Thermal insulation material - expanded polystyrene, commonly called polystyrene foam, today is most widely used in the construction and repair of residential and commercial premises. Compared with other insulation materials, these different types of expanded polystyrene have a number of significant advantages, although they also have some disadvantages. The manufacturing technology of expanded polystyrene involves foaming the polymer - polystyrene - with gaseous pentane - a low-boiling liquid from the group of hydrocarbons.
If we consider the structure of the foam, the share of solid matter in its volume does not exceed 2.0%, and 98.0% are voids, which are miniature polystyrene chambers containing air. The closest “relative” of this classic foam is penoplex, which is produced by extruding polystyrene foam. Today, these materials are often confused. Although both of them have approximately the same physical and mechanical characteristics and equal thermal insulation properties, penoplex, despite its higher cost, is in some cases preferable to use.
Main types
- pressless (made by drying polystyrene granules, brought to a foam-like state at a temperature of 80 ° C, these two processes are repeated again, then the mold is filled with everything, there it becomes knocked down when cooling; it turns out to be more fragile, but is used in production half as much isopentane, which makes the final product cheaper)
Brands of pressless foam
- extruded (it is called an extruder, because they use similar equipment in production, we will consider it later in the article)

- extrusion (field of application is packaging in the food industry)

- pressed (becomes more durable)

- autoclave
Ability to conduct heat
The foam consists of many air-filled polystyrene bubbles in a ratio of 2% film to 98% air. The general appearance of this material resembles foam, which is why it is called expanded polystyrene.

The air inside polystyrene bubbles retains temperature excellently, which is why polystyrene foam is the best heat-insulating material.
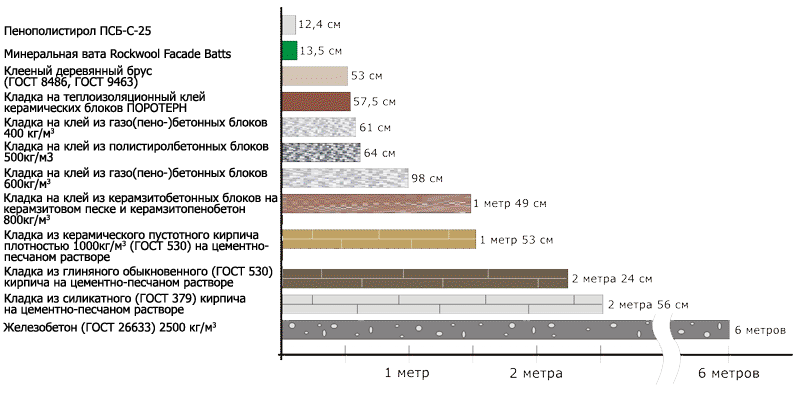
Mineral wool has greater thermal conductivity. In order to improve the performance of extruded polystyrene foam in terms of heat retention, it is necessary to increase its density. For example, cover the walls in several layers.

Main characteristics
- thermal conductivity is low (the extruder has the same thermal conductivity as other types of polystyrene foam, but the extruder is more expensive)
- durability (up to 60 years does not lose properties when the temperature changes from -40 to +40 °C throughout the year)
- moisture resistance
- it does not create an environment favorable for the development of mold and similar “life” (can only occur on the joint surface of, for example, wood)
- minimal harmfulness (it is allowed to be used in the food industry (packaging));
- a light weight
- noise insulation (3 cm thickness reduces noise up to 25 dB)
- fire resistance (we can only talk about it when it comes to fire-resistant varieties; you also need to know that in the production of fire-resistant types, a larger amount of carbon dioxide is used and if the combustion process takes place directly, then the release of this gas will be greater and it will burn, although the temperature it has a high temperature of +490 °C)
- vapor permeability (similar to wood such as oak)
- tensile strength is at least 20 MPa
- resistance to alcohols and ethers, but is easily destroyed when exposed to solvents
- does not withstand ultraviolet radiation (when using slabs, they must be covered with a protective layer of primer and painted)
Expanded polystyrene is mistakenly called polystyrene foam in everyday life. Let's look at the main differences between the characteristics:
- absorbs water and vapor
- visually they can be distinguished (it has a uniform structure, and the foam has large granules)
- density higher than foam
- mechanical strength
Polystyrene foam and polystyrene foam: brothers, but not twins
It is a widely and universally accepted opinion that polystyrene foam and polystyrene foam are different names for the same material.
Although they are obtained from the same raw materials, it is still worth noting a number of differences between these products. Here they are:
- The density of expanded polystyrene is, on average, four times the density of polystyrene foam. By increasing the structural mass of polystyrene foam parts within not too large limits, this increased density has a beneficial effect on the strength and load-carrying capacity of the products.
- The moisture resistance and vapor permeability of products made from expanded polystyrene exceeds the corresponding indicators of polystyrene foam due to the structural differences of these materials.
- Expanded polystyrene visually looks more uniform; the foam at the fracture has a granular structure.
- Polystyrene foam is cheaper than polystyrene foam.
The differences in the properties of these materials are explained by their manufacturing technologies.
Polystyrene foam is produced by treating polymer raw materials with steam. The granules increase in size, and the micropores between them increase. As a result, a weakening of the connection between granules is observed. When breaking foam plastic, the structure of this material in the form of a mosaic of granules is clearly visible .
Expanded polystyrene is more homogeneous due to the melting of granules and the formation of a uniform mass.
Photo of polystyrene foam
The whole truth about harmlessness, non-flammability and long service life
Polystyrene can serve for many years without losing its properties - tests have shown that it can be defrosted and frozen many times, and the quality of the material does not suffer. This material is not subject to combustion, since it contains special substances - fire retardants. All this seems completely correct and undeniable, but only at first glance. There are several nuances. We'll talk about them further.
Environmental issue
Unfortunately, polystyrene foam oxidizes in air. Moreover, foamed polystyrene foam, which has a looser structure, is more susceptible to this process. Extruded material oxidizes more slowly, but the same fate awaits it. Freshly laid polystyrene foam also releases styrene, since complete polymerization of the material is impossible at the production stage. Until polymerization is completed, the release of styrene will not stop.
Manufacturers are trying to dispute information about the harmfulness of polystyrene foam. They say their products are less harmful than wood. This refers to the release of harmful substances by wood when burning. Indeed, when polystyrene foam burns, it produces carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide and soot. But if polystyrene foam is heated to a temperature exceeding 80 degrees, then harmful vapors are released. They contain vapors: styrene, toluene, ethylbenzene, benzene and carbon monoxide.
Flammability issue
In fact, any polystyrene foam will burn. Manufacturers are lying when they claim that it extinguishes on its own, being less dangerous than wood - alas, this is not the case. Such a statement clearly contradicts Russian GOST 30244-94, according to which foam plastics are classified in groups G3 and G4, the most dangerous, in terms of flammability.
One way to distort the facts is to spectacularly suspend a polystyrene foam board in the air and then set it on fire. To do this, a lit burner is applied to the stove from below. The result speaks for itself - only the piece that was in contact with the burner burns out, and the fire does not proceed further. But this experience in no way corresponds to real operating conditions, and can only serve as a focus. But if you put a piece of polystyrene foam on a plane made of non-flammable material and set it on fire, it will not go out at all. After all, hot drops of polystyrene foam formed when a small piece is heated will transfer the fire to its entire surface. The result will not be long in coming - the stove will burn out completely.
If we take expanded polystyrene, which does not include fire retardants, then its smoke formation coefficient is 1048 square meters per kilogram. For polystyrene foam with a self-extinguishing effect, this figure is higher - 1219 square meters per kilogram. For rubber, for example, it is 850 square meters per kilogram, and for wood it is even less - only 23 square meters per kilogram. To make it clearer, here are the following figures: if the smoke level in a room is more than 500 square meters per kilogram, then if you stretch out your hand, you may not be able to see its fingers.
Fire retardants (most often hexabromocyclododexane) are added to polystyrene foam to increase its fire safety. In our country, it is customary to designate such expanded polystyrene with the letter “C”. This should, in theory, mean that the material has the ability to fade on its own. But in practice, it turns out that polystyrene foam with a fire retardant burns no worse than one that does not contain this additive. It only ignites worse, without doing so spontaneously at elevated temperatures. Its flammability class is G2, but after a few years it turns into G3 or G4 - the properties of the fire retardant deteriorate over time.
However, it should be noted that expanded polystyrene in building structures is never used in an open form. Facade plaster is always applied on top of this material or a screed is installed. Therefore, building structures containing expanded polystyrene are fireproof.
Service life issue
If you use polystyrene foam correctly, covering it on top with plaster or another protective and decorative layer, it will last for 30 years, no less. True, in reality, everything turns out to be not so rosy - either the craftsmen hastily put together the thermal insulation somehow, or the customer will try to save money at the expense of materials, or the inexperienced master will make mistakes when installing polystyrene foam boards.
One of these mistakes is incorrect calculation of the thickness of the insulation. It seems to many that if you take a thick thirty-centimeter slab of polystyrene foam, it will last longer and the house will be warmer. But this is not so - a material of great thickness will develop cracks and waves due to temperature changes, under which cold air will penetrate. It should be noted that in Europe the accepted norm is to insulate the outside of houses with polystyrene foam no more than 3.5 centimeters. thick. This allows you to reduce the risk of poisoning during a fire.
GOST and its size requirements

The symbol for slabs according to GOST consists of letters and numbers, which includes:
- Slab type.
- Brand.
- Sheet sizes.
- Standard designation.
If the sheet has such characteristics as a plate of foamed polystyrene with the addition of fire retardant grade 15, 1200 mm long, 600 mm wide and 40 mm thick, then the entry will look like this: PSB-S-15-1200x600x40 GOST 15588-86.
If the expanded polystyrene board does not contain fire retardant and is grade 15, and its dimensions are the same, then the entry will change and look like this:
- PSB-15-1200x600x40 GOST 15588-86.
Using the technical requirements according to Gosstandart, foaming polystyrene containing a blowing agent: isopentane or pentane is used for the manufacture of foam boards. The residual monomer styrene is added to the total mass.
On the surface of manufactured slabs ready for sale there should be no bulges or depressions more than 3 mm wide and more than 5 mm high. Dullness of the ribs and corners may be observed, but not more than 10 mm from the apex of the right angle.
Application of foamed polystyrenes
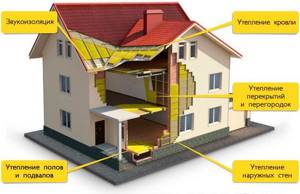
An important reason why the material has become so widespread is its low cost. The main use of expanded polystyrene is its use as insulation during construction and repair work. In addition, it is used as a heat insulator in some types of household and industrial equipment (refrigerators, thermal vans, containers), and is also used in packaging. For insulation of external and internal surfaces of walls in individual and low-rise housing construction, the most widely used polystyrene foam of the PSB-S brand of various densities. Due to its greater breathability, compared to extruded foams “Penoplex”, “Stirex”, “TechnoNIKOL”, its use allows you to create a more comfortable microclimate inside residential premises.
For external insulation of wall structures, the use of PSB-S boards is preferable for the following reasons: This type of expanded polystyrene does not require additional vapor and moisture insulation, which makes it possible to attach insulating sheets directly to the wall surface. When externally insulating walls, plastering can be carried out directly on sheets of dense foam grades (“PSB-S-35”), having previously secured a reinforcing mesh to them. Due to the ability of polystyrene foam boards "PSB-S" to withstand short-term temperatures up to +100.0°C, it is ideal for insulating the base, where the material is fixed using heated bitumen mastic.
To insulate attic and floor ceilings, you can use any type of material, and: Due to the greater density and strength of Penoplex or Technonikol, when insulating attic spaces, it is possible to lay the coating directly on the surface of the insulation. To avoid the formation of condensation when insulating floors with PSB-S sheets (slabs), the use of vapor and moisture insulation is not provided. Skirting boards, platbands and other decorative elements made of polystyrene foam are widely used for interior decoration. They can have different colors and a relief surface, which significantly increases the decorative effect of the overall cladding.
For finishing ceilings, polystyrene foam boards with dimensions of 500.0×500.0 millimeters are widely used. They have a wide range of colors that correspond to the color standards “RAL” (Germany), “NCS” (Sweden) and “MoniColor” (Finland), and the surface of some types of this finish is made in the form of bas-relief. If we summarize all the properties of various materials based on foam polystyrene, then their use during repair and construction work allows us to: Significantly reduce the cost and time required for insulating building structures for residential and domestic purposes. Increase the usable area of residential premises by reducing the thickness of external walls. Increase the environmental safety of residential buildings. The operational advantages of this material include: Reduced heating costs. Reducing financial costs for the purchase of heating equipment and heating system elements. Increasing the thermal comfort of residential premises.
Is polystyrene foam harmful inside the house? Is polystyrene foam as insulation harmful to human health?
To retain heat in a private house or apartment, external or internal wall insulation is performed.
It is important that all materials used in the construction or repair process are environmentally friendly
For example, polystyrene foam is used as insulation. How safe is it for humans and can it be used for insulation?
Is polystyrene foam as insulation harmful to human health?
Many users, in particular owners of apartments on the upper floors, prefer to carry out thermal insulation work from the inside of the room. What does this mean? Which insulation material should you prefer and what is the difference between polystyrene foam and polystyrene? Is polystyrene foam harmful to human health? If it is dangerous, then why and what are the harmful properties of polystyrene foam?
What harmful substances does foam release?
To determine whether polystyrene foam emits harmful substances, you need to consider the composition of the foam; among the harmful components it includes:
styrene (0.01-0.2%) is a substance harmful to human health that can be released into the air for another 20 years after installing the insulation. Released when the temperature exceeds 25 °C;
phenol is another chemical compound in foam that is released when exposed to direct sunlight or at temperatures exceeding 20 ° C;
formaldehyde (formaldehyde, methanal) is a toxic gaseous substance that is released at high temperatures (over 160 ° C).
It should be remembered that substances released by polystyrene foam tend to accumulate, causing deterioration in the health of people living in the room.
So, on the one hand, the balance is: ease of installation, convenience of further finishing, low cost, and on the other hand, the safety of the house and its occupants.
Is polystyrene foam harmful as insulation?
It is possible to answer unequivocally only taking into account the location of its installation and operating conditions, in particular the temperature regime.
When talking about the harmfulness of polystyrene foam, you need to consider at what temperature the foam releases harmful substances. As already noted, styrene and phenol are released at room temperature.
Many are convinced that the harm of polystyrene foam manifests itself regardless of the installation location. However, is foam plastic harmful indoors or is there no health risk when installing it on interior walls? Experts say that polystyrene foam installed on external walls is absolutely safe, since the small amount of vapors of harmful substances that can penetrate through the ventilation, even if accumulated, cannot cause significant harm.
How to eliminate the harmful effects of polystyrene foam
You can reduce or neutralize the harm of polystyrene foam as follows:
do not install in residential premises, inside rooms of a house or apartment;
when insulating walls in a house, attach polystyrene foam only to external walls and install ventilation correctly;
if it is necessary to install foam plastic on the ceiling, this should be done from the attic side (provided that it is non-residential). Installation on the balcony ceiling (from the inside) is also excluded;
do not purchase polystyrene foam produced by handicraft methods. Each seller must have a certificate confirming the styrene content;
Use only for its intended purpose, namely as external insulation. The construction of playhouses for children is, of course, unacceptable. But is polystyrene foam dangerous for animals and birds, in particular for chickens (who love to peck at it)? Manufacturers say no. After all, the lifespan of chickens is short and harmful substances simply do not have time to accumulate in their bodies.
Foiled polystyrene foam
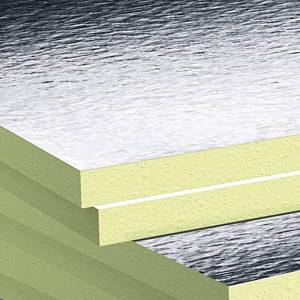
It is a mixed thermal insulation material, which is covered on both or one side with polished foil with an aluminum layer or metallized polypropylene film. Due to the metallic properties of the coating, the reflection effect can reach 97%. The choice of FPS as a solution for heated floors is considered ideal insulation. The foil layer reflects heat rays, thereby improving the insulating properties of the material. FPS is also used for insulating pipes in heating networks; thermal insulation of ventilation ducts, air ducts in ventilation and air conditioning systems; thermal insulation of walls; sound insulation between floors; used as technical insulation of process equipment.
Air-filled insulation cells perfectly combat acoustic pollution. It is insensitive to pressure, horizontal loads, liquid media, thermal instability (the upper limit of the operating range is 180 °C heat, the lower limit is 180 °C cold), it retains its original qualities for a long time: it is not inclined to dry out, swell, or deform. Its synthetic nature makes it resistant to decay, inert to the influence of chemical factors (solutions of salts, alkalis, acids), and the destructive activity of pathogenic microorganisms.
A little about the manufacturing technology of polystyrene foam
This material is obtained as a result of heating, leading to expansion of the polystyrene mass.
The raw material is pre-saturated with gas. The hot substance, increasing in volume, fills the mold perfectly. Natural gas is used as a gaseous component if there are no requirements for high fire resistance. If there are such requirements, carbon dioxide is added to the polystyrene mass. In addition, to obtain some types of expanded polystyrene that are resistant to fire, the material is impregnated with special compounds.
Polystyrene foil mats

Foiled polystyrene foam with markings
FPS is able to increase the overall energy efficiency of the facility, retain heat, and significantly reduce the cooling properties of the cement foundation on which the floor covering is installed due to its high sealing characteristics.
The solution to the problem of creating a warm floor today is FPS profile slabs. They have high mechanical strength. On top they are covered with a rigid vapor barrier film. Their surface has a special molding, which allows for reliable and convenient fastening of heating pipes of different diameters. They are laid hermetically, thanks to the side locks, reliable adhesion of the structure is ensured, which eliminates the divergence of the seams. An additional ruler is applied to the sides of the slabs for convenient adjustment of the elements; the embossed lower surface smoothes out unevenness of the flooring and helps absorb noise.
Extruded polystyrene
Extruded polystyrene (hereinafter referred to as EPS), let's consider this issue in more detail. It was invented back in 1941 in the United States of America. The range of applications is very wide: thermal insulation of floors, roofs, plinths and foundations, layered masonry and plaster facades. It is used in the construction of railways and highways, reducing the risk of freezing of subgrade soils and subsequent freezing and swelling. The material successfully solves the problems of thermal insulation of sports grounds, refrigeration units and ice arenas.
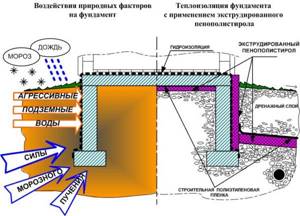
There is no ideal insulation, so the area of application is determined by the strengths and weaknesses of its characteristics. One of the main advantages is almost zero water absorption. Thanks to the closed-pore system, moisture does not pass inside; only the side cells at the cut of the insulation collect water. In a humid environment, it does not collapse and does not lose, like mineral wool, its thermal insulation capabilities. They allow the use of EPS for insulation of: basements, underground parts of buildings and structures, foundations from the ground side.
We can say with confidence that when properly combined with waterproofing, extruded polystyrene enhances its properties. The high density of the insulation gives it rigidity, compressive strength, and the ability to withstand high mechanical loads, and therefore it is practically indispensable when constructing floors, including on the ground, when installing floating screeds. The use of EPS is limited by its high degree of flammability, for example, most EPS belongs to the increased flammability group IV. They support combustion, do not die out, form melt drops, which also burn successfully and, when burned, emit flue gases with a temperature of 450°C.
For comparison, traditional foam plastic marked PMB-S belongs to the G1 flammability group, this is a low flammability group, the burning time is no more than 4 seconds, when the fire source is removed, it stops burning and goes out, because contains fire retardants. Its use should be avoided when insulating roofs, especially with a wooden rafter system.
Due to its high flammability and low vapor permeability, it is practically unsuitable for wooden structures and indoor walls. An exception is the use of EPS in SIP panels, because In the manufacture of SIP panels, artificially dried wood is used, which increases its moisture resistance. And in houses built from this kind of materials, forced ventilation should be used, only in this case mold will not appear there.

EPS cannot be used for insulating facades using the bonded thermal insulation method for the following reasons:
- zero vapor permeability, in winter it will act as a barrier to moisture that penetrates the wall from the warm air of the room. This can lead to the formation of condensation in the wall and the appearance of fungus and mold on the inner surface. For comparison, the vapor permeability coefficient of white foam is five times higher.
- the second reason for not using it on a wet facade is that, due to the structure of its surface, even the highest quality adhesive and reinforcing mixtures do not stick to it with the required strength. Over time, the plaster and reinforcing layer on such facades may begin to lag behind.
- The third reason why it should not be used on the facade is the tendency to photodestruction and thermal destruction. The destruction of the surface can be caused by sunlight, namely ultraviolet radiation. On warm sunny days, when the surface of the facade is heated above 70 ° C, the EPS begins to evaporate and decrease in size, these processes cause breaks in the thermal insulation circuit, such a system begins to lose its thermal insulation qualities and will quickly collapse.
How to choose polystyrene foam correctly
Expanded polystyrene is one of the most popular building materials. It is light, warm and cheap, and very easy to work with. Since the demand is great, there are more and more offers from manufacturers. And each of them assures that their polystyrene foam is the best, and its quality is beyond praise.
1. Lost by countless offers, do not rush to buy material. First, carefully study its parameters. If you need to insulate a facade, take polystyrene foam PSB-S, which is positioned as self-extinguishing. Its brand must be no lower than forty. And if the brand has a number of 25 or less, then don’t look in the direction of such material - it is only suitable for packaging, but not for construction work.
2. When purchasing material, check to what standards it is made. If a manufacturer manufactures products not according to GOST, but according to its own specifications, then the characteristics of the material may differ. For example, expanded polystyrene PBS-S-40 (grade forty) can have different densities - from 28 to 40 kilograms per cubic meter. It is beneficial for the manufacturer to mislead the buyer in this way - less money is spent on the production of polystyrene foam of lower density. Therefore, you cannot rely only on the number in the brand name, but you must ask to see documents confirming the technical characteristics of expanded polystyrene.
3. Before purchasing, try breaking off a piece of material from the very edge. If it turns out to be low-grade packaging foam, it will break with a jagged edge with small round balls visible on the sides. The material obtained by extrusion has regular polyhedra at the site of a neat break. The fault line will run through some of them.
4. As for expanded polystyrene manufacturers, the best of them are European ones, Nova Chemicals, Styrochem, BASF. Russian manufacturing companies, such as Penoplex and TechnoNIKOL, are not far behind them. They have a production capacity that is quite enough to produce polystyrene foam of very high quality.
What do you need to know about sizes? What are they?

Foam sheets can be standard or custom sizes.
The length and width of the standard sheet are 1000, 2000 mm. The manufacturer can cut products into other non-standard sizes.
You can often find sheets of 1200x600 that meet the needs of the buyer and are in good demand. This can be a sheet with dimensions of 500x500, 1000x1000, 1000x500 mm.
On order, you can receive a batch of expanded polystyrene with sides of 900x500 or 1200x600 and other sizes, which does not contradict the standards.
GOST allows cutting products 10 mm smaller if its length is over 2000 and its width is 1000 mm. In thickness for slabs up to 50 mm, a difference of ±2 mm is allowed, and over 50, a difference of ±3 is allowed.
If the length is not suitable for the buyer, then companies selling such products offer individual cutting.
Length and width are important only for transporting building materials from the manufacturer to the customer. The main role is given to the thickness of the material.
The length of extruded polystyrene foam (EPS) sheets is 1200-2400 mm, width - 500-600 mm, and thickness 20-150.
To select a specific value, it is recommended to start from the scope of application, for example, for thickness, the following tips:
- for the floor on the first floor - from 50 mm;
- for the second floor and above – 20-30 mm;
- for additional sound insulation on the floor - 40 mm;
- for internal wall cladding – 20-30 mm;
- for external wall cladding – 50-150 mm.