Thermal insulation (insulation, heat insulator) is a structural element or material that provides resistance to heat transfer or its reduction. Its use is the main way to prevent the occurrence of condensation in ventilation systems. Insulation for proper operation of ventilation pipes (vent pipes, vent hoses) is a necessity. In addition to protecting against moisture, insulation has an additional function - it muffles wind noise.
Fig.1 Insulation of the ventilation system
The importance of pipes for a ventilation system

Ventilation duct made of PVC sewer pipes can have any bend shape
During the air exchange process, each citizen living in a given living space should receive about 30 cubic meters of fresh air. The ventilation system must provide it. Pipes are the arteries of a complex ventilation mechanism. Using them, vapors, gases, and odors are removed from the most contaminated rooms (toilet, kitchen, bathroom, workshop, etc.). Served in “safe” rooms (bedroom, living room, etc.).
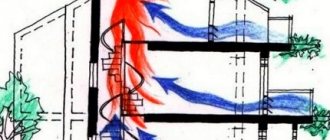
When organizing natural ventilation in areas with the formation of pollution, vertical channels with outlet to the roof are installed to move air. Through them, the stale air flow escapes into the atmosphere at a considerable height: the higher the pipe, the more effective the thrust. Log houses and frame buildings, as well as buildings where ventilation was not provided for at the design stage, are equipped with plastic pipes.
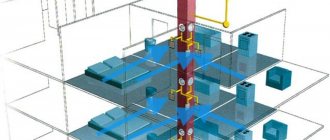
For mechanical air exchange, the use of pipes is simply necessary. The system of pipes and shafts is complemented by supply and exhaust ventilation units. The forced system consists of a special piping of rectangular or circular cross-section. The supply is carried out to each room, producing air exchange in it.
Along with metal hoses, plastic pipes are increasingly being installed. This can be either polyurethane or polyvinyl chloride. Pipe type – medium and hard. The temperature of the passing air should not exceed +70°C, otherwise the strength of the material will be impaired. This applies in particular to kitchen hoods. Recommended list of rooms where sewerage pipes can be used as ventilation:
- one-story residential buildings of small area;
- production sites of small enterprises;
- garages;
- cabins;
- warehouses;
- corridors.
As you can see, these are objects where there are no increased requirements for ventilation, but it is needed, and the traditional air exchange system is too expensive.
Misconceptions about ventilation
It is not enough to ventilate the attic; it is important that it is done correctly. However, there are several common misconceptions among people who are planning to deal with this issue.
They should be discussed in more detail.
- There is a need for ventilation only in the summer. In fact, the attic not only needs to be ventilated in the heat, but also to smooth out the large temperature difference between inside and outside the attic in winter. If this is not done, then the humidity will inevitably increase - an excellent environment for the existence of mold and mildew. It is extremely difficult to combat these phenomena, and in advanced cases, mold can penetrate inside the rooms - then there will be no need to talk about any comfort.
- Ventilation removes warm air from the room in winter. In fact, if heat is poorly retained in a house, then it is not the ventilation that should be blamed, but poor-quality thermal insulation. It is because of this that conditions are created under which moist and cold air enters the attic.
- The size of the ventilation holes does not matter. In fact, the area of these holes is important. With a small ventilation area, the effect will be practically zero. So that the room is well ventilated, and at the same time heat leaks are not allowed, for 500 sq.m. area required 1 sq.m. ventilation holes.
Why is this necessary?
The key word is condensate. Without insulation, it will inevitably form on the inner surface of the ventilation duct and flow down the inner walls, flowing through leaky joints into the main walls and ceilings. The consequences are obvious: dampening of the walls and ceiling, the appearance of mold and their gradual destruction.
The effect of condensation on the ventilation duct itself depends on what material it is made of:
- Galvanization can be damaged if the protective anti-corrosion layer is damaged. Which, however, is inevitable when cutting sheets.
- PVC and corrugated aluminum pipes tolerate contact with moisture without any consequences.
Another trouble associated with moisture condensation is the gradual freezing of frost on the inner walls of the ventilation duct outside the warm room. Over several weeks of operation in severe frosts, the pipe clearance can decrease from 100 - 150 millimeters to zero.
Where does condensate come from?
There are two reasons for its appearance.
- Human life activity is associated with excessive air humidification . When washing dishes, cooking, doing laundry, even just breathing, the atmosphere is saturated with water vapor.
However: in industrial premises this point is relevant to a much lesser extent, but insulation of exhaust ventilation is still required. Cause? See point number two.
- Meteorologists have long used the concept of relative humidity . The higher the air temperature, the more water vapor it can hold. 100 percent relative humidity is the maximum amount of water that can be contained in the air in a vapor state. However, as soon as the temperature changes, with the same amount of steam in the air, the relative humidity will change. With significant cooling, it can exceed 100%, after which excess water will inevitably begin to condense on the surface with a low temperature. In our case, on the inner surface of the ventilation duct.

Consequences of moisture condensation in the ventilation duct.
A special case
In production, there is often a need for forced ventilation with high air flow rates. In particular, to remove harmful volatile production products, sawdust, shavings, etc.
The noise of the air and what it carries becomes a serious problem in some cases. In factory premises, ventilation insulation is often aimed not so much at combating condensation, but at banal sound insulation. The methods, however, are the same.
Ventilation aerators
Installation of roof aerators
A roof aerator is a modern and convenient type of ventilation. It is a pipe covered with a cap on top. Aerators remove steam, moisture and stagnant air, providing ventilation for a cold attic in a private home. Aerators are installed on roof slopes, where air movement is ensured by differences in temperature and pressure, replacing ridge vents. Aerators can be continuous or point. Point aerators are equipped with fans and guarantee good air movement. Outwardly, they resemble fungi.
Continuous aerators are a plate along the ridge with holes. Being covered with a roof on top, they are practically invisible and provide intense air movement due to the large area of the holes.
Various types of aerators are created specifically for roofing from:
- bitumen shingles;
- flat roof;
- metal ceramics;
- ceramics.
Aerators are installed only where eaves vents are provided. There are other conditions for their installation:
- Only roofs with a slope of 15 - 45 degrees are suitable;
- a distance of at least 30 cm is maintained from the chimney or wall;
- aerators look 25 cm above the slot at both ends of the ridge;
- point models are mounted no further than 50 cm from the ridge.
Conclusion
Which insulation you choose is up to you to decide. The author's sympathies are given to foil materials based on polyethylene foam, but this is more a matter of habit. In the video presented in this article you will find additional information on this topic.
In a private house, the attic can be very warm and used as an additional room. But most often it is used as a storage room. The pipelines that run across its area make it difficult to change its purpose. If you decorate them correctly and sew them up with boxes, you will be able to make this room more cozy and comfortable.
Why is it necessary to ventilate the attic?
Properly equipped attic ventilation with your own hands allows you to eliminate the condensation that appears on the elements of the roofing pie. Ventilation ensures a flow of air, which eliminates residual moisture. By removing this moisture, the service life of all wooden structures, which the roofing pie is very rich in, increases.

In addition, there are two more seasonal features when ventilating
:
In winter, properly organized ventilation allows you to effectively combat ice dams, especially on eaves overhangs
Ice may appear due to poor ventilation; as a result, excess heat will turn into condensation, and this, in turn, into ice build-up. In summer, the moving air flow will contribute to some cooling of the roofing materials, which is especially important for bitumen-containing materials.
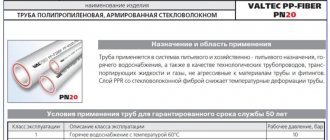
Why choose plastic pipes for ventilation?

Plastic pipes have virtually no mechanical load on the supporting structures of the building
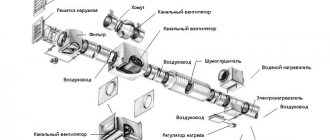
The air exhaust structure can be made of polypropylene, polyethylene, polyurethane or polyvinyl chloride pipes. Ventilation made from PVC pipes is the most popular of the listed types. It can be installed quickly and does not require any special skills. Plastic pipes have many valuable characteristics:
The pipe composition is easily assembled using connecting parts (fittings). Their diversity makes it possible to arrange an air duct of any shape. Moreover, its sagging does not exceed 4%. You can always choose the desired section size from the standard range (mm): 100, 125 or 150, 200. But there are also non-standard (non-standard) sizes. The inner surface of the pipes with a minimum degree of roughness does not allow pollutants removed from the air to settle on the walls in the form of deposits.
Shell for thermal insulation
The shell can be monolithic (in this case it is strung on a pipe) or prefabricated. The last option is used for ready-made operating systems. The shell can help out in places where the pipe runs through the wall. When winding roll insulation in such cases, difficulty may arise. Quite good results can be achieved in outdoor open areas. However, those points where the air duct turns cannot be covered with a cylinder. In such conditions, it is recommended to use insulating mats.
The shell can be made of:
- Foam plastic.
- Mineral wool.
- Extruded polystyrene foam.
- Polyethylene.
- Rubber.
During operation, a lot of noise occurs in the supply and exhaust air ducts. As the cross-section of the pipe increases, the throughput becomes higher, but the resistance also increases. Internal finishing allows you to make the surface as smooth as possible, which slows down the air flow less.

Recommendations for arranging ventilation
pay attention to the strength of the ventilation, it must withstand any weather fluctuations; you can put continuous soffits under eaves with fine screening mesh. To prevent corrosion, the holes should be made of aluminum or plastic; to prevent the formation of frost in the attic, install vents inside the room between the rafters and make holes so that they cannot become clogged with debris; You can install a fan on the roof for better air exhaust
The distance between it and the supply system must be at least 8 m; the air supply unit should be placed in the cleanest place in the attic; install a recuperator that can cool or heat the air, thereby preventing condensation from forming in a cold attic; equip ventilation pipes with grilles or diffusers;
At first glance, there is nothing complicated in arranging ventilation, but in fact it is better to take this issue seriously and consult with specialists. After all, the microclimate in the house and your health, as well as the durability of the building itself, depend on its quality.
Characteristics of insulation
The choice of material for thermal insulation of ventilation pipes is carried out according to the following criteria:
- thermal conductivity;
- vapor permeability;
- resistance to various reagents;
- temperature limit;
- compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards
Each insulation for ventilation pipes has both its advantages and disadvantages, which are determined by its structure and technical parameters.
Mineral wool
It belongs to the traditional type of insulation and has good thermal insulation properties. In addition, mineral wool and other fibers are among the most affordable materials. However, when using it for internal insulation, a seal will be required, and for external insulation, reliable protection from moisture will be required.
Mineral wool with foil outer layer
Foamed polyethylene
Available in the form of shells that tightly fit the surface of the pipes, or in rolls. It is durable, long-lasting, affordable, resistant to moisture and chemicals. In addition, foamed polyethylene is not only a good insulator, but also helps to significantly reduce vibration of air ducts.
Expanded polystyrene
It is characterized by resistance to moisture, prevents the appearance of microorganisms and corrosion. This provides reliable protection of the metal from destruction, so polystyrene foam is used not only to insulate air ducts, but also to insulate the gas pipe.
Using shell-shaped insulation, you can provide access to the ventilation pipe for repair work.

Expanded polystyrene shell to protect ventilation pipes
Polyurethane foam
It is produced in the form of a shell and in many respects is the same as expanded polystyrene, but is more resistant to fire. Therefore, polyurethane foam will be a reliable barrier in the event of a fire and will not allow the fire to spread.
Materials used
In order for the selected insulating material to perform its function, it must meet certain requirements:
- have a low thermal conductivity coefficient;
- be moisture resistant (water impregnating the insulation negates its heat-insulating properties).
When it is necessary to protect large pipes, sheet material is used, which is sold in rolls.
If you need to insulate small diameter pipes, special flexible casings of various shapes are well suited. They are equipped with a cut, have a pre-calculated wall thickness and fit the pipeline as tightly as possible.
Photo of a tube for insulation made of foamed polyethylene
The use of ready-made heat-insulating tubes has many advantages:
- the resulting insulation is sealed and effectively protects the pipe from cold outside air;
- the shell is very durable and withstands various mechanical impacts;
- the pipe has an aesthetic appearance;
- insulation is easily and quickly installed without the use of additional equipment;
- the material can be reused if necessary.
Foamed polyethylene
This insulator, thanks to its special internal structure (air bubbles enclosed in a dense thin-walled shell), perfectly protects the pipes from the cold, and you from the noise produced by the sewerage system. There are many varieties of this material, which are distinguished from each other by price and some other minor parameters.
Foamed polyethylene is an excellent material for protecting pipes
Let us dwell in more detail on the advantages provided by insulating pipelines with Thermaflex foam polyethylene tubes:
- provides a high degree of insulation of pipelines from the effects of negative ambient temperatures;
- prevents the formation of condensation and does not absorb moisture, which helps protect pipelines or their metal parts from corrosion;
- absorbs vibrations, shocks and noise, thereby increasing the comfort of using the sewer system;
- produced without the use of freon, therefore it does not have a negative impact on human health and the environment;
- resistant to mechanical stress, and also does not collapse when oil, gypsum, cement, lime, etc. come into contact with it;
- easy to install and remove, tubes can be reused;
- retains its technical characteristics throughout its entire service life.
Available in the form of tubes with an internal diameter from 7 to 114 mm. In this case, the wall thickness ranges from 6 to 20 mm. To protect larger diameter pipelines, sheet or roll material is used. It may additionally have a foil or adhesive layer.
Sheet foamed polyethylene is used for insulation of large diameter pipes
Foam rubber
This type of heat insulator has all the properties of polyethylene, but at the same time has greater elasticity. The most common insulation of pipelines is products made from Armoflex foam rubber.
The material has many undeniable advantages:
- can be operated in a wide temperature range (from – 200 to + 175 degrees Celsius);
- has high flexibility and elasticity, which facilitates and speeds up installation;
- durable;
- has increased fire resistance and does not support combustion;
- economical - allows you to repair the pipeline in the event of an accident without destroying the thermal insulation coating.
Benefits of foam rubber
Recommendations from professionals
And, finally, some important tips for those who are interested in how to properly ventilate an attic:
All ventilation elements must be resistant to any weather conditions; Be very careful about the location of the ridge vents. They are installed as close as possible to the ridge; Continuous soffits work effectively as cornice vents. The best materials for them are non-rusting aluminum or plastic. The surface of the spotlights is covered with a fine mesh; When installing attic ventilation without dormer windows, special attention should be paid to the vents between the rafters
It is important that during operation they do not become clogged with debris and dust; Hire a professional to calculate attic ventilation above the attic; Install decorative ventilation windows in the attic that will add charm and special style to your home; Equip the supply ventilation outlet to the attic in accordance with all the rules. The supply unit should be installed in the cleanest place, no closer than 8 meters from the exhaust pipe.
Installation Features
Important! For correct and high-quality installation, you must have experience in installing intra-house communications. If you lack experience, we recommend turning to professionals.
If you decide to install the structure yourself, the following reminders may help you:
- With a wide cross-section of pipes, air circulation is better (recommended minimum diameter is 14 cm).
- Short channels must be made wide enough.
- To maintain draft force, all air ducts in the house must correspond to each other.
- It is better to use the same type of thermal insulation and pipes.
- Forced ventilation should be installed when natural heat exchange is disrupted.

Insulation installation process
Video: an effective way to insulate a chimney
Insulation of ventilation pipes
Ventilation pipes must be insulated in the attic and above roof level. This procedure is carried out to avoid the accumulation of condensation, which will accumulate on the internal walls and flow down. Since the joints of the ventilation pipes are not made airtight, moisture will penetrate the supporting structures, ruin the finish and lead to the gradual destruction of the building. And the ventilation ducts themselves suffer from contact with moisture if they are made of galvanized pipes.
In winter, the opening of the ventilation duct becomes overgrown with frost and in just a month a standard pipe with a diameter of 15 cm will completely close.
The appearance of condensation in ventilation ducts is inevitable: people exhale water vapor, wash dishes, bathe and do laundry. This releases moisture into the air. The humidity of warm air in a residential building can reach 100%. When water comes into contact with the cool surface of ventilation shafts, it settles on it.
To prevent this process, the ventilation pipes in the attic are insulated. This is where the boundary between the warm air of the house and the cold air of the unheated attic passes.
The cheapest insulation option: mineral wool. It does not burn, but when wet it completely loses its qualities. Corrugation with mineral wool insulation is easier to install.
Polystyrene foam in the form of special removable “shells” is very easy to install and inexpensive. But it burns well, emitting toxic smoke, so it is not recommended for residential buildings.
The best materials for insulating ventilation ducts: polyurethane foam, polyethylene foam, polypropylene foam.
Areas of use
Let's consider the areas of application, structure, dimensions and types of shells made of foamed polyethylene. Pipelines in both residential and industrial premises, as well as cold water supply and sewer systems installed outdoors and in unheated buildings and structures, equally require reliable thermal insulation. Frosty Russian winters make it impossible to avoid using pipe protection against freezing and bursts. Systems located in the ground are protected from freezing, but need to retain heat, especially if they are heating and hot water systems. In this case, pipe insulation made of foamed polyethylene prevents heat loss. In addition to the heat-saving function, insulating shells for pipes also serve for sound insulation
This is important, especially when it comes to ventilation ducts. Telephone and other buried cables are also an area of application.
In air conditioning pipelines, pipe thermal insulation made of foamed polyethylene is needed to combat the formation of condensation, which has a detrimental effect on service life.
Insulation for pipes made of foamed polyethylene is available in the form of plates, sleeves (shells) and bundles. There are two types of insulation based on the method of their production: cross-linked and non-cross-linked.
Non-crosslinked (NEP) insulation materials have a lower density and less resistance to deformation. Visually, such material is easy to distinguish by its large cells and by the fact that after pressing it does not return to its original shape.
Cross-linked polyethylene foams (PEX) have a number of positive characteristics: they are more dense, have high strength and easily return to their original shape and size after compression, which is their undeniable advantage.
PP based insulating materials
The next position in the series of heat-insulating materials is polypropylene insulation, which has low thermal conductivity and, unlike polyethylene, low flammability and does not produce toxic smoke when burned.
To give it strength, it is reinforced with foil and plasticizers and lavsan threads are added. Produced in the form of a sheet up to 20 millimeters thick. It has excellent soundproofing properties and moisture resistance. Used for insulation of pipes, roofs, walls, balconies. The Penotherm brand, with increased moisture resistance and resistance to the release of infrared waves, is specially designed for cladding the walls of baths and saunas. This insulation is widely used when installing heated floors.
Features of installation of insulation for pipes
Installation of thermal insulation for pipes is carried out after assembling the pipeline so that it does not interfere with the joining. It is impossible to put solid sleeves on the assembled pipeline, so they are produced with cuts. Solid sleeves are also available for sale; they should be cut during installation. After installing the cut insulation on the pipes, it is fixed with special tape.
Installation should be preceded by a little preparation:
- to ensure a tight fit of the insulation to the pipes, they must be thoroughly cleaned
- if there is rust on the pipes, it should be removed
After the sleeves are put on the pipeline, they must be glued along the cuts and at the joints. If the pipes are installed inside the building, it is not necessary to glue the insulation sleeves along the entire length; you can only fix them with tape.
Calculation of attic ventilation
Those who decide to equip attic ventilation with their own hands need to carry out calculations before starting work. Only a specialist can guarantee the best result. And for the bravest ones, we have prepared a hint:

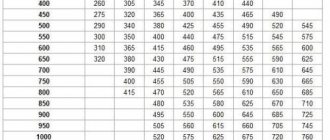
Roof ventilation summary table
The ratio of the vent area to the attic area is 1:500.
For 500 sq. meters of attic area should be 1 sq. meter of ventilation holes. As a last resort, you can be guided by a proportion of 1:300, per 200 square meters. meters of the attic should be at least 0.4 square meters. meters of air. The calculations take into account the area of true ventilation, that is, even the width of the grilles, whose ribs disrupt the movement of air flows, is excluded.
Exceeding the area of the vents is just as undesirable as not having enough. Openings that are too large can allow snow and rain to get in, because these are the most vulnerable areas of the roof, which must be remembered.
The area of the hood (ridge and pitched grilles) should be 12–15% greater than the area of the inlet (eaves vents).
Possible ways to prevent deficiencies
Insulated pipes have no disadvantages that would affect operation.
However, it is worth considering that several steel layers will be heavier than corrugated or polymer insulation. However, the installation quality is not affected by the installation process, so this characteristic is rarely taken into account.
If you have any doubts about the cost, you can make a simple calculation: compare the difference between insulated structures with the sum of the costs of pipe sets, insulation with waterproofing and the cost of fixation means. If the difference is small, you need to choose a material that is easier to install.
Ventilation device for the attic of a private house, vents, dormer windows, grilles
Owners are often afraid to install cold attic ventilation in their private homes, guided by the following assumptions.
Heat escapes from the house through attic ventilation grilles. There is an opinion that the building will cool down faster. But most often the problem lies in poor thermal insulation of walls or ceilings. By the way, moist warm air penetrates into the attic through a poorly insulated ceiling. We will tell you what its danger is in the next chapter; Ventilation of a cold attic with a hip or hip roof is only necessary in summer. According to many, ventilation grilles and windows in the attic are needed only for ventilation into the stuffiness
In fact, in winter, the ceiling of an unheated and unventilated attic will turn into a cave overgrown with ice stalactites; It doesn't matter what size the vents are. The area of ventilation windows and vents in the attic must be carefully calculated
How to do it right - read on.
Attic ventilation in a private home is an essential element of thermoregulation. Properly organized, it allows you to save money on heating or cooling the living space and keep the building itself intact. Attic ventilation above the attic is especially important.
Attic ventilation
The attic in a private house needs ventilation both in winter and in summer.
So, in the hot season, a hot roof heats the air in the attic to 150 degrees. Most of this heat is transferred to the ceiling of the upper floor, forcing the air conditioner to work harder to eliminate the excess heat. If there is no air conditioning, the owners languish in the heat and stuffiness.
In winter, air exchange is necessary to remove excess moisture. According to technical requirements, the temperature difference between the street and the attic should be 4 degrees or less. Temperature changes between the residential floor and the street contribute to the accumulation of condensation on the roof rafters. The moisture gradually freezes, creating entire cascades of icicles. When it thaws, they melt and moisture drips onto the attic floor. The supporting structures of the roof and ceiling are destroyed. Mold develops on wooden rafters.
By the way, high-quality ventilation of a cold attic prevents accumulation of snow and ice on the roof of the house.
How to insulate an air duct
Before you begin thermal insulation, you need to decide where the pipe needs insulation.

The most vulnerable place for condensation to appear is where there is a temperature difference, that is, where the pipe passes through the wall of the house, or where it passes through the roof and unheated attic.
- In the first case, the wall opening of the pipe passage is insulated with heat-insulating material, as well as the pipe itself up to the reflector.
- In the second case, the passage through the ceiling is insulated, and the pipe is wrapped with insulation until it reaches the roof.
Thus, insulation begins from the so-called dew point - the place where condensation falls.
It can be more difficult to determine the dew point in the supply ventilation system, where the amount of moisture falling into the condensate is determined by the length of the air duct and its installation features. Often, such ducts require not only insulation of the pipe, but also insulation of the valves, for example, using an electrically operated system that resembles louvers, restricting the air flow and heating the valves using tubular heating elements.
The choice of insulation option depends on the length of the pipe, the required amount of insulation and possible repair costs.
The feasibility of using one or another heat-insulating material depends on the economic feasibility.
You can determine the dew point using a table that takes into account the room temperature and humidity level.
Ventilating a Cold Attic
Ventilating a cold attic can be done easily with your own hands. This will require knowledge of a little theory and some practical skills. Providing sufficient ventilation in a cold attic will not cause any particular difficulties due to the large air volume and the absence of barriers to normal air circulation. Air exchange can be carried out through the eaves, ridge and ridge of the roof, as well as gable windows and grilles.
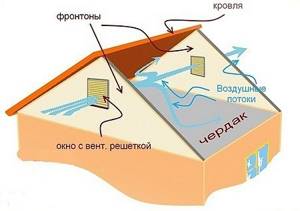
For gable roofs, ventilation of cold attics is done either through gables or through loosely fitting wooden lining of eaves overhangs. If the gables are made of stone, then holes can be made in them for dormer windows with ventilation grilles.
Dormers should be installed on opposite sides to ensure proper ventilation of the attic.
There is an alternative, more economical option. To do this, install standard ventilation grilles (pediment vents), one of which is adjustable, and the other is turned with the vents down. To protect against insects, this grille is equipped with a protective mosquito net.
Hip roofs do not have gables due to the shape of their structure, so for them there is another option for providing ventilation in the attic - using eaves overhangs. The air flow will be through the roof lining, and its exit will be from above at the ridge. If the filing is made from wood with your own hands, then small gaps are left between the bars for the passage of air. When covering the cornice with plastic soffits, such a procedure is not necessary, due to the presence of pre-made holes on the elements - perforations.
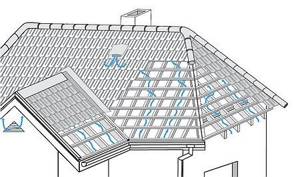
The air exits from above, through the roof ridge. Its design features depend on the type of roofing material used. As a rule, any manufacturer of roofing materials has its own ready-made and practical solutions
!
Valleys (valleys) are one of the problematic and difficult areas of the roof. To ensure normal ventilation of the attic space, point aerators are installed along the valley. However, this method is acceptable for roofs with slope angles of 45° or more.
. On flat roofs, there is a high probability of snow accumulating in the valley area and therefore such ventilation becomes ineffective in winter. You can combat this by installing forced ventilation - inertial turbines, roofing electric fans, or using high nozzles that will not be covered with snow.
DIY pipe system installation
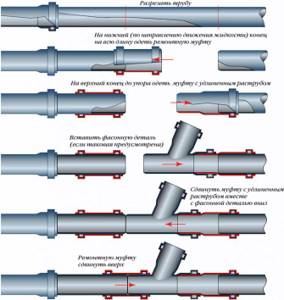
Options for connecting parts of a pipeline system made of polymer pipes
- If sewer pipes are chosen for air exchange, then the entire air duct must be assembled only from them. This will prevent a staircase structure from forming inside the duct, which will disrupt air movement.
- The future system is preliminarily schematically displayed.
- According to the scheme, markings are made on site.
- Be sure to include dimensions for each area and position of fittings.
- The cross-section of the pipes is being specified. Standard sizes: round 120 mm or square 150x150 mm.
- The diameter of the air duct is calculated (you can use an online program).
- Equipment, fasteners, pipes are purchased. When purchasing, you should be careful and take into account that the documents give the size of the outer circle, not the inner one.
- The presence of all connecting and other elements is checked. For complete compatibility of system parts and tight connections, it is better to purchase from one manufacturer.
- Fasteners for future communications are fixed along the entire marked route.
- The pipelines prepared for installation are checked for defects outside as well as inside the pipes. They should be smooth with an antistatic layer applied.
- A riser is assembled from elements of a larger cross-section.
- Air ducts are assembled and installed.
- Sections (branches) can be attached to each other with permanent or detachable connections. The second method is preferable because You can always disassemble the system for preventive maintenance.
- It would not be superfluous to seal all connections.
- Elements for connecting individual parts of pipes are selected with smooth transitions and without sharp corners.
- Ventilation sleeves are attached to the ceiling with clamps.
- They are mated to each other using fittings of the required diameters.
- All pipe sleeves converge in one place at the highest point.
- For mechanical air exchange, fans, valves, etc. are installed.
- The common pipe is placed on the roof higher above the roof.
- The entire system is tested in operation.

Plastic fan ventilation is a popular engineering solution for air exchange in a wastewater disposal system
In the case of using PVC pipes without warranty certificates, in order to avoid dangerous effects of substances released from them on people, it is best to make an exhaust hose from them. This will prevent even the accidental release of toxins into the room.
The decision to install ventilation using sewer pipes in a private house is economically justified. In addition, their performance characteristics do not cause any complaints from users, even though much more auxiliary parts are needed to assemble and fix the system than with traditional “classic” ventilation systems.
Internal and external insulation: pros and cons
There are two ways to insulate pipes: internal lining or external insulation. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Internal lining
- More difficult to install, but not subject to external mechanical temperature effects.
- To avoid reducing the internal part of the duct, it is necessary to carry out some work to increase the original area.
- The material must be vapor-tight and airtight to avoid absorption of moisture from the air.
- The outer part of the material should be smooth so as not to impede air circulation.

Example of external ventilation duct insulation
External side insulation
- Easier to install, but the material must also be vapor-tight.
- It is necessary to provide for insulation of the exhaust pipe and installation of a hydraulic barrier.
- The material must withstand mechanical stress.
- The insulation must be non-flammable, since in the event of an open fire it comes into contact with air.
- This type of insulation does not reduce the internal cross-sectional area of the pipe.
- It is not susceptible to the formation of pathogenic bacteria.
The right approach to insulation
To answer the question: how to insulate a ventilation pipe in a private house correctly and at the same time economically, you need to understand the reasons for the appearance of condensation. Temperature differences always lead to the appearance of condensation, but the most abundant release of “dew” is observed during the period of active contact between warm and cold air. The closer it can be moved to the outlet of the pipeline, the less potential danger and damage from condensate will be.
The ideal case is considered to be a situation in which the mixing of cold and hot air occurs in a section of the ventilation pipe located outside the building. But this is not always possible to implement in practice.
Therefore, for chimneys and air ducts in an unheated attic, insulation of the ducts is considered mandatory. Thanks to this, it will be possible to remove the “wet” zone - the place where dew is most actively formed - beyond the walls of the building. This solution will help, even with the active appearance of a large amount of condensation, to prevent moisture from penetrating into the walls, causing the appearance of dampness, fungus and other related troubles.

Finding the optimal location
A vertical chimney from a heating stove, fireplace or gas boiler, thanks to the release of hot air, will be completely cleared of moisture during the heating process. Horizontal air ducts, the outlet of which is located in the wall, should initially be installed with a downward slope of at least several degrees. This allows accumulated moisture to drain outside rather than inside the room. Therefore, the most important point before insulating such air ducts is to check whether there is a slope for its removal. Otherwise, even insulated ventilation pipes will become a source of problems in the future, albeit noticeably later than without any thermal insulation at all.
A mandatory place for insulating air duct pipes is an unheated attic space. It is here that the temperature difference during the cold season becomes a source of problems due to the formation of moisture. Condensation on them, regardless of whether plastic or metal pipes are used, forms both inside and outside.

Choosing the best material
In order for the thermal insulation of any plastic, metal and various other ventilation pipes to be quite effective, but also not to hit the budget, you should choose the right insulation. Today there is a fairly wide selection of materials for this, both affordable and quite expensive. The most recommended options are the following types of insulation:
- Mineral wool. An inexpensive fireproof option available at almost any hardware store. The downside of the availability of mineral wool is the complexity of installation and the need for its subsequent protection with foil or galvanization. Afraid of moisture.
- Stone wool. It has the advantages of mineral wool, as well as its disadvantages. Over time, it cakes and loses its thermal insulation properties.
- Polyurethane foam and polystyrene foam. Detachable structures for pipes of a certain diameter. Inexpensive, but providing excellent heat and moisture insulation. The disadvantage of the materials is their high fire hazard and rather low resistance to mechanical damage.
- Foamed polyethylene. Insulation offered in the form of ready-made tubes of different diameters. Inexpensive, has good thermal insulation properties, and is not afraid of moisture. The disadvantage is the need to put a heat insulator on the duct pipe, which is inconvenient or even sometimes impossible.
The choice of how to insulate the ventilation pipe is made by everyone himself. The basic rule that it is recommended to rely on when choosing is to purchase the material that will most fully solve the problem of condensation in a private ventilation network.
Where to insulate
In what places is insulation needed for ventilation pipes?
A simple solution
The simple answer to this question is obvious: where a sharp and significant cooling of the air flow is possible.
- If the exhaust ventilation is routed through a solid wall, the pipe is passed through a heat-insulated sleeve and insulated right up to the deflector.
- In a private home, insulated ventilation pipes run through the cold attic and are discharged through the gables or roof. Insulation again begins from the point where the ventilation duct noticeably cools (see also the article Insulating the attic - we consider possible options in detail).
Supply ventilation stands apart. Here, the possibility of moisture condensation on the outer walls of the supply ventilation duct depends on its length and location.
If necessary, these pipes can be insulated using the same methods as exhaust pipes, however, the influx of cold air itself can create some discomfort; adjustable fresh air ventilation dampers may even freeze.
One solution to this problem is an insulated ventilation valve. Perhaps in the reader’s imagination a ventilation grille with a layer of thermal insulation appeared? Not so.
The design in the photo bears little resemblance to ventilation blinds.
An insulated ventilation valve is a solution for large premises, primarily for office, warehouse and industrial purposes. It really is an adjustable louvers that allow you to limit the air flow and... if necessary, heat it up using tubular heaters.
Adjustment can be carried out manually - by a system of rods and levers, or using a simple electric drive. The live cross-section of the valve in a fully open state can be up to 3.5 m2, the power of heating elements can be up to 8 kW.
The function of heating elements, however, is not to supply warm air into the room. With a valve area of 3.5 m2, 8 kilowatts of thermal energy is a drop in the ocean. Heating elements only warm up the valve flaps before changing their position to avoid icing and damage.
Difficult decision
In some cases, an accurate calculation is desirable: with a large length of ventilation, the costs of insulation will be significant, and it is better to be sure of their necessity.
The key concept is dew point. This is the temperature at which droplets of condensation begin to form in air with a certain relative humidity.
A simple measurement of the relative humidity in the room and the surface temperature in different parts of the ventilation duct will give the exact boundaries of the zone that needs insulation.
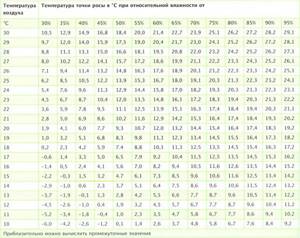
This table will help you determine the area of the duct where condensation will begin to form at the current relative humidity.