Electrolysis of water: living and dead water
There are a lot of legends and rumors about magical life-giving water. And this is not a fairy tale. There is a process called electrolysis of water.
, which gave life to the two concepts of enriched or living water, and dead water. What such “spiritualized” water gives and what should be removed from it for this will be described below. The health of any inhabitant of the Earth cannot be assessed with money, so isn’t it better to take care of it in advance?
Fears and realities - the harm of impurities
Medicine began to talk about this not so long ago. Previously, people used hard water and somehow did not notice any special ups and downs in the body for the worse. Its trouble is that it acts unnoticed and the damage from it accumulates over the years. Even today people don’t remember what spring water tastes like, but they know very well what bleach looks and tastes like.
If we talk about the likelihood of disease, then the same water in which there is a lot of chlorine (and this is almost 100% of any water in Russian cities) leads to the likelihood of developing a cancer tumor 90 percent higher than when using soft water. The problem with water rich in chlorine is trihalomethanes. These substances are the result of the close interaction of bleach and organic matter. By the way, chloroform is also trihalomethane. A substance that is not so much a sleeping pill. But also an excellent poison. Electrolysis of water helps to separate water into complete distillate and water with a bunch of impurities, almost dead.
The table summarizes all harmful impurities in water. And the diseases they cause are described.
| Impurity | Which organs are affected? |
| Nickel | Dermatological problems |
| Zinc | Urogenital system, kidneys |
| Copper | Mucosa of the liver and kidneys |
| Manganese | Nerves (even to the point of anemia) |
| Lead inclusions | Inhibition of mental development |
| Cadmium | Cancer, stillbirth |
| Nitrates | Particularly dangerous for infants (can cause blue baby syndrome) |
| Chlorine | Heart disease, cancer, autism |
| Iron | Dermatology |
To solve all the problems associated with poor quality water, you will have to install electromagnetic water softeners. The first thing that needs to be done is to analyze the composition of the water, after which a water treatment system will be created. It may include a variety of stages, but at a minimum, purifiers for drinking and industrial water are required. If there are problems with the build-up of sludge in household appliances or the smell of iron in the water, then you will have to take care of an iron remover and disinfectant. It is best to take reagent-free devices. They are safe in an environmental sense.
Electrolysis and the “killing” of water
All kinds of impurities give water taste and smell. Dissolved oxygen and organic impurities, hardness salts - all this makes the water of poor quality. If water is not electrified, then minerals and organic matter will precipitate. The taste of the water changes and changes significantly.
That is, during the electrolysis process two types of water are formed:
- Dead, in which no impurities remain, a kind of chemical substance is almost a complete distillate;
- Living water is also not real water, but water with broken bonds and a slight taste of soda present.
It turns out that although water is considered alive, after exposure to electricity there is little living left in it. Activation of water ions as a result of electric current occurs as follows: a semi-permeable membrane is immersed in water, electricity is released. Ions and electrons are massively supplied to the water. Fields in the water are massively disturbed. The water structure is breaking down. This is why electrolysis of water produces dead water.
Living water is called living water only when it contains minerals; its molecular weight is H20. With such a composition, water will not disrupt human health, but promote it. Such a process will not disrupt the macrostructure of the protein, and the internal environment will remain intact.
Electrolysis of water. Video
For a healthy person, the normal acid-base balance is 7.0. Water destroyed by electrolysis has a value of 10, or even 11.
Therefore, destructured water is not living at all, but quite the opposite. It contributes to the stagnation of potassium in the body's cells and blocks natural energy supplies. Natural flows are contained in the trinity. That is, life is a unity of flows of energy, structure and information. And if any component of the trinity is violated, the person will begin to get sick.
The process of electrolysis of water is dangerous precisely because it promotes dissociation. In water, the molecular weight changes, the equilibrium, which was achieved with difficulty, is disrupted and the polarity changes. Electromagnetic waves take a different path. This is how diseases arise.
But based on history, not all scientists adhere to this version of the development of events. There is too much negativity in her, so apparently she has not achieved much development. Although it is quite popular in Europe.
A generalized vision of the ionization technique under consideration
Creating a water ionizer with your own hands, of course, is impossible without a clear understanding of the basics of ionization technology. In addition, you should initially test the quality of tap water, which is supposed to be used for a homemade ionizer.
There are many liquid content testing kits on the market, however, the best way to conduct a water test is to contact a certified laboratory.
The main reason for this approach (testing within the laboratory) is the accurate determination of the amount of oxygen dissolved in the liquid, plus an accurate determination of the “pH” parameter.
True, the “pH” value for the liquid under study can be determined directly at home using special (litmus) paper or using an electronic “pH” meter.
Household devices that electrolyze drinking water have been offered on the market for several years. Electrolyzers produce (separately) acidic and alkaline water (ionized). Also in practice there are other names for this type of water:
- electrolyzed reduced,
- alkaline-ionic,
- electrolyzed cathode.
Acidic water is not suitable for drinking, but is successfully used for facial and hand hygiene and body care. Alkaline water, on the other hand, is suitable for drinking, so ionizer technology is considered in commercial and marketing literature primarily as useful in the treatment of:
- gastrointestinal tract,
- hypertension,
- diabetes,
- malignant tumors.
The recommendations contained in the instructions supplied with water ionization devices recommend drinking 1.5–2.0 liters of such a product, regardless of the age, gender and health status of the consumer.

One of the many models of water ionizer for home use, made at an industrial level. Meanwhile, it is quite affordable to make a water ionizer with your own hands from available parts. Perhaps the consumption of ionized drinking liquid is really useful if it actually helps alleviate symptoms in patients, complementing classical treatment methods, as some distributors of ionizers claim.
However, there may be public health concerns if ionizers are capable of causing harmful side effects in otherwise healthy people or concealing illness in apparently healthy consumers.
Types of ionizers and characteristics of produced water
The market offers many types of more or less advanced water ionizers. Most of the ionizers are made in Japan, but no less technologically advanced water ionizers are also quickly filling the market:
- U.S.A,
- Canada,
- Australia,
- China.
The average annual sales of ionizers is more than 200,000 devices priced from $600 to $3000. Meanwhile, the inventors of this kind of device (developers of the technology) are Russian scientists from the 1900s.
Technological principle of separation/purification into components
All manufactured water ionizers are connected directly to the water supply. Filtration before the ionizer is carried out through at least one activated carbon filter. This approach is necessary to reduce the level of chlorides in tap water (preventing damage to the electrolytic cell of the ionizer).
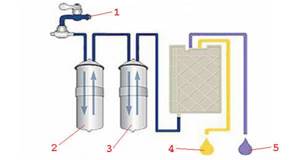
Block diagram of connecting a classic ionizer for the production of a final product purified from impurities: 1 – tap water; 2 – primary carbon filter; 3 – secondary ceramic filter; 4 – acidic pH = 4-6; 5 – alkaline pH = 8-10 The filtered liquid allows a minimum mineral content of 50 mg * l-1. These conditions are required for the production of electrolysis in a working chamber with an anode and cathode.
These elements are separated by a semi-permeable plastic-based diaphragm. Flat (mesh) electrodes are made of titanium coated with platinum. The electrolysis process produces acid and oxidized water at the anode.
When electrons pass through an electrical circuit, mineral ions (HCO3-, Cl-, HSO4-, NO3-,...) accumulate in the anode compartment. As protons and oxygen are released, the liquid acquires a pH value of 4 to 6 and an oxidation-reduction potential that can reach +900 mV.
In contrast, reduced alkaline water is formed in the cathode compartment. For this option, mineral cations (Na +, K +, Ca2 +, Mg2 +, ...) accumulate at the cathode.
As hydroxyl ions and hydrogen are formed, the pH value of the water changes from 8 to 10, and an oxidation-reduction potential of -600 mV is acceptable.
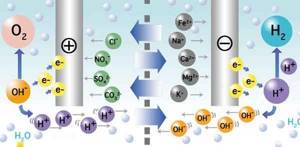
This is roughly the “picture” of the course of the chemical reaction inside the ionizer, as a result of which two types of treated liquid are obtained at the output of the device - drinking and technical. The efficiency of the device, the resulting pH values and redox potential values vary greatly and depend on:
- on the characteristics of the local water supply,
- on voltage and current values,
- on water flow and temperature.
The effect of a water ionizer from a practical point of view
The main effect of electrolysis is a significant reduction in the rH2 value (electronic activity) compared to the original tap water, while the pH values and resistivity potential remain relatively stable.
A comparison of rH2 values with those of mineral water shows that ionized water is a highly alkaline product. Compared to conventional drinking water sources, the ionizer produces pH and Eh values that are rarely found in the natural environment.
Therefore, in scientific circles such water is usually classified as synthetic water. Regarding resistance, you can find a range from 1600 to 1700 Ohm * cm, which is stable over time and remains within the acceptable official norm of 900–5000 Ohm * cm.
In terms of pH, this range can vary digitally from 6.8 to 8.7 for a given type of equipment, and also remain relatively stable over time. By comparison, the regulatory drinking water standard recommends a pH value between 6.5 and 9.
The water ionization procedure does not lead to abnormal pH values. Regarding the redox potential, the values range from -654 to +680 mV.
There are strong changes over time for negative reduction potentials and better stability for positive reduction potentials.
After adjusting for the effects of pH, rH2 (electronic activity) is between values of 2 and 45. These numbers mean that water ionizers can effectively produce oxidized water, or vice versa, water is an antioxidant.