Insulating the floor in any home is an important stage of construction. The modern market offers consumers a wide selection of necessary materials, but expanded clay remains the simplest and most affordable among them.
It has a light cellular structure with many pores filled with air. It is obtained by firing special low-melting clay, followed by foaming the mass. Sometimes sawdust or peat is added to the initial mixture. The shape of the granules is round, and their sizes can vary. In construction, the use of expanded clay as insulation is possible not only for floors, but also for walls, and sometimes ceilings. It is used as a bedding under the coating or as an additive to concrete.
The properties of expanded clay as a heat insulator depend on the size of its granules and their porosity, as well as on the strength and volumetric weight of the fraction.
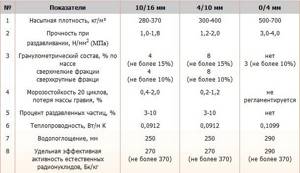
Based on the level of bulk density, the material can be divided into 10 general grades - from 250 to 800, while the indicated number determines the number of kilograms of the substance in 1 m3. If the brand has an indicator of 350, then 1 m3 of backfill will weigh 350 kg.
The size of the granules is also very important, and according to it, expanded clay is divided into the following 3 groups:
- from 5 to 10 mm;
- from 10 to 20 mm;
- from 20 to 40 mm.
The presence of both small and large fractions is allowed in an amount of about 5% of the total mass. For example, insulating the floor in a bathhouse will require medium-sized granules, since they have a higher density. To insulate a wooden house, you need large expanded clay, poured under the covering in a layer of about 20 cm.
The strength standards of insulation are established separately for each group of fractions and are determined by the method of squeezing the mass in special cylinders. In construction, this indicator is very important - it is it that allows you to calculate the specific area of application of the material, taking into account the total load on the entire structure. For example, if a bath requires larger expanded clay granules, then for an attic, attic, loggia or balcony it is better to choose smaller fractions.
Dimensions, structure and types
Divided into 3 types (based on particle size):
- Up to 0.5 cm - sand. It is usually used as a means of insulation as part of various mixtures. To insulate wooden floors with parquet flooring, tightly compacted expanded clay sand is often used. Its layer of 10-15 cm reduces heat loss by about 60%.
- From 0.5 to 4 cm - gravel. They are used to insulate floors, ceilings, attic or attic spaces, and balconies.
- The mixture obtained by crushing large granules is called crushed stone. According to the advice of experts, the best use of this type of expanded clay is thermal insulation of a concrete floor and screed installation. Often used in the construction of baths.

Reviews about the material
Expanded clay gravel has quite a few competitors in the construction market. When choosing insulation, in addition to studying and comparing technical characteristics, it is not a bad idea to read reviews from home owners.
“Insulation of the floor in a private house is always a problem for any owner. I, like many, probably chose the budget option. I started construction with a small guest house, poured the mixture into the base of the building and laid boards on top. Everything would be fine, but there is one problem - the constant quiet crunch of the backfill while walking. When insulating the floor in a wooden house using this method, you need to leave a small space under the boards.”
“When designing a house, I thought for a long time about choosing insulation. I read a lot of recommendations and reviews on the Internet. In the end, I settled on expanded clay for reasons of economy, since the cost is low. I poured it under the base of the concrete screed and into the ceilings of the attic floor - in principle I was pleased with the result, the house turned out to be warm. The big plus is that the material also provides sound insulation.”
Vyacheslav Sokolov, Yekaterinburg.
“I won’t try to make advertising for expanded clay – just facts. I used it to insulate the floor in a wooden bath: I poured a layer of 20 centimeters and left the same amount of empty space. I am more than satisfied with the result: there is no need to heat it for a long time, the room warms up quickly (after an hour you can already steam). Its only serious drawback is that it strongly absorbs moisture, so I would advise you to immediately decide on waterproofing.”
“Last year I decided to insulate the balcony. A friend recommended expanded clay - it’s environmentally friendly and doesn’t break the bank. And everything would be fine, but for normal thermal insulation you need a layer of at least 150 mm. And if we also take into account that there must be empty space between the filler and the coating, then the floor level would have to be raised by 20-25 cm. Therefore, I bought polystyrene foam for the balcony.”
“My opinion on the thermal insulation of a bathhouse with expanded clay may be controversial, given the feedback from developers, but I preferred mineral wool. With all its advantages, clay also has a drawback that is imperceptible in the construction of dry rooms, this is the ability to absorb moisture and retain it inside. As a result, not only a constant smell of dampness may appear, but also hidden mold.”
1. Naturalness. The absence of harmful additives during production, the use of pure natural raw materials (clay) makes it safe for human health.
2. High heat retention rates. It has a porous structure with many air chambers inside, so it can be used for insulation of floors, roofs, walls, and utilities.
3. Excellent sound insulation, which helps reduce noise in rooms.
4. Due to its low cost, it reduces construction costs.
5. The variety of sizes, as well as the flowability of the substance, make it possible to fill any spaces with it, without fear of the occurrence of voids and the formation of cold bridges in the future.
Characteristics and properties of the material
Loose insulation with a porous structure - expanded clay - is made from a mixture of fusible clay and shale rocks. Sawdust, peat bog and solar oil are used as additives. After foaming, the raw materials are rolled in drums, and at the next stage they are subjected to heat treatment in a high-temperature oven.
Expanded clay insulation in the form of light and durable granules measuring 2-40 mm is widely used in private housing construction. The popularity of the material is determined by its excellent heat and sound insulation properties in tandem with accessibility. Expanded clay is in demand for flooring, insulation of external walls of the house, attics and basements. In terms of heat-insulating properties, a 10 cm expanded clay layer in a wall structure is equivalent to a 25 cm thick wooden sheathing.
Pros and cons of using wall insulation
In terms of popularity as a material for insulating the external walls of a brick house, expanded clay is inferior to a number of modern insulators. This phenomenon is explained by the economic profitability and efficiency of use due to the competitive advantages of the material.
The advantages of using expanded clay for insulating external walls:
- Due to its impeccable resistance to heat transfer characteristics, bulk insulation represents a reliable barrier against heat loss during the cold season. In summer, a comfortable microclimate in the house is also maintained, since the expanded clay insulator does not allow the street heat to pass through;
- bulk material can be used in concrete mixtures, which has a positive effect on the thermal insulation properties of the structure;
- the natural composition is characterized by environmental friendliness, resistance to chemicals, and inertness to biological threats;
- expanded clay granules are unattractive to rodents and insects;
- the porosity of the structure determines the effectiveness of the solution as sound insulation of the facade.

Among the advantages of using expanded clay for insulating the external walls of a brick or frame house, they also note its non-flammability, resistance to temperature changes, ease of self-installation and the availability of the solution.
The downside is that the granules absorb moisture; protection is required in the form of concrete pouring, wall plaster or other moisture-resistant material.
Varieties of expanded clay
Expanded clay is produced in the form of such fractions as:
- gravel;
- crushed stone;
- sand.

The scope of each type is quite wide. The material is also divided by density. This parameter represents the ratio of the weight and volume of the granules. Thus, the M300 brand of expanded clay has a density of 300 kg/m³, and M400 – 350-400 kg/m³. It is important to consider that the lower the grade of the material, the higher its quality.
Types of expanded clay fractions and selection criteria
For thermal protection of the walls of the house, an expanded clay mixture of granules of different sizes is used to ensure maximum packing density of the mass. They produce material of different fractions. When choosing a bulk insulator option, a number of factors are taken into account, including the features of the structure being insulated, the climatic conditions of the region, and the type of planned work.
Gravel
Products in the form of round or oval granules are produced on the basis of a clay mixture by firing in a high-temperature rotary kiln. There are 3 fractions of expanded clay gravel:
- 20-40 mm. Due to geometric features and size, expanded clay of this fraction has a low bulk density. The product is used to create a thick thermal insulation layer. The sample is mainly in demand when arranging foundation structures, is used in the construction of a cellar, and is suitable for thermal protection of attic floors;
- 10-20 mm. As an option with optimal characteristics, expanded clay of this category is widely used in the insulation of external walls of brick houses using the well masonry method, and is used in the formation of floors and roofing piecing;
- 5-10 mm. Fine gravel is in demand as effective thermal insulation when installing underfloor heating systems.
Factors influencing the thermal conductivity value

Expanded clay is used in construction as a porous bulk insulation or as a filler in the production of lightweight concrete. The granules are obtained by firing shale or clays and have an oval, round shape, sometimes with sharp corners. The building material is produced in the form of sand.
The bulk density of expanded clay is in the range of 150 – 800 kg/m3, the volumetric weight depends on the technological regime during production. The ability to conduct heat depends on the size of the granules, the porosity of the material and its moisture content.
Expanded clay fraction
When comparing the characteristics, it is concluded that thermal conductivity decreases with increasing granule size. Medium and coarse gravel are best used for insulating unloaded roofs and wooden floors. Fine-grained expanded clay is used for lightweight floor screed.
Expanded clay fractions are installed in accordance with GOST 9757 – 90 standards:
- From 5 to 10 millimeters a small group is determined. The material is used for the production of expanded clay concrete wall blocks. Filler made from small granules is used in concrete screed coverings or floors, since large parts increase the thickness of the layer.
- From 10 to 20 mm – average fraction. The material in bulk well insulates floors and attic floors from the cold, and is used for insulating lawn areas and draining the ground. The fraction is rarely used in screeds and concrete floors; it is added to the solution if the thickness of the layer does not matter.
- From 20 to 40 mm – large granules. They insulate heating mains, basements, floors of utility rooms, and insulate the building from noise.
Layers of bulk insulation effectively protect against cold if 2-3 fractions are used simultaneously. This fills voids, increases rigidity, and prevents convection of flows.
Porosity

The raw material is placed in drums, where it rotates and is simultaneously heated to high temperatures. Under such conditions, the material swells, producing porous granules that are protected on the outside by a baked clay crust. Most of the voids are closed; the partitions between them also contain voids.
The pore size is regulated by the introduction of citrogypsum and mineral impurities into the charge during production. An additive in an amount of 1 to 3% forms closed voids up to 1 mm in size. An increase in the volume of the additive to 4–9% leads to an expansion of the pores to 1.5–2 mm, while the number of closed cavities increases. The number of insulated voids increases thermal insulation properties and reduces water absorption.
Humidity
The water absorption of expanded clay ranges from 8 to 20%. When moisture gets inside the material, the surfaces of the granules are moistened, which slowly absorb the liquid. Gradually, water enters the spheres through microscopic cracks and is retained inside. Expanded clay accumulates moisture and is difficult to release it. The mass increases, the thermal conductivity characteristics of expanded clay change, and the strength decreases.
Dry expanded clay can withstand up to 25 series of freezing and thawing, while wet expanded clay is destroyed by the expansion of water at subzero temperatures. Expanded clay is protected by hydro- and vapor barrier films from moisture.
Material application methods
The technology of insulating external walls with expanded clay is in demand when arranging brick houses, although in some cases it is also used for thermal insulation of wooden frame buildings.
The nuances of constructing insulated external walls of a house using three-layer frame technology:
- the internal (interior) part of the structure is a masonry made of expanded clay concrete blocks about 40 cm thick;
- the outer (facade) plane performs a protective function and is a facing layer of clinker, wood, stone or other finishing;
- the middle part is made of capsic cement, a mixture of expanded clay and cement in proportions of 10:1. The filler is designed to give the wall structure additional rigidity and strength.
Depending on the type of structure, 3 masonry options are used:
- masonry with diaphragms. The wall is constructed in the form of two parallel planes with an interval of 20 cm: the first is brick thick, the second is half a brick thick. After every fifth row, the gap between the two surfaces is filled with expanded clay. After compaction, the bulk insulation is filled with cement laitance;
- masonry with embedded fastening elements. The method duplicates masonry with diaphragms, while reinforcement brackets are used to fix two parallel planes of brick;
- well masonry. The technology involves the construction of parallel brick planes at intervals of 20-30 cm with ligation across the row using jumpers. The formed cavity is filled with expanded clay, compacted and filled with cement laitance.

The use of expanded clay in wall insulation
The method of insulating walls with expanded clay is selected taking into account the climate of the area, the design features of the house, the base material of the structure and the type of work.
Insulation options
Expanded clay can be laid in three ways:
Dry method
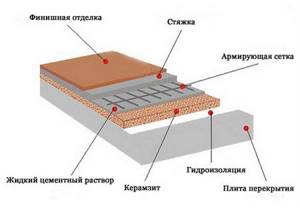
In this case, the expanded clay insulation technology consists of pouring insulation between the joists. A subfloor made of boards or plywood sheets is mounted on top.

To protect the base from moisture, a layer of waterproofing is laid under the material. This insulation option is distinguished by its speed and ease of execution.
Wet method
The photo of expanded clay insulation shows that with this method, the insulation is mixed with concrete mortar and then the space between the beacons is filled with this mixture.

The wet method is optimal for floors that require a thick layer of leveling screed. The negative side is considered to be less efficiency.

Combined method
This method consists of pouring dry expanded clay into the space between the joists, leveling it and soaking the top layer with cement mortar. After this, a leveling screed is made.

The cement mixture strengthens the expanded clay layer, helping to avoid deformation during subsequent pouring of the screed. If necessary, it is appropriate to use reinforcing mesh.

Technology of wall insulation with expanded clay
Laying in bulk makes it easy to use the material in thermal insulation of brick structures. If you plan to use expanded clay to insulate frame walls, you should know that you need to leave cavities of at least 30 cm and carefully compact the granules. It is important to take into account that an additional load is created on the load-bearing elements of the wooden structure and the foundation.
Calculation of material quantity
To calculate the required thickness of the bulk insulation layer, the following indicators are used:
- thermal conductivity coefficient of expanded clay;
- minimum layer thickness;
- wall thermal resistance parameters.
Preparatory work
At the initial stage, it is necessary to provide the base with waterproofing to protect the expanded clay from excess moisture. Moisture-proof resources are used, for example, thick film or special membrane material.
Stages of wall insulation
In private housing construction, well masonry is mainly used. The technology involves filling the cavity between the inner and outer planes of brick with a layer of bulk insulation.
- A waterproofing layer is laid on the foundation, and the base is made in the form of two rows of bricks.
- Parallel walls with connecting partitions are constructed, while the corners of the structure are made without cavities.
- Every 5 rows, the well is filled with granules, compacted, and filled with cement mortar.
- 3 rows are laid out of brick.
The work algorithm is repeated until the end of the construction of the wall structure.
Finishing
The period for gaining strength of the cement-expanded clay mixture is approximately a month. Next, you need to perform a rough finish in the form of plaster to create a moisture and vapor barrier layer. To do this, plaster the wall inside and out. At the final stage, the surface is covered with the selected cladding option. For finishing, decorative stone, clinker brick, tiles with imitation of natural materials, wood, and decorative plaster are used.
Description of thermal conductivity

The ability of insulation to transfer energy from heated layers to parts with a lower temperature is called thermal conductivity. The process is ensured by the chaotic movement of molecular particles, its intensity depends on humidity, compaction, and pore size.
The physical process of heat conduction accelerates when there is a large temperature difference between the outside and inside of the building. Spontaneous energy transfer always occurs from a hotter environment towards a colder environment and occurs before thermodynamic equilibrium occurs.
Coefficient of thermal conductivity
To numerically express a material's ability to transfer energy, there is a thermal conductivity coefficient. The indicator indicates the amount of heat flowing through a sample of material under given conditions. The test standard always has the same dimensions in length, width and area and is tested at a standard temperature difference (1 K). Heat transfer coefficient is measured in W/mK, which corresponds to the International System of Units.
The name thermal resistance coefficient is used in the construction field. The thermal conductivity of expanded clay is 0.1 – 0.18 W/m·K. High-quality material is characterized by a numerical value of 0.12 – 0.17 W/m K; insulation with such properties retains up to 80% of internal heat.
Rules and features of insulating walls with expanded clay

Heat loss through the enclosing structures of a private house is one of the main factors used in heating calculations. Insulating walls with expanded clay, a material that is used as insulation due to its durability and affordable price, can reduce significant costs for the use of energy resources Almost the only drawback of this option is the increase in construction time.

The advantages of choosing expanded clay as a filler for enclosing structures include:
- manufacturing from natural materials is a feature that makes the insulation safe and environmentally friendly;
- porosity of the structure, providing a high level of heat and sound insulation;
- resistance to external influences and durability;
- immunity to temperature changes, obtained due to the filling of expanded clay granules with air.
What is expanded clay?
Expanded clay is small granules of light weight due to small pores that are obtained as a result of clay firing. Thus, the result is a completely environmentally friendly natural material that has good technical indicators, such as:

- noise insulation - dampens shocks; thermal insulation - retains heat well; frost resistance - does not collapse at low temperatures; fire resistance - is not exposed to fire; strength - does not change its structure under the influence of cold/hot water; durability - does not change its properties under the influence of high/low temperatures temperatures, lasts longer than other insulation materials.
Equipment for the production of expanded clay
If we compare expanded clay with other thermal insulation materials, it significantly benefits in terms of service life. In addition, expanded clay is much cheaper than other thermal insulation materials in this category.
But the most important property of this material is that, for example, pouring a floor with expanded clay is an excellent option when building your own home.
Technology of wall insulation with expanded clay
One of the popular methods of insulating walls with expanded clay involves creating a three-layer house frame. The main (internal) part, with a thickness of 40 cm, is made of expanded clay concrete elements of various sizes - a durable building material with a high degree of thermal insulation. Thanks to its composition, expanded clay concrete also has high strength, which allows it to be used instead of conventional bricks, foam and aerated concrete.
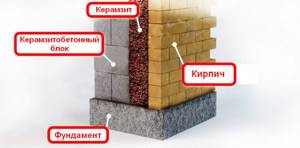
Expanded clay acts as a second layer as a wall insulation - it is mixed with cement, obtaining a mixture called capsic cement. The composition includes 1 part of the cement mixture and 10 times more expanded clay. The hardened mixture allows you to obtain a structure that is both rigid and reduces the heat loss of the building to a minimum. The small mass of hardened capsic cement practically does not increase the load on the foundation of the house and does not require its strengthening.
The last, outer layer is designed to protect the insulation and improve the aesthetic characteristics of the building. It is usually made of clinker bricks, wood or “lining”. Fiber cement boards, granite and aluminum panels can be used for this.
Other uses of the material
In addition to the frequently used 3-layer option, other methods are also used in the construction of private houses. One of them, a lightweight well one, involves performing the following actions:
- construction of two brick walls located parallel to each other, the thickness of which reaches 1/2 of a brick, and the distance is 140–340 mm;
- creating special lintels across the walls - the distance between them should be 600–1200 m;
- pouring expanded clay into the resulting cavities, tamping it and adding “cement laitance” every half meter in height.

The technique differs from the popular method in the presence of jumpers and a different composition of the filler and walls. The next option involves almost the same actions - from creating parallel enclosing structures made of brick to laying expanded clay granules as an insulating layer. The differences lie in the use of special embedded elements made of reinforcing brackets or fiberglass.
All the options described above can be used together with any other wall materials in a private house. They are also used in houses built from foam concrete or aerated concrete. In this case, the distance between the walls is reduced to 100 mm - taking into account the low thermal conductivity of such blocks, the thickness of the expanded clay can be reduced. The layer of expanded clay granules is compacted gradually, compacted and filled with cement every 500 mm in height. The installation of ventilation gaps helps increase the reliability of walls and preserve them from excess moisture.
Insulation of wooden structures
Insulating wooden walls with expanded clay leads to a number of difficulties. Typically, wood is protected with mineral wool slabs 100–150 mm thick; when choosing expanded clay granules, this figure will have to be increased by 3–4 times. The weight of a 400-mm layer is too large for a conventional log house, so an additional foundation is laid on the outside.
For this reason, insulating wood with expanded clay is unpopular in cold areas of the country. It is much more effective and profitable to use mineral wool. In addition, the correctly selected thickness of the log house sometimes allows you to do without insulation.
Expanded clay production and composition
Composition of expanded clay
The main material from which construction expanded clay is made is sedimentary clay rocks. The composition of clayey rocks is quite diverse and includes not only ordinary clay, but various impurities: quartz up to 30%, organic compounds, feldspar, carbonates and a small amount of compounds of various kinds of metals. The composition of expanded clay depends on the characteristics of a particular area where the extraction of raw materials for production was carried out.
In addition to the components originally contained in the raw material, to achieve the swelling effect, artificial impurities and organic compounds (solar and oil) can be added to the composition at the production stage.
Production of expanded clay
It depends on the composition of natural raw materials and is carried out in three main ways:
Dry production method
It is used for the production of expanded clay from the most homogeneous clay rock, with a minimum amount of impurities present. The extracted homogeneous rock is crushed and sent for roasting. It is considered the simplest and cheapest method of producing expanded clay.
Wet production method
With this method, clay rock is mixed with water and additional impurities that are necessary to obtain certain properties of expanded clay. This mixture is fed into a rotary kiln, where it clumps naturally and is dried under the influence of furnace gases.
This method is effective when using wet clay rock and the need for additional inclusions in the material.
furnace for the production of expanded clay
Plastic production method
The most expensive method by which a material with improved technical characteristics is created. In this case, we also use moistening of the raw materials and the addition of additional impurities to achieve a homogeneous mass. But unlike dry production, granules of approximately the same shape are formed from the resulting mixture on a belt press, which are fed into an oven for firing and drying. Thus, a solid expanded clay of uniform shape is obtained, with all the properties of a brick. However, unlike brick, it has greater thermal efficiency due to porosity and is significantly lighter in weight. Read more about the properties of brick.
How much will it cost to insulate walls with expanded clay?
The costs of creating expanded clay insulation are largely related to the height and perimeter of the building, the number of floors and the selected material. The amount also depends on the method of insulating the walls with expanded clay - optimal three-row, lightweight or combined. In most cases, the width of the expanded clay concrete layer is about 300–400 mm, and that of the expanded clay cement layer is 100 mm, which corresponds to a brick enclosing structure one meter thick.
With an average cost of 1 cubic meter of expanded clay about 2,000 rubles, and expanded clay concrete about 3,500 rubles. it is easy to calculate that for a wall whose inner layer is 250 mm thick and the middle layer is 100 mm thick, the costs will be approximately as follows:
- per 1 sq. m of wall will be 0.4 cubic meters. m of expanded clay concrete blocks costing about 1,400 rubles;
- the same area contains 0.1 cubic meters. m of expanded clay for 200 rubles;
- for a building with a height of 3 m and a perimeter of 32 m (for example, 8 x 8 m), the costs only for expanded clay concrete and expanded clay for wall insulation will be: 3 x 32 x (1400 + 200) = 153.6 thousand rubles.
The price of the outer layer, which is taken as facing brick or wood, may differ significantly depending on the chosen finishing option. Sometimes it is comparable in cost to insulation (from 1000 to 1600 rubles/sq. m), but can be several times higher than the costs of expanded clay and expanded clay concrete, reaching 3000–6000 rubles. for 1 “square”.
Ways to use expanded clay in landscape design
In landscape design, expanded clay can perform two functions:
- drainage: for paths and plants;
- decorative: design of flower beds, paths, alpine slides.
By decorating the front garden with multi-colored granules, you can create whole pictures. Expanded clay goes well with marble and granite of different colors.
Garden paths
This landscape design element made from medium-fraction expanded clay gravel looks very nice. But its practicality is low. If you constantly walk along such a path, then in a couple of years the gravel will turn into sand.
Options for using expanded clay:
- a layer of gravel between the concrete path and the curb will ensure dryness even in rainy weather;
- filling the space between tiles or paving stones with expanded clay sand or fine gravel (nice and dry);
- Fill the path with expanded clay concrete - a mixture of expanded clay and cement mortar.
Production of expanded clay concrete:
- Pour expanded clay (8 parts) into a concrete mixer and pour water (1.5 parts). Wait until the liquid is absorbed.
- Fill in M400 cement (1 part) and sand (2 parts).
- Knead for about 10 minutes.
How to lay a track:
- Mark the future path using twine and pegs.
- Remove the top layer of soil. The depth must be sufficient not only for the concrete coating, but also for the drainage layer.
- Compact the soil. Cover the recess with geotextile material.
- Secure the side formwork.
- Pour drainage (sand, crushed stone or gravel) in an even layer.
- Lay the reinforcing frame (chain-link mesh, pipes or wire).
- Prepare a mixture of expanded clay concrete and fill the path with it.
Tile paths
In areas with marshy soil or close groundwater, a thick layer of drainage must be placed under the paving slabs. Expanded clay sand or fine gravel is excellent for this purpose. This material absorbs moisture well, so that underground water cannot rise to the surface, and rainwater is quickly absorbed, and the tile remains dry.
Laying technology:
- Compact the prepared recess for the path and cover it with geotextiles.
- Pour a layer of expanded clay sand. The more moisture in the soil, the thicker the drainage layer should be.
- Pour a leveling layer of a mixture of sand and cement or lay a reinforcing mesh.
- Lay tiles or paving stones.
For flowers
In floriculture and gardening, expanded clay gravel is actively used for soil drainage. It does not mold or rot, and allows water and air to pass through well. The porous structure of gravel in the ground allows it to quickly absorb moisture and then, if necessary, release it. This allows you to achieve the optimal air-water balance in the soil for most plants - 35% air and 15% water.
Two ways to drain soil with expanded clay:
- A layer of gravel is poured onto the bottom of the flower pot or hole, the thickness of which depends on the size of the container (hole) and the volume of the root system. Then the roots are covered with fertile soil.
- Mix the soil with expanded clay granules and fill the hole or pot with it. This improves the aeration of the root system and provides protection from rodents in open ground.
From above, the root zone is mulched with expanded clay sand to retain moisture and prevent molding of the soil surface. And using mulch made from colored granules will add brightness and beauty.
For well masonry
Today, houses are rarely built with wells in the walls, which are filled with insulating and soundproofing material. Previously, wells were filled with slag, which still retains heat in old buildings. A modern analogue of such a filler is expanded clay gravel, which retains heat well.
Expanded clay gravel has many advantages. Therefore, it is in great demand not only in construction, but also in gardening. This material will benefit plants and decorate your garden plot.
Read with this
- Insulation of walls and floors of a frame house with expanded clay
- Floor screed with expanded clay: features and technologies
- How to make expanded clay concrete blocks with your own hands?
- How to insulate walls using expanded clay?
- Insulation of the ceiling in the bathhouse
- Insulating the floor in a bathhouse: how to do it?
- Do-it-yourself insulation of a sauna from the inside using different materials
- Perlite - what is it and what is it for?
- Fasteners for walls made of cellular and hollow material
- Insulation of the floor in a bathhouse on screw piles
Reviews from those who insulated walls with expanded clay
Despite the significant number of advantages of expanded clay aggregate, when choosing from several other options, it is worth paying attention to the disadvantages of the material. These include a high level of fragility, which it is advisable to take into account when filling and compacting capsules. Another disadvantage is the moisture resistance of expanded clay, which is accompanied by the ability to absorb moisture and retain it for a long time.
The material dries too slowly and requires good waterproofing to protect it from precipitation and humid air. All these problems are reflected in visitor reviews. Although among the comments about expanded clay, a lot has been written about its advantages.