Facade insulation system Termotek MV Facade part Base: brick, aerated concrete, ceramic block, concrete (1) Work begins with preparing the base: it must be leveled, cleaned, and existing metal objects (nails, profiles, etc.) removed. Primer Expert Universal, Expert Deep Penetration, Standard (2) To improve the adhesive properties of materials and the base, the wall is primed with Expert Universal, Expert Deep Penetration, Standard. The composition is applied with a brush. Ecotek adhesive layer (3) For the installation of insulation boards, a specialized Ecotek adhesive composition is used. It is applied with a notched trowel to the slab, holding the tool at an angle of 60°. Mineral wool board (4) Mineral wool boards begin to be glued from the corner of the building, adhering to the principle of brick bonding (vertical seams should not coincide). Disc-shaped dowels (5) To strengthen the structure, disc-shaped dowels are used; they are placed in the T-shaped joints of the seams, as well as 2-3 in the center. Base reinforced layer Termotek (6) Proceed to the construction of the base reinforced layer, for which the Termotek plaster-adhesive mixture is applied to the outer surface of the mineral wool using a trowel. Alkali-resistant mesh (7) The alkali-resistant mesh is pressed into the material to reinforce the wall. The mesh is installed with an overlap of approximately 10 cm. Expert Decor primer (8) The next step is priming before applying the finishing coat, for which the Expert Decor composition is suitable. The material is applied in a thin layer. Decorative plaster Bark beetle, Fur coat (9) Decorative plaster Bark beetle / Fur coat is used as a finishing layer. The composition is applied in a thin layer (about 3 mm), it is designed to decorate the insulation and create additional protection for the facade. Primer Standard (10) Apply a layer of finishing primer using the Standard composition. Wait for it to harden. Facade paint (11) The final stage is painting the facade with suitable paint. Basement part Base: brick, concrete (1) First, the surface of the base is cleaned of soil, dust, concrete deposits and other contaminants. Repair existing chips and potholes. Waterproofing layer Aquastop (2) A mandatory step when insulating the base is waterproofing work. To do this, use the coating composition Aquastop, which is applied in 2 layers. The material will protect the structure from dampness and mold. Ecotek adhesive layer (3) Ecotek adhesive composition is used to attach insulation boards. Apply the mixture using a spatula. Extruded polystyrene (4) Pre-cut insulation boards are applied to the base and pressed tightly, tapping lightly. Work begins from the bottom row, moving upward. Disc-shaped dowels (6) For additional strengthening of the structure, disc-shaped dowels are used. A hole for each element is pre-drilled with a hammer drill. Alkali-resistant mesh (5) An alkali-resistant mesh is used to construct the reinforcing layer. It must be secured with an overlap, otherwise cracks may appear in the structure. Base reinforced layer Termotek (7) To install the mesh, first apply the Termotek plaster-adhesive layer, and then press the mesh tightly against the insulation and press it in. Tile adhesive (8) The facing tile is used as a finishing coating. For gluing, a specialized adhesive composition is suitable, which is applied to the surface of the base with a notched trowel. Facing material (9) The facing elements are pressed tightly against the adhesive layer. The mixture that appears on the front surface is removed with a rag.
Energy saving is one of the most important issues in modern construction. Manufacturers offer new façade materials and innovative thermal insulation masonry mortars that can reduce building heating costs. Another way is to use external thermal insulation systems. This is a whole range of measures for finishing the facades of buildings aimed at preserving thermal energy inside the building. In addition to its main function, SFTK increases sound insulation, helps protect the facade from precipitation and overheating, and prevents the formation of condensation on the walls, increasing the service life of the entire building. Today there are several options for facade insulation systems. The lightweight “wet” system is the simplest and most economical. The work is carried out in compliance with a certain technology. First, using an adhesive composition, heat insulating sheets are mounted on a previously prepared (primed) base, then they are reinforced with dowels. The adhesive mixture is selected according to the type of insulation. Then a layer of reinforcing mesh is installed, which is necessary to give strength to the entire system. At the last stage, plastering is carried out. The plaster system for insulating facades involves the use of a wide arsenal of decorative finishing coatings of any colors and textures. The second option for external insulation is the heavy facade system SFTK. Unlike the first technology, it involves using a denser reinforcing mesh, installing anchors before installing the insulation, and applying a thick layer of plaster. Heavy SFTK with external plaster layers has high heat-retaining capabilities and reliably protects the facade from damage, but the work and necessary materials are more expensive.
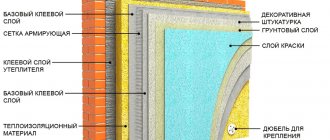
Lightweight plaster insulation system
Fundamental design solution for a lightweight plaster insulation system. 1 – capital part of the wall; 2 – adhesive layer; 3 – effective insulation; 4 – reinforced layer; 5 – reinforcing mesh; 6 – primer; 7 – protective and decorative layer; 8 – dowel-anchor
It most often includes the following layers and elements:
- rigid, effective insulation boards (mineral wool or expanded polystyrene);
- adhesive layer for attaching slabs to the base; if necessary, additional fastening with special dowel anchors is used;
- a reinforced layer in which a reinforcing polymer or fiberglass mesh with an alkali-resistant coating is embedded;
- primer to improve the adhesion of the protective and decorative layer;
- protective and decorative layer;
- additional elements that provide reinforcement to the corners of the building, window and door slopes, connections to the roof (roof), window and door blocks, plinth, etc.
The total thickness of the reinforced layer, primer and protective and decorative layer is from 3 to 8 mm. If, for example, “breathable” facing materials are used as the finishing layer, the thickness of the plaster layers can reach 15 mm or more.
Important!
Experiments carried out by an international research group led by Doctor of Technical Sciences Alexander Ketov from Perm, Russia, showed that the source of poisoning of people in a fire can be chlorine-containing compounds formed from fire retardants contained in self-extinguishing polystyrene foam (PPS-S). The worst of these compounds is phosgene (carbonic acid dichloride).
Let's consider PPS-S with a density of 30 kg/m3. According to the group, from 1.0 liters of this insulation, thermal decomposition in air produces 291.6 mg of phosgene. As is known, its two-minute exposure to air at a concentration of 3.2 mg/l is fatal. This means that the thermal decomposition of only 1.0 liters of PPS-S is sufficient to create a lethal concentration of phosgene in 92.2 liters of air.
Organobromine compounds as fire retardants are no less dangerous than chlorine-containing compounds. Thus, bromophosgene has approximately the same toxicological effects as phosgene.
As a rule, lightweight plaster systems are used based on dry building mixtures, from which adhesive and reinforcing masses are made. The individual components of these systems must be carefully selected for compatibility with each other and must be systematically tested for thermal expansion, water absorption, frost resistance, vapor permeability and adhesion of layers to each other.
Methods
So, insulating the walls of a private house from the outside has many more advantages than disadvantages
But it is important to understand the features of individual materials and structures
Houses made of expanded clay concrete blocks are insulated from the outside most often using:
- mineral wool;
- polystyrene foam;
- its more modern analogue is penoplex.
The first option is preferable due to zero fire hazard and low cost. But the problem is that the affordable price is largely negated by the need to organize a protective screen. Polystyrene foam is lightweight, also belongs to the budget group of materials, and it can be installed quickly.
Quite often people are faced with the problem of insulating the external facades of old panel houses. The main condition for high-quality thermal protection is its design in which the permeability to vapor increases from the living space to the street. There is no need to remove the outer cladding of the home; a number of technologies have been developed that make it possible to install thermal insulation on top of it.
When choosing a suitable option, you should give preference to solutions that do not overload the foundation and absorb the least amount of water. It is the significant heaviness and the presence of the dew point inside the hygroscopic thermal protection that cause the most problems for the owners of panel buildings.
Insulating dacha houses for winter living is very important.
It is imperative to provide thermal protection:
- internal floors on the ground;
- floors of the first tier (if the foundation is not insulated);
- external walls;
- cold attic floor or attic roof.
It makes no sense to single out any one of these elements, even something as important as walls. If at least one area is not insulated, all other work can be considered wasted, as well as the money spent on it. The walls must be equipped with waterproofing and vapor barrier; when choosing mineral or environmental wool for insulation, it is necessary to leave a ventilated gap of 50-100 mm. The insulation of a panel house from the outside has its own specifics. The slightest irregularities should be removed, and ideally, leveling should be done using a primer.
If paint is splitting or other finishing is falling off, all these layers are removed, even if the technology does not require such manipulation. In most cases, polystyrene foam is used for external thermal protection of concrete walls, and the most reliable way to attach it is to combine glue and dowels. The work is carried out from the bottom up; a special bar is installed at the lowest point, designed to prevent the material from slipping. Please note: it is possible to replace dowels with plastic nails. Regardless of fastening methods, it is necessary to carefully monitor any gaps that appear.
The insulation of the junction of the wall and the roof deserves a separate discussion. This work is done traditionally using stone wool, but for lovers of modern technologies it is better to focus on Macroflex foam. In many cases, a steel bonding apron is formed. Whether it is needed in a particular house, on a particular wall, only trained specialists can find out. The insulation of junctions is too complicated to be done properly by the owners of the house themselves or by randomly found freelance craftsmen.
Advantages of external thermal insulation systems
External insulation is considered the most popular - it has repeatedly proven its effectiveness. Internal thermal insulation, of course, also plays an important role in construction, but its advantages are incomparable to external ones. An external thermal insulation system has many advantages.
Reduced environmental impact
External insulation protects walls from overheating and hypothermia in any season of the year. As a result, the durability of the building increases, cracks do not appear on the facade, the plaster does not peel off, and the seams do not depressurize.
Exposure to moisture is eliminated: with external thermal insulation, the destructive effects of snow and rain are significantly reduced. There are also no ice formations in the thickness of the wall surfaces due to capillary moisture and its condensate.
Condensation protection
In the cold season, it is not uncommon for the temperature of the façade walls to drop below the “dew point”. As a result, condensation forms on the internal surfaces. The external façade insulation system prevents its appearance.
Smoothing or eliminating cold bridges
External facade insulation technology involves heat accumulation by the walls. As a result, the temperature of the coolant in the heating system decreases and the orientation of the building ceases to play a role - the temperature dependence disappears. “Bridges of cold” either smooth out or disappear.
Creating the perfect wall surface

Due to heat insulators, the wall structures of the building look smooth, and various defects inherent in stone and concrete are hidden by insulation.
High noise absorption
Most insulation materials are considered good sound insulators. Their use reduces noise coming from the street and creates a comfortable environment in the premises.
Durability
Although heat-insulating materials are constantly exposed to the environment, their production technology has long made it possible to create products that last for decades without losing their initial performance properties. 30-50 years is the average service life for any high-quality insulation.
Standards
Everything that happens in the atmosphere, including the phenomena of natural cycles and the consequences of technogenic human activity, causes increasingly sharp temperature changes, which is strongly reflected on the surfaces of structures and buildings. Without additional protection, facades gradually deteriorate under the aggressive influence of the environment.
As a result of such exposure, the building cannot effectively conserve heat during the cold season. Today in construction it is believed that, regardless of what material the walls were built from, it is necessary to carry out auxiliary insulation with a material at least 50 mm thick.
According to Russian standards, for a brick-silicate wall built with 1.5 bricks, it is necessary to use insulation with a thickness of 100-120 mm. Such a house will fully comply with current energy efficiency requirements. Naturally, the market value of such a house with subsequent insulation using facade insulation technology increases almost 2 times, but an insulated facade will subsequently bring serious savings on repairs and heating.
What is a building thermal insulation system
Insulation systems are complex finishes applied to the walls of a building, the main function of which is to preserve thermal energy indoors.
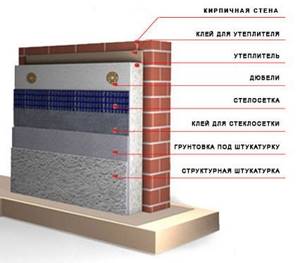
The thermal insulation system is a “pie”, which includes the following layers:
- Thermal insulation material;
- Adhesive composition;
- Reinforcing layer;
- Decorative finishing.
This design is not only an excellent heat insulator, but also has a protective function, protecting the load-bearing walls of the house and significantly extending its service life.
As insulation, various heat-insulating materials with different properties can be used: heat insulator made of porous concrete, polystyrene foam, mineral wool, extruded polystyrene foam, etc. The material can be in the form of slabs or rolls. To attach the heat insulator to the wall, special facade glue and dowel-nails are used. A reinforcing mesh and a decorative layer are applied on top.
Classifications
To protect the thermal insulation layer from destructive and pervasive atmospheric influences, various facade insulation technologies have been developed. Today, there are several options for external insulation systems for facades: wet and ventilated, siding, thermal panels, etc. Each technology has its own characteristic features.
Thermal insulation board
The efficiency of insulation work and the durability of the system largely depend on the façade slab. Facade insulation systems are made in two ways - contact and hinged. Contact methods - wet insulation, suspended methods - insulation of a ventilated facade.

If we consider the issue from the standpoint of cost, then the most economical and at the same time effective technology for insulating facades can be defined as thermal insulation systems with “wet” protection of each subsequent layer of insulation.
Thermosuba façade insulation system is economical and durable.
Over the course of 16 years, the Termoshuba has surpassed most similar systems presented on the market in Russia and the CIS countries in terms of application volumes, where a total of over 10 million square meters of the system have been installed. Consumers highly rated the quality of the system for a number of important characteristics. Despite the popularity of the “Termosuba” among consumers, research data from independent and authoritative experts is needed to determine the most important characteristics of the system, and, above all, the durability of all components. In this regard, at the request of Sarmat-Thermo LLC, the State University of Moscow conducted its own tests to determine the durability of two versions of the Termoshuba facade thermal insulation system. It is well known in the professional community that the State Institution “City Coordination Expert Scientific Center of Moscow” is the most competent organization in the field of examination of facade materials, operating with the full support of the Moscow government since 1996. In accordance with expert opinion No. 100 dated 10/05/2010. after 90 cycles of accelerated climatic tests according to method 2 of GOST 9.401-91 it was established: “Based on the totality of assessment and preservation of protective and decorative properties, the durability of the coating of thermal insulation systems “Termoshuba M” and “Termoshuba P” is 10 years with strict adherence to the technology of application and operation in conditions of an open atmosphere of a temperate climate."
For reference: The thermal insulation system for facades "Termoshuba" is a multi-layer structure, balanced in its characteristics, consisting of insulation boards attached to the surface of the walls with an adhesive polymer-cement composition; protective layer reinforced with fiberglass mesh; finishing coating made of plaster and paint. In terms of most physical and mechanical characteristics, the Termoshuba system has significant advantages over other façade systems.
Taking into account the mutual combination of structural elements, increased demands are placed on all components of the façade insulation system. The subject of special control is the calculation of vapor permeability. All layers of a light plaster façade insulation system must be combined and not impair each other’s characteristics. 16 years of operating experience in the CIS have shown that the Termoshuba system is an effective, balanced solution for insulating facades. All components of the system are ideally applicable in the conditions of the central part of Russia; experimental projects have been implemented in Khanty-Mansiysk. The necessary advice can always be obtained from the company’s technical specialists. The developer of the lightweight plaster system “Termoshuba” is the Construction Holding “Sarmat”. Founded in 1991 in Belarus. For 19 years, it has been successfully developing and implementing energy-saving technologies in mass construction. Among them are the most important areas: – design, supply and installation of the lightweight plaster system “Termoshuba” for external thermal insulation of facades of residential, administrative and industrial buildings; – the largest production of dry construction mixtures . In Russia, Termoshuba produces and supplies all components for the façade insulation system . The company's specialists provide design and technical support during installation. Our specialists will help you calculate material consumption and much more. Today, Sarmat-Thermo has production facilities in the Moscow region and offers a wide selection of Sarmat dry building mixtures , including: mixtures , tile adhesive , , plaster , screed , leveling , waterproofing .
Stage 1. Facade preparation
Facade preparation
When preparing building facades, if necessary, drainpipes, signs, metal protective elements of window openings, parapets, horizontal wall ledges and other elements that impede the work should be dismantled.
In places where elements, equipment and communications are located on the walls, the dismantling of which is unacceptable, local breaks should be made in the insulation structure in accordance with the units and parts developed in the design documentation.
Preparing walls and their surfaces
Before preparing the walls and their surfaces for the implementation of the “Termosuba” system, it is necessary to identify its outer layer, plaster and finishing layers that have collapsed or are not connected, for one reason or another, with the main material of the walls. In case of destruction of the outer layer of wall material to a depth of up to 50 mm or the need to strengthen the walls, it is allowed to apply M75 cement-sand mortar over a metal mesh. Local protruding parts of the base with a thickness of more than 30 mm should be knocked down, and overhangs of finishing layers should be removed. If the wall surfaces are contaminated with substances that reduce the adhesion of adhesives, it is necessary to clean the bases with steel brushes, spatulas or the jet method.
In case of deviations of wall surfaces from the indicators standardized in SNiP 3.03.01-87 “Load-bearing and enclosing structures” or destruction of wall surfaces to a depth of up to 30 mm, leveling must be carried out with the plaster composition “SARMALIT NM” (“SARMALIT NMM”). If the planes of the walls differ by more than 30 mm, the surfaces of the walls must be leveled by gluing a layer of expanded polystyrene or mineral wool of variable thickness. In this case, leveling pads made of expanded polystyrene grade PSB-S-25 according to GOST 15588-86 or PSB-S-25F, or mineral wool should be located under the entire area of the main glued heat-insulating board. Between the main insulation, leveling pads and the base of the wall, the adhesive composition “SARMALEP” (“SARMALEP P” or “SARMALEP M”) must be applied in a continuous layer. The use of leveling pads must be taken into account when calculating the length of the dowel-anchor.
Walls painted or finished with stone chips should be cleaned with wire brushes to remove chips or paint loosely bound to the wall. Substrates tiled with hog tiles or covered with glass ceramics should be tapped to identify peeling areas. The discovered areas must be removed and leveled with the plaster composition “SARMALIT NM” (“SARMALIT NMM”). Before installing the first row of insulation boards, wooden slats can be used as temporary horizontal support. In this case, the reinforcing mesh is inserted under the lower edge of the slabs and behind the insulation slabs by at least 100 mm, and its part located under the slabs must be glued to the load-bearing base.
Also, in the basement part of the building at the bottom of the insulation, instead of a protective corner, it is possible to use a base profile, on which the first row of insulation boards rests and thanks to which a higher quality implementation of the “Thermofur coat” system is achieved.
Heavy plaster insulation system
Model of a heavy plaster insulation system
In such a “classical” system, the total thickness of the plaster layers is, as a rule, 20–30 mm, the load-bearing functions are performed by a metal reinforcing mesh and flexible (movable) fastening elements, by means of which effective insulation slabs are attached to the main part of the wall. Compared to a lightweight stucco system, a heavy stucco insulation system uses less durable mineral wool or expanded polystyrene insulation boards.
Heavy plaster systems with movable fasteners are distinguished by the absence of strict requirements for the quality of the surface of the main part of the wall. This is especially important when insulating existing buildings.
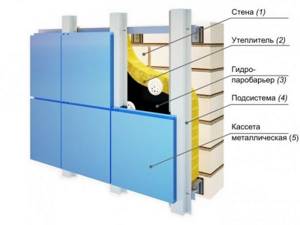
Ventilated facade system
This system includes the following elements:
- Horizontal and vertical guides fixed to the facade of the building using special fasteners;
- Thermal insulation is usually mineral wool, which increases the degree of fire safety;
- Membrane that protects from wind and moisture;
- Protective screen - this element can be represented by various materials: porcelain stoneware, metal cassettes, composite panels or siding.
Ventilated facade system
This system received this name because an air gap is provided between the heat-insulating layer and the external protective screen. Air flows remove vapors escaping from the room, which increases the efficiency of the insulation system.
Ventilated insulation system
Fundamental design solution for one of the options for a suspended ventilated façade:
1 – capital part of the wall; 2 – leveling plaster layer; 3 – gasket; 4 – supporting bracket; 5 – support bracket; 6 – pressing tongue; 7 – dowel-anchor axis for attaching the bracket to the main part of the wall; 8 – vertical support profile; 9 – rivet axis and rivet; 10 – non-flammable effective insulation; 11 – wind protection; 12 – dowel-anchor; 13 – ordinary clamp; 14 – end clamp; 15 – rivet; 16 – sealing gasket; 17 – facing slab (ceramogranite).
In general, a curtain system ventilated by outside air, or a hinged ventilated façade (ventilated façade), consists of three main elements:
- external cladding (rain screen);
- cladding frame (sub-cladding structure);
- effective thermal insulation, usually made of mineral wool.
Installation of ventilation facade. Cladding frame made of aluminum profiles
In a ventilated facade with a wooden frame (it is used mainly in low-rise buildings), it is advisable to have low-density thermal insulation, protected from blowing and fiberization by windproof material. It allows water vapor to diffuse through the wall in cold weather into the ventilated gap, but does not allow external moisture to enter the insulation. In the case of a metal (galvanized or stainless steel, aluminum) frame, in some cases, thermal insulation of relatively high density (rigid slabs) is advisable. In this case, wind protection may be absent. Moreover, in any case, water vapor passes from the room into the ventilated gap without much interference.
In a ventilated facade, due to the ventilation of the air gap, the insulation is in more favorable conditions compared to non-ventilated systems. Thanks to the gap, the temperature and humidity conditions of the premises are improved, and the actual thermal conductivity of the insulation is lower than in walls without a ventilated gap. In addition, the ventilated façade prevents overheating of the wall.
Due to the absence of “wet” processes, the ventilated façade can be installed at any time of the year. Control of work progress is simple and reliable. The ventilated façade has a high degree of maintainability. Before installing it, it is not always necessary to level the surface of the main part of the wall. The service life of a ventilated façade without major repairs is approximately up to 50 years.
How much does an insulation system cost?
The cost of an insulation system depends on many circumstances. If we assume that the standard heat transfer resistance of the outer wall is 3.2 m2×°C/W, then the approximate prices of not the most expensive insulation systems in Belarus are as follows (for insulation thickness up to 15 cm):
- light plaster systems – 35–50 US dollars per 1 m2;
- heavy plaster systems – 30–45 US dollars per 1 m2;
- ventilated systems – 50–90 US dollars per 1 m2;
Of course, the lower the quality of the elements of insulation systems, the lower not only their cost, but also their reliability and durability.
Here you can read about insulation of frame-sheathing walls and
Are walls made of cellular concrete blocks warm?
Mounted systems
Wall mounted facade insulation systems are considered more modern and have many advantages over the contact method:

- their use makes it possible to reduce energy costs for heating by more than 1.5 times;
- no need to prepare the base before installation;
- can be installed at any time of the year;
- service life is about 30 years.
Insulation boards in this case are attached to the surface mechanically - dowels or load-bearing elements are used. At a distance of 2-5 cm from the outer part of the heat insulator, elements of external finishing are placed, which perform two functions at once: the first is decorative, the second is protective.
The surface layer of the system is made of various materials - from stone and metal to ceramics and wood. You can decorate the facade with glass, which has become very popular in the decoration of office buildings. In this case, the insulation board is covered with white or black glass fiber canvas. An important advantage of ventilated facades is the removal of moisture accumulated in rooms without forced ventilation.
For the manufacture of curtain-type facades, sandwich panels are often used - structures consisting of a heat-insulating core and 2 steel sheets. They are suitable for finishing both new and reconstructed buildings. Products from different manufacturers differ in color, size and other features. However, high-quality sandwich panels are united by high reliability, durability and wide functionality.
Grinding and expansion joints

After applying the leveling layer, several hours pass depending on the weather. The tool is a construction float coated with polyurethane. After hardening, the structure is cut through to form longitudinal and transverse seams. The expansion joint serves to reduce the load on structural elements in areas prone to damage. Danger may arise from an earthquake, ground settlement, or other natural and physical impacts on the structure. The cuts are made with a special tool, dividing the wall into conditional blocks that give the building elasticity. The seams are filled with insulating material, for example, mastic. The width of the seam is 6 mm, and the distance between the cuts made is no more than 15 m. The extreme seam, going from top to bottom, is made no closer than 150 mm from the corner of the house. The cutting disc must cut through all layers, including the mesh.
Well masonry system
This system is made in three layers: the inner layer is load-bearing, the middle layer is thermal insulation, and the outer layer performs protective and decorative functions. The outer layer is usually made in the form of brickwork. This insulation system can be made using various thermal insulation materials: expanded polystyrene, mineral wool, perlite, as well as other materials that are highly durable.
Well masonry system
A distinctive feature of the well masonry system is its low price. The use of the system is justified for any type of building, as it is characterized by high thermal insulation performance.
In addition to the thermal insulation function, the well masonry system creates excellent sound insulation, which is very popular in large cities where there is a high noise level.
Installation is carried out strictly in accordance with the instructions.
Contact method
Contact insulation is based on the use of special plates made from different raw materials. This includes mineral wool, polystyrene foam, and cellular glass. For finishing, thin-layer decorative plaster is used.
Plaster finishing simultaneously performs a protective and decorative function. Considering the quite reasonable cost of insulation, the facade becomes both beautiful and quite warm. The thermal insulation system of the facade is applicable to residential buildings, both existing ones and new buildings.

Such a facade makes it possible to reduce the thickness of the walls and increase them in terms of energy savings and noise insulation. The fire safety of the “wet facade” in question is also noted.
In addition, the “wet method” does not actually increase the load on the structure of the structure. When using this technology, there is an undeniable possibility of continuous thermal insulation, even despite the impressive area of the facade.
Types of contact systems
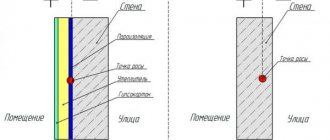
There are two types of contact insulation system for facades - light and heavy wet method. In the latter case, the functions of the supporting structure are performed by a metal mesh, which is connected to the wall and insulation with fasteners (braces and spacers).
The easy wet method involves installing a heat-insulating layer consisting of facade slabs with glue to the outer part of the wall. After fastening, the insulation material is again covered with glue, on top of which a reinforced glass fiber mesh is placed. If necessary, the slabs are attached to the wall not only with glue, but also with dowels.
Advantages of complex systems for facades
When using facade insulation systems, the color scheme of the facade can be changed at any time. Taking into account the thermal insulation system of the facade at the design stage of the building saves on expensive building materials for walls. The difference in price for a medium-sized building with and without insulation is on average about 150 thousand rubles, but if you take into account the heat savings, such finishing will pay for itself by reducing heating bills within 5-7 years.
If the structure is built from foam concrete, based on the insulation system, it is possible to use a block whose thickness is 10-15 cm thinner. When erecting a building made of brick, the fence structures are mounted in one brick and are 64 cm.
Criteria for choosing insulation
When selecting facade insulation, it is necessary to take into account the type of wall material, thickness, architectural features and dimensions. Climate and weather conditions are also taken into account. The thickness of the insulation layer is determined by the building density of the area - a building that stands alone requires a larger layer of insulation than a house located in the central part of a densely populated village.

The thermal insulation layer in facade systems is made from extruded or ordinary polystyrene foam, as well as from laminated or ordinary mineral wool. Both types of material are supplied in slabs. Mineral wool is made from glass, soda, limestone and sand. Its structure is represented by glassy thin fibers. Positively distinguished by high vapor permeability.
Making a choice
In order to determine what material to use for external wall insulation, you should answer the following questions:
- What material are the walls made of?
- What is the humidity in the area where the house is located?
- How high is the groundwater?
- What is the financial possibility of purchasing 1 m2.
- How many people will be involved in the work?
If the walls of the house are made of wood, then materials such as polystyrene foam, foil insulation and glass wool are not used.
Expanded polystyrene is flammable, which increases the fire hazard of a wooden structure.
Foil insulation almost completely seals the structure, resulting in wood rotting and mold formation.
At high humidity and close proximity to groundwater, glass wool is not used for insulation of wooden houses.
The most suitable material for insulating wooden walls is cork insulation, but its cost is quite high, so before you go to the store to purchase this product, you should make correct calculations of the total cost.
You can insulate a wooden house with cork slabs yourself. Cork is lightweight and is attached to a wooden base using nails or self-tapping screws.
If you need to insulate the outside of a stone or brick house, then polystyrene foam is the most suitable material for this purpose.
Even if groundwater is located close to the construction site, this fact does not have a negative impact on the quality of the thermal insulation layer.
As for financial costs, expanded polystyrene is the most inexpensive of the known materials for thermal insulation of walls.
To insulate brick and stone walls, basalt slabs are used, which do not absorb moisture and have high thermal insulation properties. The price of this material is quite high, but the heating costs of a house insulated with stone wool will be significantly reduced.
Installation
You can install a facade insulation system with your own hands, however, specialists with experience will cope with this task faster. Insulation work involves several stages, after each of which you need to check the absolute evenness of the surface, cleanliness and smoothness.

It is very important that there are no depressions or cracks on the surface of the walls - otherwise the finishing layer will not be continuous, and the thermal insulation will become ineffective.
Why and how to insulate a house from the outside
External thermal insulation of private houses is done to maintain a comfortable temperature in living quarters in winter. The key factor in resolving this issue is often a large number of cracks through which heat is blown out, or the weakness of the heat supply system. But the main reason leading to heat loss is that the walls of the building are made of materials with a high thermal conductivity.
During insulation, only the outer sides of the walls of a residential building are treated with thermal insulation agents. Internal insulation of surfaces leads to the fact that the heat insulating agent blocks the access of heat directly to the wall. Because of this, the dew point shifts towards the room, humidity rises and condensation begins to occur. There are three main ways to insulate the outer part of the walls of a house:
- Fastening with adhesive composition of thermal insulation agents and subsequent plastering.
- Arrangement of three non-ventilated layers of the wall, when the insulation is fixed with mortar. Afterwards, a small air layer is left and the outer wall is made of 1 brick.
- Making the façade with ventilation - insulation is applied on top of the waterproofing layer. It is covered with wind protection and sewn up with vinyl siding or other protective and decorative material.
Insulation of the outside of the house with mineral wool under siding is mainly carried out in the case of a facade with ventilation
But when choosing an option for insulating private houses from the outside, you need to take into account that any method of thermal insulation has a specific technology. At the same time, the rules for fastening insulating materials or applying heat-insulating compounds differ in the admissibility of their use in different weather conditions
For reference!
The technology for working with a specific thermal insulation material affects the time of year in which insulation work can be carried out.