Overview of extruded polystyrene foam
Density is the main characteristic of polystyrene. Classification is made precisely on this basis. Depending on its performance, the directions in which it is used will also change. This material is actively used for insulating apartments and private houses.
Extrusion method (extrusion)
The concept itself carries a description of the manufacturing process. This term literally means punching using specially designed holes.
This technology imparts many qualities to the final product, for example:
- Reliable performance in water resistance.
- Giving minimum values in the thermal conductivity index.
- Decrease in heat capacity.
Important characteristics – what else should you pay attention to?
Density, as already written, is far from the only characteristic of expanded polystyrene. Most of them come as a pleasant addition, for example, with insulation, the sound insulation of the room improves, and there is no need for additional wind protection. Water absorption of foam plastic has practically no significance at all in the process of insulating buildings. This indicator is paid attention only in cases where foam plastic is used for any underwater work. By the way, expanded polystyrene is a non-hygroscopic material, that is, it does not absorb moisture. Only a small amount of water vapor is able to penetrate into the space between the individual granules, and even then with constant contact with water.
Classification
Marking 31C
Marking 31C has established itself as a high-quality element of insulation of unloaded sections of structures. An excellent example in this direction is work with foundation walls. This marking can be found in the underfloor heating product.

31C has also found wide application in work on insulation of sewer systems. Operation is intended exclusively in structures that are protected from fire, since its fire resistance level corresponds to category G4.
Marking 35
Marking 35 has significant differences from 31C. They consist in the difference in specific gravity indicators and the general level of fire resistance. In the creation of expanded polystyrene with the marking 35, a fire retardant is used, with the help of which it is possible to increase fire resistance.

Due to its fire resistance qualities (low flammability), the product has also proven popular for roofing. The most popular work in which grade 35 polystyrene foam is used is the insulation of all kinds of structures that perform enclosing functions.
Marking 45
Expanded polystyrene with the marking 45 is superior to the first two options due to the fact that its compressive strength has a huge margin. It can be successfully used not only in insulation; it opens up all its possibilities in such large-scale work as road construction. Expanded polystyrene grade 45 is also actively used in work on runways.

- The specific gravity of polystyrene foam has little effect on heat retention performance.
- The specific gravity indicator has an impact on the strength characteristics.
- The effectiveness of insulation (thermal insulation) is affected by the thickness of the sheet.
Markings of polystyrene foam 31 and 31C have basically similar qualities. The most striking difference between these two brands lies in the categories that are responsible for fire resistance. 31 has category G1, and 31C G4.
An opposite example is marked polystyrene foam 45 and 45C. Unlike expanded polystyrene 31 and 31C, these are different on literally every point. One of the few indicators that these brands of expanded polystyrene have in common is fire resistance at the G4 level.
Installation methods

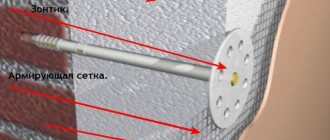
Eps boards are mounted on special adhesives and then reinforced with mushroom dowels. There are two common options for fastening with dowels - one in the center of the slab or four in the corners at the joints between the slabs.
We found out what extruded polystyrene foam is, and what differences and advantages it has over other insulation materials. It is easy to purchase in retail and wholesale stores, as well as online.
Source
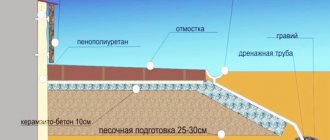
Foam plastic for wall insulation
Polystyrene foam is an economically advantageous material. Economic benefits manifest themselves not only at the construction stage, but also at the subsequent operation stage. This is achieved due to high heat retention rates for insulating walls and other structural elements, as well as a reliable level of fire resistance.

During installation, slab thickness standards must be observed. For external walls this figure is 50 mm, and for internal walls 30 mm. Density - 25.
Using this material, you can carry out work on external and external insulation of walls. Outside, the installation process takes place using cement mortars, various mounting devices, glue and other things. When installing foam plastic, the inner side will have a good level of noise protection. It is necessary to use plasterboard sheets. You can use an alternative option - plaster.
The plates that are involved in the fastening process for the outer part must meet a thickness of 50 mm. The inner side will require 30 mm. The wall, which is located on the outside of the room, must first be treated with cement mortar. It is applied using a special metal mesh. After completion of the work, we can assume that the foam has been successfully installed.
Density. Index
When working on wall insulation, polystyrene foam has a density index of 25. An external wall with a 50 mm sheet will have high heat retention rates, as well as additional sound insulation.
Polystyrene foam with a density of 25 looks quite advantageous compared to its counterpart, whose density is 15. The main differences are in quality. You can feel a big difference in the quality of foam with a density of 25 and 15 without even starting to use them.
The extruded polystyrene brands presented earlier in the article have the following density indicators:
- 31C (from 28.5 to 30.5 kg).
- 31 (from 28 to 34 kg).
- 45 (from 38.1 to 45 kg).

Vapor permeability properties
The vapor permeability indicator directly affects the efficiency of air exchange that occurs between the inside of the premises and the outside. This happens due to the fact that the air outside has a lower temperature than the inside.
When there is an exchange of air from the inside to the outside, the level of permeability should increase. In terms of vapor permeability, traditional foam plastic is superior to extruded foam.
- Traditional foam has 0.063 mg/(m*h*Pa).
- Extruded foam has 0.013 Mg/(m*h*Pa).
Why is this so? If you use extruded polystyrene foam for external insulation, this will lead to undesirable consequences. Its low vapor permeability has a high level of insulation; this will lead to the accumulation of moisture, which will not allow the materials to dry out and ventilate.
Insulation using facade foam plastic: pros and cons, installation basics
Even if we leave a piece of foam plastic in a bucket of water for several days, it will not absorb any liquid and will only become heavier by a few hundredths of a percent.
- The material is not prone to deformation from exposure to temperature changes - both heat and cold. And you can ask scientists about its durability: for example, discarded polystyrene foam in nature will decompose for decades, unlike organic matter. And the declared service life of foam insulation is more than 20 years (but, by the way, this is the lower limit).
Many people have recently been talking about the low fire safety of the material, which is, of course, one of its main disadvantages. But, firstly, for it to ignite, you need a temperature of almost +500 degrees, and this, you see, is quite difficult to achieve, so to speak, at home. However, this is a generally accepted fact: this material can still support combustion. And at the same time it also melts and releases dangerous gases (phosgene, for example). But, by the way, wood is an even more flammable material, but buildings continue to be built from it. And if certain fire safety measures are properly followed, the risk can actually be reduced to zero.
Another minus
All foam plastics are accessible to rodents. Mice, for example, gnaw passages and holes in it with particular pleasure. In order to combat impudent rodents, professionals advise: when insulating buildings using polystyrene foam, use special metal meshes that would protect the bottom of the foundation and ventilation openings. Then the insulation can remain intact.
Some pros also point to the low ability of the material to adhere to surfaces (adhesion). Additional strengthening measures are required, taking into account the installation features.
How to choose polystyrene foam?
If we want to insulate a building from the outside, we still have to figure out the type, density and size of the foam. As an external insulation, as a rule, ordinary white foam is used, which, as already mentioned, is foamed polystyrene. It comes in several varieties: M15, M25, M35. The main differences are in density and strength. M15 will be much softer and lighter than M35. If you need to insulate an outer surface that will experience certain loads, it is better to take the densest option (35). If a simple vertical wall is insulated, then they usually take 15 or 25. But by the way, this point should also be taken into account: the higher the density of the foam, the lower its porosity, and the higher its price.
And further:
It should be remembered that a “lower” foam will retain heat in the building better than the highest one. This happens again due to the structure of the material itself. The higher its density, the fewer air cells there are, which retain heat. So it turns out, according to science, the more expensive M35 will be worse for cladding a private house than M15, the cheaper option. What a paradox!
A few more tips
In choosing which foam plastic is needed for insulating walls outside, a few more valuable tips and recommendations from professionals who regularly deal with house cladding will help. Firstly, the color of the foam should be uniformly white. If there is yellowness or stains, do not take it. Foamed polystyrene granules should be approximately the same size and distributed equally throughout the volume of the slabs. And a good sheet should have uniform thickness and correct geometry throughout. This gives confidence that it was produced in compliance with the required technologies. And if the slabs suffer from curvature and visual diversity, then it is not a fact that they were not made somewhere in artisanal conditions. As a rule, such products do not have the required documents.
Wall insulation
As we learned from the material above, it is necessary to use different materials for different parts of the walls. If you do not want, for example, rotting and destruction processes to begin in your wooden bathhouse constructed with XPS, the installation of extruded polystyrene foam is excluded. Correctly, it is very simple and it is not difficult to stick to it.
The density of traditional polystyrene foam for wall insulation is 25, extruded polystyrene is 15. When working with traditional polystyrene foam, it is best to use slabs with a thickness of 50 mm; extruded polystyrene foam requires the same indicators. You can get by with a thickness of 30-40 mm.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages of extruded polystyrene foam over analogues:
- Very low moisture absorption
- Durability
- Ease of use and installation
- High thermal insulation capacity
- Strength and ability not to lose shape and volume under different operating conditions
Along with its advantages, it has some disadvantages. Among these is a low level of vapor permeability. As insulation, it is not suitable for all types of premises. If you insulate a residential building with it, it will turn into a thermos that cannot breathe. Another disadvantage is the cost, which is higher than other insulation materials. Although the technical characteristics and price of extruded polystyrene foam are adequate to each other. Finally, the sound absorption of XPS in practice is quite low.
Definition and properties
Polystyrene foam is an insulating material that has excellent heat and sound insulation properties.
The cost expression of polystyrene foam boards is much lower than for other insulation materials. The use of expanded polystyrene slabs in construction work helps reduce operating costs for heating or cooling residential or commercial buildings by tens of times.
There are several points of view that are associated with the concept of density. The unit of measurement for this parameter is kilogram per cubic meter. This value is calculated from the ratio of weight to volume. It is impossible to measure with one hundred percent accuracy the qualitative properties of polystyrene foam, which are associated with its impermeability and density. Even the weight of this insulation does not affect its thermal insulation capabilities.
Myths and realities
1. Firstly, the statement that EPS boards are short-lived does not stand up to criticism. As a result of official laboratory studies, it was found that they can withstand temperature changes with an amplitude of 40 degrees. Extruded polystyrene foam only does not like direct ultraviolet rays, so you need to cover the entire structure with materials that protect its surface well.
2. The second myth is that styrene, which is used in the production of XPS, is a very harmful component. But in fact, this colorless liquid has a second class of harmfulness and is on par with the detergents and washing powders that we use every day.
There is no release of toxic components during the combustion of EPS, since it consists of 95% air. Even after fifty years of operation, traces of styrene decomposition cannot be detected in the slabs.
3. And finally, the third myth is about the high flammability of EPS. We have already written that extruded polystyrene foam does not ignite from a cigarette butt or match. In every apartment there are many other items that are ready to burst into flames even from a small fire source: plastic, carpets, furniture, household appliances, etc. Of course, if the fire has already spread to the walls, then the EPS will also begin to burn. But only as a last resort. After all, its ignition temperature is almost 500°C. For comparison, the combustion temperature of regular cotton is 253°C.
In addition, EPS in most designs is covered on top with other materials. It is practically impossible for a spark to hit its surface.
Structure and composition of the finished material
Polystyrene foam is made from polystyrene foam balls that are filled with air.
Each thermal insulation material necessarily contains air located in the pores. The improved thermal conductivity index directly depends on the size of the atmospheric air masses contained in the material. The more there are, the smaller the thermal conductivity component will be. The foam manufacturing process comes from polystyrene foam beads that retain air.
In connection with the above, we can conclude that the concentration of polystyrene foam affects its thermal conductivity. If this value changes, then changes in thermal conductivity indicators occur within the boundaries of percentages. One hundred percent retention of air in the insulation is associated with its exceptional heat-saving ability, since air has the lowest thermal conductivity coefficient.
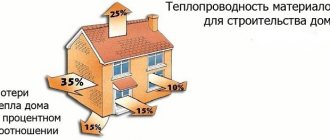
Due to the low thermal conductivity of the insulation, a high percentage of energy saving is ensured. If we compare brick with polystyrene foam, their ability to save energy will be noticeably different, because 12 cm of thermal insulation thickness is equivalent to 210 cm of thickness of a brick or 45 cm of log wall.
Types of material and their differences and features
As we have already said, polystyrene foam differs in its manufacturing method. Conventionally, it can be divided into three types.
The first type is polyurethane foam (PPU). The most common example of such foam is ordinary foam rubber. This type of material is very elastic and is characterized by the presence of open pores, due to which air and water vapor are perfectly permeable. That is why it is used in furniture production and the construction industry, producing polyurethane foam. The disadvantages of such polystyrene foam include the fact that it is short-lived and with prolonged exposure to sunlight, the material turns yellow and slowly deteriorates. It is also worth noting that, despite the fact that such foam can be self-extinguishing, its smoke is very toxic and dangerous.
The second type is polyethylene foam (PPE). This type of foam is quite elastic. You've most likely seen it in stores many times - polyethylene foam is often used to wrap fragile items when moving. The material is produced in the form of sheets of different sizes. The advantages of the material include its durability and environmental friendliness due to the absence of toxic substances.
The third type is polyvinyl chloride foam (PVC). It is elastic and contains no toxic substances. However, it is worth noting right away that PVC can only burn when surrounded by fire - it will not ignite on its own. But if this happens, the material will begin to release hydrogen chloride, which, when combined with a liquid, leads to the formation of hydrochloric acid. Because of this, smoke from PVC can be very dangerous.
We told you about the most famous types of materials used in domestic construction. We hope our information will help you choose the most suitable foam for the type of work being carried out.
Scheme of application of various brands
The following key types of expanded polystyrene are produced, differing in density and other characteristics:
- PSB-S-15, the density of this brand of foam is up to 15 kg/cu.m.
- PSB-S-25, from 15 kg/cu.m. up to 25 kg/cu.m.
- PSB-S-35, from 25 kg/cu.m. up to 35 kg/cu.m.
- PSB-S-50, from 35 kg/cu.m. up to 50 kg/cu.m.
The thermal conductivity component of foam plastic, expressed in digital values, refers to the range 0.037 W/mK - 0.043 W/mK. The indicated value can be correlated with the thermal conductivity of air, which is equal to 0.027 W/mK.
Use of polystyrene foam PSB-S-15
Polystyrene foam PSB-S-15 can be used for insulation of house facades. This type of insulation is practically not used in construction. It is used in structures that are attached to structures. These can be open balconies or verandas that serve a decorative function. Using PSB-S-15 foam plastic, shapes for facades are formed, and this allows :
- frame the corners of the house, windows;
- separate floors by creating cornices.
What is PSB-S-25 suitable for?
The density of the foam is calculated by analogy with determining the density of brick. For example, if 1 cube of foam has a density of 25, then its weight will be 25 kg. The flexural and compressive strength of foam depends on its density. The density of polystyrene foam and its brand are completely different characteristics. For example, if we take into consideration SPB-C25 or SPB-C50, the density parameter will fluctuate between 35−50 or 15−25.
Plates with a density of 25 are used to insulate the facades of a house. The standard is foam plastic, the thickness of which is 5 cm. This type of insulation is used for many purposes. Its thickness can be changed - this will depend on consumer preferences.
Polystyrene foam of maximum thickness can be used to insulate walls that are exposed to atmospheric agents. They can also be used to insulate walls, since such material perfectly prevents the appearance of fungus.
Based on the designation of the material, it is used in various construction structures, and this does not impair its quality characteristics.
Application of polystyrene foam PSB-S-35
In order to perfectly align the walls, you can change the thickness of the polystyrene foam tiles. It is not recommended to abuse the size of the thickness of the material, since this will provoke certain problems with fixing the drainage system at the corners of the building.
Before choosing insulation of the required thickness, it is recommended to find out in advance what the amount of gas pipe stock is , because it should never be covered, as this may disrupt the aesthetics of the appearance of the building. In this case, it is advisable to prefer PSB-S-35 material with a thickness of 5 cm over material with a density of 25 and a thickness of 10 cm, especially since their prices are practically the same.
Insulation with a density of 35 can be used to insulate the slopes of windows and doors, and the facades of buildings. As a rule, it costs twice as much as the same polystyrene material with a density of 25. With a thickness of 5 cm, it can be used to insulate non-residential structures and garages. With a thickness of similar insulation of 7 centimeters, it can be used for thermal insulation of residential premises.
Due to the normal level of density, it is possible to use a heat insulator with a minimum thickness , which does not imply a deterioration in the quality of insulation. If the polystyrene foam heat insulator turns out to be harder, then it can be used to provide ideal insulation of basement walls and foundations.
Polystyrene foam - how much does a cubic meter weigh?
A popular misconception is that the specific gravity of polystyrene foam should correspond to the brand. That is, if we buy grade 35 polystyrene foam, then the specific gravity of one cubic meter of polystyrene foam should correspond to 35 kg. In fact, according to GOST, the number in the stamp indicates the maximum possible weight per cubic meter, within the limits specified in the same GOST. Thus, the 15th density includes all polystyrene foam boards weighing up to 15 kg/m3 (in reality 11–12 kg/m3), the popular 25th grade includes polystyrene foam, whose specific weight ranges from 15.1 kg/m3 to 25 kg/m3 (most often in practice - 17–18 kg/m3), grade 30 includes polystyrene foam weighing from 25.1 to 35 kg/m3. In the latter case, most often manufacturers offer foam with a real density of 26–27 kg/m3. Deception? Rather, savings - given the high competition in the manufacturer market, everyone is trying to offer the material cheaper than others. And this can only be done by reducing the amount of raw materials and deteriorating the quality of the products.

Determining the quality and brand of polystyrene foam by density (weight-to-volume ratio, kg/m3) is the biggest misconception. Density is only one characteristic that plays a role in determining the grade of material produced. According to GOST 15588-86, foam plastic is characterized by compressive strength, bending strength, thermal conductivity, water resistance, slab burning time and structural stability. Of all these characteristics, density is far from the most important. For example, for 25th density polystyrene foam, GOST defines a compressive strength of at least 0.08 MPa. For grade 15, this characteristic is 0.04 MPa. GOST has one very important point - if expanded polystyrene does not correspond to its brand in any characteristic, it must be assigned to a brand of a lower class .
That is, if you buy expanded polystyrene, the specific gravity of which is from 15.1 to 25 kg/m3, but the compressive strength of the material is less than 0.08 MPa, it should be classified as grade 15.
Comparing the density of foam
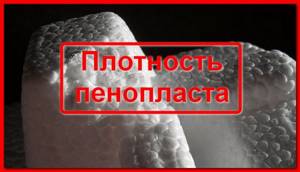
Foam density is an indicator that determines the strength characteristics of thermal insulating polystyrene foam. This thermal insulation material consists of 98% air bubbles and 2% pure polystyrene. Polystyrene is the basis of expanded polystyrene.
It is obtained by the polymerization of styrene. Expanded polystyrene has become widespread due to a number of advantages:
- No toxic compounds.
- High thermal insulation properties, thermal conductivity in a dry state - 0.029-0.036 W/(m.k).
- Light weight.
- Polystyrene foam does not enter into chemical reactions with building materials (cement, bitumen, acrylic, gypsum putty).
- Resistance to microorganisms, algae, mold, fungus.
- Durability.
Differences between polystyrene foam and manufacturing methods
Before we begin to consider the types of polystyrene foam, it is necessary to clarify the terminology. Many people call polystyrene foam a lightweight white material consisting of a huge number of white compressed balls, in general this is true, but one point needs to be clarified.
Foam plastic is a general name for a whole group of materials obtained by foaming plastics. Since various plastics can be foamed, there are a huge number of foams. For example, if polystyrene is used as a raw material, the material obtained is polystyrene foam; if polyurethane is used as a raw material, the material is polyurethane foam (one type is polyurethane foam); polyvinyl chloride foam is obtained from polyvinyl chloride.
The production technology for all foam plastics consists of three main stages:
- Mixing the components used.
- Foaming.
- Structuring.
The main technological link is foaming; at this stage, polymers are filled with gas, which determines the technical characteristics of the material.
The ratio between open and closed cells with air plays an important role in the physical and mechanical properties of polystyrene foam. Closed cells guarantee low hygroscopicity. The less the foam absorbs water, the better its thermal characteristics, the longer the material lasts.
The structure of the foam depends on the manufacturing technology and the raw materials used. Polystyrene foam, polyurethane and polyvinyl chloride have a large number of closed cells.
According to production technology, there are two main types of polystyrene foam:
- expanded polystyrene foam - (EPS)
- extruded polystyrene foam - (XPS).
Expanded polystyrene foam - (EPS)
Foamed polystyrene foam is most often used in everyday life. It is used as thermal insulation, material for packaging equipment and furniture. During its manufacture, polymers are filled with gas using foaming components.

Foamed polystyrene foam.
The technological chain consists of several stages:
- Mixing polystyrene, which is sometimes replaced by polymonochlorostyrene or polydichlorostyrene.
- Adding foaming components, which are low-boiling hydrocarbons - dichloromethane, pentane or isopentane.
- Adding additives that improve the properties of the finished material - plasticizers, fire retardants and dyes.
- Formation of granules with uniform distribution of low-boiling liquids in polystyrene.
- Treatment with steam or hot air.
- An increase in granule size as a result of sudden evaporation of low-boiling liquids.
- Structuring foam cells, giving it shape.
As a result of boiling of the foaming components, the granules increase in size by more than 50 times. The walls of the forming cells harden and merge, trapping air inside - an ideal heat insulator. The material turns out to be light, homogeneous, and retains its given shape well.

Enlarged expanded polystyrene foam granules.
Extruded Polystyrene Foam - (XPS)
The main differences in the production technology of extruded polystyrene foam are the absence of steam treatment and structuring by extrusion from a flat-slot extrusion head. Freons were used as a foaming agent in the first decades of material production; today carbon dioxide is used.
This expanded polystyrene has a continuous structure with closed-porous cells with a diameter of 0.1 - 0.2 mm.

Extruded polystyrene foam.
Extruded polystyrene foam has good thermal insulation properties and is more dense than expanded polystyrene foam. This allows the use of extruded polystyrene foam to insulate those objects for which expanded polystyrene foam is too soft. It is possible to produce extruded polystyrene foam, which will withstand loads of up to 35 tons per 1 m2.
Main brands of foam plastic
After foaming the polystyrene, the raw materials for the finished products are loaded into a container. Steam is injected into it under pressure. The granules foam and become saturated with air. At the next stage, the finished granules are dried from moisture; hot air is used for this.

When drying, the granules are shaken periodically. The finished granules are placed in bins that are calibrated according to foam grades. Molding occurs under pressure. When molding, the following types of foam are obtained, which differ in density:
The last number in the marking determines the density of the foam for insulation. Many developers do not know what the specific gravity of foam is. Density (specific gravity) is the mass of a product in its volume. The density of polystyrene grade PSB-S-15 is 15 kg/m³. Accordingly, one cubic meter of PSB-S-15 polystyrene boards weighs 15 kg.

The question arises of how to independently determine the density of foam plastic without special equipment. This is easy to do: you need to calculate the cubic capacity of the finished product and weigh it on the scales. To make a claim, the store must have in hand a state verification certificate of the scales. Weighing can be carried out directly in the store or at the construction warehouse of the materials supplier. This technical calculation of foam density will be the most optimal.
Insulating the facade with polystyrene foam: choosing polystyrene foam
We are accustomed to measuring almost all substances, liquids, materials and even gases in cubic meters. It's really convenient. After all, their costs, prices, rates, consumption rates, tariffs, supply contracts are almost always tied to cubic meters (cubes), and much less often to liters. No less important for practical activities is knowledge of not only the volume, but also the weight (mass) of the substance occupying this volume: in this case we are talking about how much 1 cubic meter weighs (1 cubic meter, 1 cubic meter, 1 m3). Knowing mass and volume gives us a fairly complete idea of quantity. Site visitors, when asking how much 1 cube weighs, often indicate specific units of mass in which they would like to know the answer to the question. As we noticed, most often they want to know the weight of 1 cube (1 cubic meter, 1 cubic meter, 1 m3) in kilograms (kg) or tons (t). Essentially, you need kg/m3 or t/m3. These are closely related units that define quantity. In principle, a fairly simple independent conversion of weight (mass) from tons to kilograms and vice versa is possible: from kilograms to tons. However, as practice has shown, for most site visitors a more convenient option would be to immediately find out how many kilograms 1 cubic meter (1 m3) of polystyrene weighs or how many tons 1 cubic meter (1 m3) of polystyrene weighs
, without converting kilograms into tons or vice versa - the number of tons into kilograms per cubic meter (one cubic meter, one cubic meter, one m3).
Therefore, in Table 1 we indicated how much 1 cubic meter (1 cubic meter, 1 cubic meter) weighs in kilograms (kg) and tons (t). Choose the table column that you need yourself. By the way, when we ask how much 1 cubic meter (1 m3) weighs, we mean the number of kilograms or the number of tons. However, from a physical point of view, we are interested in density or specific gravity. The mass of a unit volume or the amount of substance contained in a unit volume is bulk density or specific gravity. In this case, the bulk density and specific gravity of polystyrene.
Density and specific gravity in physics are usually measured not in kg/m3 or tons/m3, but in grams per cubic centimeter: g/cm3. Therefore, in Table 1, specific gravity and density (synonyms) are indicated in grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm3)
Table 1. How much does 1 cube of polystyrene weigh, the weight of 1 m3 of polystyrene. Bulk density and specific gravity in g/cm3. How many kilograms are in a cube, tons in 1 cubic meter, kg in 1 cubic meter, tons in 1 m3.
≡ October 21, 2021 Category: Dacha
What density foam is best for different types of insulation?
High-density PSB is best used for insulating industrial facilities, utilities, parking lots, roads and sidewalks. It is used in industry and the highway sector. It is able to withstand high static and dynamic loads on the plane.
This begs the question, what is the best characteristic of polystyrene foam for insulating a house? Density 35 kg/m³ is the volumetric weight of polystyrene foam for insulating walls outside. Polystyrene PSB-S-35 and PSB-S-25 correspond to this density and are suitable for thermal insulation of facades of residential buildings . Its structure will not be destroyed by mechanical impact on the plane of the slabs.
The slabs are easy to install and process, allowing you to obtain a thermal insulation effect at low material costs. This is the most popular type of slab.
PSB-S-15 foam plastic slabs can also be used to insulate house facades. It is important to exclude static and shock loads on the surface of the insulation during operation of the building. It can also be used to fill voids in structures, insulate attics, insulate underground spaces and voids in ceilings.
Extruded (extruded) polystyrene foam
Foam plastic with a density of 25 mm is most often used in construction and is considered the most versatile. To improve the thermal insulation of your home, and at the same time save money, use universal foam with a density of mm. Foam foam has the same thermal insulation as mm of concrete. If instead of concrete you use foam plastic whose thickness is millimeters, you will get significant cost savings, and the efficiency of heat and sound insulation will be even better.
Polystyrene foam is an excellent insulation material, it has good technical characteristics, but it is not recommended to use it inside residential premises. There is air inside the foam, which provides it with excellent thermal insulation. This material has no expiration date, it does not decompose or deform. Polystyrene foam is fireproof, it does not support combustion and has self-extinguishing property. Another positive characteristic of insulation is the low weight of the slabs, which does not make the structure heavier and does not require reinforcement of the foundation.
Along with excellent characteristics, polystyrene foam also has disadvantages. In contact with aggressive chemical compounds such as gasoline, kerosene, turpentine, paint thinners, etc.
Polystyrene foam practically does not allow air to pass through and has poor mechanical strength. A layer of plaster will increase its strength and also help protect it from damage by rodents. Expanded polystyrene is created from polystyrene granules.
They are filled with pentane and heated with steam. After this, the granules increase in volume by one-fold. Next, the granules are exposed to hot steam, as a result of which the balls adhere and a soft, durable material is obtained, used as insulation.
Many people prefer to use mm polystyrene foam, since this material is characterized by reliable thermal protection. Expanded polystyrene is a durable material that provides a high degree of insulation. It is suitable for use in all areas.
In the year BASF developed polystyrene foam.
Since then, it has conquered the construction market and its popularity is constantly growing. Expanded polystyrene is easy to transport and is light in weight. The price of this material per 1 cubic meter is the lowest compared to other insulation materials. This type of insulating material will protect your walls and floors from moisture all year round and keep your room warm.
When you go to a specialized store, it is difficult to figure out which material to choose for insulating the room. And it is even more difficult to calculate how much material is required to cover the area of the insulated area. To do this, you need to know at least the amount of insulation in one cube, and how to calculate the required amount of material for the job. Having universal properties, mm foam can be used both in industry and for insulating the outside of residential premises.
When buying polystyrene foam, you need to check the quality certificate to make sure that high-quality materials were used in its production.
This must be done to make sure that the insulation will not release toxins. Polystyrene foam is packed in bags. The number of sheets in such a package depends on the thickness of the foam. The foam is sold in the form of white sheets.
The standard size of cut foam is mm x mm. The range of slabs is also presented in non-standard sizes, for example, x, x, x, x. By individual order, slabs of size x can be cut. The Stolit company has been producing thermal insulation materials since the year. Stolit presents its foam plastic in construction stores in a large assortment.