Recently, many have been thinking about insulating their homes. Some insulate the entire house, while others only insulate the balcony, but everyone is faced with the question of choosing the material for the work.
There are expensive and cheap insulation materials, which ones are best? The comparative ease of installation and reasonable price leads us to two main materials - polyurethane foam and polystyrene foam. Both are types of foam and each has its own advantages and disadvantages. Which is better - polystyrene foam or polyurethane foam?
Polyurethane foam or polystyrene foam: which is better to choose for insulation?
Recently, many have been thinking about insulating their homes.
Some insulate the entire house, while others only insulate the balcony, but everyone is faced with the question of choosing the material for the work. There are expensive and cheap insulation materials, which ones are best? The comparative ease of installation and reasonable price leads us to two main materials - polyurethane foam and polystyrene foam. Both are types of foam and each has its own advantages and disadvantages. Which is better - polystyrene foam or polyurethane foam?
Installation features
The installation method is exactly what distinguishes polystyrene foam in panels from polyurethane foam. Polyurethane foam is most often sprayed in the form of a monolithic coating that has no joints and does not require serious preparation. Familiarize yourself with the technology of spraying polyurethane foam, insulation with this material does not require much time, since there is no additional installation work.
Advice from a pro There are two main types of exterior wall finishing insulated with polyurethane foam - siding and plaster. Each method has its own subtleties of applying polyurethane foam, which are important to know in advance for proper preparation of surfaces and subsequent finishing.
Advantages and disadvantages of expanded polystyrene
Ordinary polystyrene foam absorbs moisture relatively well, so you should use an adhesive with a higher density. Expanded polystyrene is a common foam plastic that everyone is familiar with. It has been used for several years now and all its pros and cons have long been known. At its core, it is 98% air bubbles enclosed in 2% polystyrene.
There are two types of expanded polystyrene - regular (foamed) and extruded. Due to its higher density, the latter has better thermophysical properties, it is stronger and more durable.
Both types of foam are available in the form of slabs of various thicknesses. How to distinguish one from the other? Try breaking off a piece from the edge of the slab. Cheap, packing foam will have small balls along the break. High-quality, extruded polystyrene foam will show regular polyhedra when broken.
The main advantages of polystyrene foam include the following:
- Styrofoam
- relatively low price;
- low thermal conductivity;
- simplicity and ease of installation;
- large selection of sheets of different thicknesses and densities.
The advantages of extruded polystyrene foam compared to conventional polystyrene foam are:
- Extruded polystyrene foam
- lower water absorption - several times less than that of conventional foam;
- higher strength;
- long service life.
Literature
- Saunders D., Frisch K. Chemistry of polyurethanes: Transl. from English M.: Khimiya, 1968;
- Lyubartovich S. A., Morozov Yu. L., Tretyakov O. B. Reaction molding of polyurethanes. M.: Khimiya, 1990. 288 p.;
Standards and norms
- Decree of the Moscow Government No. 91-PP - standards for use in thermal insulation of pipes and heating mains;
- Thermal insulation of enclosing structures of buildings and structures - STO 00044807-001-2006;
- Thermal insulation of pipelines with casting polyurethane foam VSN 462-85 (Approved by the USSR Ministry of Montazhspetsstroy);
- Sanitary rules for the production of synthetic and polymeric materials N 4783-88
What is made from polyurethane foam and where can it be used in the home?
In the workshops, sandwich panels are made from polyurethane foam from which you can build a house. An alternative technology is to spray insulation directly onto a large area of the walls and roof of the house, then line the inside with environmentally friendly panels.
Polyurethane foam shells for pipes are reliable thermal insulation that is resistant to water. And pipelines and containers, for example a water storage tank, when installed in the attic, can be insulated by spraying while insulating the entire house. Learn more about water storage tanks in the house
We can find polyurethane foam in doors, these are the most expensive products, as well as in home appliances - in water heaters and refrigerators. Compact designs and long-term temperature retention are all due to this insulation. It is also used to make decor and stucco not only inside buildings but also outside. And also a variety of objects, for example, a saddle for a motorcycle, or used inside a mattress...
What durability, changes over time
It is believed that polyurethane foam will serve without problems for at least 30 years. Let's consider how negative factors influence.
- Exposure to freezing cycles in combination with water does not have a visible destructive effect on this material. No cracks or breaks were found inside the material at any depth.
- Ultraviolet radiation has a detrimental effect on the surface layer. But at a depth of 1 centimeter over a period of 60 years, no changes were detected, even with very intense radiation.
- The thermal conductivity coefficient increases by no more than 30% over 100 years. In fact, the material retains its calculated thermal insulation values throughout its service life.
- Vibration and mechanical loads (without separation or shear) did not lead to discontinuities and crumbling of the material within the specified service life.
We advise you to study - What types of timber are there for building a house?
As you can see, the material is resistant to external influences that can usually affect the insulation layer of insulation materials. The influence of ultraviolet radiation must be reduced by using reliable paint and varnish coatings, constructing façade fencing, etc.
Advantages and disadvantages of polyurethane foam
Polyurethane foam Polyurethane foam is known as ordinary foam rubber. In everyday life we often see soft ones, but in construction we use hard ones. This material has a closed cell structure; the slabs are produced with an edge, which simplifies and reduces the cost of installation. The use of special components makes this material fireproof.
In addition to slabs, it is produced in the form of foam, which is applied to the surface using special equipment. Thanks to the use of foam, “thermal bridges” will be completely absent, and the coating will be continuous.
The main advantages of using polyurethane foam:
- It is unlikely that you can use polyurethane foam on your own for insulation - the equipment is expensive and special protective clothing is required, including a gas mask
- low thermal conductivity coefficient (almost 1.5 times higher than that of foam plastic and almost 2 times higher than mineral wool);
- moisture resistance;
- operating temperature from -70 to +110 degrees;
- 30 years is the designated service life (with proper installation, much longer);
- no deformation during the entire service life;
- resistance - rotting, fungus, moisture does not affect its properties;
- has soundproofing properties;
- environmental friendliness - approved for use even in food warehouses.
Disadvantages of polyurethane foam:
- the price is higher than polystyrene foam;
- low resistance to ultraviolet radiation.
Read about how to insulate a house with polyurethane.
Introduction
As already mentioned, most people completely do not understand the meaning of the words polystyrene foam and polystyrene foam.
Some particularly advanced ones may add the word extruded or extruded foam and combine these words at their discretion. Others believe that regular polystyrene foam is polystyrene foam, and extruded polystyrene foam is expanded polystyrene. Still others completely confuse all these words. Looks like we're about to get confused too... Oddly enough, all these people are partly right. But let's take things in order.
Foam plastic is a whole class of materials used in mechanical engineering, healthcare, gardening, of course - in construction and even in beekeeping, as well as in some other industries. The foam is based on ultra-light plastic gas-filled plastics obtained from various synthetic polymers. The name of a specific type of foam is determined depending on what polymer or resin the material is made from.
Here is just one of the classifications of polystyrene foam - according to the type of polymer or resin used:
- alkene foams - made from polyethylene and polypropylene;
- urea foams - made from urea-formaldehyde resins (Penoizol);
- polyvinyl chloride foams - made from polyvinyl chloride resins;
- polystyrene foams - made from expanding polystyrene with or without the addition of a fire retardant (expanded polystyrene, extruded polystyrene foam);
- polyurethane foams - made from polyesters and polyisocyanates with the addition of a fire retardant (polyurethane foam insulation);
- Phenolic foams - made from resol or novolac phenol-formaldehyde resins and phenolic alcohols.
Thus, polystyrene foam is a general term for foamed plastics, and polystyrene foam is one of the types of foam plastic. Therefore, to say that polystyrene foam and expanded polystyrene are the same thing is tantamount to saying that a UAZ car and the word car itself are one and the same, or that a rose and a plant are one and the same.
All types of foam plastic have a low thermal conductivity coefficient and, as a result, have excellent thermal insulation qualities, which is why they are very often used for wall insulation.
READ MORE: Game consoles for TV - how to choose the best one
Almost all foam plastics release very toxic substances during combustion. Therefore, their applicability in the construction of residential buildings imposes certain restrictions on design documentation.
What to choose
Unfortunately, there is no ideal material that will suit absolutely everyone. For some, it will not be suitable due to the high price of polyurethane foam; for others, the service life of polystyrene foam will not suit them. Therefore, weigh all the pros and cons, but keep in mind that the disadvantages are not complete contraindications for use. Knowing the properties of insulation, you can make the best choice and not regret later about the money spent.
For example, if you want to insulate a garage or a wooden house on your property, choose cheaper polystyrene foam. 10-15 years of foam service life will be quite enough for this type of building. If funds allow, purchase extruded polystyrene foam. Just remember that ultraviolet rays destroy foam.
If you want to improve the thermal insulation of your home or apartment for many years, it would be wise to choose polyurethane foam. The costs will be higher, but you will enjoy the benefits of insulating your home for many years to come. The higher costs of quality installation will pay off over time.
Read about the technology of wall insulation with polystyrene foam here.
For an overview of the advantages and disadvantages of polystyrene foam, watch the video:
A couple of reviews about EPPS
Leonid, 35 years old, Omsk: Used polystyrene foam to insulate the walls of a residential dacha. The house is small and heated in winter, so there were no problems with the appearance of moisture inside the insulating “pie”. I carry out repairs every 5-7 years, which means that during this time the insulation will not have time to sag and lose its qualities.
Vitaly, 45 years old, Khabarovsk: Expanded polystyrene does not weigh down the structure and retains heat well, so I chose this material. I heard that it is flammable, but the house uses a minimal amount of fire-hazardous coatings, for the most part concrete, brick, plastic, and metal are used everywhere.
Structural features and advantages of materials
In order to have a more detailed understanding of both insulation materials and form the correct conclusions when comparing them with each other, it is worthwhile to become more familiar with the properties of each.
Expanded polystyrene

Both insulation materials have a similar “nature” (they are made from the same raw materials), but their production technology is different and this determines everything. Expanded polystyrene is known among ordinary consumers as polystyrene foam. It belongs to the group of polymers and is obtained by foaming polystyrene.
The insulation comes in two varieties: foamed and extruded. The latter is characterized by greater density, which significantly improves the thermal insulation properties of the material and also extends its “life”.
What is polyurethane foam and what does it come in?
This material is a type of plastic. It has a cellular foam structure, and the composition of polyurethane foam is dominated by a gaseous substance - from 85 to 90 percent. Numerous tiny cells, isolated from each other, are filled with gas. The remaining few percent of the volume is the solid part - the thin walls of these cells.
Polyurethane foam was invented by German scientists from the company IG Farben, led by the famous Otto Bayer. However, in those days this name was not yet popular. So, in the laboratory of the city of Leverkusen, after a series of experiments, a new material was obtained, the properties of which turned out to be unique. It became clear that this substance had a lot of potential applications.
Various types of polyurethane foam are in great demand today - after all, they are very simple to produce, and right away on the construction site. In this case, the two liquid components, when mixed, enter into a chemical reaction. If the required proportions are observed, a polymer is synthesized, which is a hardened foam. By modifying the preparation recipe, you can obtain polyurethane foams that differ in properties from each other. Some of them are suitable for thermal insulation of windows and doors, others for insulating houses made of brick or reinforced concrete, and still others for a variety of pipelines.
Video: The process of producing polyurethane foam
So, depending on the proportion of the starting substances, we obtain polyurethane foams with cells of different sizes, the walls of which have different thicknesses and, accordingly, strength. We will not list all types of polyurethane foam that can be obtained by changing the recipe. Let's look at the two most popular materials of this group.
1. The familiar foam rubber, scientifically called elastic polyurethane foam, has a density of 5 to 35 kilograms per cubic meter. We encounter this material every day in the form of washcloths and sponges, filling in chairs and sofas, lining in shoes and clothes, as well as shockproof packaging.
2. Rigid polyurethane foam has recently begun to be used in construction work. But today scientists can already say what will happen to it in years to come - the material is being studied and tested. In addition, some laboratories conducted experiments in which polyurethane foam was subjected to an artificial aging procedure. Both the results turned out to be the same. It is safe to say that polyurethane foam insulation does not like contact with mineral acids and organic solvents. But he is not at all afraid of water and oil products.
In our country we use a fairly large number of brands of rigid polyurethane foam – about 30. They are used both individually and in various combinations with each other. It all depends on the purpose of the application - it could be insulating a house, protecting it from noise, or creating an insulating layer on refrigeration equipment. This material has received such wide application possibilities due to its wonderful properties.

Spraying polyurethane foam on the insulated surface.
Comparative characteristics

Thermal conductivity
One of the key factors influencing the final choice of a particular insulation for a home. The optimal options have low thermal conductivity, while reducing the thickness of the material during installation is allowed.
Comparing polystyrene foam and polyurethane foam, there is a clear leadership of the former: 0.04-0.06 W/m*K versus 0.019-0.028 W/m*K. Due to its denser structure, polystyrene foam retains heat better, but at the same time weighs more (however, this criterion is not considered important when choosing a suitable insulation).
Strength
Expanded polystyrene is considered a fairly durable material, which was incorporated into it at the production stage (its structure is very homogeneous). But polyurethane foam is a set of molecules connected to each other by exposure to high temperatures.
If we compare in terms of indicators, the bending resistance of polystyrene foam is 0.4-1 MPa, and that of polyurethane foam is 0.07-0.2 MPa. It is the mechanical impact that often causes the destruction of the latter - it simply crumbles. Any bend or impact during installation is enough to damage the insulation.
Expanded polystyrene is characterized by significant strength, which makes it a suitable option for installation on load-bearing walls: it is not afraid of temperature changes, deformation, is not subject to shrinkage, etc.
Flammability
Fire resistance or flammability is an important indicator, especially when it comes to insulating a roof or premises or houses made of wood. Both materials under consideration have similar flammability classes: G2 (polyurethane foam) and G3 (expanded polystyrene). G2 implies that the material has an average flammability index, G3 - that the material is flammable.
In fact, the high flammability rate is a key disadvantage of both insulation materials. It is for this reason that manufacturers began to massively add fire retardants to the product being created - special components that prevent the ignition of insulation. If it is created according to technology, in the event of a fire, its attenuation will be almost instantaneous.
Environmental friendliness
Unfortunately, both polystyrene foam and polyurethane foam are toxic materials. But only when they are exposed to high temperatures: they emit toxic gas. It is for this reason that both insulation materials are recommended exclusively for external repair and construction work.
By the way, if the installation and operation technology is followed under normal conditions, none of the materials under consideration pose any danger to human health and the environment.
Moisture resistance
Hydrophobicity is one of the key criteria for choosing insulation and should never be ignored. The resistance of a material to moisture indicates how much it will be able to withstand humidity during operation. The water absorption rate must be minimal, otherwise it threatens the destruction of the insulation, an increase in its weight (this will increase the load on the structure), and loss of the main property - thermal insulation.
Our experts conducted a simple but revealing experiment: they immersed sheets of polystyrene foam and polyurethane foam in water for a day. The first absorbed only 0.2% of the water volume (a very small figure), the second - about 2%. This significant difference is due to the structure of expanded polystyrene: its closed cells practically do not allow water to pass through.
Vapor permeability
The level of vapor permeability also cannot be ignored, because it depends on this whether additional use of a vapor barrier layer will be required. If we talk about polyurethane foam, then its vapor permeability indicator is approximately 0.05 units, but for polystyrene foam it is actually zero. This means that the latter option does not allow steam to pass through, so you don’t have to worry about additional protection (but only if we are talking about “breathable” surfaces).
Sound insulation level
None of the options under consideration can be considered suitable for use as sound insulation. Since the densities of both materials are close, they will not have any significant differences in the level of noise absorption. If you need to provide a room or house with high-quality noise insulation, we recommend additionally using building material specially designed for this purpose.
Comparison
Each of the materials mentioned has its own properties. First, let's touch on the most significant characteristic - thermal conductivity. In this regard, the advantage of polyurethane foam is noted. Moreover, it is important that it is produced not only in the form of panels, but also as an aerosol product that is sprayed onto objects. If polyurethane foam is used in this way, a monolithic coating is obtained that exactly follows the topography of the base.
Expanded polystyrene does not require such an effective application method. It is mounted to the surface in the form of solid slabs. The gaps between them cause heat leakage and deterioration of sound insulation. The difference between polystyrene foam and polyurethane foam is that it does not interact well with adhesives and plaster compositions. Meanwhile, polyurethane foam can be firmly fixed to the surface. In addition, this material absorbs moisture less, which has a positive effect on heat conservation.
It is worth noting that polystyrene foam begins to disintegrate and release hazardous substances at a lower temperature - approximately sixty degrees Celsius. Therefore, it is not recommended to insulate the roof with it, especially in the southern regions with the scorching sun. As for the fire safety indicator, the materials discussed themselves do not burn for a long time. But if there is a constant source of fire, then polystyrene foam quickly becomes engulfed in flames. The process is accompanied by the separation of melting fragments and the saturation of the air with a large amount of toxins. The second material burns worse.
What is the difference between polystyrene foam and polyurethane foam regarding their service life? Here the second type of product wins again. Polyurethane foam retains its beneficial qualities much longer. This is partly due to the fact that it is not subject to deformation. Expanded polystyrene is compressed over time, and its thermal insulation properties noticeably deteriorate. As a result, polyurethane foam is the leader in all respects. It is not surprising that the price is higher.
Polyurethane foam or polystyrene foam – what to choose?
At the moment, a wide range of different thermal insulation materials are used in the construction and industrial industries, but polyurethane foam and polystyrene foam can rightfully be considered the most popular. These materials have become widespread due to their low price, ease of use and their characteristics.
The question logically arises: But what to choose? Which of these materials is cheaper, which has better thermal insulation, longer service life and environmental friendliness?
Let's take a closer look at the technical characteristics and properties of the thermal insulation leaders and choose the winner.
Polyurethane foam (PUF) and expanded polystyrene foam (EPS) have a truly wide range of applications: these materials are used in road construction, for insulation of residential and industrial buildings, in the production of sandwich panels and refrigeration equipment, pipes, and even for electronics packaging.
Is polyurethane foam (PUF) lighter than extruded polystyrene foam (EPS)?
First of all, one is itching to destroy the legend that insulated vans with filled polyurethane foam (PPU) are lighter than glued vans with extruded polystyrene foam (EPS). Optimal thermal insulation properties of both materials are achieved at a density of 40 kg/m³. Considering that the heat transfer coefficients of PPU and EPPS are approximately equal, differing only by 2 thousandths of W/m²*K, it can be argued that in both glued and jellied sandwiches with the same isothermal properties (for example, 0.7 W/m²*K) the thickness of the insulation the material must be the same. This means that with the same densities of materials, their weight in the vans will be the SAME. We also note that, for example, for a van measuring 5.3x2.6x2.5 m with 12 euro pallets, an increase of 10 mm in insulation thickness will add only 27 kg of weight.
Comparison of polyurethane foam or polystyrene foam
We will compare these materials using the example of the production of industrial refrigeration doors and freezers. It is clear that in the production of such equipment, all characteristics of the thermal insulation material without exception are important:
- Coefficient of thermal conductivity;
- Lifetime;
- Price;
- Strength of the material;
- Operating temperature;
- Hygroscopicity;
- Fire safety;
- Bio- and chemical stability;
- Resistance to changes in shape/volume;
- Environmental friendliness;
Specifications
The main and most important parameter of a thermal insulation material (especially in the production of refrigeration equipment), as is known, is its thermal conductivity. When comparing polyurethane foam and expanded polystyrene in this parameter, polyurethane foam will be more effective, since its thermal conductivity coefficient is 0.019 - 0.028 W/m*K, versus 0.04 - 0.06 W/m*K for expanded polystyrene. The table below shows the comparative technical characteristics of polyurethane foam (PUF) and expanded polystyrene foam (EPS).
| Material | Density (kg/m3) | Thermal conductivity coefficient (W/m*K) | Operating temperature (°C) | Service life (years) | Porosity |
| PPU | 25 – 750 | 0.019 – 0.028 | -160…+150 | 50 | closed |
| teaching staff | 40 – 150 | 0.04 – 0.06 | -100…+80 | 15 | closed |
As can be seen from the table, polyurethane foam (PUF) has a wider temperature range of operation, which is important when used in refrigeration equipment (where the temperature inside the room is several times different from the temperature outside). Also (PPU) has a significantly longer service life.
But these are not all the characteristics by which these materials can be compared. Let's look at the physical properties of PUF and PPS.
Physical properties
In the production of refrigeration doors and chambers, an important role is played by such characteristics as the flammability of the material, its hygroscopicity (ability to absorb moisture), strength, and environmental friendliness. The table below shows the comparative physical properties of polyurethane foam (PUF) and expanded polystyrene foam (EPS).
| Property | Expanded polystyrene (PPS) | Polyurethane foam (PPU) |
| Fire safety | Flammable | Not flammable |
| Environmental friendliness | At temperatures above 60°C it releases phenol. | Complies with sanitary standards, can be used at temperatures up to 180 °C without fear. |
| Hygroscopicity | When moisture gets on the panel, it is absorbed and when exposed to low temperatures, it freezes and destroys the foam. | Non-hygroscopic, repels water from the surface. |
| Strength | Brittle, breaks easily, prone to cracking. | Quite durable, density 5 times higher than polystyrene foam. |
| Bio/chemical resistance | High humidity can cause mold and mildew to appear on the slabs, which will cause an unfavorable microclimate in the room. | Moisture resistant. Not subject to rotting or mold. |
| Resistance to changes in shape/volume | Over time, the material settles and contracts, which negatively affects thermal insulation. | The properties of the material do not change throughout the entire service life. |
Expanded polystyrene
The heart of a SIP panel is its insulation core. The most common insulation option is polystyrene foam. It has minimal thermal conductivity, is hygroscopic and is inexpensive.
You can read more about the reasons for the popularity of polystyrene in our article “The whole truth about polystyrene.”
Choose panels with polystyrene foam grade PPS14 (PSB-S25) or PPS16 (PSB-S25F)
Brands of expanded polystyrene according to GOST differ from each other primarily in terms of density. The more kg of grain per 1 m3 of sheet, the better such a SIP panel retains heat and the higher the load it can withstand. But the cost of such expanded polystyrene is higher!
A cube of PPS10 material (density 10 kg/m3) costs an average of 2000 rubles/m3. A cube of PPS16 material (at least 16 kg/m3) costs almost 3,000 rubles/m3! But it is not so easy for the customer to distinguish them visually and tactilely.
That is why buyers who are chasing a low price are often brought to the site SIP panels with PPS10 or PPS11 expanded polystyrene with a density of 10 and 11 kg/m3, respectively.
The Ilya-Stroy company decided to be transparent in the issue of polystyrene foam used, offering customers 2 prices for SIP panels with PPS14 and PPS16
- The standard option is PPS14 (according to the old GOST PSB-S25) - insulation density 14 kg/m3. With fire retardants that block spontaneous combustion of the material. Optimal combination of price and physical properties.
- Premium option - PPS16 (according to the old GOST PSB-S25F) - insulation density from 16 kg/m3. With fire retardants that block spontaneous combustion of the material.
Thermal conductivity of PPS14 is no more than 0.038 W/(m*K). And the thermal conductivity of PPS16 is 0.036 W/(m*K). The difference is only 0.002 W/(m*K). That is why we offer PPS14 as a standard, more affordable option. And we produce PPS16 to order.
Be careful: unfortunately, many estimates indicate PPS16 (PSB-S25F), but in fact panels with “lightweight” expanded polystyrene arrive at the site. Don't skimp on the walls of your future home! Unfortunately, customers do not feel the catch when they encounter a suspiciously low price. They tend to believe in luck: “I was lucky, I found a profitable option,” “Such a deception will definitely not happen to me.” Etc.
The correct foam in SIP panels must contain “flame retardants”
Choose only polystyrene foam type PSB-S (self-extinguishing). This material contains special fire-fighting additives - fire retardants, which block the spontaneous combustion of foam without direct contact with a fire source.
Comparison results between polyurethane foam and polystyrene foam
For ease of perception, we have presented the comparison results in a separate table.
| Parameter | Expanded polystyrene (PPS) | Polyurethane foam (PPU) |
| Thermal insulation properties | ||
| Lifetime | ||
| Price | ||
| Material strength | ||
| Operating temperature | ||
| Hygroscopicity | ||
| Fire safety | ||
| Bio- and chemical stability | ||
| Resistance to changes in shape/volume | ||
| Environmental friendliness |
So, based on the comparison results, we can definitely say that polyurethane foam (PPU) as an insulation material is superior to expanded polystyrene foam (PPS) in almost all characteristics.
What is better polystyrene foam or polyurethane foam?

If you are deciding which is better - polystyrene foam or polyurethane foam, you should compare the properties of these materials. In addition, you need to take into account operating conditions , because in different rooms it may be preferable to use one or another option. To conduct a full comparative analysis, the following factors are taken into account: structure, service life, strength and thermal insulation characteristics, hygroscopicity, noise absorption efficiency, density and some other parameters. The cost of the product is also important.
Briefly about 2 materials
Expanded polystyrene (EPS) is a gas-filled, closed-porous material based on polystyrene; its cells contain natural or carbon dioxide; there is also a vacuum version. There are 2 types:
- foamed;
- extruded (extruded).

Polyurethane foam (PPU) is a group of gas-filled plastics. The material is based on polyurethane. It can be rigid, elastic and self-foaming. If the characteristics of polyurethane foam and polystyrene foam are considered, you should know that both options are similar in most respects.

Polyurethane foam, its properties
Not so long ago, construction companies began to use insulation technology using polyurethane foam mixtures. Polyurethane foam (PPU) itself is a type of gas-filled plastic. Structurally, the material resembles many cells filled with carbon dioxide.

The high level of popularization of this material can be explained by its ease of use. It is possible to create the required consistency at a construction site by mixing several components. As a result of a chemical reaction, the resulting material has the appearance of hardened foam. Depending on the needs, specialists can obtain several forms of polyurethane, with different qualities:
- Rigid, most often used for sealing cracks when installing window units and door frames.
- Soft, used for thermal insulation work on pipeline installation.
- Conditionally rigid, it has found application as a material for insulating all types of walls in residential buildings.
The material itself has found use in many areas: in the production of refrigeration equipment, in the manufacture of furniture products. In addition, elastic polyurethane has extensive use in light industry as a fabric with amazing energy-saving properties. In medicine, it is used in the field of orthopedics as a substance ideal for the manufacture of prosthetic structures.
But more and more polyurethane foam is used for insulation in shipbuilding and the automotive industry. Construction companies often use a foam form of polyurethane foam to insulate roofs, basements, walls and floors of houses.

Comparative table of characteristics of polyurethane foam and polyethylene foam
These types of insulation are approximately equally popular, due to their properties. If you are interested in the question of polyurethane foam or polystyrene foam - which is better, it is recommended to compare them according to their main characteristics. The result can be seen in the table:
| Options | Polyurethane foam | Expanded polystyrene |
| Density, kg/m³ | 25-750 | 45-150 |
| Thermal conductivity coefficient, W/(m*K) | 0,019-0,028 | 0,04-0,06 |
| Structure | Closed-cell | Closed |
| Operating temperature, °C | -160…+180 | -100…+60 |
| Environmental friendliness | Polyurethane foam retains its properties and does not emit harmful substances when heated to the maximum value (+180°C). | Expanded polystyrene at a temperature of +60°C begins to release a compound dangerous to human health - phenol. |
| Duration of operation, years | With proper installation, the service life is unlimited, in other cases it is 50 years. | 42278 |
| Fire hazard | Incombustible | More susceptible to combustion. In high temperature conditions, burning areas can become separated, which contributes to the spread of fire. |
| Hygroscopicity | Does not absorb moisture. | It is more susceptible to liquids and is able to partially absorb them. |
| Appearance | Does not lose properties throughout the entire period of operation. | Over time, it shrinks and undergoes deformation due to loss of properties. |
Comparison of materials by performance characteristics
You can also compare insulation materials according to the degree of installation complexity. Thus, polyurethane foam is characterized by increased adhesion , which allows for quick insulation. Expanded polystyrene requires the use of special compounds. In addition, it is advisable to make a crate. PU foam is resistant to the formation of mold and mildew . For this reason, the material can come into contact with moisture without the risk of loss of properties. Expanded polystyrene, on the contrary, is prone to the formation of mold.
PU foam retains its properties and structure throughout the entire period of operation, even under the influence of moisture, low and high temperatures. For this reason, there is no need for periodic inspection and maintenance of the thermal insulation “pie” structure.
Polyurethane foam is easier to transport because it does not deform during transit. This applies to rigid and flexible boards. Expanded polystyrene is a more fragile material and is often deformed during transportation.
Extruded polyurethane foam technical characteristics – World of Glazing
The use of mineral wool is recommended for external insulation of a house, roof, attic and attic insulation.
Rigid slabs can withstand heavy loads, do not change their shape for decades and may require replacement only as a result of moisture accumulation and the formation of cracks due to shrinkage of the low-density material.
The cost of insulation with cotton wool is affordable.
There is always a need for insulation of a house, apartment, or commercial premises. It is very important to decide on the choice of materials in time. There are many offers on the market.
In this article we will look at the features and advantages of certain materials and compare them according to the main parameters required for high-quality insulation, namely, thermal conductivity, weight of the insulation, layer tightness, complexity and cost of installation, water absorption, flammability indicators and service life.
The basis of stone wool is basalt. It is produced in various densities and packaged in the form of rolls or slabs.
This material has become widespread in the insulation of premises for various purposes, since wool has a low thermal conductivity coefficient (0.048-0.070 W/ (m*K at a density of 50-200 kg/m3) and copes well with its task.
Mineral wool does not burn. Thanks to its porous structure, it is parapermeable (0.49-0.6), but at the same time absorbs moisture well. This can lead to “caking” of the insulation and a decrease in the effectiveness of thermal insulation.
When installing cotton wool, it is necessary to provide personal protective equipment for clothing, hands, face and respiratory tract from basalt dust.
The wool must be hermetically sealed with plasterboard or other facing materials so that home owners do not risk their health and do not inhale flying basalt particles.
The cotton wool manufacturer does not deny the use of binding components in the form of formaldehyde and phenols in production.
Their quantity does not exceed the maximum permissible concentrations and is no more than 4%.
FIBERGLASS
The material is based on sand, soda, glass industry waste and limestone.
Fiberglass with a length of 15-50mm, has high strength, elasticity, and has good sound absorption. Normally, glass wool has a light shade.
When phenol formaldehyde resins are added, the color changes to light gray.
Glass wool is a durable material. Service life up to 40 years. Its thermal conductivity coefficient is 0.034-0.040 W/m·K. Fiberglass is a low-flammable material, it is chemically inert and is not interesting to insects and rodents.
Areas of application of insulation are insulation of partitions, insulation of roofs, walls, ceilings.
The main disadvantage of fiberglass is the release of glass particles during installation and further operation. Therefore, during installation it is necessary to use respiratory and skin protection, and the insulation surface must be covered with a sealed layer.
Expanded polystyrene (PPS)
Successfully took its place for insulating the house. Expanded polystyrene effectively retains heat and has a low thermal conductivity of 0.038-0.05 W/(m*K).
Its area of application is to insulate a house from the outside, since polystyrene foam is flammable and releases toxins into the atmosphere when burned.
The disadvantage of PPS is low parapermeability.
Extruded PPS is a durable, moisture-proof material. Available in slab form.
Lack of elasticity and rigidity make it impossible to install insulation on uneven surfaces. This leads to the formation of cold bridges and significant heat loss.
Polyurethane foam (PPU)
Currently, in order to create high-quality insulation of the house, polyurethane foam material has been used.
PPU insulation allows you to reduce energy consumption and reduce heat loss to a minimum in cold seasons, and also helps stop the penetration of warm air from the external environment in summer. PPU is not affected by temperature changes.
Due to the peculiarities of installation and texture, polyurethane foam fills all cracks and holes. The insulated surface has no joints. This quality eliminates “cold bridges” and prevents the penetration of precipitation, insects and noise.
The ease of installation of polyurethane allows you to insulate surfaces of any complexity and is applied to all building materials, since polyurethane foam has 100% adhesion to materials.
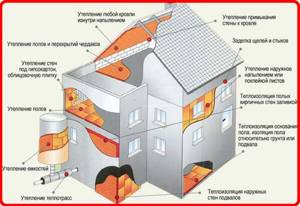
The use of polyurethane foam is the insulation of attics, roofs, garages, and industrial facilities of complex configuration.
Polyurethane foam is an environmentally friendly material. The composition of polyurethane foam does not include flammable substances; therefore, the material practically does not support combustion.
Spraying with polyurethane is used for insulation of new houses and during the reconstruction of existing buildings. Simplicity of installation allows you to complete a large amount of work in a short time and hand over the object on the day of installation.
Foam insulation is a smart investment that, by reducing the cost of heating and air conditioning a home over a long service life, will pay for itself within 2-3 years and increase the assessed value of your home.
Comparison of characteristics of polyurethane foam and other insulation materials
Thermal conductivity, W/m*Kelvin
0.019-0.028 “hard polyurethane foam” 0.03-0.035 0.037-0.056
0.03-0.04 “soft polyurethane foam”
Main indicators Sprayed polyurethane foam Extruded polypropylene foam Mineral wool using Rockwool as an example
Vapor permeability mg/m*h*Pa
0.02-0.005 “hard polyurethane foam” 0.018 0.49-06
0.08-0.1 “soft polyurethane foam”
Moisture absorption by volume, % by weight
0.58% “hard polyurethane foam” 0.2-0.4% 1.5%
1.72% “soft polyurethane foam”
restores its properties after drying
Safe, Approved for use in residential buildings by the Ministry of Health of the RSFSR No. 07/6-561 dated December 26, 1986
Continuous layer without joints Satisfactory Satisfactory
when attached to vertical surfaces with dowels, cold bridges are formed at the attachment points; when attached to vertical surfaces with dowels, cold bridges are formed at the attachment points
high (200m2 per shift) Average Average
Dependence of cost on surface complexity
Does not depend Significantly increases Significantly increases
Service life with preservation of properties
Layer thickness with equivalent thermal insulation properties
Cost of materials, 1m2
240 rub/m2 “light polyurethane foam” 370 rub/m2 450-560 rub/m2 (incl.
480rub/m2 “hard polyurethane foam” (including fasteners, wind and moisture protection and vapor insulation)
200rub/m2 300-350rub/m2 for 2 layers 250-350rub/m2 including installation of films
Source: https://vsmservis.com/ekstrudirovannyy-penopoliuretan-tehnicheskie-harakteristiki/
Comparison by cost
Protecting surfaces with polyurethane foam insulation is a more expensive technology. So, thermal insulation of 1 m² will cost 150-1500 rubles. In this case, the price is formed taking into account the thickness of the material: from 10 to 100 mm. This means that in order to insulate a surface of 1 m² with a 50 mm thick layer of polyurethane foam, you need to prepare about 850 rubles. The high price of this type of thermal insulation is due not only to the production technology of the material, but also to the high cost of the equipment.
If you are deciding which is better - polyurethane foam or polystyrene foam, you should know that the latter option is offered at a lower cost. For comparison, insulating an area of 1 m² with EPS boards will cost several times less - 300 rubles, provided that the thickness is 50 mm. Good polystyrene foam boards, characterized by large dimensions and high density, are more expensive.
Parameters of sprayed insulation
It’s worth saying right away that, as with any other insulation, it is preferable to insulate the walls of buildings from the outside. If you insulate from the inside, the outer wall will freeze. How many defrosting/freezing cycles it will withstand depends on the material, but rarely will such a house last more than 10 years.
When insulating the outside with polyurethane foam, a final exterior finish is required - the surface has a very unattractive appearance. But there are no problems with freezing of the walls, the building will last a long time.
There are no problems with the roof at all. Roofing materials are designed to withstand repeated freezing, so roof insulation with polyurethane foam can be done from the inside, spraying it directly onto the “underside” of the roofing material or onto the sheathing.

Sprayed thermal insulation can be applied to any surface, and the roof can be insulated from the inside
Whether to insulate the house from the outside or from the inside, we figured it out. Now a little about the layer thickness. Insulation with polyurethane foam is usually made of large thickness. This is not due to the fact that small is not enough. Usually, just according to thermal characteristics, an insulation thickness of 2-3 cm is required, but they make it at least 5 cm. This is so that under any conditions the dew point ends up in the thickness of the thermal insulation, and not in the wall material. Since polyurethane foam is non-hygroscopic, it cannot get wet, condensation simply does not occur, and excess moisture is removed naturally due to the vapor permeability of the material.
For what purposes is it better to use?
PPU and PPS have their own advantages over each other; for this reason, in some conditions it is preferable to use one or another insulation option. For example, it is better to use PPU if the following tasks arise:
- it is necessary to create effective wind protection;
- it is necessary to realize the requirement of high adhesion;
- creation of a seamless thermal insulation structure;
- short installation time.
Summary
If you plan to purchase polystyrene foam or polyurethane foam, you must take into account that in terms of the main parameters the second option wins. It is non-flammable, has a high density, wear-resistant, lasts a long time, and is non-hygroscopic. Expanded polystyrene is cheaper, but at the same time it has a fairly low thermal conductivity, which is often also an important criterion when choosing.
If self-foaming polyurethane foam is considered, its installation requires the use of expensive equipment. However, it is not advisable to purchase such equipment for one-time use. It must be said that polyurethane foam and polystyrene foam are universal insulation materials, but you should choose the appropriate option based on operating conditions.











