Which liquid for underfloor heating is better to choose - water or antifreeze?
In a water heated floor system, water (distilled, from a well, with the addition of alcohol) is mainly used as a coolant, but antifreeze can also be added.
From the article you will learn in what cases you need to use this or that liquid, consider their positive and negative sides, operating features, and also find out which liquid is best suited for water heated floors.
- What liquids are used in heated floors
- Water
- Distilled water
- Well water
- Antifreeze for heated floors
- Technical alcohol
- Which coolant for heated floors is better to choose?
Criterias of choice
The selection of antifreeze for floor heating systems is carried out taking into account all the technical and structural features of the heating equipment. Since the main function of ready-made coolants is protection against freezing, when choosing a solution you should pay attention to the temperature limit for its use.
When using antifreeze for heated floors in residential premises, it is first necessary to consider such an indicator as complete safety of use and the absence of toxic substances in the composition.
To choose an effective coolant for a floor heating system, you should consider the following points:
- presence and composition of additives;
- the ability to combine with metals, plastic, zinc or rubber;
- temperature threshold;
- duration of use.
Additives that improve the properties of antifreeze must meet the design requirements of floor heating equipment. If a metal circuit is installed, it is recommended to pay attention to the quality of anti-corrosion additives. To protect rubber elements, special softening agents are required.
The main reasons for draining water from a heated floor system
There can be quite a few reasons why you need to drain the water from the heating system pipeline yourself - from the upcoming long absence of residents from the house to replacing the water in the system with antifreeze. In order to do everything correctly and not cause damage to the heating system, we will look in more detail at how to drain the water from a heated floor yourself.
A common reason for the need to drain the coolant is the preservation of the heating system for the winter when using ordinary water in the circuit. Before the onset of cold weather, this event is mainly carried out at dachas and country houses that are not used in winter. To simplify and speed up the draining process, special equipment is used.
Mobile air compressors (electric motor driven)
Important! In seasonal housing, failure to drain water from the heating circuit of underfloor heating before frost sets in can result in the system defrosting, so using antifreeze as a coolant is undoubtedly preferable - in addition to being resistant to low temperatures, these liquids are less subject to wear on pump parts.
Another equally important measure when operating underfloor heating is preventive maintenance on the heating system. Boiler water contains a lot of impurities, which, when heated, precipitate or form layers on the walls of the pipeline. Due to a decrease in the internal clearance of heat pipes, the circulation of the coolant in the system is disrupted and heat transfer is reduced. For this reason, when using water, the coolant must be drained once or twice a year.
A water circuit filled with antifreeze does not suffer from this problem. In this case, the coolant is replaced every 3-5 years - provided that the boiler is operated without overheating (for heated floors, the maximum permissible heating temperature threshold for the coolant is 45-55 0 C).
One type of antifreeze for filling the circuits of underfloor heating systems
Another reason for the need to drain the coolant may be the liquid losing its physical properties. A change in the characteristics of antifreeze occurs after overheating - the solution begins to foam, filling individual sections of the heat pipes with foam, which disrupts the circulation of the coolant in the system and reduces heat transfer.
Failure to comply with the technology for installing heated floors, or the use of materials not intended for contact with chemicals, causes the occurrence of corrosive processes in the heating system, as a result of which the circulation of the coolant is also disrupted and leaks in the water circuit occur.
Naturally, you will have to drain the water from the heated floor pipeline when replacing it with antifreeze - modernization.
These are the main reasons for the need to empty the underfloor heating system and, regardless of the base, the water must be drained in accordance with all the rules, following safety precautions and observing the technological sequence of the component operations.
How to choose antifreeze for heating
On the market you can find a fairly large assortment of antifreezes for heating. And before you make a choice towards one product or another, you need to decide on the temperature threshold for antifreeze. There are two types of antifreeze, according to temperature characteristics:
- With a temperature threshold of minus 65 degrees, calculated for the conditions of the far north;
- And with a threshold of minus 30 degrees, designed for a more benign climate, in the middle zone.
There are also antifreezes with an intermediate temperature threshold. An example is the famous Galan Potok -40C 50l, with a freezing point of minus 40 and a capacity of 50 liters. Based on the content of the main antifreeze substance, antifreezes are divided into the following compositions:
- Aqueous salt solutions (suitable for PVC pipelines or galvanized metal pipes, in combination with aluminum radiators).
- Alcohol-containing compounds (suitable for all types of pipes and heating elements).
- Oil antifreeze (suitable for all types of pipes).
Interesting fact!
Craftsmen and self-taught inventors, back in Soviet times, adapted transformer oil(!) as antifreeze for heating houses and country cottages.
Determine the required antifreeze consumption
How to calculate the required antifreeze consumption yourself, so that later there is no excess left, or vice versa, so as not to buy less than required? You can calculate the required amount of antifreeze with only a superficial knowledge of mathematics. To do this, you need to remember a few nuances:
- 1m3=1000 liters;
- The area of a circle is determined by the formula , where , a – radius (given in meters);
- The volume of pipelines (displacement) is determined by the formula , where is the number of pipes in meters;
- One cast iron section of the radiator contains 1.45 liters of water.
- The volume of registers and convectors is calculated using the same formula as pipelines;
- The volume of the heating boiler is indicated in the passport; if there is no passport or the boiler is homemade, then we calculate the volume of the heating boiler as well as the pipelines (often home-made and factory-made heating boilers are made from large-diameter pipes);
- Ultimately, the coefficient should be taken into account - 1.05 (plus 5% of the total requirement)
Example:
- We have a heating boiler with a capacity of 80 liters, a pipeline with a total length of 56 meters, a diameter of 20 mm and cast iron radiators in the amount of 15 sections.
The calculation will look like this:
- Pipelines - 3.14 (value) X 0.01 (pipe radius in meters) X 56 meters = 0.01758 m3 or 17.58 liters;
- Cast iron radiators - 15 sections x 1.45 liters = 21.75 liters;
- Heating boiler – 80 liters;
- Total – 17.58+21.75+80= 119.33 liters
- Total, taking into account the increasing factor (necessary for an emergency and creating a small reserve) - 119.33X1.05 = 125.3 liters.
Articles on the topic
The main source of heat transfer in a hydronic floor heating system is the coolant. In most cases, water is used as the liquid circulating in the network through pipes. But many experts recommend using special antifreeze for heated floors for these purposes. In this case, the main thing is to choose the right reagent that will improve the quality of heating and will not harm the equipment.
Content
Should you use antifreeze in your heating system?

Increasingly, not water is poured into the cottage heating system as a coolant, but a high-quality glycol solution containing anti-corrosion and anti-scale additives. When and why should you do this?
Water or antifreeze?
In winter, in the event of an emergency power outage or a drop in gas pressure in the cottage heating system, many of its elements (boiler, radiators, expansion tank, circulation pump, pipes) can be damaged in two or three days by the frozen water in them, the volume of which increases by 9% when moving into ice. If the water is not specially prepared in advance, then additional conditions arise for metal corrosion and scale formation, which impair heat transfer and increase energy costs. To eliminate this phenomenon, antifreeze is used as a coolant instead of water. Antifreeze (from the English freeze - “freeze”) is a liquid with a freezing point below 0°C. It is prohibited to use automotive coolant (coolant according to GOST 28084-89 as amended in 2007) containing nitrites and amines, as well as phosphate and silicate compounds, which form fumes harmful to humans and animals.
In addition, the service life of the coolant is only 2–3 years, and the composition of the additives and their quantity are insufficient to ensure the operation of heating systems. Such a liquid is not designed to be diluted with water at all, especially tap water. You should also be careful with salt water antifreezes such as “Assol”, “Burtas”, etc. Although they are safe for people, they are characterized by high corrosiveness and crystallization of salts when water evaporates. The heating system will quickly become clogged with scale, salt deposits and rust.
The procedure for commissioning a warm water floor
The first launch of a warm water floor can be divided into three stages:
- Filling the system with coolant
- Setting up a heated floor system
- Warming up and drying the floor screed
Filling the underfloor heating system with coolant
If you followed all the recommendations on our website, you should remember that the process of installing a heated floor involves crimping the system before pouring the floor screed or flooring (if it is a wooden floor or decking).
If you don't know what we're talking about, we recommend you read it. So, one of the methods of crimping is crimping a warm water floor with water. Therefore, if you followed this method, then, in principle, you have already done half the work. The floor pipe system is filled with water; it remains to fill the remaining part of the heating with water, which includes the boiler and radiators, if any. Another question is when the pressure testing was done with air, or was not done at all, or instead of water it is planned to use a special non-freezing liquid for heating as a coolant. In the latter case, you will have to drain all the water from the heated floor used for pressure testing.
Before filling the heated floor with coolant, all taps that must be open during heating operation must be opened. This includes:
- Circuit valves or flow meters that are located on the manifold
- Shut-off valves for the supply and return pipes of the manifold
- Three-way valve for underfloor heating mixing unit
- Automatic air vents on the collector and other heating areas
If the three-way valve has a thermostatic head, set it to the maximum value. If it is missing, unscrew the valve to the maximum.
Further actions depend on what you plan to pour into the system, water or antifreeze, as well as whether you have an open or closed heating system.
Let's consider the option of filling a closed type heating system, fed from a water supply system.
Filling heated floors with a closed heating system
To do this, as already mentioned, we open all the valves of the heated floor comb and the valve for heating replenishment from the water supply. At the same time, you will hear the sound of water moving through the pipes and air leaving the automatic air vents. Wait until air stops coming out of the auto vents. After all sounds stop, turn on the heated floor circulation pump. The air vents will begin to operate again, and the sound of air passing through the circulation pump will be heard. In this mode, run the pump for several minutes until most of the air leaves the system.
Next, close all valves or flow meters (depending on your manifold) except one. This is necessary so that the main pressure of the pump is concentrated in one loop and air under pressure comes out of the open circuit loop. Drive the circuit until the sound of bubbles is no longer heard. Once this has happened, open the valve of the next loop and close the previous one. So “pump up” all existing circuits. After completing the pumping of the last loop, you can open all the previous ones. If the heating system has radiators without automatic air bleeders, be sure to bleed air from them using the existing special Mayevsky valve on the radiator.
At this point, the heating system, which includes a water heated floor, is considered complete and the heated floor can be put into operation. But more on that below. First, let's consider more options for filling the heated floor and the entire system under other circumstances.
Filling a heated floor with an open heating system
An open heating system is considered when the system has an open type expansion tank at the top point of the entire heating system, into which coolant is constantly added as it evaporates.
To fill such a system, you must have at least a drain valve at the lowest point of the heating system. Filling is done through it, using a hose coming from the water supply. But the correct option would be to first fill the heated floor through special taps on the manifold, designed to fill and drain the system, again using a hose.
Filling the contours of a heated floor is carried out using the same method as for a closed type. Only here can you immediately push the system until water appears in the expansion tank. As air leaves the heated floor and the system as a whole, it is necessary to turn on the water from time to time, as its level will drop. Don't forget to bleed air from radiators if you have them.
Filling the heating system and heated floors with antifreeze
Antifreeze in the heating system has one good advantage. It will not freeze at sub-zero room temperatures. This becomes especially important when the premises are not permanently lived, for example, in a country house, where the owners come for the weekend, and between visits they turn off the boiler, or the boiler is solid fuel, requiring constant replenishment of fuel. If there is also a warm floor in such a house, this becomes even more relevant. If you simply drain the water from a conventional pipe or radiator system, then from a warm water floor this is a kind of problem.
This method can be used to fill not only antifreeze, but also regular water. For example, when there is no water supply nearby, or the water in the water supply contains a large amount of salts, which is not very good for the heating system. Therefore, they take water, for example clean melt water, and fill the heating system with it.
To perform this work, you will need a special crimping machine, which can be rented from a company specializing in this. It's not worth buying it just for once.
The hose from the pressure tester is connected to the supply manifold, antifreeze or water is poured into the pressure tester bath and you begin pumping, adding coolant to the pressure tester bath as needed. At the same time, you will hear the sound of air escaping from the air vents. Each contour is also filled in separately. After filling the entire system, you can turn on the pump to expel the remaining air. At the same time, you can “play around” with closing the contours for better pressure in individual loops.
If it just so happens that you couldn’t find a special crimping machine, you can use a regular vibration pump like a “stream” or “baby”.
Results
If the use of antifreeze is unavoidable (low winter temperatures and non-permanent residence in the house), it is safer to use propylene glycol compounds. In terms of their characteristics, they are not inferior to ethylene glycol, although they are more expensive, but they are absolutely harmless. In all other cases, it is better to use water (softened or distilled - your choice) as a coolant for a warm water floor. To insure against defrosting of the system in this case, lay polyethylene pipes in the screed - they normally withstand several freezing cycles. But it must be said that liquid in a heated floor can freeze only at a floor temperature of -5 o C or -10 o C, and this is impossible if the system is stopped even for a couple of days in extreme cold.
What happens if you pour water from a well into a heated floor?
Kardinale FORUMHOUSE user
Hi all! Help me solve the problem. I have a heated floor installed. Filled with water from the well. Look what happened after the summer heat. The water bloomed. There's some mucus inside. The system works, but I want to flush it. And most importantly, how to avoid this in the future?
MycraftUser FORUMHOUSE
I advise you:
- Flush the system.
- Remove all ferrous metal components and replace them with copper, stainless steel, etc.
- Fill the closed system with water purified by reverse osmosis.
- Additionally, install a sludge separator.

If you think that rust in a heated floor will lead to nothing, look at the photos taken by Mycraft.
This is what pipes clogged with rust look like.
TP combs.
System elements and branches.
And this is an experiment that Mycraft conducted. Two cans of water. On the left is plain water, on the right is desalted water. Samples of metals commonly used to make heating system components - copper, brass, steel and aluminum - were added to the jars. The water was periodically heated and cooled.
Start of the experiment:
11 months later:
In 2 years.
As they say, comments are unnecessary.
Do not pour water from a well or distilled water into the heated floor, because... The pH value of distilled water decreases after contact with air when filling the system. As a result: the acidity level of distilled water increases and acid corrosion can occur. Pour into warm, specially prepared coolant or demineralized water.
Rules for using antifreeze
Filling the system with a new mixture can only be done after it has been cleared of the previous “filler” and checked for leaks and cracks. Remember that you need to achieve complete sealing to avoid operational problems.
If necessary, carry out preventive maintenance and replace worn parts.
When you understand that the batteries and pipes are in order, you can begin the most time-consuming procedure - adding antifreeze. It is important to do this immediately after preparing the mixture (antifreeze, as you already know, will need to be diluted with water) so that it remains homogeneous.
Remember that antifreeze is a rather capricious chemical “cocktail” that requires a special approach.
When working with it, we recommend following these simple rules:
- A test run of the system should be carried out with minimal power. Next, the speed will need to be increased up to normal,
- Antifreeze can only be poured into single-circuit boilers,
- gas boilers are literally designed to be filled with antifreeze. If you try to optimize the performance of an electrical installation by adding antifreeze to it, this can lead to serious overheating,
- strictly follow the instructions on the antifreeze container and the recommendations from the manufacturer of your heating equipment. Otherwise, you may get into trouble due to clogged filters. This leads to a decrease in heat transfer due to breakdown of pumping systems.
What is the best antifreeze for the heating system of a country house?
From the point of view of safety and equipment service life, the best antifreeze for home heating is propylene glycol. Glycerin is more accessible, and even if it freezes, it will not damage the equipment. But he is “not indifferent” to rubber gaskets. Ethylene glycol can be chosen if you definitely have a single-circuit boiler and a closed heating system, the reliability of which you are absolutely sure of. Or maybe it’s better to pay an extra couple of thousand rubles and sleep peacefully?
Below are the main characteristics of the most popular non-freezing coolants.
Possibility of dilution with water
Warm House – Eco
Features of using water or antifreeze for heating
Manufacturers indicate on their electrical equipment parameters based on idle water. This concerns the performance and pressure supplied by the pump unit. If antifreeze is poured into the circuit, the operation of the equipment changes, which requires a certain safety margin from the pump.
The pump itself can be installed by yourself, but it is better to involve specialists who know the nuances of working with this equipment. The wet rotor, called an impeller, is installed only horizontally, which allows you to do without losing a third of its power.
For proper circulation of antifreeze throughout the circuit, the electric pump must work half as powerful as in the case of water.

The contour and overall diameter of heating pipes increase when using liquid compositions other than water. Antifreeze has low heat transfer, so the coolant must circulate much more actively throughout the circuit.
Not every pipe in the system can work with this composition, so it is necessary to select only those pipes that have the required diameter and low reactivity to chemical additives in the coolant composition.
Types of antifreeze and their properties
There are three main types of ready-made coolants on the modern market, which are successfully used in underfloor heating water circuits. Each individual group of antifreeze has its own composition, advantages and features of use.
Glycerin based solution
The coolant, the main component of which is glycerin, is successfully used for heating systems in houses of various types. Its main advantage is the absence of harmful components, which ensures its safe use in residential areas.
Glycerin-based antifreeze is non-flammable and has a relatively high level of heat transfer. The solution can withstand a maximum temperature of -30 degrees, which allows, if necessary, to turn off the heated floor system in severe frosts in winter.
The reagent consists of glycerin water and various additives that help improve its technical characteristics. For a metal pipeline, the mandatory presence of an anti-corrosion additive is required, since the use of a pure glycerin solution can lead to destruction of the system structure.

Antifreeze for heated floors based on glycerin
The main advantages of glycerin-based coolant include:
- safety and environmental friendliness of use;
- the presence of additives that prevent corrosion processes;
- Possibility of use for up to eight seasons in a row;
- fire safety;
- no negative impact on parts of the heating structure made of rubber or plastic;
- resistance to fairly low temperatures -30 degrees.
When the temperature limit is exceeded, glycerin antifreeze crystallizes. But at the same time it practically does not increase in volume. This property eliminates the possibility of pipeline rupture in the most severe frosts.
There are few disadvantages of using it:
- high viscosity of the solution, which requires the installation of high-power pumps;
- At elevated temperatures, the glycerin reagent can be converted into a substance with a pungent odor - acrolein.
When used in a floor heating system, parts made of plastic or non-polar rubber must be sufficiently durable and of high quality.
Ethylene glycol aqueous solution
Antifreeze with the lowest cost and fairly high efficiency. But its use is somewhat limited due to high toxicity. In this case, the freezing temperature of the viscous solution reaches -60 degrees. This characteristic allows the reagent to be used in the harshest winter conditions.
The coolant ethylene glycol contains special additives that prevent the rapid chemical process caused by the main substance.
The advantages of using ethylene glycol-based antifreeze include:
- good thermophysical characteristics;
- high temperature threshold;
- absence of scale and other deposits in the system.

Along with significant advantages, ethylene glycol solution has significant disadvantages:
- Toxicity. This antifreeze is quite poisonous. Therefore, its use in open systems is prohibited. Inhalation of ethylene glycol vapor for several hours causes severe poisoning of the body, and ingestion can cause death. If the solution is spilled on the floor covering, a chemical reaction occurs that leads to damage to the material.
- High requirements for the presence of anti-corrosion additives. An aqueous solution of ethylene glycol can destroy almost all materials, including metal. Therefore, antifreeze must contain sufficiently high-quality and highly effective additives that prevent the formation of corrosion.
- Flammability. The ethylene glycol solution ignites when the water evaporates. The reagent must be diluted by at least 45 percent. There is a risk of fire when only 15 percent water is present.
If you plan to use a coolant based on ethylene glycol, then the heating system must be designed as a closed circuit. However, it is not recommended to pour such antifreeze into double-circuit lines.
Coolant propylene glycol
This antifreeze not only has decent technical characteristics, but also has the highest level of safety. Crystallization of the solution begins only at -60 degrees, which allows its use in severe frosts without draining the system.
Propylene glycol coolant has many advantages:
- no corrosive effects;
- environmental friendliness and harmlessness;
- does not contribute to the formation of solid deposits inside pipelines;
- has high thermophysical properties;
- the possibility of fire and explosions is excluded.

Among the negative aspects of using propylene glycol, one can note a high level of fluidity and a negative effect on elements containing zinc.
What are the disadvantages of water as a coolant for heated floors?
The main disadvantage of water as a coolant is that it freezes at subzero temperatures.
But this minus does not apply to permanent residences.
Agree, if force majeure circumstances occur , for example, the electricity is turned off or the boiler breaks down, you will not sit back and wait for the house and all utilities to freeze .

A water heated floor is a heat-inertial system that works like a heat accumulator and retains heat for a long time.
How to fill coolant
Before pouring the heated floor, you need to close all the valves of the manifold assembly and connect the hose to the inlet tip. If you are planning to flush the system, then it is also better to attach a hose to the outlet tip, the second end of which should be led into a sewer, container or drain hole.
Start pouring with one loop. The valves on this circuit open (all others are closed), it fills, air is released (bleeder valves hiss). Turn on the pump for a short time. The air vents begin to hiss again, the pump is turned off. We waited until all the air came out and turned on the pump again. Repeat until air stops escaping, then proceed to fill the next loop.
The design and principle of operation of a liquid electric floor
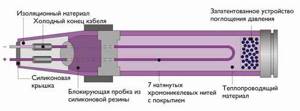
The main difference between the design of such a floor is its heating element. The liquid electric floor is a thick-walled pipe with a two-centimeter diameter made from special polyethylene.
Coolant (a special brand of antifreeze) is poured into this pipe. In it, along the entire length of the pipe, a chrome-nickel cable with seven cores is laid, lined with high-resistant Teflon. Both ends of the pipe are sealed. The poured coolant is motionless, which allows you to do without additional equipment (see comparison with water floors below).
The coolant, when heated, creates excess pressure, nucleate boiling occurs, leading to uniform and rapid heating of the entire system.
What is antifreeze for?

In some cases, a coolant such as water can cause corrosion processes, scale and deposits in the system pipes; in addition, if the boiler freezes and stops working, it can rupture them. This is especially true in those houses where residents are not permanently present (country houses, dachas) and there is no way to control the correct operation of the heating system. Antifreeze used in heating systems has a low freezing point, which prevents it from freezing when the boiler or pump is turned off.
Freezing of the coolant occurs when sediment forms in certain sections of the pipeline, when batteries are connected incorrectly, or when the pipe comes into contact with a poorly insulated wall. Also, water freezing can occur due to the low power of the heating boiler or a large area of the heated room.
Negative consequences can be avoided if you use antifreeze as a coolant, which not only does not freeze at low temperatures, but also contains additives that prevent the formation of scale and rust.
What is antifreeze?
Antifreeze is a chemical solution that, unlike water, does not freeze at temperatures below 0 degrees Celsius.
When water freezes, it expands and can rupture heating pipes, radiators, and damage plumbing fixtures, for example, a siphon under the sink or a toilet.
Important! Antifreeze , depending on the chemical composition, will not freeze at temperatures below -30...-65 ° C. At lower temperatures, the substance does not harden, but turns into a jelly-like form.
How to pour antifreeze into an open system
This is exactly the case when you should buy safe propylene glycol. It's all about the open expansion tank communicating with the atmosphere. Since it is located within the house (usually in the attic), small amounts of fumes can enter the living spaces. In general, pouring antifreeze into an open system is not advisable. It is better to convert it into a closed one, from where it will not evaporate.

The diluted concentrate is poured through an expansion tank or make-up valve using a pump. In this case, all Mayevsky air valves installed on radiators must be open. As the tank is filled, the taps are closed, after which the coolant level is brought to approximately 1/3 of the expansion tank.

Advice. Before you pump antifreeze into the heating system of your home with your own hands, you need to make sure that all shut-off and control valves are open.
After starting and warming up the boiler, you need to bleed the air through the batteries again. If the level of heated coolant in the expansion tank has dropped, then add antifreeze to about half.
USEFUL TIPS
When pouring antifreeze, check whether it precipitates when mixed with water. If yes, then use distilled water.
Never pour antifreeze into galvanized pipelines!
Antifreeze ages, so it must be replaced at intervals specified by the manufacturer (4–5 years), flushing the system with special compounds.
Do not use automobile antifreeze in heating systems, as it contains additives that are not permissible for use in residential premises.
Use special sealants for installing the heating system that ensure high reliability of connections (for example, winding and gel for pipes Record, Santekhmaster).
Consult with specialists regarding the operation of boilers in systems where the coolant is antifreeze - there are a lot of nuances. For example, flow-through boilers with forced thermal conditions in heat exchangers with a high degree of finning are characterized by short-term overheating of the heat exchanger walls at moments of maximum load when turning the boiler on and off - and here you need to be extremely careful when choosing a coolant.
Another example: starting a system with a cast iron boiler should be done at minimum power with a gradual return to operating mode.
It is worth keeping in mind that diluting antifreeze by more than 50%, in addition to increasing the freezing point, also leads to a deterioration in its anti-corrosion properties, as well as to the precipitation of hardness salts dissolved in water.
If dilution with water by more than 50% is still necessary, then additional additives will need to be added to the resulting solution.
To dilute antifreeze, it is recommended to use water with a hardness of up to 7 units. If you do not know the hardness of the water, we recommend that you first mix a small amount of antifreeze with water in the required proportion in a transparent container and make sure that there is no sediment.
Antifreezes based on monoethylene glycol are poisonous: be careful when refueling and servicing heating systems and do not use such antifreezes in dual-circuit systems.
Before pouring antifreeze into the heating system, we recommend testing the operation of the system on water and performing a pressure test of the system to make sure there are no leaks, as well as the absence of foreign impurities.
Features of using non-freezing liquids

Glycol antifreezes for the heating system of a country house are the most common on the domestic market. Before pouring the finished mixture into the CO at home, you should consider some points, namely:
- All water-glycol compositions are more viscous (than water). To compensate for the increased hydraulic resistance, it is necessary to use more powerful pumping equipment or make the pump rotate faster.
- Experts note that glycerin and glycol antifreezes have a significantly higher expansion coefficient when heated. If you decide to switch from water to antifreeze, you should provide a larger expansion tank.
- All glycol and glycerin antifreezes have a lower heat capacity. In other words, they deliver 15-20% of heat to heating devices. If you want to ensure that the efficiency of the heating system does not decrease when switching to “anti-freeze”, then you should provide radiators of higher power.
Advice: There is an option that does not require increasing the power of the batteries: it is necessary to increase the speed of the coolant in the circuit.
vote
Article rating