Home › Ventilation › Ventilation with recirculation
You can order ventilation with recirculation on a turnkey basis by calling by phone in Moscow. We design and supply ventilation with recovery throughout Russia. We ask you to send your written application by email or through the form on the website.
- Operating principles of recirculation ventilation
- Ventilation with recirculation and heating
- Ventilation with recirculation without heating
- Basic scheme for supply and exhaust ventilation with air recirculation
- Additional recirculation ventilation schemes
- Premises where the use of recirculation is prohibited
- Pros and cons of the system
- Hood with recirculation is an exhaust and ventilation device
Send an application and receive a design proposal
Ventilation with air recirculation is a system where part of the air taken from the room is mixed with cold outside air, heated to the required temperature and then supplied to the room. Moreover, this system can only be used if the air coming from the room does not contain harmful substances and toxic impurities. Whereas the volume of outside air in this mixture must comply with all sanitary and hygienic standards specified in SNiP, and must be no less than the value of the sanitary standard provided for this type of room.
“Standard Climate” is a professional climate control company, ready to implement turnkey solutions to any problems regarding climate control and other engineering equipment. We will carry out a full cycle of work: selection of equipment, design, installation, delivery and maintenance. You can submit an application on the website airclimat.ru. Call now: +7(499) 350-94-14
. Submit your application
Note : Recirculation does not mean mixing of air within one room, including that accompanied by heating (cooling) by heating units (devices) or fans. Air recirculation is the mixing of room air with outside air and supplying this mixture to this or other rooms.
Operating principles of recirculation ventilation
The general scheme of operation of a supply and ventilation system with recirculation is as follows: street air is supplied into the room through the supply air, which after some time is drawn into the exhaust system. Some of it is irretrievably thrown out into the street, and some goes into the mixing chamber. There, the air is mixed with the fresh influx, cooling or heating it (depending on the type and settings of the system), then it enters the heater or air conditioner, from which it again enters the room through the ventilation pipes. The main purpose of recirculation is to reduce the load on air treatment systems (heaters, air conditioners, etc.).
To ensure that the air in the room remains fresh and breathable, when using recirculation in the ventilation system, the following conditions must be met:
- The volume of clean air coming from outside must be at least 10% of the capacity of the air handling unit;
- The air entering the room must contain a maximum of 30% of harmful substances from their maximum permissible concentration.
Prices for models from different manufacturers
The cost of this type of hood will depend on the material, design, additional features, reliability of the filter systems, as well as the manufacturer’s brand. We invite you to familiarize yourself with the most budget options.

A Hansa flat recirculation hood will cost you approximately 3 thousand rubles. A Liberty Base hood with similar properties will cost about 4.7 thousand. The Pyramida technique is popular today: recirculating hoods from this manufacturer are valued at 5 thousand rubles or more.
You can purchase even better options for hoods from the manufacturer Ventolux - such models will cost from 8.5 thousand rubles. The minimum cost of a Gorenje hood with recirculation mode is about 7.5 thousand rubles.
More well-known models with high functionality and modern design will cost you much more. For example, an Electrolux inclined recirculating hood will cost approximately 40 thousand, and Bosch equipment will cost an average of 55 thousand rubles.
Tip: For maximum air purification efficiency in the kitchen, purchase a recirculating hood with air exhaust. Such models are the most expensive.
Ventilation with recirculation and heating
Cold outside air is mixed with warm air taken from the room, heated to the required temperature, and then supplied to the room
- fans are on
- Outdoor and exhaust air valves are open
- the heater is working (see Fig. 1)
Fig.1 Fig.2
- supply and exhaust fans included
- the external, exhaust and recirculation air valves are open, each depending on the set amount of external air
- the heater is working (see Fig.2)
Typical faults
Subject to moderate use and careful handling, the service life is unlimited. Failure is caused by exceeding the permissible current, a short circuit in the circuit, and the negative consequences of an accident or shock.
In practice, there are cases of poor contact between the block and the terminals, blown fuse, and mechanical damage.
Don't forget to periodically ventilate the interior. Every second technical inspection, replace the cabin filter and troubleshoot the external air supply channels.
Ventilation with recirculation without heating
During the transition period, when the outside air temperature rises and the indoor heating system is operating, the task of the supply ventilation system is reduced only to supplying fresh air. In this case, you can do without additional heating of the air after recirculation.
- fans are on
- The return air valve opens in proportion to the supply air temperature requirements
- The outside air valve closes in proportion to the supply air temperature requirements
- the heater does not work (see Fig. 3)
Fig.3 Fig.4
- supply and exhaust fans included
- External, exhaust and recirculation air valves are open - depending on the supply air temperature requirements
- the heater does not work (see Fig. 4)
The use of air recirculation in ventilation systems is allowed only during cold and transitional periods of the year (for air conditioning units at any time of the year). In this case, outside air must be supplied to the room in an amount not less than that specified above.
Air recirculation is not allowed:
- from premises in the air of which there are pathogenic bacteria and fungi in concentrations exceeding those established by the State Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision of Russia, or pronounced unpleasant odors
- from premises in which the maximum external air flow rate is determined by the mass of emitted harmful substances of the 1st and 2nd hazard classes
- from rooms in which there are harmful substances that sublimate upon contact with the heated surfaces of air heaters, if air purification is not provided in front of the air heater
- from premises of categories A and B (except for air and air-thermal curtains at external gates and doors)
- from 5-meter zones around equipment located in rooms of categories B1-B4, D and D, if explosive mixtures of flammable gases, vapors, aerosols with air can form in these areas
- from laboratory premises for research and production purposes, in which work can be carried out with harmful or flammable gases, vapors and aerosols
- from local suction systems for harmful substances and explosive mixtures with air
- from vestibule locks
Exhaust fan
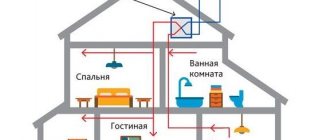
An exhaust fan is a device that is used to control the indoor environment by removing unwanted odors, particles, smoke, moisture, and other contaminants that may be present in the air. These devices can also be integrated into heating and cooling systems. Common bathrooms and kitchens are equipped with them, and they are usually easy to install, so they can be found in many other places. Can be configured into a living room design. To install, you will need several tools, and you must be able to work with electricity, since the device has an electrical wire.
Exhaust fan application
The classic use for an exhaust fan is in the kitchen or bathroom. These areas are usually filled with steam, and steam can encourage mold growth, which is not desirable. An exhaust fan can be used to circulate warm, moist air outside where it can disperse without causing harm. Exhaust fans can also filter kitchen odors from outside so they don't linger indoors, and when people are preparing food, can help keep the air in the kitchen clean.
To control temperature, an exhaust fan can be used during hot months to push warm air out, creating negative pressure inside the home. This is facilitated by air flow from outside, and the outside air can be cooler, helping to cool the home. An alternative to this device may be an air conditioner, or in addition to air conditioning.
These devices can also be useful in garages and workshops to ventilate the space. Because these areas can develop strong odors and people can work with potentially hazardous chemicals in them, exhaust fans can be used for comfort and safety.
An exhaust fan is especially important when people work with things such as solvents that are not healthy or safe to inhale.
In addition, it is important to remove fumes from paint, varnish and similar types of chemicals. Also intended for direct air supply outside the home
Any enclosed space can be ventilated with an exhaust fan, from a large storage warehouse to a storefront. These devices are also used in scientific laboratories to provide circulation that will draw potentially hazardous substances away from people working in the laboratory. They are also used to vent warm air in operating rooms so that anesthetic gases are dissipated. That's why large restaurants rely on heavy-duty exhaust fans to keep the kitchen air clean.
Also intended for direct air supply outside the home. Any enclosed space can be ventilated with an exhaust fan, from a large storage warehouse to a storefront. These devices are also used in scientific laboratories to provide circulation that will draw potentially hazardous substances away from people working in the laboratory. They are also used to vent warm air in operating rooms so that anesthetic gases are dissipated. That's why large restaurants rely on heavy-duty exhaust fans to keep the kitchen air clean.
Basic scheme for supply and exhaust ventilation with air recirculation
Most often, to organize supply and exhaust ventilation with recirculation, a scheme based on the use of a combination of a fan coil and a chiller is used. The fan coil replaces the indoor unit of the air conditioner, working as an active battery. This is a prefabricated unit in which there is a drainage system for organizing the outflow of condensate formed in the summer, a fan, a heat exchanger and an air filter. A chiller is a water heater that, depending on the time of year, heats or cools water, which then transfers its temperature to the incoming air.
The temperature of the coolant in the chiller is controlled from the control panel. This system allows for full or partial air heating in winter and air conditioning in summer. The volume of the room does not matter, since there are systems designed specifically for supermarkets and other large buildings. The advantage of this system is the ability to ventilate a large number of rooms in one building under a single climate regime. The air intake and exhaust points from the fan coil unit are routed using standard ventilation ducts.
As for recirculation control, it is carried out using remotely adjustable dampers or grilles, which are controlled from a remote control. The temperature of the incoming air varies depending on the time of year, while the temperature of the supply air supplied to the room should be comfortable. Its required value is set on the control panel. The chiller heats or cools the outside air to a predetermined value; it enters the heat exchanger, mixing with the air returned from the room, as a result of which it leaves the supply diffuser at the optimal temperature.
The amount of air that needs to be taken from the room and mixed with outside air depends on the set temperature parameters in the room. It is by this criterion that the installed position of the dampers is determined. The dampers themselves are mounted at the points of air intake from the room, as well as on the street air intake line. The dampers are controlled synchronized and carried out from the remote control. Its parameters are adjusted by specialists individually in each case.
Additional recirculation ventilation schemes
- Recirculate indoor air using a ceiling fan
Recirculation using a single ceiling fan and indoor ductwork is not intended to introduce or change the volume of outside air. Such schemes, devoid of a fan coil and connection to the street air intake, are used in a number of types of premises (cafes, shops, administrative buildings) solely to increase air mobility in the work area.
Attention! This option cannot be called full recirculation, because with it air is taken from one part of the room to another so that it does not stagnate.
- Indoor air recirculation using a fan coil unit
Recycling according to this scheme is quite common. The fan coil unit contains a heat exchanger for cooling or heating the air, and an industrial fan that moves it. In fact, this is a duct air conditioner, or rather its analogue. Such a system is mounted separately from the main supply and exhaust ventilation and works as follows: air is taken from some areas of the room, supplied through air ducts to a heat exchanger, where it is heated or cooled, after which it is sent through another network of air ducts to other areas of the room.
The use of this system can be considered rational in small and medium-sized rooms, where supply and exhaust ventilation is represented, for example, only by wall fans mounted in ventilation shafts. Here, the implementation of full-fledged combined recirculation ventilation is difficult and impractical, and this approach will create an acceptable microclimate at minimal cost without the need to completely redo all ventilation.
- Recirculation using a fan coil with the addition of outside air
The basis here is the same system with a fan coil as in the previous case, with the only difference - it has the ability to take air from the street. The street fence is regulated manually or by an automatically controlled gate. Its use is justified mainly when effective supply and exhaust ventilation is already installed in the room, which there is no desire or opportunity to modernize.
Such a system can be used to heat or cool indoor air, as well as as an auxiliary air handling unit.
How to install the device
Installation of recirculation equipment is quite simple. Typically, accessories include brackets for hanging such devices. All you need to do is make markings at a certain height from the slab, drill holes and secure the eyes horizontally.
Then hang the housing on them and make sure that the device is in a horizontal position. SNiP rules provide for a hood height above an electric stove of 70 cm, and above a gas stove - 80 cm.
If you purchase a model for the island area in the kitchen, the device must be fixed to the ceiling and not to the wall.
When the device is fixed, you need to connect the electrical wiring if there is no outlet nearby. It is recommended to lay electrical wires in cable channels and then connect them in a junction box.
Premises where the use of recirculation is prohibited
According to the regulatory document SNiP 41-01-2003, ventilation with air recirculation cannot be installed in premises:
- where air mass flow rates are determined based on the amount of harmful substances formed;
- where there are high concentrations of various fungi and pathogens;
- where there are harmful substances that sublimate upon direct contact with heated surfaces;
- which are classified as categories A and B;
- where work is carried out involving the use of harmful and flammable gases, as well as steam;
- which are classified as categories B1 and B2 and where harmful dust and aerosols can be released;
- where there are systems containing local suction of harmful substances and explosive mixtures; their airlock vestibules created.
Air recirculation is limited:
- within the same apartment, hotel room or single-family home
- outside the same room in public buildings
- outside one or more rooms in which equally harmful substances of hazard classes 1-4 are released, except for the rooms listed in the section above “Air recirculation is not allowed.”
Video description
More about ventilation calculations in the video:
Ssection = V * 2.8/w, where Ssection is the cross-sectional area, V is the volume of air mass (m³/hour), w is the speed of air flow inside the highway (m/sec) (average from 2 to 3), 2, 8 – dimensional matching coefficient.
For installation, it is necessary to calculate how many diffusers (intake and outlet openings) and their parameters are required. The dimensions of the nozzles are calculated based on the cross-sectional area of the main pipeline, multiplied by 1.5 or 2. To calculate the number of diffusers, use the formula: N=V/(2820 * W * d2), where V is the volume of air mass consumed per hour, W is speed of movement of the air mass, D – diameter of the round diffuser.
For rectangular diffusers, the formula is transformed as follows: N=π * V/(2820 * W * 4 * A * B), π is the number pi, A and B are the section parameters.
In any case, calculations of ventilation systems should be carried out by professionals - if something is forgotten or not taken into account, then the cost of the mistake is the need to redo the calculations and work.
A full calculation of supply ventilation is done using specific software Source ventisam.ru
Pros and cons of the system
- PLUS OF THE SYSTEM:
A system with air recirculation allows you to reduce energy consumption for heating air (sometimes for cooling), since the thermal power of the heater or cooler is spent mainly on changing the temperature of only that part of the air that is taken from the street.
- DISADVANTAGES OF THE SYSTEM:
Cannot be used everywhere (see SNiP below)
When operating the system in cold climates, the disadvantage of the system is that the mixing of outside and recirculated air is not good enough.
Features of choosing a hood
Basically, the hood is selected according to parameters such as depth and width. They are determined by the dimensions of the hob. Ideally, the unit should be several centimeters wider than the stove. This has a positive effect on the efficiency of exhaust air mass intake.
Different models of autonomous hoods differ in their range of functions. The more there are, the more expensive the equipment. Manufacturers equip them with electronic panels with displays for more convenient control and monitoring of the device’s operation. Sometimes there are programmable timers and sensors that automatically turn on the fan when humidity and temperature changes.
Special sensors can independently regulate the performance of the hood. The presence of a remote control in the kit allows you to start and turn off the unit without direct contact. When choosing, you should strive to ensure that the functionality of the model meets specific requirements as much as possible. It is irrational to pay for unused functions.