The PPU shell is a semi-rigid (rigid) cylindrical product made of low-density polyurethane foam, which provides insulation, and, more precisely, thermal insulation of various pipelines. Such insulation is considered the most effective for pipes with coolant or products of the petrochemical industry. Technical parameters of the state of channels with PPU insulation are continuously monitored by the UEC (operational remote monitoring) system.
The so-called “shell” made of polyurethane foam is used for thermal insulation of pipelines for various purposes.
Advantages of shells for pipe insulation

Polyurethane foam shell is most suitable for insulating pipes. This insulation is characterized by a number of advantages:
- reusable;
- resistance to mechanical, biological, chemical, and atmospheric influences due to high density and chemical composition, including resistance to rodents and pests;
- durability;
- easy and quick installation at any temperature;
- Possibility of installation without the use of additional fasteners;
- environmental friendliness;
- quick dismantling if repairs to a pipeline section are necessary;
- use for insulation of underground and above-ground communications;
- does not weigh down the structure;
- shows inertness to fungi and mold;
- light weight;
- low thermal conductivity coefficient;
- noise insulation properties.
Advantages of PPU insulation
The great popularity of polyurethane foam insulation is due to its high protective properties and ease of use:
- products made from polyurethane foam are very light, do not put pressure on the pipes and do not weigh down the structure;
- polyurethane foam does not emit harmful chemical compounds even when heated;
- the degree of expansion of the material is completely insignificant;
- the small thickness of the insulation walls allows you to significantly save space;
- PU foam does not react with chemicals;
- due to their high heat resistance, the products do not melt even if hot water is supplied through the pipes;
- the level of thermal insulation allows you to maximally maintain the initial temperature of substances transported through pipes;
- PU foam is resistant to corrosion, rot and mold, and is also resistant to fungus and other microorganisms;
- no condensation forms on the surface;
- installation of polyurethane foam shells is very simple and quick, does not require special equipment or personal protective equipment;
- if necessary, the insulation can be easily removed and access to the pipes;
- installation can be done at any temperature and humidity;
- PPU shell can be reused on other pipes;
- The warranty period is 30 years or more.
Interesting! An excellent advantage of polyurethane foam shells over mineral wool insulation is the absence of the “winter soaring effect”, i.e. When snow gets on the outer insulation, it does not melt, but remains in its original state.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of using shells include:
- comparatively cheap (compared to using a heating cable); the possibility of insulating both newly created and already functioning lines; ease of installation and the absence of the need for a large “arsenal” of tools.
There are also disadvantages:
- the need to accurately select the diameter of the shell to the diameter of the pipe (whereas roll insulation does not require this); difficulty in passing pipe sections in the wall; difficulty in passing turns, branches, diameter transitions; lack of possibility of insulating sections of flange connections, location of filters, valves, check valves ;presence of seams (longitudinal and transverse) that remain after joining the shell segments.
Production methods and types of coatings
For the needs of industrial and civil construction, new heating mains are manufactured so-called. pre-insulated pipes. In this case, the prepared polyurethane foam fills the space between the object being insulated and a special formwork having a larger diameter. The result is a finished product, on the surface of which a protective polyurethane foam layer has already been applied.
Polyurethane foam shells are manufactured in accordance with industry standards and specifications. Depending on the operating parameters determined by the area of application and the pumped media, they are available in two types:
| Brand | Temperature range, °C |
| CT1 | from 100 to 120 |
| CT2 | from 100 to 150 |
Polyurethane foam shells can be produced without coating or have a protective layer: foil, fiberglass, glassine, galvanized steel, which depends on the operational and strength characteristics of the structure. Without additional protection by a casing, shells are used indoors or serve as the bottom layer of insulating “pies.”
Main types of thermal insulation coatings for pipes:
- Foil (foil paper). It is used indoors and to protect internal communications. Not suitable for heating mains with ductless or ducted installation.
- Reinforced foil (armafol). Recommended for economical insulation of networks, both internal and external. Protects against the effects of precipitation under conditions of significant temperature changes.
- Moisture resistant or fiberglass. Suitable for all types of pipelines laid outdoors by air. Provides a durable outer insulating layer and reliably protects against ultraviolet rays. Withstands mechanical loads and is considered optimal in terms of strength properties.
- Glassine (bitumen paper). The roofing material is resistant to ultraviolet radiation, but is inferior to fiberglass in strength.
- Galvanized steel casing. Used for open-laying trunk networks, process lines, gas and oil transportation systems. It serves as both ultraviolet and anti-vandal protection, and in terms of cost it is even preferable to fiberglass.

The variability of insulation will help ensure the required quality and reduce your costs
Polyurethane foam shells for pipes can withstand more than 1 thousand freezing cycles without changing consumer properties. And if you follow the recommendations for transportation and storage, it allows you to increase the service life of technological communications.
What is polyurethane foam and its scope of application in everyday life
Polyurethane foam is called foamed or gas-filled polyurethane, consisting of 85 - 90% of inert gas or air. Depending on the density, the material can be hard or soft; the average consumer is well aware of its soft form in the form of foam rubber and the technology for producing foam material using polyurethane foam.
In the household, polyurethane foam shells can be used in the following communications:
- For insulation of external sewer pipeline. When discharging wastewater in areas with an autonomous sewer system into a septic tank, it is technically problematic to lay the pipeline below the freezing depth of the soil, which in areas with a temperate climate can reach 2 m. In this case, the PPU shell for the pipes will serve as a thermal insulator and prevent freezing of the pipeline with liquid waste.
- Thermal insulation of external water supply. With autonomous water supply, water is drawn from a well or borehole, and the pipeline is laid underground at a depth below the soil freezing level. If it is not possible to lower the water supply to the recommended depth, a heat-insulating polyurethane foam shell for pipes will significantly reduce the distance of laying the pipeline from the soil level.
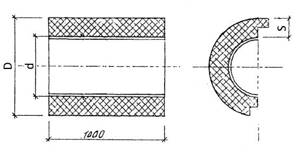
Rice. 2 Dimensional parameters of steel pipes in polyurethane foam insulation with a shell made of thin sheet steel according to GOST 30732-2006
- Thermal insulation of internal heating pipes. Individual heating systems are usually installed with a boiler installed in the basement. To supply coolant to the radiators, the pipeline line travels considerable distances, while the working fluid loses its heat along the way. To reduce heat losses, the most effective method is to insulate pipes with shells.
- Thermal insulation of external communications. In the private sector, hot water is often required in buildings built at some distance from the house with a heating boiler. For its transportation, an external or underground pipeline is used, insulating the pipes with shells, which simultaneously perform waterproofing functions.
- Thermal protection from hot heating pipes. Many individual heating systems use a metal pipeline in which the circulating coolant can be heated to temperatures of +80 °C. If you accidentally touch the metal pipe shell, it is easy to get burns, for protection against which polyurethane foam shells can be used.
- Soundproofing. If the riser or pipes in the water supply or heating lines begin to make noise, or extraneous sounds arise in them when liquid passes, and the problem cannot be solved, you can simply isolate the noisy area with a heat-insulating shell, reducing the noise level in the room by several decibels.
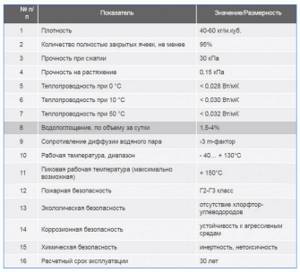
Rice. 3 Technical characteristics of polyurethane foam insulation
PPU shell - types of protective coatings
To protect the surface of polyurethane foam insulation from exposure to UV radiation, mechanical damage and other external factors, the PU foam shell is made with various types of protective coatings:
| The covering material based on aluminum foil and fiberglass has mechanical and chemical strength, is not affected by moisture, protects against negative ultraviolet radiation, significantly increasing the service life of the PU foam shell. The foil “smoothes out” thermal inhomogeneities, reducing the likelihood of heat losses, and gives a finished look to the insulated objects. Used for internal communications. |
| Fiberglass protection provides higher resistance of the polyurethane foam shell to atmospheric, biological, physical and chemical influences; fiberglass is a difficult-to-combustible material, is not subject to rotting processes, and additionally gives the insulated objects an aesthetic appearance. Recommended for indoor and outdoor use. |
PPU shell coated with galvanized steelThe steel coating provides a high degree of protection for the polyurethane foam shell from mechanical damage and other environmental factors, and gives additional rigidity to the insulating layer. This type of protective coating is used for indoor and outdoor applications. |
Insulation of PPU pipelines: main advantages
The use of rigid polyurethane foam (hereinafter referred to as PPU) for thermal insulation of heat and water supply pipelines is dictated by the following unique qualities of PPU:
- Lowest thermal conductivity coefficient;
- Durability (at least 20 years);
- High technological efficiency of processing;
- Reliable anti-corrosion protection of pipelines;
- Acoustic insulation ability;
- Possibility of insulating products of any size and configuration;
- Impossibility of theft of thermal insulation on unguarded objects;
- PU foams behave stably at temperatures up to +110– +120 degrees. Celsius;
When working on objects operating at higher temperatures (steam pipelines), it is recommended to reduce the temperature to the specified limits, using basalt or mineral wool heat insulators certified for work at higher temperatures as primary thermal insulation.

Polyurethane foam used as the second layer of thermal insulation protects the first layer from the effects of external factors (precipitation) and completes the thermal insulation. When working on cryogenic pipelines for polyurethane foam there are no restrictions on the lower temperature threshold. When working on oil and gas pipelines, as a rule, polyurethane foam is subjected to additional fire safety tests.
The main disadvantages of the spraying method:
- Excessive consumption of components when working on small-section pipes and strong winds;
- The practical impossibility of working on cold surfaces;
Features of each
No matter how many materials claim to be universal, each one has installation and operation features that determine their scope of application.
Expanded polystyrene
The insulation for PPU and PPS pipes has structural locks for reliable connections and to prevent the formation of cold bridges. PPU shell is recommended for thermal insulation of networks laid in the ground. Insulation made of PPS, polyurethane foam for pipes is characterized by low resistance to sunlight. Under direct sunlight, the structure of the thermal insulation is destroyed. The shell made from polyurethane foam has zero moisture absorption, high biochemical stability, and extreme fire hazard.
The shell of PPU, PPS can withstand a large static load without compressing under the weight of the earth, maintaining its thermal insulation properties.
cold lock
Basalt based

Basalt wool shell
Thermal insulating shells made of basalt are best used when insulating an external pipeline. The main argument confirming this is the excessive water absorption of the material. Saturation with water leads to a complete loss of thermal insulation properties. It is restored only after the basalt fiber has completely dried. The use of hydrophobic impregnations has a slight effect on this indicator.
Dimensions and diameters

The size and thickness of the insulation layer are selected depending on the operating conditions
The shell is used for thermal insulation of above-ground and underground communications. The protective casing is formed from two or more segments connected to each other. The larger the diameter of the shell, the more segments there are. The shell is made of a soft and flexible material, for example polyethylene foam, and can be made in the form of a cylinder with a longitudinal section. Shells made of relatively dense material, designed for small diameter pipes, up to 2 inches, consist of semi-cylindrical segments. If the pipe diameter is from 2 to 3 inches, there are already 3 segments. For larger diameter pipes, shells consisting of quarter-circle segments are designed.
The thickness of the insulation from which the shell is made varies from 9 to 90 mm. Insulation with a larger diameter and thickness will cost more. Based on this parameter, the shell is selected taking into account the requirements for thermal insulation efficiency.
Length dimensions also range from 1 to 2 m. The latter characteristic is determined by the ease of transportation, manufacturing and installation.
Specifications
PPU shell designTerminology: d – internal diameter of the shell; s – thickness of the shell wall; D is the outer diameter of the shell; PPU – thermal insulation made of polyurethane foam; | Symbol for polyurethane foam shell: PU shell d (s) Example designation: Shell PPU 108 (40 mm)
|
Polyurethane foam shell
| Outer diameter of steel pipe | Shell dimensions | |||
| Outside diameter | Thickness | Volume | Weight | |
| d,mm | D,mm | s,mm | linear m/m³ | linear m/kg |
| 32 | 122 | 40 | 0,014 | 1,00 |
| 45 | 128 | 0,016 | 1,06 | |
| 57 | 137 | 0,018 | 1,17 | |
| 76 | 156 | 0,025 | 1,40 | |
| 89 | 169 | 0,029 | 1,56 | |
| 108 | 188 | 0,036 | 1,78 | |
| 133 | 213 | 0,046 | 2,09 | |
| 159 | 239 | 0,058 | 2,40 | |
| 219 | 299 | 0,090 | 3,12 | |
| 273 | 353 | 0,125 | 3,77 | |
| 325 | 425 | 50 | 0,180 | 5,65 |
| 426 | 526 | 0,277 | 7,17 | |
| 530 | 630 | 0,397 | 8,74 | |
| 630 | 750 | 60 | 0,563 | 12,48 |
| 720 | 840 | 0,706 | 14,11 | |
| 820 | 920 | 50 | 0,847 | 13,11 |
| 920 | 1040 | 60 | 1,082 | 17,72 |
| 1020 | 1140 | 1,300 | 19,53 | |
| 1220 | 1340 | 1,796 | 23,15 | |
PPU shell made of polyurethane foam from the manufacturer at a low price according to TU 5768-001-54532153-01. Production and delivery to all regions. Price list for polyurethane foam shells.
PPU shell parameters
- shell length 1000 mm;
- diameter of insulated pipe: from Ø18 mm – Ø1420 mm;
- thermal insulation thickness: from 22 mm – 300 mm.
Polyurethane foam bends significantly speed up the process of installing thermal insulation for a rotary section of the pipeline.
Parameters of PPU bends
- diameter of the insulated pipe: from Ø 22 mm - Ø 1020 mm;
- thermal insulation thickness: from 30 mm - 300 mm;
- rotation angle 45˚,90˚.
According to the customer's technical specifications, it is possible to manufacture polyurethane foam shells and bends for pipelines of any diameter with different thicknesses of thermal insulation!
PPU shells and bends are used for thermal insulation:
- gas and oil pipelines;
- hot water supply and heating lines, both above-ground and underground;
- pipelines for various purposes, chemical and food industries;
- pipelines for technological purposes;
- communications laid in the far north and permafrost areas.
Advantages of polyurethane foam shells:
- High thermal insulation efficiency due to the low thermal conductivity coefficient of polyurethane foam;
- Moisture resistance and biochemical resistance of polyurethane foam to solvents, oils, acids;
- Environmental safety and durability of polyurethane foam, service life more than 30 years;
- Quick installation of polyurethane foam shells by fastening with ties, staples, wire, or special polymer adhesives;
- When performing the work, no special tools or personal protective equipment are required; polyurethane foam can be easily processed with a knife;
- Possibility of repeated use of polyurethane foam shells in case of dismantling;
- Thermal insulation work can be carried out at any time of the year;
- Wide temperature range of application of polyurethane foam from -180°С to +120°С.
Physical and mechanical characteristics of products without coating (PUF shell)
| Indicator name | Standard for the brand | |
| CT1 | ST2 | |
| Apparent density, kg/m3 | From 30 to 50 | St. 60 to 80 |
| Thermal conductivity coefficient, W/(m K), no more | 0,030 | 0,035 |
| Tensile strength, MPa, not less | — | 0,4 |
| Number of closed pores, % not less | — | 85 |
| Water absorption for 7 days, cm3/m2, no more | 200 | 250 |
| Heat resistance according to Vicat, °C, not less (with a load of 1 kg) | 120 | 150 |
| Flammability group (according to SNiP) | G4 | G4 |
Methods for installing polyurethane foam shells
Installation of polyurethane foam shell is simple and does not require special skills. Two workers per shift can insulate at least 300 meters of pipeline. The material is easily processed with a regular knife, which allows you to quickly trim the inside of the shell for a thick weld or other protruding parts of the pipeline.
There are 2 installation methods: sealed one-piece, using glue and quick installation without gluing the PU shells.
Installation using polyurethane glue
Vipol PK-200 glue is applied to the end of one of the shells being joined, after which the adhesive surface is treated with water using a sprayer. Then 2 shells are installed with technological fixation within 24 hours using bandages. The result is that the PU shell is securely secured with a seamless, permanent connection. More details
Quick installation
Quick installation is carried out by attaching the PU shell to the pipe with plastic ties, steel or polypropylene tapes, or binding wire. This fastening method leaves access to damaged pipes, fistulas and cracks, and makes it possible to reuse the PU foam shell. More details
Attention! The insulated pipe must be treated with anti-corrosion primer. When installing the PU shell, the pipe must be dry! The presence of moisture under the shell will cause a greenhouse effect and, as a result, severe corrosion of the metal
Projects with our participation Certificates of conformity
Proper installation of the polyurethane foam shell will ensure the reliability and durability of the thermal insulation, so we recommend that you familiarize yourself with the following information:
Recommendations for installing polyurethane foam shells Recommendations for working with polyurethane glue
A detailed description of all the products offered by our company necessary for the installation of polyurethane foam shells can be found in the “Products for Installation” section.
We remind you that to obtain information about prices for our polyurethane foam products and place an order, simply send a request to [email protected]
or call any of the phone numbers listed on the website.
Laying a pipeline using polyurethane foam pipes
It is worth remembering that the ends of the stripped insulation must be covered with non-flammable material during welding.
Installation of the PPU product consists of the following main stages:
- The thermal insulation is stripped to a distance of no more than 300 mm from each edge of the product;
- a welded joint is made, which must be checked for strength using a portable flaw detector;
- A heat-shrinkable sleeve is mounted on the pipe;
- the cavity under the heat-shrinkable sleeve is filled with polyurethane foam, after which the sleeve is settled in place by heating it, thereby ensuring the tightness of the outer layer of the joints.
When sealing joints, you should know that, due to the fact that polyethylene and polyurethane foam are flammable materials, the ends of the stripped insulation must be covered with any non-flammable material during welding work. To protect the outer shell, you can use, for example, asbestos fabric.
Often, installation of pipes that have pre-installed thermal insulation is carried out using horizontal drilling. In a large populated area, digging up a busy highway is very problematic. However, how to insulate a pipe if it has already been pulled through a horizontal puncture in the ground? And this is where a product with a polyethylene shell, on which thermal insulation is pre-installed, comes to the rescue.
Materials used
The key parameters of any heat insulator depend on what kind of material it is. The main characteristic is thermal conductivity, so we will compile a list of insulation materials, taking into account only:
Mineral wool galvanized shell on the pipeline
- Polyurethane foam (PPU) - up to 0.03 W/mK. Expanded polystyrene (foam) - about 0.045 Extruded polystyrene foam - about 0.035-0.04. Mineral wool and “related” materials (basalt, stone, glass wool) - about 0.045. Foam rubber shell - about 0.04. Cross-linked polyethylene - about 0.035-0.04.
If there is possible contact with moisture, you should also consider how well the insulation tolerates it. From the above list, only mineral wool products do not “like” humidity too much, as they begin to cake and can crumble.
Scope of application of polyurethane foam shell
PPU insulation replaces mineral wool products and is used for insulation:
- heating systems,
- hot and cold water supply,
- sewerage systems,
- housing and communal services pipes, heating mains, oil and gas industry pipelines, etc.
We recommend that you read: Types of control valves and their features

It is also possible to use it to protect electrical and fiber optic cables, insulate the interconnect line of split systems to avoid the formation of condensation, and so on.
Interesting! Due to the excellent thermal insulation properties of polyurethane foam, heat losses are 2-3% versus 20-30% when using mineral wool.
Thermal insulation materials for shell production

The shell material is selected depending on the operating conditions of the pipes
The range of modern insulating materials fully meets the listed requirements. Shells for pipe insulation are made from the following materials:
- polyurethane foam;
- expanded polystyrene;
- basalt insulation;
- foamed polyethylene;
- synthetic rubber.
The insulation is insulated to protect against mechanical damage and increase the efficiency of insulation:
- foil;
- fiberglass and fiberglass;
- galvanized and stainless steel.
Polyurethane foam

Polyurethane foam does not absorb water, therefore it is used for underground communications
Polyurethane foam is a material with a fine-bubble, closed-cell structure. It contains approximately 95% closed cells. PPU shell for pipes has the following technical characteristics:
- low thermal conductivity (0.037-0.042 W/m2*K);
- high density (40-60 kg/m3);
- does not absorb water (1.5-3%);
- operating temperature range: -180°C to +130°C.
Fixation with the help of additional elements leads to the formation of seams, due to the presence of which heat loss increases. In order to seamlessly connect the segments, polyurethane glue is used; it is recommended to fill the free space with polyurethane foam.
Expanded polystyrene

Polystyrene foam cannot be used without insulation from sunlight
Expanded polystyrene shells are used primarily for insulating ventilation, water supply, and sewer pipelines located in the ground, since the material has low resistance to ultraviolet radiation. It causes structure destruction. When insulating overhead communications, it is necessary to wrap the shell with something or paint it.
Advantages:
- does not absorb moisture;
- exhibits resistance to biochemical influences;
- withstands significant static load.
Disadvantages of polystyrene foam:
- fire hazard;
- not resistant to mechanical stress.
Basalt insulation

Basalt wool is not used for insulation of pipes located in the ground
It is recommended to use basalt shell for insulating external pipelines. Its main disadvantage is high water absorption, which cannot be compensated even with the help of hydrophobic impregnations. Once wet, the shell completely loses its thermal insulation properties. Operating temperature range: -40°C to +74°C.
Advantages:
- light weight;
- Fire safety;
- UV resistance;
- environmental friendliness;
- biological stability.
Disadvantages: used only for insulating plastic pipes.
Foamed polyethylene

Foamed polyethylene does not absorb moisture
The polyethylene foam shell is a flexible and lightweight material in the form of a cylinder 1.2 or 2 m long with a slot. The operating temperature range varies from -40°C to +95°C. Due to the special plasticity of the material, it is recommended to fix it with plastic or metal tightening clamps.
Advantages:
- relatively low price;
- has the properties of steam, noise and heat insulation;
- resistance to aggressive environments;
- protects against the development of corrosion;
- environmental friendliness.
Disadvantages: absorbs moisture.
Synthetic rubber

Synthetic rubber is not afraid of moisture and ultraviolet radiation, suitable for any communications
Synthetic rubber is superior to many materials in its performance characteristics. Thermal insulating shell made of this material is produced in the form of cylinders with a longitudinal cut, which can be mounted by putting the casing on the pipeline and gluing along the cut.
Advantages:
- UV resistance;
- resistance to aggressive environments;
- minimum level of water absorption;
- effective insulation;
- vapor tightness;
- long service life;
- resistance to mechanical stress.
In order to improve the appearance, the insulation is painted.
Review of basic materials
The most commonly used polymers in production are polyethylene foam, polystyrene foam, polyurethane foam, and mineral wool. The first type of shell is produced in the form of cylinders with a slot and is well suited for use in field conditions. Their advantages include flexibility, an impressive range of operating temperatures (from -40 to +95°C) and low price. The main disadvantage of polyethylene is its ability to absorb water, which necessitates a complex of waterproofing works. In addition, soft polyethylene slides off the pipe and requires fixation with special tape.
The shell for thermal insulation made of foam plastic (expanded polystyrene) has great rigidity and is produced in the form of two half-cylinders connected by locks, or without them. The advantages of this material include high thermal characteristics, lack of moisture absorption and resistance at temperatures from -50 to +70°C. The main disadvantages: fire hazard, low mechanical strength, requiring protective covers, and the high cost of transporting relatively small volumes of material.

A foam “shell” will help protect pipes from bad weather.
However, according to a number of criteria, mineral wool does not meet modern requirements for thermal insulation materials, and its scope of application is limited only to plastic pipes.
This is interesting: the characteristics of mineral wool.
The rigid closed-cell structure of polyurethane foam (PPU) practically does not absorb moisture and can withstand temperatures from -180 to +130°C. Gas-filled insulation looks like a cylinder made up of several elements with a locking or lockless connection method. In the first case, the ends of the half-segments are processed according to the tongue-and-groove principle; in the second, the edges have smooth edges. To obtain a 100% seamless connection of the segments to each other, polyurethane glue and additional tie with bandages are used.

Lack of locks does not mean lack of quality
When fixing elements with polymer clamps, wire or metal tapes, the connection will have seams, and this will lead to an increase in heat loss in the line. To insulate shaped assemblies, special bends, elbows, tees and connection angles of 90, 120 and 180° are used. To connect the shells along the length, a special shaped element is used - a coupling.
Installation nuances
First of all, when installing the shell, it is necessary to determine the diameter of the pipeline - so that you can select the appropriate diameter of the shell.
If it is larger than that of the pipe, the insulation will hang on it. If it is larger, the insulation will have gaps: the shell segments simply will not meet.
To fasten the segments (we will consider this option, and not the whole shell - it is the most relevant) the following can be used:
- Wire - in this case, the applied thermal insulation is wrapped with it.
- Glue – joints (both longitudinal and transverse) are lubricated and glued together.
- Groove - halves are connected to each other with a latch. Adjacent segments can be connected either with a latch or with glue.
- Adhesive tape.
The first option is good because it allows you to get a detachable connection: if necessary, you can simply unwind the wire, get a “bare” pipeline, and after completing the inspection (or work) you can put the insulation back.
The glued segments will only have to be cut. However, they can then be glued together, but the quality of the connection will be significantly lower. And every extra gap is a bridge of cold.
Stages of work
Thermal insulation of this type is installed as follows:
- The pipeline is cleared of old and unnecessary insulation (if used and not required).
- The areas that need to be insulated are measured.
- The number of shell segments is calculated.
- The insulation is installed from one “obstacle” (this could be a flange, turn, joint, fittings) to another.
- Each segment is attached using the chosen method (glue, groove, wire, or a combination thereof).
- If several fastening methods are used (for example, groove and tape, or groove, glue and tape, or any other combination), a second (third, fourth) fastening tool is used.
- Each segment is installed so that its transverse joint (cut) does not coincide with the joint of the adjacent one.
- If surface protection is used, it is installed and the joints are sealed.
- If necessary, areas that could not be insulated with a shell are separately insulated (by other methods: heating cable, rolled materials, spraying, paint).
Installation and Operation Basics

Joints should be coated with glue to reduce heat loss
Before installing the shell, the pipes must be inspected to eliminate the risk of leaks. Then the pipeline should be cleaned of traces of corrosion and coated with primer twice.
Insulation segments should be installed with longitudinal seams offset by 5-10 cm. To ensure a higher quality of insulation, the joints should be taped with foil or regular tape.
Having covered the pipeline with a protective casing, secure the insulation with clamps, wire or steel tape. Then, roofing material, fiberglass or roofing felt is wrapped over the shell, if there is no factory protective coating. The protection is also secured with plastic or metal clamps. The joints are coated with glue to reduce heat loss.
Necessary properties and requirements for shells for pipe insulation

Shell insulation with a lock for fastening to the pipe
The shell for pipes is a cylinder, cut on one side, or segments fastened together according to the tongue-and-groove principle. Insulation without grooves can be fixed using clamps, wire, or glue. After fastening, a protective casing is formed on the surface of the pipe.
Curved elements are provided for insulating tees, branches, bends, and junction angles. To connect the shell along its length, a separate shaped element is used - a coupling.
Such communication protection does not insulate, but avoids heat dissipation or heating due to high ambient temperatures.
The shell must match the diameter of the pipeline on which it will be mounted. The material from which the insulation is made must be resistant to low and high temperatures.
Basic requirements for thermal insulation for pipes:
- long service life;
- easy installation;
- low thermal conductivity;
- resistance to mechanical stress;
- protection against burns due to accidental touch;
- biological and chemical passivity;
- ability to maintain a constant coolant temperature.
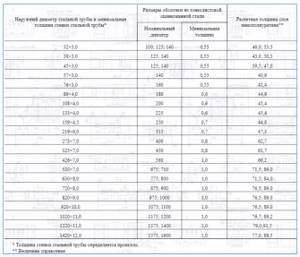
PPU shells. Standard sizes of manufactured shells grade ST-1 and ST-2)
| Pipeline diameter, mm | 15 | 18 | 20 | 25 | 28 | 32 | 45 | 45 | 57 | 57 | 76 | 89 | 108 | 114 |
| Shell wall thickness, mm | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 40 | 40 | 50 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 60 | 40 | 40 | 40 |
| Pipeline diameter, mm | 114 | 133 | 159 | 159 | 159 | 159 | 219 | 219 | 219 | 273 | 273 | 273 | 325 | 325 |
| Shell wall thickness, mm | 30 | 30 | 30 | 50 | 60 | 80 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 50 | 60 |
| Pipeline diameter, mm | 377 | 377 | 426 | 426 | 530 | 530 | 630 | 630 | 630 | 720 | 720 | 820 | 820 | 1020 | 1020 |
| Shell wall thickness, mm | 50 | 60 | 50 | 60 | 50 | 60 | 50 | 60 | 80 | 50 | 60 | 50 | 60 | 50 | 60 |
Types of polyurethane foam shells
The standard shell configuration is a hollow cylinder (or semi-cylindrical segments) of polyurethane foam without any additional coating.
Such products are most susceptible to mechanical stress, as well as moisture and UV rays, but they are excellent for use in ordinary household premises. External use is also permissible, but then the shell must be additionally wrapped, for example, with aluminum foil.
To ensure protective properties, additional layers are applied to the basic equipment:
- foil paper improves waterproofing properties, which allows the shell to be used in conditions of high humidity;
- armofol protects against UV radiation and further reduces heat loss;
- galvanized steel increases resistance to mechanical stress and also protects from sunlight and precipitation.
- fiberglass combines all the protective properties, and also practically does not weigh down the shell.

Related Posts
- What are polyurethane foam pipes and where are they used?
- Effective methods of thermal insulation of sewer pipes
- How to insulate an outdoor water pipe
- Disadvantages of polypropylene pipes in home heating
- Choosing non-flammable insulation for walls and ceilings: tips and tricks
- Features of using PVC sewer pipes with a diameter of 50 mm
- Which pipes for heated floors to choose: characteristics and installation methods
- What kind of pipes are used for the gas pipeline?
- Sprayed insulation in polynor cylinders: advantages and principle of operation, thermal insulation inside and outside buildings
- Spray insulation
- Isover thermal insulation overview
- What sizes of sandwich pipes are best to use for a chimney?
- Which rehau pipes are best for heating and water supply?
- Thin-walled metal pipe for electrical wiring
- Insulation of a veranda in a wooden house
- Rules for laying sewer pipes
- Dismantling of heating systems
- How to choose high-quality pipes for water supply in an apartment
- Which pipes are best to choose for a water well?
- Properties and types of dowel mushrooms for fastening insulation
- Copper pipes and their use in air conditioners
- Trenchless pipe laying options
- Do-it-yourself insulation of a well for the winter
- Types of roll insulation and the distinctive features of each of them. roll insulation for walls: choosing the best thermal insulation special thermal insulation coating
- Dimensions and installation of pipes for a bath
Read with this
- What are polyurethane foam pipes and where are they used?
- Effective methods of thermal insulation of sewer pipes
- How to insulate an outdoor water pipe
- Disadvantages of polypropylene pipes in home heating
- Choosing non-flammable insulation for walls and ceilings: tips and tricks
- Features of using PVC sewer pipes with a diameter of 50 mm
- Which pipes for heated floors to choose: characteristics and installation methods
- What kind of pipes are used for the gas pipeline?
- Sprayed insulation in polynor cylinders: advantages and principle of operation, thermal insulation inside and outside buildings
- Spray insulation