Home › Ventilation › Ventilation of residential buildings
You can order ventilation of a residential building with turnkey installation by calling us by phone in Moscow. We design and supply ventilation systems throughout Russia. We ask you to send your written application by email or through the form on the website.
- The influence of indoor ventilation on humans
- Regulatory Requirements
- Residential building ventilation systems
- Design of ventilation in a residential building
- Ventilation calculation
- Installation
- Recommendations from experts
Send an application and receive a CP
The purpose of ventilation is to provide sanitary and hygienic conditions for a person to stay indoors - temperature, relative humidity, air speed (mobility) and air purity, for which ventilation devices must assimilate or remove excess heat, moisture, and gases , vapors, dust while maintaining a certain air mobility in the room. Ventilation systems are designed to ensure air parameters within the work area. The working or service area of a room is a space 2 m high above the floor or platform where there are places for permanent or temporary residence of people.
“Standard Climate” is a professional climate control company, ready to implement turnkey solutions to any problems regarding climate control and other engineering equipment. We will carry out a full cycle of work: selection of equipment, design, installation, delivery and maintenance. You can submit an application on the website airclimat.ru. Call now: +7(499) 350-94-14
. Submit your application
Heating systems
6.3.1. In heated rooms, normalized air temperature must be maintained.
6.3.2. In buildings where there is no heating system, it is allowed to use local heating in workplaces and equipment repairs.
6.3.3. Flights of stairs may not be heated in cases provided for by the provisions of SNiP.
6.3.4
Heating is designed taking into account uniform heating and taking into account the heat consumption for heating air, materials, equipment and other things. A heat flux of 10 W per 1 sq. is taken as a unit.
m.
Paragraph 6.4 considers all the requirements for heating pipelines, where they can be laid and where they cannot be laid, they regulate the laying methods, and the service life is included in the design. Indicate the permissible error standards for the slopes of laid water, steam and condensate pipes under various conditions of the direction of steam movement and water speed.
Paragraph 6.5 discusses everything related to heating devices and fittings , which radiators can be installed, connection diagrams, locations, distance from the walls.
Paragraph 6.6 considers all issues related to stove heating : in which buildings it is allowed, what are the requirements for stoves, the temperature of their surfaces, sections and heights of chimneys.
VI. Design – stage 3. Implementation of plans and diagrams of ventilation systems.
To carry out any drawings in the construction industry, the main platform is CAD AutoCAD; if we are talking about the design of utility networks (in particular ventilation systems), then to carry out more detailed and high-quality projects it is necessary to use additional software - CAD MagiCAD. However, over the past couple of years, the BIM design program Revit has begun to gain popularity in Russia, allowing you to create a complete information model of a building, including architectural, design and engineering solutions. The MagiCAD and Revit programs have their pros and cons, so the format for issuing documentation to the Customer is determined at the time of drawing up the design assignment. Read about the comparison of software systems for design in this article.
Plans and diagrams of ventilation systems must be carried out in accordance with GOST 21.602-2016 and GOST R 21.1101-2013, which were already mentioned in Section III “Regulatory documents”
All designers have their own, somewhat individual culture of documentation (callout text styles, line thicknesses, symbols of network elements and equipment, and so on), but the main requirements for any Customer are the readability of drawings (correctly selected scales of the drawing and callout text) and information content drawings (all callouts necessary for installation and commissioning of systems are correctly placed).
The influence of indoor ventilation on humans
From the point of view of energy saving, modern research has proven that due to ventilation systems in a house or apartment, up to 30 percent of all possible heat losses occur here.
By installing modern plastic windows in the premises of the house, we naturally significantly save heat here, but at the same time, we also significantly reduce ventilation, that is, air exchange here. For a person, such improvement of our homes, as a rule, does not lead to an improvement in the conditions of his work and rest, but rather the opposite.
As modern special studies have shown, a reduced level of ventilation in rooms leads to a significant lack of oxygen here, and, accordingly, to our rapid fatigue when doing any work, our headaches, as well as our poor and uncomfortable rest and sleep here.
It has also been fully proven that insufficient ventilation in the room always leads to increased humidity in the house. In such an unventilated house, as a rule, the windows and walls always “cry”, and especially with the onset of cold weather. Mold and mildew often appear on the ceilings and walls of rooms; their appearance clearly deteriorates and does not bring us any satisfaction.
In addition, fungal spores from the walls, spreading in the air of the house, can cause various, and quite serious, diseases of the respiratory system in humans. We have now turned our homes into a thermos, where we are warm, but not at all comfortable to be, and sometimes even dangerous to our health. Therefore, “proper” ventilation in the house significantly increases the comfort of working and living in it.
Types of residential buildings
Considering residential buildings, we can divide them into standard and individual. Typical are sample templates that demonstrate ready-made solutions where key points have been developed. They are used for large-scale developments.
In such blanks, minor adjustments are made according to local conditions. For example, orientation to the area or location of connection to networks.
A special house, with unique layouts and facades, with personal wishes and ideas is called individual.
There is also a division into multi-apartment and single-apartment buildings.
Multi-apartment buildings are those that have shared premises and utilities outside the apartment boundaries.
This also includes boarding schools, hostels and hotel complexes. Often in high-rise buildings there are other non-residential objects: parking lots, retail outlets, service organizations and others.
Air supply
To create an air space that meets hygienic and technological requirements,
establish the required frequency of air exchanges. For a number of premises it is found in the codes of rules, for others it is determined by calculation.
In order to save money and ensure uninterrupted operation, ventilation is used with natural draft. Air supply is ensured by supply air infiltration
and through door leaks. The direction of movement of air masses is organized by the windows to the bathroom, bathroom and kitchen.
With air supply for both the whole house and apartment
spaces collide not only with workers from organizations involved in the construction or operation of a building, but also with ordinary residents. For example, over time, the traction in the channels disappeared. Or after installing plastic windows, an influx from the common corridor was noticed. Of course, the tenant is looking for a solution to the problem. And it is imperative to take into account that there is a regulatory framework that regulates this area.
a complex of project documents in reality
The facility must undergo state or independent examination to ensure compliance with the requirements of the State Construction Committee of Russia. And only after a positive conclusion is a set of working drawings developed.
Regulatory Requirements
Let's start by studying the current regulatory documents. Current SNiPs for ventilation of residential buildings are 2.04.05-91 “Heating, ventilation and air conditioning” and 2.08.01-89 “Residential buildings”.
For the convenience of the reader, we will bring together the key requirements of the documents.
Temperature
For a living room, it is determined by the temperature of the coldest five-day period of the year.
- If its value is above -31C, it is necessary to maintain at least +18C in the rooms.
- When the temperature of the coldest five-day period is below -31C, the requirements are slightly higher: the rooms must be at least +20C.
For corner rooms that have at least two common walls with the street, the norms are 2 degrees higher - +20 and +22C, respectively.
Useful: the variability of requirements is due to the fact that at low temperatures and increasing heat loss, the dew point (the point in the thickness of the enclosing structure where condensation of water vapor begins) shifts towards the inner surface. The indicated temperatures exclude freezing of the wall.
Consequences of freezing.
For bathrooms, the minimum temperature is +18C, for baths and showers - +24.
Air exchange rates
What are the standards for ventilation of residential premises (more precisely, the rate of air exchange in them)?
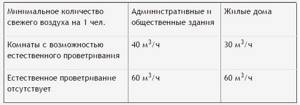
| Room | Minimum air exchange |
| Living room | 3 m3/hour per 1 m2 area |
| Kitchen | 60 m3/hour for electric stoves and 90 m3/hour for gas stoves |
| Bathroom, toilet room | 25 m3/hour |
| Combined bathroom | 50 m3/hour |
Additional requirements
What other requirements and recommendations can be found in SNiP for heating and ventilation of residential buildings?
- The ventilation scheme may provide for air exchange between separate rooms. Simply put, you can organize an exhaust hood in the kitchen, and air flow in the bedroom. Actually, the document specifies the recommendation: exhaust ventilation should be provided in kitchens, bathrooms, bathrooms, toilets and drying cabinets.

In Stalinka buildings you can see two ventilation grilles in the kitchen area. One of them opens into a chimney: the houses were built for stove heating.
- The ventilation of the apartment must be connected to a common ventilation duct no lower than 2 meters from the ceiling level. The instructions are intended to minimize the likelihood of the rod overturning in windy weather.
- When using separate rooms in a residential building for public needs, they are equipped with their own ventilation system, not connected to the general one.
- When the temperature of the coldest five-day period is below -40C for three-story and higher buildings, it is allowed to equip fresh ventilation with heating systems.
- Gas boilers and water heaters with combustion products discharged into general ventilation are allowed to be installed only in buildings no higher than five floors. Solid fuel boilers and water heaters can only be installed in one- and two-story buildings.
- It is recommended to supply supply air to rooms with constant occupancy. Which, in fact, again leads us to the already mentioned scheme: air flow through the living rooms and exhaust through the kitchen and bathroom.
Acceptable humidity levels, temperature dependence
Humidity and temperature standards in office premises are specified in SNiP 41-01-2003. The optimal indicators are:
- Air temperature from 20 to 24 °C.
- Air humidity is from 35 to 60%.
The normal air temperature may change depending on the employee’s workload and the time of year. With a high level of physical activity in the cold season, it is 18-20°C. Violation of these norms is punishable at the legislative level. According to Part 1 of Article 5.27.1 of the Administrative Code, the amount of the fine is:
- from 2000 rubles for officials;
- up to 50,000-80,000 for legal entities.
Sanitary rules and regulations
- SanPiN 2.2.4.548-96 “Hygienic requirements for the microclimate of industrial premises” - these sanitary rules and standards are intended to prevent the adverse effects of the microclimate of workplaces and industrial premises on well-being, functional state, performance and human health.
- SanPiN 2.4.1.3049-13 “Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for the structure, content and organization of the operating mode of preschool educational organizations” - these sanitary and epidemiological rules and standards are aimed at protecting the health of children when carrying out activities related to education, training, development and health improvement, care and supervision in preschool organizations.
- SP 1009-73 “Sanitary rules for welding, surfacing, and cutting of metals” - these rules apply to all types of welding, surfacing and thermal cutting of metals used in industry and construction.
VIII. Design – stage 5. Drawing up specifications for products, equipment and materials.
The specification is one of the most important parts of the working documentation, since it is according to the specification that estimates will be drawn up and equipment and materials necessary for the installation of ventilation systems will be purchased. Here is an example of a completed specification in Excel. Requirements for fulfilling the specification are regulated in GOST 21.602-2016.
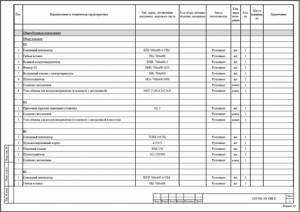
It is interesting to note that for ventilation systems in accordance with GOST 21.602-2016 it is not necessary to take into account the shaped elements of air duct systems (bends, transitions, tees, tie-ins) in the specification. Sometimes, for the convenience of purchasing shaped network elements, Customers require detailed specifications; this is usually specified when drawing up technical specifications. Taking into account the use of specialized CAD systems for the design of utility networks, the specification of shaped elements is calculated automatically.
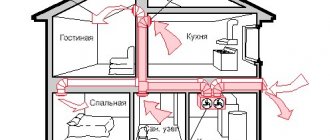
Ventilation schemes for residential buildings
Depending on the construction plans, ventilation may have a completely different design. In this section we will try to figure out how ventilation works in a panel house using diagrams and talk about the degree of effectiveness of one or another type of ventilation.
The most successful ventilation scheme in a panel house is individual, when each apartment has a separate duct with access to the roof.
In this case, the ventilation shafts are not connected to each other, the draft inside the pipe improves, and polluted air from neighboring apartments does not enter the house. Another variation of this ventilation scheme in a Khrushchev building is that from each apartment separate channels lead to the roof, where they are connected into a single pipe that carries air masses to the street.
Unfortunately, quite often the simplest, but ineffective method of ventilation is used, in which air from all apartments enters a single large shaft - the same way ventilation is arranged in a Khrushchev-era building. This allows you to save space and costs during the construction of a building, but has a lot of unpleasant consequences:
- the entry of dust and unpleasant odors from other apartments - residents of the upper floors, where the air rises naturally, are especially susceptible to this;
- rapid contamination of the common ventilation pipe;
- lack of sound insulation.

There are several other ways to exhaust air through ventilation shafts - with horizontal ducts in the attic and pipe outlets into the attic without a chimney. In the first case, horizontal air ducts reduce air draft, and in the second, the attic becomes dirty due to the lack of outlet to the street. The ventilation scheme in Khrushchev and other Soviet-type buildings, although budget-friendly, is inconvenient for residents.
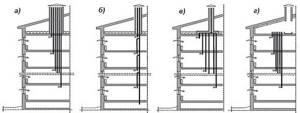
Schematic diagrams of some natural ventilation systems in residential buildings: (a) - without prefabricated ducts; (b) - with vertical collecting channels; (c) - with horizontal prefabricated channels in the attic; (d) - with a warm attic
Fortunately, there is a modern ventilation system that automatically extracts and supplies air. Its design includes a fan that forces air into the shaft. It is usually located in the basement of a building. An exhaust ventilation system of the same power is placed on the roof of the house, which forcefully removes polluted air masses from the air duct. This is the simplest ventilation scheme in an apartment building. It can also be arranged using energy-saving equipment - recuperators. The task of the recuperator is to remove heat (or cold) from the exhaust air and transfer it to the supply air.
Ventilation shafts, as a rule, come from the basement of a multi-story building, additionally providing its protection from dampness and fumes. Ventilation of the basement is provided using natural draft, and in modern houses air supply units are also installed here. To remove damp air from the basement, common ventilation shafts are used, with openings on each floor and in each apartment.
Ventilation of the basement, the place where the natural ventilation system begins, is one of the main conditions for its proper operation. To do this, vent holes are made in the basement walls, through which fresh air enters the basement. It not only reduces humidity at the base of the house, but also creates draft in the common house shaft.
The shape of the holes can be simple - round or square. They must be placed at a sufficient distance above the ground so that water and dirt from the street do not get inside. The optimal distance from the ground is at least 20 cm. The holes should be placed evenly around the perimeter of the basement; if there are several rooms in it, it is necessary to organize several vents in each. The vents must not be closed, otherwise the entire principle of operation of the ventilation of an apartment building will be disrupted. To prevent animals from entering the basement, the openings are covered with a metal mesh.
IV. Design – stage 1. Collection of initial data for the design of ventilation systems
The first stage of design is collecting initial data. Usually, at the beginning of the design, you receive from the Customer the section “Architectural Solutions” (architectural plans of the building, sections), the section “Technological Solutions” (if it is required within the framework of a given building) and Technical Specifications.
Specialists of Inkom Design LLC formulate the main provisions of each design specification for each section. The technical specifications drawn up by our specialists ultimately form an integral part of the design contract.
Let's consider the basic necessary initial data for designing ventilation systems:
- Section "Architectural solutions". To design ventilation systems you need: plans, sections, presence and height of suspended ceilings. It happens that there are no sections of the building, just as there is no explication of suspended ceilings with heights, but, usually, all this data can be more or less accurately obtained upon request from the Customer;
- Section "Technological solutions". If the section is carried out within the framework of the designed building, it is necessary to design ventilation systems in accordance with this section. This section contains information about:
a) technological equipment in the building;
b) harmful emissions from technological equipment;
c) necessary microclimate parameters;
d) the number of people in the premises;
d) operating mode of the building, and so on.
If this section of the project is not carried out within the framework of the designed building (for example, a small office building), then at a minimum you need to find out from the Customer the number of people in each office space, or, in agreement with the Customer, set a certain number of employees per m2 of office space (usually It is believed that per person working in an office there is 8-10 m2 of office space).
- Fundamental solutions for ventilation systems. After receiving and studying AR (Architecture) and TX (Technology), we offer and further discuss with the Customer fundamental solutions for ventilation systems, such as:
a) the presence of natural or mechanical ventilation in the premises
b) location of ventilation equipment;
c) breakdown into ventilation systems;
d) places where the main air ducts are laid, and so on;
- Method of heating ventilation. In the vast majority of cases, public and residential buildings (built-in parts) have supply ventilation systems. To design, it is necessary to understand how the incoming outside air will be heated in them; it can be an electric air heater or a water heater. For a water air heater, you need to know the parameters of the heat supply water in the supply and return pipelines (usually they are around 90/70 ºС).
- Additional requirements for the project. Depending on the type of buildings and premises, additional requirements may apply to the project. These may be requirements for the routing of air ducts, the location of air distribution devices (diffusers, grilles), air flow rates in certain rooms, the layout and composition of ventilation units, documentation, drawing up specifications, and so on. It is advisable to check with the Customer about the presence of special requirements for the project, as well as to coordinate certain fundamental decisions with the Customer during the design process.
After collecting all the necessary initial data, you can begin designing.
Calculation of apartment ventilation
Natural or artificial ventilation of a residential building is calculated by specialists during the construction of the building, and the residents of the building receive apartments with a “default” ventilation system. It will not be possible to change the design of the ventilation system in a Khrushchev-era building; this will require serious intervention in the structure of the building. However, using various devices you can improve air circulation in your apartment. To do this, it is necessary to carry out calculations.
If you are not satisfied with the ventilation in your apartment, you can install additional hoods in the kitchen and fans on grilles in the bathroom. In this case, you should remember the basic rule - the amount of air exhausted should not exceed the amount entering the apartment. In this case, the ventilation systems will work as efficiently as possible. Some models of hoods and fans can operate on air flow - they are worth installing if the room is not ventilated enough through windows and doors.
Particular attention should be paid to the power of exhaust devices; for small apartments, a capacity of 50 to 100 m³ of air per hour will be sufficient. To accurately determine what load will be optimal for the device, you can measure the amount of air mass in the room. To do this, the area of the apartment is summed up and multiplied three times. The resulting volumes of air must completely pass through the fans within an hour.
You can organize additional air flow using air conditioners, hoods and fans. Together, these devices will perform the main tasks of room ventilation:
- a kitchen hood will cleanse the room of unpleasant odors, grease and smoke, filling it with clean air;
- fan in the bathroom - remove moist air;
- air conditioner - cools and dehumidifies the air in a room.
These devices will ensure good circulation of air masses in different rooms and regulate their cleanliness - they are simply irreplaceable in the bathroom and kitchen.
The amount of supply air can exceed the volume of exhaust air by 15–20%, but not vice versa.
Installation
The installation of ventilation in a residential building must be approached from the perspective of what system has been chosen. If this is a natural model, then the main thing is to lay the risers correctly. You will have to tinker with forced ventilation, especially if it is an extensive network. The simplest option is to install wall fans, for which you simply make holes in the walls with a crown and a hammer drill to the diameter of the pipe, where the equipment is inserted.
From the outside, that is, from the street, the pipe is covered with a canopy and a grill. A decorative grille is installed on the inside. Here it is important to very correctly connect the fan to the electrical supply network. To do this, the walls are usually chipped, where the power cable from the fan to the junction box is laid. True, this is done at the stage of repair or finishing. If the installation is carried out in a renovated room, then it is recommended to lay the wiring in special plastic boxes.
It should be noted that supply and exhaust ducts can be equipped with fans if the house has a comprehensive air exhaust system. In this case, as in the case of calculating natural ventilation, the maximum parameter is determined from two calculated ones: exhaust and inflow. It is on the basis of the calculations made that the fan, or more precisely, its performance, is selected.
It is easy to install a monoblock device. The main task is the correct choice of installation location. As practice shows, preference is given to the street near the wall of the house. Although the option in the office room solves the problem of equipment freezing. This device is convenient because it already includes all the necessary devices that are responsible not only for air exchange, but also for the purity of the supplied air flow.
In general, you can make exhaust or supply ventilation yourself if you carry out preliminary calculations correctly. You cannot select equipment and air ducts by eye. It may happen that their power and cross-section will be insufficient to cope with the volume of the internal premises.
Home ventilation care
Often, ventilation does not work due to a clogged air duct or outlet grille. You can clean the ventilation ducts yourself within your apartment by removing the grille and cleaning the walls of the pipe with a brush, broom or vacuum cleaner. Particular attention must be paid to the mesh covering the entrance to the mine - it acts as a filter on which all contaminants remain.

Complete cleaning of general building ventilation is carried out by a special service at the request of residents.
First, the performance of the exhaust ducts is diagnosed and a work plan is drawn up. To check the cleanliness of mines, a video camera on a cable is often used - it allows you to determine where dirt accumulates and where the pipe is deformed.

After this, cleaning of the air duct begins. Professionals use weights, pneumatic brushes, weighted brushes and other tools. Ordinary residents should not engage in such work - this can damage the integrity of the pipe.

Natural ventilation in a multi-storey building is not very effective compared to mechanical ventilation, but it requires cleaning less often. A team of specialists should be called once every few years if there are clear signs of air duct contamination. Automatic ventilation systems experience greater loads and require more thorough cleaning. The maintenance of such systems is often carried out by the companies that install them.
Monitoring the performance and increasing the efficiency of home ventilation is one of the key points in creating a healthy microclimate in your home. By taking a number of measures to improve the ventilation of your home, you will rid yourself of dust, unpleasant odors, and kitchen or bathroom products in the air.
Rules for users
Personnel and private users of ventilation systems are prohibited from:
- violate the integrity of the complex, air exhaust and connecting elements;
- connect gas appliances to the system;
- disconnect or remove fire retardant and ventilation devices provided for by the project;
- close openings, ventilation grilles, exhaust ducts;
- burn off accumulated deposits yourself, and so on.
The requirements for the ventilation system of industrial premises are formulated taking into account the development of procedures for personnel. Workers who maintain production facilities must act in accordance with instructions and ensure:
- compliance with the cleaning schedule of valves and outlets;
- disconnecting the parts of the system being repaired from the rest;
- the required frequency with which the efficiency of ventilation systems is checked and their prevention is carried out;
- turning off ventilation during fire alarms;
- control over the serviceability of the fans - there should be no deflections or breaks on the blades, the wheels must be balanced and their smooth running must be monitored, grounding devices must be checked regularly.

Schematic diagrams of natural ventilation
Many years of practice in the construction of apartment buildings have led to the selection of several of the most effective schemes for creating a ventilation system. The choice of one scheme or another depends on many factors: the shape of the building, the number of floors, street air pollution in the area, and noise level.
Diagrams of a traditional exhaust system
An exhaust ventilation system with natural impulse is recognized as traditional, that is, when air exchange in rooms is carried out due to the difference in temperature and pressure.
This means that exhaust air is discharged through ventilation shafts and ducts to the outside (on the roof), and fresh air enters through windows, doors or special supply valves.
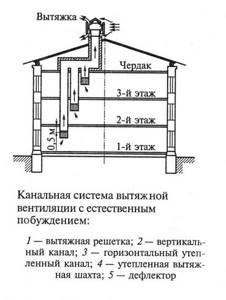
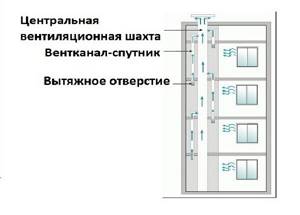
One of the options for installing ventilation shafts in a multi-storey building
The option of laying separate shafts for each apartment is not currently being considered, since it was feasible in the era of low-rise construction.
It is clear that for high-rise buildings from 9 floors and above it is physically impossible to equip many parallel channels.
Therefore, two recognized rational schemes are used in construction:
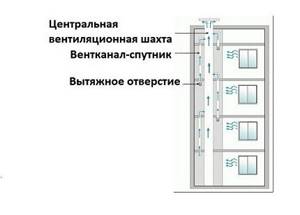
- All shafts lead to the attic and are united there by a horizontal channel. Contaminated air is removed from the channel through a single exit, located in the most convenient location.
- Individual apartments are connected to a common riser (shaft) by parallel satellite channels, thus exhaust air is discharged above the roof through vertical channels.
The fundamental difference lies in two points: the presence/absence of a horizontal collector in the attic and the presence/absence of common shafts in the risers.
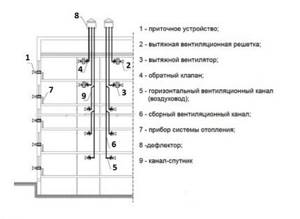
Diagram of a ventilation device with satellite channels. An important nuance: for the upper floors, the idea of a separate direct outlet of used air has been implemented
Local drainage from the upper floors is due to the fact that in order to create traction, there must be a horizontal channel at least 2 m in height above the apartment.
Separately removed channels, as well as the common shaft, must be properly insulated, otherwise condensation will form in the attic, resulting in premature destruction of materials and mold.
Installation of a horizontal attic box is carried out taking into account special requirements. For example, its diameter must be sufficient so that no backdraft is created and air does not return to the channels. This is fraught with the possibility of exhaust gas getting into the apartments on the upper floors.
The calculation of the diameter of the box should be carried out by experienced engineers. To ensure that the air moves in a given direction and does not return back, cuts are installed inside the channel
Sometimes it is not possible to install a bulky horizontal channel. Then they make do with a narrow pipe section, but for the upper floors they use the same local system - separate hoses inserted into the attic.
Natural ventilation, which is equipped in almost all old houses, has a significant advantage - it does not require power supply.
However, its effectiveness depends on the temperature difference in the building and the room, and shafts and channels require constant cleaning, which is rarely done in practice.
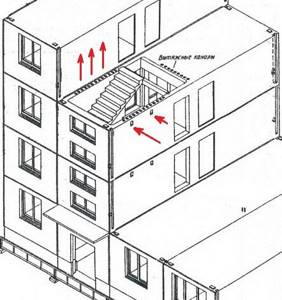
Features of the location of channels in a 9-story building
In typical houses, the air change process occurs naturally. An influx of fresh air masses occurs in the apartments, and the exhaust air is discharged through ventilation shafts equipped with satellite channels.
Most often, ducts are laid from exhaust vents in apartments according to the “through 2 floors” scheme, but they can also be floor-by-floor.
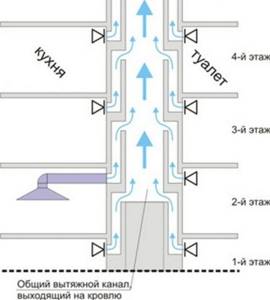
Ventilation diagram typical for a standard multi-storey building. The common exhaust shaft goes directly to the roof, satellite channels are laid in parallel and connected alternately
According to the standards, drainage from 8-9 floors is carried out not through a common shaft, but separately. When drawing up such a diagram, average atmospheric conditions are taken into account, that is, the air temperature outside is +5 ° C and the absence of wind.
This scheme is recognized as low-effective, since when natural conditions change, the functionality of natural ventilation decreases. For example, in extreme heat it is useless. It is also possible that the ventilation ducts become clogged, which completely blocks air movement.
If there is no normal hood, emergency cleaning will be required. Although it is usually carried out every 5-6 years.
Forced type systems
In modern housing construction, plastic and metal-plastic structures are used to seal window and balcony openings. Double-glazed windows made of polymers and aluminum are stronger than wood, but often completely block the natural channels for fresh air.
The doors also fit tightly to the floor, making the rooms completely airtight. There is no air intake, and in the absence of an effective supply system, the exhaust system becomes useless.
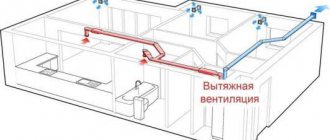
To solve the problem of access to fresh air in all apartments, special equipment is installed in luxury residential buildings - air handling units.
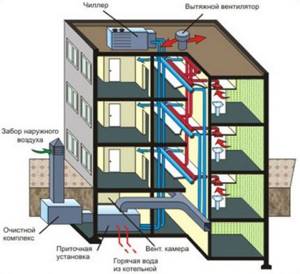
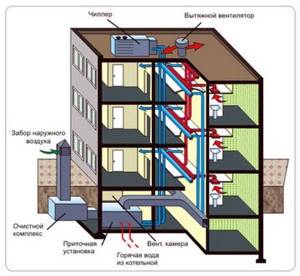
An example of installing a supply and exhaust system in an apartment building. Downstairs, in the basement or plinth, supply equipment with air filtration and heating is installed, on the roof - a chiller and a fan
The supply and exhaust ventilation system is quite complex, and to install its individual elements you will need to allocate space in the basement (supply air heating) and on the roof (fan and chiller).
Unlike natural ventilation, incentive ventilation is energy-dependent. In addition, it consists of a set of complex devices that are controlled from a single remote control.
The SHUV is installed next to the supply equipment, in the basement, and only qualified service personnel have access to it.
We can say that in residential high-rise buildings all three types of ventilation are present, with natural being the most common, and the installation of a forced or combined system is still limited.
The order of operation of ventilation using the example of a typical project
The most common panel project is a nine-story building. The principle of operation of the hood is the same. Air from the street, through windows and cracks, enters the apartment. The exhaust occurs through satellite ventilation ducts in the kitchen or bathroom. One, or less often several, channels from the hood are connected to the main pipe. These channels are connected to the main shaft through two floors. These shafts are quite bulky and take up a lot of space. A large-panel house will most likely be equipped with such a system.
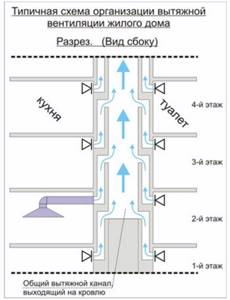
Such a scheme for a house of 9 floors assumes the presence of a warm attic. The outlet from the 8th and 9th floors goes directly into the atmosphere, bypassing the common channel. The scheme for a 9-storey building was designed based on the complete absence of wind and an outside air temperature of +5.
Despite the fact that natural ventilation in such houses is not very effective, it requires almost no maintenance, and blockages rarely occur. There have been cases where ventilation ducts became clogged with building materials during the construction of a house. Such a surprise subsequently affected the quality of the hood. Most often, cleaning the mine is required once every 5-6 years.
During repairs, many people block the air flow in some place. They unknowingly think that this will not affect the hood, but the process of air renewal in the apartment becomes difficult or stops completely.
The most common actions leading to interference and disruption of natural ventilation:
- installation of sealed plastic windows;
- interior doors with seal;
- installation of various fans in the hood.
In order not to disrupt the operation of the natural ventilation draft, it is forbidden to obstruct the inflow and outflow of air. For plastic windows, it is necessary to install inlet openings or arrange an external inlet separately. Doors between rooms are equipped with bars at the bottom. The cross-section of the exhaust duct should not be blocked by fans.
Circle of potential clients
Determine the circle of your potential clients. Who, for some strange and inexplicable reason, still has YOUR personal money that you urgently need to pick up?
So, we start planning project sales by answering the question of who your potential clients are, taking into account, of course, your very specific specifics.
Design organizations (design institutes, design and engineering bureaus, architects and designers) General construction contractors Subcontractors Installation organizations Municipal customers Corporate customers Clients of your competitors Projects under construction
A good indicator that you want this customer is that they are already buying a lot from your competitor.
Possible options for arranging ventilation in high-rise buildings
Modern ventilation in a panel house is equipped with single exhaust pipes. From the sanitary facilities, each floor has its own pipe going to the roof. In this option, there is no possibility of penetration of foreign odors and the entire system functions evenly and reliably.
Another good option is when all vertical channels flow into a common horizontal collection manifold, which is located in the attic. The air from it exits to the street through one common pipe.
The most unstable method is when a small satellite channel from each apartment enters a common ventilation shaft. This ventilation scheme in a panel house is significantly cheaper to install and increases living space, but constantly brings a lot of problems to residents. The most common one is the flow of various odors from one apartment to another.
Vent. mine with satellite channel
The best ventilation option is electromechanical forced air supply and exhaust systems. They are used in modern new buildings, except low-budget ones. The supply installation of such a system is located in the basement or on the side of the main building. It supplies filtered and heated or cooled air to all rooms and spaces. On the roof, in turn, there is an electric exhaust fan with exactly the same design power as the supply fan. It is designed to remove contaminated mixtures from apartments through hoods.
This is one of the primitive schemes of the device. A more complex one, which can be equipped in a modern high-rise building, is equipped using new energy-saving technologies. For example, recuperators are devices that allow you to take heat or cold from the exhaust air and give it to the supply air.
Ventilation recommendations
The consequence of installing modern sealed windows and doors is the unsatisfactory performance of ventilation elements and its non-compliance with SNiP recommendations. Few people are ready to keep the windows slightly open at any time of the year to bring in the required amount of air, even in cold weather. In the absence of efficient operation of the hood, the humidity indicator increases, the saturation of the air with carbon dioxide increases, and the oxygen saturation decreases. In such a room microclimate, when air humidity is higher than normal, mold and various fungi multiply well. This is very harmful to the human body and is not aesthetically pleasing.
The way out of the situation is quite simple. It is necessary to acquire a forced ventilation system. It will eliminate the problems of air renewal, and the use of a recuperation system allows you to maintain a comfortable microclimate and fresh air with minimal energy consumption.
VII. Design – stage 4. Drawing up an explanatory note/General data.
This section of the project is a textual descriptive part of the applied design solutions. As described above, in section II “Composition of the project for ventilation systems”, at stage P an explanatory note is carried out according to Resolution No. 87, and in the working documentation general data according to GOST 21.602-2016.
The explanatory note and general data can be carried out both after the plans for the ventilation systems are ready (so that the routing of the systems can be described, to give additional instructions on the intricacies of the designed system), and in parallel with the plans (subsequently, before the release of the project, the text part is reviewed again and edited if necessary).
Ventilation calculation
Let's consider the calculation of natural ventilation as the simplest. To do this, it is necessary to designate two parameters: the minimum amount of air entering from the outside (Qp) and the minimum volume to be removed from the house (Qv). Both table values from SP 54.13330.2011 are the first in table No. 1, the second in table No. 2.
Both are based on the dimensions of the house's rooms. Therefore, the input data is:
- The area of all living rooms (there are three) is 60 m².
- Ceiling height – 3 m.
- Attached storage room – 4.5 m².
- The house has a kitchen, bathroom and toilet, in which the air exchange rate is respectively: 90; 25; 25 m³/h.
First of all, the overall air exchange in the rooms is determined, for which it is necessary to multiply the air exchange of residential premises, equal to 30 m³/h, by the number of rooms - 3. 60x3=180 m³/h. This is the value of the supply volume that passes through the living quarters.
The air exchange values of all utility rooms are added up: 90+25+25=140 m³/h.
The frequency of air changes in the pantry is determined. A multiplicity of 0.2 is used here. That is, you need to multiply the volume of the pantry by this indicator: 4.5x3x0.2 = 2.7 m3/h.
Now we need to add the last two values: 140+2.7=142.7 m³/h. This is the exhaust air volume. Next, you need to compare the exhaust and supply air: it turns out that there is more supply air. We take this as the basis for the calculation.
Now we need to calculate the cross-section of the air duct. For example, if it is square with sides of 10 cm or round with a diameter of 150 mm, then the productivity of such a pipe with natural ventilation is 30 m³/h. If risers of this section are used in the construction of a house, then it is necessary to install: 180/30 = 6 risers. To reduce the number of hoods, you can increase the cross-sections by selecting them according to the air duct performance table.
The principles for calculating other types of ventilation systems are based on the same parameters.
"Clean" rooms
While talking about what air exchange systems for non-residential facilities are, we need to talk about what is so remarkable about the ventilation of clean rooms. First of all, it should be noted that the latter are so named because for each of them there is a maximum permissible level of pollution. Simply put, “clean” premises are non-residential facilities for which air quality is critically important. These include:
- research laboratories;
- places of production of medicinal products;
- workshops where microcircuits are manufactured;
- wards that provide special requirements for keeping patients in them, etc.
It is not difficult to guess that ventilation systems installed in such non-residential buildings must provide an extremely “fine” microclimate. Their main purpose is to maintain the composition of the atmosphere, the concentration of suspended particles in which does not exceed a given level. The dimensions of the latter are truly microscopic (0.4 microns, 0.6 microns, etc.), which makes this task even more difficult.
If we highlight the key technical requirements for “clean” ventilation systems, they are as follows:
- minimizing the number of pathogenic microorganisms contained in the atmosphere;
- ensuring air quality that meets the specified parameters (temperature, humidity, maximum permissible concentration of harmful inclusions, etc.);
- reducing to zero the likelihood of static electricity in the air, as well as its accumulation.
In addition, the installation of such systems involves the use of three-stage air purification: it belongs to the “ultra-fine” category, which allows it to achieve all the required results.