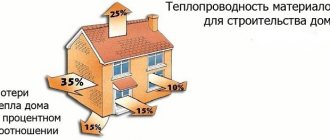
Everyone talks about it, but no one has seen it. They understand that it is needed, but they don’t know where to get it. They understand that they need to lower it, but they don’t know how. After all, we are talking about the ability of insulation to prevent the transfer of thermal energy through the area it occupies, or, more simply, about its low thermal conductivity. The thermal conductivity of polystyrene foam is the main characteristic that determines the procedure for its use in insulating buildings and structures.
Lifetime
Most manufacturers indicate a service life of 20-30 years. This is the warranty time during which the useful properties of the material are within acceptable limits. Recent studies by European scientists have shown surprising and encouraging results. When demolishing houses built 40-50 years ago using polyurethane foam, scientists found that its properties remained virtually unchanged. The structure and texture remained the same as originally. Further laboratory studies only confirmed the durability of this material.
Environmental friendliness
An important parameter that modern builders are paying more and more attention to. During the production process, polyurethane foam goes from liquid to solid in 30 seconds
After this, harmful fumes from its surface stop. If it is heated to 450 Cº, carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide will begin to be released. However, the same thing can be observed when wood is heated. Polyurethane foam does not emit compounds harmful to the human body
Strength
With a low density (0.015-0.05 g/cm3), polystyrene foam has high bending and compressive strength. Due to this, it is used in the construction of roads and runways.
Dimensional stability
In a building structure, expanded polystyrene does not shrink, does not dry out, does not move, and does not change configuration.
Durability
Long service life is ensured by proper operation. According to research, no irreversible changes occur in polystyrene foam within the range from -1800C to +800C. With prolonged exposure to higher temperatures, the material is destroyed, but within a few minutes polystyrene foam can withstand temperatures of +950C. This allows the material to be used in cases where short contact with hot bitumen is required. Recommended operating temperature - from -200 to +85°
Facade insulation
The service life of expanded polystyrene is also extended by the fact that the material is not susceptible to rotting. Manufacturers indicate the service life range of the material from 15 to 60 years.
Ease of use
The low weight of the material makes it easier to transport and install, and practically does not create additional loads on supporting structures and foundations, which opens up wide possibilities for use in the reconstruction of old buildings.
Conventional tools can be used for cutting. The use of special protective equipment is not required during operation. Work can be carried out at any time of the year.
What does thermal conductivity depend on?
The ability of polystyrene foam boards to retain heat depends mainly on two factors: density and thickness. The first indicator is determined by the number and size of air chambers that make up the structure of the material. The denser the slab, the greater the thermal conductivity coefficient it will have.
Density dependence
In the table below you can see exactly how the thermal conductivity of expanded polystyrene depends on its density.
| Density (kg/m3) | Thermal conductivity (W/mK) |
| 10 | 0.044 |
| 15 | 0.038 |
| 20 | 0.035 |
| 25 | 0.034 |
| 30 | 0.033 |
| 35 | 0.032 |
The background information presented above, however, most likely, can only be useful to home owners who have used polystyrene foam to insulate walls, floors or ceilings for quite some time. The fact is that when producing modern grades of this material, manufacturers use special graphite additives, as a result of which the dependence of thermal conductivity on the density of the plates is reduced to almost nothing. You can verify this by looking at the indicators in the table:
| Brand | Thermal conductivity (W/mK) |
| EPS 50 | 0.031-0.032 |
| EPS 70 | 0.033-0.032 |
| EPS 80 | 0.031 |
| EPS 100 | 0.03-0.033 |
| EPS 120 | 0.031 |
| EPS 150 | 0.03-0.031 |
| EPS 200 | 0.031 |
Dependence on thickness
Of course, the thicker the material, the better it retains heat. For modern expanded polystyrene, the thickness can range from 10-200 mm. According to this indicator, it is usually classified into three large groups:
- Plates up to 30 mm. This thin material is usually used to insulate partitions and interior walls of buildings. Its thermal conductivity coefficient does not exceed 0.035 W/mK.
- Material up to 100 mm thick. Expanded polystyrene of this group can be used for cladding both external and internal walls. Such stoves retain heat very well and are successfully used even in regions of the country with a harsh climate. For example, a material 50 mm thick has a thermal conductivity of 0.031-0.032 W/Mk.
- Expanded polystyrene with a thickness of more than 100 mm. Such dimensional slabs are most often used for the manufacture of formwork when pouring foundations in the Far North. Their thermal conductivity does not exceed 0.031 W/mK.
Calculation of the required material thickness
It is quite difficult to accurately calculate the thickness of polystyrene foam needed to insulate a house. The fact is that when performing this operation, a lot of different factors should be taken into account. For example, such as the thermal conductivity of the material chosen for the construction of insulated structures and its variety, the climate of the area, the type of cladding, etc. However, it is still possible to approximately calculate the required thickness of the slabs. To do this you will need the following reference data:
- an indicator of the required thermal resistance of enclosing structures for a given specific region;
- thermal conductivity coefficient of the selected brand of insulation.
Actually, the calculation itself is carried out according to the formula R=p/k, where p is the thickness of the foam, R is the thermal resistance index, k is the thermal conductivity coefficient. For example, for the Urals the R indicator is 3.3 m2•°C/W. Let’s say that a material of the EPS 70 brand with a thermal conductivity coefficient of 0.033 W/mK is selected for wall insulation. In this case, the calculation will look like this:
That is, the thickness of the insulation for external enclosing structures in the Urals should be at least 100 mm. Typically, home owners in cold regions sheathe walls, ceilings and floors with two layers of 50 mm polystyrene foam. In this case, the slabs of the upper layer are positioned so that they overlap the seams of the lower one. This way you can get the most effective insulation.
Thermal conductivity coefficient of materials.
The table below shows the values of the thermal conductivity coefficient for some materials used in construction.
| Material | Coeff. warm W/(m2*K) |
| Alabaster slabs | 0,470 |
| Aluminum | 230,0 |
| Asbestos (slate) | 0,350 |
| Fibrous asbestos | 0,150 |
| Asbestos cement | 1,760 |
| Asbestos cement slabs | 0,350 |
| Asphalt | 0,720 |
| Asphalt in floors | 0,800 |
| Bakelite | 0,230 |
| Concrete on crushed stone | 1,300 |
| Concrete on sand | 0,700 |
| Porous concrete | 1,400 |
| Solid concrete | 1,750 |
| Thermal insulating concrete | 0,180 |
| Bitumen | 0,470 |
| Paper | 0,140 |
| Light mineral wool | 0,045 |
| Heavy mineral wool | 0,055 |
| Cotton wool | 0,055 |
| Vermiculite sheets | 0,100 |
| Woolen felt | 0,045 |
| Construction gypsum | 0,350 |
| Alumina | 2,330 |
| Gravel (filler) | 0,930 |
| Granite, basalt | 3,500 |
| Soil 10% water | 1,750 |
| Soil 20% water | 2,100 |
| Sandy soil | 1,160 |
| The soil is dry | 0,400 |
| Compacted soil | 1,050 |
| Tar | 0,300 |
| Wood - boards | 0,150 |
| Wood - plywood | 0,150 |
| Hardwood | 0,200 |
| Chipboard | 0,200 |
| Duralumin | 160,0 |
| Reinforced concrete | 1,700 |
| Wood ash | 0,150 |
| Limestone | 1,700 |
| Lime-sand mortar | 0,870 |
| Iporka (foamed resin) | 0,038 |
| Stone | 1,400 |
| Multilayer construction cardboard | 0,130 |
| Foamed rubber | 0,030 |
| Natural rubber | 0,042 |
| Fluorinated rubber | 0,055 |
| Expanded clay concrete | 0,200 |
| Silica brick | 0,150 |
| Hollow brick | 0,440 |
| Silicate brick | 0,810 |
| Solid brick | 0,670 |
| Slag brick | 0,580 |
| Siliceous slabs | 0,070 |
| Brass | 110,0 |
| Ice 0°C | 2,210 |
| Ice -20°С | 2,440 |
| Linden, birch, maple, oak (15% humidity) | 0,150 |
| Copper | 380,0 |
| Mipora | 0,085 |
| Sawdust - backfill | 0,095 |
| Dry sawdust | 0,065 |
| PVC | 0,190 |
| Foam concrete | 0,300 |
| Polystyrene foam PS-1 | 0,037 |
| Polyfoam PS-4 | 0,040 |
| Polystyrene foam PVC-1 | 0,050 |
| Foam resopen FRP | 0,045 |
| Expanded polystyrene PS-B | 0,040 |
| Expanded polystyrene PS-BS | 0,040 |
| Polyurethane foam sheets | 0,035 |
| Polyurethane foam panels | 0,025 |
| Lightweight foam glass | 0,060 |
| Heavy foam glass | 0,080 |
| Glassine | 0,170 |
| Perlite | 0,050 |
| Perlite-cement slabs | 0,080 |
| Sand 0% moisture | 0,330 |
| Sand 10% moisture | 0,970 |
| Sand 20% humidity | 1,330 |
| Burnt sandstone | 1,500 |
| Facing tiles | 1,050 |
| Thermal insulation tile PMTB-2 | 0,036 |
| Polystyrene | 0,082 |
| Foam rubber | 0,040 |
| Portland cement mortar | 0,470 |
| Cork board | 0,043 |
| Cork sheets are lightweight | 0,035 |
| Cork sheets are heavy | 0,050 |
| Rubber | 0,150 |
| Ruberoid | 0,170 |
| Slate | 2,100 |
| Snow | 1,500 |
| Scots pine, spruce, fir (450…550 kg/cub.m, 15% humidity) | 0,150 |
| Resinous pine (600…750 kg/cub.m, 15% humidity) | 0,230 |
| Steel | 52,0 |
| Glass | 1,150 |
| Glass wool | 0,050 |
| Fiberglass | 0,036 |
| Fiberglass | 0,300 |
| Wood shavings - stuffing | 0,120 |
| Teflon | 0,250 |
| Paper roofing felt | 0,230 |
| Cement boards | 1,920 |
| Cement-sand mortar | 1,200 |
| Cast iron | 56,0 |
| Granulated slag | 0,150 |
| Boiler slag | 0,290 |
| Cinder concrete | 0,600 |
| Dry plaster | 0,210 |
| Cement plaster | 0,900 |
| Ebonite | 0,160 |
How to calculate wall thickness
In order for the house to be warm in winter and cool in summer, it is necessary that the enclosing structures (walls, floor, ceiling/roof) must have a certain thermal resistance. This value is different for each region. It depends on the average temperatures and humidity in a particular area.

Thermal resistance of enclosing structures for regions of Russia
In order for heating bills not to be too high, it is necessary to select building materials and their thickness so that their total thermal resistance is not less than that indicated in the table.
Calculation of wall thickness, insulation thickness, finishing layers
Modern construction is characterized by a situation where the wall has several layers. In addition to the supporting structure, there is insulation and finishing materials. Each layer has its own thickness. How to determine the thickness of insulation? The calculation is simple. Based on the formula:
Formula for calculating thermal resistance
R—thermal resistance;
p—layer thickness in meters;
k is the thermal conductivity coefficient.
First you need to decide on the materials that you will use during construction. Moreover, you need to know exactly what type of wall material, insulation, finishing, etc. will be. After all, each of them makes its contribution to thermal insulation, and the thermal conductivity of building materials is taken into account in the calculation.
First, the thermal resistance of the structural material (from which the wall, ceiling, etc. will be built) is calculated, then the thickness of the selected insulation is selected based on the “residual” principle. You can also take into account the thermal insulation characteristics of finishing materials, but usually they are a plus to the main ones. This is how a certain reserve is laid down “just in case.” This reserve allows you to save on heating, which subsequently has a positive effect on the budget.
We advise you to study - Vapor barrier - which side to lay it correctly towards the insulation and other features of the use of membranes
An example of calculating the thickness of insulation
Let's look at it with an example. We are going to build a brick wall - one and a half bricks long, and we will insulate it with mineral wool. According to the table, the thermal resistance of walls for the region should be at least 3.5. The calculation for this situation is given below.
- First, let's calculate the thermal resistance of a brick wall. One and a half bricks is 38 cm or 0.38 meters, the thermal conductivity coefficient of brickwork is 0.56. We calculate using the above formula: 0.38/0.56 = 0.68. A wall of 1.5 bricks has this thermal resistance.
- We subtract this value from the total thermal resistance for the region: 3.5-0.68 = 2.82. This value must be “added” with thermal insulation and finishing materials.
- We calculate the thickness of mineral wool. Its thermal conductivity coefficient is 0.045. The thickness of the layer will be: 2.82 * 0.045 = 0.1269 m or 12.7 cm. That is, to ensure the required level of insulation, the thickness of the mineral wool layer must be at least 13 cm.
If the budget is limited, you can take 10 cm of mineral wool, and the missing amount will be covered with finishing materials. They will be inside and outside. But, if you want your heating bills to be minimal, it is better to use the finishing as a “plus” to the calculated value. This is your reserve during the lowest temperatures, since thermal resistance standards for enclosing structures are calculated based on the average temperature over several years, and winters can be abnormally cold
Therefore, the thermal conductivity of building materials used for finishing is simply not taken into account
What is the thermal conductivity of polystyrene foam Properties and characteristics
Thermal conductivity is a value indicating the amount of heat (energy) passing through 1 m of any body per hour at a certain temperature difference on one side and the other. It is measured and calculated for several initial operating conditions:
- At 25±5 °C - this is a standard indicator enshrined in GOSTs and SNiP.
- “A” – this means dry and normal humidity conditions in the premises.
- “B” – all other conditions are included in this category.
The actual thermal conductivity of polystyrene foam granules pressed into a lightweight slab is not as important in itself as in conjunction with the thickness of the insulation. After all, the main goal is to achieve an optimal level of resistance of all layers of the wall in accordance with the requirements for a particular region. To obtain the initial numbers, it will be enough to use the simplest formula: R = p÷k.
- Heat transfer resistance R can be found in special tables of SNiP 23-02-2003, for example, for Moscow they take 3.16 m ° C / W. And if the main wall, according to its characteristics, does not reach this value, it is the insulation (mineral wool or the same polystyrene foam) that should cover the difference.
- The p index indicates the required thickness of the insulating layer, expressed in meters.
- Coefficient k is precisely what gives an idea of the conductivity of bodies, which we focus on when choosing.
The thermal conductivity of the material itself is checked by heating one side of the sheet and measuring the amount of energy transferred by conduction to the opposite surface per unit time.
What you need to know about the thermal conductivity of polystyrene foam
The thermal conductivity of polystyrene foam is quite low, because the air that is at the base of the material also has such characteristics. Therefore, the described insulation parameter varies from 0.037 to 0.043 W/mK; as for air, this characteristic is 0.027 W/mK.
Expanded polystyrene is manufactured in accordance with GOST 15588-86 and is characterized by excellent energy saving, increased service life, and can reduce heating costs and protect against freezing. Such properties are preserved even when exposed to low temperatures and high humidity, so expanded polystyrene can be used in warehouse conditions, as well as in refrigeration equipment structures.
The thermal conductivity of polystyrene foam is low, so this material can be used not only for interior but also for exterior decoration. However, this characteristic will vary depending on the density. The higher it is, the higher the styrene content, the worse the polystyrene foam will retain heat. For example, if we are talking about extruded polystyrene foam, then its thermal conductivity will be 0.028 W/mK, because styrene granules in this case are in the structure of a single sheet, and there are no gaps between them.

Low thermal conductivity basis
Polystyrene foam (expanded polystyrene foam) owes all its positive and negative properties to styrene and a special production technology.
First, styrene is saturated with gas or air, turning it into hollow granules. Then, under the influence of hot steam, the volume of the granules increases multiple times, followed by sintering in the presence of a binder composition. Thus, the resulting sheet consists of many spheres of regular shape filled with gas.

The styrene walls are thin but very durable. Even with considerable effort, it is not so easy to destroy the shell. The gas contained inside remains motionless under any operating conditions, providing high thermal insulation of the protected volume.
The filling of the insulation volume with gases depends on its density. Varies from 93 to 98%. The higher the percentage, the lower the density, the lighter the material, the higher the thermal conductivity, and usually the higher the quality of insulation and other important characteristics.
Advantages and disadvantages of the material
Polystyrene insulation has the following advantages:
- does not create additional load on the foundation of the building and supporting structures;
- durability - the service life of the material is at least 40 years, while it does not lose its characteristics;
- ease of transportation and installation;
- good adhesion and interaction with adhesives;
- resistance to temperature changes and exposure to most aggressive environments.
Also, most modern types of polystyrene foam insulation are treated with special compounds that protect the material from rodents and pests.

At the same time, polystyrene foam also has disadvantages.
Low vapor permeability. To avoid the accumulation of steam indoors when using polystyrene foam as insulation, it is necessary to equip it with good supply and exhaust ventilation.
Not resistant to UV radiation. For this reason, the foam must be hidden from exposure to sunlight.
Loss of performance qualities when interacting with solvents, which does not allow applying paints and varnishes to EPS.
Low resistance to external mechanical influences
Polystyrene foam is a fairly fragile material, so when working with it, care must be taken so that it does not break or crack.

It is not the material itself that is toxic, but the fumes of stylol, which decrease over time and do not exceed the maximum permissible and safe for humans. Therefore, experts advise using PPP, which has been “staying” in the warehouse for quite a long time. The flammability of expanded polystyrene depends on the production technology. For example, polymer granules filled with carbon dioxide have the ability to self-extinguish.

Difficulty of choice
Some might argue that this is an unfair comparison. It is impossible to compare materials that are so different in their origin and internal composition. Fine. Then let’s compare modern insulation materials: mineral (basalt), foamed and extruded polystyrene foam, polyurethane foam.
The comparison is clearly not in favor of slabs and mats made of fibrous materials. Their heat capacity is almost 1.5 times greater than that of foam plastic. This immediately reduces their consumer value and puts them at the bottom level in this indicator.
It is quite difficult to compare the thermal conductivity of extruded polystyrene foam and polystyrene foam. Physically and mathematically the indicators are very close. Recognizing the leadership of extruded polystyrene foam, which has a lower thermal conductivity coefficient, foamed polystyrene meets it with its advantage - price. The difference of 4 hundredths of a unit of the specified coefficient is covered by foamed polystyrene at a price that is 4 times lower than that of famous competitors.
Even when comparing the thermal conductivity of polyurethane foam and polystyrene foam, we can say that foamed polystyrene foam “takes impact well.” The thermal conductivity coefficient of polyurethane foam is only 30% less than that of foamed polystyrene. And the price... Do not forget that its installation requires certain qualifications and equipment. Which will require additional costs. You can insulate your home with polystyrene foam yourself.

So there is a lot to think about before making a choice of insulation.
Main characteristics of insulation
Let us first provide the characteristics of the most popular thermal insulation materials, which you should first pay attention to when choosing. Comparison of insulation by thermal conductivity should be made only on the basis of the purpose of the materials and room conditions (humidity, presence of open fire, etc.)
We have further arranged in order of importance the main characteristics of insulation.
Comparison of building materials
Thermal conductivity. The lower this indicator, the less thermal insulation layer is required, which means that insulation costs will also be reduced.
Moisture permeability. The lower permeability of the material to moisture vapor reduces the negative impact on the insulation during operation.
Fire safety. Thermal insulation should not burn or emit toxic gases, especially when insulating a boiler room or chimney.
Durability. The longer the service life, the cheaper it will cost you during operation, since it will not require frequent replacement.
Environmentally friendly. The material must be safe for humans and the environment.
Issues of vapor barrier and waterproofing
An important requirement during the construction and improvement of a house is the correct implementation of all work to ensure ventilation and waterproofing, since it is the incorrect installation of these components that significantly reduces the performance of the structure.
When insulating walls with polystyrene, waterproofing is not needed. It should be taken into account that if there is a high passage of groundwater under the building, it is necessary to waterproof the basement and foundation.
Since polystyrene foam does not allow air and water to pass through, there is no need to lay a vapor barrier layer when insulating walls from the outside.
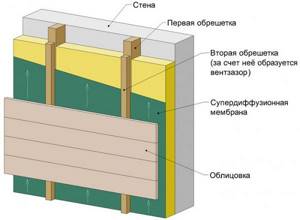
Wall insulation cake under siding
Scope of application of EPPS
Comparison of the required amount of insulation.
Another advantage of the material is its wide range of applications. Low thermal conductivity allows it to be used in road construction as insulating bases. Modern refrigeration units cannot do without the use of this material. In addition, it is actively used in the process of reconstructing heaving sections of highways.
The low thermal conductivity of the insulation allows it to be used in agriculture as a heat insulator on farms.
EPPS is widespread in the field of industrial and civil construction.
Among the new extensive areas of application of XPS, individual construction can be distinguished. A particularly promising area is the production of sandwich panels. This material is no less popular among individual developers. For example, when installing a roof, the slabs are laid over waterproofing, which additionally protects it from damage and temperature changes. And when carrying out reconstruction work, expanded polystyrene allows you to reduce costs. Moreover, it is permissible to carry out this kind of process when the existing heat-insulating layer has become unusable.
We advise you to study - Which foundation is better for a house made of timber
If it is intended to insulate a pitched roof, extruded polystyrene foam is laid on top of the rafters.
If it is necessary to insulate a wooden floor, heat insulation slabs must be laid between the rough and finishing layers, and fixation must be made between the joists. This allows for minimal heat loss through the floor. Sometimes it is necessary to insulate the floor of the first floor. The effectiveness of EPS in this case can be increased by laying the material in two layers, moving the sheets to overlap the seams. In this case, the EP slabs will be located between the waterproofing membrane and the screed. The material will guarantee not only excellent thermal protection, but also hydro- and vapor barrier, which will prevent the penetration of moisture from the underground.
EPS can be used in tandem with a heated floor system. This is possible due to the excellent strength characteristics of the plates. In this case, laying must be done on the interfloor ceiling, protecting it all with a dividing screed.
Due to its characteristics, EPS can be used when constructing the outer insulation layer of the foundation without the use of protection. The slabs will perform functions even in conditions that differ in groundwater pressure.
EPPS is a relatively new material, constantly being improved, which allows it to be actively used in construction.
Distinctive features of PPE insulation
Specifications
Thermal insulation made of foamed polyethylene is a product with a closed-porous structure, soft and elastic, having a shape appropriate for its purpose. They have a number of properties that characterize gas-filled polymers:
- Density from 20 to 80 kg/m3,
- Operating temperature range from -60 to +100 0C,
- Excellent moisture resistance, in which moisture absorption is no more than 2% of the volume, and almost absolute vapor tightness,
- High noise absorption even with a thickness greater than or equal to 5 mm,
- Resistant to most chemically active substances,
- No rotting or fungal damage,
- Very long service life, in some cases reaching more than 80 years,
- Non-toxic and environmentally safe.
But the most important characteristic of polyethylene foam materials is their very low thermal conductivity, due to which they can be used for thermal insulation purposes. As you know, air retains heat best, and this material has plenty of it. The heat transfer coefficient of polyethylene foam insulation is only 0.036 W/m2 * 0C (for comparison, the thermal conductivity of reinforced concrete is about 1.69, plasterboard - 0.15, wood - 0.09, mineral wool - 0.07 W/m2 * 0C).
INTERESTING! Thermal insulation made of foamed polyethylene with a layer thickness of 10 mm can replace a 150 mm thickness of brickwork.
Application area

Foamed polyethylene insulation is widely used in new and reconstructive construction of residential and industrial facilities, as well as in automotive and instrument making:
- To reduce heat transfer by convection and thermal radiation from walls, floors and roofs,
- As reflective insulation to increase the heat output of heating systems,
- To protect pipe systems and pipelines for various purposes,
- In the form of an insulating gasket for various cracks and openings,
- For insulating ventilation and air conditioning systems.
In addition, polyethylene foam is used as packaging material for transporting products that require thermal and mechanical protection.
Is polyethylene foam harmful?
Supporters of the use of natural materials in construction may talk about the harmfulness of chemically synthesized substances. Indeed, when heated above 120 0C, foamed polyethylene turns into a liquid mass, which can be toxic. But under standard living conditions it is absolutely harmless. Moreover, insulation materials made from polyethylene foam are superior to wood, iron and stone in most respects. Building structures using them are light, warm and low cost.
Factors influencing thermal conductivity
Thermal conductivity depends on the density and thickness of the insulation, so it is important to take it into account when purchasing. Density is the mass of one cubic meter of materials, which according to this criterion are classified as very light, light, medium and hard
Lightweight porous products are used to cover interior walls and load-bearing partitions, while dense ones are used for exterior work.
Modifications with lower density are lighter in weight, but have better thermal conductivity parameters. A comparison of insulation materials by density is presented in the table.
| Material | Density indicator, kg/m3 |
| Minvata | 50-200 |
| Extruded polystyrene foam | 33-150 |
| Polyurethane foam | 30-80 |
| Polyurethane mastic | 1400 |
| Ruberoid | 600 |
| Polyethylene | 1500 |
The thickness of the material also affects the degree of heat transfer. If it is excessive, the natural ventilation of the premises is disrupted. Small thickness causes cold bridges and condensation on the surface. As a result, the wall will become covered with mold and mildew. You can compare the thickness parameters of materials in the table.
| Material | Thickness, mm |
| Penoplex | 20 |
| Minvata | 38 |
| Cellular concrete | 270 |
| Brickwork | 370 |
Expanded polystyrene Penoplex, thickness: 30 mm
Clear filter
- Insulation materials Expanded polystyrene 175
- Foam plastic 47
- Wholesale 8503
- Discounts 117
- New items 16
Brand
- 2440
- TechnoNIKOL 1683
- Mosstroy-31 1480
- Technoplex 685
- Carbon Eco 378
- Extrol 305
- Carbon Prof 284
- KREDO 201
- Thermit 173
- Foam 160
- URSA 147
- Polyspen 91
- LLC PenoMaster 72
- Styrex 57
- Carbon Solid 54
- Teploizol 48
- RavaTHERM 42
- Stoplex 35
- Teploplast 31
- Fasadograd 31
- FORMAT 22
- Athlone 18
- Graphite 14
- Ravaterm 9
- Europlex 8
- Isoplex 8
- Drops 8
- Styropen 7
- Timplex 7
- Styrofoam 6
- Bateplex 6
- Plizeks 5
- ALASKA 5
- Polytherm 5
- Hitfom 5
Show all Brand Pressure type Condition Purpose Production method Thickness
- 507
- 50 mm 962
- 100 mm 471
- 20 mm 465
- 40 mm 393
- 80 mm 169
- 60 mm 95
- 120 mm 67
- 150 mm 67
- 250 mm 54
- 70 mm 54
- 180 mm 51
- 90 mm 50
- 130 mm 49
- 160 mm 49
- 200 mm 49
- 110 mm 48
- 140 mm 48
- 170 mm 48
- 190 mm 48
- 210 mm 45
- 220 mm 45
- 230 mm 45
- 240 mm 45
- 500 mm 43
- 600 mm 39
- 10 mm 35
- 400 mm 32
- 300 mm 29
- 1180mm 24
- 1000 mm 13
- 585 mm 10
- 5 mm 6
- 8 mm 6
- 0.05 mm 5
- 2 mm 5
Show all Country of origin Delivery Payment Availability
Expanded polystyrene Penoplex, thickness: 30 mm, buy products from reliable companies and suppliers at a favorable price. Submit your order or write a message.
By rating By price By alphabetical With photo List Gallery Products and services Companies
Demand
Goods and services in RUSSIA Search in Rostov-on-Don 175 goods and services from 106 suppliers
- from 5,250 rub./m3
- In stock
Wholesale / Retail
- 10.01.19
Decorative heat-insulating panels ZODIAC Material: Aluminum-galvanized sheet, aluminized paper, polyurethane foam Working surface size: 3.8 m * 0.38 m
Submit order Add to cart
- Industrial Holding AMK-Group 6 Online Chelyabinsk
- +7 show number
- Save supplier
- 33 reviews
- In stock
Wholesale
Available 20mm, 30mm, 40mm, 50mm, 100mm Mineral insulation OSB, DSP, fiberglass reinforcement, masonry mesh
Submit order Add to cart
- STROYKOMPLEKT 6 Online Kazan
- +7 show number
- Save supplier
- 4 reviews
- In stock
Wholesale / Retail
Penoplex is a modern material. This brand of thermal insulation boards is ideal for insulating country houses or city apartments (insulating walls, balconies, loggias).
Submit order Add to cart
- STROYTORG 2 Online Novosibirsk
- +7 show number
- Save supplier
- 2 reviews
- In stock
Wholesale / Retail
Wide range of high quality building materials. Prompt delivery using our own transport. Cargo handling. Consultation and assistance in choosing products. Call - we are always glad to see you!
Submit order Add to cart
- Chebykin A.N. 1 Online Rostov-on-Don
- +7 show number
- Save supplier
- 1 review
- In stock
Wholesale / Retail
This material is used in construction for thermal insulation on walls, ceilings, roofs and floors.
Submit order Add to cart
- Building materials database 5 Online Rostov-on-Don
- +7 show number
- Save supplier
- 9 reviews
- In stock
Wholesale / Retail
Suitable for insulating country houses (walls, floors, facade, roof, foundation, cellar, basement, bathhouse, sauna, swimming pool, gym) or city apartments (insulating walls, balconies, loggias). Does not absorb moisture. The warmest of all insulation materials.
Submit order Add to cart
- CONSTRUCTOR 1 Online Rostov-on-Don
- +7 show number
- Save supplier
- Add a review
- 1 more product from the supplier
- In stock
Wholesale
For use in private housing construction and renovation. Density / Size 32kg/m3 (1200x600x30). Quantity m3/m2 in 1 pack 50mm 12 pcs 0.2592m3 8.64m2
Submit order Add to cart
- CSK Southern Federal District 2 Online Rostov-on-Don
- +7 show number
- Save supplier
- Add a review
- In stock
Wholesale / Retail
Delivery of building materials seven days a week! Building materials (plasterboard, profiles, plaster, putty, tile adhesive, cement, expanded clay, crushed stone, brick, chipboard, chipboard, fibreboard, plywood, osb, primers, insulation, paint) wholesale and retail.
Submit order Add to cart
- Tikaradze D.R 3 Online Rostov-on-Don
- +7 show number
- Save supplier
- Add a review
- In stock
Wholesale / Retail
Thickness 30 mm. The material will create a hard, lightweight, moisture-resistant and continuous thermal insulation layer. Number of pieces per package: 14 pieces.
Submit order Add to cart
- Construction systems 7 Online Rostov-on-Don
- +7 show number
- Save supplier
- 2 reviews
- In stock
Wholesale / Retail
Size 600x1200x30 (0.2592 m3/8.64 m2). It is used for thermal insulation of roofs, walls, plinths, foundations and floors; they do not absorb moisture, therefore they are used for rooms with high levels of humidity. Service life more than 50 years.
Submit order Add to cart
- JOINT-SL 1 Online Rostov-on-Don
- +7 show number
- Save supplier
- 1 review
- 1 more product from the supplier
- In stock
Wholesale / Retail
ConTRAST is the official representative of the PENOPLEX plant! These are always wholesale prices! It's always fast delivery! This means always having the material in stock! Call and see for yourself!
Submit order Add to cart
- Trading House GC ConTRAST 5 Online Rostov-on-Don
- +7 show number
- Save supplier
- Add a review
- 7 more supplier products
- In stock
Wholesale / Retail
We sell building materials with delivery: hay sand - 30 rub./bag cement - from 240 rub./bag crushed stone - 60 rub./bag, plaster from 210 rub./m 30 kg dry building mixtures, glue, plaster, putty, plasterboard, profile, fasteners.
Submit order Add to cart
- StroyBaza-YUG 1 Online Rostov-on-Don
- +7 show number
- Save supplier
- Add a review
- In stock
Wholesale / Retail
The ConTRAST company, on dealer terms, sells PENOPLEX thermal insulation at wholesale prices of any thickness in any volume + components. Always available in our warehouse. Delivery throughout Krasnodar and the region! Same day pickup! Discounts! Call!
Submit order Add to cart
- Trading house ConTRAST 5 Online Krasnodar
- +7 show number
- Save supplier
- 1 review
- 1 more product from the supplier
- In stock
Wholesale / Retail
Use in industrial and civil construction.
Submit order Add to cart
- EKATERINODAR - STROY 1 Online Krasnodar
- +7 show number
- Save supplier
- 1 review
- 1 more product from the supplier
- In stock
Wholesale / Retail
Penoplex extrusion! All thicknesses are always available in stock: 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 100 mm! Professional consultation and estimate FREE! We will quickly deliver anywhere in the region! Various components for insulation in stock! Call and leave requests!
Submit order Add to cart
- YugRegionSnab Online Znamensky
- +7 show number
- Save supplier
- Add a review
- 3 more supplier products
- In stock
Wholesale / Retail
Material for insulation of walls, ceilings, facades, plinths, foundations, floors. It is light in weight and easy to install. Does not absorb moisture.
Submit order Add to cart
- YugStroyTechnology 4 Online Krasnodar
- +7 show number
- Save supplier
- Add a review
- 5 more supplier products
- In stock
Wholesale / Retail
Manufacturer: Penoplex, Russia. Material group according to flammability: G4 (highly flammable). Environmental safety of the material: Safe. Thermal conductivity class: Low. Packaging: Pack. Material type: G (flammable). Material delivery form: Plate.
Submit order Add to cart
- ALEA Online Krasnodar
- +7 show number
- Save supplier
- Add a review
- 5 more supplier products
- In stock
Wholesale / Retail
PENOPLEX insulation - ALL SIZES: 20 mm, 30 mm, 40 mm, 50 mm, 100 mm. Always AVAILABLE in stock in Krasnodar: adhesive foam for penoplex, fasteners, mesh. Fast delivery throughout the city and region. Competent consultation. CALL THE SALES DEPARTMENT offers you favorable conditions for cooperation. Direct deliveries from the factory, manufacturer's warranty, transit delivery, volume and retail discounts. Our specialists will offer you materials of different price categories.
Submit order Add to cart
- LLC Insulation Technologies 5 Online Krasnodar
- +7 show number
- Save supplier
- 7 reviews
- 19 more supplier products
- In stock
Wholesale / Retail
Flammability group G4, compressive strength of at least 0.20 MPa. Edge shape: 30, 50 mm - L, 20 mm - straight. In 1 sheet 0.0208
Submit order Add to cart
- Formula Roofing 1 Online Krasnodar
- +7 show number
- Save supplier
- Add a review
- 1 more product from the supplier
- In stock
Wholesale / Retail
Thickness 30 mm. The material will create a hard, lightweight, moisture-resistant and continuous thermal insulation layer. Number of pieces per package: 14 pieces.
Submit order Add to cart
- TS Building Systems 7 Online Krasnodar
- +7 show number
- Save supplier
- Add a review
- In stock
Wholesale / Retail
Extrusion material for inversion roofing, floors, foundations, basements. Technical characteristics of penoplex: 1200x600x50 (0.252 m3)
Submit order Add to cart
- COMPANY TEPLY HOUSE 7 Online Izhevsk
- +7 show number
- Save supplier
- 34 reviews
- In stock
Wholesale / Retail
Guarantee of the BEST price for extruded polystyrene foam! Brand: Penoplex Country of origin: Russia Length (mm): 1185 Width (mm): 585 Thickness (mm): 30 Quantity per package (pcs): 13 Area per package (m2): 9.012
Submit order Add to cart
- Basic element Online Chelyabinsk
- +7 show number
- Save supplier
- 3 reviews
- 1 more product from the supplier
- In stock
Wholesale / Retail
Packaging: 12 pcs; 8.32 sq.m.; 0.25 m3. The material can be used for thermal insulation of floors on the ground and foundations of buildings for various purposes.
Submit order Add to cart
- Production and construction association Kub Online Krasnoyarsk
- +7 show number
- Save supplier
- 1 review
- 1 more product from the supplier
- In stock
Wholesale / Retail
thermal insulation boards, which are ideal for insulating walls, balconies, loggias. The use of Penoplex thermal insulation boards for thermal insulation of various enclosing structures allows us to avoid “cold bridges”,
Submit order Add to cart
- Afina South 2 Online Simferopol
- +7 show number
- Save supplier
- 4 reviews
- In stock
Wholesale / Retail
Penoplexes are made from extruded polystyrene foam, used for thermal insulation of residential and commercial premises.
Order
- WhereMaterial Online Moscow
- +7 show number
- Save supplier
- Add a review
- In stock
Wholesale / Retail
Thickness 30mm, length 1200mm, width 600mm. There are 14 slabs in the package = 10.08 m2 (0.3024 m3).
Submit order Add to cart
- A5 5 Online Novosibirsk
- +7 show number
- Save supplier
- 15 reviews
- To order
Wholesale / Retail
Thickness 30 mm. The material is used for insulation of roofs, walls, plinths, foundations and floors of buildings.
send an order
- Progress 2 Online Omsk
- +7 show number
- Save supplier
- Add a review
- 3 more supplier products
- In stock
Wholesale / Retail
Sheet, universal. Our company is an official dealer of many factories. Lowest prices in the region. Your own car park. Your own cars. Your own sales points.
Submit order Add to cart
- MegaproM 3 Online Omsk
- +7 show number
- Save supplier
- Add a review
- 1 more product from the supplier
- In stock
Wholesale / Retail
Density, kg/m3: 28.0-33.0; Compressive strength MPa: 0.25 Wide range of roofing and facade materials, mastic, roofing felt, glass insulation, polyurethane foam and sealants.
Submit order Add to cart
- Cybermarket 6 Online Perm
- +7 show number
- Save supplier
- 1 review
- 2 more supplier products
Place a request
Didn't find the product you're looking for?
Thinner, warmer
In order to visualize this physical quantity, let’s compare the thermal conductivity of polystyrene foam with other building materials. Imagine that you are standing and looking from the end at sections of walls made of different materials. First, a concrete wall 3.2 m thick floats before your eyes, then brickwork of 5 bricks (1.25 m), then a relatively thin wooden partition the width of an adult’s forearm (0.40 m). And somewhere at the very end, an inconspicuous sheet of foam plastic 0.1 m thick. What unites all these materials of immense thickness? Only one.
Using its low thermal conductivity, you can significantly reduce the consumption of building materials that are quite expensive to purchase and install. A house built with 2.5 bricks is as reliable as a house with walls 5 bricks thick. Only in the first case, heating costs are higher. Do you want a warmer home? There is no need to build another wall like this. It is enough to insulate the wall with a 50 mm slab. Feel the difference. 2.5 bricks around the perimeter of the house and a sheet of foam plastic 50 mm thick. We save time, money, effort.
Technology of thermal insulation of external walls with polystyrene foam
There are several ways to install polystyrene foam on the facade:
- On glue.
- Mechanical fastening using dowels.
- Combining method. Both glue and fasteners are used. It's more reliable.
Everyone can choose the appropriate option for themselves, but professionals recommend using the latter method. In order for the entire structure to remain securely adhere to this plan.

Preparatory work
It all starts with preparing the foundation. This stage is as important as fixing the insulation or finishing it. Here they do the following:
- If the building was previously covered with finishing, it is removed.
- Remove fasteners and hanging structures.
- The wall is cleaned of dirt, grease stains, solution build-up, and dust.
- Prime the surface. For porous materials, such as foam or gas block, choose a deep penetration primer and apply it in 2 layers. It is also desirable that the composition be antibacterial. Then the main structure will be protected from harmful microorganisms. The soil allows you to increase the adhesion of the material from which the load-bearing walls are made, and therefore securely fix the insulation to the base.
- Next, install the starting profile at the border of the base and the beginning of the wall. It will serve as a support for the foam. The profile is fixed immediately along the perimeter of the entire building. Be sure to check the horizontal position using a building level.
- Now we begin to prepare the adhesive solution. The glue should only be suitable for polystyrene foam; other brands will not work. Cooking instructions are on the package. Be sure to adhere to the proportions, otherwise the material will not stick to the wall.

Bonding boards
The finished solution must stand for some time so that all components react with each other. Next, proceed to gluing the insulation boards:
- A thin layer of the solution is applied around the perimeter of the foam board. In these places, the mixture must be rubbed into the material - this increases adhesion.
- Make 2-3 small blots in the center.
- The slabs are installed in the starting profile from the lower left corner of the house.
- The foam is pressed tightly against the wall so that the solution is evenly distributed under the sheet. If excess adhesive solution is visible, remove it with a spatula. The evenness of the installation is checked using a building level.
- Glue is also applied to the next plate and pressed tightly against both the wall and the previous sheet.
- In the second row, the vertical joints should not coincide. To do this, the foam is shifted 15–20 cm to one side.
- After all the walls are completely covered with insulation and the adhesive solution has set, begin mechanical fixation. Make holes using a hammer drill and install disc-shaped dowels.

Installation of the reinforcing layer
When the glue is completely dry, begin reinforcing the surface of the foam. For this use:
- An adhesive solution, perhaps the same one that was used to fix the slabs to the wall.
- Fiberglass mesh.

There is also a special technique for gluing the mesh:
- First of all, apply a thin layer of glue using a spatula.
- Pieces of mesh 15–20 cm wide are glued to the corners. The mesh element is laid in such a way that the two walls have identical segments. Using a clean spatula, press the fiber into the adhesive solution.
- If it doesn’t work out, add glue on top and smooth it out.
- Next, we begin to reinforce the wall.
- A mesh is placed on the corner element with an overlap of 10 cm. It is also pressed into the solution with a spatula.
- When this layer has dried, apply the finishing layer to completely hide the mesh under the glue.
Applying a decorative layer
After applying the last layer of glue, wait until it dries completely. Next, it is customary to cover the foam insulation with plaster. This may be a decorative option with an original pattern or a regular, even layer painted in a suitable color.
After all the work is completed, the house will be warm and updated at the same time. And this is a solution to two problems at once. Of course, whether to choose polystyrene foam for insulating a house or not is everyone’s business. The nuances of choice and technical characteristics listed above are quite enough to make the right choice.
Classification of expanded polystyrene
Regular foam
Thermal insulation material obtained by foaming polystyrene. As mentioned above, its volume is 98% air, which is sealed into granules. This speaks not only of its excellent thermal insulation qualities, but also of its sound insulation properties.
The main advantage of the material is the lack of ability to absorb moisture. In addition, it does not rot or biodegrade. Durable material, light weight and easy to use. It can be glued to any building material.
Expanded polystyrene is easy to burn, but it contains a substance called a fire retardant. This is what gives the foam the ability to self-extinguish. In addition, expanded polystyrene cannot be used to insulate facades. This is due to its low vapor permeability. And in order to carry out work with foam plastic under the roof, you should carefully consider the ventilation system.
Use depending on the brand of material
- PSB-S 15. The marking of polystyrene foam indicates that it can be used to insulate structures that are not subject to mechanical stress. For example, insulation of the roof, the space between the slings and the ceiling.
- PSB-S 25 and 25F. Common markings for polystyrene foam. It says that any surface can be insulated. Walls, facades, ceilings or flooring, roofing.
- PSB-S 35 and 50. This material can be used to insulate objects that are under constant high load.
Extruded polystyrene foam
Thermal insulation material, which has high effect and quality. It is most often used to insulate building envelopes. And the thermal conductivity coefficient ranges from 0.027 to 0.033 W/m K.
The structure of the material is cellular. And the complete closure of each cell provides absolute protection against water penetration. Therefore, this material is recommended for use where humidity is high or where the material can come into contact with water. This is insulation of the basement or foundation of a cottage. Even in conditions of insufficient waterproofing, extruded polystyrene foam will retain its thermal insulation qualities.
In addition, this material is highly resistant to various deformations. This feature allows it to be used as insulation for surfaces bearing heavy loads. For example, facades can be insulated with extruded polystyrene foam. Especially if the cladding material is very heavy.
As for the temperature. Expanded polystyrene is able to withstand sudden changes, from -120 to +175 degrees. At the same time, its structure remains intact and unharmed.
The disadvantages of this material are flammability, but, like polystyrene foam, its constituent elements can cause it to extinguish. Contact of polystyrene foam with complex carbohydrates can lead to destruction.
Classes and grades of foam plastic
Foam classes
There are only two classes of foam: pressed and non-pressed. From the names it is clear that these materials have different production methods. The first is made using pressing equipment, the second - by sintering at high temperatures. But this production line also uses pressing equipment. However, the classification is what it is.

Expanded polystyrene suspension pressless
Which class the foam belongs to can be determined visually. Bespressovy is a complex of fairly firmly glued round and oval granules. The structure of this material is porous, the strength depends on the density.

Pressed polystyrene foam
Pressed sheet has the appearance of a fairly smooth sheet, the density of which varies and depends on the brand of the product. This material has excellent technical and performance characteristics.
Foam brands
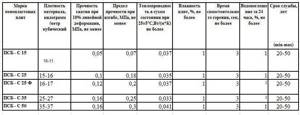
Foam brands
Polystyrene foam produced using the non-press method is designated by the abbreviation PSB. Press - PS. The product name may also contain other letters, each of which indicates a feature of this product.
- A – the canvas has the correct geometric shape of a parallelepiped and a smooth edge;
- B – the edge of the product has an L-shaped cut;
- P – cutting of the blades is done with a hot string;
- F - façade or made using special forms;
- C – self-extinguishing;
- N – the product is suitable for external use.
The numbers in the name of the PPP indicate its density.
Brands of pressless foam
PSB-15
The most inexpensive product with a high degree of fragility. Used as a thermal insulation and packaging material, it crumbles easily and has low hygroscopicity. Traditionally used for insulating balconies and loggias, country houses, containers and outbuildings.

Foam plastic PSB S-15
PSB-25

Foam plastic of different brands
This brand of foam plastic is often supplemented with the letter “F”, so the material is recommended for insulating facades. Due to its higher density than PSB-15, it is used for the manufacture of landscape and interior decorative elements.
PSB-35

Expanded polystyrene PSB-S-35
A universal material with a wide range of applications. It is used for insulation of utilities, heat and gas mains, production equipment, thermal insulation of roofs and attics. Involved in the production of multilayer panels (including reinforced concrete) as a thermal insulation gasket.
PSB-50
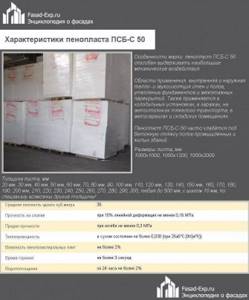
Characteristics of polystyrene foam PSB-S 50
This material has the highest density among non-press foams. Demanded as a heat and sound insulator for objects of any purpose. It is able to provide high-quality protection from the cold, therefore it is used in the construction of underground communications, garages and parking lots, and in road construction.
Characteristics of brands of pressless foam.
| Index | PSB-15 | PSB-25 | PSB-35 | PSB-50 |
| Compressive strength at 10% strain (MPa) | 0,04 | 0,08 | 0,14 | 0,18 |
| Density (kg/m3) | 15,0 | 15,1-25,0 | 25,1-35,0 | 35,1-50,0 |
| Thermal conductivity (W/mK) | 0,1 | 0,43 | 0,38 | 0,38 |
| Water absorption during the day in% of the total volume | 4 | 3 | 2 | 2 |
Technical characteristics of extruded polystyrene foam
The performance and mechanical characteristics of this thermal insulation material require special consideration.
Thermal conductivity
, regardless of brand, lies in the range from 0.03 to 0.04 W/(m 0 K). Such indicators make it possible to use expanded polystyrene foam for insulating any building elements, as well as highways, runways, etc.
We advise you to study - How to choose a chainsaw - detailed instructions
Density of slabs
, depending on the modification of the material, can be from 20 to 50 kg/m 3 ;
Moisture resistance. Thanks to the closed porous structure and chemical composition, the material does not deteriorate under the influence of dampness, condensation and even direct contact with water
The only weak point is the end surfaces, the waterproofing of which should be given special attention
Health safety
allows the use of extruded polystyrene foam even in medical and children's institutions. The plates do not emit harmful fumes even at high temperatures. In addition, the thermal insulation layer is usually covered with a layer of finishing materials (plaster, putty, drywall, etc.).
High strength parameters
. The permissible stress, depending on the modification, ranges from 18 to 20 t/m2.
Other characteristics of extruded polystyrene foam include:
- Frost resistance.
The material retains its thermal insulation properties even at -70 0 C; - Low vapor permeability
, from 0.007 to 0.008 mg/(m h Pa); - The antiseptic properties
of the material practically eliminate the occurrence of fungal colonies; - Long service life
. Regardless of operating conditions, expanded polystyrene foam is guaranteed to last at least 45 years.

Such indicators will certainly arouse increased consumer interest. In addition, it is also important that installation can be done with your own hands, and the cost of the material is relatively low.
Thermal conductivity and density of penoplex, comparison with polystyrene foam PSB
A comparative table of the values of the thermal conductivity coefficient, density of penoplex and polystyrene polystyrene PSB of various brands in a dry state at a temperature of 20...30°C is presented. Their operating temperature range is also indicated.
Penoplex thermal insulation, in contrast to non-pressed polystyrene foam PSB, is produced at elevated temperatures and pressures with the addition of a foaming agent and extruded through an extruder. This production technology provides penoplex with a closed microporous structure.
Penoplex, compared to polystyrene foam PSB, has a lower thermal conductivity coefficient λ , which is 0.03...0.036 W/(m deg) . The thermal conductivity of penoplex is approximately 30% lower than that of such traditional insulation as mineral wool. It should be noted that the thermal conductivity coefficient of polystyrene foam PSB, depending on the brand, is in the range of 0.037...0.043 W/(m deg).
The density of penoplex ρ according to the manufacturer is in the range from 22 to 47 kg/m 3 depending on the brand. The density of PSB expanded polystyrene is lower - the density of the lightest brands PSB-15 and PSB-25 can range from 6 to 25 kg/m 3, respectively.
The maximum temperature for using Penoplex expanded polystyrene is 75°C. For PSB foam it is slightly higher and can reach 80°C. When heated above 75°C, penoplex does not melt, but its strength characteristics deteriorate. The manufacturer does not report how much the thermal conductivity coefficient of this thermal insulation material increases under such conditions.
Positive and negative properties of polyurethane foam
For a more convenient understanding of the essence, properties and scope of the material, you need to have an idea not only of the physical and chemical properties, but also know its positive and negative sides.
Positive
- Polyurethane foam has good adhesion. It adheres to wood, metal, and concrete surfaces without any problems. It does not require additional fasteners. Due to its elastic structure and method of application, polyurethane foam fits well on uneven substrates. Before applying it, the surface does not require additional treatment with primer or paint.
- PPU has a low cost. It is produced directly on the construction site by mixing two components. There are no costs for additional transportation and manufacturing.
- Polyurethane foam is a lightweight material that does not load building structures.
- In addition to heat and sound insulation, polyurethane foam strengthens load-bearing walls, making the structure stronger and more durable.
- It is practically unaffected by extremely low and high temperatures. PU foam is not destroyed by cyclic freezing and thawing.
- The polyurethane foam coating has a monolithic structure. There are no gaps for the appearance of cold bridges. The wind doesn't blow through it.
Negative
- Polyurethane foam quickly degrades under the influence of ultraviolet rays. Therefore, it does not remain open, but requires protection. It can be covered with a layer of paint or plastered. The use of various cladding panels is also suitable.
- Polyurethane foam is a non-flammable material. Still, it is not recommended to use it in places of possible contact with open fire. If this is technically impossible, then the polyurethane foam is covered with fire-resistant plasterboard.
Polyethylene foam insulation

The invention of polyethylene foam insulation (or polyethylene foam, PPE) raised the solution to the problem of thermal insulation to a completely new level. This lightweight and plastic material, which has a very high thermal protection coefficient and a host of other advantages, has pushed into the background a number of other insulating materials that require large physical and material investments. It can be easily used both at home and for industrial purposes.
Fire resistance
Being a combustible material, polystyrene foam has good fire resistance, since the spontaneous combustion temperature is +4910 C. This indicator is 1.8 times higher than that of wood, for which +2600 C is enough. In the absence of fire within 4 seconds, the combustion dies out. During combustion, the material releases about 1000 MJ/m3 of energy, while wood - 7000-8000 MJ/m3 - which means that when burning polystyrene foam, the temperature increase will be much lower.
Manufacturers offer self-extinguishing polystyrene foam made with the addition of fire retardants. However, experiments show that the self-extinguishing effect is lost over time, and in the design the material, which was initially classified as belonging to the G2 flammability group, after some time already corresponds only to the G4 class (research carried out at the Research Institute of Industrial Safety and Emergency Situations of the Ministry of Emergency Situations of Belarus).
At the same time, it should be recognized that the products released during the combustion of different brands of polystyrene foam are still poorly studied.
Resistance to biological and chemical factors
Polystyrene is able to retain its properties even in contact with:
- saline solutions, for example sea water;
- soap solutions and detergents;
- bleaching agents (chlorine water, hydrogen peroxide, hypochloride);
- acids (except for concentrated acetic and nitric);
- ammonia;
- lime;
- plaster;
- adhesive solutions;
- water-soluble paints;
- cement.
Expanded polystyrene is not suitable for animal food and does not promote the development of algae and microorganisms. During installation, termites and rodents should be prevented from accessing the foam, as they can cause damage. Partially decomposes under the influence of bitumen solutions and organic solvents. Stability is determined by the quantitative ratio of closed and open pores, which depends on the type and brand of material.
What is penoplex
Heat loss through the walls of a building can range from ¼ to 1/3 of the total.
Increasing thermal resistance due to the inclusion of special coatings in the design of external walls makes it possible to reduce its thickness and reduce the consumption of other building materials. Wall insulation is necessary not only to prevent heat from escaping from the house in the cold season, but also to excessive heating of the room in the summer, so the correct choice of a heat insulator determines the financial costs not only during construction, but also during operation (heating, air conditioning).
Differences from other options
In the name of this insulation, you should pay attention to the word “extruded”, since a different production technology distinguishes it from ordinary polystyrene. The molten polymer is passed under high pressure through small nozzles, resulting in a dense foam board with a thickness of 20 to 100 mm as a result of solidification. The molten polymer is passed under high pressure through small nozzles, resulting in a dense foam board with a thickness of 20 to 100 mm as a result of solidification.
The molten polymer is passed under high pressure through small nozzles, resulting in a dense foam board with a thickness of 20 to 100 mm as a result of solidification.
The technical characteristics of various brands of penoplex are presented in the summary table:
Of the presented types, only 45 are used for making road surfaces, the rest are used for insulating residential buildings.
Meaning of indicators
The fine-porous structure of penoplex (100 - 200 microns) makes it a fairly light but durable material. Its characteristic qualities are:
- resistance to mechanical loads (when laid on a flat surface);
- low vapor permeability (thickness 20 mm is comparable to 1 layer of roofing felt);
- moisture resistance allows use on the outside of walls, in bathhouses, bathrooms, basement levels without heating;
- the insignificant coefficient of thermal conductivity expands the possibilities of use in thin partitions created with your own hands: balcony railings, veranda walls, extensions or garages;
- low weight does not lead to a significant increase in the load on the base when covering already designed structures (insulation of individual apartments in a multi-storey building);
- the density of the polymer allows the use of conventional cutting tools to adjust sheets to size when performing work;
- chemical resistance to most compounds used in construction (exceptions: gasoline, diesel fuel, acetone, enamels, oil paints, formaldehyde, acetate-based solvents). For more information about the qualities of the material, watch this video:
Calculate the thickness of the insulation
Thermal insulation of the outer wall reduces heat loss by two or more times. For a country, most of whose territory belongs to a continental and sharply continental climate with a long period of low negative temperatures, like Russia, thermal insulation of enclosing structures provides a huge economic effect.
Whether the thickness of the heat insulator for external walls is correctly calculated determines the durability of the structure and the microclimate in the room: if the thickness of the heat insulator is insufficient, the dew point is located inside the wall material or on its inner surface, which causes the formation of condensation, high humidity, and then the formation of mold and fungal infection.
The method for calculating the thickness of insulation is prescribed in the Code of Rules “SP 50. 13330. 2012 SNiP 23–02–2003. Thermal protection of buildings."
Factors influencing the calculation:
- Characteristics of the wall material - thickness, design, thermal conductivity, density.
- Climatic characteristics of the building area - the air temperature of the coldest five-day period.
- Characteristics of materials of additional layers (cladding or plaster of the inner surface of the wall).
The insulation layer that meets regulatory requirements is calculated using the formula:
In the “ventilated facade” insulation system, the thermal resistance of the curtain wall material and the ventilated gap is not taken into account in the calculation.
Water absorption of polystyrene foam
A rather important property of foam insulation is its non-hygroscopicity or, as they say, water absorption of foam.
Unlike mineral wool, polystyrene can be completely immersed in water for hours and still not lose its thermal insulation properties. Unfortunately, the hygroscopicity of this material is not absolute; in twenty-eight days of complete immersion, water absorption can reach up to three percent of the volume. This is, of course, a trifle, and in no way affects thermal conductivity, but water that has penetrated into the insulation can freeze at low temperatures, thereby destroying the material itself. Therefore, facades covered with polystyrene foam boards must be plastered with special reinforcing mixtures, followed by priming and painting.