above.

Granulation of waste paper is a fairly new but promising industry, since this type of raw material does not require expensive drying complexes. Granules made from paper and cardboard (and in some countries granulation of old banknotes has been established) produce a large amount of heat and have a tiny percentage of non-combustible residues.

Chicken and horse manure pellets are more expensive than wood pellets. It is a valuable and nutritious fertilizer for soils. Horse manure pellets sell for around €1.25 per kilogram. Processing manure and droppings into fertilizers is not only profitable, but also a necessary step, since storing such waste directly harms the environment.
The same can be said for the processing of hydrolysis lignin, a by-product of hydrolysis plants. In Russia, there is only one lignin granulation plant in the Arkhangelsk region, and meanwhile its reserves in the country amount to tens of millions of tons. In terms of calorific value (more than 21 MJ/kg) and ash content (less than 3%), lignin is an excellent raw material for pellet production.

Expanding the raw material base for the production of fuel pellets makes it possible to benefit from the disposal of huge amounts of biological waste, as well as solve environmental problems associated with their storage. Switching from fossil fuels to environmentally friendly fuels reduces emissions of harmful substances into the air. The creation of new pellet and briquette production creates new jobs in the agricultural industry and helps its overall development.
Making your own briquettes
Euro-firewood with your own hands is a feasible task for those who want to obtain this type of fuel. To produce them, you will need to purchase basic equipment, which is available for sale in specialized departments. You can prepare the unit for operation either independently or with the help of specialists, but often the devices are already set up and configured to certain parameters. In addition, there are special training courses on the operation, adjustment, and troubleshooting of this equipment. Mechanisms for the production of briquette fuel can also be purchased from organizations offering finished products.
Below are the main equipment needed to produce briquettes with your own hands:
- crushing machine -
a grinder for raw materials, which will be needed if not only sawdust is used as the starting material; - a mechanism for pressing
into the required shape (impact-mechanical and hydraulic presses for fuel briquettes, screw design); - drying chamber
for the finished product; At this point, you can save significantly if on the territory of a private farm there are the necessary conditions for natural drying of finished products.
Let's see how you can build a press for fuel briquettes with your own hands from unnecessary materials.
Raw materials for production
The most accessible waste in fairly large populated areas is waste paper. With an average purchase price of 4–6 rubles/kg, this type of fuel becomes profitable. For example, charcoal in bulk will cost 10–20 rubles/kg.
But there is some competition here - such raw materials are successfully harvested for the production of cardboard. Other types of organic matter include:
- waste from woodworking production: sawdust, shavings, wood chips;
- agricultural material: hay, straw, sunflower or pumpkin seed husks, nut shells;
- natural material: peat, dry plant stems, bark, fallen leaves, reeds.
It is allowed to use woven material made of pure cotton, linen, silk - artificial materials should not be included in their composition.
To form briquettes, one type of material is used, that is, paper with paper, straw with straw. When using sawdust, it is necessary to ensure that the mixture contains wood waste from one type of vegetation. The admixture of bark or wood chips is allowed no more than 5% of the total mass.
The moisture content of the raw materials does not matter much, since during the production process it still needs to be moistened, but for storage the material must be dry, otherwise there is a high risk that it will begin to rot.