Do-it-yourself material recycling
If you want to know exactly how you can recycle polystyrene foam, we suggest you consider the step-by-step instructions. All you need is enough foam and a crusher. Then you can get polystyrene foam granules and use them for your own purposes. If you don’t have your own foam crusher, you can make one yourself. After all, factory models have a very high price.
Here's what you'll need to have a new useful tool on your farm:
- sewer PVC pipe, diameter 50 mm;
- tape measure and marker;
- metal file;
- a wooden beam that would fit inside the pipe;
- metal screws;
- screwdriver and drill;
- metal studs with bolts;
- Chipboard or plywood to create a box.

Using this set of tools and materials, you can create a working foam crusher. With its help, sheets or others will turn into crumbs. The mechanism is based on a moving part with teeth, which crush the foam into granules. And thanks to the container or box, it is easier to direct the material to the rotating mechanism. You will learn exactly how to create a crusher in this video.
So, when the crusher is ready, you can start working. Here's what to do:
- Choose a suitable location. Alternatively, choose a garage, warehouse, storage room or shed.
- Install the crusher, taking care of the container underneath it, where the crumbs will fall. This could be a bucket, bag or wooden box.
- Foam sheets are easy to crush. But as for figured products, it is better to break them into pieces with your hands in advance.
- Now all that remains is to turn on our homemade unit and gradually process the raw materials.

Thanks to this technology, most of the granules will remain intact. This means that they will cope with their task better than ever. You just need to be careful, as the foam is electrified and very light
It is important to make sure that there are no drafts in the room, otherwise you will have to remove everything from the floor later. Now the foam can be collected in bags and used immediately or stored until it has its time
Note! If you melt the foam with acetone, it can be used in liquid form as glue. Although the mixture cannot be called safe
Materials for production
Since there are several types of such material, accordingly, it is produced from various raw materials. The most popular today are products from:
- polystyrene;
- polyurethane;
- polyvinyl chloride;
- polyethylene.
Let's take a closer look at the production of each of these types of foam:
- Polystyrene foam is made from styrene polymers. This substance has minimal strength and can be easily dissolved with gasoline or acetone. This type of foam is formed by gas-filling styrene granules. Also, the procedure for obtaining such substances involves the use of additional substances that improve the structure or color the product itself.
- Polyurethane foam has good technical characteristics, which depend on the procedure for obtaining such a substance. Polyurethane polymers are very often used in various industries. The structure of foam made from such substances can be different (hard or elastic), which is obtained from certain types of these raw materials. This material is obtained by foaming using special gases.

To obtain polyvinyl chloride foam, they resort to heating the raw material and then foaming it under the influence of various gases. To obtain a material with the original characteristics, the resulting mixture can be pressed.
The mechanical properties of polystyrene foam are also controlled using special substances that are added during its production process.
Polyethylene is used as a raw material for the preparation of such products. The foam made from it is soft and almost colorless.
Such products are used as wrapping for packaging various plumbing fixtures and household appliances. Such material is also obtained under the influence of gases that penetrate the pores of polyethylene.
Polystyrene foam is popular as insulation, and therefore it is often used to insulate the facades of houses.
Watch the video to see how polystyrene foam is made:
All stages of foam production technology are considered. The equipment needed to produce this material is listed. Recommendations are given that you should definitely read before purchasing.
Many of us have come across expanded polystyrene more than once, tried it to the touch, made something from it, used it in construction, for home improvement. However, not everyone knows what the foam manufacturing technology is and what its features are.
Oddly enough, there is nothing super complicated in the production of this material. And it is noteworthy that now quite a lot of low-quality polystyrene foam has appeared on the market, which is made without taking into account the relevant norms and regulations.
Some craftsmen manage to create a small production line even in an ordinary garage. Yes, don't be surprised.
And this must be taken into account when purchasing - not all Vasya Pupkins strictly adhere to the prescribed technological standards. And what standards can there be in a garage?
Advantages of equipment for foam materials:
- the cost of automated lines quickly pays off due to the reduction in maintenance costs and the involvement of a minimum number of personnel; the installations are compact in size and do not require the allocation of premises or large areas; the modular design ensures the quick replacement of faulty units, the modernization of the existing configuration when performance requirements change; new location, dismantled lines are transported by conventional vehicles.
Companies that offer to buy machine equipment for the production of foam materials provide a guarantee for their products, organize delivery, and perform installation and commissioning work. Specialists from such manufacturers conduct classes with staff, teaching the basics of technological processes, maintenance and repair of installed models. Almost all equipment is designed for long-term and intensive use, which eliminates work stoppages due to sudden breakdowns.

Extruded polystyrene foam is a synthetic thermal insulation material consisting of polystyrene granules mixed at high pressure and temperature with the introduction of a foaming component and subsequent extrusion from the extruder. It is also called extruded polystyrene foam, abbreviated as EPS, or XPS.
Raw materials and technology
Polystyrene foam is made from special expanded polystyrene foam. Its cost largely depends on the manufacturer and fraction. The price of raw materials for the production of polystyrene foam ranges from $2 per 25 kg.
When purchasing expanded polystyrene, pay special attention to its quality. Domestic raw materials can be purchased at a low price, but this may negatively affect the quality of the finished product
Imported polystyrene foam allows you to obtain high-quality material with a small amount of defects. Recently, the main raw materials have been purchased from China.
Pay attention to the quality of polystyrene, as well as the duration of its storage. The older the raw material, the longer the foaming process will take and the more difficult it is to achieve the density of the foam granule
What is needed to produce expanded polystyrene?
- Raw materials (expanded polystyrene foam);
- Steam (temperature about 110 degrees);
- Electricity (voltage 980 W);
- Cold water;
- Equipment.
Production technology
When the starting material enters the pre-expander, the granules are inflated and turned into balls. If necessary, this process is repeated. After foaming, the granules increase in volume. This foam production technology is used to produce low-strength material.
Video on the topic Video on the topic
Advantages of using automated lines:
- the ability to purchase installations of high or low productivity, taking into account the requirements for the quantity of finished products at a particular enterprise; collapsible design of most modules that can be quickly dismantled and replaced; automatic control of production process parameters, a wide selection of settings and adjustments, emergency mode signaling; ease of access to structural components elements to replace faulty elements or upgrade components.
The catalog presents equipment whose manufacturers guarantee trouble-free operation and perform installation and commissioning work.

Equipment for the production of foam concrete or expanded polystyrene is used in the production of rectangular blocks or sheets, which are in demand in the construction of housing, public, industrial and other buildings. The materials are used for the construction of horizontal enclosing structures inside buildings, creating sound and heat insulation. Finished blocks or sheets of expanded polystyrene are delivered to construction sites in batches on pallets (up to 50 pcs.) in plastic packaging and packs of 5–10 sheets.
Using recycled polystyrene foam
Construction is a process that requires large investments. And if you have polystyrene foam, it will definitely find its use at a construction site. For example, foam chips can be used as filler for site depressions and uneven areas. It is clear that they cannot level the road, but it is easy to make a path or other unevenness. Recycled polystyrene foam can be filled into a well of different hole or cavity diameters.
Note! Over the years, the material will not change and will remain in the form and form in which it was left. It perfectly absorbs and thaws moisture
Therefore, metal containers with polystyrene foam are not so susceptible to corrosion.

In the construction business, recycled polystyrene foam is used to create lightweight bricks. Its structure is such that it is popularly called perforated. Even lightweight concrete has appeared, which, as experts say, is no less durable than regular concrete. This is polystyrene biton - an excellent building material. It consists of Portland cement, foam granules itself, water and an air-entraining additive. Sometimes sand is added to the mixture.

Another area of use is design. Designers love foam plastic very much and use it in a variety of ways. It is used to decorate walls, create pots, plant pots or similar accessories. Garden figurines or stands look very nice. They are created by pouring them into molds and heating them. You can find a variety of options for making polystyrene at home.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages of extruded polystyrene foam over analogues:

- Very low moisture absorption Durability Easy to use and install High thermal insulation ability Strength and ability not to lose shape and volume under different operating conditions
Along with its advantages, it has some disadvantages.
Among these is a low level of vapor permeability. As insulation, it is not suitable for all types of premises. If you insulate a residential building with it, it will turn into a thermos that cannot breathe.
Another disadvantage is the cost, which is higher than other insulation materials. Although the technical characteristics and price of extruded polystyrene foam are adequate to each other. Finally, the sound absorption of XPS in practice is quite low.
How polystyrene foam is made
Previously we told. We remember that this material consists of numerous cells filled with air. This means that the manufacturing process must include foaming the material.
That’s right: the foaming process is one of the most important in the production of expanded polystyrene
.
However, that's not all.
Consider:
Stages of foam manufacturing technology
Typically the process includes:
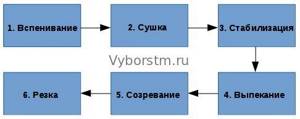
Now in more detail:
1. Foaming.
During this process, the raw materials are placed in a special container (foaming agent), where, under pressure (a steam generator is used), the granules increase approximately 20-50 times. The operation is completed within 5 minutes. When the granules reach the required size, the operator turns off the steam generator and unloads the foam material from the container.
2. Drying the resulting granules.
At this stage, the main goal is to remove excess moisture remaining on the granules. This is done using hot air - it is directed from bottom to top. At the same time, for better drying, the granules are shaken. This process also does not last long - about 5 minutes.
3. Stabilization (tracking).
The granules are placed in bunkers, where the aging process takes place. The duration of the process is 4...12 hours (depending on the ambient temperature and the size of the granules).
Important note: the polystyrene foam manufacturing technology may exclude the 2nd stage (drying). In this case, stabilization (tracking) will last longer - up to 24 hours
4. Baking.
This stage of foam production is often called molding. The idea is to connect the previously obtained granules together. To do this, they are placed in a special mold, after which the granules are sintered under pressure and under the influence of high temperature water vapor. Lasts approximately 10 minutes.
5. Maturation (aging).
The goal is to rid the resulting polystyrene foam sheets of excess moisture, as well as remaining internal stresses. To do this, the sheets are placed in a free space in the production workshop for several days. In some cases, ripening can take up to 30 days.
6. Cutting.
The manufactured foam blocks are placed on a special machine, on which the blocks are cut into sheets of appropriate thickness, length, width. This manufacturing process is performed using nichrome strings heated to a specific temperature. Accordingly, both horizontal and vertical cutting of blocks is carried out.
This is how foam is made.
Of course, after the above 6 stages, the 7th stage can be performed - processing the remaining trimmings
. As a result, they are mixed with other granules, which will then undergo the same processes - sintering, curing...
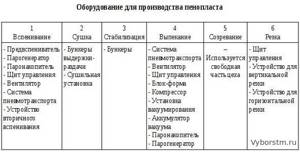
The equipment that is used in the production of polystyrene foam is shown in table form:
Features of foam production technology
When producing foam concrete or expanded polystyrene, the raw materials in the form of sand or polymer substances undergo preliminary preparation and are then fed to the line for forming finished products. To obtain polystyrene foam, polystyrene granules are foamed, which are then dried, steamed, vacuumed and sheets of expanded polystyrene are formed under pressure.
Finished products are packaged using automatic devices and unloaded into storage areas. Expanded polystyrene packaging is lightweight and therefore does not require complex lifting equipment. Heavier foam blocks are placed on pallets, which can be lifted with a forklift or cranes with the appropriate sling set.
The process of creating polystyrene foam
This material is made from expanded polystyrene by foaming it. Almost 98% of it consists of gas. There are 6 stages of creating polystyrene foam in an industrial environment:

Let's look at each of the stages. To begin with, the raw materials are poured into a foaming agent, after which the steam generator generates pressure at which the granules begin to increase from 20 to 50 times. The entire foaming process takes 5 minutes. When the desired size is reached, the raw materials are unloaded for drying. It is needed so that excess moisture on the granules evaporates. Everything happens due to hot air directed from bottom to top. Drying and shaking takes about 5 minutes.
Then the raw materials are moved to bunkers, where they are aged for 4-12 hours. The foam is then formed or baked. The main task is to connect all the granules, creating a slab or other desired element. To do this, they are poured into a mold and subjected to pressure under high temperature from steam. Baking lasts 10 minutes. Next, the finished foam must be left to rest to get rid of moisture and tension inside. Sometimes ripening lasts a whole month. At the end of this stage, the block is installed on a machine that cuts the material into shape. The machine has nichrome strings that heat up and cut foam with ease.

The production also processes foam plastic. After all, when created, pieces remain. So they are processed. Why recycle material at all?
Stages of polystyrene foam production
The technology for manufacturing polystyrene foam consists of foaming suspension polystyrene. To obtain the desired result, use steam. Next, the granules are sintered. Then a large block is formed, which is subsequently cut into sheets. But, before loading the raw materials into the bunker, the granules are mechanically mixed with various modifier additives.
To make the finished material more fire resistant, fire retardant additives are added to its composition. To protect polystyrene foam from the effects of heat and oxygen, antioxidants and heat stabilizers are used, and abiotic components are used to prevent molding. In the production of extruded polystyrene foam, nucleate stabilizers are introduced, which help to obtain a more uniform and fine pore structure.
Return to contents
Foaming polystyrene granules
Technological diagram for the production of expanded polystyrene sheets.
Foaming of suspension polystyrene occurs in two stages. Moreover, for each batch of raw materials the optimal time for passing this stage is determined. It depends on the quality of the raw materials. This period must be strictly observed, since if the time intervals increase, the granules may be destroyed.
The first stage of material processing takes place in the pre-expander. This unit is a container with holes in the bottom through which steam is supplied. It is also equipped with an activator for stirring the granules. During foaming (about 5 minutes), the temperature in the container is maintained at about 100-110° C.
The foaming process occurs as follows. Thanks to the action of water vapor, pentane, which is part of the suspension polystyrene granules, is activated. They soften and grow in volume, and the amount of material can increase 30-50 times. The integrity and tightness of the cells are maintained.
To accelerate the foaming process, the granules are mixed using a mechanical activator. At the end of this cycle, the material rises under pressure. Through the unloading window it is pushed into an intermediate container, and then, using pneumatic transport, it is moved to a bunker for storage.
Return to contents
Drying and curing foam granules
Scheme of polystyrene foam as insulation.
Polystyrene granules that have been foamed contain about 10-15% moisture. There is a vacuum inside them, as condensation of pentane and steam residues has occurred. As a result, under the influence of these factors, compression of the granules may occur, which will lead to a decrease in the volume of the material and an increase in bulk density. It is for this reason that the foam production technology involves a drying stage.
The purpose of this stage:
Due to the fact that warm air (about 35° C) penetrates into the cells of the material, polystyrene acquires the necessary parameters of compression resistance. Moreover, the lower the bulk density of the material, the faster air will be absorbed.
The drying process takes about 5 minutes. In some cases, it is combined with the transportation stage. During material transfer, humidity can be reduced to 6-3%. In addition to the loss of moisture, drying contributes to a significant increase in the fluidity of the material.
Scheme of the main types of polystyrene foam.
This, in turn, allows the aging bins to be filled more efficiently. These special devices consist of a metal base with a fixed bag made of breathable fabric. Granules are stored in them at a temperature not exceeding 22-28° C. The duration can range from 6 hours to a day. This time depends on the volumetric bulk weight of the granules: as the weight decreases, the period increases, but it should not exceed 14 days, since during this period isopentane evaporates and the granules lose their ability to foam.
Meanwhile, there are several methods of aging. To reduce the holding time, the method of pumping granules using an air flow from hopper to hopper is used. With this approach, 2-3 hours are enough for the material to acquire the necessary indicators of water absorption and strength.
Return to contents
Block production and cutting
The production or baking of blocks is carried out in a special block mold. This rectangular steel device has double walls, and the inside is perforated (this is necessary for steam supply).
Diagram of an expanded polystyrene panel.
After the mold has warmed up, granules are poured into it and it is hermetically sealed. Re-foaming is also carried out under the influence of water steam under pressure.
The quality of expanded polystyrene is affected by the timely termination of the formation process. If it is interrupted before the required time, then the insufficiently foamed granules will not fuse well. If the material is overexposed, the cells are destroyed and shrinkage phenomena appear. In both cases, the quality of the product deteriorates significantly.
Making polystyrene foam at home
First you need to purchase raw materials - foaming polystyrene. Expandable polystyrene is a product of the chemical industry
When purchasing it, you should pay attention to the warranty storage lines. The rule here is that the “older” the foaming polystyrene granules are, the longer the foaming process takes and the more difficult it is to obtain the required density
It is important to immediately draw the attention of readers of this article to the fact that making small quantities of polystyrene foam at home is, to put it mildly, unprofitable. If the conditions require insulating boards or baguettes, which fill the building materials market, it is much easier and cheaper to buy them and not fool yourself
But for enthusiasts who specialize in the production of exclusive designer products (like handmade craftsmanship), technology will be useful - making polystyrene foam at home
, which will be described below. Since this material adheres well, it is possible to invent and come up with complex products from segments of different shapes and cross-sections.
What can foam molds be made from?
Various materials can be used to make foam molds, from ceramics to wood. Molds made of steel or tin-casting molds last a long time.
You can also use heat-resistant plastic. If you decide to use silicone culinary molds as forms for polystyrene foam, they must be strengthened with alabaster or plaster - simply fill a suitable container with alabaster or gypsum solution and dip the mold into it to the very edges. It is quite difficult to weld the finished product to the mold, as is gluing foam plastic to other surfaces.
Manufacturing technology and processing of polystyrene foam at home
The technology for producing polystyrene foam at home involves two-stage steaming of the raw materials. In this case, all kinds of household appliances can be used as a source of steam: a steam mop or a Karcher-type washing unit with a steam generation function.
The amount of steam generated by these devices will be quite sufficient for the production of small products that fit on the palms of the hands. As a rule, these products are used to decorate the interior of premises.
The first steaming of polystyrene foam can be organized in a regular metal bucket. Fill it 20% (1/5) of the volume with foaming polystyrene granules, immerse the hose from the steam generator into the thickness of the granules and, running the device in a circular motion, treat the granules with steam.
After a certain period of time, the granules will increase in size and fill the bucket to the very top. Now you should distribute the primary processed raw material into molds and process it with steam until the granules stick together.
Now you don’t need to mix them, just lower the hose to the bottom of the mold and turn on the steam generator. Thus, you will get a kind of gap into which you can attach the foam and easily remove it from the mold.
It should be taken into account that the thinner and more prominent the product, the smaller the diameter of the primary granules (after the first foaming-steaming). And the larger they are, the lighter and more fragile the finished product.
The production of building materials has always brought good income. This also applies to polystyrene foam. Today, this material is in great demand in the domestic market.
If you decide to open your own business and make a good fortune, pay attention to the business plan for the production of polystyrene foam. To implement this idea, you will not need a large start-up capital, as is the case with, for example, so any aspiring entrepreneur can start this business
Premises requirement
A business requires a specially equipped premises that meets all the requirements for this type of activity. The size of the room must be at least 70 m2. Part of it needs to be allocated for storing finished products, that is, a warehouse. The height of the workshop should be 3-5 meters. The room must be equipped with electricity. In addition, it is necessary to organize the supply of dry water steam with a certain pressure.
In order for production to be reliable, fast and profitable, you should first purchase a foaming agent, which will be useful at the first stage of production. For aging you will need a special bunker. There is a complex for cutting polystyrene foam, without which production would also not be possible. Packs foam blocks using an automatic or semi-automatic machine.
Expanded polystyrene boards are a popular building material. The foam production business will bring high income, but do not forget about the high level of competition in this area. A large number of products are made from polystyrene foam. Businessmen involved in this business buy foam plastic in bulk from manufacturers. By making products yourself, at home, you can save a lot of money, but when organizing a business, it is important to use only high-quality equipment and raw materials. Making polystyrene foam at home is a profitable and profitable business!
Expanded polystyrene is used as a thermal insulator with excellent functions. It is produced in the form of slabs, which is quite convenient for installation and cutting if necessary. The cost of expanded polystyrene is not too high, which, together with its strength, hygroscopicity, and excellent thermal insulation properties, has a positive effect on the choice of this particular insulation. You can not only buy expanded polystyrene in ready-made form, but also make it yourself. This does not require sophisticated equipment. Real benefit from such work is possible if large-scale production is planned, for example, when building a house. If you need to insulate a couple of walls, then it is better to buy polystyrene foam.
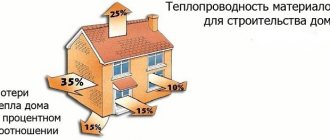
Due to its thermal insulation properties, expanded polystyrene can be used as external thermal insulation for roofs, foundations and walls.
Foam manufacturing technology directly affects quality
As we said above, the market is now filled with a considerable amount of low-quality material. It can be produced in garages or some warehouses.
But the main problem is not where the material is made (although the environment also affects quality), the main problem is not following all the rules for making polystyrene foam.
What deviations may there be from the correct production of expanded polystyrene?
The most varied - from poor-quality granulation to poor, inaccurate cutting of foam blocks into sheets.
Some smart guys don’t carry out stabilization or aging at all. For them, the speed of production of polystyrene foam is exclusively important.
Because of this, things get much worse:
- it may turn out to be fragile, fragile,
- granules may be poorly connected to each other,
- density may be uneven.
This can also occur due to low-quality, faulty equipment that was used in production - foamers, dryers, compressors, steam generators, etc.
And another important point
: with poor manufacturing technology, foam plastic may have a sharp, unpleasant odor. The following picture is possible: they brought brand new sheets of expanded polystyrene home, placed them in a garage or other room and... soon they heard that the room was filled with some kind of pungent, unpleasant smell.
This is very bad. This means that the foam is still “floating”, releasing harmful substances. It is especially dangerous when such low-grade material is stored in residential areas.
Scope of application of foam plastic
- Lightweight filler for compartments that ensure unsinkability of ships (usually small ones);
- Material for the production of floats, life jackets and bibs;
- Material for the manufacture of medical containers, including for the transportation of donor organs;
- Polystyrene foam is an excellent heat and sound insulator for construction;
- Structural building and finishing material (shape-forming and decorative elements);
- Thermal insulator in household appliances (for example, refrigerators);
- Packaging for various goods (especially fragile ones), including food;
- Material of models used in lost wax casting (of metals).
Location
To choose the right geographical location for a business, it is necessary to conduct thorough market research. The most favorable regions for doing business are those regions in which the supply of a given product does not completely cover the demand. In such a place you can safely launch your commercial project.
Do not forget to clearly work out and include in the business plan the ways of selling the finished material. This is a very important point on which the profitability of your enterprise largely depends. In addition, the seasonality of the business should be taken into account. During a period when demand for products falls, you can switch to the production of foam products. This will allow you to ensure a stable year-round income.
The main consumer of polystyrene foam is. Each of them is already collaborating with other manufacturers
You need to attract their attention to your product with low prices, but at the same time good quality. To ensure stable sales of products, it is necessary to find regular wholesale buyers, for example, and conclude agreements with them
Expandable polystyrene
Modern technology
The technology for producing foaming polystyrene is a fairly modern invention. This technology has revolutionized the barriers to entry into the insulating materials market, making this production cheap and accessible. Organizing the production of products made from foaming polystyrene requires several tens of thousands of dollars, and the technological process is simple and straightforward. Therefore, similar production can be found in almost every locality.
Each granule consists of evenly distributed microscopic dense cells filled with air. As a result, a uniformly foamed mass with a very thin closed-cellular structure is formed. 1 m3 of such material is 98% filled with air contained in 3-6 billion closed cells. Due to its internal structure, it has very low thermal conductivity, close to the thermal conductivity of still air (thermal conductivity coefficient of air is about 0.00006 cal/cm sec. deg., i.e. through every square centimeter with a temperature difference of 1°C and with a thickness of 1 cm, 0 is transmitted .00006 calories for 1 second). Thus, polystyrene is a rigid foamed polystyrene mass hardened during cooling with closed cells filled with air and is an environmentally friendly building material.
Expandable polystyrene products
in the production of polystyrene foam blocks and slabs of various configurations for heat and sound insulation of buildings and premises for any purpose (walls, roofs, floors, warehouses, pavilions, residential buildings, garages, basements, loggias);
in the manufacture of packaging of complex shapes for various devices that require shock protection during storage and transportation; in the manufacture of components for cars, watercraft, and decorative interior products;
in the production of polystyrene concrete - lightweight concrete based on cement binder and foamed polystyrene filler, used in the manufacture of thermal insulation blocks and slabs, monolithic thermal insulation of attics, roofs, external walls, floors, etc.;
for the production of finishing materials for the ceiling - tiles, baseboards, rosettes;
Quite new areas of application of foaming polystyrene are the production of permanent formwork for monolithic housing construction and shells for thermal insulation of pipelines.
Two production technologies – bulk polymerization and suspension polymerization
In the production of foaming polystyrene, the main methods are suspension polymerization and bulk polymerization. The most modern and effective is the second method of obtaining IPN. In addition to the fact that bulk polymerization is a more economical production method, the quality of the final product varies greatly. Expanding polystyrene produced by bulk polymerization allows for the production of higher quality and more complex products.
Bulk polymerization
The method of producing polystyrenes by polymerization in bulk with incomplete conversion of monomers is currently one of the most common due to its high technical and economic indicators. In the domestic industry, the bulk polymerization method was chosen as the preferred method in the 70s, and currently about 50% of products are produced using this method. This method has an optimal process flow diagram. The process is carried out according to a continuous circuit in a system of 2-3 devices connected in series with mixers; the final stage of the process is often carried out in a column-type apparatus. The initial reaction temperature is 80-100°C, the final temperature is 200-220°C. Polymerization is interrupted when the degree of styrene conversion is 80-90%. The unreacted monomer is removed from the polystyrene melt under vacuum and then with water vapor until the styrene content in the polymer is 0.01-0.05%. Stabilizers, dyes, fire retardants and other additives are added to polystyrene and granulated. Block polystyrene is characterized by high purity. This technology is the most economical (it does not involve the operations of washing, dehydrating and drying finely dispersed products) and is practically waste-free (unreacted styrene is returned for polymerization). Carrying out the process until incomplete conversion of the monomer (80-90%) allows the use of high polymerization rates, control of temperature parameters, and ensure acceptable viscosities of the polymerized medium. When carrying out the process to deeper degrees of monomer conversion, it becomes difficult to remove heat from the highly viscous reaction mass, and it becomes impossible to carry out polymerization in an isothermal mode. This feature of the bulk polymerization process has led to increasing attention being paid to other production methods, and, first of all, to the suspension method.
Suspension polymerization
Suspension polymerization is a competing technological process that develops in parallel with bulk polymerization and is based on the low solubility of vinyl monomers in water and the neutrality of the latter in radical polymerization reactions. The process is used to produce specialty grades of product, mainly expanded polystyrene. The suspension production method is a semi-continuous process and is characterized by the presence of additional technological stages (creation of a reaction system, isolation of the resulting polymer) and periodic use of equipment at the polymerization stage. The process is carried out in reactors with a volume of 10-50 m3, equipped with a stirrer and a jacket. Styrene is suspended in demineralized water using emulsion stabilizers; The polymerization initiator (organic peroxides) is dissolved in monomer drops, where polymerization occurs. As a result, large granules are formed in a suspension of the polymer in water. Polymerization is carried out by gradually increasing the temperature from 40 to 130°C under pressure for 8-14 hours. The polymer is isolated from the resulting suspension by centrifugation, after which it is washed and dried. The laws of suspension polymerization are close to the laws of polymerization in the monomer mass, but the heat removal and mixing of the system components are significantly facilitated.
Russia has outdated technologies
As already noted, in Russia, foaming polystyrene is produced using a currently outdated method - the method of suspension polymerization of styrene in the presence of a blowing agent. (The exception is the line installed at Gazprom neftekhim Salavat with a capacity of 10 thousand tons per year).
For several decades now, the predominant method of producing expandable polystyrene on the world market has been the method of continuous polymerization in mass, which makes it possible to obtain more advanced products with higher performance indicators.
Expanding polystyrene, produced by continuous polymerization in bulk, when used, gives a better yield of the finished material (color, clarity of boundaries, flexibility, density) and can significantly reduce raw material consumption rates. The main advantage of the first suspension polymerization is the longer shelf life of the granules, which is caused by the presence of isopentane molecules inside the granules.
Therefore, despite the fact that more than half of the UPS consumed in Russia is supplied from abroad, the capacities of domestic producers are idle.
Domestic manufacturers
The production of foaming polystyrene in Russia is carried out at three enterprises:
1. Gazprom neftekhim Salavat, Salavat 2. SIBUR plastic, Uzlovaya 3. Angarsk polymer plant (Irkutsk region)
The Omsk Chemical Company has capacities for suspension polymerization. Moreover, this is the most modern production of foaming polystyrene in Russia. In the 1980s, VPS was produced in Omsk, but then production was stopped. At present, the management of the Omsk Chemical Company does not intend to resume the production of foaming polystyrene.
Forecast of production volumes in 2006-2010.
Forecasting the volume of domestic production of expandable polystyrene is associated exclusively with the commissioning of new capacities. The ability to utilize installed capacity remains very significant. The line at the Angarsk Polymer Plant is idle; Omsk Chemical Company has the capacity to produce EPS. However, suspension technologies for the production of EPS are hopelessly outdated, and resuscitation of obsolete technologies is unlikely to be promising.
Currently, two petrochemical companies are considering organizing the production of expandable polystyrene - SIBUR and Nizhnekamskneftekhim.
1. JSC "Plastic", Uzlovaya
SIBURA management has outlined ambitious plans to reorganize production at JSC Plastic (Uzlovaya). Reconstruction of the existing installation for suspension polymerization is planned for 2006. In addition, it is planned to purchase equipment for producing expandable polystyrene through continuous polymerization in the mass. The volume of lines planned for installation has not yet been approved. It can be assumed that Sibur’s plans include the organization of new production at the level of 50 thousand tons per year. Sibur also plans to organize the production of foaming polystyrene in Perm at the Sibur-Khimprom site. The estimated capacity of future production is 50 thousand tons per year.
2. OAO Nizhnekamskneftekhim
The Nizhnekamsk enterprise entered into an agreement with the Korean company LG International Cor. The Korean company LG Chem acts as the licensor of the VPS process. with the participation of LG International. The production capacity will be 37.8 thousand tons per year.
The background to the question is that in the fall of 2003, the Korean company LG International Corp. together with the joint-stock companies Tatneft, Nizhnekamskneftekhim and Svyazinvestneftekhim (all Tatarstan) signed an agreement on the creation of the joint-stock company Tatar-Korean Petrochemical Company (TKNK), the purpose of which is the construction of a large oil refining and petrochemical complex in Nizhnekamsk. The subject of the negotiations was the creation in Nizhnekamsk (Republic of Tatarstan) of the largest petrochemical and oil refining complex with a project cost of 1 billion 300 million US dollars, as well as the participation of the South Korean corporation in the design and construction of two production facilities - foaming polystyrene and linear polyethylene. The planned launch of the line for the production of expandable polystyrene is scheduled for 2007.
Production in the CIS countries
In addition to 3 Russian enterprises - Gazprom neftekhim Salavat, Plastik (Uzlovaya), Angarsk Polymer Plant - foaming polystyrene is produced in the CIS by the Stirol Concern (Gorlovka, Ukraine) and the Plastics Plant (Aktau, Kazakhstan).
JSC Concern Stirol (Gorlovka, Ukraine)
The production of foaming polystyrene was introduced at the enterprise back in 1965. The original design capacity was 16 thousand tons per year (reconstructions made it possible to increase the capacity to 17.8 thousand tons per year). At that time it was still the Gorlovka Nitrogen Fertilizer Enterprise, which was acquired in 1976. Concern Stirol was registered as a joint stock company on September 1, 1995.
In September 2002, a new workshop for the production of foaming polystyrene was opened (on the site of old equipment that was dismantled), with a capacity of 24 thousand tons per year, consisting of four production lines. The project was carried out at the expense of the concern's own funds. The total amount of funds invested in the purchase of equipment and construction and installation work amounted to slightly more than 16 million hryvnia.
The design part of the work was carried out by Stirolinzhproekt, the installation of equipment and communications was carried out by the construction and installation department Stirolkhimmontazh of the Stirolkhimremstroy trust, while the technology, basic engineering, polymerization equipment and four reactors were supplied by the Hungarian company Inter-Kemikal KFT and the American company PST International.
The new production made it possible to reduce the time of one polymerization cycle to 12 hours (previously it was 28 hours), to reduce the number of personnel servicing the installation, but, most importantly, the physical and mechanical properties of polystyrene were improved (the yield of granules of the main fraction ranging in size from 0.5 mm to 2 mm is 99.5%).
LLP "Sat Operating Aktau" (Aktau, Kazakhstan)
LLP "Sat Operating Aktau" - former "Plastic Plant", Aktau, Republic of Kazakhstan - the last of the industrial polystyrene production facilities commissioned in the former USSR. Production started in 1981. Then the enterprise was called Shevchenko plant. Today, along with the Omsk Chemical Company, it is the most powerful and modern polystyrene production facility inherited from Soviet times.
The plant was built in 1976-1980 on the basis of complete imported equipment. The huge production, built by the Soviet Union in 1980 with the participation of French specialists (), was organized according to a complete technological scheme - from the synthesis of styrene monomer to the production of finished forms of polystyrene. Moreover, profitability was achieved through the use of local hydrocarbon raw materials in the primary synthesis. AKPO produced 100 thousand tons of foaming polystyrene and 110 thousand tons of impact-resistant polystyrene per year, which accounted for more than half of the total production of these products in the USSR. With the collapse of the Union, the demand for AKPO products did not weaken, and it is stable not only within the CIS, but also in the world.
From 1994 to 2000, the plant operated on a shortened schedule due to an accident at an ethylbenzene plant in December 1993. The unique technical complex for the synthesis of styrene was lost, and purchasing the monomer abroad was economically pointless: in this case, the cost of the finished product exceeded its market value. Neither the region nor the republic were able to reanimate the destroyed complex on their own.
In 2001, the plant experienced a rebirth, when, after the acquisition of the plant’s property complex by the Ekstraplast Trading House at an auction (on a competitive basis), polystyrene production was restored. Ekstraplast LLC heads a group of industrial enterprises, united into a common financial structure, operating in the chemical industry of Russia and Kazakhstan.
Thus, the largest chemical association in the CIS was created, consisting of two Russian (Tomsk Plant of Composite Materials and Plastics and Tomsk Petrochemical Plant) and two Kazakh (Atyrau Petrochemical) plants. To resume production, the parent company allocates more than $15 million to the plant, with about half of this amount intended to replenish the working capital of the plant. High quality products are ensured by the use of modern processes from the world's leading companies - Emejota (USA), Rhone Pоjil (France). In December 2001, only one line was launched. Its productivity is 2.5 thousand tons of polystyrene per month. In 2002, the second line was launched.
However, these plans were not destined to come true. Sustainable production of polystyrenes has never been established. Since August 2003, the plant practically did not work, wages were not paid, and tax payments were not repaid. The main problem is that Trading House Ekstraplast LLC was unable to solve the problem of supplying raw materials. In 2005, Trading House Ekstraplast LLC was forced to abandon the plant. The owner was a Kazakh company close to the state - Atoll Joint Stock Company, a subsidiary of SAT&Co and KazMunayGas Exploration Production JSC.
The further development of the enterprise is connected with the implementation of the State Program for the Development of the Petrochemical Industry of the Republic of Kazakhstan. By 2010, it is planned to increase the production of all types of polystyrene at ZPM to 150 thousand tons per year. So many bold statements are based on the Government’s plans to open gas processing plants, which will have to solve the raw materials problem. The cost of polystyrene obtained from the latter is significantly lower than prices in the CIS countries due to the high capacity of the production line (subject to 70-100% load) and will be even lower if the enterprise is provided with domestic raw materials close to production.
Import supplies
Currently, more than half of the consumed volume of this polymer is imported to Russia. As already mentioned, imported expanded polystyrene differs significantly from domestic one. EPS manufactured by bulk polymerization is imported and has incomparable consumer advantages. In Russia, IPS is currently produced using the suspension polymerization method. (The line installed at Salavatnefteorgsintez is not yet operating in industrial mode). The exception is supplies from Ukraine and Kazakhstan. Concern Stirol also produces EPS using the suspension polymerization method. Today, this is the most modern production of EPS in the CIS and in terms of its properties, EPS produced by Concern Stirol significantly surpasses the products of Russian factories. In 2006, supplies of EPS were resumed again from the Plastics Plant in Aktau (Kazakhstan).
Recycling materials: why and how
If we talk about large-scale production, the goal is clear - there is a lot of waste, and this means additional funds. What can we say about us, ordinary users? The thing is that over the years there is more and more material in the house. It takes up space and accumulates more. It is not recommended to burn it, as it releases harmful substances, and throwing it away is also not an option.

So it turns out that the correct and effective solution is to recycle it or do it yourself. This type of recycling of polystyrene foam will help you use it for another purpose and get rid of excess garbage at home.
To do this yourself, it is important:
- will be determined for the purpose of processing and creating polystyrene foam;
- choose the optimal place where you can bring everything to life;
- will determine the method of influencing foam waste.
Many people choose to use polystyrene foam as packaging material. Storing it in finished form is problematic, but grinding it will help solve the problem. To start recycling, you need a foam crusher.
There are several ways to recycle or dispose of polystyrene foam:
Some may ask: why do I need crushed foam? It can be used not only for transportation, but also as a thermal insulation material. Let's look at where else it will come in handy.
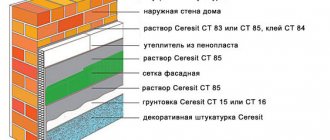
Why is it necessary to insulate houses made of gas silicate blocks?
External insulation is always better than internal insulation, since the dew point moves not into the wall, but into the insulation layer.
Before insulating gas silicate blocks, which are cellular concrete, you need to familiarize yourself with their characteristics. In the construction market, gas silicate has gained great popularity due to its high performance properties. This material is durable, environmentally friendly, soundproofing and economical. Savings are ensured by heat retention. A building made of cellular concrete reduces heating costs by up to 40%.
But it is worth considering such a disadvantage as the ability to transmit moisture. Gas silicate perfectly absorbs liquid due to its porous structure and masonry joints, so the wall should be protected. The solution to this problem is to insulate the gas silicate from the outside.
Conclusions on the production of polystyrene foam
- The technology is quite simple, but requires mandatory compliance with all prescribed norms and rules.
- Material (which will look like high-quality material) can be obtained even with significant deviations from the production rules. And “handicraft” companies (bad people) take advantage of this.
Therefore: buy only products from reliable, trusted manufacturers (who monitor quality)
. Check that sellers have the appropriate quality certificates.
Now you know how polystyrene foam is made, you know the main features of manufacturing technology and which material should be preferred. Good luck!