Parameters for starting heating
As autumn approaches, the temperature outside becomes lower and lower, people touch their batteries every day and hope that today they will become hot. If this does not happen, then the residents look for the culprits, but in fact, all standards for the supply of heat to houses are specified in Resolution No. 354 of 2011.
This document states that heat is supplied at an outside temperature of 8 degrees Celsius, if it lasts for five days in a row . If this indicator fluctuates in one direction or the other over the specified time, then the radiators and risers in the apartments will remain cold.
Heat is supplied only on the sixth day and, as a rule, in most cases the heating season begins on October 15 and ends on April 15.
In this video you will learn the temperature standards in the apartment:
Standards for an apartment
Temperature standards in heating radiators are different for a particular room. The air in apartments should be heated to the following level:
- living area and kitchen - +18°C;
- corner apartments - +20°C;
- bathroom and toilet - +25°C.
Corner apartments should be heated more strongly due to the presence of cold corner walls. The standards for common premises are slightly different:
- entrance — +16°C;
- elevator — +5°C;
- attic and basements - +4°C.
Measurements in a residential area are made on the internal walls no closer than a meter from the outer wall and one and a half meters from the floor level.
If the parameters do not comply with the standards, the consumer must notify the management company. After the required checks, the heat charge can be reduced by 0.15% per hour of deviation from the standards.
Humidity
There are standards not only for heating in the house but also for humidity. This indicator can change in an apartment due to various factors, for example, due to a malfunction of ventilation. The problem must be solved by municipal institutions.
In winter, humidity should be between 30-45%, but 60% is acceptable. And the temperature norm is +18+24 degrees. There are no humidity standards in the kitchen and bathroom, since these rooms have operational characteristics.
Battery temperature
There are minimum and maximum standards. Sometimes, even when heating is started, there is not enough heat in the room due to the fact that the temperature of the radiators is far from the standards. The reason for this is the banal airiness of the system. You can fix the problems with the help of a specialist or yourself using a Mayevsky crane.
If the problem arises due to worn-out riser pipes or batteries, then you simply cannot do without the help of specialists. If the heating system did not work and the air in the apartment was colder than specified in GOST standards, then this entire period is not subject to payment.
There are no minimum temperature standards for heating radiators, so it is customary to rely on the air parameters in the apartment. Normal air parameters during the heating period are +16…+25°C.
To document that the temperature of the heating system does not meet the norm, it is necessary to invite an authorized representative of the heating service provider. What the water temperature in the batteries should be is described in SNiP 41−01 of 2003:
- If a two-pipe design is used in the room, then 95°C is the maximum.
- The norm for a single-pipe design is +115°C.
- The winter temperature norm for heating radiators in an apartment is +80…+90°C. If it approaches +100°C, then urgent measures must be taken to prevent water from boiling in the system.
Although many battery manufacturers often specify a maximum temperature threshold that is high, you should not reach it frequently as this will damage the battery.
To ensure that the heating complies with GOST standards, you need to take your own measurements and understand what the temperature of the water in the heating radiators is:
- An ordinary mercury thermometer can be used, but then 2°C will need to be added to the result obtained.
- An infrared thermometer will also work.
- The alcohol thermometer must be tightly tied to the battery, wrapped in thermal insulation.
If the results obtained are far from normal, then you need to submit an application to the heating network office with a request to carry out control measurements .
A commission will visit the apartment and make all the necessary calculations.
Choosing a heating system for a private home
The operating principle of a single-pipe heating system is to supply coolant to the upper floors; all radiators are connected to the downward pipeline. It is clear that it will be warmer on the upper floors than on the lower ones. Since a private house, at best, has two or three floors, the contrast in heating the premises does not threaten. And in a one-story building there will generally be uniform heating.
What are the advantages of such a heat supply system:
- ease of design and installation;
- stable hydrodynamic regime;
- lower material costs compared to other types of heating systems;
- maintaining natural circulation at increased water pressure.
The disadvantages of the design are high hydraulic resistance, the need to turn off the heating of the entire house during repairs, restrictions on connecting heating devices, the impossibility of regulating the temperature in a single room, and high heat losses.
For improvement, it was proposed to use a bypass system.
Bypass is a section of pipe between the supply and return pipelines, a bypass path in addition to the radiator.
They are equipped with valves or taps and allow you to regulate the temperature in the room or completely turn off a separate battery. A single-pipe heating system can be vertical or horizontal. In both cases, air pockets appear in the system. The system inlet temperature is maintained at a high temperature to warm all rooms, so the piping system must withstand high water pressure.
Two-pipe heating system
The principle of operation is to connect each heating device to the supply and return pipelines. The cooled coolant is sent through the return pipeline to the boiler.
Additional investments will be required during installation, but there will be no air pockets in the system.
Actions in the absence of heat
If there is any discrepancy between the heating system and GOST, you need to find the cause of the cold radiators. The best person to deal with this will be the specialists of the supplier company, who will be able to officially record the temperature in the living room.
If the problem is caused by poor quality maintenance of the systems of an apartment building, then the solution to the problem lies entirely with the organization supplying the heat. At the same time, all residents should be recalculated for heat or they should be completely exempt from paying if the radiators did not heat at all.
Any application from the residents of the house to the communal structure must be considered as soon as possible, and the commission must record on the spot the fact of inadequacy of the services provided.
Knowing what the temperature of the radiators in the apartment should be and at what period the heating starts, each resident of an apartment building can determine for himself whether the temperature indicators comply with the established standards. This will help you take action in time and solve the heat problem.
What to do if there is no heating?
In the event that GOST for heating in an apartment is far from its norm, it is necessary to determine the cause of cold radiators. To do this, it is better to call representatives of the relevant service , since they can simultaneously record the temperature in living quarters.
If the problem is poor quality maintenance of the home heating system by heating network workers, then all the burden of troubleshooting will fall on the organization. At the same time, residents of the house must either be recalculated for heating if the radiators do not heat enough, or record the period when they were completely cold and be exempt from payment.
Thus, the law on heating of apartment buildings (2017) guarantees residents protection if utility services fail to comply with their duties .
Any application from them must be considered as soon as possible, after which a special commission comes and documents the discrepancies.
Knowing how many degrees the heating should be in the apartment, and at what time the system is turned on, each owner can independently determine whether the indicators comply with heating standards in the apartment and take measures if this is not the case.
With the arrival of autumn cold, when thermometer readings drop to 8-10 degrees Celsius, and real winter begins in the northern regions of Russia, the use of the word form “heating season” becomes appropriate. And during this period, it makes sense to understand the basic standards for coolant temperature in the heating system, which are regulated by the state.
When the heating season arrives, owners of private houses and cottages independently open the valves and nozzles of boiler systems. In apartment buildings, things are a little different, and residents are forced to wait impatiently for a plumber from the management company, who will start the heating system and allow people to feel confident in the future.
It is no secret that in multi-apartment buildings of economy class, heating is carried out through a centralized heat supply system. All heating lines are hidden in the basement, and the supply of coolant is regulated using water valves, behind which there are sump tanks and risers. Passing through the last nodes, the liquid is supplied to batteries and radiators, which start heating the surrounding space.
The number of valves must correspond to the number of risers. The presence of these elements allows one apartment to be disconnected from the general system for the duration of any repair work. The spent coolant ends up in the return pipe and also partially penetrates the hot water supply network.
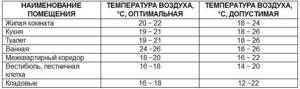
The creation of liquid for a heating installation occurs at a thermal power plant or in a boiler room. Heat supply standards in an apartment building are regulated by the relevant building rules: the coolant must be heated to 130−150 degrees Celsius. When drawing up current standards, it is necessary to take into account the parameters of the ambient air. For example, for the Southern Urals, minus 32 degrees should be taken into account.
Read more: How the queue for improving housing conditions is moving
To prevent the liquid from boiling, it is supplied to the network under a pressure of 6-10 KGS. However, this is only a theoretical statement. In fact, a significant part of the heating mains operate at 95-110 degrees Celsius, which is explained by their poor condition.
The concept of “norm” is very loose. Heating radiators never warm up to the temperatures possessed by the coolant. In this case, the energy-saving function will be assigned to another part of the system - the elevator unit, which is a jumper between the direct and the return pipe. According to current standards, the temperature of the liquid in the system through the return pipe in winter can be 60 degrees Celsius.
During the cold winter season, it is time to heat the apartments.
According to the law of the Russian Federation, we are provided with high-quality central heating at subsidized prices.
What should you really expect during the heating season? How high quality and effective it will be.
How to determine that the water temperature in the radiators is below normal?
A device that measures surface temperature with a beam.
The quality of heating is often determined by the air temperature in the room. If you feel that the rooms are cool, you need to measure the temperature. The maximum permissible temperature is +18 degrees. If it is lower, then you need to identify the cause. The main reasons may be leaky windows and doors, but a more compelling reason is low water temperature in the radiators.
To determine what the temperature of the batteries in your apartment should be, there are special calculations. They are compiled by specialists who compare the temperature of the water in the radiators and the ambient temperature. You need to call a special service that will measure the temperature in the heating radiators in your apartment. The obtained data is compared with the temperature graph data. This graph has already calculated what temperature should be in the direct and return water supply pipes.
Table. Temperature graph of the ratio of heating to ambient temperature.
| Ambient temperature | Direct water temperature | Return water temperature |
| -15 | 105 | 70 |
| -10 | 92 | 63 |
| -5 | 78 | 56 |
| 65 | 48 | |
| +5 | 50 | 39 |
These data are given for a single-pipe heating system, with water supplied from bottom to top. According to the table, when the outside air temperature is, for example, -10 degrees Celsius, the return water temperature should be at least 63 degrees. And this does not depend on which floor the measurements are taken - on the first or fifth. In a two-pipe heating system, the water temperature at -15 outside is allowed to be 95 degrees with direct water supply.
Each locality has its own temperature chart. It is approved by the city administration.
If the battery temperature in the apartment is below normal, this means that the boiler room is saving on heating. After water measurements, specialists draw up a report, and utility workers must correct all problems. At the same time, everyone has the right to demand a recalculation of heating fees. The rent should be reduced according to the square footage of the apartment. The temperature of the water in the radiators is one of the main factors in a warm home. According to battery temperature standards, a coolant must be supplied to the apartment, the degree of heating of which ranges between 80-85 degrees.
It is very simple to make heating with heating elements in your home, and each heat exchanger will not depend on the others. To do this, simply screw the heating element into the bottom end of the battery and connect it to the electrical network.
Here you will find everything about infrared heating of a private house: reviews, calculations and drawings.
Calculation of the optimal temperature of the heating device
The most important thing is that the most comfortable temperature for human existence is +37°C.
When choosing a radiator, you need to calculate whether the thermal power of the device is enough to heat the room. There is a special formula for this:
S*h*41:42,
- where S is the area of the room;
- h – room height;
- 41 – minimum power per 1 cubic m S;
- 42 – nominal thermal conductivity of one section according to the passport.
Please note that a radiator placed under a window in a deep niche will produce almost 10% less heat. A decorative box will take 15-20%.
When you use a radiator to maintain the desired temperature in a room, you have two options: you can use small radiators and increase the water temperature in them (high temperature heating) or install a large radiator, but the surface temperature will not be as high (low temperature heating) .
With high temperature heating, radiators are very hot and can cause burns if you touch them. In addition, at a high temperature of the radiator, the decomposition of dust settled on it may begin, which will then be inhaled by people.
When using low temperature heating, the appliances are slightly warm, but the room is still warm. In addition, this method is more economical and safe.
Cast iron radiators

The average heat output of a separate section of a radiator made of this material ranges from 130 to 170 W, due to the thick walls and large mass of the device. Therefore, it takes a lot of time to warm up the room. Although this also has the opposite advantage - high inertia ensures long-term retention of heat in the radiator after the boiler is turned off.
Methods for measuring water in radiators
When considering the question of how to measure the temperature of a battery in an apartment, the following methods can be distinguished:
- an ordinary thermometer (on the surface of the radiator);
- infrared thermometer;
- alcohol thermometer;
- special electrical device.
When measuring with a regular thermometer, you need to add 1-2 degrees to the result. A more accurate result will be given by an infrared device, the error of which is 0.5 degrees.
In order to regularly monitor the temperature of the water in the batteries, you can use an alcohol thermometer. To do this, the device is attached with tape to the radiator and wrapped in heat-insulating material.
The battery may not heat up evenly.
You can also use an electric version of the thermometer for measurements. To do this, a wire with a thermocouple is wound to the battery, and it takes readings of the degree of heating. If a consumer calls a special commission to measure the temperature of heating radiators in an apartment, then their device must have a quality certificate and first pass state inspection. The actions of specialists must comply with GOST 30494-96 (clause 4 in the “Control methods” section).
If the temperature of the heating pipes in the apartment is higher than normal, then it can be adjusted in several ways:
- using special devices;
- ventilation;
- using thick curtains.
There are special taps with which you can regulate the temperature. They are installed on each radiator. A simpler method is to ventilate the room. You can also simply use curtains made of dense material, which will let less sunlight into the room. It is much easier to deal with high room temperatures than low ones. What to do if the minimum temperature of the batteries in the apartment is lower than indicated in the temperature chart? To do this you should:
- call utility services;
- insulate windows, doors and walls;
- install new radiators.
If you don’t know how to check the temperature of the batteries in the apartment, you can call specialists. Also read: “Blowing and cleaning batteries.”
Utility services measure plumbing and heating systems. After this, an act is drawn up. Then, if the tenant's claims are confirmed, utility companies must increase or decrease water heating. Another way would be to install new heating radiators. Details about the installation can be found in the video:
You should pay attention to the material from which the batteries are made.
Aluminum radiators have high thermal conductivity, so they will transfer heat well. But cast iron, although they are able to retain heat longer, will release it more slowly. Because of this, the room will take a long time to warm up.
The speed of water movement also affects the temperature in the heating pipes in apartments. Don’t forget that corner apartments are always cooler, because they have more walls in contact with the street. To reduce heat loss, it is necessary to insulate the walls. Insulating windows and doors through which cold air enters will also not be superfluous.
Even the most fashionable and modern infrared heating of a private home consumes the same amount of electricity as any other electric heater of equal power, even the most ancient one.
You can read more about infrared heating and energy consumption in this article.
What should you know about the temperature in heating radiators in an apartment?
You can screw a thermal head into the end of the battery.
To live comfortably in an apartment, you need to monitor the temperature of the batteries. To do this you need:
- independently measure the temperature of the pipes (use regular, infrared, alcohol thermometers or a special electrical device with a thermocouple);
- call utility workers if the temperature does not meet the standards (as a rule, it is lower than required);
- if the temperature of the battery during the heating period in the apartment is higher than normal, then special taps can be used to regulate it.
A pleasant microclimate in an apartment is the key to health, so do not neglect it. In addition, the degree of air humidity plays a crucial role. If it is too dry, respiratory problems may result. The amount of fresh air is also standardized for each room separately. According to many experts, the standards are somewhat too high, so even if the air exchange is only half, this is quite acceptable.
The annual rise in price of resources forces the end consumer to think not only about their savings, but also about the quality of the utility services provided. One of the most significant expense items in paying for an apartment is heating, so consumers monitor its parameters especially carefully. To do this, it is worth finding out what the normal temperature of the batteries in the apartment is in 2019.

Temperature standards for the heating system in an apartment building
The heating circuit in apartment buildings is built in cooperation with a centralized system to which the pipes are connected. Through them, the coolant is directed to the apartment building, where its further supply is regulated by inlet valves. After this, the water goes through the risers and eventually ends up in the radiators and radiators of each apartment.
The described processes, as well as everything related to the rules for providing the population with utility resources, are reflected in the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated May 6, 2011 No. 354 “On the provision of utility services to owners and users of premises in apartment buildings and residential buildings” (hereinafter referred to as Decree No. 354). Heating quality requirements are set out in Section VI of Appendix No. 1 to the rules of Decree No. 354.
In addition, detailed rules for the provision of heating services are prescribed in the Order of Rosstandart dated June 11, 2014 No. 544-st “GOST R 51617-2014. National standard of the Russian Federation. Housing and communal services and management of apartment buildings. Public utilities. General requirements" (hereinafter - GOST R 51617-2014) and "GOST 30494-2011. Interstate standard. Residential and public buildings. Indoor microclimate parameters”, approved by order of Rosstandart dated July 12, 2012 No. 191-st (hereinafter referred to as GOST 30494-2011).
These acts establish the parameters of the coolant for the heating system of an apartment building. Thus, the temperature of the coolant (water) when supplied to the system is equal to the temperature of the water when it leaves the heating boiler. As a rule, the coolant should be brought to a temperature of 130-150 °C, but this indicator also depends on the outside temperature in the region.
Typically, the water leaving the boiler should have a temperature of 115 °C.
However, the standard temperature in the heating system can be within 95 ° C or 105 ° C (for different systems).
Next, to create comfortable conditions in the room, the proper condition of the parameters of the riser, which conducts water from the heating unit to the apartment, is ensured. They vary depending on the summer and winter seasons.
Of course, in practice, the temperature of the coolant in the riser depends on the operation of the thermal power plant and on heat loss on the way to the house. However, the riser temperature in winter should be in the range of 70-90 °C.

Scope and purpose of the temperature graph
The temperature schedule is developed by heating engineers in the design services of heat supply organizations using a methodology that takes into account specific local conditions. The formula for calculating the temperature schedule includes the heat loss of the transported medium in the segment from the heat supply source (CHP) to the buildings. The graphs are drawn up for the temperatures of the transported coolant: at the output of thermal power plants and boiler houses, at the entrance of houses, after the elevator unit in the central heating substation, ITP and its passage through apartment radiators (return).
A temperature table or graph shows the relationship between the temperature of the atmospheric air and the coolant at the system inlet. It also necessarily contains the temperature indicators of the water in the return line, which should be maintained in the heating circuit.
The schedule carries the following functional load in the maintenance and operation of heating networks:
- The standard temperature of the coolant in the heating system, shown in the tables, observed by maintenance specialists, allows you to maintain the same comfortable microclimate in the premises, regardless of the state of the external atmosphere.
- It is used when analyzing operating modes and carrying out adjustment operations in heating networks.
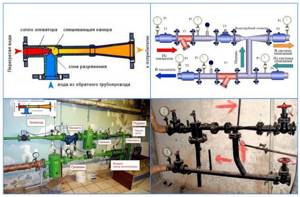
Rice. 8 Elevator unit - diagram and appearance
- Provides fuel savings for water heating by maintaining optimal temperature in the return line. This allows the consumer and the heat supply organization to reduce financial costs for heating.
- Energy resource savings are also ensured by drawing up individual schedules taking into account the climatic characteristics of the region, technical characteristics and sizes (diameters) of pipes, materials (thermal conductivity) of the walls of buildings.
- Allows you to optimally distribute not only thermal energy, but also maintain the desired temperature in the hot water supply lines connected to heating networks.
- The graph takes into account various maximum heating values of the working fluid at a thermal power plant; the following indicators are taken as the standard: 150, 130, 120, 105 and 95 °C.
- The use of tables allows you to carefully use fittings, equipment and pipes, depending on the material of their manufacture, service life, physical characteristics and dimensions. For example, for worn-out heating networks, gentle operation is selected in heating mode 95 70.
- Allows automatic regulation of coolant parameters by setting digital values on automation devices in accordance with tabular data.
- Based on the tables, fittings, equipment, heating boilers, pipes, radiator heat exchangers are selected that meet the maximum temperature ranges of heating networks.
- Also, to ensure the required temperatures, in accordance with the table, the diameter of the pipes is calculated, the insulated areas and the heat insulator of the pipeline are selected: its material, thickness.
- In addition to heating parameters, the graph often indicates the temperature characteristics of heated water in hot water supply and ventilation systems associated with the heating circuit.
- If necessary, the temperature graph 95 to 70 from the heating networks table can be used in the heating system of a private house.
Rice. 9 Temperature graph example
Air temperature standards in the apartment
The feeling of comfort from heating a room is subjective. However, there are uniform standards determined by the physiological needs of a person, as well as the purpose of the premises in which he resides.
Although there is a fairly wide range of standards that prescribe what the temperature of the water in the heating system of an apartment building should be, the standards for the thermal conditions of the air in the apartment are very unambiguous.
So, in accordance with the standards, during the heating season the following temperature regime must be maintained in the apartment:
- in the living room - 18 °C;
- in a living corner room - 20 °C;
- in the bathroom - 25 ° C;
- in the toilet (separated from the bathroom) - 18 ° C;
- in a shared bathroom - 25 °C;
- in the kitchen - 18 °C.
This standard according to GOST allows you to preserve the health of residents without exposing them to adverse conditions.
Battery temperature standard
Factors affecting room heating include thermal conductivity, other technical characteristics, as well as the order of installation of batteries. Therefore, compliance with the rules for their installation and use will ensure that the temperature of the heating radiators in the apartment and in the house meets the established standards.
In addition, you should carefully consider determining the number of battery sections depending on the area of the room. For example, a device in which the coolant is heated to an identical temperature will have a different effect on the heat flow with sections 5 and 7 on it.
Coordination of coolant and boiler temperatures
Regulators help coordinate the temperature of the coolant and the boiler. These are devices that create automatic control and adjustment of return and supply temperatures.
The return temperature depends on the amount of liquid passing through it. Regulators cover the liquid supply and increase the difference between the return and supply to the level required, and the necessary indicators are installed on the sensor.
If the flow needs to be increased, a boost pump can be added to the network, which is controlled by a regulator. To reduce the heating of the supply, a “cold start” is used: that part of the liquid that has passed through the network is again transported from the return to the inlet.
The regulator redistributes the supply and return flows according to the data collected by the sensor, and ensures strict temperature standards for the heating network.
How to find out the temperature of the coolant in the batteries
When doubts arise about the quality of the heating services provided, and the inhabitants of the apartment simply begin to freeze, measures should be taken to determine the cause. To do this, measure the temperature:
- air in the room;
- pipes;
- batteries;
- coolant - water in the heating system.
The data obtained will help you understand whether the room is really unreasonably cold or whether it is just a subjective feeling.
It must be taken into account that independent measurements of heating indicators are not direct evidence of violation of standards. However, they can serve as a basis for filing a complaint and inviting representatives of the service organization for control measurements.
Determining the water temperature in the central system
It should be noted that reliably measuring the temperature of the coolant in a central heating system is not so easy. The most accurate indicator remains only the air temperature in the room. However, you can do the following:
- Open the tap if it is installed on the radiator in the apartment.
- Place a container under it, after placing a thermometer there.
- Collect water.
- Wait for the final thermometer reading.
This indicator must comply with the described standards, but upward deviation from them is also allowed. The maximum temperature deviation is up to 4 °C.
In addition, if air is detected in the heating system of the apartment, you should contact the service organization.
Determining hot water indicators
There is another way to establish the truth, related to the fact that the temperature of the heating batteries in the apartment and the hot water supply are directly related. Therefore, it is advisable to measure the water degree like this:
- Open the hot tap.
- Wait 3 minutes for the water to heat up to maximum.
- Take a container and place it under the stream without closing the tap.
- Place the thermometer in the center of the container.
- Wait for the final readings from the device to be received.
If the device shows a number from 60 to 75 °C, everything is normal with the coolant. If the temperature data is lower, it is possible that the water in the heating system is not heated enough.

Housing and communal services in Russia
About the temperature graph of the heating system
From the series of articles “What to do if it’s cold in the apartment”
What is a temperature graph?
The water temperature in the heating system must be maintained depending on the actual outside air temperature according to a temperature schedule, which is developed by heating engineers of design and energy supply organizations using a special methodology for each heat supply source, taking into account specific local conditions. These schedules should be developed based on the requirement that during the cold period of the year an optimal temperature* of 20 - 22 °C is maintained in living rooms.
When calculating the schedule, heat losses (water temperature) in the area from the heat supply source to residential buildings are taken into account.
Temperature schedules must be drawn up both for the heating network at the outlet of the heat supply source (boiler house, thermal power plant), and for pipelines after the heating points of residential buildings (groups of houses), i.e. directly at the entrance to the heating system of the house.
Hot water is supplied from heat supply sources to heating networks according to the following temperature schedules:*
- from large thermal power plants: 150/70°C, 130/70°C or 105/70°C;
- from boiler houses and small thermal power plants: 105/70°C or 95/70°C.
*the first digit is the maximum temperature of direct network water, the second digit is its minimum temperature.
Depending on specific local conditions, other temperature schedules may apply.
Thus, in Moscow, at the outlet of the main heat supply sources, schedules of 150/70°C, 130/70°C and 105/70°C (maximum/minimum water temperature in the heating system) are used.
Until 1991, such temperature schedules were approved annually before the autumn-winter heating season by the administrations of cities and other settlements, which was regulated by the relevant regulatory and technical documents (NTD).
Subsequently, unfortunately, this norm disappeared from the NTD; everything was handed over to those “who care for the people”, but at the same time, who did not want to miss out on profits to the owners of boiler houses, thermal power plants, and other factories - steamships.
However, the regulatory requirement for the mandatory preparation of heating temperature schedules was restored by Federal Law No. 190-FZ of July 27, 2010 “On Heat Supply”. Here is what is regulated in Federal Law-190 according to the temperature schedule (the articles of the Law are arranged by the author in their logical sequence):
“...Article 23. Organization of the development of heat supply systems for settlements, urban districts...3. Authorized... bodies [see. Art. 5 and 6 FZ-190] must carry out the development, approval and annual updating* * of heat supply schemes, which must contain: ... 7) Optimal temperature schedule ... Article 20. Checking readiness for the heating period ... 5. Checking readiness for heating. period of heat supply organizations... is carried out in order to...readiness of these organizations to fulfill the heat load schedule, maintain the temperature schedule approved by the heat supply scheme ... Article 6. Powers of local government bodies of settlements, urban districts in the field of heat supply 1. To the powers of local government bodies of settlements, urban districts for the organization of heat supply in the relevant territories include: ...4) fulfillment of the requirements established by the rules for assessing the readiness of settlements and urban districts for the heating period, and monitoring the readiness of heat supply organizations, heating network organizations, and certain categories of consumers for the heating period ; ...6) approval of heat supply schemes for settlements, urban districts with a population of less than five hundred thousand people...; Article 4, paragraph 2. To the powers of the fed. Spanish organ authorities authorized to implement state policies in the field of heat supply include: 11) approval of heat supply schemes for settlements, mountains. districts with a population of five hundred thousand people or more... Article 29. Final provisions...3. Approval of heat supply schemes for settlements ... must be carried out before December 31, 2011.”
And here is what is said about heating temperature schedules in the “Rules and Standards for the Technical Operation of Housing Stock” (approved by the Post of the State Construction Committee of the Russian Federation dated September 27, 2003 No. 170):
“...5.2. Central heating 5.2.1. The operation of the central heating system of residential buildings must ensure: - maintaining optimal (not lower than permissible) air temperature in heated rooms; — maintaining the temperature of the water entering and returning from the heating system in accordance with the schedule for qualitative regulation of the water temperature in the heating system (Appendix No. 11); — uniform heating of all heating devices; 5.2.6. In the operating personnel room there must be: ...e) a graph of the temperature of the supply and return water in the heating network and in the heating system depending on the outside air temperature, indicating the working pressure of the water at the inlet, the static and the highest permissible pressure in the system;..."
Due to the fact that home heating systems can be supplied with coolant with a temperature no higher than: for two-pipe systems - 95 ° C; for single-pipe - 105 ° C; at heating points (individual house or group houses for several houses), before supplying water to houses, hydraulic elevator units are installed, in which direct network water, which has a high temperature, is mixed with cooled return water returning from the heating system of the house. After mixing in the hydraulic elevator, the water enters the house system at a temperature according to the “house” temperature schedule of 95/70 or 105/70°C.
Below, as an example, is the temperature graph of the heating system after the heating point of a residential building for radiators according to the top-down and bottom-up scheme (with outside temperature intervals of 2 °C), for a city with an estimated outside air temperature of 15 °C (Moscow, Voronezh , Eagle):
WATER TEMPERATURE IN DISTRIBUTION PIPELINES, degrees. C
AT DESIGNED OUTSIDE AIR TEMPERATURE
| current outside temperature, °C | diagram of water supply to radiators | |||
| "down up" | "top down" | |||
| server | back | server | back | |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 10 | 32/34 | 29 | 33/35 | 31 |
| 8 | 38/40 | 34 | 40/42 | 35 |
| 6 | 44/47 | 38 | 45/49 | 39 |
| 4 | 49/53 | 41 | 51/55 | 43 |
| 2 | 54/59 | 45 | 56/61 | 46 |
| 0 | 59/65 | 48 | 61/66 | 49 |
| -2 | 64/70 | 51 | 66/72 | 53 |
| -4 | 69/76 | 54 | 70/77 | 55 |
| -6 | 74/81 | 57 | 75/82 | 58 |
| -8 | 79/87 | 60 | 78/88 | 61 |
| -10 | 83/92 | 63 | 84/93 | 64 |
| -12 | 88/97 | 66 | 88/96 | 66 |
| -14 | 93/102 | 69 | 93/103 | 69 |
| -15 | 95/105 | 70 | 95/105 | 70 |
Explanations: 1. In gr. 2 and 4 show the values of water temperature in the supply pipeline of the heating system: in the numerator - with an estimated water temperature difference of 95 - 70 °C; in the denominator - with a calculated difference of 105 - 70 °C. In gr. 3 and 5 show the water temperatures in the return pipeline, which are identical in their values at calculated differences of 95 - 70 and 105 - 70 °C.
Temperature graph of the heating system of a residential building after a heating point
Source : Rules and regulations for the technical operation of housing stock, appendix. 20 (approved by order of the State Construction Committee of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 1997 No. 17-139).
Since 2003, the “Rules and Standards for the Technical Operation of the Housing Stock” (approved by the Post of the State Construction Committee of the Russian Federation dated September 27, 2003 No. 170), appendix. eleven.
| Current temperature outdoor tour air, °C | Heating device design | |||||||||
| radiators | convectors | |||||||||
| water supply diagram to the device | convector type | |||||||||
| "from below - down" | "from below - up" | "top down" | K.P. | Comfort | ||||||
| water temperature in distribution pipelines, degrees. C | ||||||||||
| I submit- good | back | server | back | server | back | server | back | server | back | |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
| DESIGN OUTDOOR AIR TEMPERATURE -15 °C | ||||||||||
| 10 | 30/32 | 28 | 32/34 | 29 | 33/35 | 31 | 31/33 | 29 | 33/36 | 32 |
| 9 | 33/35 | 30 | 35/37 | 32 | 37/39 | 33 | 34/36 | 31 | 38/41 | 35 |
| 8 | 36/38 | 32 | 38/40 | 34 | 40/42 | 35 | 37/40 | 33 | 42/45 | 37 |
| 7 | 39/41 | 34 | 41/44 | 36 | 43/46 | 37 | 40/43 | 35 | 45/48 | 39 |
| 6 | 42/45 | 35 | 44/47 | 38 | 45/49 | 39 | 43/36 | 37 | 47/51 | 41 |
| 5 | 44/48 | 37 | 46/50 | 39 | 48/52 | 41 | 47/49 | 39 | 50/54 | 43 |
| 4 | 47/51 | 39 | 49/53 | 41 | 51/55 | 43 | 48/52 | 40 | 53/57 | 45 |
| 3 | 50/54 | 41 | 52/56 | 43 | 53/58 | 45 | 51/55 | 42 | 55/60 | 47 |
| 2 | 52/57 | 43 | 54/59 | 45 | 56/61 | 46 | 54/58 | 44 | 59/63 | 48 |
| 1 | 53/58 | 44 | 57/62 | 46 | 58/64 | 48 | 56/61 | 46 | 60/66 | 50 |
| 0 | 57/62 | 46 | 59/65 | 48 | 61/66 | 49 | 59/64 | 47 | 63/68 | 51 |
| -1 | 60/65 | 48 | 63/67 | 50 | 63/69 | 51 | 61/67 | 49 | 65/71 | 53 |
| -2 | 63/68 | 49 | 64/70 | 51 | 66/72 | 53 | 64/69 | 50 | 67/74 | 54 |
| -3 | 65/71 | 51 | 67/73 | 53 | 69/75 | 54 | 66/72 | 52 | 70/76 | 55 |
| -4 | 68/74 | 53 | 69/76 | 54 | 70/77 | 55 | 69/75 | 54 | 72/79 | 57 |
| -5 | 70/77 | 54 | 72/78 | 56 | 73/80 | 57 | 71/78 | 55 | 74/81 | 58 |
| -6 | 73/78 | 56 | 74/81 | 57 | 75/82 | 58 | 73/81 | 57 | 76/84 | 59 |
| -7 | 75/82 | 57 | 76/84 | 59 | 77/85 | 60 | 76/83 | 58 | 78/86 | 61 |
| -8 | 78/85 | 59 | 79/87 | 60 | 78/88 | 61 | 78/86 | 60 | 81/89 | 62 |
| -9 | 80/88 | 61 | 81/89 | 62 | 83/90 | 62 | 81/89 | 61 | 83/91 | 63 |
| -10 | 83/91 | 62 | 83/92 | 63 | 84/93 | 64 | 83/92 | 63 | 85/92 | 64 |
| -11 | 85/94 | 64 | 86/96 | 64 | 86/95 | 65 | 86/94 | 64 | 87/96 | 65 |
| -12 | 88/97 | 65 | 88/97 | 66 | 88/96 | 66 | 89/97 | 66 | 89/98 | 67 |
| -13 | 90/99 | 67 | 90/100 | 67 | 91/100 | 67 | 90/100 | 67 | 91/100 | 68 |
| -14 | 93/102 | 68 | 93/102 | 69 | 93/103 | 69 | 93/102 | 69 | 93/103 | 69 |
| -15 | 95/105 | 70 | 95/105 | 70 | 95/105 | 70 | 95/105 | 70 | 95/105 | 70 |
| DESIGN OUTDOOR AIR TEMPERATURE -20 °C | ||||||||||
| 10 | 29/30 | 27 | 30/32 | 28 | 32/33 | 29 | 30/31 | 28 | 33/35 | 31 |
| 9 | 31/33 | 28 | 33/35 | 30 | 34/36 | 32 | 32/34 | 30 | 36/38 | 33 |
| 8 | 35/36 | 30 | 36/38 | 32 | 37/39 | 33 | 35/37 | 31 | 39/42 | 35 |
| 7 | 36/38 | 32 | 38/40 | 34 | 40/42 | 35 | 37/40 | 33 | 42/45 | 37 |
| 6 | 38/41 | 33 | 40/43 | 35 | 42/45 | 37 | 40/42 | 35 | 44/47 | 39 |
| 5 | 41/44 | 35 | 43/46 | 37 | 45/48 | 39 | 42/45 | 36 | 47/50 | 41 |
| 4 | 43/46 | 37 | 45/49 | 39 | 47/50 | 40 | 44/48 | 38 | 49/53 | 42 |
| 3 | 45/49 | 38 | 47/51 | 40 | 49/53 | 42 | 47/50 | 39 | 51/55 | 44 |
| 2 | 48/51 | 40 | 50/54 | 42 | 51/56 | 43 | 49/53 | 41 | 53/58 | 45 |
| 1 | 50/54 | 41 | 52/56 | 43 | 54/58 | 45 | 51/55 | 42 | 56/60 | 47 |
| 0 | 52/56 | 43 | 54/47 | 45 | 56/61 | 46 | 53/58 | 44 | 58/63 | 48 |
| -1 | 54/59 | 44 | 56/61 | 46 | 58/63 | 48 | 55/60 | 45 | 60/65 | 49 |
| -2 | 56/61 | 45 | 58/63 | 47 | 60/65 | 49 | 58/63 | 47 | 62/67 | 51 |
| -3 | 59/64 | 47 | 61/66 | 49 | 62/68 | 50 | 60/65 | 48 | 64/70 | 52 |
| -4 | 61/66 | 48 | 63/68 | 50 | 64/70 | 51 | 62/68 | 49 | 66/72 | 53 |
| -5 | 63/69 | 50 | 65/71 | 51 | 66/72 | 53 | 64/70 | 51 | 68/75 | 54 |
| -6 | 65/71 | 51 | 67/73 | 53 | 68/75 | 54 | 66/72 | 52 | 70/76 | 55 |
| -7 | 67/74 | 52 | 69/75 | 54 | 70/77 | 55 | 68/75 | 53 | 72/78 | 57 |
| -8 | 69/76 | 54 | 71/78 | 55 | 72/79 | 56 | 70/77 | 55 | 73/81 | 58 |
| -9 | 72/78 | 55 | 73/80 | 57 | 74/81 | 58 | 52/79 | 56 | 75/83 | 59 |
| -10 | 74/81 | 57 | 74/82 | 58 | 76/83 | 59 | 75/82 | 57 | 77/85 | 60 |
| -11 | 76/83 | 58 | 77/85 | 59 | 78/86 | 60 | 77/84 | 59 | 79/87 | 61 |
| -12 | 78/86 | 59 | 79/87 | 60 | 80/88 | 61 | 79/86 | 60 | 81/89 | 62 |
| -13 | 80/88 | 61 | 81/89 | 62 | 82/90 | 62 | 81/89 | 61 | 83/91 | 63 |
| -14 | 82/90 | 62 | 83/91 | 63 | 84/92 | 63 | 83/91 | 63 | 84/93 | 64 |
| -15 | 84/93 | 63 | 85/94 | 64 | 86/94 | 65 | 85/93 | 64 | 86/95 | 65 |
| -16 | 86/95 | 65 | 87/96 | 65 | 88/97 | 66 | 87/96 | 65 | 88/97 | 66 |
| -17 | 89/98 | 66 | 89/98 | 66 | 89/99 | 67 | 89/98 | 66 | 90/99 | 67 |
| -18 | 91/100 | 67 | 91/100 | 68 | 91/101 | 68 | 91/100 | 68 | 92/102 | 68 |
| -19 | 93/103 | 69 | 93/103 | 69 | 93/103 | 69 | 93/103 | 69 | 93/103 | 69 |
| -20 | 95/105 | 70 | 95/105 | 70 | 95/105 | 70 | 95/105 | 70 | 95/105 | 70 |
| DESIGN OUTDOOR AIR TEMPERATURE -25 °C | ||||||||||
| 10 | 28/29 | 26 | 29/30 | 27 | 30/32 | 28 | 28/30 | 27 | 32/33 | 30 |
| 9 | 30/31 | 27 | 31/33 | 29 | 33/35 | 30 | 31/32 | 28 | 34/36 | 32 |
| 8 | 32/34 | 29 | 34/36 | 31 | 35/37 | 32 | 33/35 | 30 | 37/39 | 34 |
| 7 | 34/36 | 30 | 36/38 | 32 | 37/40 | 34 | 35/37 | 31 | 39/42 | 36 |
| 6 | 36/38 | 32 | 38/40 | 34 | 40/42 | 35 | 37/40 | 33 | 42/44 | 37 |
| 5 | 38/41 | 33 | 40/43 | 35 | 42/45 | 37 | 39/42 | 34 | 44/47 | 39 |
| 4 | 40/43 | 35 | 42/45 | 37 | 44/47 | 38 | 41/44 | 36 | 46/49 | 40 |
| 3 | 42/45 | 36 | 44/47 | 38 | 46/49 | 40 | 43/47 | 37 | 48/52 | 42 |
| 2 | 44/47 | 37 | 46/50 | 39 | 48/52 | 41 | 45/49 | 38 | 50/54 | 43 |
| 1 | 46/50 | 39 | 48/52 | 41 | 50/54 | 42 | 47/51 | 40 | 52/56 | 44 |
| 0 | 49/52 | 40 | 50/54 | 42 | 52/56 | 44 | 49/53 | 41 | 54/58 | 45 |
| -1 | 50/54 | 41 | 52/56 | 43 | 54/58 | 45 | 51/55 | 42 | 57/60 | 47 |
| -2 | 52/56 | 42 | 54/58 | 44 | 56/60 | 46 | 53/58 | 44 | 57/62 | 48 |
| -3 | 54/58 | 44 | 56/61 | 45 | 57/62 | 47 | 55/60 | 45 | 59/65 | 49 |
| -4 | 56/60 | 45 | 58/63 | 47 | 59/64 | 48 | 57/62 | 46 | 61/67 | 50 |
| -5 | 58/63 | 46 | 59/65 | 48 | 61/66 | 50 | 59/64 | 47 | 63/69 | 51 |
| -6 | 59/65 | 47 | 62/67 | 49 | 63/69 | 51 | 61/66 | 49 | 65/70 | 52 |
| -7 | 61/67 | 49 | 63/69 | 50 | 65/70 | 52 | 62/68 | 50 | 66/72 | 53 |
| -8 | 63/69 | 50 | 65/71 | 52 | 66/73 | 53 | 64/70 | 51 | 68/74 | 54 |
| -9 | 65/71 | 51 | 67/73 | 53 | 68/75 | 54 | 66/72 | 52 | 70/76 | 55 |
| -10 | 67/73 | 52 | 69/75 | 54 | 70/76 | 55 | 68/74 | 53 | 71/78 | 56 |
| -11 | 69/75 | 53 | 70/77 | 55 | 72/78 | 56 | 70/76 | 54 | 73/80 | 57 |
| -12 | 71/77 | 55 | 72/79 | 56 | 73/80 | 57 | 72/78 | 56 | 75/82 | 58 |
| -13 | 73/80 | 56 | 74/81 | 57 | 75/82 | 58 | 73/81 | 57 | 76/84 | 59 |
| -14 | 74/82 | 57 | 76/83 | 58 | 77/84 | 59 | 75/83 | 58 | 78/86 | 60 |
| -15 | 76/84 | 58 | 77/85 | 59 | 78/86 | 60 | 77/85 | 59 | 79/87 | 61 |
| -16 | 78/86 | 59 | 79/87 | 60 | 80/88 | 61 | 79/87 | 60 | 81/89 | 62 |
| -17 | 80/88 | 61 | 81/89 | 62 | 82/90 | 62 | 81/89 | 61 | 87/91 | 63 |
| -18 | 82/90 | 62 | 83/91 | 63 | 83/92 | 63 | 82/91 | 62 | 84/93 | 64 |
| -19 | 84/92 | 63 | 84/93 | 64 | 85/94 | 64 | 84/83 | 63 | 86/95 | 65 |
| -20 | 86/94 | 64 | 86/95 | 65 | 87/97 | 65 | 86/95 | 65 | 87/96 | 66 |
| -21 | 87/96 | 65 | 88/97 | 66 | 88/98 | 66 | 88/97 | 66 | 89/98 | 67 |
| -22 | 89/99 | 66 | 90/99 | 67 | 90/99 | 67 | 90/99 | 67 | 90/100 | 67 |
| -23 | 91/100 | 68 | 92/101 | 68 | 92/101 | 68 | 91/101 | 68 | 92/102 | 68 |
| -24 | 93/103 | 69 | 93/103 | 69 | 93/103 | 69 | 93/103 | 69 | 93/103 | 69 |
| -25 | 95/105 | 70 | 95/105 | 70 | 95/105 | 70 | 95/105 | 70 | 95/105 | 70 |
| DESIGN OUTDOOR AIR TEMPERATURE -30 °C | ||||||||||
| 10 | 27/27 | 25 | 28/29 | 26 | 29/30 | 28 | 28/29 | 26 | 31/32 | 29 |
| 9 | 29/30 | 27 | 30/32 | 28 | 31/33 | 29 | 30/31 | 27 | 33/35 | 31 |
| 8 | 31/32 | 28 | 32/34 | 30 | 34/35 | 31 | 32/33 | 29 | 35/37 | 33 |
| 7 | 32/34 | 29 | 34/36 | 31 | 36/38 | 32 | 34/35 | 30 | 38/40 | 34 |
| 6 | 34/36 | 30 | 36/38 | 32 | 38/40 | 34 | 35/37 | 32 | 40/42 | 36 |
| 5 | 36/38 | 32 | 38/40 | 34 | 40/42 | 35 | 37/40 | 33 | 42/44 | 37 |
| 4 | 38/40 | 33 | 40/42 | 35 | 41/44 | 37 | 39/42 | 34 | 43/47 | 38 |
| 3 | 40/42 | 34 | 42/45 | 36 | 43/46 | 38 | 41/44 | 35 | 45/49 | 40 |
| 2 | 41/44 | 35 | 43/47 | 37 | 45/48 | 39 | 43/46 | 37 | 47/51 | 41 |
| 1 | 43/46 | 36 | 45/49 | 39 | 47/50 | 40 | 44/48 | 38 | 49/53 | 42 |
| 0 | 45/48 | 38 | 47/50 | 40 | 49/52 | 41 | 46/50 | 39 | 51/55 | 43 |
| -1 | 47/50 | 39 | 49/52 | 41 | 50/54 | 43 | 48/52 | 40 | 52/57 | 45 |
| -2 | 48/52 | 40 | 50/54 | 42 | 52/56 | 44 | 50/53 | 41 | 54/59 | 46 |
| -3 | 50/54 | 41 | 52/56 | 43 | 54/58 | 45 | 51/55 | 42 | 56/60 | 47 |
| -4 | 52/56 | 42 | 54/58 | 44 | 55/60 | 46 | 53/57 | 44 | 57/62 | 48 |
| -5 | 53/58 | 43 | 55/60 | 45 | 57/62 | 47 | 55/59 | 45 | 59/64 | 49 |
| -6 | 55/60 | 44 | 57/62 | 46 | 59/64 | 48 | 56/61 | 46 | 60/66 | 50 |
| -7 | 57/62 | 45 | 59/64 | 47 | 60/66 | 49 | 58/63 | 47 | 62/68 | 51 |
| -8 | 58/63 | 47 | 60/66 | 49 | 62/67 | 50 | 60/65 | 48 | 64/69 | 52 |
| -9 | 60/65 | 48 | 62/67 | 50 | 63/69 | 51 | 61/67 | 49 | 65/71 | 53 |
| -10 | 62/67 | 49 | 63/69 | 51 | 65/71 | 52 | 63/69 | 50 | 67/73 | 54 |
| -11 | 63/69 | 50 | 65/71 | 52 | 66/73 | 53 | 64/70 | 51 | 68/75 | 54 |
| -12 | 65/71 | 51 | 67/73 | 53 | 68/74 | 54 | 66/72 | 52 | 70/76 | 55 |
| -13 | 67/73 | 52 | 68/75 | 54 | 70/76 | 55 | 68/74 | 53 | 71/78 | 56 |
| -14 | 68/75 | 53 | 70/77 | 55 | 71/78 | 56 | 69/76 | 54 | 73/80 | 57 |
| -15 | 70/77 | 54 | 71/78 | 56 | 73/80 | 57 | 71/78 | 55 | 74/81 | 58 |
| -16 | 72/78 | 55 | 73/80 | 57 | 74/81 | 58 | 73/80 | 56 | 75/83 | 59 |
| -17 | 73/80 | 56 | 75/82 | 58 | 76/83 | 59 | 74/81 | 57 | 77/84 | 60 |
| -18 | 75/82 | 57 | 76/84 | 59 | 77/83 | 60 | 76/83 | 58 | 78/86 | 61 |
| -19 | 77/84 | 58 | 78/85 | 60 | 79/87 | 59 | 77/85 | 59 | 80/88 | 61 |
| -20 | 78/86 | 59 | 79/87 | 61 | 80/88 | 61 | 79/87 | 60 | 81/89 | 62 |
| -21 | 80/88 | 61 | 81/89 | 62 | 82/90 | 62 | 81/89 | 61 | 84/91 | 63 |
| -22 | 82/90 | 62 | 82/91 | 62 | 83/92 | 63 | 82/90 | 62 | 84/92 | 64 |
| -23 | 83/92 | 63 | 84/93 | 63 | 85/93 | 64 | 84/92 | 63 | 85/94 | 65 |
| -24 | 85/94 | 64 | 86/94 | 64 | 86/95 | 65 | 85/94 | 64 | 87/96 | 65 |
| -25 | 87/95 | 65 | 87/96 | 65 | 88/97 | 66 | 87/96 | 65 | 88/97 | 66 |
| -26 | 88/97 | 66 | 89/98 | 66 | 89/98 | 67 | 89/98 | 66 | 90/99 | 67 |
| -27 | 90/99 | 67 | 90/100 | 67 | 91/100 | 67 | 90/100 | 67 | 91/100 | 68 |
| -28 | 92/101 | 68 | 92/101 | 68 | 92/102 | 68 | 92/101 | 68 | 92/101 | 68 |
| -29 | 93/103 | 69 | 93/103 | 69 | 94/103 | 69 | 93/103 | 69 | 94/103 | 69 |
| -30 | 95/105 | 70 | 95/105 | 70 | 95/105 | 70 | 95/105 | 70 | 95/105 | 70 |
| DESIGN OUTDOOR AIR TEMPERATURE -35 °C | ||||||||||
| 10 | 26/27 | 25 | 27/28 | 26 | 28/29 | 27 | 27/28 | 25 | 30/31 | 28 |
| 9 | 28/29 | 26 | 29/30 | 27 | 30/32 | 29 | 29/30 | 27 | 32/34 | 30 |
| 8 | 29/31 | 27 | 31/33 | 29 | 32/34 | 30 | 30/32 | 28 | 34/36 | 32 |
| 7 | 31/33 | 28 | 33/35 | 30 | 34/36 | 31 | 32/34 | 29 | 36/38 | 33 |
| 6 | 33/35 | 29 | 35/37 | 31 | 36/38 | 33 | 34/36 | 31 | 38/40 | 35 |
| 5 | 34/36 | 31 | 36/38 | 32 | 38/40 | 34 | 36/38 | 32 | 40/42 | 36 |
| 4 | 36/38 | 32 | 38/40 | 34 | 40/42 | 35 | 37/40 | 33 | 41/44 | 37 |
| 3 | 38/40 | 33 | 40/42 | 35 | 41/44 | 36 | 39/41 | 34 | 43/46 | 38 |
| 2 | 39/42 | 34 | 41/44 | 36 | 43/46 | 38 | 40/43 | 35 | 45/48 | 39 |
| 1 | 41/44 | 35 | 43/46 | 37 | 44/48 | 39 | 42/45 | 36 | 46/50 | 41 |
| 0 | 42/45 | 36 | 44/48 | 38 | 46/50 | 40 | 44/47 | 37 | 48/52 | 42 |
| -1 | 44/47 | 37 | 46/49 | 39 | 48/51 | 41 | 45/48 | 38 | 50/54 | 43 |
| -2 | 45/49 | 38 | 47/51 | 40 | 49/53 | 42 | 47/50 | 39 | 51/55 | 44 |
| -3 | 47/50 | 39 | 49/53 | 41 | 51/55 | 43 | 48/52 | 40 | 53/57 | 45 |
| -4 | 48/52 | 40 | 50/55 | 42 | 52/56 | 44 | 50/54 | 41 | 54/59 | 46 |
| -5 | 50/54 | 41 | 52/56 | 43 | 54/58 | 45 | 52/55 | 42 | 56/60 | 47 |
| -6 | 51/56 | 42 | 53/58 | 44 | 55/60 | 46 | 53/57 | 43 | 57/62 | 48 |
| -7 | 53/57 | 43 | 55/60 | 45 | 57/61 | 47 | 54/59 | 44 | 58/64 | 49 |
| -8 | 54/59 | 44 | 56/61 | 46 | 58/63 | 48 | 56/60 | 45 | 60/65 | 49 |
| -9 | 56/61 | 45 | 58/63 | 47 | 59/65 | 49 | 57/62 | 46 | 61/67 | 50 |
| -10 | 57/62 | 46 | 59/65 | 48 | 61/66 | 49 | 59/64 | 47 | 63/68 | 51 |
| -11 | 59/64 | 47 | 61/66 | 49 | 62/68 | 50 | 60/65 | 48 | 64/70 | 52 |
| -12 | 60/66 | 48 | 62/68 | 50 | 64/70 | 51 | 62/67 | 49 | 65/71 | 53 |
| -13 | 62/67 | 49 | 64/70 | 51 | 65/71 | 52 | 63/69 | 50 | 67/73 | 54 |
| -14 | 63/69 | 50 | 65/71 | 52 | 67/73 | 53 | 64/70 | 51 | 68/75 | 55 |
| -15 | 65/71 | 51 | 67/73 | 53 | 68/74 | 54 | 66/72 | 52 | 69/76 | 55 |
| -16 | 66/73 | 52 | 68/74 | 53 | 69/76 | 55 | 67/74 | 53 | 71/78 | 56 |
| -17 | 68/74 | 53 | 69/76 | 54 | 71/77 | 56 | 69/75 | 54 | 72/79 | 57 |
| -18 | 69/76 | 54 | 71/78 | 55 | 72/79 | 56 | 70/77 | 55 | 73/81 | 58 |
| -19 | 71/78 | 55 | 72/79 | 56 | 73/81 | 57 | 72/79 | 56 | 75/82 | 58 |
| -20 | 72/79 | 56 | 74/81 | 57 | 75/82 | 58 | 73/80 | 57 | 76/83 | 59 |
| -21 | 74/81 | 57 | 75/83 | 58 | 76/84 | 59 | 75/82 | 57 | 77/85 | 60 |
| -22 | 75/83 | 58 | 77/84 | 59 | 78/85 | 60 | 76/84 | 58 | 79/86 | 61 |
| -23 | 77/84 | 59 | 78/86 | 60 | 79/87 | 61 | 78/85 | 59 | 80/88 | 61 |
| -24 | 78/86 | 60 | 79/87 | 61 | 80/88 | 61 | 79/87 | 60 | 81/89 | 62 |
| -25 | 80/88 | 60 | 81/89 | 61 | 82/90 | 62 | 80/89 | 61 | 82/91 | 63 |
| -26 | 81/89 | 61 | 82/91 | 62 | 83/91 | 63 | 82/90 | 62 | 84/92 | 64 |
| -27 | 83/91 | 62 | 84/92 | 63 | 84/93 | 64 | 83/92 | 63 | 85/94 | 64 |
| -28 | 84/93 | 63 | 85/94 | 64 | 86/94 | 65 | 85/93 | 64 | 86/95 | 65 |
| -29 | 86/95 | 64 | 86/95 | 65 | 87/96 | 65 | 86/95 | 65 | 87/96 | 66 |
| -30 | 87/96 | 65 | 88/97 | 66 | 88/97 | 66 | 88/97 | 66 | 89/98 | 67 |
| -31 | 89/98 | 66 | 89/99 | 67 | 89/99 | 67 | 89/98 | 66 | 90/99 | 67 |
| -32 | 90/100 | 67 | 91/100 | 67 | 91/100 | 68 | 91/100 | 67 | 91/101 | 68 |
| -33 | 92/102 | 68 | 92/102 | 68 | 92/102 | 68 | 92/102 | 68 | 93/102 | 69 |
| -34 | 93/103 | 69 | 94/103 | 69 | 94/103 | 69 | 94/103 | 69 | 94/104 | 69 |
| -35 | 95/105 | 70 | 95/105 | 70 | 95/105 | 70 | 95/105 | 70 | 95/105 | 70 |
| DESIGN OUTDOOR AIR TEMPERATURE -40 °C | ||||||||||
| 10 | 25/26 | 24 | 27/27 | 25 | 28/29 | 27 | 26/27 | 25 | 29/33 | 28 |
| 9 | 27/28 | 25 | 28/29 | 26 | 30/31 | 28 | 28/29 | 26 | 31/33 | 29 |
| 8 | 29/30 | 26 | 30/31 | 28 | 31/33 | 29 | 29/31 | 27 | 33/35 | 31 |
| 7 | 30/31 | 28 | 32/33 | 29 | 33/35 | 31 | 31/33 | 29 | 35/37 | 32 |
| 6 | 32/33 | 29 | 33/35 | 30 | 35/37 | 32 | 33/34 | 30 | 37/39 | 34 |
| 5 | 33/35 | 30 | 35/37 | 31 | 36/39 | 33 | 34/36 | 31 | 38/41 | 35 |
| 4 | 35/36 | 31 | 36/39 | 33 | 38/40 | 34 | 36/38 | 32 | 40/43 | 36 |
| 3 | 36/38 | 32 | 38/40 | 34 | 39/42 | 35 | 37/39 | 33 | 41/44 | 37 |
| 2 | 37/40 | 33 | 39/42 | 35 | 41/44 | 36 | 39/41 | 34 | 43/46 | 38 |
| 1 | 39/41 | 34 | 41/44 | 36 | 42/45 | 37 | 40/43 | 35 | 44/48 | 39 |
| 0 | 40/43 | 35 | 42/45 | 37 | 44/47 | 38 | 41/44 | 36 | 46/49 | 40 |
| -1 | 42/44 | 36 | 44/47 | 38 | 45/49 | 39 | 43/46 | 37 | 47/51 | 41 |
| -2 | 43/46 | 36 | 45/48 | 38 | 47/50 | 40 | 44/47 | 38 | 49/53 | 42 |
| -3 | 44/48 | 37 | 46/50 | 39 | 48/52 | 41 | 46/49 | 39 | 50/54 | 43 |
| -4 | 45/49 | 38 | 48/52 | 40 | 50/53 | 42 | 47/50 | 40 | 52/56 | 44 |
| -5 | 47/51 | 39 | 49/53 | 41 | 51/55 | 43 | 48/52 | 41 | 53/57 | 45 |
| -6 | 48/52 | 40 | 51/55 | 42 | 52/57 | 44 | 50/54 | 41 | 54/59 | 46 |
| -7 | 50/54 | 41 | 52/56 | 43 | 54/58 | 45 | 51/55 | 42 | 56/60 | 47 |
| -8 | 51/55 | 42 | 53/58 | 44 | 55/60 | 46 | 52/57 | 43 | 57/62 | 47 |
| -9 | 53/57 | 43 | 55/59 | 45 | 56/61 | 46 | 54/58 | 44 | 58/63 | 48 |
| -10 | 54/58 | 44 | 56/61 | 46 | 58/62 | 47 | 55/60 | 45 | 59/65 | 49 |
| -11 | 55/60 | 45 | 57/62 | 47 | 59/64 | 48 | 57/61 | 46 | 61/66 | 50 |
| -12 | 57/62 | 46 | 59/64 | 47 | 60/65 | 49 | 58/63 | 47 | 62/68 | 51 |
| -13 | 58/63 | 46 | 60/65 | 48 | 61/67 | 50 | 59/64 | 48 | 63/68 | 51 |
| -14 | 59/65 | 47 | 61/67 | 49 | 63/68 | 51 | 61/66 | 48 | 64/70 | 52 |
| -15 | 61/66 | 48 | 63/68 | 50 | 64/70 | 51 | 62/67 | 49 | 66/72 | 53 |
| -16 | 62/68 | 49 | 64/70 | 51 | 65/71 | 52 | 63/69 | 50 | 67/73 | 54 |
| -17 | 63/70 | 50 | 65/71 | 52 | 67/73 | 53 | 64/70 | 51 | 68/75 | 55 |
| -18 | 65/71 | 51 | 66/73 | 52 | 68/74 | 54 | 66/72 | 52 | 69/76 | 55 |
| -19 | 66/72 | 52 | 68/74 | 53 | 69/76 | 55 | 67/73 | 53 | 71/77 | 56 |
| -20 | 67/74 | 53 | 69/76 | 54 | 70/77 | 55 | 68/75 | 54 | 72/79 | 57 |
| -21 | 69/75 | 53 | 70/77 | 55 | 72/78 | 56 | 70/76 | 54 | 73/80 | 57 |
| -22 | 70/77 | 54 | 72/79 | 56 | 73/80 | 57 | 71/78 | 55 | 74/81 | 58 |
| -23 | 71/78 | 55 | 73/80 | 57 | 74/81 | 58 | 72/79 | 56 | 75/83 | 59 |
| -24 | 73/80 | 56 | 74/81 | 57 | 75/83 | 58 | 74/81 | 57 | 76/84 | 60 |
| -25 | 74/81 | 57 | 76/83 | 58 | 77/84 | 59 | 75/84 | 58 | 78/85 | 60 |
| -26 | 76/83 | 58 | 77/84 | 59 | 78/85 | 60 | 76/84 | 59 | 79/87 | 61 |
| -27 | 77/85 | 59 | 78/86 | 60 | 79/87 | 61 | 78/85 | 59 | 80/88 | 62 |
| -28 | 78/86 | 60 | 79/87 | 61 | 80/88 | 61 | 79/87 | 60 | 81/89 | 62 |
| -29 | 80/88 | 60 | 81/89 | 61 | 82/90 | 62 | 80/88 | 61 | 82/91 | 63 |
| -30 | 81/89 | 61 | 82/90 | 62 | 83/91 | 63 | 82/90 | 62 | 83/92 | 64 |
| -31 | 82/91 | 62 | 83/92 | 63 | 84/92 | 64 | 83/92 | 63 | 85/93 | 64 |
| -32 | 84/92 | 63 | 85/93 | 64 | 85/94 | 64 | 84/93 | 63 | 86/95 | 65 |
| -33 | 85/94 | 64 | 86/95 | 65 | 86/95 | 65 | 86/94 | 64 | 87/96 | 66 |
| -34 | 87/95 | 65 | 87/96 | 65 | 88/97 | 66 | 87/96 | 65 | 88/97 | 66 |
| -35 | 88/97 | 66 | 88/98 | 66 | 89/98 | 66 | 88/97 | 66 | 89/99 | 67 |
| -36 | 89/99 | 66 | 90/99 | 67 | 90/99 | 67 | 90/99 | 67 | 90/100 | 67 |
| -37 | 91/100 | 67 | 91/101 | 68 | 91/100 | 68 | 91/100 | 68 | 92/101 | 68 |
| -38 | 92/102 | 68 | 92/102 | 68 | 93/102 | 69 | 92/102 | 68 | 93/102 | 69 |
| -39 | 94/103 | 69 | 94/104 | 69 | 94/104 | 69 | 94/103 | 69 | 94/104 | 69 |
| -40 | 95/105 | 70 | 95/105 | 70 | 95/105 | 70 | 95/105 | 70 | 95/105 | 70 |
Explanations:
- In gr. 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 are given for each type of heating device and the current outside air temperature the values of the water temperature in the supply pipeline of the heating system: in the numerator - with a calculated water temperature difference of 95 - 70 °C; in the denominator - with a calculated difference of 105 - 70 °C. In gr. 3, 5, 7, 9, 11 are given for each outside air temperature and type of heating device, water temperatures in the return pipeline with calculated differences of 95 - 70 and 105 - 70 °C, coinciding in their values.
- In the case when the heating system has various types of heating devices (for example, radiators according to the “top-down”, “bottom-down”, “bottom-up” schemes, convectors K.P., etc.), water temperature in the supply and return pipelines should be taken at the highest value of all heating curves.
- When supplying heat from a local boiler house to several residential buildings with different heating systems, the water temperature in the supply main of the heating network should be maintained at the highest according to the highest heat release schedule of all heating systems of buildings supplied with heat from this boiler house.
- At other design temperatures of the outside air, it is necessary to determine the temperature of the water in the supply and return pipelines of the heating system by interpolating the corresponding values from two tables: one with the nearest large and the other with the nearest smaller design temperature of the outside air. So, for example, if the estimated outside air temperature is -18 °C, then in a heating system with radiators with a top-down water supply to the device, with an estimated water temperature difference of 105 - 70 degrees. C and the current outside air temperature is -5 °C, the supply water temperature will be: 72 + (80 - 72) x (20 - 18) / 5 = 75.2, or rounded 75 °C.
- The graph of qualitative regulation of water temperature in a heating system with “Comfort” type convectors is given for devices with a fin pitch of 10 mm; when using “Comfort” convectors with a fin spacing of 5 mm in heating systems, its values should be taken as for radiators with a top-down water supply to the device.
- In order to save heat, the air temperature in heated rooms at night (from 0 to 5 o'clock) is recommended to be reduced by 2 - 3 ° C from the set level of 18 - 20 ° C by lowering the temperature of the water supplied to the heating system. The reduction in coolant temperature should be established experimentally for each boiler room and central heating station.
WATER TEMPERATURE IN DISTRIBUTION PIPELINES, degrees. C
AT DESIGNED OUTSIDE AIR TEMPERATURE
-20 HAIL C
| current outside temperature, hail C | diagram of water supply to radiators | |||
| "down up" | "top down" | |||
| server | back | server | back | |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 10 | 30/32 | 28 | 32/33 | 29 |
| 8 | 36/38 | 32 | 37/39 | 33 |
| 6 | 40/43 | 35 | 42/45 | 37 |
| 4 | 45/49 | 39 | 47/50 | 40 |
| 2 | 50/54 | 42 | 51/56 | 43 |
| 0 | 54/47 | 45 | 56/61 | 46 |
| -2 | 58/63 | 47 | 60/65 | 49 |
| -4 | 63/68 | 50 | 64/70 | 51 |
| -6 | 67/73 | 53 | 68/75 | 54 |
| -8 | 71/78 | 55 | 72/79 | 56 |
| -10 | 74/82 | 58 | 76/83 | 59 |
| -12 | 79/87 | 60 | 80/88 | 61 |
| -14 | 83/91 | 63 | 84/92 | 63 |
| -15 | 85/94 | 64 | 86/94 | 65 |
| -16 | 87/96 | 65 | 88/97 | 66 |
| -18 | 91/100 | 68 | 91/101 | 68 |
| -20 | 95/105 | 70 | 95/105 | 70 |
WATER TEMPERATURE IN DISTRIBUTION PIPELINES, degrees. C
AT DESIGNED OUTSIDE AIR TEMPERATURE
-25 HAIL C
| current outside temperature, hail C | diagram of water supply to radiators | |||
| "down up" | "top down" | |||
| server | back | server | back | |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 10 | 29/30 | 27 | 30/32 | 28 |
| 8 | 34/36 | 31 | 35/37 | 32 |
| 6 | 38/40 | 34 | 40/42 | 35 |
| 4 | 42/45 | 37 | 44/47 | 38 |
| 2 | 46/50 | 39 | 48/52 | 41 |
| 0 | 50/54 | 42 | 52/56 | 44 |
| -2 | 54/58 | 44 | 56/60 | 46 |
| -4 | 58/63 | 47 | 59/64 | 48 |
| -6 | 62/67 | 49 | 63/69 | 51 |
| -8 | 65/71 | 52 | 66/73 | 53 |
| -10 | 69/75 | 54 | 70/76 | 55 |
| -12 | 72/79 | 56 | 73/80 | 57 |
| -14 | 76/83 | 58 | 77/84 | 59 |
| -16 | 79/87 | 60 | 80/88 | 61 |
| -18 | 83/91 | 63 | 83/92 | 63 |
| -20 | 86/95 | 65 | 87/97 | 65 |
| -22 | 90/99 | 67 | 90/99 | 67 |
| -24 | 93/103 | 69 | 93/103 | 69 |
| -25 | 95/105 | 70 | 95/105 | 70 |
Estimated outside air temperatures during the cold period
in a number of Russian cities
(source – SNiP 23-01-99 “Building climatology”)
| City | Temperature, minus OS | City | Temperature, minus OS |
| Arkhangelsk | 18 | Magadan | 22 |
| Astrakhan | 12 | Novosibirsk | 24 |
| Belgorod | 13 | N.Novgorod | 17 |
| Bryansk | 14 | Eagle | 15 |
| Barnaul | 23 | Omsk | 24 |
| Vologda | 14 | Petrozavodsk | 16 |
| Voronezh | 15 | Permian | 20 |
| Vladimir | 16 | Rostov-on-Don | 11 |
| Volgograd | 17 | Ryazan | 16 |
| Vladivostok | 18 | Sochi | +1 |
| Vorkuta | 26 | St. Petersburg | 13 |
| Verkhoyansk | 53 | Saratov | 16 |
| Ekaterinburg | 20 | Samara | 18 |
| Ivanovo | 17 | Salekhard | 29 |
| Irkutsk | 26 | Tyumen | 22 |
| Krasnodar | 7 | Ulyanovsk | 19 |
| Kaliningrad | 8 | Ufa | 20 |
| Kursk | 14 | Ulan-Ude | 30 |
| Kostroma | 17 | Khabarovsk | 27 |
| Kazan | 18 | Chelyabinsk | 21 |
| Kirov | 19 | Chita | 31 |
| Moscow | 15 | Yaroslavl | 17 |
| Murmansk | 16 | Yakutsk | 48 |
Request a specific temperature schedule for the heating system of your home, approved by the administration of your city (locality), from the relevant housing and communal services organizations and monitor its implementation. Saving a person who is freezing is the work of not only the housing and communal services, but also the person who is freezing!
author: housing and communal services specialist Yuri Kalnin
See also other articles from the series “What to do if it’s cold in your apartment”:
- About the lack of heating of the boiler room.
- The main malfunctions of the heating system, their possible symptoms, causes and actions of freezing.
- How and with what to measure the temperature of water in radiators and heating pipes in an apartment?
- Is it profitable to demand a recalculation of heating fees?
How to measure battery temperature correctly
When the issue with the coolant is clarified, you can think about how to measure the temperature of the battery in the apartment. This is easy to do in the following ways:
- Use a regular household thermometer. You need to apply it to the battery and wait until it warms up. To account for the error, it is better to add 1-2 degrees to the data obtained.
- Use an alcohol thermometer, attaching it to the radiator with tape, and then insulating it with insulating material, such as foam rubber. The information obtained by this method is indicative in dynamics. The device can be left for a long period to continuously monitor the situation.
- Use an infrared thermometer. In practice, they have a small error, and do not require direct contact with the heating device. And the result is given instantly.
- Use an electrical measuring instrument with a thermal ramp and sensor. The sensor is installed on the battery, and when the “measure temperature” function is selected, the device displays its value.
What to do if standards are violated
If you find that the radiators in the apartment are cold, you should find out whether this is a problem exclusively for this room or whether all residents of the house are faced with it. A collective appeal always attracts more attention than an individual one.
If the quality of heating is unsatisfactory and does not comply with SNiP, a complaint can be filed:
- to a service organization: homeowners association, management company, housing construction cooperative;
- resource supply company;
- emergency dispatch service;
- housing inspection. It usually operates a special hotline for such requests.
Organizations will receive the complaint over the phone and then register it. After this, specialists will establish and eliminate the cause of the lack of heating, recording a violation.
Later, based on the heating network inspection report, a recalculation for the period of no heat occurs.
If the above organizations do not take any measures to restore heating, you should file a complaint with Rospotrebnadzor and the prosecutor's office.
conclusions
The legislator established standards for the characteristics of the heating system, paying special attention to the optimal temperature in the living room. Its value is the most important for residents, and it is also easy to check. If it is lower than required, it means the battery is not heated enough. And in case of non-compliance with the standards, you can file a complaint with the service organizations, not forgetting about recalculating the fee if it is discovered that heating services are of inadequate quality.
Lawyer. Member of the Bar Association of St. Petersburg. More than 10 years of experience. Graduated from St. Petersburg State University. I specialize in civil, family, housing, and land law.











