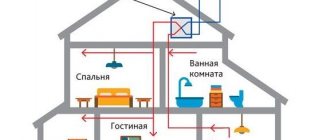
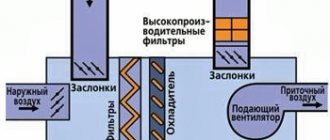
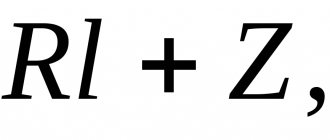The importance of air exchange
Depending on the size of the room, the air exchange rate should be different.
The task of any ventilation is to ensure an optimal microclimate, humidity level and air temperature in the room. These indicators affect a person’s comfortable well-being during work and rest.
Poor ventilation leads to the proliferation of bacteria that cause respiratory tract infections. Food products begin to spoil quickly. Increased humidity levels provoke the appearance of fungus and mold on walls and furniture.
Fresh air can enter the room naturally, but compliance with all sanitary and hygienic indicators is possible only with a high-quality ventilation system. It must be calculated for each room separately, taking into account the composition and volume of air, design features.
For small private houses and apartments, it is enough to equip shafts with natural circulation of air flows. But for industrial premises and large houses, additional equipment is required in the form of fans that provide forced circulation.
When planning a building for an enterprise or public institution, the following factors must be taken into account:
- high-quality ventilation should be in every room;
- it is necessary that the composition of the air complies with all approved standards;
- enterprises require the installation of additional equipment that will regulate the air speed in the air duct;
- For the kitchen and bedroom it is necessary to install different types of ventilation.
In order for the air exchange system to meet all requirements, it is necessary to calculate the air speed in the air duct. This will help you choose the right device.
Technical calculations are free and anonymous =)
- Heating Calculation of heat load based on aggregated indicators MDK 4-05.2004
- Collector diameter calculation
- Calculation of expansion tank for heating
- Calculation of the number of stages of the DHW heat exchanger
- Calculation of DHW heating
- Calculation of the length of compensators for thermal expansion of pipelines
- Calculation of water speed in a pipeline
- Dilution of propylene and ethylene glycol
- Calculation of the diameter of the balancing washer
- Checking the functionality of the elevator heating system
- kg/s to m3/h. Converting the mass flow rate of the medium into volumetric flow.
- Online replacement of Prado radiators with Purmo
- Examples of hydraulic calculations for heating systems
- Sanext Calculation of diameter and settings of Sanext DPV valve
- Calculation of the Sanext heating system floor collector
- Marking RKU Sanext
- Replacing Danfoss AB-QM valve with Sanext DS
- Quick replacement of L and T-shaped tubes with Stabil pipe
- Calculation of gravitational pressure
- Calculation of air conditioner power based on heat flow into the room
- Calculation of resistance in the VK pipeline
- Technical and economic calculation of heat and fuel
- Calculation of the painting area of a metal profile
- Technical unit converter
Rules for determining air speed in an air duct
The air flow rate in the ventilation is directly related to the level of vibration and noise in the system. These indicators must be taken into account when calculating behavior. The movement of the air mass creates noise, the intensity of which depends on the number of pipe bends. Resistance also plays a big role: the higher it is, the lower the speed of movement of air masses will be.
Noise Level Standards
Based on sanitary standards, the maximum possible sound pressure levels in the premises are established.
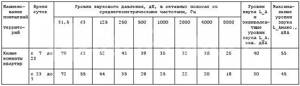
Exceeding the listed parameters is possible only in exceptional cases when it is necessary to connect additional equipment to the system.
Vibration level

During operation of any ventilation device, vibration is produced. Its performance depends on the material from which the air duct is made.
Maximum vibration depends on several indicators:
- the quality of gaskets that are designed to reduce vibration levels;
- pipe manufacturing material;
- duct size;
- air flow speed.
General indicators cannot be higher than those established by sanitary standards.
Air exchange rate
Air masses are purified through air exchange; it is divided into forced and natural. In the second case, it is achieved by opening windows, vents, in the first through the installation of fans and air conditioners.
For an optimal microclimate, air changes should occur at least once an hour. The number of such cycles is called the air exchange rate. It must be determined in order to establish the speed of air movement in the ventilation duct.
The frequency rate is calculated using the formula N=V/W, where N is the frequency rate per hour; V is the volume of air that fills a cubic meter of room per hour; W is the volume of the room in cubic meters.
Calculation procedure
The calculation algorithm is as follows:
- An axonometric diagram is drawn up listing all the elements.
- Based on the diagram, the length of the channels is calculated.
- The flow rate in each section is determined. Each individual section has a single cross-section of air ducts.
- After this, calculations are made of the speed of air movement and pressure in each individual section of the system.
- Next, friction losses are calculated.
- Using the required coefficient, the pressure loss due to local resistance is calculated.
During the calculation process, at each section of the air distribution network, various data will be obtained that must be equalized with the branch of the greatest resistance using diaphragms.
Algorithm and formulas for calculating air speed
Calculation of air flow can be done independently, taking into account the conditions and technical parameters. To calculate, you need to know the volume of the room and the multiplicity rate. For example, for a room of 20 square meters, the minimum value is 6. Using the formula gives 120 m³. This is the volume that must move through the channels within an hour.
The speed in the duct is also calculated based on the cross-section diameter parameters. To do this, use the formula S=πr²=π/4*D², where
- S – cross-sectional area;
- r – radius;
- π – constant 3.14;
- D – diameter.
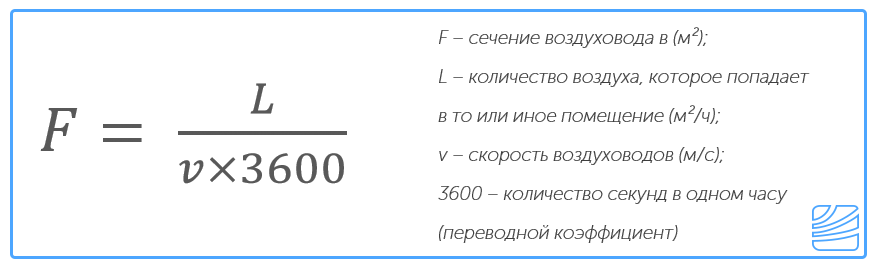
Once the cross-sectional area and air flow rate are known, its speed can be calculated. To do this, use the formula V=L/3600*S, where:
- V – speed m/s;
- L – flow rate m³/h;
- S – cross-sectional area.
The noise and vibration parameters depend on the speed in the air duct cross-section. If they exceed the permissible standards, you need to reduce the speed by increasing the cross-section. To do this, you can install pipes from a different material or make a curved channel straight.
Description of the ventilation system
Air ducts are certain elements of the ventilation system , which have different cross-sectional shapes and are made of different materials. To make optimal calculations, you will need to take into account all the dimensions of the individual elements, as well as two additional parameters, such as the volume of air exchange and its speed in the duct cross-section.
The main function of the ventilation system is to maintain air balance and a favorable microclimate. This means that the air a person breathes will not contain excess moisture, heat and pollution.
Violation of the ventilation system can lead to various diseases of the respiratory system and significantly reduce the resistance of the immune system. Also, excess moisture can lead to the development of pathogenic bacteria and the appearance of fungus. Therefore, when installing ventilation in homes and institutions, the following rules apply:
- A ventilation system must be installed in each room.
- It is important to maintain air hygiene standards.
- Places with different functional purposes require different ventilation system equipment designs.
In this video we will look at the best combination of hood and ventilation:
In order for all requirements to be met, it is necessary to make the correct calculations and select the necessary equipment for the flow of air (air ducts and other devices).
This is interesting: calculating the area of air ducts.
Air flow calculation
It is important to correctly calculate the cross-sectional area of any shape, both round and rectangular. If the size is inappropriate, it will be impossible to ensure the desired air balance. An air duct that is too large will take up a lot of space. This will reduce the space in the room and cause discomfort to residents. If the calculation is incorrect and a very small channel size is chosen, strong drafts will be observed. This occurs due to a strong increase in air flow pressure.
Sectional calculation

To calculate the speed at which air will flow through the pipe, you need to determine the cross-sectional area. The following formula is used for calculation: S=L/3600*V, where:
- S – cross-sectional area;
- L – air flow in cubic meters per hour;
- V – speed in meters per second.
For round air ducts, it is necessary to determine the diameter using the formula: D = 1000*√(4*S/π).
If the duct is rectangular rather than round, instead of the diameter, you need to determine its length and width. When installing such an air duct, the approximate cross-section is taken into account. It is calculated by the formula: a*b=S, (a – length, b – width).
There are approved standards according to which the ratio of width to length should not exceed 1:3. It is also recommended to use tables with standard dimensions offered by air duct manufacturers.
Round ducts have an advantage. They are characterized by a lower level of resistance, so during operation of the ventilation system the level of noise and vibration will be minimized.
Helpful Tips and Notes
By drawing conclusions using formulas or carrying out calculations in an online calculator, you can calculate that the speed of air masses in the cross-section of pipes directly depends on their dimensions. The smaller the diameter of the pipes, the higher the air speed will be . Thanks to this, we can identify several important points:
- Building air ducts of small dimensions is much simpler and more convenient.
- Small-diameter pipes are much cheaper, and prices for additional equipment (gates and valves) are reduced.
- Increased installation flexibility. It becomes possible to position the air ducts as required, so there is practically no need to adapt to circumstances
But when installing a small-diameter duct, it is important to remember that high air speed will increase the pressure on the pipe walls , as well as the resistance of the system. Consequently, a high-power fan will be required and other additional elements will be needed. Therefore, when working with ventilation, it is important to accurately make all calculations so that savings do not lead to even greater costs or losses. If the building does not comply with the ventilation standards of SNiP, then it will simply not be allowed for operation.
Material and cross-sectional shape of air ducts
Round ducts are most often used in large enterprises. This is due to the fact that their installation requires many square meters of room space. Rectangular sections are most suitable for residential buildings; they are also used in clinics and kindergartens.
Steel is most often used to make pipes. For a round section it should be elastic and hard, for rectangular ones it should be softer. Pipes can be made of textile and polymer materials.
What is a duct?
The duct is the main element of the air distribution system. It is a collection of metal or plastic pipes placed to ensure air balance. The principle of operation of the air duct is to supply and exhaust air using special fans.
Basic characteristics of the air duct:
- shape (round or rectangular);
- cross-sectional area;
- rigidity (flexible, semi-flexible and rigid).
The performance of the ventilation system and its functionality as a whole depend on these characteristics.
Correct selection of air duct parameters, taking into account all the features of the room, will ensure its long-term and efficient operation.
Choosing the right ventilation pipes

Before designing a ventilation system, all indicators of speed, noise and vibration must be taken into account. It is necessary to make calculations taking into account the area of the room to ensure high-quality air exchange. The material of manufacture also plays a big role in the choice.
Galvanized steel air ducts are considered the most universal. They can be operated at high temperatures and pressures. They can be used for any climate zones.
Air ducts made of black steel are most often used in industry. They are heat and fire resistant, but are subject to severe corrosion.
Aluminum corrugated air duct has a high degree of flexibility, strength and elasticity. The material is resistant to high temperatures. But such an air duct has a drawback. Due to the high aerodynamic resistance, there is a lot of noise during operation.
Plastic air ducts are distinguished by their high strength, long service life and ease of installation. They are popular due to their low cost and light weight. The downside is low resistance to high temperatures.
Polyisocyanurate pipes are often installed in residential buildings. They are characterized by high fire safety properties, long service life, and ease of installation.
Which deflector to choose
If you want to install a cap - a traction amplifier at minimal cost and not maintain the product during operation, we recommend choosing static models - a Volper or TsAGI deflector. The latter option is preferable for making it yourself.
Advice. Select the size of the nozzle according to the diameter of the exhaust barrel. If a rectangular shaft is removed from the house, the selection is made using an equivalent circular section. That is, it is necessary to calculate the diameter of the channel, then take a circle of similar area. An adapter is used during installation.
Recommendations for choosing different deflectors:
- If there is insufficient or no draft, it is better to install dynamic versions of the hoods - rotary or weather vane.
- When buying a rotating nozzle, do not go cheap. Inexpensive products use an open hinge - a regular bushing that will freeze in winter. Choose a weather vane or turbo deflector with a sealed bearing.
- An H-shaped cap is useful in areas with constant strong winds. In other cases, it is better to take TsAGI.