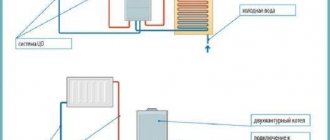
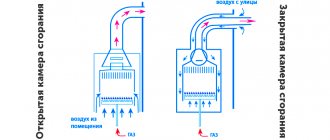
For space heating, closed and open heat supply systems are used. The latter option additionally provides the consumer with hot water. In this case, it is necessary to monitor the constant replenishment of the system.
A closed system uses water only as a coolant. It constantly circulates in a closed cycle, where losses are minimal.
Any system consists of three main parts:
- heat source: boiler room, thermal power plant, etc.;
- heating networks through which coolant is transported;
- heat consumers: air heaters, radiators.
Features of an open system
The advantage of an open system is its cost-effectiveness. Due to the long length of pipelines, the quality of water deteriorates: it becomes cloudy, acquires color, and has an unpleasant odor. Trying to clean it up makes the method of application expensive.
Heating network pipes can be seen in big cities. They have a large diameter and are wrapped in thermal insulation. Branches are made from them to individual houses through a thermal substation. Hot water is supplied for use and to the heating radiators from a common source. Its temperature ranges from 50-75°C.
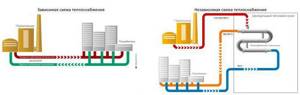
Connection of heat supply to the network is carried out in dependent and independent ways, implementing closed and open heat supply systems. The first is to supply water directly - using pumps and elevator units, where it is brought to the required temperature by mixing with cold water. An independent method is to supply hot water through a heat exchanger. It is more expensive, but the quality of water for the consumer is higher.
Design and operational features of the systems - notes for home craftsmen
The expansion tank may be installed next to the circulation pump. Moreover, both of these elements of the system can be placed with the heating boiler in the same room. This means that you will achieve a reduction in the footage of the main line and save on the purchase of additional pipes. And the need to install fewer pipe products will please any home craftsman who is accustomed to doing home repairs with his own hands.
A closed heating system is equally effective for a private house with a small area and for spacious cottages. It can be installed even in very spacious industrial and special facilities. This distinguishes closed systems from open ones, which function effectively only in buildings with a small area.

Closed heating system in a cottage
Note! In most cases, the circulation unit and expansion tank are placed on the return line, thereby increasing the time of its use (the cooled coolant causes less operational damage to the pump).
But there are also devices that can be placed on the supply pipe. Such pumps are treated with a special lubricant, which perfectly protects them from the negative effects of hot water.
Features of a closed system
The thermal main is designed as a separate closed circuit. The water in it is heated through heat exchangers from the CHP mains. Additional pumps are required here. The temperature is more stable, and the water is better. It remains in the system and is not collected by the consumer. Minimal water losses are restored by automatic replenishment.
A closed autonomous system receives energy from the coolant supplied to the heating points. There the water is brought to the required parameters. Different temperature conditions are supported for heating systems and hot water supply.
The disadvantage of the system is the complexity of the water treatment process. It is also expensive to deliver water to heating points located far from each other.
Security group
A safety group is placed on the supply pipeline at the outlet of the boiler. She must control its operation and system parameters. Consists of a pressure gauge, automatic air vent and safety valve.
The boiler safety group is placed on the supply pipeline before the first branch
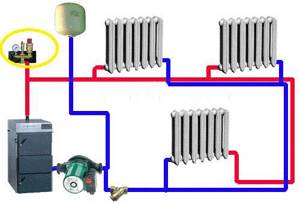
The pressure gauge makes it possible to control the pressure in the system. According to recommendations, it should be in the range of 1.5-3 Bar (in one-story houses it is 1.5-2 Bar, in two-story houses it is up to 3 Bar). If you deviate from these parameters, appropriate measures must be taken. If the pressure drops below normal, you need to check if there are any leaks, and then add some coolant to the system. At increased pressure, everything is somewhat more complicated: it is necessary to check in what mode the boiler is operating, whether it has overheated the coolant. The operation of the circulation pump, the correct operation of the pressure gauge and the safety valve are also checked. It is he who must discharge excess coolant when the threshold pressure value is exceeded. A pipe/hose is connected to the free branch pipe of the safety valve, which is discharged into the sewer or drainage system. Here it is better to do it in such a way that it is possible to control whether the valve works - if water is discharged frequently, you need to look for the reasons and eliminate them.
Security group composition
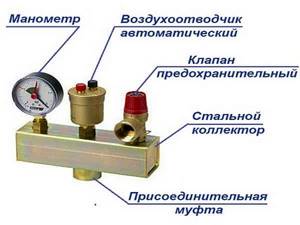
The third element of the group is an automatic air vent. Air trapped in the system is removed through it. A very convenient device that allows you to get rid of the problem of air locks in the system.
Security groups are sold assembled (pictured above), or you can buy all the devices separately and connect them using the same pipes that were used to wire the system.
Heating network pipes
Currently, domestic heating networks are in disrepair. Due to the high wear and tear of communications, it is cheaper to replace the pipes for the heating main with new ones than to engage in constant repairs.
It is impossible to immediately update all old communications in the country. During the construction or major renovation of houses, new pipes in polyurethane foam insulation (PPU) are installed, which reduce heat loss several times. Pipes for the heating main are made using a special technology, filling the gap between the steel pipe located inside and the shell with foam.

The temperature of the transported liquid can reach 140°C.
Using polyurethane foam as thermal insulation allows you to retain heat much better than traditional protective materials.
Positive aspects and disadvantages
The closed version of the water system has gained popularity due to its many advantages:
- there is no contact with the atmosphere - there is no loss of coolant due to evaporation;
- antifreeze can be used to fill the network in a periodically heated building;
- here there is no need for large-diameter pipes laid with a significant slope, as is done when installing mains with natural circulation of water;
- there is no heat loss through the sealed expansion tank, so the scheme is considered more economical;
- water under pressure warms up much faster and boils at a higher temperature, which reduces the risk of vapor lock formation in an emergency;
- a closed type system lends itself well to regulation both in individual areas and as a whole.
Note. Tightness provides another important advantage - the coolant is not saturated with atmospheric air through the open tank. Air bubbles can enter the pipelines only through make-up from the water supply or through cracks in the tank membrane.

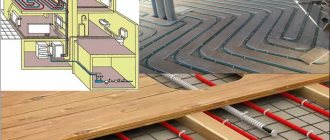
Laying pipelines in the floor and inside walls
Small pipeline diameters and forced circulation are the most important arguments in favor of modern closed heating networks. All wiring can be hidden in walls or floors, and pipes can be laid with a minimal slope. It serves only to drain water during repairs or flushing of radiators and lines.
Now about the fly in the ointment. The fact is that the closed heating system of a private house is unable to function autonomously, since it depends on electricity powering the pump. Therefore, if there are frequent power outages, it is recommended to get an uninterruptible power supply unit or an electric generator so as not to be left without heat.
Reference. On the Internet you can find alternative options - closed systems modeled after gravity (gravity-flow) ones. That is, large pipes with significant slopes. But then half of the above advantages are lost, and the cost of installation increases.
The second negative point is the difficulty of removing air pockets during the process of pouring water, pressure testing and starting the heating. But this minus will not become a problem if air is removed according to generally accepted technology.
Heat supply of multi-apartment residential buildings
Unlike a dacha or cottage, the heat supply of an apartment building contains a complex layout of pipes and heaters. In addition, the system includes control and security controls.
For residential premises, there are heating standards that indicate critical temperature levels and permissible errors, depending on the season, weather and time of day. If you compare closed and open heat supply systems, the first one better supports the necessary parameters.
Communal heat supply must ensure the maintenance of basic parameters in accordance with GOST 30494-96.
The greatest heat losses occur in the stairwells of residential buildings.
Heat supply is mostly produced using old technologies. Essentially, heating and cooling systems must be combined into a common package.
The disadvantages of centralized heating of residential buildings lead to the need to create individual systems. This is difficult to do due to problems at the legislative level.
Circulation pump
The circulation pump ensures the operation of the closed heating system. Its power depends on many factors: the material and diameter of the pipes, the number and type of radiators, the presence of shut-off and thermostatic valves, the length of the pipes, the operating mode of the equipment, etc. In order not to go into the intricacies of calculating power, the circulation pump can be selected according to the table. Select the nearest larger value for the heated area or the planned thermal power of the system, and find the required characteristics in the corresponding line in the first columns.
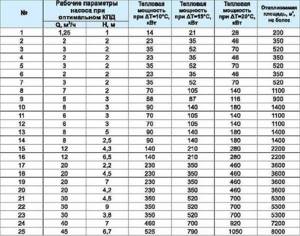
You can select the parameters of the circulation pump from the table
In the second column we find the power (how much coolant it can pump in an hour), in the third - the pressure (system resistance) that it is able to overcome.
When choosing a circulation pump in a store, it is advisable not to save money. The entire system depends on its performance. Therefore, it is better not to save money and choose a trusted manufacturer. If you decide to buy unknown equipment, you need to somehow check it for noise levels. This indicator is especially critical if the heating unit is installed in a residential area.
Strapping scheme
As mentioned earlier, circulation pumps are installed mainly on the return pipeline. Previously, this requirement was mandatory, today it is only a wish. The materials used in production can withstand heating up to 90°C, but it’s still better not to take risks.
In systems that can also operate with natural circulation, during installation it is necessary to provide for the ability to remove or replace the pump without the need to drain the coolant, as well as for the possibility of operation without a pump. To do this, a bypass is installed - a workaround through which coolant can flow if necessary. The installation diagram of the circulation pump in this case is shown in the photo below.

Installation of a circulation pump with bypass
In closed systems with forced circulation, a bypass is not needed - without a pump it is inoperative. But two ball valves on both sides and a filter at the inlet are needed. Ball valves make it possible, if necessary, to remove the device for maintenance, repair or replacement. The dirt filter prevents clogging. Sometimes, as an additional element of reliability, a check valve is also installed between the filter and the ball valve, which will prevent the coolant from moving in the opposite direction.
Autonomous heat supply of a residential building
In old-type buildings, the design provides for a centralized system. Individual schemes allow you to choose the types of heat supply systems in terms of reducing energy costs. There is the possibility of turning them off mobile if there is no need.
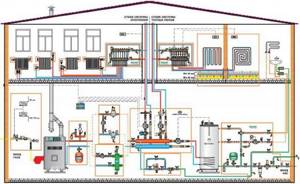
Autonomous systems are designed taking into account heating standards. Without this, it is impossible to put the house into operation. Following the standards guarantees comfortable living conditions for the residents of the house.
The source of water heating is usually a gas or electric boiler. It is necessary to choose a method for flushing the system. In centralized systems, the hydrodynamic method is used. For autonomous use, you can use a chemical one. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the safety of the influence of reagents on radiators and pipes.
About the intricacies of self-installation of systems with a membrane tank
The installation diagram for heating elements is simple. First install the heating unit, then the remaining parts in the following order:
- pipes (all planned wiring);
- heating batteries;
- shut-off valves;
- expansion tank.
Follow the installation procedure strictly and you will not have any problems.
Remember that you need to arrange a closed system in such a way that at any time you can turn off a failed element without stopping the operation of the entire heating complex. To drain water from individual radiators, ball or other shut-off valves are installed at their outlet and inlet. A bypass (spare) line must be installed. It makes it possible to direct the coolant directly to the battery.

Shut-off valves for draining water from the radiator
Also, do not forget about the need to install a security group. It is placed at the outlet of the heating installation. When pressure increases, this group automatically releases it to acceptable limits, thereby protecting the system from breakdown.
Seal all joints between pipes and individual parts of the heating complex with sealant or plumbing flax. Select fittings carefully to create a cohesive system. Connecting products made of brass and bronze have maximum resistance to pressure surges.

How to organize heating of a particular building is up to the owner to decide for himself. If we are talking about a private residential building, then the most common heating option is a closed system with forced circulation. Compared to an open one, it has a number of significant advantages, and therefore is more widely used, regardless of the dimensions of the structure, its purpose, the complexity of the circuit configuration and the parameters of its components.
What is a closed heating system with forced circulation, what are its advantages, what are the features of such a scheme - all these questions can be answered in this article.
Open system
But before considering its specifics, you should understand the terminology. It is precisely because of ignorance of some of the nuances that people who do not have professional training often get confused in definitions. The fact is that not everyone understands the fundamental difference between a closed heating system (CS) and an open heating system (OS).
Forced movement of the coolant (its circulation) can be organized in both. To avoid substitution of concepts in the future, you should immediately answer a number of questions.
What is the difference between ZS and OS? Any liquid expands when heated. Since the coolant is water (less often, antifreeze or its analogues), it is necessary to somehow compensate for the increase in pressure in the pipes, otherwise depressurization of the system cannot be avoided. To do this, an expansion tank is included in the circuit. In the OS it is open type, and the pressure is regulated by the atmosphere.
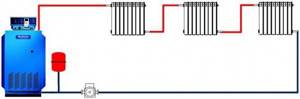
Closed heating system
In a closed circuit, it is completely sealed, and its internal diaphragm (membrane) is responsible for compensating for expansion.
What is the meaning of forced circulation? The movement of liquid does not occur due to the pressure difference at the outlet and inlet of the heat generator (as they say, by gravity), but is carried out by a pump, which is one of the components of the circuit.
Comparing different systems, you can see that each has both pros and cons, although the system with forced circulation has many more advantages. Its significant drawback is only one thing - “binding” to the power supply/voltage. When it is turned off, the pump and boiler will stop.
On a note! When choosing this particular heating option, it is necessary to foresee in advance how to organize an alternative electricity supply. Therefore, the cost estimate should immediately include the cost of purchasing an autonomous power source.
Legal basis for relations in the field of heat supply
The relationship between energy companies and consumers is regulated by the Federal Law on Heat Supply No. 190, which came into force in 2010.
- Chapter 1 outlines the basic concepts and general provisions that define the scope of the legal framework of economic relations in heat supply. It also includes the provision of hot water. The general principles of organizing heat supply are approved, which consist in creating reliable, efficient and developing systems, which is very important for living in the difficult Russian climate.
- Chapters 2 and 3 reflect the broad scope of powers of local authorities, which manage pricing in the field of heat supply, approve the rules of its organization, accounting for heat energy consumption and standards for its losses during transmission. The full power in these matters makes it possible to control heat supply organizations that are classified as monopolists.
- Chapter 4 reflects the relationship between the heat supplier and the consumer based on the contract. All legal aspects of connection to heat networks are considered.
- Chapter 5 reflects the rules for preparing for the heating season and repairing heating networks and sources. It describes what to do in case of non-payment under the contract and unauthorized connections to heating networks.
- Chapter 6 defines the conditions for the transition of an organization to the status of self-regulatory in the field of heat supply, the organization of the transfer of rights to own and use a heat supply facility.
Users of thermal energy must know the provisions of the Federal Law on heat supply in order to assert their legal rights.

How to fill heating pipes
We decided to highlight this issue, since filling a closed system must be carried out according to a certain algorithm so that there are no air pockets left:
- First, all heating devices must be cut off from the mains using taps. Open the remaining fittings completely and turn on the water supply. Fill the pipes slowly so that air has time to escape through the valve on the safety group.
- When the pressure reaches 1 bar (watch the pressure gauge), stop filling and turn on the circulation pump for a few minutes to squeeze out any remaining air.
- Leave an assistant to maintain the pressure at 1 bar, while you alternately open the radiator valves and bleed air using Mayevsky taps.
- When finished, start the boiler and pump, warm up the coolant and bleed the air from the batteries again.
After making sure that all pipelines and heating devices are completely warmed up, increase the pressure in the network to 1.5-2 Bar at a boiler temperature of 80 ° C.
Drawing up a heat supply diagram
The heat supply scheme is a pre-design document that reflects legal relations, conditions for the functioning and development of the heat supply system for an urban district or settlement. In relation to it, federal law includes certain norms.
- Heat supply schemes for settlements are approved by executive authorities or local governments, depending on the population size.
- For the corresponding territory there must be a single heat supply organization.
- The diagram indicates energy sources, indicating their main parameters (load, work schedules, etc.) and range.
- Measures are indicated to develop the heat supply system, conserve excess capacity, and create conditions for its uninterrupted operation.
Heat supply facilities are located within the boundaries of the settlement according to the approved scheme.
Installation rules

The rules for connecting equipment and creating a system depend on its type.
Requirements for installation of an open system
When setting up you should:
- Select the lowest point for the heat source and the highest point for the tank.
- Use pipes with a large diameter for the movement of coolant.
- A narrow pipeline is necessary to normalize pressure.
- Install a high riser that will distribute the water evenly.
- Avoid a large number of turns, forks and connections.
- Install the system in a limited space - up to 159 square meters.
- In private households it is better to install a good circulation system.
The open system is suitable for a small country house or cottage.
Installation procedure for a closed system

If a closed heating system with a pump and expansion tank is installed, you must:
- Place the boiler in the basement and the expansion tank in the attic.
- Ensure high-quality thermal insulation of rooms with a container and riser.
- Do not use a large number of shaped elements.
- Avoid overheating the water.
- Drain the coolant if the system does not start in winter.
- Form a pipe slope of 2-3 mm per 1 m of contour.
The principles for calculating the cross-section and slope of a closed heating pipeline are prescribed in SNiP 2.04.01-85.