No circulation, heating failure - why
Failure in the heating system, deficiencies, imperfections, all lead to cold radiators.
If there is no coolant circulation, then the reason needs to be determined. Most often, the answer to why the heating does not work is on the surface, obvious. Let's look in order at the main causes of heating malfunctions, why water does not circulate through the pipes, and what needs to be done first.
Let's start with the simplest and most obvious reasons.
It's clogged and clogged.
Every heating system must have a coarse filter. A very small device with a fine mesh and a sump (installed downwards! or at least to the side) saves equipment, pumps, and the boiler from coolant contamination that will be present in any system. Wood shavings, broken threads, rust, water sediment…. everything is retained by the mesh in the filter.
The sedimentation tank must be periodically untwisted and the mesh cleaned.
If the circulation in the heating system of a private house is disrupted, then the first thing you need to do is check the filter, which should be installed on the return line in front of the boiler.
Air in the system, airing
Airing can occur in any closed piping system where air removal measures have not been taken. Air is always present in the coolant, including in a dissolved state, is released during pressure changes, and accumulates at the highest points. Including in the boiler.
Automatic air vents are installed at characteristic, highest points of the system, as well as on collectors and special separators - the normal circuit is equipped with a special air catching device in which air bubbles are released from the coolant.
In addition, Mayevsky valves (manual air vents) should be on each radiator, and also possibly in other elevated places.
Checking the air supply, bleeding the air, installing air vents are common actions if circulation stops and the batteries are cold.

The circulation pump does not work
In private homes, the reason why the heating system stops working is a breakdown of the electrical equipment that controlled the movement of the coolant through the pipes.
If the heating suddenly stops working, then you need to check the functionality of the circulation pump near the solid fuel boiler or the pump in the automated boiler. In addition, the same unit can be installed in each circuit, which must work properly.
Bad polypropylene pipes
Often the consumer (customer) believes that polypropylene pipes are absolutely reliable and cannot cause heating problems or cold radiators.
But polypropylene is much more insidious than old steel or metal-plastic pipelines. Each place of soldering (welding) is a potential increased resistance in the system or a cause of cessation of circulation (weakened movement of water through the batteries), due to deposits of material inside.
It is impossible to control the quality of connections from the outside; all that remains is to cut out pieces, resolder, and remake polypropylene pipes.
Poor performance of a polypropylene system is a real problem for the home installer. Good professionals don’t take on this material at all.

Bad project
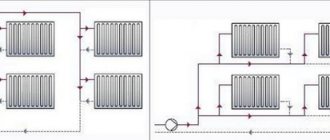
It is not uncommon for poor circulation to occur where there is poor design. Typically, the batteries are not connected correctly, according to some sequential circuit, where the last battery in the circuit receives much less coolant.
Another bad design is single-pipe circuits, where it is also difficult to establish the necessary coolant circulation through each battery.
If the radiators do not heat up evenly, or there is poor coolant circulation on individual heating devices, first of all you need to consider how the connection corresponds to the classic circuits - shoulder, associated, radial. It is necessary to bring home heating to normal design standards, and then expect good circulation and uniform heating of the radiators.
Small diameter, overgrown pipes
Old steel pipes become overgrown with rust and deposits from the inside, their throughput capacity decreases significantly over time, and there is only one solution - they need to be replaced with modern ones.
But even during installation, for the sake of economy, mistakes can be made with the choice of pipeline diameter - on mains, on groups of heating devices, diameters of 16 or 20 mm can be installed. The result is noise in the pipes, excessive consumption of electricity, and insufficient coolant flow. What pipe diameters should you choose?
A complex system
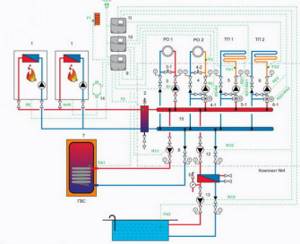
A type of bad design is an incorrectly designed complex heating system consisting of many heating circuits and several boilers. Here entire circuits will not work correctly if the work of one affects the neighboring one.
As a rule, one boiler (the backup one does not count) and three circuits - boiler, radiators, heated floors with their pumps are coordinated normally, and no questions arise. But if you connect another working boiler plus a circuit (for example, heating a garage and greenhouse), then the system will become complex. It is difficult to say how the coolant will circulate in it without equalizing the pressures at the connection points.
In complex systems, a competent design is important, installing a hydraulic arrow or an equal pressure ring; more information about the hydraulic separator can be found here
No balancing
Many home heating schemes involve balancing; balancing and control valves are installed in them. For example, between floors, between shoulders, and for each radiator. The taps cover the direction with less hydraulic resistance; accordingly, more coolant will flow to other points.
Unbalancing and installation
Another reason why water does not circulate in the heating system is improperly carried out imbalance during renovation or redevelopment of the apartment. This is affected by the uncontrolled installation of new radiators and heated floors.

The radiators on some floors continue to function normally, while on others they will remain cold because no coolant is supplied to them. Although the craftsmen can easily balance the distribution of water across all risers, in several apartments the system will not work.
If some residents removed the thermostats when replacing heating equipment, then heat will not flow into their neighbors’ homes. To fix this problem, you need to eliminate the thermostats in all apartments. You can increase the heat supply if you follow the example and also replace all radiators. Bimetallic or aluminum batteries fit harmoniously into modern heating systems. You must first obtain permission to replace devices, since you cannot do this yourself.
In a private house, batteries located closer to the boiler heat up more than others. To restore the balance, you need to turn off the control valves and limit the access of the coolant to nearby radiators. But sometimes the new battery does not heat up. If the entire system worked normally before its installation, then the problem lies in improper installation. When welding several polypropylene pipes, the master overheated the product, which caused its internal diameter to decrease. A specialist must redo all the work free of charge. All structural elements must be securely and efficiently fastened.
Signs of poor heating
When rooms are not heated enough in winter, you can feel it right away. Problems with heating in an apartment make themselves felt by discomfort for the inhabitants, the appearance of dampness on the walls and strange noises spreading through metal pipelines throughout the entire house.
Problems that arise with the heating system can be characterized by a number of symptoms:
- the system as a whole is functioning poorly;
- the heat supply on different floors is not the same;
- radiators in one room are hot, in another barely warm;
- the “warm floor” system warms up unevenly;
- noise and seething in the pipes is heard;
- Coolant is leaking from pipes or radiators.
Possible breakdowns and ways to eliminate them

troubleshoot the problem as necessary. By the way, it is recommended to protect the pump from surges in the network by installing a reliable stabilizer. This move will also protect the pump from the burning of a fuse, which fails as a result of constant pressure drops in the network
So, if something goes wrong with your circulation pump and it refuses to work, then we’ll try to repair the unit ourselves.
Important: but if you are not confident in your abilities or do not have the appropriate tool at hand, then it is better to contact a specialized center
If the pump makes a hum, but the impeller does not rotate
The reasons may be the following:
- Presence of a foreign object in the impeller area;
- The rotor shaft has oxidized due to long-term downtime of the unit;
- Loss of power supply to the mechanism terminals.
In the first case, you need to carefully remove the pump from the heating system and unscrew the housing in the area of the impeller. If a foreign object is found, remove it and rotate the shaft by hand. When assembling the pump in the reverse order, it is necessary to install a reliable filter on the pipe.
If there is oxidation, then clean it well, lubricate all movable elements of the working unit and reassemble the pump in the reverse order.
If there is a problem with the quality of the power supply, then you will have to check the voltage using a tester. First, completely replace the cable in all sections of the cable and if a break or fault is detected. Then, if the cable is OK, check the voltage at the terminals. If the tester shows infinity, a short circuit has occurred. If it shows less voltage, it means that the winding has broken. In both cases, the terminals are replaced.
If the unit shows no signs of life at all
This can happen if there is no voltage in the network. Using a tester, check the voltage and, if necessary, correct the problem.
By the way, it is recommended to protect the pump from surges in the network by installing a reliable stabilizer. This move will also protect the pump from the combustion of a fuse, which fails as a result of constant pressure drops in the network.
If the pump starts but then stops
The reasons may be:
- Presence of scale between the moving elements of the unit;
- Incorrect pump connection at the terminals.
In the first case, you will have to disassemble the pump and check it for scale. If detected, limescale deposits are removed and all joints between the rotor and stator are lubricated.
If there is no scale, then check the tightness of the fuse on the unit. You should remove it and thoroughly clean all the clamps. Here it is also worth checking that all wires in the terminal box are connected correctly in phases.
If the pump makes a loud noise when turned on
The reason for this is the presence of air in a closed circuit. It is necessary to release all air masses from the pipes, and install a special unit in the upper part of the pipeline to prevent the formation of air locks.
Another reason could be wear on the impeller bearing. In this case, you need to disassemble the unit housing, check the bearing and, if necessary, replace it.
If the pump is noisy and vibrates
Most likely, the issue is insufficient pressure in the system. It is necessary to add water to the pipes or increase the pressure in the area of the pump inlet.
If the pressure is still low
Here it is worth checking the direction of rotation of the working unit in the pump body. If the wheel does not spin correctly, then an error was probably made when connecting the device to the terminals in phases when using a three-phase network.
Another reason for a decrease in pressure may be too high a viscosity of the coolant. Here the impeller experiences a lot of resistance and does not cope with the assigned tasks. You will have to check the condition of the mesh filter and clean it if necessary. It would also be useful to check the cross-section of the inlet and outlet pipes and, if necessary, set the correct operating parameters of the pump.
Possible problems with heating systems
The cold weather is coming and you want the house to be warm and cozy, and for this the heating system must work properly.
But sometimes it causes troubles due to various problems, and many questions arise related to its operation, for example, why the radiators crackle, why the radiator does not warm up completely.
Before considering possible malfunctions of the heating system, let’s remember what types of radiators exist:
- Steel panel radiators, called convectors.
- Cast iron radiators.
- Steel tubular radiators.
- Aluminum radiators, which, in turn, are divided into cast and extruded.
- Bimetallic radiators.
When you choose the types of heating batteries, photos can be found on specialized Internet sites, where there is information about their characteristics.
Currently, many people are installing a protective screen for radiators. There are two types of these screens:
- a full-fledged protective casing that covers the radiator from all sides;
- Radiator covers that serve as decoration and cover only the front part of the radiator.
Protective screens for heating radiators are divided according to the type of material made. They can be divided into metal, wood and plastic.
The disadvantage of protective screens is that they obstruct the flow of thermal air and lead to heat loss.
Possible malfunctions in heating systems and their elimination
During the operation of heating systems, various problems may occur, the causes of which may be the following:
- Air pockets that occur in any section of the pipeline. This may be caused by malfunctions of the air collectors. It can be eliminated by bleeding air from the system, and you should also check the correct operation of all radiators so that there are no air bubbles.
- Incomplete opening of shut-off valves on the supply or return lines. In order for the heating system to work normally, it is necessary to completely open the shut-off valves.
- The risers or wiring to the heating equipment may be clogged. The clogged area is disassembled, cleaned and put back in place; in case of severe clog, it is removed from the system.
- Boiling of water in the heating system. To eliminate this malfunction, an expansion tank is installed in the return or supply line.
What is the difference between heating supply and return
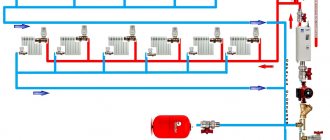
Heating was invented to keep buildings warm and to ensure uniform heating of the room. At the same time, the design that provides heat should be convenient to operate and repair. A heating system is a set of parts and equipment used to heat a room. It consists:
- A source that creates heat.
- Pipe lines (supply and return).
- Heating elements.
Heat is distributed from the starting point of its creation to the heating block using a coolant. This could be: water, air, steam, antifreeze, etc. The most commonly used coolant fluids are water systems. They are practical, since all kinds of fuel are used to create heat, and they are also able to solve the problem of heating various buildings, because there are actually many heating schemes, varying in properties and cost. They also have high operational safety, productivity and optimal use of all equipment as a whole. But no matter how complex the heating systems may be, they are united by the same operating principle.
Briefly about return and flow in the heating system
The water heating system, using a supply from the boiler, supplies heated coolant to the radiators, which are located inside the building. This makes it possible to distribute heat throughout the house. Then the coolant, that is, water or antifreeze, having passed through all available radiators, loses its temperature and is supplied back for heating. The most simple heating structure consists of a heater, two lines, an expansion tank and a set of radiators. The conduit through which heated water from the heater moves to the batteries is called the supply. And the water conduit, which is located at the bottom of the radiators, where the water loses its original temperature and returns back, will be called return. Since water expands when heated, the system provides a special tank. It solves two problems: a supply of water to saturate the system; accepts excess water, which is obtained during expansion. Water, as a heat carrier, is directed from the boiler to the radiators and back. Its flow is ensured by a pump, or natural circulation.
Supply and return are present in one and two pipe heating systems. But in the first there is no clear distribution into the supply and return pipes, and the entire pipe line is conditionally divided in half. The column that leaves the boiler is called the supply, and the column that comes out from the last radiator is called the return. In a single-pipe line, heated water from the boiler flows sequentially from one battery to another, losing its temperature. Therefore, at the very end the batteries will be the coldest. This is the main and probably the only disadvantage of such a system.
But the single-pipe version will have more advantages: lower costs for purchasing materials are required compared to a 2-pipe; the diagram looks more attractive. It is easier to hide the pipe, and you can also lay pipes under doorways. The two-pipe system is more efficient - two fittings are installed in parallel into the system (supply and return).
This system is considered more optimal by experts. After all, its work revolves around supplying hot water through one pipe, and cooled water is discharged in the opposite direction through another pipe. In this case, the radiators are connected in parallel, which ensures uniform heating. Which of them establishes the approach must be individual, taking into account many different parameters.
There are only a few general tips to follow:
- The entire line must be completely filled with water; air is a hindrance; if the pipes are airy, the heating quality is poor.
- It is necessary to maintain a sufficiently high fluid circulation rate.
- The difference in supply and return temperatures should be about 30 degrees.
What is the difference between heating flow and return?
And so, let’s summarize the differences between supply and return in heating:
- Supply – coolant that flows through water pipes from a heat source. This could be an individual boiler or central heating of the house.
- Return water is water that, having passed through all the heating radiators, goes back to the heat source. Therefore, at the input of the system there is supply, and at the output there is return.
- It also differs in temperature. The feed is hotter than the return.
- Installation method. The water conduit that is attached to the top of the battery is the supply; the one that connects to the bottom is the return line.
Sounds from heating devices
If you hear a howl in the middle of the night, then most likely the system has leaked. A cloud of steam and a characteristic whistle will immediately indicate a gust or a failed valve. In some cases, it is enough to close the tap to bring the heating system into working condition.
If no obvious causes are found, and the howling is accompanied by a crackling sound, it is necessary to check the pressure. Perhaps the flying scale blocked the free flow of the coolant, which caused increased pressure - it is urgent to stop the boiler, drain the water and look for the problem.

It happens that the batteries start to “shoot” - this is another reason to be wary. Such noise is typical for bimetallic batteries when the pressure in the system does not coincide with the calculated one.
When purchasing heating appliances, you need to take into account the operating parameters of the boiler and select the appropriate radiator. Otherwise, the problem may result in a rupture of the heating device due to water hammer, which is completely inappropriate in the winter cold.
Heated water is not able to compress; it needs to move freely along the contour. Banal deposits in pipes can provoke an increase in pressure and rupture of pipes due to water hammer.

Another reason is an air lock, which can be eliminated through the Mayevsky drain valves located at the ends of the batteries. The procedure is simple, and anyone can handle it.

Coarse filter
As mentioned above, one of the reasons that there is no coolant circulation may be the accumulation of debris in the pipeline. To completely avoid this, again, we don’t save on pennies, but install a coarse filter in front of each device:
Using a filter, catching dirt is easier than correcting the consequences of clogged pipelines or boiler heat exchangers.
Conclusion! We place coarse filters in front of each heating system device (pump, boiler, etc.) and in front of each plumbing fixture. We do NOT save pennies to “buy” problems. There are arrows stamped on the filter housing indicating the direction of movement of the coolant or water in the water supply...
The filter needs to be cleaned regularly. And this is very simple to do: close the valves before and after the filter - unscrew the plug (1) on the filter - remove and rinse the mesh under the tap - put it in place and tighten the plug. All. Not like changing pipes