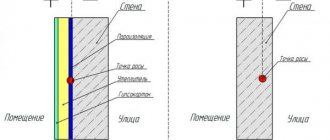
Thermal and sound insulation is an important step in the process of building a house. Of course, you can install a fireplace and a bunch of heaters, but this will not save you from the sounds of the street and will require large financial investments both in purchasing the heaters themselves and in paying electricity bills.
The best option for insulating and soundproofing a house is mineral wool. It consists mainly of natural materials and, among other things, also increases the fire safety of the house. It is also quite easy and quick to install, lasts a long time and is not that expensive. Let's look at the features of this insulation.
Composition of mineral wool
Mineral wool is distinguished by its density characteristics and composition. Its base (90% mineral wool) consists of various rocks, for example, gabbro-basalt or carbonate. These are by-products that remain during the metal production process. The remaining 10% comes from supplements.
Binders are used to unite the fibers of the material. Most often, their role is performed by a phenol-based resin. The top layer of mineral wool is kraft paper with the addition of aluminum or polyethylene particles.
Areas of application
Mineral wool is the best insulation in terms of price and result, so there are many areas and ways of using it. Here are just the main ones:

- insulation of ventilated facades;
- insulation in three-layer masonry;
- internal insulation of ceilings, floors and walls;
- production of wall panels and roofing pies;
- internal thermal insulation of the roof;
- external wall insulation;
- in the process of manufacturing reinforced concrete products;
- insulation of all types of pipelines;
- insulation of loggias and balconies.
You can order high-quality and inexpensive mineral wool by contacting TsKFI LLP.
Performance characteristics
Since mineral wool is able to cope with increased loads, it is used in the construction of standard structures, as well as when installing insulation followed by the production of a heavy concrete screed (in this case, it is recommended to choose durable slabs 5-20 cm high).
Healthy! The service life of the insulation is 20-30 years.
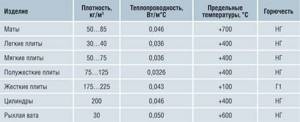
If we talk about the density of the material, it depends on the shape of the mineral wool:
- the minimum density for light slabs and loose wool is 30-40 kg/m3;
- a little more for soft slabs - 50-75 kg/m3;
- for mats this figure is 50-85 kg/m3;
- semi-rigid slabs – 75-125 kg/m3;
- the highest density of cylinders is 200 kg/m3.
The material is not flammable, but the maximum temperature also depends on the shape of the product. For mats it is +700 degrees, for cylinders, light, soft and semi-rigid slabs this figure is +400 degrees. For rigid slabs +100, and for loose wool the limit reaches +600.
Mineral wool has high density and thermal insulation characteristics. They may differ depending on the specific type of material.
Details Mineral wool
Mineral wool is the general name for all inorganic fiber insulation materials. According to the characteristics of production, the type of raw materials, and characteristics, mineral wool is divided into three types: slag wool, glass wool, basalt insulation, which is sometimes called basalt or stone wool.
The concept of mineral wool according to GOST 52953-2008 “Thermal insulating materials and products. Terms and Definitions” includes the following types of cotton wool:
— Glass wool (Mineral wool made from molten glass): Insulation made from staple glass fiber, glass wool is an insulation material that, in terms of production technology and characteristics, has much in common with mineral wool. To produce mineral thermal insulation from glass wool, the same raw materials are used as for the production of ordinary glass or waste from the glass industry. The price of glass wool is relatively low.
— Rock wool (Mineral wool, made primarily from the melt of igneous rocks): Basalt insulation made from mineral basalt wool (stone wool) is the most universal thermal insulation in its characteristics. The production of mineral thermal insulation is carried out from rocks of the basalt group. Basalt insulation made from mineral and stone wool, like no other material, combines excellent thermal insulation and sound insulation characteristics with a high degree of fire resistance. Basalt insulation made from mineral stone wool is widely used in civil engineering, industry, and low-rise construction. Basalt mineral insulation for walls is perfect for thermal insulation of a multi-storey building or industrial building, as insulation for country houses, cottages, summer houses, baths, and they are quite affordable.
— Slag wool (Mineral wool made from molten blast furnace slag): a type of mineral wool. It is made from molten metallurgical slags by processing them into glassy fibers. It is used mainly in the form of finished products (slabs, mats, shells, etc.) made with a synthetic binder.
Mineral wool thermal insulation products are the most common. According to some data, their share among all used TIM (thermal insulating materials) is about 80%. Mineral wool is thin and flexible fibers obtained by cooling a mineral melt previously crushed into drops and stretched into threads. Depending on the type of raw material, mineral wool is divided into stone and slag. The raw materials for the production of stone wool are rocks - diabase, basalt, limestone, dolomite, etc. Slag wool is obtained from the slag of ferrous and non-ferrous metallurgy. The world's leading manufacturers use exclusively rocks as raw materials, which allows them to produce high-quality mineral wool with a long service life. It is recommended to use it for critical structures - in cases where their long-term reliable operation is required. The quality of mineral wool TIM is greatly influenced by the binder. For construction purposes, it is preferable to use products with a phenolic binder, since the urea binder is less water-resistant. There is no need to be afraid of phenol release. With strict adherence to the production process, complete neutralization and polycondensation of phenol occurs. So, when talking about the properties of mineral wool products, we will mean only high-quality mineral wool based on rocks and synthetic (phenolic) binders.
Mineral wool (depending on the type of feedstock) can have a different fibrous structure, specified technologically: horizontally layered, vertically layered, corrugated or spatial, which expands the possibilities of its use in certain structures. It is characterized by significant resistance to high temperatures and chemicals. Mineral wool also has excellent heat and sound insulation properties. Currently, a significant amount of mineral wool is produced, which is widely used in construction. Its areas of application are thermal insulation of walls and ceilings; mineral wool is also widely used for insulation of high-temperature surfaces (furnaces, pipelines, etc.), fire protection of structures and as a soundproofing material in partitions and acoustic screens.
Properties of mineral wool
There are a number of documents (GOSTs) according to which the main indicators of mineral wool products are regulated:
1. GOST 9573-96 “Heat-insulating mineral wool slabs with a synthetic binder”
2. GOST 21880-94 “Thermal insulating mats made of mineral wool”
3. GOST 22950-95 “Mineral wool slabs of increased rigidity with a synthetic binder. Technical specifications"
Most manufacturers currently produce mineral wool according to their own Technical Specifications (TU), these documents prescribe much higher requirements for the produced insulation than those that appeared in GOST.
— Combustibility: The main property of mineral wool, which distinguishes it from many other TIMs, is non-flammability combined with high heat and sound insulation ability. In addition, mineral wool TIMs are resistant to temperature deformation, non-hygroscopic, chemical and biological resistance, environmentally friendly and easy to install. According to fire safety requirements, mineral wool products belong to the class of non-combustible materials (NG). Moreover, they effectively prevent the spread of flame and are used as fire insulation and fire protection.
— Thermal conductivity: The thermal conductivity of mineral wool products consists of three components: thermal conductivity of the fibers, thermal conductivity of the air and moisture located between the fibers, as well as heat transfer by radiation. The thermal conductivity of a solid base, as the main component of the overall thermal conductivity, depends on the geometry and orientation of the fibers in space. For a given density, the most effective thermal insulator is mineral wool with chaotically located and randomly oriented fibers.
— Strength: Fiber orientation affects not only thermal conductivity, but also the strength characteristics of mineral wool products. Their compressive strength increases with increasing number of vertically oriented fibers. Thus, the higher the percentage of vertically oriented fibers, the lower the density of the mineral board can be used to provide a given compressive strength. Therefore, technologies for forming mineral wool boards that provide a high percentage of vertically oriented fibers are the most progressive.
— Shrinkage: An important property of mineral wool materials is negligible shrinkage (including thermal) and preservation of their geometric dimensions throughout the entire period of operation of the building. This ensures that there are no “cold bridges” that would otherwise inevitably form at the joints of the insulation boards.
— Hygroscopicity: Mineral wool has extremely low hygroscopicity: the moisture content in products made from it under normal operating conditions is 0.5% by volume. However, on-site storage and installation of thermal insulation often occurs in wet conditions (for example, during rain). To minimize water absorption, mineral wool is usually impregnated with special water-repellent compounds (silicon-organic compounds or special oils).
— Chemical resistance: Mineral wool insulation materials are characterized by high chemical resistance. Moreover, mineral wool is a chemically passive medium and does not cause corrosion of metals in contact with it. The thermal insulation and mechanical properties of mineral wool products remain at their original level for decades.
Scope of application of types of mineral wool
- as unloaded insulation of horizontal, vertical and inclined building envelopes of all types of buildings.
— in plaster-type external insulation systems.
- as a thermal insulation layer in suspended ventilated facades.
- in systems with insulation on the inside of the building envelope.
— systems with insulation inside the building envelope (three-layer concrete or reinforced concrete panels, three-layer sandwich panels with metal sheathing, layered masonry).
— as thermal insulation of industrial equipment, tanks and pipelines of heating networks, main oil and gas pipelines, process pipelines of power plants, metallurgical, petrochemical and other industrial enterprises.
- as a lower heat and sound insulating layer in multi-layer coverings of flat roofs, including when laid on a surface without a cement screed.
- as a heat and sound insulating layer in flat roof coverings, including when laid on a surface without a cement screed.
- as a top heat and sound insulating layer in multi-layer coverings of flat roofs, including when laid on a surface without a cement screed.
Mineral wool is intended for the manufacture of heat-insulating and sound-proofing products, as well as as a heat-insulating material in construction and industry for insulating surfaces with temperatures up to + 700 °C. It must be remembered that in products made of mineral (stone) wool on a synthetic binder (phenol-formaldehyde resins) at a temperature of about 300-350 ° C, the process of destruction of the binder begins. Depending on the area of application and technical characteristics, manufacturing companies produce thermal insulation materials from mineral wool of various brands.
— Soft slabs and mats: As a rule, they are used in frame structures.
— Rigid and semi-rigid mineral wool slabs: Designed for use in facilities where the insulation is subjected to mechanical stress either during installation work or during operation. The compressive strength of rigid products directly depends on the density of the insulating material and the content of the binder. Semi-rigid slabs that can withstand mechanical loads up to 5 kN/m2, rigid slabs that can withstand loads up to 12 kN/m2. Such slabs are used, for example, in reinforced concrete three-layer panels (sandwich-type structures). Often such plates have special grooves for draining condensate. This is especially important where it is not possible to install ventilation air gaps. For example, in the same reinforced concrete three-layer panels, especially since the outer cladding has low vapor permeability.
A wide range of applications determines the wide range of mineral wool products produced by leading manufacturers, which includes:
— Plates for thermal insulation of metal, brick and concrete parts of a building: As a rule, they are pressed between the corresponding structural elements.
— Mats for insulation of rafter and underground structures: These products must be protected from moisture by installing a vapor barrier on the “warm” side.
— Special windproof boards: They are recommended for use as wind protection over soft slabs in wall and rafter structures.
— Double-layer thermal insulation boards with layers of different densities: They are designed specifically for “ventilated” facades. They are installed in such a way that the denser part is located outside (on the side of the ventilation gap), and the less dense part is adjacent to the wall (base).
— High -rigidity slabs: Designed for insulating flat roofs and serving as the basis for roll and mastic roofing.
— Special slabs have been developed : which, when used as a top layer (with two-layer roof insulation), give the roof the necessary slope
The effect of mineral wool on human health
The potential danger of mineral wool thermal insulation products as a source of carcinogenic factors - dust and phenol-formaldehyde resins - has served as the basis for many studies of its effects on humans and animals[. For example, in December 1997, the European Union published a directive classifying different types of mineral wool according to the degree of danger. According to this directive, mineral wool was considered an irritant (irritant); It was assigned to carcinogenic hazard group 2 (potentially dangerous) or 3 (insufficient data for a reliable assessment) depending on the content of alkali and alkaline earth metal oxides and fiber size. A very strict approach to assessing the dangers of artificial mineral fibers has been adopted in Germany. Many types of mineral fibers that are considered safe in other countries are prohibited here; which causes serious concern for manufacturers. In 2001, the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) prepared a report assessing the carcinogenicity of man-made mineral fibers, according to which glass (continuous glass fiber), stone and slag wool are classified as group 3 in terms of hazard (for mineral wool from these materials there is no sufficient evidence carcinogenicity to humans, and evidence of carcinogenicity to animals is limited). However, mineral wool made from fire-resistant ceramic fibers and some types of discontinuous glass fibers are classified as hazard group 2B (for these types of mineral wool there is reasonable evidence of carcinogenicity to animals).
According to the classification of the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), confirmed in the USA in 2009 by the NTP (National Toxicology Program) organization, mineral wool products cannot be classified as carcinogens for humans.
IARC classification (IARC/CIRC)
— Group 1 (and gents, carcinogenic to humans): wood dust, benzene, tobacco, asbestos.
— Group 2: 2A (agents likely to be carcinogenic to humans): diesel vehicle exhaust, use of tanning lamps. 2B (agents that may be carcinogenic to humans): coffee, gasoline, saccharin, dry cleaning fluid, vegetables in brine.
— Group 3 (and gents that cannot be classified as human carcinogens): mineral wool, caffeine, tea.
— Group 4 (and gents that are probably not carcinogenic to humans): caprolactam (a monomer used in the synthesis of the polymer Nylon-6).
The use of fastening resins in mineral wool is regulated both technologically (there are, as a rule, less than 4% of them, and these are solid resins that are stable under operating conditions) and by regulating the emission (release) of their components. In this case, the goal is to ensure that the content of the relevant substances in the air is below the maximum permissible concentration, even if we are talking about a closed room volume. This approach (standardizing the content of a substance in a material and its release from it in order to ensure maximum permissible concentrations) is common for different materials and the substances included in their composition. Measurements of the fiber content in the air of isolated rooms showed that their content is significantly lower than the maximum permissible concentrations established in the European Union, even during the installation of structures, when the heat-insulating material has open contact with air.
Like
Add a comment
Only registered users can leave comments. Swearing, flooding, insults of other users, and unreasoned statements are prohibited. Links to other sites and advertising, only with the permission of the administrator or employee of the company.
JComments
Glass wool
This is the most accessible and cheapest type of material. Judging by the name, it’s easy to guess that this mineral wool is made from recycled glass. Additionally, it contains sand, lime and some chemically aggressive reagents. The thickness of the fibers of the material is from 5 to 15 micrometers, and the length is 15-50 mm.

But it is worth clarifying several important features of glass wool. Firstly, it contains formaldehyde. In this regard, it can only be used for non-residential buildings (for example, an industrial workshop, workshop or warehouse). Secondly, glass fibers are very fragile. They can easily get into your eyes, skin, and even your lungs. Therefore, protective clothing is required when working with the material.
If we talk about characteristics, the thermal conductivity coefficient of glass wool ranges from 0.030 to 0.052 W/m K. The material can withstand from -60 to +450 degrees. Glass wool is characterized by low hygroscopicity.
Minplita is. Minslab insulation: dimensions, weight, characteristics and cost. How to choose for your home
The topic of energy and thermal efficiency is quickly gaining popularity in the construction market. Houses with similar characteristics are becoming increasingly popular and more and more companies are appearing that offer their services for the construction of such houses.
But what about those who already have their own home? How to make it as comfortable and energy efficient as possible? The answer is simple - insulate. In this article you will learn about one of the most important materials for the construction of private houses - mini-slab insulation.
high-quality and reliable heat-insulating material. The production process of this insulation begins with shaft melting furnaces. There, when exposed to high temperatures, a mineral solution is formed from various components of natural origin, which is subsequently converted into mineral wool by blowing or centrifugal methods.
To obtain a mineral slab, the wool is treated with either synthetic resins or bitumen (depending on the purpose of the slab), and then pressed and dried. At the end, the finished product has a dense structure, does not wrinkle, which facilitates the transportation process, and does not lose its properties for a very long time.
Where is it used?
Most often, mineral slabs are used in construction. Moreover, the methods of its use are quite diverse:
- thermal insulation of facades (read: how to insulate a wooden house from the outside);
- insulation of floors;
- industrial engineering;
- thermal insulation for plumbing equipment, as well as pipelines, heating and water supply systems;
- insulation on roofs and attics;
- the space between the rafters is also insulated with a mini-slab;
- residential construction. Here the mini-slab finds the widest application, since it can participate in all stages of construction - from the basement to the attic.
Slab brands
It is customary to classify mineral slabs according to those areas in which they bring maximum effect. Therefore, the division took place as follows.
General building insulation:
- Technolight.
- Rocklight.
Facade insulation:
- Technoblock.
- Technofas.
- Technovent.
- Technovent N.
Roof insulation:
- Technoruf.
- Tekhnoruf V.
- Tekhnoruf N.
- Roofing wedge (fillet).
Industrial insulation:
- Technosandwich.
Acoustic insulation:
- Technoacoustic.
- Technoflor.
Comparative characteristics of minislabs
The first characteristic by which comparisons are made between different slabs is size and strength:
- P-75. A slab that cannot withstand heavy loads. Suitable for insulation of ventilated roofs, attics, and internal insulation.
- P-125. Produced mainly in Russia, it is highly durable. It is used for insulation between joists, as well as walls, roofs and ceilings.
- PPZh-200. High rigidity plate. Able to withstand more loads, therefore it is used in industrial construction.
Specifications:
- Low thermal conductivity of the material, which reduces heating costs. The fibers do not allow heated air to pass through, but they also do not provide an influx of cold air, so it is worth taking care of ventilation in advance.
- Soundproofing. Due to the fibrous structure, the slab perfectly absorbs vibration caused by sound vibrations, therefore the noise level from the outside is significantly reduced.
- Non-flammability. Mineral board can withstand up to a thousand degrees Celsius, making it excellent fire protection.
- Life time. Minslab does not rot, so its service life is quite long. And rodents will not be able to make passages in it or take it away to build their own housing.
- Water absorption. This figure is slightly higher than one percent, which allows the material to better retain its heat-insulating properties.
- Environmentally friendly. The ministove is made from natural materials, and at high temperatures there is no release of harmful substances. When working with this insulation, you do not need to wear glasses and gloves, because small particles of the fabric do not spread through the air.
Manufacturers and cost
From a large number of manufacturers, having selected the most popular ones on the market, you can provide the following information:
- Rockwool light: 1000x600x100 – 23 kg/m2 – 450 RUR/pack – 1900 RUR/m3.
- Isorok Light BATTS: 1000x600x100 – 40 kg/m2 – 400 rub./packaging – 1800 rub./m3.
- Isover light: 1200x600x100 – 34 kg/m2 – 600 RUR/pack – 2000 RUR/m3.
- Ursa Geo P20: 1250x600x50 – 20 kg/m2 – 2700 rub./packaging – 2500 rub./m3.
- TechnoNIKOL Rocklight: 1200x600x50 – 30 kg/m2 – 400 rub./pack – 1500 rub./m3.
At first glance, the price for a mineral stove may seem expensive, but if you calculate what savings on heating it can bring and imagine what comfort it can provide, then thinking about the cost will seem extremely insignificant and inappropriate.
Slag
This insulation is made from blast furnace slag, which in turn is metallurgical waste. Because of this, slag wool is characterized by residual acidity, so if the insulation comes into contact with metal, then over time the oxidation process will begin. This material is also quite hygroscopic, so during the construction process you will have to think about high-quality waterproofing.

Healthy! Slag wool is very prickly, which complicates the process of its installation. It is not suitable for processing pipes or facades. This is a rather fragile material, so you definitely need to use protective clothing, glasses, gloves, etc.
The thickness of the slag wool fibers is 4-12 microns, and the length reaches 16 mm. Thermal conductivity ranges from 0.460 to 0.480 W/mK. Temperature ranges from -50 to +300 degrees.
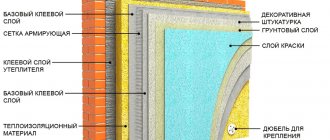
Technology for installing material to the facade of a building
Installation involves the following steps:
- Initially, the facade is freed from objects protruding beyond the walls, and damaged plaster is restored.
- The walls are being primed.
- After preparing the walls, they begin to strengthen the guide profile. It is attached to the wall surface with dowels.
- A special adhesive is used to attach mineral slabs. Apply glue to the cotton slab and press it firmly against the wall. After which the plate is smoothed.
- After gluing the initial row of slabs, they move on to the next row, connecting with the bottom one.
- The glued slabs are additionally secured with dowels for reliability.
- A layer of glue is applied to the installed slabs, and a reinforcing alkali-resistant mesh is “sunk” in it.
- The top is plastered.
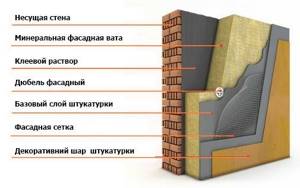
Insulating the facade with mineral wool
The decorative coating should not be made of acrylic. Such plaster does not allow air to pass through and can contribute to the accumulation of moisture in the mineral wool.
Stone wool
The material is made from gabbro and diabase fibers. This is the optimal insulation option in terms of its characteristics. Stone wool does not have the disadvantages of the previous types. It is tensile strength, not brittle, not prickly, does not shrink and can withstand temperatures from -45 to +600 degrees. The length of the insulation fibers is 16 mm, and the thickness is 5-12 micrometers. Thermal conductivity indicators are at the level of 0.048 – 0.077 W/m·K.

In addition, the material does not absorb liquid well. Thanks to all this, it can be safely used for residential premises and heated rooms. During the work you will also not have to resort to protective equipment for your eyes, skin, or respiratory tract. Sheets of cotton wool bend easily and do not break.
Basalt wool
Its composition is similar to stone wool. True, there is a little more fiber. Their thickness ranges from 5 to 15 microns, with a length of up to 50 mm. Also, unlike other types of wool, basalt material does not contain adhesive additives or mineral components. Thanks to this, such insulation can withstand from -190 to +1000 degrees.
In addition, basalt wool is the most resistant to moisture. The thermal conductivity level of basalt material ranges from 0.035 to 0.039 W/mK. Also, basalt wool can provide excellent noise protection, in the range of 0.9-99 dB.

Healthy! If the life of glass wool is up to 30 years, then the basalt composition can last up to 80 years.
Thus, for a living space, the best option would be to choose basalt or stone wool. But you should also pay attention to the labeling of the material.
Mineral wool brands
The characteristics of the insulation can be determined by the markings:
- P-75. This is a flexible material with a density of 75 kg/m3. Mineral wool P-75 is usually used for horizontal surfaces that are not planned to be loaded, as well as for structures and communications with a very slight slope. This type of material is suitable for roofing, ceilings, attics, heating and ventilation pipes.
- P-125. The density of this composition is 125 kg/m3. Mineral wool of this type differs from the previous one in that it has improved sound insulation. Also P-125 is more flexible mineral wool. It is considered the best solution if the house is built from gas or foam blocks. P-125 is used for insulating facades, balconies, and interior partitions.
- PZh-175. This mineral wool has the highest rigidity. Thanks to this, it is excellent for loaded as well as vertical structures. The density of PZh-175 is 175 kg/m3. Mineral wool meets the minimum fire safety requirements and provides excellent noise protection. Typically, the material is laid on surfaces made of wood, concrete or steel.
- PPZh-200. This material has the highest density - 200 kg/m3. In addition, PPZh-200 is a non-flammable composition, so it can be used in the construction of retail departments, warehouses and other facilities. However, installation is only possible on flat surfaces, which will only be subject to static loads. This material is not flexible, as it contains an internal reinforcing layer.

Also, when choosing the best material, you should pay attention to its rigidity.
Selection of mineral wool
If you go by the rigidity of the composition, then you should pay attention to the following nuances:
- Soft insulation is best suited for insulating pipes, chimneys, and roofing “pies”.
- Semi-rigid mineral wool is more often used for insulating facades. Also, mineral wool of this type is often placed between sandwich panels.
- Rigid compounds are optimal for flat surfaces made of metal or wood.
The thermal conductivity indicator is selected in accordance with temperature indicators in winter. It is also worth considering the thermal conductivity of the building walls themselves. As a rule, mineral wool is purchased with a small margin of “temperature stability” in order to be prepared for any weather conditions. But you shouldn’t be too zealous either, since in this case the material will cost more.
Also, do not skimp on the manufacturer. It is better to give preference to Ursa, Rockwool, Paroc, and Isover. Germany has the most stringent requirements for insulation materials, which is why their quality is much higher.

Negative impact min. cotton wool per person
Despite all the advantages and practical specifics of the insulation material, mineral wool still has certain disadvantages. The main disadvantage is the adverse effect on the human body if safety rules and personal protection are not followed when installing cotton wool.
Mineral
The heat insulator is susceptible to temperature changes over a long period of time. As a result, its structure is destroyed and a little dust appears. Through a variety of holes and cracks in the wall, it enters the living room where people live and breathe this dust.

Particularly dangerous are fake fibers that are less than three microns in size. Such small particles are not excreted from the body through exhalation, but settle in the lungs. Over a certain period of time, the number of deposited fibers accumulates and the formation of such unpleasant and dangerous diseases as bronchitis, dermatosis, benign tumors and oncology begins.
The composition of binding resins, which includes aqueous solutions of formaldehyde, can also cause damage to human health. They are often added to mineral wool
to improve its quality. In addition to cotton wool, other building materials that can be found in today's apartment also contain harmful resins - plywood, chipboard and more. Due to this, it is not surprising that in one room the level of formaldehyde in an aqueous solution can exceed the norm many times over.
Its contribution to the shortcomings of min. cotton wool
It also brings in the fact that the key raw material for its production is metallurgical waste. By its very nature, a heat insulator is considered environmentally friendly. But most manufacturers, in order to reduce the cost of manufacturing cotton wool, use industrial slag with a very high content of toxic components such as mercury, lead, and cadmium.

In order to reliably insulate your own home and not risk the health of family members, you need to buy only certified mineral wool
and exclusively from trusted and conscientious manufacturers who produce their own product in accordance with all international sanitation standards and requirements.
Disadvantages and advantages of mineral wool
Mineral wool can be selected for any project (both a residential building and a warehouse). In addition to this, mineral wool is different:
- Resistant to chemically aggressive components.
- The ability not to change its properties over the entire operational period.
- Low shrinkage rates. Much depends on the density of the composition, but as a rule, shrinkage never exceeds 5%.
- Ease of processing.
- Vapor permeability. This means that condensation will not accumulate, which will protect surfaces from premature wear.
If we talk about the disadvantages of mineral wool, many note its high hygroscopicity. But not all compositions absorb water; there are some that are very resistant to moisture. It is also worth paying attention to the presence of formaldehyde in cheap formulations. When heated, compounds hazardous to the body will evaporate.
And one more minus: some types of mineral wool are very fragile. Their fibers should not get into human lungs or eyes.
Advantages of the material
Mineral wool is one of the most popular slab insulation materials today. And this is not surprising, given its many advantages, such as:
- excellent thermal insulation characteristics;
- Fire safety;
- resistance to most types of chemical attack;
- resistance to various biological influences;
- good sound insulation characteristics;
- ability to cope with significant static loads;
- vapor permeability, eliminating the accumulation of condensation under the insulation;
- environmental friendliness;
- durability - the material can serve for more than 45 years without losing its original characteristics.
The only disadvantages of this material include the fact that you can work with mineral wool only with protective gloves and a mask/respirator, as well as the need to waterproof the insulating layer, since the material loses its characteristics when interacting with moisture.