Thermal properties of wood
All breeds have their own characteristics. They light up at different temperatures and give off their own amount of energy. Each tree has different indicators. This needs to be considered in more detail. Especially for people who use such natural material in private homes.
Detailed information is visible in the video:
Rock ignition temperature
Various types of wood are suitable for heating homes. Everyone's combustion methods are different. Certain firewood produces a high flame, while others produce a low flame. Naturally, the heat transfer is different. Also greatly influenced by the amount of oxygen entering the firebox, volumetric weight, and percentage of humidity.
The combustion temperature is affected by the section of the tree, its species, and its density. All factors are integral.
The table provides useful data:
| Name of wood | Ignition temperature | t ° fire |
| Alder | 552 | 1117 |
| Poplar | 468 | – |
| Pine | 624 | 1090 |
| Birch | 816 | 1069 |
The information is not about all species, but you can understand what the ignition temperature of wood is when heated. There is a generally accepted minimum value of 450 degrees. But this depends on many conditions.
How wood behaves at different temperatures
If the degrees increase, then the strength of the natural material becomes less. As they decrease, it increases. If a tree is frozen, it becomes stronger. Temperature has a stronger effect on wet wood than on dry wood.
When humidity levels increase significantly, wood undergoes plasticization. The material can be bent. During freezing, humidity increases brittleness. The material will not last for a long period. This leads to splitting.
Firewood selection
Here you need to know some nuances. For example, beech and ash give a high temperature, but they are not suitable for heating a conventional stove, sauna or bathhouse. Due to its high cost.
Birch firewood is ideal for steam rooms. They need a temperature of 816-820 degrees Celsius to ignite.
Oak and larch are also good choices. They need approximately the same number of degrees. If you need to light a fire, pine needles are suitable.
The best choice is pine. It can also be used for the oven. Such trees have a high resin content. It will clog the chimney and will need to be cleaned constantly. Conifers are suitable for such purposes in extreme cases. Do not put wet firewood in the firebox. They burn poorly and create smoke.
How to choose correctly
It should be said right away that although beech or ash is characterized by a high combustion temperature of firewood, using them to fire a stove or bathhouse is quite expensive and unprofitable.
This article will help you make a sauna stove yourself: https://teplo.guru/pechi/bannye/stroim-pech-dlya-bani.html
Therefore, it is customary to use birch firewood, which burns at 800-820 degrees. Also, oak and larch, burning at 840-900 degrees, are suitable for these purposes.
Coniferous tree species - pine - are most suitable for a fire. However, no one prohibits its use as heating for a stove. At a combustion temperature of 610-630 degrees, half as much firewood will be used as oak or birch.
- low combustion temperature;
- smoke and soot formation.
Because they contain a large amount of resins. The latter settle on the walls of the chimney, clog it over time and require cleaning. Therefore, the use of softwood for these purposes is not very desirable and is recommended only in extreme cases.
In addition, you should pay attention to the moisture content of the firewood, since its percentage has a direct impact on the combustion process. Accordingly, wet material will burn poorly and create a large amount of smoke.
This article will help you figure out whether wood or briquettes are better for heating: https://teplo.guru/kotly/toplivnyie-briketyi-ili-drova.html
How did man master fire?
Fire was known to people who lived in the Stone Age. People absolutely could not always make fire on their own. Man's first acquaintance with the combustion process, according to scientists, happened empirically. Fire, obtained from a forest fire or conquered from a neighboring tribe, was protected as a very expensive thing that people had.
Over the course of some time, people have noticed that certain materials have qualities that are more conducive to combustion. For example, dry grass or moss can ignite with just a few sparks.
Over the years, again empirically, people learned to make fire using improvised means. Historians call man’s first “lighter” tinder and flint, which produced sparks when they struck each other. Later, humanity learned to make fire using a twig placed in a special recess in the wood. The ignition temperature of the wood was achieved due to the intensive rotation of the end of the twig in the recess. Many Orthodox communities continue to use these methods today.
Much later, in 1805, the French chemist Jean Chancel invented the first matches. The discovery became widespread, and a person could safely draw fire if necessary.
Mastering the combustion process is considered a decisive factor that gave impetus to the formation of civilization. In addition, in the near future, combustion will remain such an argument.
Burns like a match
Briefly about the structure of a match. It consists of a stick and a head. Sticks are made from wood, cardboard and cotton cord impregnated with paraffin. The wood chosen is soft species - poplar, pine, aspen. The raw material for sticks is called match straw. To avoid smoldering of the straws, the sticks are impregnated with phosphoric acid. Russian factories make straw from aspen.
The head of a match is simple in shape, but complex in its chemical composition. The dark brown head of the match contains seven components: oxidizing agents - Berthollet salt and potassium dichromate; glass dust, red lead, sulfur, bone glue, zinc white.
- poplar – 468;
- aspen – 612;
- pine – 624.
The fire temperature of a match is equal to the fire temperature of wood. Therefore, the white flash of the sulfur head is replaced by the yellow-orange tongue of the match.
If you look closely at a burning match, you will see three zones of flame. The bottom one is cool blue. The average is one and a half times warmer. The top is the hot zone.
Consequences of heating wood
A process where an area of rock is exposed to an external heat source and fire appears. It could be paper set on fire with a match, or something else. What is the combustion temperature of paper? Paper can ignite if there is an ignition source on its own, releasing light and heat.
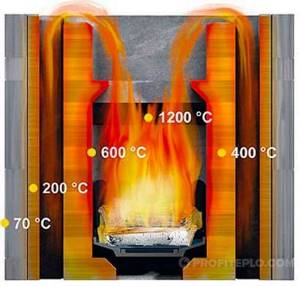
At a temperature of 120-150°C, the wood begins to char. Self-igniting coal is formed.
When the degrees reach 250-350°C, the material will begin to thermally decompose into its components. The surface of the tree will begin to smolder, but the flame cannot be seen. Brown smoke will appear. The breed has already warmed up and is ready to move into a new stage.
Ignition
The initial stage of the combustion process in which thermochemical reactions are accelerated. Activates at temperatures of 460 degrees and above.
Ignition is affected by volume, humidity, external heat source, draft and other factors. If the rock is wet, the ignition process is difficult.
Additional energy is required to evaporate water. Also, thermal conductivity slows down. A massive round tree burns worse. Rectangular with a small cross-section - good. An unplaned wood surface is more likely to ignite than a smooth surface. It is also important that there is enough oxygen supplied. Otherwise you will have to wait a long time for the fire.
Self-ignition
The process is possible without the influence of external sources. For example, a certain area of the rock is overheated. It starts to char. Charcoal reacts with oxygen. A flammable mixture appears above the surface.
High temperature ignites the formation. Smoldering charcoal appears on the fibers of the boards. To avoid spontaneous combustion, especially if the rock is located near fire sources, you need to remove uneven areas. Then the emergency will not happen.
Combustion products
In the process, gaseous particles and solid particles turn into smoke. Their composition depends on the type of wood. These are compounds of chemical elements with oxygen.
Combustion products are:
- carbon dioxide;
- water vapor;
- nitrogen;
- carbon monoxide;
- sulphur dioxide.
The listed products cannot burn in the future. Except for one exception. It is carbon monoxide. Particulate matter in smoke is soot. The composition of the products depends on the combustion conditions. It may or may not be complete.
If there is not enough air, acrid smoke appears. It is very dangerous for humans. Often inhaling it in large quantities is fatal.
Temperature readings in the oven
The combustion process is associated with isometric processes, during which a large amount of heat is released. However, for stable combustion, wood must be heated to a certain degree. Factors contributing to the combustion of fuel wood:
- wood type;
- material moisture;
- volume of incoming air.
This is interesting: the heat of combustion of coal and charcoal.

One of the factors of combustion temperature is the type of wood
To ignite wood in a stove, it is necessary to heat the wooden surface from a separate heat source to a temperature of 120-150°C. With further heating, the percentage of pyrolysis gases increases and a fire appears. An important role in the occurrence of fire is played by:
- heating source power;
- cross section of wood;
- air flow speed;
- density of the material.
Along with the calorific value of firewood, its thermal power is of interest. Each type of wood burns in its own way - one allows you to get a high flame temperature, while the other gives the opposite picture. Most stoves have a heating power of about 6-8 kW, meaning the temperature in a wood-burning stove can reach approximately 500 to 1000°C.
Which wood burns better and which burns worse?
Dry wood burns best. Wood soaked in moisture also burns, but it takes considerable temperature and some time to remove and evaporate the moisture. This process is in most cases accompanied by a distinctive hissing sound. Not everyone knows that when “damp” wood burns, vinegar acid is released. This fact shows up very poorly on furnace equipment and on the overall combustion efficiency. It is highly recommended to use dry firewood, and also buy firewood in the spring so that it has time to dry before the cold weather arrives.
Factors affecting combustion temperature
The combustion temperature of firewood in a stove depends not only on the type of wood. Significant factors are also the moisture content of the wood and the traction force, which is determined by the design of the heating unit.
Effect of humidity
For freshly cut wood, the moisture content ranges from 45 to 65%, with an average of about 55%. The combustion temperature of such firewood will not rise to maximum values, since thermal energy will be spent on moisture evaporation. In accordance with this, the heat transfer of the fuel is reduced.
In order for the required amount of heat to be released during the combustion of wood, three ways are used
:
- almost twice as much freshly cut firewood is used for heating rooms and cooking (this results in increased fuel costs and the need for frequent maintenance of the chimney and flues, in which a large amount of soot will settle);
- freshly cut firewood is pre-dried (logs are sawn, split into logs, which are stacked under a canopy - natural drying to 20% humidity requires 1-1.5 years);
- dry firewood is purchased (financial costs are compensated by the high heat transfer of the fuel).
The calorific value of freshly cut birch firewood is quite high. Fuel made from freshly cut ash, hornbeam and other hardwoods is also suitable for use.
Effect of air supply
By limiting the flow of oxygen into the firebox, we reduce the combustion temperature of the wood and reduce the heat transfer of the fuel. The combustion duration of the fuel load can be increased by closing the damper of the boiler unit or stove, but saving fuel results in low combustion efficiency due to suboptimal conditions. For wood burning in an open fireplace, air flows freely from the room, and the intensity of the draft depends mainly on the characteristics of the chimney.
The simplified formula for ideal wood combustion is as follows:
:
C + 2H2 + 2O2 = CO2 + 2H2O + Q (heat)
Carbon and hydrogen are burned when oxygen is supplied (left side of the equation), resulting in heat, water and carbon dioxide (right side of the equation).
In order for dry wood to burn at maximum temperature, the volume of air that enters the combustion chamber must reach 130% of the volume required for the combustion process. When the air flow is blocked by the dampers, a large amount of carbon monoxide is formed, and the reason for this is a lack of oxygen. Carbon monoxide (unburned carbon) goes into the chimney pipe, while the temperature in the combustion chamber drops and the heat transfer of firewood decreases.
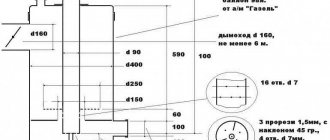
An economical approach when using a solid fuel boiler with wood is to install a heat accumulator, which will store excess heat generated when the fuel burns in an optimal mode, with good draft.
You won't be able to save fuel like that with wood stoves because they heat the air directly. The body of a massive brick stove is capable of accumulating a relatively small part of the thermal energy, while with metal stoves the excess heat goes directly into the chimney.
If you open the ashpit and increase the draft in the furnace, the combustion intensity and heat transfer of the fuel will increase, but heat loss will also increase. When wood burns slowly, the amount of carbon monoxide increases and heat transfer decreases.
Implementation
And so, we all know that incandescent lamps are very inefficient and, in addition to their main purpose, are good sources of heat.
If we move on to the numbers, a 50W halogen lamp heats up to about 200 degrees, 75W about 230 degrees. This way we get a heat source with the desired temperature - cheap and cheerful.
And so we need 10 minutes of free time and the availability of all the components. Go.
Preparing the Heater
We take the lamp, if it has protective glass - you can remove it and clean the glass and reflector from the glue that attaches this glass - this is easier to do, after the first use - it will warm up well and the glass will fall off on its own (I did this).
We put the glass in place (it will fall out - it doesn’t matter to us) and wrap the lamp in foil, leaving the contacts free. This will slightly raise the temperature created by the lamp and get rid of excess light (which is a byproduct for us)
Connecting the power cable
I’ll say a little about the terminal for the lamp - as a rule, they are made of ceramics, wires with silicone insulation - all this is for safe operation at high temperatures.
We connect the power cord by twisting and insulating it. All e-charcoal is ready for use.
Installation on a hookah =)
We install our e-charcoal on the hookah. It is better to fix the network cable.
Making a cap for a hookah.
Attention! The foil should not be used to short circuit the terminal taps; it is better to avoid contact between the foil and the terminal at all. Plug it in - if it lights up it means it’s working
To reduce the glow, we reduce the outlet of the cap (as shown in the previous figure). Subject to short circuit warning
We plug it into the outlet - if it lights up, it means it’s working. To reduce the glow, we reduce the outlet of the cap (as shown in the previous figure). Subject to short circuit warning.
Factors influencing the burning temperature of firewood
There are several factors that contribute to combustion:
- The type of wood used for combustion.
- Humidity of the material.
- The volume of air entering the firebox.
These are the main indicators that you need to pay special attention to, since the efficiency of burning wood and the temperature that can rise during the combustion process will depend on them
Humidity level
Wood moisture plays a key role during ignition, so such an important point requires separate consideration. Any tree that has just been cut down has a certain moisture content. In most cases this figure is 50%. But in some cases it increases to 65%. This means that this type of material will dry for a very long time under the influence of high temperatures before igniting.
Part of the heat will be spent only to remove excess moisture through evaporation. For this reason, the temperature will not reach the maximum value. Under this condition, heat transfer will decrease.
To get maximum benefit, there are several basic options you should use:
- The most suitable option is drying. To do this, the tree is cut into small pieces and then stored in a dry place in a barn or shed. Under natural conditions, the drying process will take approximately 1 year. And if the firewood is stored longer and lasts two summers, then its humidity will be 20%. This is already the optimal indicator.
- The second option is less preferable - burn what you have, not paying attention to humidity. But in this situation, you will have to spend twice as much firewood to create the desired temperature. In addition, you should be prepared to clean the chimney of soot.
The better the wood is dried, the higher the combustion temperature can be achieved. And the release of heat depends on this. There will be no heat with wet wood.
Warming up process
Heating is the heating of a specific area of wood material to a temperature sufficient to ignite the entire surface.

The process will then continue as coal is formed. When heated to 250-350 degrees, the selected material will begin to decompose into its components. Then smoldering begins, but the flame does not appear yet. At this point, you can observe the formation of smoke. As the temperature continues to rise, the level of pyrolysis gases increases—an outbreak occurs. The wood will burn completely.
Flammability of materials
The flammability is directly affected by the percentage of moisture contained in the selected rock. The power of the heating source plays an important role, as does the cross-section of the wood and the air flow rate.
To make the flame burn faster, it is advisable to use light wood that has high porosity. Wet wood will burn very slowly because it will dry out before it can form an open fire.
Combustion also depends on the shape of the tree - it is advisable to use a rectangle, since a circle will take much longer to burn. To speed up the process, it is necessary to select a material with a small cross-section and sharp edges
It is important to ensure that the required amount of oxygen is supplied to the area being flared.
The combustion temperature of firewood and flammability are also greatly influenced by the design of a home stove. It can be made from different materials and this directly affects the combustion temperature of the materials placed inside. If the stove is massive, then the wood in it will burn almost completely, but this process will take a very long time
Great care must be taken when using. Failure to comply with safety measures can lead to a fire in a wood-burning sauna at a high combustion temperature of the stove.

A potbelly stove, made of steel sheet, cools quickly, while the heat is distributed throughout the surrounding space, but first it will move from the combustion zone to the walls, and only then into the room.
Combustion process
As you observe the operation of the furnace, you may wonder why the supplied air does not affect the color of the resulting flame. Oxygen should have a chemical effect and give the soot a bright color, which can even turn white. But this phenomenon can be easily explained, because the particle size also affects the temperature. The smaller it is, the lower the temperature will be. Therefore, the small hot particles develop the same temperature as the gas that surrounds them. It should also be noted that each type of wood has a certain heat transfer. To find out these numbers, you can study the table, which shows all the thermal conductivity indicators for each type of material.
Wood burning efficiency
During the combustion of rock, thermal energy is released. With its help, the building is heated. The combustion efficiency depends on the temperature of the wood in the stove.
This is influenced by several factors:
- breed variety;
- humidity;
- combustion intensity;
- conditions under which combustion occurs (what kind of draft).
These are the main indicators of the combustion efficiency of this natural fuel. They require special attention. Depending on the type of wood, it is used for cooking barbecue on the grill, heating, and other needs. Let's take a closer look.
Humidity and combustion intensity
If the tree was cut down not very long ago, it will be damp. This is also affected by the time of year. It contains 45-65% moisture. The combustion intensity, for example, in a fireplace, will be low. The fire needs to expend energy to evaporate the water. In this case, the heat transfer will be low.
Stages of wood combustion.
There are ways to help you get the right amount of energy:
- put twice as much wood in the fireplace (financially expensive);
- sawing and splitting wet logs;
- buy well-dried firewood.
Only felled rock should not be used for heating, except for birch. In their raw form, hornbeam and clear are suitable.
The influence of draft in the stove
She needs to be closely monitored. Otherwise, the tree will not burn normally. The draft directs the released substances with air flows to the exhaust system. To test it, you need to light the paper in the oven with the door open and the damper on the chimney. If it doesn't exist, it's bad.
You can find out if there is no traction by the following signs:
- when opening the fire door, smoke comes out;
- it emerges from convection cracks;
- You can hear popping noises from the air regulator.
Factors influencing cravings:
- properly designed chimney;
- its height must exceed the ridge of the roof and the buildings located nearby;
- the pipe where combustion products escape into the air must be insulated;
- absence or presence of ventilation;
- atmospheric phenomena.
To improve traction, you should use a deflector, weather vane and gate. And it’s good to check it with aspen.
What is the combustion process?
Combustion is a process at the boundary of physics and chemistry, consisting in the transformation of a substance into the final product. At the same time, thermal energy is released in huge quantities. The combustion process is mainly accompanied by the emission of light, which is called a flame. Also, during the combustion process, carbon dioxide is released - CO2, an excess of which in an unventilated room can lead to headaches, suffocation and even death.
For the process to proceed normally, a number of mandatory conditions must be met.
First of all, combustion can only happen if there is air. In a vacuum, the combustion process is unrealistic.
Behavior of structures during a fire
The peculiarity of the destruction of wooden structures is that upon direct contact with open fire, they are destroyed (charred) at an average speed of one millimeter per minute.
| Smallest section size, mm | Wood charring speed V, mm/min | |
| glued | whole | |
| 120 mm or more | 0,6 | 0,8 |
| Less than 120 mm | 0,7 | 1,0 |
As a result of this, the initial cross-section of elements made of wood is reduced, and at the same time their strength decreases. The consequence of these processes is the complete destruction of all components of these structures.
When considering the nature of the behavior of wood structures, it is necessary to take into account the design features of the material used, which can be represented by the following varieties:
- homogeneous wood pulp;
- glued reinforced beams;
- plywood structures.

As for structures with complex compositions (floor beams, for example), manufactured by gluing, their behavior during combustion is significantly influenced by the heat resistance of the adhesive compositions used. With the right glue, the rate of destruction of these building elements is noticeably reduced. The same can be said about plywood materials, the signs of thermal decomposition of which are their gradual delamination.
If you do not take into account the peculiarities of breaking the adhesive bonds, in all other respects they behave like ordinary homogeneous structures.
Finally, about burning coal dust
The fine fraction remaining from ordinary coal is also a valuable fuel. The problem lies in the loading - most of the dust immediately spills into the ash pan. If you load it on top of firewood, the access to oxygen is blocked and combustion worsens. In such cases, you can use 3 methods:
- Dedovsky. Coal dust is mixed with water, made into cakes and dried in the sun.
- Briquetting. If you have a lot of dust, it makes sense to make or order a screw press for forming coal briquettes at home.
- Add water to the fine fraction and load it into the firebox in old plastic bags.
The last method is the simplest and fastest to implement. Water is added to the dust in a ratio of 1:10, the substance is thoroughly mixed and placed in bags. The boiler is accelerated to operating temperature using wood, then 2-3 such portions are loaded into the firebox. The method is described in more detail in the video:

Watch this video on YouTube
Is it possible to have a fire in a bathhouse?
Such emergency incidents are not uncommon. According to statistics, the sauna's embrace of flame is associated with the chimney. It requires regular cleaning. A fire happens if there is a lot of soot in it.
A fire in a bathhouse can also be caused by faulty electrical wiring. Sometimes the oven itself. It happens that people violate safety rules and a fire occurs. It is important what material the room is made of. It should insulate well.
Detailed information is visible in the video:
Fire safety when working with wood
Natural material easily catches fire. Any careless act can lead to an unpleasant or dangerous situation. Wood has different combustion temperatures. It depends on the breed. But they are not too big.
To maintain safety, you must do the following:
- use wet plaster;
- use fire retardant pastes;
- do cladding;
- use varnishes, enamels;
- apply fire retardant.
This will help protect yourself when working with wood.
What is the combustion temperature of wood?
It’s hard to meet such a person who has not encountered wood burning in his life.
Most people have gone on a hike at least once, which is not complete without lighting a fire. Some have a lot of experience in lighting house stoves and sauna stoves. Most people have tried wood burning at least once in their lives with a specialized device or a magnifying glass. But not all people wondered at what temperature wood could ignite. Is there a difference between the combustion temperature of different types of wood? The reader has a unique opportunity to delve into these issues and obtain a lot of valuable information.
How to measure the temperature of coals in a barbecue
The temperature of the coals in the grill can be determined with a certain accuracy without the use of special instruments. All you need to do is place your hand about 10 cm above the grill.
The number of seconds you can withstand will be equal to the approximate temperature of the coals:
- 1 sec – from 350 °C and above
- 2 sec. – around 300 °C
- 3 sec. – about 250 °C
- 4 sec. – 220 °C
- 5 sec. – less than 200 °C

Temperature of coals in the grill

Author of articles, expert on survival and emergency situations. I have experience working in the structures of the Ministry of Emergency Situations. I love traveling with tents.
Thermal properties of wood
Different types of wood produce different amounts of heat. For example, dry, seasoned wood produces more heat than freshly cut wood. This is due to the fact that during the initial chemical reaction, all the heat is transferred into the evaporation of water from the wood. The less moisture in the material, the sooner you can get heat. Hardwoods burn longer than softwoods and produce more heat. Some of the most valuable types of trees with excellent thermal characteristics are:
- oak;
- beech;
- hornbeam;
- larch.
In this video you will learn how to check the moisture content of firewood:
Thermal characteristics of wood
Wood species differ in density, structure, amount and composition of resins. All of these factors affect the heating value of wood, the temperature at which it burns, and the characteristics of the flame.
Poplar wood is porous, such firewood burns brightly, but the maximum temperature reaches only 500 degrees. Dense wood species (beech, ash, hornbeam), when burned, emit over 1000 degrees of heat. Birch indicators are slightly lower - about 800 degrees. Larch and oak burn hotter, producing up to 900 degrees of heat. Pine and spruce firewood burns at 620-630 degrees.
Firewood quality and how to choose the right one
Birch firewood has the best ratio of thermal efficiency and cost - it is not economically profitable to burn with more expensive species with high combustion temperatures.
Spruce, fir and pine are suitable for making fires - these conifers provide relatively moderate heat. But it is not recommended to use such firewood in a solid fuel boiler, stove or fireplace - they emit insufficient heat for effective heating of the home and cooking, and burn with the formation of a large amount of soot.
Low-quality firewood is considered to be fuel made from aspen, linden, poplar, willow and alder - porous wood emits little heat when burned. Alder and some other types of wood “shoot” embers during combustion, which can lead to a fire if wood is used to fuel an open fireplace.
When choosing, you should also pay attention to the moisture content of the wood - damp wood burns worse and leaves more ash.