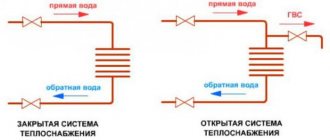
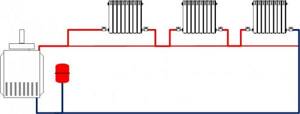
Single pipe vertical system
A single-pipe vertical system is characterized by coolant circulation in a closed loop. When installing such a heating network, radiators are connected in series, so there is a significant difference between the degree of heating of the first and last batteries. However, this disadvantage can be compensated for by the short length of the highways.
For additional adjustment, heating devices of single-pipe systems are equipped with various types of pipeline fittings. In the range of TM Ogint it is represented by the following devices:
- angle and straight thermostatic valves;
- thermostatic kits;
- shut-off valves allowing autonomous repairs without shutting down the entire network.
To ensure the efficient functioning of a single-pipe circuit with natural circulation, it is advisable to install a Mayevsky valve with a cap for a screwdriver or another type of air vent on the heating radiators.
The advantages of a vertical single-pipe network include:
- minimal consumption of materials;
- the optimal amount of coolant, the volume of which can be adjusted by selecting the diameter of the pipes;
- possibility of installing the system without using a circulation pump.
However, it is effective for small rooms, and to heat rooms with an area of 40 m2 or more, you will have to install several risers, otherwise it will be difficult to achieve a comfortable temperature. Therefore, installation of a single-pipe vertical system is advisable in apartment buildings with a height of at least 5 floors. In addition, it is necessary to have good insulation and small rooms.
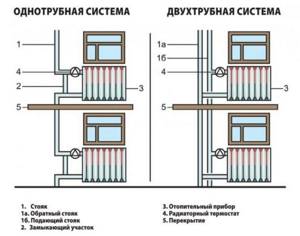
One-pipe or two-pipe system
Currently, multi-storey buildings have one of these systems, each of them has both advantages and disadvantages.
A single-pipe heating system connection diagram is usually used in small buildings and among its positive qualities:
- It can be used from anywhere in the building, making the system universal. For example, you can start running pipes from the coldest part of it (northern).
- Installation requires less pipes and time , which significantly saves money.
- For single-pipe systems, parallel or series connection of batteries is most often used. In this case, pipes can run not only along the floor, but also be hidden in it .
The disadvantages of a one-pipe system are:
- Lack of ability to regulate the heating process.
- Increased pressure, which requires pipes and radiators of special strength.
- The system is more efficient when the coolant is supplied from above.
For a two-pipe scheme, many “problems” are unimportant, since the supply and return pipes work separately in it, and radiators are installed between them.
For example, heating schemes for a 1-room apartment will look like horizontal two-pipe systems.
Among the advantages of the scheme:
- It can be combined with any type of coolant supply.
- As a rule, when using a two-pipe system, the coolant enters the radiators at the same temperature, which allows the rooms to be heated evenly.
- The pressure in the pipes is lower, so they last longer.
- They can be installed in buildings of any number of floors.
- The system is easy to repair in case of an accident, as it has locking devices.
This scheme is the most popular, despite the fact that it requires more installation time and consumables.
Two-pipe vertical system
A vertical two-pipe heating system involves the installation of two lines for transporting the coolant. One of them supplies the heated working medium, and the second serves as a drain after cooling. Since the radiators are connected in parallel, it is necessary to ensure that the pipelines are laid next to each other.
An additional line increases the cost of materials and the volume of coolant, for the movement of which natural circulation is not enough, since hydrodynamic resistance increases. For efficient operation, autonomous engineering heating systems in private cottages are equipped with powerful circulation pumps.
According to the method of supplying coolant, two-pipe networks are usually with top wiring. This option for organizing heating is more efficient and requires less effort during installation. A system with bottom wiring is labor-intensive to install and difficult to operate the equipment.
The use of a vertical two-pipe scheme in multi-apartment buildings provides the following advantages:
- the ability to supply coolant with the same degree of heating to all heating devices, regardless of the floor;
- ease of flushing and carrying out preventive maintenance when preparing the pipeline for operation.
A heating network of this design is almost not prone to the formation of air jams. To completely eliminate the likelihood of their occurrence, you can install one of the air vent options offered by TM Ogint. For radiators, a Mayevsky tap is sufficient, but for the entire system an automatic device will be required.
In the context of rising tariffs for heating housing in multi-apartment buildings, it is important to not only regulate the temperature, but also control the heat consumption. A two-pipe vertical heating system allows the installation of in-house heat metering devices. The use of individual heat consumption meters in each apartment is complicated by the peculiarities of legislation and the need to install the device on each riser.
The range of heating equipment TM Ogint allows you to select components for laying vertical systems of different types. A large selection of thermostatic and shut-off valves, as well as other types of pipeline fittings, makes it possible to create an effective heating network at minimal cost. High quality products ensure the functioning of heating systems for a long time.
Horizontal and vertical heating distribution in an apartment building 2021
The level of heat supply directly depends on the type of wiring of the heating system in an apartment or house. The most common schemes are single-pipe and two-pipe horizontal heating systems.

Heating system design
In any apartment, all elements of the heating system are connected according to one scheme or another. The pipeline can be routed vertically or horizontally.
In the first case, the main sun lounger is located in the basement. Riser pipes of smaller diameter extend from it, to which pipes and radiators in the apartment are connected. The main advantage of vertical wiring is its low cost and simplicity.
A single-pipe vertical system can have top or bottom wiring. Both types have their own technical characteristics. When installing a single-pipe vertical system with overhead pipe distribution, the supply pipeline is laid in the attic or on the technical floor. From the sun lounger, the coolant is supplied to the apartments through series-connected risers.
Such a system is static. It will not be possible to scale it by changing the number of radiators and installing regulators. It can save pipes during installation, but requires the installation of a large number of heating devices. Single-pipe vertical systems are well suited for projects that involve natural circulation of coolant.
A two-pipe system with bottom wiring has a supply pipeline and a return line. They are laid on the floor surface or in the floor, for example, in a screed. When implementing such a system, the coolant enters each battery independently. This scheme is not without nuances. Each radiator must have a tap through which air can be vented.
Unlike single-pipe systems, two-pipe systems are adjustable circuits. Communications built in this way make it possible to turn off any heating device in the network. Overconsumption of radiators is also not typical for them, but the total length of the pipeline will be significantly greater compared to a single-pipe scheme. In apartment buildings, the two-pipe system has one more nuance. It is almost impossible to install an individual heat meter here. And the use of communal heat meters is beneficial mainly for residents of the first floors.
The basis of the horizontal distribution is the supply riser, passing through all floors. Sun loungers are connected to the riser, supplying heat to individual apartments. The use of horizontal wiring requires careful insulation of the riser, since significant heat loss occurs here. To reduce heat loss as much as possible, risers are often installed in specially equipped shafts.
Single-pipe circuits have a narrow scope of application - heating large areas. Therefore, they are almost never installed in residential buildings. Horizontal two-pipe system
well suited for providing heat to apartment buildings.
Installation of a two-pipe heating system in general terms is as follows:
- From the main supply riser, a supply and return pipe are laid on each floor, and radiators are also connected.
- Shut-off valves are installed on all radiators, without exception.
An important advantage of the scheme is the ability to connect/disconnect heat on a floor-by-floor basis. Sunbeds can be laid in the floor screed. This scheme allows the use of radiators with bottom connections. All this has a good effect not only on heat supply, but also on the aesthetic appeal of apartments. It is impossible not to note another important fact - the possibility of installing individual heat meters.
For all its undeniable advantages, the system is not ideal. The difficulty lies in the need to install compensators for a significant length of the main line. The operation of the system as a whole is also becoming more complicated, since the installation of shut-off valves and air valves is required on each radiator, without exception.
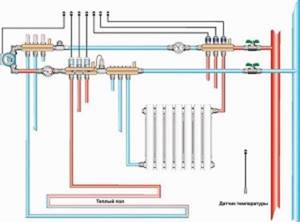
Heating wiring diagram in a private house
We should also talk about another popular wiring scheme - this is a two-pipe manifold floor-to-floor system. Its peculiarity lies in the installation of supply and return manifolds on each floor. As in the case of the already described option, the heart of the system is the common supply riser. If there are a large number of consumers in the house, it is possible to install several risers. Two collectors are installed on each floor - supply and return, and from them there are pipelines supplying coolant to the radiators.
Unlike traditional options, the collector floor scheme has a significant pipeline length. Considering that metal-plastic pipes are used for installation of the circuit, the implementation of such a project turns out to be more expensive than conventional options.
Important! Despite this drawback, collector circuits, from the point of view of operational features, are much more efficient and simpler than other options. This makes them increasingly popular not only in multi-storey buildings, but also in individual construction.
The two-pipe collector system guarantees an even supply of heat to all rooms. For comparison, it is worth remembering the operating principle of single-pipe circuits. In them, heat is supplied and removed through one pipe, and radiators are connected in parallel. As it moves through the pipeline, the coolant cools down. As a result, the further the radiators are located from the supply pipe, the colder the water in them, and, as a result, the lower the air temperature in the room. It is impossible to install regulators in such connection diagrams. Therefore, even within the same apartment it is impossible to achieve uniform heat.
Two-pipe circuits make it possible to reduce this disadvantage to a minimum. The cooled coolant is removed from the system via the return line. The water does not cool down as it moves from radiator to radiator, which means that all rooms will have approximately the same temperature. Such thermal indicators provide the most comfortable microclimate in the apartment. We must not forget that in such systems it is possible to install temperature regulators. And this gives not only comfort, but also savings and efficient use of funds. In general, the installation of an expensive collector circuit pays for itself within 2–3 heating seasons.

Installation of heating systems
Important differences between two-pipe beam (collector) systems are:
- Flexibility and scalability of the scheme.
- Possibility of installing thermostats on each radiator.
- The need to ensure forced circulation of the coolant using circulation pumps.
- Each circuit is a separate system with additional equipment and automation.
- There is no need to install air vents on radiators.
- High system reliability, reduction in the number of accidents and leaks.
- High resistance to water hammer.
- Aesthetics
This is interesting: Emergency balcony: who repairs it, how to write an application for balcony repair in 2021
We can talk about the economic and operational advantages of horizontal two-pipe collector systems for a very long time, but we cannot fail to note another advantage of them - aesthetics. Modern man values comfort. Even inexpensive renovations are done, if not with the involvement of a designer, then at least using the latest design trends. The presence of risers throughout the apartment does not go well with modern design. In old houses, the issue of risers is aggravated by another significant problem - constant smudges and leaks that can kill even the best and most expensive repairs.

In two-pipe manifold circuits, all pipelines are laid in the floor screed. Not only do they not spoil the apartment, they are absolutely invisible. Laying pipes in a screed is possible thanks to the use of modern materials - plastic and metal-plastic. They are not subject to corrosion, are not afraid of low temperatures and even freezing of the coolant.
Horizontal radial patterns also make it possible to ensure truly high comfort in each room thanks to the possibility of installing heat regulators. The temperature of the house is regulated depending on the weather outside the window. The result is a highly energy efficient system.
Among all existing heating network installation schemes, the best option remains a horizontal radial two-pipe system. Despite the higher cost of installation, it is becoming increasingly popular not only in multi-storey buildings, but also in private housing construction. This popularity of collector circuits is explained by a unique combination of excellent technical, operational, economic and aesthetic indicators.
Houses can use horizontal and vertical wiring of the heating system. In modern multi-storey construction, horizontal wiring is increasingly used, which demonstrates good technical, aesthetic and operational characteristics. This article will discuss the horizontal layout of the heating system.
Horizontal heating distribution has a number of advantages:
- High degree of heat transfer control . In such a scheme, it is very easy to monitor heat consumption due to automatic remote control.
- Possibility of individual configuration of each section . On any section of the circuit, you can adjust the temperature separately, depending on the specific needs of the room.
- Possibility of hidden installation . The horizontal heating system is perfect for hidden installation, which allows you to visually unload the room and thereby improve its interior.
- Reliability . When using good components and proper installation, a horizontal system can operate for several decades without problems.
Among the shortcomings, the following points can be highlighted:
- Sometimes it becomes necessary to manually configure the system;
- In case of mechanical damage, serious problems arise with the system.
Horizontal and vertical heating systems have a lot of differences, so to choose a suitable design you need to study them in detail. Further we will talk only about the horizontal system.
There are several types of horizontal wiring:
- Single-pipe;
- Two-pipe;
- Two-pipe manifold.
Each scheme needs to be considered in more detail.
In such a system there are several heat sources through which heating pipes pass. The coolant moves through such a system and transfers heat to devices located in certain sections of the circuit. Single-pipe horizontal heating in an apartment building has good efficiency and is relatively inexpensive.
The advantages of such a system are as follows:
- Minimum cost;
- Easy installation;
- Wear resistance and long service life;
- The ability to fully warm up a building of any size.
- The ability to adjust the temperature on each individual device is limited;
- Weak resistance to mechanical damage.
A key feature of single-pipe wiring is the need to gradually increase the size of the radiators in the order of their distance from the heat generator - this rule allows you to balance the heat transfer. In the case of a long system, heating collectors will have to be installed more often so that the coolant does not have time to lose temperature.
This horizontal heating distribution in an apartment building, as the name implies, includes two main lines, along one of which the coolant moves forward, and along the second it returns to the heat generator. Heat transfer is carried out through radiators, which are installed under windows or near walls facing north, because the most noticeable cold flows come from them.
A two-pipe system must be equipped with shut-off valves. These elements allow, if necessary, to turn off individual parts of the system without stopping the entire heating circuit. In addition, compensators are needed that neutralize the negative effects of pressure. A properly assembled system can normally withstand maximum pressure and water hammer, and will not freeze even at subzero temperatures.
The advantages of such a system include:
- No temperature difference between inlet and outlet;
- Possibility of application in buildings of any configuration;
- Possibility of switching off a separate section of the circuit without completely stopping the system.
The main and most noticeable disadvantage is the difficulty of fine-tuning the temperature if the system has a large number of branches - vertical wiring of the heating system in this regard is somewhat simpler, but not as effective.
This horizontal wiring diagram has a closed structure, consisting of several branches, each of which is connected to its own devices. As a rule, polymer or polyethylene pipes are used for such wiring - their strength and performance characteristics are quite sufficient for the normal operation of the system, and they are cheap.
In such a system, the connection goes directly to the collector, which ensures uniform distribution of thermal energy throughout the entire heated area. With this scheme, the supply and return circuits operate independently of each other. The coolant passes through the radiators and is sent back for the subsequent heating cycle. The result is a closed system, the operation of which is regulated automatically.
Horizontal parallel wiring is quite suitable for arranging any projects, since the design includes several simple elements that are easy to customize. What is important is that when using this scheme, radiators do not need to be equipped with air bleed valves.
The system must have a good circulation pump - heating operation in the horizontal installation option under consideration is only possible if there is a pump. The distribution panel, in which all the equipment is located, is usually placed in corridors or bathrooms, and for multi-story buildings, the option of placing the panel in the basement is quite suitable.
This is interesting: Fine for unauthorized gas connection in 2021
The list of advantages of such a layout is as follows:
- Low cost of arrangement;
- Possibility of hidden installation;
- Possibility of combining several individual elements into one system;
- Possibility of full heating of large areas;
- No water hammer.
There are also disadvantages, and the most prominent among them are:
- Difficulty of installation;
- The need to use pipes of the same diameter.
During installation, it is necessary to pay attention to the quality of thermal insulation of the heating system, especially the riser. It would not be superfluous to arrange an insulated box intended for installing a riser. In any case, it is better to entrust the design and installation of a two-pipe manifold circuit to specialists who have experience in carrying out such work.
Horizontal wiring of the heating system has a number of positive qualities and is well suited for a wide variety of conditions. Arranging such wiring in a complex configuration cannot be called simple, so it is worth hiring specialists for this work.
Heating wiring is a diagram of the location of heating devices and pipes connecting them. The efficiency of the heating system, its efficiency and aesthetics significantly depend on the type of wiring. Main types of heating wiring:
- Single-pipe and double-pipe
- Horizontal and vertical
- Dead-end and with counter-movement of coolant
- Heating with top and bottom wiring
A specific heating system must have one of two characteristics from all four groups of characteristics. For example, the wiring can be single-pipe horizontal with upper heating wiring and dead-end movement of the coolant, or it can be two-pipe horizontal with lower wiring and counter movement of the coolant, etc. Let's consider these schemes based on the possibility of installing a heat meter for apartment heat metering.
It became most widespread in the Soviet Union from 1960 to 1999 due to the low cost and ease of laying utilities. The engineers of that time did not think too much about the problems associated with its applications.
This wiring system is common mainly in houses built before the beginning of 2000. In such houses, the supply line runs along the technical floor or in the basement of the house, and the coolant enters each battery sequentially (gradually cooling) through vertical risers.
Advantages: low pipe consumption. Because of it, some unscrupulous developers continue to create houses with such wiring to this day. Disadvantages: the impossibility of turning off individual heating devices and the impossibility of adjusting them, excessive consumption of heating devices, and large heat losses of the coolant. Which implies the impossibility of installing residential heat meters .
If with a one-pipe distribution the coolant moves along one solid circuit through all the radiators, then with a two-pipe system there are two risers: from one the coolant enters the radiator, and into the other it leaves.
With a two-pipe heating system with bottom wiring, the supply and return main pipelines pass in the floor of the lower floor of the building or in the basement, and the coolant flows independently into each radiator.
Advantages: good regulation of the heating system, the ability to separately turn off each heating device, no overconsumption of heating devices.
Disadvantages: the length of pipelines increases compared to a single-pipe scheme, the practical impossibility of installing apartment heat meters.
- Metrological problem . The heat meter is considered to be working correctly when the difference in coolant temperatures between the inlet and outlet (supply and return) is more than 3 o C. The heat consumption of 1 radiator, depending on the size, fin coefficient and heating area, ranges from 0.5 o C to 2 o C.
- The need to install heat meters on each riser , which is expensive and very troublesome. In the future, the user will have to manually take readings from each of the meters, sum them up and submit them to the heat supply organization. Risk of mathematical error and human factor. High verification costs, which partially offsets the savings from installation and increases the payback.
- The scope of application of the device is written in the heat meter passport . For example, for Ultraheat T-230 - “The meter is used to account for energy consumption in apartments, cottages, apartment buildings and small businesses... the temperature in the supply and return pipelines is measured.... etc.". There is no word anywhere about the battery, and there is no supply or return pipeline on the battery.
All of the above reasons are arguments for heat supply organizations not to take into commercial accounting heat meters installed in houses with a vertical heating system.
The only way to organize heat metering with a vertical heating distribution scheme is through heat distributors.
In this case, the main pipeline goes through all floors; on each floor there are heating niches, in which, through branches from the risers, each of the rooms on the floor has its own connection (via horizontal pipes located in the floor) to the general heating system.
Horizontal single-pipe circuits are rarely used, they have a rather narrow scope of application and they are not used for heating apartment buildings, so here we will consider options for two-pipe wiring.
Looking at the figure, you can see that from the main supply and return risers along the perimeter of the room, pipelines are laid in the floor to each heating device. Each apartment has its own heating system input. A heating niche with main risers can be located both in the apartment itself and in the common corridors (on the floor of the apartment or 1 floor below the apartment), depending on the design of the in-house heating distribution.
Each radiator is equipped with Mayevsky valves for bleeding air, and often automatic air collectors are installed on each of the floor heating outlets.
This wiring scheme is the most common in multi-storey residential buildings due to its ease of execution and affordability for developers.
Advantages: similar to a two-pipe vertical system, plus there are no risers on each heating device (except for main risers). It is possible to switch off the heating system on a floor-by-floor basis and use radiators with bottom connections, which, along with laying main pipelines in the floor structure or in the baseboard, allows you to minimize the number of open pipes and improve the aesthetics of the interior of the premises.
This is interesting: Checking the accuracy of the estimated cost of major repairs in 2021
In such heating systems, apartment heat meters can be used.
Disadvantages: the need to use pressure compensators in high-rise buildings, complicated operation due to the presence of air valves on each heating device, high heat loss in the floor and through the building envelope.
In the heating niches at the outlets from the main pipeline (riser) on each floor there are collectors - supply and return. From the collectors, supply and return pipelines under the floor are led individually to each radiator in the apartment.
Advantages: similar to two-pipe horizontal heating systems with higher reliability of the system as a whole, high level of energy efficiency and lower energy consumption for heating.
Disadvantages: long supply pipelines, high cost.
The radial wiring scheme is innovative for our country. Today, such a system is becoming increasingly popular in construction.
In such heating systems, apartment heat meters can be used.
When routing heating pipes, various schemes are used that determine the operating features of the system, material costs, and methods for connecting radiators. The heating distribution diagram in a modern apartment building is, as a rule, carried out using vertical technology, which most fully satisfies the requirements of non-standard layouts.
The vertical scheme differs from the horizontal analogue, first of all, in minor heat losses. This feature is due to the carefully thought-out arrangement of the main pipes, which function as risers.
Interestingly, this technique owes its appearance to new construction standards in the country. Initially, it was not widespread, which is due to certain installation nuances. Things changed dramatically when five-story Khrushchev-era buildings began to be actively built in the USSR, the area of apartments in which was small, and therefore there was no need for horizontal wiring. In order to save money, a vertical methodology was created, characterized by a number of nuances:
- There are several risers with circulating coolant running vertically, to which radiators are connected;
- Each of the radiators can be configured separately;
- The coolant enters the premises through a separate circuit.
If we talk about private cottages, then such a heating distribution can be used there, but the owners need to prepare for some difficulties. An example of such a problem is that most batteries on the modern market are designed for connection to horizontal systems; they have the appropriate arrangement of pipes, technological holes and sections. Thus, the circuit, ideally, needs special radiators designed specifically for vertical installation.
Another problem arises from this feature. As you know, it is better to install radiators closer to the floor, this will allow for effective air exchange without unnecessary effort. Cold air, according to the laws of physics, will fall down, and heated air will rise up. A vertical radiator is extremely difficult to install in this way, which is why the heating is insufficient.
- The number of floors is greater than or equal to five;
- Each individual room has a small area;
- Sufficient thermal insulation of walls.
If we talk about heat energy metering, it is recommended to install the meter directly on the riser.
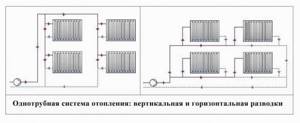
Read in more detail: Diagram and installation of a two-pipe heating system.
The scheme may involve the presence of one or two pipes:
- The option with one pipe implies that the coolant circulates in a closed loop, and the radiators are connected in series. This design feature leads to the fact that the temperature of the last battery will be lower than that of the first devices. However, with a short contour, this shortcoming is naturally corrected. As an additional way of adjustment, you can use the taps between the radiator pipes. Minimum volumes of materials for forming the system, no need for a circulation pump, small volume of circulating coolant - these properties can be attributed to the advantages of the technology.
- The two-pipe scheme is based on the installation of two circuits. The first is used to supply coolant to the radiators, while the second sends cooled water to the boiler for new heating. When laying, you must remember that the pipes must run next to each other, because the radiators are connected in parallel. An additional pipe increases the total volume of coolant used; often it is impossible to supply it by gravity, and therefore it is necessary to install a circulation pump. However, despite some installation inconveniences, the system is more reliable than the first option, since the formation of an air lock is eliminated.
To complete the picture, it is worth considering the horizontal wiring method. Its advantages are as follows:
- In the event of an emergency, it is possible to disconnect only the damaged battery. The method is also convenient when changing heating devices in a separate apartment; there is no need to cover the entire riser.
- It is possible to install energy meters in each apartment, thanks to which residents will be able to adjust the operation of the batteries so that it is both economical and contributes to the formation of an optimal microclimate. For example, during a long business trip or vacation, the room temperature is artificially lowered.
- The technique is independent from the rest of the apartments in the house, and therefore the owner arranges the heating in full accordance with personal requirements. There are no risers in the apartment, and individual pipes can be laid in niches, which is valuable when creating designer interiors.
- It is believed that this technology is more durable.
- The pipes are not laid in the walls, but in special niches and corrugations. This approach is optimal from the point of view of maintainability; the lightweight structure can be easily disassembled to get to the emergency area.
Thus, a residential building can be supplied with heat using any of the described schemes. In order to make the best choice, it is necessary to take into account all the nuances, positive and negative aspects of decisions. Even the vertical option, which may seem inferior to its horizontal counterpart, in a multi-storey building guarantees effective heating with small financial investments during the installation stages.
»
Other
How to get a free register of owners of MKD 2021
Read more
Great article 0
Vertical layout
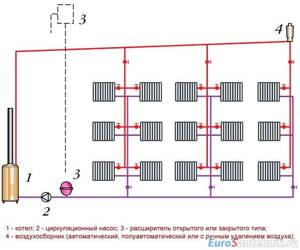
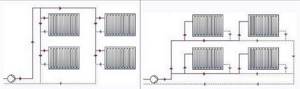
This type of wiring is still used in apartment buildings, since this type is most suitable for heating a large number of floors. Also, vertical wiring saves materials and is easier to install. This type of circuit can be one-pipe or two-pipe, and the two-pipe type is more preferable. The two-pipe vertical heating distribution also allows you to change heating devices without stopping the entire heating system. Heaters can be equipped with automatic or manual temperature control valves.
A single-pipe vertical type circuit does not allow radiators to be turned off individually, but the installation of such a system requires much less pipes than a two-pipe circuit. The vertical type of wiring allows you to evenly distribute heat throughout the room, but the heated area of the rooms is somewhat limited. It is advisable to use vertical wiring if the building has three floors or higher.
Vertical wiring also allows you to organize a heating system that will not be equipped with a circulation pump. This technical solution is applicable to private housing construction. The main disadvantage of a vertical heating scheme is that it cannot be scaled. It may also cause inconvenience that it will not be possible to regulate the temperature in each individual room.
Vertical heating wiring can have an upper or lower location. These two types have some special features. If a single-pipe vertical distribution of the upper type is used, then the supply is carried out from the attic, where a special tank (bed) is installed. Next, the coolant from the reservoir is distributed into risers, which supply heat to the heating devices.
The vertical type distribution with bottom supply is equipped with a reservoir in the basement, from which water flows into the risers. The coolant moves upward along the risers, simultaneously passing through the heating devices in each apartment. If the vertical distribution is installed according to a two-pipe scheme, then adjustable heating devices can be used in its circuit. Heat metering devices can also be connected to such a system.
Horizontal intra-apartment wiring
In many new buildings it is possible to find a relatively exotic scheme: outlets from risers enter the apartment, allowing heating devices to be installed to suit any layout. Along with this, the diameter of the risers and outlets is selected so that the horizontal contour in your apartment does not set the heating parameters in the apartments higher or lower.
In addition to an arbitrary layout, a horizontal circuit with an output and one input allows for the establishment of thermal energy metering. As the price of heating per square meter increases, the installation of meters becomes more and more urgent.

How to correctly install heating in the horizontal circuit of a separate apartment?
According to the author’s humble point of view, the most reasonable thing would be to adapt the Leningrad or barracks wiring diagram to this situation.
- An unbroken ring of DN25 size is laid around the perimeter of the apartment. Under the doorways it is sunk into the screed or laid under the flooring.
- Heating devices cut parallel to the ring without breaking it. The size of the eyeliners is DN20. The connection diagram for a separate radiator is bottom or diagonal.
- Any radiator is equipped with an air vent in one of the upper plugs. Optionally, chokes or thermal heads and shut-off valves on the connections can be installed.
Relevance for autonomous heating
An example of a vertical heating scheme for a private two-story house.
The first problems may arise at the stage of connecting the batteries. This is due to the location of the pipes and the design of the heating device itself. Almost all models are designed for installation in a horizontal system. Therefore, experts recommend installing special vertical wall-mounted heating radiators.
However, the peculiarities of their functioning should be taken into account. The lower the battery is located, the more efficient it will work. Cold air has more mass than warm air, so it concentrates near the floor. The battery's job is to heat it up. Therefore, it should be located as low as possible. Narrow vertical heating radiators are structurally unable to fully perform this task.
But this is not the only drawback characteristic of vertical wiring of the heating system. This can be solved by slightly increasing the length of the radiator inlet pipes. If you adhere to the canons of the scheme, another problem will arise. It consists of tying vertical tubular heating radiators to the location of the thermal risers. For rooms with a small square footage this is not significant. However, if the room has an area of 40 m2 or more and there are 2 external walls, it will be necessary to install several thermal risers.
To summarize, we can highlight the following conditions when installing a vertical single-pipe heating system makes sense:
- Relatively large number of floors. Usually from 5 or more;
- Relatively small area of rooms;
- Good thermal insulation and uniform heat distribution throughout the room.
Alas, these characteristics are unusual for most private cottage houses. That is why they prefer to install a horizontal heating system as one of the best ways to maintain a comfortable temperature.
In old apartment buildings with a two-pipe vertical heating system with bottom wiring, to account for heat, you need to install a meter on each riser. There can be from 2 to 5.
Horizontal heating distribution
In a horizontal heating system, the radiators of each floor are connected to a separate riser. Vertical pipes are missing partially or completely.
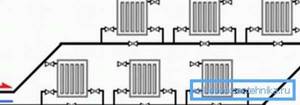
Schemes of heating systems with two-pipe horizontal distributions

Schemes of heating systems with single-pipe horizontal distributions
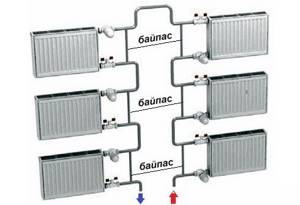
To balance a two-pipe horizontal heating distribution, an adjustable bypass is used, for example, an H-shaped Herz-3000 unit.
Any horizontal scheme can have a parallel or dead-end fluid movement.
The key advantage of horizontal wiring is the ability to implement hidden installation in the structure of walls or floors. For this purpose, metal-polymer pipes are used, which have greater thermal expansion than metal pipes. They are laid using length compensators. At the same time, the problem of air removal arises, which can be solved in one of the following ways:
- installation of Mayevsky crane;
- installation of automatic air vents;
- use of pipes with an oxygen barrier;
- increasing the tightness of the system.
To implement this scheme, it is necessary to organize forced circulation of the coolant.
Where is it used?
It is logical to assume that the horizontal distribution scheme of thermal circuits is more suitable for private houses with individual heating. But in practice, such wiring is successfully used for door-to-door service in apartment buildings. Each apartment receives its own branch of the distribution heat circuit with its own metering, however, no regulation methods are proposed without a special jumper.

But there is another argument in favor of using such systems exclusively in private engineering – the premium quality of the materials. Indeed, if vertical systems are usually based on metal pipes, then horizontal ones are mounted from polymer materials with a heat-resistant coating. Obviously, cross-linked polyethylene PEX significantly increases the cost of the technical implementation of such a scheme. But it is the durability and reliability of this material that allows the use of horizontal heating systems in low-class apartment buildings. Costs for both installation and maintenance of the system are reduced. For example, if for welding work with metal pipes in vertical risers it is necessary to connect a highly qualified welder, then the technology for assembling contours from plastic pipes is within the power of a home craftsman. Using permanent connections, it is easy to assemble the structure and only in extreme cases is cross-linked propylene welded with special soldering stations at the joints.
Selecting radiators
Aluminum and bimetallic radiators have been in greatest demand lately. Their characteristics include improved heat dissipation, as well as durability (for bimetallic devices it is longer)
Steel appliances are noticeably inferior on all fronts, but cast iron products are quite worth paying attention to. In addition to heat transfer, cast iron batteries are also resistant to corrosion. In a private home, you can install any type of radiator, since the heating system in them operates under low pressure, and the possibility of water hammer is excluded
Sometimes batteries are installed in the floor, which is very original and beautiful. Aluminum radiators are beautiful in appearance, quite efficient, but do not have a long service life and are quite expensive. But cast iron batteries will cost much less, and they will last much longer, although they produce less heat.
In a private home, you can install any type of radiator, since the heating system in them operates under low pressure, and the possibility of water hammer is excluded. Sometimes batteries are installed in the floor, which is very original and beautiful. Aluminum radiators are beautiful in appearance, quite efficient, but do not have a long service life and are quite expensive. But cast iron batteries will cost much less, and they will last much longer, although they produce less heat.

To install heated floors and radiators on the same collector in an apartment with central heating, the choice should be made between cast iron and bimetallic products. Only they are distinguished by sufficient strength and durability to work successfully under the influence of high pressure and possible water hammer, as well as when in contact with an aggressive coolant environment.
It would be best, of course, to purchase bimetallic radiators. Leading European manufacturers: Sira, Global Style, Radena, Regulus-system. Their cost is quite acceptable for the consumer
If we consider Russian brands, then we should pay attention to the company Rifar, in particular, to the radiators of the Rifar Monolit model. In terms of quality and properties, these products are quite on par with their European counterparts, but much cheaper.
System installation
Installation of heating system components and even laying of pipelines is possible after completion of construction, but it is recommended to carry out technical operations with commissioning activities as the house is being built. This allows, if necessary, to make adjustments to design solutions at the stages of finishing work. The most labor-intensive process is organizing a horizontal heating system for underfloor water heating. In this case, you will need to install a concrete screed on top of the pipes or heating mats. In contrast, wall-mounted convectors and radiators require virtually no “dirty” work and are mounted to surfaces using brackets.

Choosing pipes
Modern design of heat supply systems is 95% based on the use of plastic, polyethylene, and corrugated stainless steel pipes. Each of them has its own disadvantages and advantages.
Metal and copper pipes also have the right to exist, but due to their tendency to corrosion, high cost, and complexity of installation, their use is declining. Preference is given to plastic products that are not inferior in characteristics. For detailed recommendations on choosing heating pipes, watch the video.
Metal-plastic, polypropylene pipes
Metal-plastic pipes are widely used when laying water supply, heating, and heated floors. They bend well, are easy to install, can withstand significant temperatures and pressure, and have a budget price.

Metal-plastic consists of heterogeneous layers with different coefficients of thermal expansion. Application experience shows that when using metal-plastic for hot water supply, the layers separate, and the pipe fails after 5-7 years. This type of installation of heating pipes in the floor is not recommended.
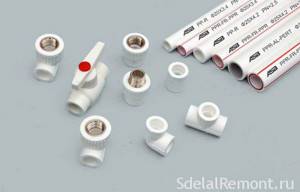
Polypropylene pipes
Polypropylene has no layers and easily withstands the service life guaranteed by the manufacturer. The main disadvantage is the need to strictly observe the temperature and heating time with a soldering iron during installation. Polypropylene has low thermal conductivity and cannot be used for heated floors.
Corrugated stainless steel pipe
Corrugated stainless pipe, developed using innovative technologies, is recommended for laying heat supply networks. When using such a product, it is easy to install floor heating in a new building or replace old pipelines.

Corrugated stainless steel pipe
Here are some advantages of its use:
- bends easily;
- provides simple connection of fittings, facilitates and speeds up the installation process;
- the corrugated structure compensates for fluctuations in linear dimensions and hydraulic shocks;
- durability;
- does not corrode, there is no sediment on the walls.
PE-X pipes
PE-X – products made from cross-linked polyethylene. Cross-linking is the process of imparting strength to the connection of polyethylene molecules, obtaining a round-shaped product. The pipes are marked (GOST 52134-2003 for Russian manufacturers) indicating the stitching method:
PE-Xa molecules are cross-linked by peroxides. This is an expensive, time-consuming process. PE-Xb – steam crosslinking. The process is simple, so these are the cheapest products in the PE line. PE-Xc - cross-linking with radioactive isotopes.

Polyethylene allows oxygen to pass through well, which allows bacteria to grow inside the heating elements. To prevent oxygen from passing to the coolant, the product is made multilayer. A layer of EVOH is inserted inside.
Innovative developments have led to the creation of polyethylene that is more resistant to high temperatures - PE-RT. In modern construction, heating pipes in an apartment are laid across the floor using PE-RT.
Important! It is recommended to choose a pipe marked PE-RT/EVOH/PE-RT; it is five-layer and does not allow oxygen molecules to pass through to the coolant.
| Name. | Diameter, |
Regulatory means
In systems organized in multi-apartment buildings, simple mechanical thermostats are more often used, through which the heating mode is adjusted. It is recommended to turn off such regulators when people are unoccupied for energy saving purposes only in single-family houses. Since the thermal insulation properties of the materials of floors and internal walls are lower than those of external surfaces, after the horizontal heating system is turned off, heating of the home will occur at the expense of neighboring apartments. For this reason, thermostats are used in residential apartment buildings that limit the ability to adjust the temperature regime to both maximum and minimum values.
Selecting a radiator for vertical wiring
Methods of connecting radiators
For the systems discussed above, it is difficult to find vertical water heating batteries. This is due to the limited ways to connect them to the circuit. The greatest heat transfer from the radiator will be with a one-sided upper and lower location of the pipes.
In most cases, vertical tubular heating radiators are characterized by the installation of mounting units on one side. From the point of view of distributing hot water throughout the entire volume of the structure, a detailed scheme is considered the most effective.
Accuro-Korle
Radiator Accuro-Korle Caftan
Currently, this is one of the most famous manufacturers of vertical wall-mounted radiators. A feature of its models is the predominance of Hi-Tech style. A striking example of such a design solution is the Caftan line of radiators. They can perform not only the functions of a heating device, but also a heated towel rail. Currently, the average cost of a Caftan ranges from 30 to 43 thousand rubles.
The Escape model is a typical tubular hydronic vertical heating coil. The strict classic shape will make it possible to fit the radiator into almost any interior of a bathroom or hallway. Its cost is slightly lower than that of Caftan - from 23 to 34 thousand rubles. with the same technical characteristics.
Radiator Accuro-Korle Escape
In addition to this well-known manufacturer, there are several reliable suppliers of such radiators - Caftan (Turkey), Kermi (Germany), Jaga (Belgium). Alas, the economy segment of the vertical battery market does not exist as such. The only way out is to make a similar design yourself. But its technical characteristics will be significantly lower than those of factory models. This is another factor in the unpopularity of vertical wiring of the heating system.
Should I give preference to a vertical heating system? Wiring, radiators, and batteries for it will not be cheap, and installation has a number of significant drawbacks. The main thing is to find out for yourself the feasibility of installing it. It can be used for a small apartment building with autonomous heating. But first you need to make all the required calculations.
The video shows an example of a vertical two-pipe heating system in an administrative building:
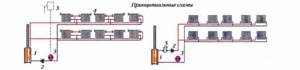
Single-pipe heating system diagram
Single-pipe heating system: vertical and horizontal distribution.
In a single-pipe heating system, the supply of hot coolant (supply) to the radiator and the removal of cooled coolant (return) are carried out through one pipe. All devices relative to the direction of movement of the coolant are connected to each other in series. Therefore, the temperature of the coolant at the inlet of each subsequent radiator along the riser is significantly reduced after heat is removed from the previous radiator. Accordingly, the heat transfer of radiators decreases with distance from the first device.
Such schemes are used mainly in old central heating systems of multi-storey buildings and in autonomous gravity-type systems (natural coolant circulation) in private residential buildings. The main defining disadvantage of a single-pipe system is the impossibility of independently adjusting the heat transfer of each radiator separately.
To eliminate this drawback, it is possible to use a single-pipe circuit with a bypass (a jumper between the supply and return), but in this circuit, the first radiator on the branch will always be the hottest, and the last the coldest.
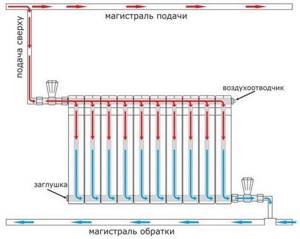
Multi-storey buildings use a vertical single-pipe heating system.
In multi-storey buildings, the use of such a scheme allows saving on the length and cost of supply networks. As a rule, the heating system is made in the form of vertical risers passing through all floors of the building. The heat output of radiators is calculated during system design and cannot be adjusted using radiator valves or other control fittings. Given modern requirements for comfortable indoor conditions, this scheme for connecting water heating devices does not satisfy the requirements of residents of apartments located on different floors, but connected to the same heating system riser. Heat consumers are forced to “endure” overheating or underheating of air temperature during the transitional autumn and spring period.

Single-pipe heating in a private house.
In private houses, a single-pipe scheme is used in gravity heating networks, in which hot water circulates due to the differential densities of heated and cooled coolants. Therefore, such systems are called natural. The main advantage of this system is energy independence. When, for example, in the absence of a circulation pump in the system connected to the power supply networks and in the event of power outages, the heating system continues to function.
The main disadvantage of the gravity single-pipe connection scheme is the uneven distribution of coolant temperature across the radiators. The first radiators on the branch will be the hottest, and as you move away from the heat source, the temperature will drop. The metal consumption of gravity systems is always higher than that of forced ones due to the larger diameter of the pipelines.
Video about the installation of a single-pipe heating circuit in an apartment building:
Features of the vertical heating system
Vertical wiring of the heating system is used in both autonomous and centralized heating networks. Depending on the method of transporting the working medium through the pipeline, it can be with natural or forced circulation. In the first case, the coolant moves due to the difference in density. In low-rise buildings with an autonomous heating network with forced circulation, the movement of the working medium occurs due to the pump, and in the presence of centralized communications - due to pressure drops.
According to the coolant supply option, the following vertical heating systems are distinguished:
- with top wiring. The pipeline for such networks is laid in the attic or under the ceiling;
- with bottom wiring. Installation of lines for transporting the working fluid is carried out through the basement or in the floor screed.
Compared to a horizontal heating system, a vertical heating network is not prone to the formation of air pockets and allows you to control the temperature of the batteries. TM Ogint offers a large selection of thermostatic valves and thermostatic elements, with the help of which you can establish and maintain a comfortable microclimate in the room.
Depending on the design nuances, the vertical heating network can be single-pipe or double-pipe. When choosing a specific type of system, the number of floors of the building and the need to install individual heat meters are taken into account.
Criteria for selecting a heating wiring diagram
Let us outline the main criteria for choosing wiring:
- height of the house: heating distribution with forced water movement is suitable for cottages of any number of floors;
- living area: the radius of the natural circulation line is limited to 30 m;
- purpose of the structure: for permanent residence, heating distribution with forced circulation is preferable;
- budget: the cost of pipes and shut-off valves for a single-pipe distribution without a pump is 1.5-2 times lower than for a two-pipe circuit with forced fluid movement;
- a single-pipe scheme with top heating distribution and natural movement of coolant is suitable for buildings with an attic space in which the top distribution is installed;
- stable electricity: necessary for the operation of the circulation pump;
- To install a heated floor, you should choose between a manifold and two-pipe configuration.
Users seeking maximum automation of the process should consider a manifold or two-pipe wiring with a pump. The use of shut-off valves and thermostats ensures control of heat transfer from radiators.
Beam horizontal systems with two pipes
An even more technologically complex heating system, in which the advantages of a two-pipe scheme increase. If horizontal wiring as such is the concept of constructing an individual branch with heating for a separate apartment, then the radial diagram assumes partial isolation of the circuits already inside this branch. Supply and return pipes are provided for each heating device. What does this mean in practice when operating a horizontal heating system? Firstly, more accurate, convenient and efficient control with zonal microclimate adjustment. Secondly, it becomes possible to organize circuits with their own shut-off valves, automatic control system, etc. On the other hand, for the full functioning of the beam model, the installation of circulation pumps and a distribution manifold with the ability to cover all consuming circuits on the branch is required.
Terminology
First, to avoid confusion, let's define the terms.
- An elevator or heating unit is a place where the control of the heating system and hot water supply of a house or part of it is concentrated.
In addition: the elevator unit brings the pressure and temperature of the coolant to optimal values for the operation of the heating system. Thus, the difference between the supply and return lines of the highway reaches 4 kgf/cm2, while at the same time, a difference of 0.2 kgf/cm2 is sufficient to circulate water through the batteries.
- The water-jet elevator is the main element of the elevator unit, a mixing chamber in which warmer supply water is mixed with the return water involved in repeated circulation.
- Suction is a pipe connecting the supply and return in the elevator unit. Through it, the colder water of the return pipeline enters the repeated circulation cycle.
- Bottling (bottling) is a horizontal pipe that supplies coolant from the elevator unit to the risers.
- Risers are vertical sections of the heating system that supply water specifically to heating devices.
- Connectors are pipes connecting the riser to the battery.

So, what specific wiring diagrams for heating systems can be used in multi-apartment buildings? What specific elements do they include?
Types of radiator connections
The main methods of connecting heating system devices are several types:
- Lateral (standard) connection;
- Diagonal connection;
- Bottom (saddle) connection.
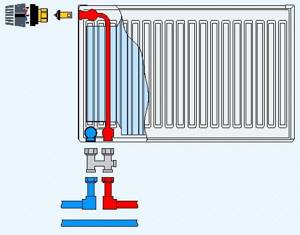
Side connection

Lateral radiator connection.
Connection from the end of the device - supply and return are located on one side of the radiator. This is the most common and effective connection method; it allows you to remove the maximum amount of heat and use the entire heat transfer of the radiator. As a rule, the supply is at the top and the return is at the bottom. When using a special headset, it is possible to connect from bottom to bottom, this allows you to hide the pipelines as much as possible, but reduces the heat transfer of the radiator by 20 - 30%.
Diagonal connection
Diagonal radiator connection.
Connection diagonally to the radiator - the supply is on one side of the device from the top, the return is on the other side from the bottom. This type of connection is used in cases where the length of a sectional radiator exceeds 12 sections, and a panel radiator is 1200 mm. When installing long radiators with side connections, there is uneven heating of the radiator surface in the part furthest from the pipelines. To ensure that the radiator heats up evenly, a diagonal connection is used.
Bottom connection

Bottom connection from the ends of the radiator
Connection from the bottom of the device - supply and return are located at the bottom of the radiator. This connection is used for the most hidden installation of pipelines. When installing a sectional heating device and connecting it using the bottom method, the supply pipe approaches on one side of the radiator, and the return pipe on the other side of the bottom pipe. However, the heat transfer efficiency of radiators with this scheme is reduced by 15-20%.
Bottom radiator connection.
How everything works
First, some general information.
Hot water supply and heating of an apartment building begins with the introduction of a heating main into the house. Two lines are led through the foundation from the nearest thermal chamber - supply (through which process water, also known as the coolant, enters the building) and return (the water, accordingly, returns to the thermal power plant or boiler room, giving off heat).
In the thermal chamber at the entrance to the house (as an option - at the group entrance to several houses located in close proximity to each other) there are shut-off valves or taps.

Thermal chamber at the installation stage
The heating point, also known as the elevator unit, combines several functions:
- Provides a minimum temperature difference between the supply and return of the heating system;
Reference: the upper peak of the supply temperature is 150 degrees, while according to the temperature schedule, the return flow should return to the thermal power plant cooled to 70°C. However, such a difference would mean extremely uneven heating of the heating devices, so water with a more modest temperature - up to 95 degrees - flows from the elevator into the heating circuit.
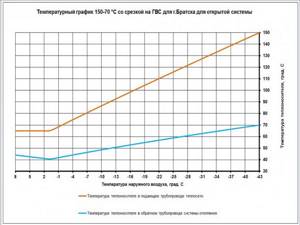
Temperature graph of the supply and return lines of the heating main depending on the outside temperature
- Organizes the supply of hot water to the hot water system and its shutdown throughout the house in case of accidents and routine repairs;
- Allows you to stop and reset the heating system;
- Allows you to take control measurements of temperature and pressure;
- Provides purification of coolant and water for domestic hot water needs from large contaminants.
The heating system can be organized:
- With top filling: supply filling takes place in the attic or technical floor under the roof of the house, and return filling is located in the basement or underground. Each heating riser is turned off independently of the others by two taps at the top and bottom of the house;

Top filling: heating supply is distributed throughout the attic
It’s interesting: there is also a reverse scheme - with supply in the basement and bottling of the return in the attic. However, it is much less popular and, as far as the author knows, is used mainly in small buildings with their own boiler rooms.
- With bottom filling: supply and return are distributed throughout the basement; heating risers are connected to the bottling outlets one by one and connected in pairs by jumpers on the top floor or attic. Each jumper is equipped with an air vent (Maevsky valve or a conventional valve) to bleed the air plug.
The hot water supply system in buildings built in the 70s and in older houses is usually a dead-end system - completely identical to the cold water supply system. From a practical point of view, this means that hot water during water tapping has to be drained for a long time before it is heated, and heated towel rails installed on DHW connections heat up only during water tapping.

Dead-end hot water system: water needs to be drained for a long time before it heats up
In newer buildings, hot water supply and heating of a residential building operate according to the general principle - water continuously circulates through the circuits, ensuring a constant temperature of the heated towel rails and instant heating of the water when disassembled.
The video in this article will help you learn more about how the heating and water supply systems of residential buildings work.
Stabilization of pressure in the heating system
Expansion of water as a result of heating is a natural process. In this indicator, the pressure may exceed a critical value, which is unacceptable from the point of view of heating operation. In order to stabilize and reduce pressure on the internal surfaces of pipes and radiators, it is necessary to install several heating elements. Adjusting the heating system in a private home will be much easier and more efficient with their help.
Adjusting the expansion tank
Expansion membrane tank
It is a steel container divided into two chambers. One of them is filled with water from the system, and air is pumped into the second. The air pressure value is equal to normal in heating pipes. If this parameter is exceeded, the elastic membrane increases the volume of the water chamber, thereby compensating for the thermal expansion of water.
Before adjusting the pressure drop in the heating system, you need to check the condition and settings of the expansion tank. You can adjust the pressure in the heating system by purchasing a tank model with the ability to change it in the air chamber. As an additional measure, install a pressure gauge to visually monitor this value.
However, if there is a significant surge in pressure, this measure will not be enough. This way you can adjust the pressure drop in the heating system if it does not exceed a critical value. Therefore, it is recommended to install additional devices.
How to adjust a security group
Heating safety group
This group of devices includes the following elements:
- Pressure gauge . Designed for visual monitoring of the heating system operation;
- Air vent . If the water temperature exceeds 100 degrees, excess steam acts on the valve seat of the device, releasing air from the pipes;
- Safety valve . It works in the same way as a water drain, but is needed to drain excess coolant from the pipes.
How to adjust a heating radiator using this unit? Alas, it is designed to prevent emergency situations throughout the entire system. Batteries require another device to be installed.
Mayevsky crane
Structurally, it is similar to a safety valve. A special feature is its small size and the ability to be mounted on a radiator pipe with a small diameter.
In order to correctly adjust heating radiators, you need to know in what cases the Mayevsky tap is used:
- Eliminating air pockets in radiators. By opening the valve, air is released until the coolant flows;
- Setting the critical pressure value parameters. If an emergency expansion of water occurs, the valve opens and the pressure in the radiator stabilizes.
Design of the Mayevsky crane
The last function is additional and is most often not used. This task is best handled by the security team. Proper adjustment of heating in the house should include all of the above elements.
When independently regulating a two-pipe heating system while the boiler is running, you need to constantly monitor the readings of thermometers and pressure gauges.
Private houses, apartments from the developer
The last remark, in fact, brings us close to the next section of the article. Its topic is heating diagrams for a private house: pipe routing and insertion of heating devices.
The upper and lower filling schemes described above are quite applicable for a two- or three-story cottage. However, they are not always optimal in terms of material savings, fault tolerance and temperature distribution. Well, let's explore the alternatives.
Horizontal wiring differs from standing (vertical) in that heating devices located at the same level are connected to each other. If there are two or more floors, the outline of each of them is drawn horizontally.
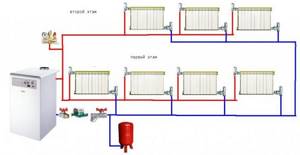
Horizontal wiring for two floors.
Wiring from a boiler or other heat source can be:
- Single-pipe . All devices are connected into the gap of a single ring encircling the perimeter of the room, or (which is much more reasonable) parallel to it. There can be several such rings - according to the number of rooms or floors;

The simplest one-pipe scheme.
- Two-pipe. Each radiator is a jumper between the supply and return threads. It is believed that two-pipe wiring allows for a more uniform temperature distribution.

Section of two-pipe wiring with radiator connections.
In practice, however, it is quite capricious, since it requires throttling of the devices closest to the boiler and precise adjustment of the chokes. The price of non-compliance with this recommendation is defrosted distant heating devices: without chokes, the entire coolant begins to circulate through nearby radiators.

Each radiator in a two-pipe system must be equipped with throttles for adjustment.
It is worth noting that the problem of balancing a two-pipe system is very elegantly solved in the so-called Tichelman loop . In fact, it consists of several parallel contours of the same length.
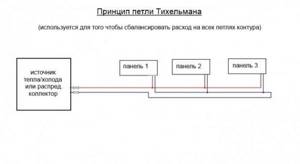
Tichelman loop.
Another solution that allows you to evenly distribute the thermal load is collector wiring . In this case, each device is connected by a pair of connections to collectors responsible for turning off or adjusting the temperature. This scheme involves laying pipes in screeds or grooves: hardly a dozen parallel pipes on the walls will decorate the design of your home.
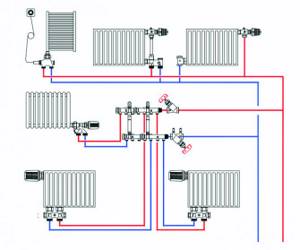
Collector and series wiring can be combined in one heating system.
Finally, a two-pipe distribution can be dead-end (when the direction of movement in the supply and return is opposite) and parallel (the movement of the coolant in two lines is parallel, the system is a vicious circle).

Something like this.
Which scheme is better for a studio apartment or a small cottage?
In my opinion - single-pipe (“Leningradka”), plinth (installed at the bottom of the walls), with radiators connected parallel to the main ring and embedded in a “bottom-down” pattern . It attracts with its absolute fault tolerance, ease of launch and undemanding balance.
Two steps away from ideal.
I'll elaborate on this statement a little:
- Defrosting any individual section of the circuit is impossible in principle as long as coolant circulates in it. The ring, however;
- The operation of a separate device (air lock, shutdown, throttling) does not have any effect on the operation of the remaining batteries. Circulation in the ring will continue in any case;
- To start the ring, just open the valve or gate valve. All air will be forced into the batteries located above and can be vented at any time through Mayevsky taps or automatic air vents. Moreover, it will not interfere with the operation of the batteries even without bleeding: circulation will go through the lower collector of the device.
Heating temperature control
An important parameter of any heating system is the optimal temperature regime for its operation. A ratio of hot and cooled coolant of 75/50 or 80/60 is considered suitable. However, this value is not always acceptable for certain parts of the network. How to properly adjust the heating in the house in this case? Installation of special equipment is required. Some of them are designed for adjusting heating radiators.
Mixing units
Three-way valve
Their main element is a two or three-way valve. One of the pipes is connected to the heating pipe with hot water, the second to the return pipe. The third is mounted on a section of the main line where it is necessary to ensure a lower level of coolant temperature.
As additional options, the mixing units are equipped with a temperature sensor and a thermostatic control unit. A signal is received from the sensor about the heating level of the coolant and it opens or closes the mixing valve, thereby regulating the two-pipe heating system. Most often, such mechanisms are installed in water-heated floor collectors.
If you need to adjust the heating of a water heated floor in an apartment building, you need to take into account the temperature conditions of the pipes. Most often it does not exceed 45 degrees.
Servo drives
Servo drive for radiators
How to adjust the heating in an apartment building if it is not possible to independently change the temperature of the water in the pipes? This requires the installation of special shut-off valves. You can limit yourself to installing simple taps - with their help, the flow of coolant into the radiators is regulated. However, in this case, the adjustment will have to be done independently each time. The best option would be to install servos.
The design of this device includes a thermostat and a servo drive. To work, you must perform the following steps.
- Set the desired temperature value on the thermostat.
- The servo drive will automatically open or close the flow of coolant into the radiator.
In addition to similar models, you can purchase an economy version that includes only a thermostat. In this case, the level of adjustment will not be as accurate. But how to adjust the heating system in an apartment building if old radiators are installed? There are models of thermostats that are designed for installation in cast iron radiators. This measure will make the temperature settings for the apartment more accurate.
Thermostats cannot be used to regulate the pressure drop in the heating system. They will only limit the flow of coolant into the radiator without affecting the temperature regime of the entire system.
Connection diagrams for water heated floors
Now let's look at practical diagrams for connecting a heated floor in a house.
Direct connection from the boiler
This scheme is the easiest to install, but has a number of limitations for implementation.
- Firstly, it can only be used in low-temperature boilers with the ability to regulate the coolant temperature. As a consequence, this scheme can only be used when there is no radiator heating, and the heated floor is the only source of heat in the house.
- Secondly, despite the apparent simplicity of installation, the circuit is “capricious” when it comes to connection nuances and requires experience in such work.
This connection diagram is implemented using 3-way or 2-way valves.
3 way valve
The task of a 3-way valve is to mix hot (direct) and cold (reverse) coolant flows. In the diagram you see an option for installing a 3-way valve. Here it plays the role of a thermostat.
A thermostat is a device that ensures a constant temperature, in our case, the coolant.
This scheme has a number of features. Firstly, it does not work in circuits longer than 35-40 meters. Secondly, it is not suitable if you need to separately regulate the temperature of each circuit.
- The first drawback is eliminated by installing temperature sensors with servo drives and thermostatic valves on each circuit.
- The second drawback is eliminated by installing a circulation pump.
2 way valve
An alternative to the 3-way valve is the 2-way valve or feed valve.
Its task is to provide not a constant, but a periodic addition of water. This mixture is ensured by a thermal head with a temperature sensor included in the valve design. Essentially, a 2-way valve either cuts off hot water from the boiler or adds it to the system.
The advantage of this scheme is its simplicity and the impossibility of overheating. The disadvantage is the 200 meter limitation of the heating area. The limitations in installing circulation pumps with the organization of parallel or sequential (popular) type of mixing are solved.
Connection diagram of VTP through a pumping and mixing unit
This circuit is used to simultaneously connect radiators (main heating) and water heated floors (additional heating) to the heating boiler.
To implement this scheme, you will need a collector unit with a pumping and mixing unit. The manifold assembly is sold ready-made and is included in the assembly of the underfloor heating manifold cabinet. The price of the collector unit is 10-20 thousand rubles. Experienced craftsmen assemble the pumping and mixing unit themselves.
The task of the pumping and mixing unit is to provide a high flow rate of the coolant in the system with the possibility of accurate and, most importantly, independent temperature control. Thanks to the pumping and mixing unit, the water-heated floor circuits operate independently from the radiator circuits.
This independence of the circuits ensures guaranteed reliability of operation and quality of connection of the water heated floor system in the house.
Direct connection of the ETP from the heating radiator
Used to connect one thread of underfloor heating in a small room up to 10 square meters. meters.
Connecting the TP through a thermostatic valve is the simplest and at the same time the most controversial connection method. And that's why.
Firstly, this method only works for very small rooms of no more than 10 square meters. meters. Secondly, this scheme does not provide a high coolant velocity and the temperature difference between the coolant inlet and outlet reaches 40-45˚C, instead of the standard 5-10˚C.
To briefly describe the essence of connecting a heated floor through a thermostatic valve, this is another room heating radiator, only laid in the floor. A loop is made in the radiator heating circuit, a tee is installed, a valve is cut in and an air vent is installed.
Adjustment in such a circuit is made through a thermal head with a sensor (surface or submersible) attached to the heating pipe. There are options for adjusting the air temperature in the room.
Hydraulic separator
This circuit is used in combined heating circuits with radiators. In essence, it is a diagram of the hydraulic separation of a radiator heating system and a warm floor system.
If a circulation pump is used in a radiator heating system, then the presence of a second pump in the mixing unit can lead to a conflicting violation of the hydraulic modes.
To operate two pumps in parallel, a hydraulic separator or heat exchanger is installed in the heating system. Example on the diagram.