Industrial production is characterized by specific working conditions, which may include toxic, gas, and heat emissions from technological equipment into the environment. To eliminate such negative factors, industrial ventilation is organized inside the industrial workshop - a complex, multi-level system for normalizing microclimatic parameters. Designed to remove harmful heat and gas emissions from industrial equipment from the personnel working area.
Types of industrial ventilation
The classification of industrial ventilation is carried out according to the criteria of localization, direction and method of operation. Let's take a closer look.
According to the principle of operation
- Natural. It is based on the natural circulation of air flows with different temperatures, pressures, and densities. Heavy cold air flow displaces lighter and warmer air. In an industrial building, this process can occur through natural gaps, leaks in window and door openings, or organized supply and exhaust openings covered with grilles and deflectors. Depends on atmospheric conditions, wind strength and direction, time of year (in winter, ventilation is better due to strong draft). This method is not suitable for all industries, especially where there are harmful emissions from operating equipment. Can be installed, for example, in agricultural premises.
- Artificial ventilation. If production involves a side effect in the form of toxic heat and gas emissions, mechanical ventilation of production premises is strictly required. The main function is to remove the exhaust air flow from the personnel work area, prevent the penetration of harmful vapors into other rooms, compartments, as well as supply fresh street air (purified or unpurified) in a general flow or targeted. It is organized using mechanical means of supplying and removing air masses (supply and exhaust fans, roof units). It is a more effective way to clean and circulate air flow inside an industrial workshop.
According to the principle of localization
- General exchange. Designed to uniformly clean the entire workshop from harmful technological heat emissions, normalizing temperature and humidity levels and air movement speed. Quickly copes with a small percentage of air pollution.
- Local ventilation. It is used when there is localization of a large amount of toxins, vapors, smoke, etc. in a certain place. Installed directly above the source of increased heat and gas generation. Exhaust hoods or flexible ducting connected directly to the equipment may be used. Used in conjunction with a general ventilation system as additional air purifying equipment.
- Emergency. It is installed and used in the future in case of emergency, for example, fire, excessive release of toxic substances from industrial equipment, high levels of smoke, etc.
Based on the principle of flow direction
- Supply ventilation installations. The principle of operation is based on the displacement of warm exhaust air by a cold influx through organized exhaust openings at the top of the workshop. They can be either natural or mechanical.
- Exhaust ventilation units remove exhaust air flow along with burning particles, smoke, toxic fumes, excess heat, etc. Structurally, they can be general or local, most often with forced motivation, since it is quite problematic to remove polluted air naturally.
- The supply and exhaust unit is used most often and provides the necessary circulation of air masses inside the industrial workshop. Most often with mechanical equipment (supply and exhaust fans).
Where is industrial ventilation used?
An industrial ventilation unit is most in demand for solving air exchange problems in cold (metal and woodworking, welding), hot (metal melting, cooking) and steaming (wet heat treatment of products) production areas. They are also used in the commercial sector - in shopping centers, hotels, offices, etc.
In the photo: Examples of the use of industrial ventilation in production
Examples of the use of industrial ventilation in production
Welding shop.
The work of the welding shop is accompanied by large emissions of harmful substances - fluorine, ozone, nitrogen oxide and dioxide, carbon monoxide. The use of local and general supply and exhaust ventilation helps solve the problem of effective air purification. The first is installed in areas where impurities are released, preventing their further spread throughout the room. The general exchange provides sufficient air exchange.
Medical laboratory.
With the help of industrial ventilation, the required level of humidity and temperature is maintained, which allows you to preserve medicines and reagents in proper quality. To do this, an air humidifier is additionally installed in the system. Ventilation also neutralizes unpleasant odors and helps bring carbon dioxide levels to standard values.
Storage in warehouses
. Long-term and reliable storage of goods in warehouse complexes requires the fulfillment of a number of conditions to ensure certain conditions. It is necessary to maintain the required level of temperature and humidity, which depend on the specifics of the product, to ensure air exchange in the required volume. This allows you to keep the cargo intact and avoid losses. Only industrial ventilation can effectively solve these problems at facilities with such a large area.
Equipment for ventilation of industrial premises
The forced supply ventilation system consists of the following elements:
- air ducts;
- fan;
- air filters;
- air valves;
- air intake grilles;
- sound-absorbing insulation;
- heater (air heating);
- automatic control unit if necessary.
The mechanical exhaust ventilation device is organized according to the same model, with the exception of the air heater and filters, which are not needed for the removed air.
Hot shop ventilation: installation features
Local exhaust ventilation of industrial premises is organized by exhaust hoods, flexible air ducts connected to the general air exchange system.
In addition, supply and exhaust ventilation can be equipped with a heat recuperator to save energy when heating the incoming flow. The supply masses are heated by the heat of the removed air, without mixing with it.
Design and principle of operation
Installation of industrial ventilation is necessary for high-quality purification of polluted air, without which it is impossible to comply with all sanitary and hygienic requirements for the production process and worker safety.
Industrial ventilation systems are classified according to the type of design and principle of operation into the following types:
- Gravitational.
These include dust-sediment chambers used in industries characterized by strong dust formation. Such systems promote the sedimentation of large particles.
- Inertial dry cyclone and louvered type.
Such systems are characterized by differences in compactness and design. They allow you to clear air masses of dry dust.
- Inertial wet type.
Such systems effectively cope with air purification by removing dust by moistening the masses.
- Fabric filters.
The principle of operation of these devices is to filter air flows due to the accumulation of numerous contaminants in the pores of the filter element.
- Electrostatic precipitators.
Air purification in such systems occurs by eliminating mechanical impurities using an electric charge, as a result of which contaminants are deposited on the filter electrodes.
Requirements for industrial ventilation
Ventilation and air conditioning of production premises is regulated by the general requirements of SanPiN, as well as parameters specific to the particular workshop of the enterprise. These include:
- mechanical ventilation of industrial premises must comply with fire safety rules;
- removal of substances hazardous to health and emissions without allowing personnel into the work area;
- a hygienic and fire safety certificate is required for the materials from which the elements of the ventilation system are made;
- anti-corrosion coating of air ducts, or they must be made of materials resistant to such influences;
- the thickness of the coating of ventilation ducts with flammable paint should not exceed 0.2 mm;
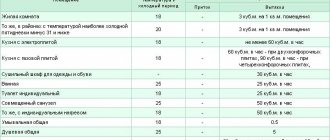
- for personnel work areas located directly inside the workshop, the concentration of harmful substances should not be more than 30%;
- Humidity and air flow speed indicators are not standardized in the summer;
- in winter, the air temperature inside the workshop with personnel located there is at least 10⁰ C, in the absence of people - at least 5⁰ C;
- in summer, the temperature indicators of the internal and external air flows are equal, or the internal temperature does not exceed the external temperature by more than 4⁰ C;
- workshops that are not used in the summer do not regulate the requirements for industrial ventilation in terms of temperature;
- the overall noise level inside an industrial workshop should not exceed 110 dBa, this includes the operating noise of the ventilation system.
The above list is quite general. In practice, the requirements for ventilation of industrial premises are supplemented by individual production parameters, workshop design, specifics of the products, etc. In addition, it is necessary to take into account how heating and ventilation interact inside the workshop. It should also be taken into account that lighting and ventilation of industrial premises are also interconnected.

Features of the ventilation system of the hotel complex >>>>
Air exchange naturally
Natural ventilation in enterprises is based on natural draft, but it depends on certain conditions:
- How different is the air temperature outside from the temperature in the workplace?
- Wind speed.
The simplicity and accessibility of the natural system will not require the management of the enterprise to spend extra money on its equipment. There is no need to waste electricity to operate it. The only bad thing is that the effectiveness of its operation depends entirely on the weather and time of year.
Ventilation system
For better natural ventilation, it is necessary to position the equipment so that the air flow can freely circulate between the rows. Opposite the passages, windows are made in the walls, through which clean air enters. In addition, workshops must have windows or transoms that must be opened regularly. You just need to monitor the temperature in the rooms.
Ventilation device. Stages of work
According to SNiP, industrial ventilation and air conditioning must be installed in all areas of the workshop without exception.
Ventilation and air conditioning of industrial premises perform the following tasks:
- removal of air masses filled with excess heat, toxic fumes, gas formations, burning particles, smoke, etc.;
- additional cleaning with a filtration system of the air flow emanating from process equipment and containing hazardous impurities;
- supplying personnel with a constant flow of fresh air, normalizing the temperature and humidity balance, which determines sanitary and hygienic control.
Installation of a ventilation system for industrial premises occurs in several stages:
- preparatory – the initial stage at which design and corresponding calculations are carried out. Based on this, the optimal equipment is selected, components, main elements, and units are transported;
- assembly - individual elements and air ducts are assembled into a single complex. The ventilation system is installed, the electrical component is assembled, and connected to the electrical network;
- commissioning – test check of correct functioning, quality, efficiency, signing of the commissioning certificate.

Features of ventilation in a hairdressing salon >>>>
Ventilation of the meat industry
Examples of ventilation system calculations are based on the specifics of the functioning of various departments:
- raw materials, machine, extrusion, separation of semi-finished products: general forced exhaust from the upper tier, there is also an influx of fresh air supplied down evenly throughout the room;
- ventilation of the sausage shop (hard smoked sausages, smoked pork meats), thermal and offal departments: general mechanical with additional local ventilation, in summer the influx into the upper zone is natural (in winter - with mechanical stimulation);
- dumpling compartment: local exhaust hoods are used, air supply units in the upper zone supply the flow evenly, the movement speed is low;
- smoke generating zones: general exhaust ventilation from the upper tier, the inflow is supplied directly to the work area mechanically in winter and in the off-season, natural supply in summer.
Design of ventilation for industrial premises
Designing ventilation for industrial premises is a complex, multi-component process that is best entrusted to professional design engineers with many years of experience in this field. List of actions carried out when designing a ventilation system for industrial premises:
- preparation of technical specifications for design, which includes the necessary requirements for organizing air exchange, parameters of technological equipment;
- approval of technical specifications;
- an aerodynamic calculation of general ventilation and local air exhaust in industrial premises is carried out, the purpose of which is to determine the optimal internal cross-section of air ducts;
- selection of ventilation equipment according to calculated characteristics and parameters;
- selection of additional elements necessary for setting up and balancing the ventilation system;
- drawing up drawings of the future ventilation system using specialized programs;
- drawing up distribution diagrams of key system components in accordance with standards and requirements.

Ventilation of a repair shop
A special feature is the uneven, intense release of welding aerosols in certain areas. When repairing large-sized equipment and machines, it is impossible to organize local exhaust hoods. There may also be restrictions on the heat supply of the repair and technical unit.
The workshop ventilation drawing is drawn up in accordance with all related factors. It is possible to organize local climatic zones of a certain structure. At the height of the welding fume accumulation, air ducts are installed through which the air flow is diverted and filtered. On the other hand, an inflow (purified with the addition of fresh air mass) is supplied above the working area, thus creating air circulation.

Ventilation of industrial buildings. Documentation
The required documentation when designing and installing a ventilation system includes:
- basic information about the specifics of production, the design of premises, buildings;
- general diagram of the optimal location of ventilation equipment;
- ventilation system specification;
- a list of materials from which elements of the future installation must be made;
- documents on thermal and fire insulation of ventilation ducts;
- drawings of the ventilation network, including a building diagram, floor level marks, dimensions and diameter of ventilation ducts, the intersection of air ducts with other structural elements and sections of their insulation;
- separate drawings of important nodal connections and connections;
- diagrams of non-standard fastenings, if they will be used;
- diagrams of atypical structures, elements, units.
What you need to know about bakery ventilation
To install a ventilation system, a technological map is required, which defines a list of parameters that must be fulfilled:
- features of installation work related to the specifics of production;
- requirements for transportation of materials, products, quality of work performed, safety work, etc.;
- schemes for production quality control of work performed;
- determination of the degree of quality of equipment, materials, work technology;
- list of necessary transport, material, technological resources;
- installation work schedule;
- technical, economic costs.

Types of installations that can be used in industrial settings
The air exchange process in production can be adjusted by installing different types of ventilation systems. Modern ventilation networks are classified into several main types: natural, mechanical and combined ventilation. Each type of system has its own characteristic features, pros and cons, which must be taken into account when choosing a specific type of network for installation in production.
Natural ventilation systems
Networks of this type operate on the basis of elementary laws of physics - on the difference in pressure indicators inside and outside the room, temperature spread. Such a system could be:
- Unorganized
. Air flows will penetrate into the building through cracks, gaps, and other types of openings that were not specially equipped; - Organized
. In this case, the network is equipped with the use of special and supply channels, and the arrangement of openings for ventilation. All these simple devices will allow you to regulate the volume and strength of air masses entering the internal space.
Umbrellas or deflector devices can be additionally installed above the system’s air ducts, which will enhance draft.
Mechanical (artificial) ventilation systems
Air exchange in a network of this type will be provided by special fans. The network itself has a more complex structure compared to natural systems and the costs of its design and organization will be much higher, but they are well worth the benefits listed below:
- Allows you to remove contaminated air from a specific point in the room;
- Allows you to regulate air temperature and humidity;
- The supply of clean air can be organized directly to the workplace, and its removal and subsequent deep cleaning from foreign impurities can also be organized;
- It can be equipped with effective filtering devices that can ensure that the permissible pollution levels of the local atmosphere comply with the requirements of construction, sanitary and administrative standards.
Artificial ventilation units have their own classification into separate subtypes: they can be supply, exhaust, or combined. A specific solution for the ventilation network is selected based on the operating conditions of the equipment and the characteristics of the production process carried out at the enterprise.
Supply air exchange
The main function of this type of installation will be to provide the workspace with clean air.
It is installed mainly in enterprises where, during the work process, there is a significant release of heat into the local atmosphere, and the release of harmful compounds in small concentrations is observed. Polluted air is discharged through special channels (ventilation shafts). Additional draft is provided by the flow of natural ventilation. Supply units can be:
- Monoblock
. An extremely simple type of equipment that does not require complex maintenance. However, such devices have a high market value. When installing a network, first install the unit itself, placing it in the right place, and then connect the air duct system to it and connect the entire system to the electrical network; - Typesets
. These devices have an affordable price, but you won’t be able to install them yourself, since their installation has special specifics
Supply ventilation systems can be used to create a local climate with certain parameters, since, if necessary, they can be equipped with heaters, air conditioners, filters and humidifiers.
Exhaust air exchange
Systems of this type are designed to blow contaminated air masses out of the working space.
In its stand-alone version, it is used mainly for removing dirty air from a specific area of the workspace, as well as for production areas in which there is no significant release of toxic compounds (in warehouses, utility rooms). The flow of clean air is ensured by infiltration. Depending on the coverage area, such installations are classified into two types:
- General exchange installations
. The system will ensure the movement of air flows throughout the space; - Local settings
. Remove contaminated masses from a specific area.
Combined systems
Such a system will simultaneously provide work areas with clean air and remove contaminated air masses from them.
This is a universal type of ventilation system that can be used in enterprises with increased requirements for the quality and volume of air exchange processes. In order for such a system to work effectively, it is necessary to carry out a number of calculations on the basis of which a detailed design is made. Channels for the entry of clean air masses are installed in such a way as to prevent the entry of contaminated air into the places of permanent residence of personnel.
Calculation of the ventilation system for a production room
Calculation of ventilation of production premises should be carried out only by highly qualified specialists. The process is quite complex, taking into account many nuances that need to be linked into an overall effective ventilation scheme so that it shows the necessary results.
It must be remembered that the calculations always take into account the types of ventilation of production premises that it is decided to install. As an example, we briefly present two calculation formulas.
The first of them is used for workshops in which there are no emissions harmful to human health:
L = I * n
L – the required air mass flow for a specific workshop or room;
I – air flow for one person, determined by sanitary and hygienic, building standards;
n – number of personnel.
For premises where hazardous substances are expected to be released from process equipment, a different calculation formula is used:
L = L m.v. + ( m v.v. – L m.v. (Su.v. – Sp.v.)) / (C1 – Sp.v.)
L m.v. – air flow removed by local hoods;
m i.v. – hazardous substances (mg/h) coming from outside;
Su.v. – amount of hazardous substances (mg/m³) in the removed air;
Sp.v. – amount of toxic substances in the supply air;
C1 – amount of hazardous substances (mg/m³) allowed by standards.
If several types of hazardous substances are released, calculations are made for each of them using this formula, and the results are summarized.

Ventilation of welding workplaces
Ventilation in welding production is designed to especially efficiently and thoroughly clean the air masses from harmful impurities, since welding work is one of the most harmful types of work for human health; oxides of nitrogen, carbon, fluorine and many other various chemical compounds are certainly formed during the welding process.
The type and organizational type of ventilation of such a workshop depends, first of all, on the dimensions and production capacity of welded-joined products.
If the capacity of the welding shop is small, and the volume of products produced is also insignificant, then local ventilation can be organized at the welding workplace.
If technological processes involve constant local movement of workers throughout the entire workshop area, then the organization of mobile posts with local ventilation loses its relevance. In this case, it is advisable to organize general-exchange ventilation. As a rule, such an exhaust affects the lower and upper parts of the room, and forced flows additionally provide heating of the room, which is especially important for welding work in the cold season.
Industrial ventilation has long ceased to be a simple production necessity. In various modern industries (capacities and volumes), ventilation has begun to act as the most important engineering complex, because the correct organization and subsequent implementation of measures to equip production with ventilation systems contributes to the creation of a healthy microclimate in workshops and production areas. This means that it makes it possible to carry out high-quality technological processes, aimed at complying with basic safety regulations, and also contributes to the correct organization of each workplace, and most importantly, eliminates harm to the health of the worker involved in production.
We recommend: Optimal blind area dimensions: width, slope, thickness
Installation of industrial ventilation
Industrial exhaust and supply ventilation systems are launched into the installation process only after the project has been approved and all preliminary work has been carried out and agreed upon. The installation location and location of the main elements are determined at the design stage.
First, the main structural elements are installed. Afterwards, the air duct system is separated from them. During installation, many features are taken into account, for example, the spatial orientation of the ventilation ducts, the material they are made of, the design of the ceiling, building elements, the presence of beams, etc.
All this directly matters for how the ventilation units and air duct pipes will be attached. In industrial workshops, ventilation ducts are mounted to the ceiling. For commercial premises, it is preferable to use plastic channels due to their more attractive design. Most often, rigid or flexible air ducts are used, which have their own advantages and features.
Installation is carried out in strict accordance with the design and calculations, while observing the necessary requirements for ventilation of production premises.

Emergency ventilation in production
It is an independent installation that is necessary to ensure safe working conditions in production with the likelihood of the release of harmful and hazardous substances.
The emergency system device works only for exhaust. This is necessary to avoid polluted air from entering different places.
Ventilation of industrial premises is a labor-intensive and energy-consuming process that requires specialized knowledge and skills. Regardless of the type and type of ventilation device in production, two main factors must be observed: correct design and functionality. Subject to these conditions, a correct and healthy microclimate is ensured.
Industrial ventilation control
To monitor the quality of the microclimatic environment directly inside the personnel’s work area, industrial ventilation control is carried out. It is necessary to distinguish between checking the efficiency of the ventilation system, air ducts and production control of ventilation systems.
In the first case, it means checking the air flow inside the ventilation ducts and distribution grilles, checking the compliance of these indicators with the design calculations.
In the second, industrial control of ventilation means taking the parameters of the air environment specifically in the personnel’s work area, determining the level of humidity and temperature for compliance with sanitary standards. Also, monitoring the ventilation systems of industrial premises is intended to monitor the level of hazardous, toxic substances in the air flow, and whether the designed air exchange rate is being observed.
This procedure is quite expensive and is carried out by accredited laboratories. As a rule, industries that emit hazardous substances into the air during their activities are inspected, as are health care institutions and other socio-cultural and socially important facilities that are subject to periodic inspections by the state.
Performs the following tasks:
- control of ventilation systems in industrial premises is intended to ensure safe working conditions, primarily for personnel;
- ensures safe conditions for the production of products;
- monitor temperature and humidity indicators, air exchange rate parameters, concentration of harmful vapors in the work area for subsequent adjustment of the operation of the ventilation system (if necessary);
- minimize the occurrence of dangerous, emergency situations at work.
Ventilation systems control
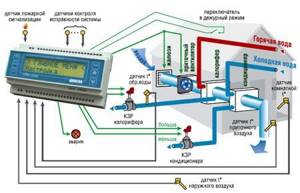
Automation of ventilation system control allows you to optimize the process and reduce operating costs. This approach allows us to minimize human participation in management and reduce the risk of the “human factor”. Automatic control involves the installation of sensors that record air temperature/humidity, concentration of harmful substances, degree of smoke or gas contamination. All sensors are connected to a control unit, which, thanks to the specified settings, turns the equipment on or off. Thus, automation helps to comply with sanitary standards, quickly respond to emergency situations and save significant money.