The ventilation system of a private house should ensure a flow of fresh air into all rooms of the house and stimulate its renewal. The air duct system and openings for air flow are called supply air. Air ducts and exhaust openings are exhaust. Everything seems to be simple.
But in practice, the question of the most efficient design of a ventilation system is one of the most controversial. One of the most controversial issues is whether ventilation can be vented into the attic. It may be better to dispose of waste and contaminated air mass directly, i.e. through the wall?
In the article we presented, all aspects of constructing a ventilation system for a country house are discussed. We will introduce you to the regulatory requirements and nuances of the organization. Our recommendations will help you decide on the most practical option.
SNiP requirements for ventilation systems
The requirements of SNiP can be considered redundant, but they still need to be fulfilled. They clearly prescribe not only the minimum required air exchange for each room, but also regulate the characteristics of each of the system elements - air ducts, connecting elements, valves.
The required air exchange is:
- for the basement - 5 cubic meters per hour;
- for living rooms - 40 cubic meters per hour;
- for the bathroom - 60 cubic meters per hour (plus a separate air duct);
- for a kitchen with an electric stove - 60 cubic meters per hour (plus a separate air duct);
- for a kitchen with a gas stove - 80 cubic meters per hour with one working burner (plus a separate air duct).
It is logical to equip the bathroom and kitchen with a forced ventilation system, even if natural ventilation is sufficient for the rest of the house. Exhausting air from the basement to avoid the concentration of carbon dioxide, which is heavier than air, is also often provided by a separate air duct.
The air circulation diagram in the house, made in the style of infographics, gives an idea of the flow of air flows. It is very important to check the functionality of the system after installing the duct system
Homeowners who are not ready to turn the roof of their house into a palisade of air ducts often think about how best to arrange ventilation communications within the attic. After all, I would like the design not to be too bulky.
But is it possible to remove exhaust air through the roof structure and its supporting frame - the rafter system? And if this solution is acceptable, what is the best way to implement it? What equipment will be required for installation?
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
By watching this video, you can get additional information about ventilation of metal roofing using aerators:
Video instructions for installing ventilation outlets:
Video about installing ventilation pipes on a metal tile roof:
In order for a metal roof to last for a long time without repairs, it is necessary to install roof ventilation. Installing ventilation equipment will not require huge material costs. And the desire to save money will lead to serious problems in the future.
It will also be expensive to correct errors made during installation, which is why it is so important to take into account every nuance of the installation technology.
Tell us about how you arranged the ventilation of your own metal tile roof. Share with site visitors technological subtleties known only to you. To leave a comment, ask a question, or post a photo related to the topic of the article, use the block below.
Source
Consequences of incorrect ventilation outlet
If the project did not provide for the organization of a heated insulated attic, then, as a rule, in private houses the attic is an unheated room. The temperature in the attic is lower than in the house. When warm air from the duct, saturated with moisture from breathing, electrical appliances, and heating systems, enters a colder room, the moisture condenses.
In summer, this can lead to the formation of fungus and even rotting of the ceilings. In winter, moisture freezes and turns into frost and ice. There is nothing good about these snow and ice build-ups either. In winter, they contribute to the formation of microcracks. In the summer they can melt and flood the attic.

The air within the attic should be completely changed at least twice a day. This frequency of air exchange will eliminate the formation of fungus, which irreversibly destroys the wooden components of the roofing system
There is a solution: to install ventilation in the attic in a private house, a number of important conditions must be met, these are:
- the presence of a ventilation outlet from the attic to the street;
- installation in the attic space of the attic with its own ventilation system;
- installation of a mechanical ventilation system in the house - supply and exhaust with a recuperator installed in the attic.
Depending on whether the ventilation system is forced, natural or combined, its methods of venting to the attic also differ.
Attic space: the need for ventilation
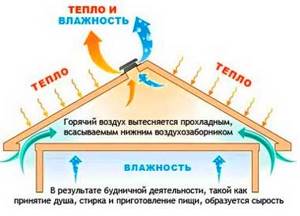
Ventilation is involved in the heat exchange processes of the entire residential building. During the hot season, the roof can heat up over one hundred degrees, and heated hot air enters the house, aggravating the heat in it. In cold weather, other problems may arise. Cooled air forms drops of condensation on insulated floors: this moisture negatively affects wooden elements.
Even basic ventilation can prevent premature damage to the rafters.
Attic ventilation ensures mixing and equalizing the temperatures of the roof structure and the external environment. It prevents the formation of ice during the melting of the snow cover, avalanches and the appearance of large icicles. Setting up a high-quality air exchange system is actually extremely important.
Natural ventilation with access to the attic
Gravitational ventilation, also known as natural ventilation, ensures air circulation according to the principle familiar from school: warm air is lighter than cold air. Warm air rises through exhaust ducts located as high as possible. Cooler air from the supply ducts enters the house.
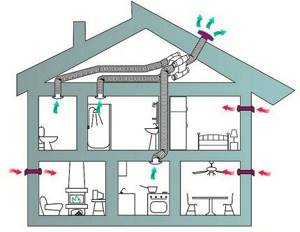
Ventilation ducts in a one- and two-story private house can be combined into one system only if there is a good ventilation system in the attic itself. This reduces the number of air ducts on the roof
If effective under-roof ventilation is properly arranged in the attic and in the roof pie, then the exhaust air exhaust systems can be fully or partially combined.
The circulation and removal of contaminated air mass within the attic will be ensured by:
- fan risers;
- aerators (an air duct with access to the street, which forcibly ensures constant air circulation in the attic);
- proper installation of a roofing pie (the simplest is ventilation using two gaps under the roof and above the rafters);
- roof vents that cut directly into the roof system.
If a natural ventilation system is organized within an unheated attic, a rational solution is to combine all the ventilation pipes in the attic to be discharged through a common ventilation shaft.

A single riser vent can solve condensation problems in your attic. The natural ventilation system closes on it
If the attic is sufficiently ventilated, condensation will not accumulate in it. Unfortunately, roof vents or attic gaps do not always provide it fully.
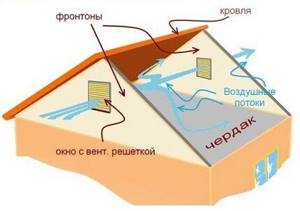
Ventilation of the cold triangle of an unheated gable roof (called a gable or gable) is carried out by installing ventilation windows or openings with access to the street. This ensures there is sufficient air circulation in the attic
Dormers and attic vents that can be closed and opened should provide more air circulation than other methods of natural attic ventilation. For example, supply and exhaust openings drilled in the gables.
Why is it necessary to ventilate the attic?
Properly equipped attic ventilation with your own hands allows you to eliminate the condensation that appears on the elements of the roofing pie. Ventilation ensures a flow of air, which eliminates residual moisture. By removing this moisture, the service life of all wooden structures, which the roofing pie is very rich in, increases.

In addition, there are two more seasonal features when ventilating
:
- In winter, properly organized ventilation can effectively combat ice dams, especially on eaves. Ice may appear due to poor ventilation; as a result, excess heat will turn into condensation, and this, in turn, into ice build-up.
- In summer, the moving air flow will contribute to some cooling of the roofing materials, which is especially important for bitumen-containing materials.
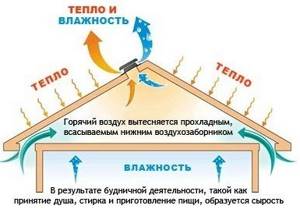
Combined ventilation outlet to the attic
A good solution for a simple ventilation system is:
- separate outlet to the attic for kitchen and bathroom exhaust pipes with forced exhaust;
- a separate outlet to the attic with further connection to the vent riser (or without connection) of exhaust pipes from the remaining residential premises.
This is the simplest and most effective way to provide ventilation at home without a supply and exhaust ventilation system with a recuperator.
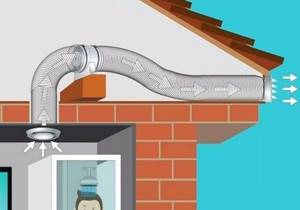
In combined ventilation schemes, a device for forcing air movement is installed either in the exhaust or in the supply openings
Fans of combined ventilation system options operate either for exhaust or for supply. In the first case, fresh air enters on its own, trying to fill the vacated space. In the second case, the portion pumped from the street removes the waste air mass from the room.
Common myths about ventilation
Some people have doubts about the need for ventilation. Therefore, disagreements arise. Let's try to figure out whether it is possible to do without this system:
- Heat escapes through ventilation in winter. This is the most common opinion. If it takes a long time to heat the house, and cooling occurs very quickly, then air exchange does not affect this problem in any way. This is due to shortcomings when installing insulation materials. But if the insulation is of poor quality, it can release moist air into the attic. As a result, condensation appears and wooden floors begin to rot.
- Ventilation of a hip or hip roof is only necessary in summer. In fact, if air exchange is disrupted in winter, icicles will grow and mold and mildew will appear.
- It doesn't matter how much area the ventilation hole will occupy. This opinion is erroneous and it is not recommended to place holes by eye. Such ventilation will cause poor air circulation. It is worth adhering to a certain scheme: for every 500 m2 there is 1 m2 of ventilation.
Including the attic in the ventilation system
An attic built instead of an attic is essentially another room. Which is good from the point of view of optimizing the living space, but somewhat complicates the installation of the ventilation system in the traditional way.
There should be a ventilated attic space between the attic and the roof. Fresh air must be allowed to circulate freely in the roofing pie and within the attic or furnished attic.
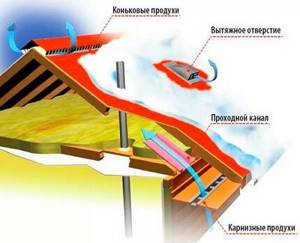
Natural ventilation occurs due to the gravitational movement of the air mass. Cold air comes from the holes under the roof ridge, warm air leaves from the ridge hole, aerator
In the process of installing a roofing pie, it is necessary to construct vents - longitudinal ventilation holes. They start from the eaves line and end at the ridge line. Provided by installation of battens and counter-battens on rafter legs.
In the eaves area, street air enters these ventilation ducts. In the ridge area, the air flow exits, taking with it condensation and household fumes that have penetrated from the living quarters into the attic space.
The ventilation system for the rest of the house is also ducted into the attic. Exhaust ducts and risers from the house and from the attic can be combined and connected to an aerator. However, you need to be sure that there is sufficient air circulation.
System of dormer windows and vents
One of the common measures for arranging attic ventilation in a private house is air exchange carried out by dormer windows. In this case, you don’t need to use a system of holes, vents and gaps. According to experts, this method is not extremely effective, but condensation does not accumulate in the room. The rules are as follows:
- The size of such windows should be at least 60x80 centimeters.
- Windows are installed on opposite gables.
- The windows are placed at an even distance from the cornice, the sides of the building and the ridge.
- The distance between two adjacent windows is at least one meter.
- The window can be installed directly into the ventilation grille in the attic.

This method of air exchange is popular in the construction of dachas and country houses. But there is also a disadvantage of such a system: air can stagnate under the dormer window and above it. But if you choose high-quality building materials and carry out the installation correctly, condensation will not accumulate in the attic space. Another, simpler way is to place vents. So how to create ventilation yourself, without resorting to the help of specialists?
In a private house, you can do the ventilation of a cold attic yourself. Evidence that condensation has accumulated is the appearance of an unpleasant smell of mustiness and dampness. Violation of comfort prompts many to immediately take up tools and begin fixing problems. In order for the ventilation system to ensure optimal air exchange, condensation does not accumulate and heat loss does not occur, it is important to pre-design all elements. If the roof is gable, the arrangement will not raise questions or problems. After the planning stage, you can start working:
- Vents are made in the gables.
- Wind slopes are covered on the sides of the roof with wood.
- All cracks are made uniformly, creating airflow over the entire surface of the attic.
Important! If the gables are made of stone, then there can be no gaps, and, armed with a tool, you need to make a couple of dormers in the surface.

Supply and exhaust ventilation with recuperator
This is the simplest, most expensive way to vent ventilation into the attic. It is necessary to purchase a recuperator - a device that ensures the movement of air flow while simultaneously mixing in a fresh portion of air and heating it to a comfortable temperature.
The entire circulation system is connected to the recuperator; the principle of its operation is quite simple. Heat from heating devices and boiler rooms is often wasted. So why not use it to partially heat cold air?
The cool air drawn in by the recuperator from the street is not only prepared by mixing with the already heated air mass, but is also cleaned of harmful and unpleasant impurities suspended in the air. In addition, the recovery equipment is equipped with heaters that heat the air flows.
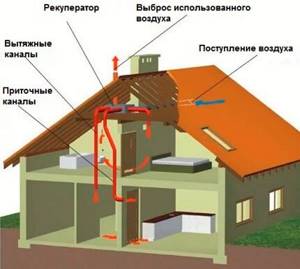
A schematic representation of a ventilation system with a recuperator in the attic looks quite simple. You just need to purchase a recuperator, install and connect air ducts to it
A prerequisite for the functioning of a system with an integrated recuperator is its compulsory nature. Air enters and is removed from the room by two constantly running fans. Otherwise, the recuperator simply will not work; the device provides too much aerodynamic resistance.
Valves and dampers are installed along the entire length of the air ducts to ensure proper flow distribution. Additional meshes must be installed at the inlet and outlet of the recuperator to prevent dust and grease from entering the device. The exit to the street is closed with additional bars against birds and insects.
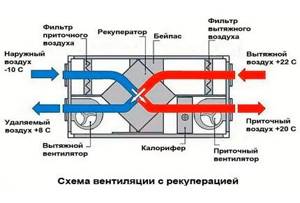
The recuperator cannot operate without fans. Thus, having a constant source of energy in the house becomes of utmost importance. If electricity in a private home disappears regularly and for a long time, it is better not to use this system
Modern recuperators can be programmed using buttons on the control panel. Such devices are even more expensive, but their ease of use makes them attractive.
What about condensation, a major problem in the attic? Condensation does not accumulate in the recuperator, does not settle on the walls and beams of the attic, but quietly and peacefully flows into a pan located under the device.
In winter, in an unheated attic, this can become a problem, since in severe frosts the recuperator’s power may not be enough. In this case, you can install another heating device next to the recuperator box.
Ventilation features
To avoid mistakes when designing ventilation with your own hands, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- When designing air circulation in a warm attic, you should calculate the rigidity of the structure: whether the ventilation can cope with the wind pressure and temperature changes.
- Soffits for cornices should be made of plastic or aluminum. These materials do not corrode, so they will last for many years.
- If there is a fan in the hood, then the supply equipment must be installed at a distance of at least 8 meters from it.
- To avoid the appearance of condensation, it is necessary to regulate the air temperature using a recuperator.
- It is recommended to observe for a couple of weeks which direction the winds blow most often. Ventilation must be provided in this direction. Sometimes this single direction is enough.
It is very important to choose the right location for the ventilation holes. They should be located in the cleanest area of the attic because they should not become clogged, otherwise it will block air exchange.
It is very important to understand that ventilation is required at any time of the year. In the summer, it prevents strong heating of the living space, and in the winter, it will not allow the formation of dampness. Therefore, if you design the ventilation correctly, your stay in the house will be convenient and comfortable.
Source
Condensation in the attic is not a problem
The main enemy of attic ventilation systems is condensation. The cheapest way to combat it is to install the natural ventilation system in a well-ventilated cold attic with a complete or partial closure of the system to a vent pipe or some other exhaust ventilation device.
If the house has an attic instead of an attic, you should not forget about integrating the attic into the ventilation system or creating a separate ventilation system for the attic and the rest of the house.
A forced ventilation system with a recuperator installed in the attic is the simplest, but also the most expensive way to install a ventilation system in the attic.
Causes of condensation
A sign of condensation is the characteristic musty smell of dampness. The formation of condensation and all the accompanying problems are affected by the following installation errors:
- no good ventilation;
- the roof does not have high-quality thermal insulation;
- improper vapor barrier, waterproofing;
- defects in building materials.
The accumulation of condensation under the roof leads to the fact that the insulated ceilings begin to rot, mold and mildew develop. This may also be due to insufficient ventilation holes.
The norm is to have 1 square meter of ventilation openings for every 500 square meters of attic space. In order for moisture to begin to evaporate, it is necessary to create conditions for mixing internal and external air.
The system is extremely necessary in the summer heat, when the roof heats up over 100 degrees. Very often people neglect ventilation, assuming that heat leaks through it during the cold season.
Heat loss is due to poor thermal insulation. Cold, damp air entering the under-roof space serves as a condition for the inevitable formation of mold. Therefore, it is necessary to ventilate the attic not only in summer, but also in winter.
Why are many people afraid to insulate a cold attic?
- The first myth is that ventilation causes the rooms of a private house to become cold. In fact, heat escapes due to poor-quality thermal insulation of the walls and ceiling, and ventilation of a cold attic has absolutely nothing to do with it.
- The second myth is that you only need to ventilate the attic space in the summer to save the living quarters of the house from stuffiness. This is fundamentally wrong, since it is in winter that moisture passing through the ceiling and accumulating in a cold attic will turn it into an “impenetrable forest” filled with icicles.
- The third myth is that ventilation of a cold attic is already carried out through natural gaps in the gable structure. In fact, in order for the ventilation of the premises to be sufficient, it is necessary to make vents, the size and quantity of which are strictly calculated.
Properly organized ventilation of the attic space in a private house allows you to preserve the roof structure for a long time, saves significant funds on heating and air conditioning of residential premises, and also prevents the accumulation of snow and icing of the roof during the cold season.
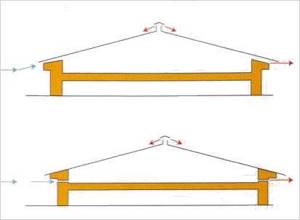
The most common type of attic ventilation is cornice-ridge ventilation. Convection air movement is created by openings along the entire perimeter of the eaves overhang and exhaust openings along the ridge of the building. Despite the fact that the design of such a cold attic ventilation system seems very simple, it requires correct execution and accurate calculations.
Rafter system
In order for the hip roof to be sufficiently rigid and reliable, it is necessary to arrange all its elements in a certain way.
Sloping types of rafters need to be attached to the internal corners of the walls, while diagonal ones - to the external ones . This is fundamentally important. Due to the fact that the slanted rafters bear a large load, their length should also be greater.
The slanted rafter legs should become a support for the shortened rafters of the slopes , which are called narozhniki. Most often they are made from two paired legs.
Diagonal rafters must be supported by one or two supports . For this purpose, racks made of timber are used. The struts should be placed in such a way that an angle of 45 degrees is formed between them and the horizontal support.
The intermediate rafter legs should rest on one side of the ridge beam and the other on the mauerlat . They should be placed in steps of 1-1.2 meters. Every second rafter is best connected to load-bearing walls using twists.
They can be made from ordinary wires, the radius of which is 2 millimeters. Using a reverse bracket, the intermediate frame should be connected to the Mauerlat.
The half-legs or half-legs (as they are often called) should rest on the mauerlat on one side and on the diagonal leg on the other.
Construction of a hipped roof truss system: drawings and diagrams below.
Drawing of the rafter system
Rafter system diagram
Natural and artificial type
According to the type of stimulation of the movement of air masses, ventilation systems are divided into natural and artificial:
- Natural, they are also gravitational. They operate due to the difference in density and temperature of the air mass outside the window and indoors. Warm exhaust air with a lower density rushes upward and is drawn out into the vents, and is replaced by a denser cold stream flowing from behind the window.
- Artificial, they are also mechanical. They work by continuously stimulating air flow with fans. They are installed on the exhaust or supply side; it happens that they are installed on both the supply and exhaust components, but only one direction is always involved.
The gravity type of ventilation directly depends on weather conditions. In the summer heat, its work spontaneously stops, because... the pressure between the air inside and outside is equalized. It happens that in hot weather the air flows in the opposite direction: from the house/apartment to the street.
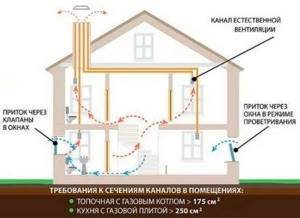
Natural ventilation is energy independent. There are no expensive devices in its scheme. It is cheaper to assemble and maintain, but inferior to forced ones in terms of capabilities and efficiency
Fresh air enters naturally through leaks in window and door openings with frames, through open vents and periodically opened doors. Outflow is through barred ventilation openings located in kitchens and bathrooms.
Apartments in the old housing stock were ventilated according to a natural pattern. Nobody was going to mechanize it. Now in these apartments designed for natural influx, plastic sealed windows are installed. Because of them, the normal movement of air is disrupted, therefore, together with a plastic window in a high-rise building, a supply wall valve should be installed.
Supply or exhaust valves into the wall should be used in private houses in which the construction of mechanical supply and exhaust ventilation is not planned.
Using a valve, inflow or outflow will be ensured in the cheapest but most effective way. In this case, the entire system will receive the status of combined – i.e. partially mechanized.
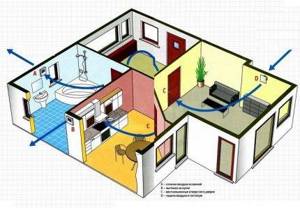
The simplest options for combined ventilation systems, partially mechanized by local fans, include systems with supply or exhaust valves, as well as kitchen hoods without recirculation with an air duct connected to the ventilation shaft
Mechanical ventilation is the most expensive and difficult type of system to implement, requiring the inclusion of a recuperator or air heater, an air handling unit. Its air ducts are laid behind false walls, suspended or suspended ceilings, and laid out in building structures during the construction of a house.
Naturally, if the owner decides to install supply and exhaust ventilation, he will not skimp on material for the ventilation ducts. It is unlikely that he will buy sewer pipes. It is better to purchase plastic air ducts that can be connected to ventilation equipment without problems and unnecessary tricks.
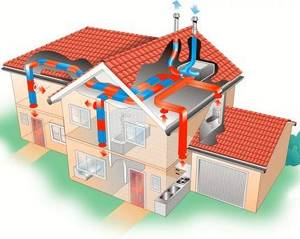
A unit located in the attic of the house is responsible for the operation of supply and exhaust ventilation. It pumps in fresh air and removes waste material, regardless of weather conditions.
In private houses, exhaust ducts from bathrooms and kitchen hoods are either discharged separately into the attic or combined into a common shaft located in the middle of the building. This reduces the loss of usable area and the shaft reaches the roof at the highest point, which provides excellent traction.
The plastic sewer pipe passing through the attic must be lined with insulation. Otherwise, the pipe will collapse due to temperature changes. Hotter air will always come out of the kitchen than in the environment, which means that due to unstable expansion, deformation or violation of the tightness of the channel is possible.
A cap must be installed on top of the pipe - a ventilation deflector that protects from precipitation.
Drawing up a ventilation diagram for a home
The ventilation scheme is drawn up before the construction of a house begins or before the start of a major renovation. If this is the first option, then the internal walls of the house, separating the boiler room, kitchen, bathroom and toilet, are chosen to install the ventilation shafts. These are the rooms that need ventilation the most.
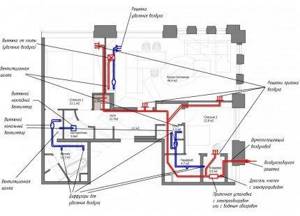
To arrange everything correctly and install the equipment, you need to take a house plan. If it is two or three floors, then a plan for each floor will be required (+)
On the diagram you need to mark ventilation ducts for supply and exhaust air that will pass through the rooms. It is imperative to indicate where the supply valves, fans, recuperators and other equipment provided in the selected ventilation system will be located.
Based on the drawn up diagram, it is necessary to calculate the power of the units for each room and select the diameters of the ventilation pipes.
Another important point is that you should take into account the need for fresh air in m3 of each room.
According to regulations, different rooms need to provide different amounts of fresh air per hour:
- for the kitchen – 60 m3 with an electric stove and 90 m3 with a gas stove;
- for bathrooms – 25 m3 per hour;
- with combined bathrooms - 50 m3;
- for offices, children's rooms, living rooms - 3 m3 per 1 m2 of area.
For boiler rooms it is necessary to lay a separate ventilation duct. Taking into account the standards, you need to calculate the need for fresh air and select the appropriate power of equipment that can provide the required air flow speed
Moreover, it is important to make a reserve of 30% so that the system does not work at the limit of its capabilities
Hip roof device
The hip roof structure consists of four slopes. It has two peaks, which are connected to each other by a structural element - a ridge beam .
Instead of vertical gables, houses with hip roofs have triangular slopes. Because of this, the side slopes have the shape of a trapezoid.
The main axis of the roof , which carries the load, is the ridge beam . It is he who connects all the roof slopes. Other important structural elements are attached to it - the frame and corner rafters.
Corner rafters act as the basic elements of load distribution. They connect the corner of the structure with the corner of the ridge . Most often they are made the same in thickness as timber.
The leg itself extends slightly beyond the edge of the structure. If the building is quadrangular, four such rafters will be needed.
The central part of the structure is formed by an intermediate frame - intermediate rafters, which are attached in pairs to each other on a ridge beam and brought out onto the mauerlat. They are not installed in the hip area . Their number may vary depending on the length of the building.
The ordinary frame consists of rafters that connect to the ends of the ridge and extend onto the load-bearing walls of the building on each side. Their number is six.
Construction of a hipped hipped roof
Hip roof - design
How to choose the right forced ventilation unit
The selection of a forced ventilation unit is carried out according to the following main parameters:
- Productivity, m3*hour
- the amount of air supplied to the house and removed from the premises per unit of time. - Pressure is the pressure required to overcome the aerodynamic resistance created by all elements of the ventilation system.
- The efficiency (coefficient of performance) of a recuperator is an indicator of the efficiency of heat transfer to fresh air supplied to the house from the air removed from the premises.
The minimum amount of air that the ventilation unit must circulate is determined by sanitary standards. Standard air exchange values for the premises of a private house are given in the previous article. The performance of the ventilation unit must be greater than the sum of the standard values for all rooms of the house.
In practice, to simplify calculations and create some performance reserve, another indicator is used - the air exchange rate. This is a value indicating how many times the air in the room should be changed within an hour.
According to Russian sanitary standards, the air exchange rate in a private house must be at least 0.35 times/hour.
For example, the total volume of all ventilated rooms in a house is 450 m3
.
Then the minimum required performance of the ventilation unit is 450 m3
x 0.35
1/hour
= 157.5
m3/hour
.
In addition, it is necessary to check that one more condition is met - the air exchange in the house should not be less than 30 m3/hour
per person living in the house.
If this condition is not met, then the air exchange rate is taken to be greater than 0.35. It is necessary to provide some reserve capacity for the ventilation unit to supply additional air to the heating boiler, fireplace, kitchen hood, or in case of receiving guests.
Therefore, in practice, the performance of a ventilation unit is determined by taking the air exchange rate in a private house within the range of 0.5 - 0.8
1/hour
.
It should be remembered that the ventilation unit, like any pump, has a curvilinear dependence of performance on pressure. The greater the pressure (aerodynamic resistance of the ventilation system), the lower the performance of the ventilation unit. This means that the shorter the air ducts and the larger their cross-section, the lower the requirements for the parameters of the ventilation unit - the cheaper the unit, and the lower the energy consumption for ventilation.
Calculating the aerodynamic resistance of a ventilation system and determining the required pressure is a rather complex task. It is better to entrust the decision to specialists.
The correct choice of ventilation unit parameters can only be made based on calculations. Often contractors do not bother with this and offer to install a ventilation unit that is obviously more powerful, and therefore noisier and more expensive.
The size of the reduction in heating costs directly depends on the efficiency of the recuperator.
The efficiency of cross-shaped heat exchangers does not exceed 60%. In some models of ventilation units, two such heat exchangers are installed, placing them in series one after another. The efficiency of the system increases by another 20%.
The most expensive ventilation units may contain even more effective solutions - rotary heat exchangers and even heat pumps (heat pipes). The efficiency of such devices reaches 90%. In Russian conditions, with relatively low fuel prices, it will not be possible to recoup the costs of installing such units.
When choosing a ventilation unit, you should also pay attention to other parameters that are significant for the developer:
- The noise level created by the ventilation unit.
If the block is placed on a wall or ceiling adjacent to the bedroom, you should choose a block with a minimum noise level or you will have to spend money on additional sound insulation. - The maximum electrical power consumed by the electric heaters of the ventilation unit may exceed the capabilities of the electrical network. Think about whether it would be more profitable to heat the air using a heat exchanger connected to the heating system.
- Assess the cost of replacing filters, the frequency of their replacement and their constant availability for sale.
- If fresh air will be taken in through a ground heat exchanger, then choose a ventilation unit equipped with a bypass.











