Having built a private house, the owner gets the opportunity not only to live outside the city, but also to furnish his home to his own taste. The level of comfort can be increased thanks to pieces of furniture, unusual design or heated floors.
A two-story structure allows you to install a warm floor on the second floor, and with proper installation, there will be no common mistake when the first floor is overheated and the second floor is too cool. Let's take a closer look at how to make a heated floor on the first floor while heating the second floor without wasting extra resources.
Which heating system should I choose for the second floor of the house?
To heat the main and auxiliary rooms in the house, you need to choose the correct wiring diagram. This involves choosing the optimal heating system option based on many parameters: type of coolant, characteristics of floor heating, area of the house and required heat parameters.
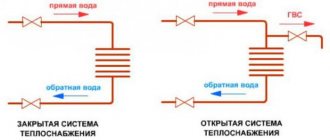
The water heated floor system has gained the most popularity as an alternative to electric or air.
The general heating scheme of a house with 2 floors is taken as a basis, which is altered as necessary. It is recommended to involve a specialist, since changing an existing project or creating a new one with your own hands is too important an undertaking to allow for the possibility of mistakes.
The heating system of a residential building is a set of equipment that includes a pipeline and a boiler, several radiators, sensors, thermostats, fittings and much more. The correct calculation and combination of these devices allows you to achieve the maximum level of thermal comfort.
Thermal insulation of the house
The first thing you need to pay attention to when designing is the thermal insulation of your home. And the better the thermal insulation is, the lower the heat loss coefficient will be, and therefore the less energy will be required to maintain the temperature in the room at a given level. But thermal insulation of a house is not only insulation of the walls; it is also necessary to insulate the floor, and most importantly the ceiling. You need to turn your home into a comfortable “thermos” for living. There is a good thermos that keeps the temperature for a day, but there is also a bad thermos in which the water becomes cold after 5-6 hours. Same with the house. One house will cool down in 5-6 hours, and the other will be warm in a day.
Of course, the quality of thermal insulation materials is important. They should not lose their thermal insulation properties over time. And the expression: “the more, the better” will be right on point. The larger the thermal insulation layer, the lower the heat loss coefficient, which means your home will be like a “good thermos”. For example, it will be very good if the walls of the house, floor and roof are insulated with extruded polystyrene foam 100 mm thick or other heat-insulating material at least 100 mm thick.
Windows and doors are important elements in the construction of a country house. Poor quality and poor installation can negate all efforts to insulate the room. We will talk about how to choose the right windows and doors so that they do not turn out to be a “weak link” in article 8. I will take this information from a person who has been involved in window systems for more than 20 years. This will be the expert opinion of a “window” specialist.
Wiring systems for two-story houses
Existing wiring diagrams for heating systems:
- with one or two pipes;
- with top or bottom wiring;
- with risers located vertically or horizontally;
- with the movement of water along a highway or along a dead-end branch;
- with natural or forced circulation.
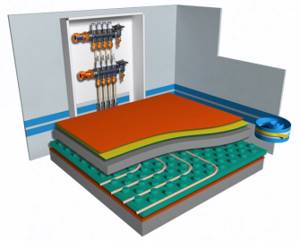
Warm floors in a two-story house will be most productive when choosing wiring with a forced type of coolant circulation. The equipment complex consists of a manifold and pipeline, expansion tank, boiler and heating devices. The pump provides water supply.
Professionals usually make manifold wiring, one-pipe or two-pipe circuits. When choosing a system with one pipe, it will be quite difficult to regulate the heat in different rooms - it is impossible to shut off one radiator separately from the rest.

The two-pipe scheme is universal and will fit perfectly into a two-story house, allowing you to install a circulation pump for the heated floor circuit. The heating power is enough for heated towel rails on each floor and other appliances.
Selecting a laying scheme
There are four main options for a warm water floor scheme in a 2-story wooden house: “snail”, “double snake”, “snake” and a combined system. The choice of a specific installation method depends on the size of the room and the presence of cold zones in it.
- "Snail". The pipes are laid in a spiral, where the “hot line” alternates with the “cold” line, which allows heat to be evenly distributed throughout the room.
- "Double Snake" It is a variation of the previous scheme, where the pipes alternate, but they are mounted in “loops”. Typically used in long and narrow rooms, where laying in a spiral is unprofitable due to the limited width, which does not allow the required spacing between the lines to be maintained.
- "Snake". Used if there are places in the room that are cooler than others, for example near windows. This is a sequential scheme that allows you to concentrate pipes with heated coolant in areas with lower temperatures.
- Combined system. In it, some pipes are laid spirally, and some in series. Most often it is used in rooms of irregular shape.
The choice of a specific scheme depends on a combination of a number of factors, which include the geometry of the heated room, the material and thickness of the walls (which determines heat loss), the diameter of the pipes used and similar factors.
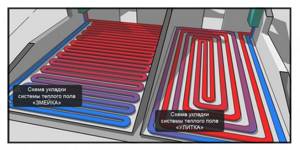
Various laying schemes
Choosing a location for the expansion tank
How to choose the right location for an expansion tank? This question often arises among owners who plan to install warm floors on the second floor with their own hands. If there is an attic and basement, the heating circuit must be made with lower and upper wiring.

Heating expansion tank
Experts recommend taking into account several features:
- The option with lower piping involves installing the tank in the basement. From there, water will flow into the system thanks to the pump;
- With overhead wiring, the boiler is placed in the attic, from where the hot coolant will be supplied through the riser to the radiators and heating equipment.
Construction material
Before you begin installing the floor on the second floor using wooden beams, you should make a list of all the necessary materials. This will allow you to avoid unexpected downtime and delays during work caused by the need to purchase additional building materials.
Beams
The basis of the entire structure of interfloor wooden floors is beams. They act as load-bearing elements, and the strength of the structure depends on them. For them, a beam or carriage with a section of 15 x 15 cm or 18 x 18 cm is usually taken.
This cross-section is usually enough to provide sufficient rigidity for a specific load of 400 kg per sq.m. In this case, it is necessary to comply with the parameters recommended by construction standards: the span length is 4 m, and the step between the beams is 60 cm. Based on these parameters, you can also calculate the required amount of timber.
The table shows the recommended cross-sectional dimensions of the load-bearing beam for a certain span length.
| № | Span length (mm) | Beam cross section (mm) |
| 1 | 2000 | 75×150 |
| 2 | 2500 | 100×150 |
| 3 | 3000 | 100×175 |
| 4 | 3500 | 125×175 |
| 5 | 4000 | 125×200 |
| 6 | 4500 | 150×200 |
| 7 | 5000 | 150×225 |
However, in the absence of timber and small values of the expected loads on the floor, it is quite possible to use boards 50 or 40 mm thick, knocked together in pairs and placed on edge. This option is suitable for installing floors in an attic or in a small country house.
Beams made from wood of stronger species (larch, oak) can rarely be found on the open market, and their price is incomparably higher, and pine wood, after appropriate treatment with antiseptics, will be little inferior in durability to the same larch.
Flooring
Typically, the flooring of interfloor floors is two-tiered: below are subfloors, on which insulation is laid, and on top is a pre-finish flooring mounted on top of the load-bearing beams. Decorative flooring is laid directly on it.
To determine the nature and amount of material for the flooring, you should clearly think through the design of the floors.
When constructing a subfloor, either 5 x 6 cm bars, packed onto load-bearing beams, or grooves made in the beams can be used as support for the flooring boards. The latter option is quite labor-intensive, so most often 5 x 6 cm bars are used to create support.
To calculate the required number of bars, it is enough to count the number of beams and multiply them by the length of each of them. We multiply the resulting footage (the total length of all beams) by two more (since the bars will be packed on both sides of each beam).
A wide range of materials can be used for finishing flooring. This can be plank flooring, plywood, chipboard panels, MDF, OSB, etc. Each of these materials has its own advantages and disadvantages, after reading which you can choose one of them. To calculate the required amount of material, simply calculate the area of the room.
This will save you from having to interrupt your work and buy the missing part.
Impregnations
To maximize the service life of wooden structures, they must be treated with antiseptic materials.
It would also be useful to treat the wood with fire retardants, which increase its fire safety.
To calculate the required amount of impregnation, you should read the instructions for its use - the approximate consumption of the mixture per sq.m. is always indicated there.
Waterproofing
Since wood is afraid of moisture, waterproofing materials are always used during construction.
This can be a roll waterproofing used to create a water-repellent layer between wooden floor structures and the finishing coating, or between wood and brick (stone, cinder block, etc.).
Heat and sound insulation
If it is necessary to create a barrier to noise or cold, insulating materials are used in the construction of floors. Most often, mini-slabs or polystyrene foam are used for these purposes. Their total number in area should be approximately equal to the area of the room. For more information about floor insulation, watch this video:
Fastening materials
To fasten wooden floor elements, you should purchase screws, nails, steel angles, anchor bolts and other consumables
When purchasing screws and nails, you should pay attention to their length
Those. To securely attach a magpie board to a beam, you will need 120 mm nails or 80 mm long self-tapping screws.
Selecting components for heated floors in a private home
A water heated floor is made from many pipes connected by fittings and other elements. It is recommended to choose metal-plastic pipes due to their durability and reliability. Installation of these materials does not require the involvement of specialists, so all work can be done by hand.
Metal-plastic pipes are affordable, durable and invulnerable to corrosion, the polymer circuit does not become clogged, the circuit connections are made with threaded connections, so there is no need to buy a soldering iron.
The coefficient of expansion due to heating is considered a disadvantage, since improper installation causes the system to malfunction.
There is an analogue - polypropylene, but working with it will require a soldering iron and experience in carrying out such work. We must not allow any mistakes or shortcomings in our work. Steel pipes are used very rarely because they rust.
A stainless steel or galvanized pipeline requires threaded connections made with special equipment. Copper pipes are very durable and reliable, but are expensive.

The boiler is purchased based on financial capabilities, while focusing on the type of fuel that is more accessible and inexpensive subject to regular consumption. Increasingly, private homes are using gas as a highly environmentally friendly fuel.
If the boiler is small, it can be installed in a closet or other little-used room of the house. Hanging models are placed on the wall, which saves usable space. Large boilers are located outside, in an extension or a separate building.
Diagrams and installation instructions for one boiler
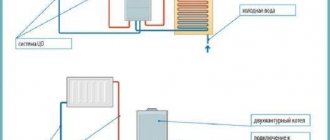
The simplest and most economical way to build a combined heating system in a private house is considered to be a scheme with a radiator and heated floor from one boiler. All elements and the circulation pump are already installed from it.
There are wall-mounted boilers that already have a pump built into them. When using a floor-standing model, it will have to be installed separately.
When directly connected to a gas appliance (this is the model that experts recommend installing when installing a combined heating method in private homes), it is recommended to install a container for condensate. Installing a conventional gas boiler will lead to rapid failure of the heat exchanger.
Gas equipment is placed in rooms with ceilings of at least 2 meters. Ventilation is required.
If a solid fuel model is used, then to connect the heated floor to it, you need to install a buffer tank. Its function is to limit the temperature regime, since it is difficult to directly regulate the temperature.
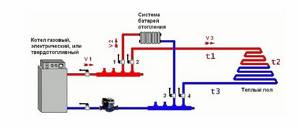
The principle of operation of heating according to a combined scheme - warm floor and battery from one boiler is as follows. The heated water is directed to the mixing unit, where it rests against the safety head. The thermal head determines its temperature, and if it exceeds the required level, the valve opens and the hot and cold coolant is mixed to the required degree.
Then the water is distributed along the contour lines of the floor and radiators. After passing through the entire pipeline, it returns to the heat generator for heating.
The connection diagram for underfloor heating and radiators from one boiler includes the following elements:
- boiler with expansion tank - heats the coolant;
- hydroarrow - wiring, in the form of a pipe with four branches, through which water moves;
- radiator and sex pump - they supply fluid to the collector unit;
- collector - floor loops are connected to its outputs, and hot water is supplied;
- mixing unit - in it the coolant for the TP is diluted;
- thermostat - a head that opens or closes the flow of water into the circuits.
System installation
After constructing the floor “pie” - leveling the base, hydro and thermal insulation and laying the heating elements, you can proceed to installation work and connecting a combined heating system from one boiler (warm floor and radiators). Let's look at the process step by step:
- The boiler is installed and its piping is made (in a private house it is often installed in a separate building). The room must have a chimney and air flow.

- The pipes from the radiators are connected to the water heater, and a pump is mounted between them.

- The floor circuits are connected through a device in which the water is diluted to the required temperature. For this purpose, the following are used: a mixing unit, a 2- or 3-way valve, they are attached to the supply pipe.

- A circulation pump is installed.

- The floor contours are connected through a comb to a source of hot water; it is the coolant that will heat the room.

Installation of a collector system
In heating residential buildings with two or more floors, a two-pipe collector system is often used, when the direct and reverse supply of coolant to the collector is located in a special cabinet. A supply type collector collects water and transfers it in portions through pipes on the wall to the radiator.
The main advantage of this option is the ability to disguise the installation and not spoil the interior.
Collector-type heating is carried out on one or two floors, but with a two-story option, you will have to make an expansion tank on the 2nd floor. Pipes with hot water are installed under the ceiling or window sill, and control taps are installed on radiators.
Installation involves the use of a beam or collector circuit, in which different temperatures are adjusted in each room of the house. Radiators are connected to collectors, creating forced circulation.
This will minimize the temperature difference between the outlet and inlet and make the heating system compact.
Ball-type valves will allow you to exclude a separate radiator from the general circuit, and the operation of the system remains stable. Installing a manifold type system means that each circuit is independent and can be equipped with a separate pump, automatic equipment and multiple valves.
What to consider in advance
Advice: To reduce damage in the event of a break in a “warm floor” pipe, each circuit should be equipped with a shut-off valve.
To understand how you can install water heating in the floor in a wooden house on the second floor, you should know that there are a number of factors that have a direct impact on the installation scheme, the method of laying pipes and the choice of materials for work.
- A warm floor has one limitation, which determines the entire course of future installation: one circuit can heat no more than 30 m2 of area. Exceeding this value leads to unjustified expenses for maintaining the required level of pressure and temperature in the network, therefore, when calculating, the total area is divided into sectors, each of which is heated separately, but with a connection to a common distributor.
- The installation technology involves laying a damper tape, which will “dampen” thermal expansion, movement of the building structure and protect the floor covering from deformation. In small rooms, the tape is laid near the walls; in case of an impressive area heated by several circuits, a damper is additionally equipped to separate each of them.
- “Warm flooring” does not go well with parquet. A thick board has too low thermal conductivity and will require excessive heating power from the boiler to maintain a normal temperature. The ideal option would be porcelain stoneware floor slabs, laminate without backing or linoleum. They transmit heat sufficiently and retain it for a long time, distributing it throughout the room.
- Experts do not recommend choosing metal pipes for water heating. Their service life is significantly lower than their metal-plastic and polypropylene counterparts, at a higher weight and cost. Although the first option is supported by the high thermal conductivity of the metal, which affects the overall temperature in the room.
Taking these factors into account, it is easy to avoid unnecessary expenses on arranging and maintaining the functioning of the entire system.
Underfloor heating system on the second floor
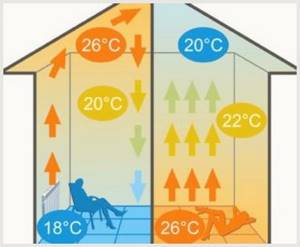
A heated residential building must have rational heat distribution. It is not uncommon for it to be hot on the first floor and cold on the second floor. To avoid such a mistake, it is recommended to make a warm floor and include it in the overall heating scheme. Warm flows rise upward, to the second floor, and cold flows remain below, where they are heated by the floor covering.
When to install a heated floor system? At the stage of major repairs or during construction, since the contour is located inside a cement-sand screed.
If floor heating is being done after renovation or construction, aluminum heat distribution plates will help ensure even heat distribution. Manifold connection of several rooms on one floor allows you to achieve maximum comfort in winter, heat flows evenly warm the room, and not very hot water is needed for the system to function.
The finished heating system must comply with heating engineering standards; for this it is worth consulting with professionals.

Pros and cons of heated floors
The heating system in the form of heated floors has both positive and negative factors. There are good qualities that are characteristic of all types of floor heating structures:
Convenience of living
- high level of convenience: it is pleasant for children to walk on the floor, sit on it, and play;
- relatively low coolant temperature;
- no radiators requiring additional decoration;
- possibility of thermal regulation;
- heated floors are 20% more economical than radiators;
- the design slowly gains heat, but also slowly releases it, making the temperature in the house more stable and uniform;
- there are no drafts in the room.
Each design has its own advantages, for example, heated floors are characterized by rapid heating and precise temperature regulation; hydraulic systems do not have electromagnetic radiation.
But heated floors , in addition to most of the positive parameters, also have disadvantages. Heated floors have certain limitations on the final floor covering. In winter, the consumption of electrical energy increases significantly and there is electromagnetic radiation. Cables are not placed under plumbing equipment.
The disadvantages of heated water floors
This may include the possibility of a pipeline leak if the laying technology is violated. After the installation of traditional heating has taken place, the floor is raised by a concrete screed by at least ten centimeters. To equip the system, additional equipment is required (water pump), equipment for a box for collectors. Temperature control is difficult.
Preparatory stage
Before calculating a water heated floor, decide on the desired temperature for a given room
It is the same for all underfloor heating schemes. You need to start by calculating the power of the system, taking into account the area of the room, the optimal temperature, and actual heat losses. The power of heated floors should be increased for rooms located on the first and last floors, if the facade walls do not have insulation in accordance with the requirements of existing standards, if the finishing coating is made of natural stone or ceramic slabs.
Necessary conditions for high-quality operation of water floors
Old flooring should be removed and the base leveled if necessary. The height difference across the entire area of the room cannot exceed five millimeters, otherwise the load on the pump increases significantly. In addition, there is a high risk of air locks forming and difficulty in removing them.
Two-pipe heating
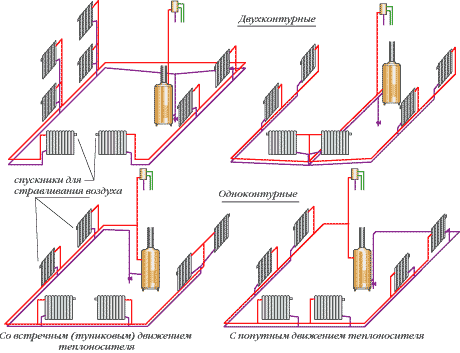
The two-pipe heating system has found application in large two-story houses, as it has significantly less heat loss from radiator to radiator. The structure of the system includes two main lines: hot and cold. In the first, the heated liquid is supplied to heat consumers, in the second, the cooled coolant is discharged. In this case, the highways do not have any direct connection with each other.
The expansion tank is installed on a separate primary branch of the hot main, much higher than the pipelines. Closed models are usually selected. Valves can be installed in front of radiators, allowing you to selectively turn off individual rooms from heating, but closing too many valves can lead to excess pressure and leaks, especially in systems with forced circulation and with incorrect thermal calculations.
Dead-end circuit and Tichelman loop
Initially, all two-pipe heating systems worked according to a direct dead-end circuit. This meant that the radiator, which was the first to receive hot coolant, was the first to release cooled coolant, which entailed a consistent loss of pressure in the radiators and a decrease in their efficiency. Although not as significant as with a single-pipe arrangement. The dead-end circuit is still used for heating small buildings, as it requires significantly less material consumption during installation and is not so demanding on pump power.
Heating with gas boiler

Gas boilers are the main source of energy in most modern heating systems. They guarantee high performance at relatively low energy costs, are highly reliable and safe, of course, subject to all installation standards and regulations.
However, in recent years there has been a trend of constant growth in prices for natural gas, which will soon equate the unit costs of its purchase with the costs of maintaining an electric heating system. And two-story houses are most often built with large areas. As long as gas availability remains, we recommend heating your two-story house with a gas boiler.