In order for the heating of industrial premises to meet the requirements of the regulations, it is important to take into account the design features of the engineering system and industrial areas. High ceilings, large windows, doors, the need to provide heat for workplaces - there are many nuances. Let's consider options for highways, types of heating and devices for heating buildings with increased areas. It would be useful to review ways to save energy so that heat does not warm up the upper part of buildings under the ceilings, due to which about 80% of thermal energy is lost.
Types of industrial boilers
To heat industrial heating radiators or supply hot water to heat exchangers to heat air, enterprises install medium- and high-power heat generators. Most often, enterprises use the following types of units:
- gas water heating;
- gas steam;
- solid fuel water heating;
- diesel
The most common of all are gas industrial boilers that heat water. They are fully automated, have several safety levels and have the highest efficiency - more than 90%. To increase efficiency, these units are equipped with water economizers, which remove heat from the flue gases and increase the efficiency of the installation by another 3-5%. The number of personnel required to service gas boilers is minimal, as is the frequency of maintenance.

Gas steam boilers are not installed specifically for heating; their task is to produce steam of specified parameters for technological needs. But if such a unit is available, then it simultaneously provides the workshop with heat. To do this, steam is passed through a plate or shell-and-tube heat exchanger, where it heats the water supplied to the heating system. A boiler for steam production is more complex than a hot water boiler; the highest requirements are placed on it.

In recent years, solid fuel industrial boilers have become increasingly popular. Despite the relatively low efficiency (depending on the type of unit), these installations are in demand in woodworking, agricultural and other enterprises associated with the availability of inexpensive wood or coal. Heat generators are not as easy to use as gas heaters and require constant supervision by maintenance personnel. Currently, the following industrial solid fuel boilers are used to heat industrial premises:
- burning wood and coal with manual loading;
- coal with automatic fuel supply;
- pellet
For small and medium-sized buildings, units with manual loading can be used. Where there is no possibility or desire to maintain extra personnel, it is customary to install industrial hot water boilers with automatic supply of coal, pellets or wood chips. Although the listed heat generators still need to be cleaned of ash at least once a week.

Central water heating
In this case, the source of the heat resource is the local boiler house or central heating system. Heating is carried out thanks to the coolant, which circulates through the pipes and heats the heating radiators. The advantage of this solution is the possibility of relatively uniform heating of large areas.
Water heating of industrial buildings can be implemented in several ways. First of all, the system may differ in the type of fuel on which it can operate. Therefore, the choice of boilers depends on the availability of energy.

Industrial gas boiler
The most commonly used boilers are the following types:
| Gas | If it is possible to connect to a gas pipeline, then gas equipment would be a good option. However, it should be taken into account that the price of this type of fuel tends to increase. |
| Solid fuel | They can be an economical solution, however, their operation is a rather labor-intensive process. True, some models are automated, i.e. There is no need to load fuel into the firebox with your own hands. However, in any case, you will have to take care of the firebox and chimney. Therefore, before giving preference to this type of equipment, it is necessary to estimate all its advantages and disadvantages. |
| Liquid fuel boiler | The disadvantage is the need for a separate room and container for storing fuel. In addition, the stock will have to be constantly replenished, which is associated with additional transportation costs. |
| Electrical | The equipment is convenient to use, however, it has one drawback - the high cost of operation. Therefore, as a rule, it is used only in cases where it is impossible to install other equipment or it is necessary to organize heating of a production space of 70 square meters or less. |

It must be said that combination boilers that can operate on different types of fuel are excellent solutions. In particular, they are able to solve the heating problem in the event of interruptions in gas or electricity supply. Their only drawback is their high cost.

The main parameter by which these devices are classified is the types of burners that are installed. The following types of equipment are most often found on sale:
| Gas-wood boilers | If necessary, they allow you to switch from gas to solid fuel, for example, to save money. |
| Gas-diesel | As a rule, they have high power and allow heating large areas. |
| Gas-diesel-wood | The equipment has greater functionality, however, it has low power and low efficiency. |
| Gas-diesel-electricity | Quite a powerful and versatile equipment option. |
| Gas-diesel-wood-electricity | These units are the most functional, but at the same time the most expensive. |
Advice! To save fuel, you can set the boiler to maintain a lower temperature during non-working hours than during working hours.
In addition to the type of equipment, water heating differs in the way the heating radiators are connected.
There are two schemes:
- Single-pipe connection - all heating radiators in this case are connected in series to one pipe through which the coolant circulates. This option is suitable for heating only small rooms, since in large systems the last radiators in the chain heat up much less than the first.
- Two-pipe connection - this scheme involves the use of separate pipes for supplying hot coolant and discharging cold coolant. This ensures more uniform heating of all radiators.
In industrial systems, as a rule, a two-pipe circuit is used.
Radiant heating - economical systems for large industrial buildings
To heat industrial premises, “light” and “dark” infrared heaters are installed. Natural or liquefied gas is used as a heat source. In buildings where, for some reason, gas equipment cannot be installed, suspended radiant panels are installed.
Features of the operation of different types of infrared heaters
In “light” heaters, gas is burned using a special burner, the surface temperature of which can reach 900 degrees. A hot burner provides the necessary radiation. “Dark” heaters (they are also called “pipe” heaters due to their design) are radiators with reflectors that are designed to direct radiant energy to the desired areas of the room. Tube infrared devices heat up less (up to 500 degrees) and have less harsh radiation, which significantly expands their scope of application.
Suspended radiant panels are universal, they are widely used in category, industrial and warehouse premises of all types. The systems operate using a steam/water intermediate coolant. The water in the devices heats up to 60-120 degrees, and the steam - up to 100-200. Today this is the most convenient and economical way to heat industrial premises and enterprises.
Pros and cons of radiant heating
Infrared heaters have the following undeniable advantages:
- quick heating of rooms (15-20 minutes);
- the possibility of creating warm zones in unheated rooms;
- no energy loss for heating “extra” area”;
- minimal heat loss in systems operating without coolant;
- savings on maintenance, since there is no need to change filters, check, repair pumps, etc.;
- comfortable microclimate: the air does not dry out, the floor heats up and serves as a secondary heat source.
Infrared heaters cannot be installed:
- if the ceiling height is below 4 m;
- in industries where radiation affects product quality or technological processes;
- in premises of fire categories A, B.
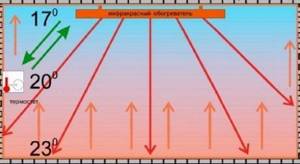
How does an infrared heater work?
Which autonomous heating for industrial premises to choose?
But first you need to decide on the types of production premises, their characteristics and functions. So, most often there are warehouses, workshops and industrial buildings themselves. When choosing effective heating, you should take into account the features of such systems, which include:
- maximum efficiency;
- possibility of heating rooms with large areas;
- If possible, heaters should heat the air both inside and outside.
In addition, the choice of the right system is usually influenced by factors such as the specifics of the production process and the cost of equipment, as well as much, much more. Next, we will look in more detail at the pros and cons of each possible option.
We recommend: What is better, autonomous or individual heating?
OUR PROPERTIES
Object: Pharmaceutical plant
Installation of storm drainage made from polyester pipes was carried out.
Object: Administrative building, Moscow
Installation of heating, water supply and sewerage systems. Installation of plumbing fixtures.
Object: Administrative building, Moscow
Installation of heating, water supply and storm sewerage.
Object: Administrative building, Moscow
Installation of a cascade boiler house using diesel fuel with a capacity of 600 kW.
Object: Sports complex
Installation of heating convectors
Object: Administration building, Moscow
Installation of a cascade boiler room using Viessmann boilers
You will find other examples of our objects in the OBJECTS section
System design
In order to organize air heating of premises, it is necessary to draw up all the necessary design documents. It is best to entrust this matter to professionals in this field. Otherwise, improper organization can result in increased noise levels in the premises or an imbalance in thermal conditions.
The organization of such an issue as heating and ventilation of industrial premises should resolve the following issues:
- Identify the preliminary level of heat loss that will be characteristic of a particular room.
- Calculate the power of the heat generator taking into account unproductive heat costs.
- Calculate the amount of heated air, as well as the required temperature regime.
- Determine the diameter of the channels through which air flows, and also identify possible pressure losses due to negative characteristics of the main line.
After the calculation of the heating system of an industrial building has been made, and such a project has been drawn up, you can purchase the necessary equipment.
Operating principle and types of air heating for home
There are two types of systems:
- Using air heaters. The scheme repeats heating with a liquid carrier, but heated air is used instead of water. The gas receives heat from the duct heater and is transported through a pipeline to the room. The scheme is rarely used, since constant changes in gas temperature cause the air ducts to lose their tightness, which reduces the efficiency of the network.
- Open type heating. The principle of operation is this: the heat generator warms up the air flows supplied by the air duct into the room. In the room, warm gas comes out, mixes with the air, warming up the entire space. The cooled gas is sucked in by a pipeline laid below and sent for heating. The cycle is repeated as many times as necessary to achieve the desired temperature in the room. This scheme is considered practical and convenient for use in homes.
There is also a distinction between local and central networks. Local circuits are circuits that heat one local object, for example, a house; central circuits are used for heating multi-apartment buildings, public and industrial facilities.
Based on the type of circulation, systems with full and partial air recirculation and direct-flow systems are distinguished. Direct-flow networks are centralized schemes in which the coolant is heated and moved through air distributors to each room separately.
Central networks are channel highways. This could be air heating of an industrial premises, but the schemes are not suitable for private houses, especially when transporting coolant over a long distance - you will have to purchase additional powerful fans, which is not always advisable.
Ventilation project for industrial premises
Meteorological conditions in the working area of the production premises of boiler houses should be taken according to the Sanitary Standards for the Design of Industrial Enterprises, based on the following categories of work in terms of severity:
light - in switchboard rooms and laboratories;
heavy - in boiler rooms and ash rooms when operating solid fuel boilers with manual maintenance of combustion devices:
average - in other rooms.
Table 10.2 When designing heating systems, the calculated air temperatures in the rooms should be taken according to Table 10.2.
In rooms with heat emissions, heating should be provided only in cases where excess heat does not ensure that the air temperatures specified in Table 10.2 are maintained in the production area. At design outdoor temperatures of minus 15° C (parameters B) and below, the heat balance in the lower zone of the boiler room (up to 4 m high) should be additionally checked.
Air heating systems should be designed for industrial premises. In auxiliary premises, as well as in laboratories, switchboards and workshops, it is allowed to install heating systems with local heating devices. The maximum temperature on the surface of heating devices in rooms where dust emission is possible, when installing boilers for working on coal and shale, should not exceed 130 ° C, for working on peat - 110 ° C. In these rooms, heating devices with a smooth surface should be provided, as a rule, registers are made of smooth pipes.
For rooms with obvious excess heat, natural ventilation should be provided. If it is impossible to ensure the necessary air exchange through natural ventilation, mechanical ventilation should be designed. Ventilation systems, methods of air supply and removal should be adopted in accordance with Table 10.2.
For boiler rooms with permanent maintenance personnel operating on gaseous fuel, at least three air exchanges per hour should be provided, excluding the air sucked into the furnaces of combustion boilers. The design of exhaust fans installed in these boiler rooms must exclude the possibility of sparking.
When designing the ventilation of boiler rooms, it is necessary to provide for the purification of air removed by aspiration units (before release into the atmosphere) in accordance with the Sanitary Standards for the Design of Industrial Enterprises.
For premises of liquid fuel pumping stations, a tenfold air exchange per hour should be provided. Air removal from these premises should be provided in the amount of 2/3 from the lower and 1/3 from the upper zones of the total amount of air removed. In the premises of liquid fuel pumping stations with category B production facilities, two supply and two exhaust ventilation units with a capacity of 100% each should be provided; It is allowed to use one supply and one exhaust unit with backup fans.
If the room height is less than 6 m, the air exchange rate should be increased at the rate of 25% for each meter of height reduction.
Air temperature in the working area of production premises, ventilation systems, methods of air supply and removal
Ventilation of industrial premises must solve two main tasks: remove exhaust air and provide an influx of fresh air. The first task is important, since the exhaust air may contain harmful substances in the form of gases, heavy impurities, as well as excess heat. The second task is determined by SNiP in order not to commit violations of the technological process in production.

Types of ventilation for industrial premises
According to the method of air movement, ventilation can be mechanical and natural. Ventilation of industrial premises, as a rule, is mechanical, but ventilation of warehouses can be carried out naturally. The mechanical system is divided into supply, exhaust and supply and exhaust. At large enterprises, only the last option is used. In small workshops and private workshops, an air supply system is usually installed, which is quite sufficient.
Based on the method of coverage, a distinction is made between general and local ventilation systems for industrial premises. Both options are often used simultaneously. General ventilation is intended, first of all, to combat excessive temperature increases in industrial premises during various technological processes. Local ventilation is installed in places where there is the strongest emission of process dust or toxic substances.
Depending on the duration of operation, ventilation of industrial premises and warehouses can be constant or emergency. With the help of constant ventilation, a normal microclimate is maintained in the room under normal production conditions. Emergency ventilation is activated when, for some reason, the room cannot be ventilated or the main ventilation fails.
System design
In order to organize air heating of premises, it is necessary to draw up all the necessary design documents. It is best to entrust this matter to professionals in this field. Otherwise, improper organization can result in increased noise levels in the premises or an imbalance in thermal conditions.
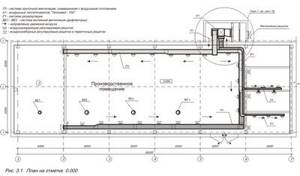
Air heating project for a production workshop
The organization of such an issue as heating and ventilation of industrial premises should resolve the following issues:
- Identify the preliminary level of heat loss that will be characteristic of a particular room.
- Calculate the power of the heat generator taking into account unproductive heat costs.
- Calculate the amount of heated air, as well as the required temperature regime.
- Determine the diameter of the channels through which air flows, and also identify possible pressure losses due to negative characteristics of the main line.
After the calculation of the heating system of an industrial building has been made, and such a project has been drawn up, you can purchase the necessary equipment.
Heating calculation
To carry out a thermal calculation, before planning any industrial heating, you need to use the standard method.
Qt (kW/hour) =V*∆T *K/860
Where:
- Qt – heat load on the heated space;
- V – internal area of the room requiring heating (W*D*H);
- ∆ T – the value of the difference between the external and desired internal temperature;
- K – heat loss coefficient;
- 860 – recalculation per kW/hour.
The heat loss coefficient, which is included in the calculation of the heating system for industrial premises, varies depending on the type of building and the level of its thermal insulation. The less thermal insulation, the higher the coefficient value.
Using the emergency ventilation system
SNiP provides for a design where industrial ventilation is combined with emergency ventilation. Emergency ventilation is a completely independent type of installation that is used to ensure safety at work. First of all, this applies to those industrial buildings and premises where the release of harmful gases is possible, as well as in explosive production.
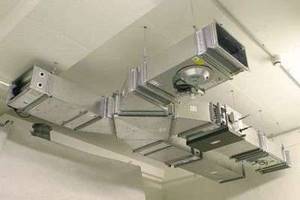
Emergency ventilation system
Ventilation of emergency industrial buildings can use:
- All main ventilation systems with backup fans. Such installations are usually designed for emergency air flow.
- If the main systems and the emergency system do not cope with the task, then backup fans available for industrial ventilation are connected to the ventilation operation.
- Only an emergency system when using the main one is impractical or impossible for various reasons.
Emergency industrial ventilation is arranged only in such a way as to ensure exhaust air exhaust. It is not performed by the supply air due to the avoidance of mixing fresh air with harmful gases, as well as due to the inadmissibility of the transfer of exhaust air from one room to another.
For example, ventilation of the battery room is necessary so that hydrogen, which is released during storage of batteries, does not mix with oxygen, forming an explosive mixture.
Air heating of industrial premises
This method of heating production areas became popular back in the 70s. The operating principle is based on heating the air with heat generators, water or steam heaters. Air is supplied through collectors to those areas where it is necessary to maintain the desired temperature. To distribute air flows, special distribution heads or louvers are installed. This is far from an ideal heating method; it has significant drawbacks, but is used quite widely.
Central and zonal systems
Depending on the needs of building owners, it is possible to equip uniform heating of the entire room or individual zones. Central air heating is a device that takes air from outside, heats it and supplies it to the premises. The main disadvantage of this type of system is the inability to regulate the temperature in individual rooms of the building.
Zone heating allows you to create the desired temperature in each room. To do this, a separate heating device (most often a gas convector) is installed in each room, which maintains the set temperature. The zone system is economically beneficial because it uses exactly as much energy as is needed for heating, and wasteful expenses are minimized. There is no need to lay air ducts during installation.
An experienced specialist must determine the appropriate type of system and calculate the air heating of the production premises. The following factors are taken into account:
- heat losses;
- required temperature conditions;
- amount of heated air;
- power and type of air heater.
Advantages and disadvantages
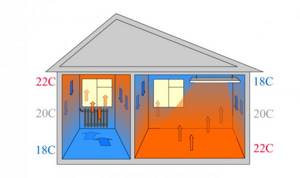
Important advantages include quick heating of the air and the ability to combine heating with ventilation. The disadvantage is due to a well-known law of physics: warm air rises. A warmer zone is created under the ceiling than at human height. The difference can be several degrees. For example, in workshops with ceilings 10 m high, the temperature at the bottom can be 16 degrees, and in the upper part of the room - up to 26. To maintain the desired thermal conditions, the system must operate constantly. This wasteful energy consumption forces owners to look for other methods of heating buildings.

Scheme of air heating of an industrial premises
SNiP standards for heating industrial premises
All standards and rules are set out in the joint venture. 2.2.1.1312-03, the requirements are as follows:
- The level of heat loss is no more than 3 degrees temperature difference between the inside and outside of the workshop. Therefore, when choosing a scheme and radiators for heating industrial premises, it is necessary to take into account the total heat loss of the building, the cost of heating not only the air, but also the equipment.
- Maximum heating of the coolant +90 C, 1.0 MPa.
- If the system does not use water, then other liquids must meet the requirements of production processes - the relevance of using a non-water coolant will have to be justified.
- The stairwells are not heated.
- If the workplace occupies more than 50 m2, the temperature regime is maintained with heating of the coolant to +90 C; in local areas of intermittent operation, heating of the coolant can be reduced to +80 C.
- Gas boilers can only be used with an afterburner; the release of combustion products is not allowed.
Electric boilers or local heaters are selected in accordance with the requirements of industrial buildings.
Heating scheme
Despite the above, we will not use radiant heating for our scheme. The fact is that most of the industrial buildings are still of the Soviet type, with large heat losses. They require the most inexpensive heating option, preferably using alternative fuel.

So, the average volume of such buildings is 5760 cubic meters, and in order to make up for losses, a power of 108 kilowatts per hour is required. These are very approximate figures and depend on a number of factors. Let us only note that we must have another 30% power reserve. Our fuel is wood and pellets.
In order to obtain the power we need, about 40 kilograms of fuel per hour are required, and if in production there is an eight-hour working day (plus an hour break), then 360 kilograms of fuel will be required per day. On average, the heating season is 150 days, which means that in total we will need 54 tons of firewood. But this value is maximum.
Now let's calculate the cost. (see table)
Since competition in the domestic market is growing every day, manufacturers are forced to pay attention to all cost items. If you look at this list, then far from the last position will be the cost of heating various industrial premises
Since the cost of energy resources has increased, their percentage of cost has also increased.

Air heating of production premises
If earlier such a question as choosing the most economical option was not yet so pressing, now it is positioned in the category of the most relevant. Air heating of a production facility in such a situation is often considered as the most effective and at the same time the most economical option.
Types of heating of industrial buildings, workshops and warehouses
Among the heating features of such premises, I would like to highlight the following:
- Heating equipment should be used as efficiently as possible.
- The need to heat large areas.
- Heaters are required to heat not only the air inside, but also outside. Their location does not matter.
The choice of one heating method or another should be influenced not only by the characteristics of the heat source, but also, say, by the specifics of the production process, the financial side of the issue, and so on. Now let's look at the positive and negative of each type.
Steam heating
This type of heating is used for industrial buildings. It has both pros and cons.
Advantages
- Permanently high air temperature (one hundred degrees and above).
- You can heat a room in record time, as well as cool it if necessary.
- The number of floors of buildings does not matter; steam heating is acceptable for any number of floors.
- heating equipment, and even the pipeline, are small in size.
Important ! The steam system is well suited for heating industrial premises, much more than, say, heating with water. Ideal for periodic heating.
Flaws
- The main disadvantage is the strong noise performance during operation.
- In addition, steam consumption, and therefore heat transfer, cannot be controlled.

The approximate cost of such heating for one season can range from 32 to 86 thousand rubles, depending on the selected fuel. We took an average industrial building, the total area of which is approximately 500 meters, and the ceiling height is 3 meters.
It is not advisable to install steam heating in buildings where aerosol or dust, as well as flammable gases, are released.
Water heating
If water heating is chosen, the heat source can be a local boiler house or a centralized heat supply. The main component of such a system is a boiler that can run on gas, solid fuel, and even electricity. But it is best to use either gas (about 80 thousand per season) or coal (about 97 thousand), since other options will cost more, which raises doubts about the advisability of their use.
Features of water heating
- High pressure.
- Heat.
- It is used primarily in the role of “standby” heating of the building, with the temperature set to plus 10. Of course, if this does not contradict production technology.
Air heating
Air heating of industrial premises can be both local and centralized. It is characterized by the following features:
- Air is always moving.
- Therefore, it is changed and cleaned periodically.
- The temperature is distributed evenly throughout the room.
- All this is absolutely safe for the human body.
Through air ducts, heated air enters the building, where it mixes with what is already present and acquires the same temperature. In order to minimize energy costs, most of the air is purified using filters, heated back and released into the room.

But outside air is also supplied in accordance with sanitary standards. But if during production some harmful or toxic substances are released, then the recycling procedure will be in question. In this case, the heat from the exhaust air must be recovered.
If local air heating is used, then the heat source should be located in the very center of the building (this can be heat guns, VOA and others). But in this case, only internal air is processed, but no fresh air is supplied from outside.
Ceiling heating systems
Radiant heating in the form of ceiling panels is used not only in industrial facilities, but also, for example, in greenhouses, greenhouses and even in multi-apartment residential buildings.
A significant difference between such systems is that they heat not only the air, but also the walls, floor, all objects and people in the building. The air is not heated at all and, therefore, does not circulate, which allows employees to avoid allergies or colds.
Infrared heating
Not every company is ready to spend a lot of money on an air heating system, so many prefer to use another method. Infrared industrial heating is becoming increasingly popular every day.

An infrared burner operates on the principle of flameless combustion of air located on the porous part of the ceramic surface. The ceramic surface is distinguished by the fact that it is capable of emitting a whole spectrum of waves that are concentrated in the infrared region.
The peculiarity of these waves is their high degree of permeability, that is, they can freely pass through air currents in order to transfer their energy to a certain place. The stream of infrared radiation is directed to a predetermined area through various reflectors.
Therefore, heating industrial premises using such a burner allows for maximum comfort. In addition, this heating method makes it possible to heat both individual work areas and entire buildings.
Main advantages
At the moment, the use of infrared heaters is considered the most modern and progressive method of heating industrial buildings due to the following positive characteristics:
- quick heating of the room;
- low energy intensity;
- high efficiency;
- compact equipment and easy installation.
By performing the correct calculation, you can install a powerful, economical and independent heating system for your enterprise that does not require constant maintenance.
Scope of application
It is worth noting that such equipment is used, among other things, for heating poultry houses, greenhouses, cafe terraces, auditoriums, shopping and sports halls, as well as various bitumen coatings for technological purposes.
The full effect of using an infrared burner can be felt in those rooms that have large volumes of cold air. The compactness and mobility of such equipment makes it possible to maintain the temperature at a certain level depending on the technological need and time of day.
Safety
Many people are concerned about the issue of safety, since they associate the word “radiation” with radiation and harmful effects on human health. In fact, the operation of infrared heaters is completely safe for both humans and equipment located in the room.
Water heating of residential and industrial buildings
Water heating is the radiator heating we are used to. There are many heating schemes for buildings. Each building and structure has its own individual characteristics, so there is no “template” for installing building heating
Particular attention should be paid to the calculation and selection of equipment for installation. When calculating water heating systems for buildings, the main emphasis should be on thermal and hydraulic calculations
During installation, special attention should be paid to the quality of laying heating mains and pipelines, because This will allow you to avoid leaks and unplanned repairs in future operation. This type of heating is more common in residential buildings, administrative and office centers.
Common mistakes and how to fix them
The calculation of the heating system itself is an important and complex stage in the development of heating. Special computer programs help specialists perform all calculations. However, errors may still occur.
One of the common problems is the incorrect calculation of the thermal power of the heating system or the lack thereof. In addition to the high cost of radiators, their high power will cause the entire system to become unprofitable. That is, the heating will work more than necessary, wasting fuel on it. High room temperature will burn a lot of oxygen and require regular ventilation to reduce it.
If the thermal power is calculated to be lower, the boiler will quickly wear out. This situation can be corrected only by installing an additional heating method or completely replacing the entire system.
If the heating system heating devices were not calculated correctly or the installation was performed, the overall efficiency of the system will also drop. Such errors can reduce the operation of heating devices by half. You can fix everything by reinstalling the radiators.
The reason for additional costs may be an error in the power of the heating boiler. If its value is greater than that of heating radiators, then a double cost overrun will occur. To correct such an error, you will need to replace the boiler, heating elements or the entire system.
Hydraulic calculation of heating system pipelines and its other components will not only minimize further costs, but also create an efficient heating system.
Air heating of a private house with air conditioning
Inverter air conditioners can also be used for space heating. Their cost is almost twice the price of similar units that perform the cooling function. When using an air conditioner, there is no need to design an air heating system. The air is heated in the external unit, then transferred through the duct to the internal one and directed into the room with the help of a fan. The operational capabilities of such an air conditioner are limited.
The external unit cannot operate at temperatures below -7 ° C (this indicator may differ in individual models). A conventional split system provides comfortable indoor conditions in the autumn-spring period, when central (or autonomous) heating is not yet turned on or has already been turned off.
On a note! When using a split system for heating, you must strictly adhere to the temperature level specified in the instructions. The most common consequence of non-compliance is a burned out compressor.

Heat pump air conditioners can heat and condition a room.
Air conditioners with heat pumps are suitable for year-round use. Such units provide air heating and air conditioning even at -25 °C. If in a conventional air conditioner, during heating, electrical energy turns into thermal energy, then the pumping system pumps warm air from one medium to another. That is, during cooling, excess heat with the participation of the refrigerant is released into the street - during the heating process, everything happens exactly the opposite: warm air increases the temperature of the cold street air.
Advantages of air heating
Among the advantages offered by air heating of industrial buildings are the following:
- Efficiency that reaches a value of 93%. In order to organize air heating of industrial premises and enterprises, there is no need for intermediate heating devices.
- Such systems can be easily integrated with systems such as ventilation. Thanks to this, the room can be maintained at exactly the required temperature.
- Air heating has a minimal level of inertia. The room temperature will begin to rise as soon as the equipment is turned on.
- Due to the fact that such room heating is the most efficient, it is possible to increase the economic performance of production.
- The cost of production is slightly reduced.
Advantages and disadvantages of air heating
Compared to conventional liquid coolant, air heating has a wide range of advantages:
- Extremely high efficiency. The performance of heating circuits reaches 90%.
- The ability to quickly turn on/off without having to drain the coolant. During the period of conservation for the winter, you will not have to worry about cleaning network devices, and when starting the main line, turning on the heat generator will be enough to quickly put the equipment into operation.
- Relatively low cost. The system does not contain shut-off valves, adapters, radiators and other elements, this is a clear financial saving.
- Versatility. The network works for heating and cooling, providing a comfortable temperature in any season.
- Reduced inertia. This property allows you to quickly heat or cool the air in the room.
- Integration of additional equipment. To increase comfort, ionizers, humidifiers, purifiers and other types of devices, including filter units, are built into the system - this is especially useful for rooms with high requirements for air purity.
- Uniform and smooth heating. When flows move, there will be no unheated zones in the room, reducing the risk of condensation on the ceiling.

The possibility of arranging the scheme in houses of any number of floors is an additional plus. But there are also disadvantages.
Disadvantages of air heating:
- Energy dependence. The network will not work without power supply, so if there are interruptions in the network, you need to install a generator.
- Regular inspection and renovation. Air ducts are constantly exposed to hot and cooled masses, so they can warp, sometimes cracks appear in the joint area - all defects should be eliminated in a timely manner.
Another disadvantage is installation during the construction phase, especially for air ducts built into the floor; moreover, the entire network is not modernized and will not change its operational characteristics.
Similar documents
Development of master plans for enterprises and industrial areas. Constructing a wind rose. Construction of an industrial building. Heat consumption for heating the building. Calculation of water heating, supply ventilation, water supply and sewer networks.
course work, added 12/24/2009
Features of installing a heating system when building a modern house. Promising developments in this area. Classification of heating systems, assessment of their efficiency. Description and technical characteristics of various types of two-pipe heating systems.
course work, added 11/17/2009
General characteristics of the building. Design of heating and hot water supply systems. The operating principle of water heating systems with natural circulation. Pipeline accessories. Carrying out welding work. Hydraulic testing of heating systems.
thesis, added 11/02/2009
Types of heating systems and their mode of operation. Advantages and disadvantages of heating systems depending on the type of coolant. Standard thermal conditions for various premises. Correct placement of heating devices and increasing their efficiency.
thesis, added 06/20/2014
Calculation of heat transfer of the outer wall, floor and ceiling of the building, thermal power of the heating system, heat loss and heat release. Selection and calculation of heating devices of the heating system, heating point equipment. Hydraulic calculation methods.
course work, added 03/08/2011
Convective or radiant heating of premises, carried out by a special technical installation. Schematic diagrams of water heating with natural circulation. Heat pipelines of central systems. Comparison of the main coolants for heating.
abstract, added 02/20/2014
Thermal engineering calculation of enclosing structures. Development of a heating system, determination of thermal loads. Hydraulic calculation of water heating. Selection of heating point equipment. Design of ventilation systems, calculation of air exchanges.
course work, added 12/01/2010
Climatic characteristics of the construction area. Thermal engineering calculation of external building envelopes. Determination of the thermal power of the heating system. Design and calculation of heating and ventilation systems. Calculation of air exchange.
course work, added 12/24/2010
Thermal engineering calculation of the first floor floor, external walls and insulated attic floor. Description of the designed heating system. Calculation of heat loss through external fences. Hydraulic calculation of heating and ventilation systems.
course work, added 02/20/2015
Studying the activities and procedures for completing construction projects. Study of types of heating systems for a two-story cottage. Installation of radiators. Installation of risers and connections from them to devices. System testing.
practice report, added 12/08/2013
Posted on https://www.allbest.ru/
Specialty: 270116 “Installation, adjustment and operation of electrical equipment of industrial enterprises and civil buildings”
The course project involves designing a heating and ventilation system for an industrial building.
The building is a one-story repair shop.
Building dimensions:
L = 105 m
B = 24 m
H = 8 m
The walls are made of brickwork, the side walls have double glazing. The roof is a roofless roof made of reinforced concrete slabs with a cement screed with a layer of insulation and waterproofing.
There are double-leaf wooden gates on the front wall. The floor is covered with asphalt concrete (on the ground).
The windows are double sash with double glazing (distance between panes 30÷60 mm).
The heating system used in the building is a two-pipe system with bottom wiring, connected to the heating network through a control unit located along the facade wall. The heating source is water from a thermal station.
Coolant parameters: external heating network temperature – 70 ÷ 150 ºС
The water temperature in the local network is 70 ÷ 95 ºС.
Ventilation – supply and exhaust with natural and mechanical impulse.
The heating system of buildings, regardless of their type of purpose (residential, industrial, industrial, administrative, high-rise, etc.), is a system that combines air and water heating. This system can be built on the basis of both central and autonomous heating. They will differ only in the presence or absence of the energy source itself - a boiler or heat generator.

Choosing a heating system for industrial premises

Warehouses also need heating
For heating industrial buildings, central heating systems (water or air) are most often used, but in some cases it is more rational to use local heaters.
But in any case, when choosing a production heating system, you need to rely on the following criteria:
- Area and height of the room;
- The amount of heat energy needed to maintain the optimal temperature;
- The ease of maintenance of heating equipment, as well as its suitability for repair.
Now let's try to understand the positive and negative aspects that the above-mentioned types of heating of industrial premises have.
Central water heating
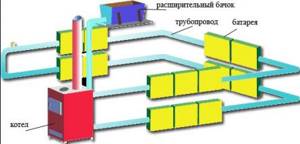
Scheme of traditional water heating
The source of the heat resource is a central heating system or a local boiler house. Water heating consists of a boiler, heating devices (radiators or convectors) and a pipeline. The liquid heated in the boiler is transferred to the pipes, giving off heat to the heating devices.
Water heating of industrial buildings can be:
- Single-pipe - here it is impossible to regulate the water temperature.
- Two-pipe - here temperature control is possible and is carried out thanks to thermostats and radiators installed in parallel.

Scheme of water heating production in the case of a local boiler house
As for the central element of the water system (that is, the boiler), it can be:
- gas;
- liquid fuel;
- solid fuel;
- electrical;
- combined.
You need to choose based on the possibilities. For example, if it is possible to connect to a gas main, a gas boiler would be a good option. But keep in mind that the price of this type of fuel increases every year. Plus, there may be interruptions in the central gas supply system, which will not benefit the production enterprise.

Gas industrial boilers
An oil-fired boiler requires a separate safe room and fuel storage tank. In addition, you will have to regularly replenish fuel reserves, which means taking care of transportation and unloading - additional costs of money, labor and time.

Viessmann liquid fuel boilers of different capacities
Solid fuel boilers are unlikely to be suitable for heating industrial premises, unless they are small in size. Operating and maintaining a solid fuel unit is a rather labor-intensive process (loading fuel, regularly cleaning the firebox and chimney from ash).
True, at present there are automated solid fuel models into which you do not need to load fuel yourself; a special automatic intake system has been developed for this. Also, automated models allow you to set the desired temperature.
However, you will still have to take care of the firebox and chimney for a solid fuel boiler. The fuel used here is pellets, sawdust, wood chips, and, if placed manually, also firewood. Although this type of boiler requires labor-intensive operation, it is the most inexpensive.

Solid fuel boiler Retra 3M
Electric boilers are also not the best option for large industrial enterprises, since the electricity consumed costs a pretty penny. But heating a production space of 70 square meters using this method is quite acceptable. However, do not forget that in our country, periodic power outages for several hours have long been a common occurrence.
As for combination boilers, they can be called truly universal units. If you have chosen a water heating system and want to get efficient and uninterrupted heating of your production as a result, then take a closer look at this option.
Although a combination boiler costs several times more than previous units, it provides a unique opportunity - practically not to depend on external problems (interruptions in the centralized heating system, gas supply and electricity supply). Such units are equipped with two or more burners for different types of fuel.
Built-in types of burners are the main parameter for dividing combined boilers into subgroups:
- Gas-wood heating boiler - you don’t have to worry about interruptions in gas supply and rising fuel prices;
- Gas-diesel - will provide high heating power and comfort in a large room;
- Gas-diesel-wood - has expanded functionality, but you have to pay for it with lower efficiency and low power;
- Gas-diesel-electricity is a very effective option;
- Gas-diesel-wood-electricity – an improved unit. It can be said that it provides complete independence from possible external problems.
Combined unit
Everything is clear with boilers, now let's see whether water heating in production fits the selection criteria that we initially outlined. Here it’s worth mentioning right away that the heat capacity of water, compared to the heat capacity of the same air, is several thousand times greater (at the usual temperatures of air (70°C) and water (80°C) in the heating system).
In this case, the water consumption for the same room will be thousands of times less than the air consumption. This means that fewer connecting communications will be required, which is certainly a big plus, given the design of industrial premises.
Note! A water heating system allows you to control the temperature: for example, you can set standby production heating (+10°C) during non-working hours, and set a more comfortable temperature during working hours.
Air heating

Air heater
This type is the very first artificial heating of premises. So air heating systems have been proving their effectiveness for quite a long time and, it should be noted, are in constant demand.
All this thanks to the following positive aspects:
- Air heating assumes the absence of radiators and pipes, instead of which air ducts are installed.
- Air heating shows a higher level of efficiency compared to the same water heating system.
- In this case, the air is heated evenly throughout the entire volume and height of the room.
- An air heating system can be combined with a supply ventilation and air conditioning system, which allows you to obtain clean air instead of heated air.
- It is impossible not to mention regular changes and air purification, which has a beneficial effect on the well-being and performance of employees.

Air ducts
In order to save money, it is better to choose combined air industrial heating, which consists of natural and mechanical air circulation. What does it mean?
The word “natural” means the intake of already warm air from the environment (warm air is available everywhere, even when it is -20°C outside). Mechanical induction is when the duct takes cold air from the environment, heats it and delivers it into the room.

Air heating production diagram
For heating a large area, air heating systems for industrial premises are perhaps the most rational option. And in some cases, for example, at chemical plants, air heating is the only permitted type of heating.
Infrared heating
How to heat an industrial premises without resorting to traditional methods? Using modern infrared heaters. They work on the following principle: emitters generate radiant energy above the heated area and transfer heat to objects, which in turn heats the air.
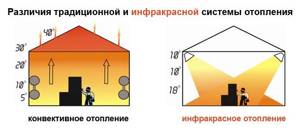
The figure clearly shows the operating principle of infrared heating
Information! The functionality of infrared heaters can be compared to the Sun, which also uses infrared waves to heat the earth's surface, and as a result of heat exchange from the surface, the air is heated.
This principle of operation eliminates the accumulation of heated air under the ceiling and, as a result, large temperature changes, which is very attractive for heating industrial enterprises, since most of them have high ceilings.
IR heaters are divided into the following types according to their installation location:
- ceiling;
- floor;
- wall;
- portable floor.

Infrared ceiling heaters
By type of waves emitted:
- shortwave;
- medium wave or light (their operating temperature is 800°C, so they emit soft light during operation);
- long-wave or dark (they do not emit light even at their operating temperature of 300-400 ° C).
Wall-mounted IR models
By type of energy consumed:
- electrical;
- gas;
- diesel

Infrared Ceiling Film
Gas and diesel infrared systems are more profitable and their efficiency is 85-92%. However, they burn oxygen and change the humidity in the air.
By type of heating element:
- Halogen - the only drawback is that if dropped or subjected to a strong impact, the vacuum tube may break;
- Carbon - the main heating element is made of carbon fiber and placed in a glass tube. The biggest advantage compared to other IR devices is lower energy consumption (about 2.5 times). If dropped or subjected to a strong impact, the quartz tube may break.
- Tenovye;
- Ceramic - the heating element is made of ceramic tiles assembled into one reflector. The principle of operation is the flameless combustion of a gas-air mixture inside a ceramic tile, as a result of which it heats up and transfers heat to surrounding surfaces, objects, and people.
IR heaters are most often used for heating:
- industrial premises;
- shopping and sports facilities;
- warehouses;
- workshops;
- factories;
- greenhouses, greenhouses;
- livestock farms;
- private and apartment buildings.

IR ceiling heaters
Advantages of infrared heating:
- First of all, it should be noted that IR heaters are the only type of devices that allow for zone or spot heating. Thus, different parts of the production facility can be maintained at different temperatures. Zone heating can be used to heat work areas, parts on a conveyor belt, car engines, young animals on livestock farms, etc.
- As mentioned above, IR heaters heat surfaces, objects and people, but do not affect the air itself. It turns out that there is no circulation of air masses, which means there is no loss of heat and drafts and, as a result, fewer colds and allergic reactions.
- The low inertia of infrared heaters allows you to feel the effect of their action immediately after starting, without preheating the room.
- Infrared heating is very economical, due to its high efficiency and low energy consumption (up to 45% less energy than traditional methods). There is probably no need to explain that this significantly reduces the financial costs of the enterprise and quickly pays back all the funds invested in infrared heating.
- IR heaters are durable, lightweight, take up little space, are easy to install (each product comes with detailed installation instructions) and require virtually no maintenance during operation.
- Infrared heaters are the only type of heating devices that can provide effective local heating (that is, without resorting to centralized heating systems).
Industrial heating systems
To organize heating of industrial premises, it is necessary to take into account the fundamental differences between industrial buildings and residential and administrative buildings. They are as follows:
- large dimensions and ceiling heights;
- low degree of insulation;
- the presence of many drafts or constantly opening gate openings;
- the presence of technological equipment that generates heat;
- emissions of harmful substances into the workshop space that must be removed;
- The cost of energy resources for industry is usually higher than for the population.
In addition to the listed features, industrial heating systems when heating buildings must provide optimal temperatures in workplaces or maintain the microclimate required for storing a particular product.
Currently, to create certain indoor conditions, the following heating systems for industrial buildings are used:
- water;
- air;
- infrared heating.

Traditional one- and two-pipe systems, where water is used as a coolant, successfully operate in small and medium-sized buildings with ceiling heights of up to 5 m. Although it should be noted that single-pipe schemes are implemented infrequently, since the large length of networks and a large number of batteries make water industrial heating inefficient. Typically, the role of heating devices is played by steel registers made of smooth pipes or convectors.

In buildings whose ceilings are at a height of 5 m or more, water heating with registers becomes impractical. Warm air, heated by the radiators, rises to the upper zone of the workshop, leaving the lower part, where people work, cold. At metallurgical and chemical enterprises, water heating of industrial premises will also not be effective, even despite the low height of the buildings.

The reason is a large number of harmful substances released during technological processes. They are removed using supply and exhaust ventilation, which is why the air in the workshop is renewed 4-10 times per hour; it is impossible to quickly warm it up with radiators. In practice, 2 systems are combined into one and air heating of buildings is organized. Moreover, the entire volume of the room is not heated; air of a normalized temperature is supplied from top to bottom into the area where people are and work.

Large industrial enterprises, for example, pipe or metallurgical shops with a length of 500 m or more, shipyards and hangars with a height of 60 m, cannot be fully heated due to economic infeasibility. In such giant buildings, it is customary to provide local heating using portable or stationary fan heaters. In addition, infrared electric heating has recently been introduced into production workshops. Wall-mounted or hanging appliances do not heat the air, but objects and surfaces located within their radius of action.

Air heating systems
Such heating can be done either local or centralized; and it is distinguished by the following features:
- air masses are constantly in motion;
- the air is regularly changed and cleaned;
- the temperature is more evenly distributed throughout the rooms;
- harmless to humans.
The heated air enters the workshop through air ducts, where it is mixed with the existing air. Moreover, most of it then passes through special filters, is heated again and used. Thus, energy losses are minimized. In addition, such a system provides air supply from outside, which already meets sanitary standards. However, if during the production process some harmful substances are released into the atmosphere, then such a recycling system is unlikely to be effective and safe. In this case, you will have to completely remove all the air coming out.
Note that when using local air heating, the heat source is located in the center of the building. The latter is usually taken as VOA, heat guns and the like. However, only the air inside can be processed in this way, and fresh air masses will not be supplied.

Airborne solar collector
Heating and heating of industrial buildings
An ideal solution for buildings with ceiling heights above 4 m, such as production workshops, hangars, warehouses, garages.
Gas infrared heating avoids the problems typical of traditional convective heating systems:
Annual flushing of systems, leaks, maintenance and repair of pumps, thermal insulation of heating mains, etc.
We offer a full range of SBM infrared heaters.
Modular heaters of various powers from 2.8 kW to 30 kW and more. Allows you to organize a guaranteed ideal level of comfort regardless of the installation height of the heaters.
The heaters are equipped with a “dual control” feature to provide greater comfort and lower energy consumption in well-insulated buildings.
Infrared heating of the workshop
The operating principle of infrared heaters is to heat surfaces due to the effects of infrared radiation. If the heating system of the welding shop is designed for spot heating of certain zones, then it is best to use these devices. Effective heating with infrared heaters for workshops should begin with the selection of heating elements. Currently, two methods of generating IR radiation are used.
Carbon heaters
Carbon Ceiling IR Heater
Its design consists of a bulb, inside of which there is a carbon spiral, and a reflective element. When current passes through the heating element, it glows due to high electrical resistance. As a result, IR radiation is released.
To focus thermal energy, a reflector made of stainless iron or aluminum is provided.
IR electric heaters can be used as additional heating in a carpentry shop. They are mounted above those work areas where a stable temperature regime is required. The advantages of electric infrared heaters include:
- Easy installation;
- The ability to regulate the heating temperature by changing the supplied current power;
- Small overall dimensions.