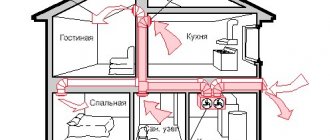
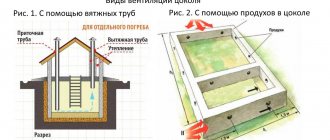
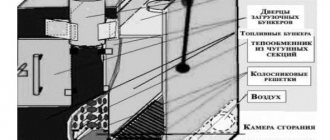
One of the indicators that influences the provision of an optimal microclimate in premises for various purposes is the air exchange rate. This term refers to the number of complete cycles of changing air masses in a room within a unit of time, for example an hour.
The rotation of air masses ensures:
- removal of air containing pathogenic and pathogenic microorganisms;
- replacing oxygen containing carbon dioxide with a new volume of air, which creates comfortable conditions for human mental activity;
- optimal values of temperature and humidity in the room, which influence human performance and create the specified conditions for storing various products;
- elimination of air containing unpleasant odors.
The required values of air exchange rates, depending on the purpose of the room, are indicated in special SNiP tables. Rotation of air masses is ensured through the combined use of natural and artificial ventilation.
The flow of oxygen is ensured through windows, doors and using special fans. However, given the tendency to use materials and technologies that ensure the tightness of these structures, close to absolute values, the use of systems that provide oxygen flow in the construction of buildings is a prerequisite for achieving air exchange rates.
These problems are solved by equipping walls and windows with supply valves, which, in addition to tightness, ensure the supply of the required amount of oxygen per unit of time.
Air exchange rate in retail premises (shops)
| № | Room | Estimated air temperature for the cold period of the year, °C | Air exchange rate or the amount of air removed from the premises | |
| influx | hood | |||
| 1 | Sales areas of stores with an area of 400 m2 or less: | |||
| food | 16 | — | 1 | |
| non-food | 16 | — | 1 | |
| 2 | Sales areas of stores with an area of more than 400 m2: | |||
| food | 16 | By calculation | By calculation | |
| non-food | 16 | By calculation | By calculation | |
| 3 | Razrubochnaya | 10 | 3 | 4 |
| 4 | Unloading premises | 10 | By calculation | By calculation |
| 5 | Premises for preparing goods for sale (if placed in a separate room), picking, receiving | 16 | 2 | 1 |
| 6 | Storerooms (unrefrigerated): | |||
| bread, confectionery; | 16 | — | 0,5 | |
| gastronomy, fish, milk, fruits, vegetables, pickles, wine, beer, drinks; | 8 | — | 1 | |
| shoes, perfumes, household chemicals, chemicals; | 16 | — | 2 | |
| other goods | 16 | — | 0,5 | |
| 6.1 | Room for preparing goods for sale (if placed in a separate room), picking, acceptance, expeditions | 16 | 2 | 1 |
| 7 | Premises for displaying new products (if placed in a separate room) | 16 | 2 | 2 |
| 8 | Ironing | 16 | By calculation | By calculation |
| 9 | Garbage chambers (unheated) | — | — | — |
| 10 | Room for mechanized pressing of paper waste | 16 | — | 1,5 |
| Storage facilities: | ||||
| 11 | packaging materials and equipment | 16(8) | — | 1 |
| 12 | exchange fund containers | — | — | 1 |
| 13 | containers | 8 | — | 1 |
| 14 | cleaning equipment, detergents | 16 | — | 1,5 |
| 15 | Linen room | 18 | — | 0,5 |
| 16 | Workshops, laboratories | 18 | 2 | 3(2) |
| 17 | Refrigerated containment chambers: | |||
| meat, semi-finished products, gastronomy | 0 | — | — | |
| fish | -2 | — | — | |
| vegetables, fruits, confectionery, drinks | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| ice cream, dumplings, etc. | -12 | Periodically | ||
| food waste | 2 | — | 10 | |
| 18 | Air cooled machine rooms | 5 | By calculation | |
| 19 | Water-cooled refrigerated machine rooms | 5 | 2 | 3 |
| 20 | Office premises, staff room, main cash register, security room, automated control center | 18 | — | 1 |
| 21 | Dressing rooms, utility room for catering establishment staff, meal room | 16 | — | 1 |
| 22 | Public toilets for customers and staff toilets | 16 | — | 50 m3/h per toilet |
| 23 | Showers | 25 | — | 5 |
| 24 | Dispensary room (if the store is located in the underground floors) | 20 | — | 60 m3/h per person |
| 25 | Premises for receiving and issuing orders | 12 | — | 1 |
| 26 | Glass container reception premises | 16 | — | 1 |
| 27 | Health center | 20 | 1 | 1 |
General information
Air exchange is one of the quantitative parameters characterizing the operation of the ventilation system in enclosed spaces. In addition, it is considered the process of replacing air in the internal spaces of a building. This indicator is considered one of the most important in the design and creation of ventilation systems.
There are two types of air exchange:
- 1. Natural. It occurs due to the difference in air pressure inside and outside the room.
- 2. Artificial. This is done through ventilation (opening windows, transoms, vents). In addition, it includes the entry of air masses from the street through cracks in walls and doors, as well as through the use of various air conditioning and ventilation systems.
Its value is determined not only by SNiP, but also by GOST (state standard). A set of measures that need to be taken to maintain optimal conditions in residential apartments and office premises depends on this indicator.
Air exchange rate in the premises of public catering establishments
| № | Names of premises | Design air temperature, °C | Air change rate per hour | |
| influx | hood | |||
| 1 | Hall, distribution room | 16 | According to calculations, but not less than 30 m3/h per person. | |
| 2 | Lobby, antechamber | 16 | 2 | — |
| 3 | Cookery store | 16 | 3 | 2 |
| 4 | Hot shop, confectionery baking room | 5 | According to calculations, but not less than 100 m3/h per person. | |
| 5 | Shops: pre-cooking, cold, meat, poultry, fish, herbs and vegetables processing | 18 | 3 | 4 |
| 6 | Production Manager's Office | 18 | 2 | — |
| 7 | Room for flour products and finishing of confectionery products, linen | 18 | 1 | 2 |
| 8 | Room for cutting bread, for preparing ice cream, serving room, utility room | 18 | 1 | 1 |
| 9 | Washing: tableware, kitchen utensils, vessels, containers | 18 | 4 | 6 |
| 10 | Director's office, office, main cash register, rooms for waiters, staff, storekeeper | 18 | 4 | 6 |
| 11 | Dry food pantry, equipment pantry, wine and vodka pantry, beer storage room | 12 | — | 1 |
| 12 | Pantries of vegetables, pickles, containers | 5 | — | 2 |
| 13 | Reception | 16 | 3 | — |
| 14 | Engine room of refrigerated chambers with air-cooled units | By calculation | By calculation | By calculation |
| 15 | The same, with water-cooled units | — | 3 | 4 |
| 16 | Repair shops | 16 | 2 | 3 |
| 17 | Premises of public organizations | 16 | 1 | 1 |
| 18 | Refrigerated storage chambers: | |||
| meat | 0 | — | — | |
| fish | -2 | — | — | |
| dairy and fat products, gastronomy | 2 | — | — | |
| semi-finished products, including highly prepared | 0 | — | — | |
| vegetables, fruits, berries, drinks | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| confectionery | 4 | — | — | |
| wines and drinks | 6 | — | — | |
| ice cream and frozen fruit | -15 | — | — | |
| food waste | 5 | — | 10 | |
| 19 | Smoking room | 16 | — | 10 |
| 20 | Unloading premises | 10 | By calculation | By calculation |
Notes: 1. The air temperatures in the rooms (except for refrigerated chambers) indicated in the table are calculated when designing heating systems.
2. In buffets, bars, cocktail lounges, banquet halls located in separate rooms, the air ratio is minus 3.
3. The air temperatures in the refrigerated chambers indicated in the table are maintained around the clock throughout the year. In chambers for the simultaneous storage of meat and fish or meat and fish semi-finished products, accept temperatures of ±0 ° C; for semi-finished vegetable products +2 °C; for storing all products (1 chamber in the enterprise) ±2 °C.
Design
When arranging a ventilation system in an office with your own hands, you can select and install decorative grilles, but it is better to entrust the drawing up of the project and its technical implementation to specialists if you want to get the desired effect in full.
Design includes the following:
- Calculation of heat inflows separately for each room, taking into account the architectural features of the building.
- Calculation of ventilation power, which is determined by the intensity of the air exchange created.
- A diagram of all communications in an axonometric form.
- Calculation of the aerodynamics of air ducts, which will allow you to determine the optimal sizes of ventilation ducts and possible pressure losses in the system.
- Selection of a complete set of necessary equipment to ensure efficient and uninterrupted operation of ventilation.
- Calculation of the required heating of the supply flow.
- Preparation of related documentation.
At the same time, it is still important to decide on such important points as:
- Placement of ventilation equipment. Ideally, a special ventilation chamber is created for this.

- Configuration and location of channels.
- Power consumption of the electrical equipment used.
- Need and placement of drainage system.
- Possibility and features of access to devices after completion of installation work.
- Ability to make changes and modifications to the system configuration.
To create a professional design for a ventilation system in an office, design specialists will also need various diagrams and drawings that will be used to plan future communications. The most important documents of this type for design are:
- Project of a natural ventilation system created in the office during the construction stages of the office center.
- Architectural plan of the facility indicating the installation locations of doorways and windows.
- A diagram of the interior of the office with the designation of all workplaces, places where furniture and equipment are installed.
Air flow rates for modulated equipment
| № | Equipment | Brand | kW | Air quantity, m3/h | |
| Exhaust | Supply air | ||||
| 1 | Electric stove | PE-0.17 | 4 | 250 | 200 |
| 2 | PE-0.17-01 | 4 | 250 | 200 | |
| 3 | Electric stove | PE-0.51 | 12 | 750 | 400 |
| 4 | PE-0.51-01 | 12 | 750 | 400 | |
| 5 | Frying cabinet | ShZhE-0.51 | 8 | 400 | — |
| 6 | ShZhE-0.51-01 | 8 | 400 | — | |
| 7 | ShZhE-0.85 | 12 | 500 | — | |
| 8 | ShZhE-0.85-1 | 12 | 500 | — | |
| 9 | Electric device, cooking | UEV-60 | 9,45 | 650 | 400 |
| 10 | Mobile boiler | KP-60 | — | — | — |
| 11 | deep fryer | FE-20 | 7,5 | 350 | 200 |
| 12 | Cooking kettle with capacity, l: | ||||
| 100 | KE-100 | 18,9 | 550 | 400 | |
| 160 | KE-160 | 24 | 650 | 400 | |
| 250 | KE-250 | 30 | 750 | 400 | |
| 13 | Steamer | APE-0.23A | 7,5 | 650 | 400 |
| APE-0.23A-01 | 7,5 | 650 | 400 | ||
| 14 | Electric frying pan | SE-0.22 | 5 | 450 | 400 |
| SE-0.22-01 | 5 | 450 | 400 | ||
| SE-0.45 | 11,5 | 700 | 400 | ||
| SE-0.45-01 | 11,5 | 700 | 400 | ||
| 15 | Steam table | ITU-0.84 | 2,5 | 300 | 200 |
| ITU-0.84-01 | 2,5 | 300 | 200 | ||
| 16 | Mobile food warmer | MP-28 | 0,63 | — | — |
Source: “Design of public catering establishments” Reference manual for SNiP 2.08.02-89
Procedure for installing ventilation
At the initial stage, you should carefully study the room, take measurements, find out its nature and purpose. Next, by solving simple mathematical formulas, you need to calculate the amount of purified air required for a given room. After the concept of future work has been determined, it is necessary to calculate the entire system, observing all the requirements of the room, its dimensions and the choice of equipment.
Sources
- https://tion.ru/ventilyaciya/v-ofise/
- https://ultrasale.ru/services/ventilyaciya-v-ofise.html
- https://mega.ru/ventilyatsiya/kak-vypolnyaetsya-proektirovanie-ventilyatsii-ofisov
- https://www.AirClimat.ru/Proektirovanie-ventilyatsii-ofisov.htm
- https://alpa.pro/stati/ventiljacija-i-kondicionirovanie-v-ofise/
- https://www.AirFresh.ru/ventilyatsiya-ofisov.htm
[collapse]
Air exchange rate in the premises of sports and recreational institutions
| № | Names of premises | Design air temperature, °C | Air change rate per hour | |
| influx | hood | |||
| 1 | Gymnasiums without seats for spectators (except for rhythmic gymnastics halls) | 15 | According to calculations, but not less than 80 m3/h per student | |
| 2 | Rhythmic gymnastics halls and choreographic classes | 18 | According to calculations, but not less than 80 m3/h per student | |
| 3 | Rooms for individual strength and acrobatic training, individual warm-up before competitions | 16 | 2 | 3 |
| 4 | Workshops | 16 | 2 | 3 |
| 5 | Classrooms, teaching rooms, rooms for instructors and coaching staff, judges, press, administrative and engineering staff | 18 | 3 | 2 |
| 6 | Household premises for workers and public order officers | 18 | 2 | 3 |
| 7 | Fire station room | 18 | — | 2 |
| 8 | Wardrobe for outerwear for exercising | 16 | — | 2 |
| 9 | Locker room (including for massages) | 25 | Balanced including showers | 2 (via showers) |
| 10 | Showers | 25 | 5 | 10 |
| 11 | Massage | 22 | 4 | 4 |
| 12 | Sanitary facilities: | |||
| common use | 16 | — | 100 m3/h per toilet or urinal | |
| for those working out (at the changing rooms) | 20 | — | 50 m3/h per toilet or urinal | |
| personal use | 16 | — | 25 m3/h per toilet or urinal | |
| 13 | Washrooms in public sanitary facilities | 16 | — | Due to sanitary facilities |
| 14 | Inventory in the halls | 15 | — | 1 |
| 15 | Storerooms and warehouses: | — | ||
| with permanent presence of service personnel; | 16 | — | 2 | |
| with short-term stay of service personnel | 10 | — | 1 | |
| 16 | Warehouses for reagents, household chemicals and paints | 10 | — | 2 |
| 17 | Rooms for drying sportswear | 22 | 2 | 2 |
A ventilation project begins with collecting initial data
To complete a project, designers will need information. This is information about the features of the location, volume and technologies of future production. The initial data includes the following:
- Laundry category, its location (free-standing building or built-in, as part of a hotel or residential complex);
- Clarification of the services provided. This can be regular washing or dry cleaning of clothes and furniture;
- Enterprise capacity (amount of clothing processed per shift);
- Construction volume and layout of premises;
- Planned number of staff and visitors.
Due to the rather complex specifics of laundry ventilation, projects are trusted only to experienced designers who are able to deal with the problems of an unfavorable microclimate. Compliance with standards and a professional approach help them organize normal working conditions for staff, washing, drying and comfort for visitors.
Air exchange rate in the premises of a financial institution
| № | Names of premises | Design air temperature, °C | Air change rate per hour | |
| influx | hood | |||
| 1. | Operating and cash rooms | 18 | Based on the assimilation of excess heat and moisture, but not less than twofold air exchange | |
| 2. | Common work rooms, coin counting desks | 18 | 2 | 2 |
| 3. | Room for meetings and negotiations | 18 | 3 | 3 |
| 4. | Banknote counter | 18 | 3 | 3 |
| 5. | Computer equipment premises, computer center | 18 | Based on the assimilation of heat and moisture excess | |
| 6. | Communications (teletypewriter) and photocopying room | 18 | 2,5 | 2,5 |
| 7. | Offices and reception areas | 18 | 1,5 | 1,5 |
| 8. | Archive, storage room for forms, storage room for equipment and inventory, storage room for banking materials, room for storing personal belongings of cashiers | 18 | — | 1,5 |
| 9. | Repair shops | 18 | 2 | 2 |
| 10. | Meal room, buffet | 16 | 3 | 4 |
| 11. | Room for storing weapons, loading and cleaning weapons | 16 | — | 1 |
| 12. | Boxes for cash-in-transit vehicles | 18 | According to the design standards for parking garages | |
| 13. | Security premises with fire station | 18 | 1 | 1,5 |
| 14. | Women's personal hygiene rooms | 23 | — | 5 |
| 15. | Sanitary facilities | 16 | — | 50 m3/h per toilet or urinal |
| 16. | Lobby | 16 | 2 | — |
| 17. | Dressing rooms | 16 | — | 2 |
| 18. | Premises for placing sources of uninterruptible power supply | 16 | Based on the assimilation of heat and moisture excess | |
Ventilation systems control
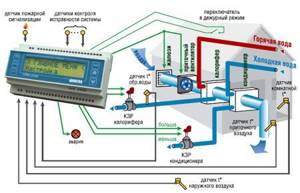
Automation of ventilation system control allows you to optimize the process and reduce operating costs. This approach allows us to minimize human participation in management and reduce the risk of the “human factor”. Automatic control involves the installation of sensors that record air temperature/humidity, concentration of harmful substances, degree of smoke or gas contamination. All sensors are connected to a control unit, which, thanks to the specified settings, turns the equipment on or off. Thus, automation helps to comply with sanitary standards, quickly respond to emergency situations and save significant money.
Air exchange rate in administrative and domestic buildings
SNiP 2.09.04—87*
| № | Premises | Temperature during the cold season | Frequency or volume of air exchange, m3/h | |
| Inflow | Hood | |||
| 1. | Lobbies | +16° | 2 | — |
| 2. | Heated passages | Not lower than 6°C of the design temperature of the rooms connected by heated passages | — | — |
| 3. | Streetwear wardrobes | +16° | — | 1 |
| 4. | Dressing rooms for joint storage of all types of clothing with incomplete dressing of workers | +18° | Based on compensation for exhaust from showers (but not less than one air exchange per hour) | According to clause 4.8 |
| 5. | Dressing rooms for showers (pre-showers), as well as with a complete change of clothes for workers a) dressing rooms for work clothes | +23° | 5 | 5 |
| b) dressing rooms for home (street and home) clothes | +23° | Based on compensation for exhaust from showers (but not less than one air exchange per hour) | According to clause 4.8 | |
| 6. | Showers | +25° | — | 75 m3/h for 1 shower screen |
| 7. | Restrooms | +16° | — | 50 m3/h for 1 toilet and 25 m3/h for 1 urinal |
| 8. | Washrooms at restrooms | +16° | — | 1 |
| 9. | Smoking rooms | +16° | — | 10 |
| 10. | Rooms for rest, heating or cooling | +22° | 2 (but not less than 30 m3/h per 1 person. | 3 |
| 11. | Premises for women's personal hygiene | +23° | 2 | 2 |
| 12. | Rooms for repair of workwear | +16° | 2 | 3 |
| 13. | Shoe repair facilities | +16° | 2 | 3 |
| 14. | Premises of departments, design bureaus, public organizations, area: a) no more than 36 m2 | +18° | 1,5 | — |
| b) more than 36 m2 | +18° | By calculation | ||
| 15. | Rooms for drying work clothes | According to technological requirements within 16-33°C | Same | |
| 16. | Rooms for dust removal of work clothes | +16° | « | |
Source: Administrative and domestic buildings SNiP 2.09.04—87*
Calculate the diameters of ventilation ducts
Further calculations are somewhat more complicated, so we will provide each step with examples of calculations. The result will be the diameter and height of the ventilation shafts of our one-story building.
We distributed the entire volume of exhaust air into 3 channels: 100 cubic meters. The hood in the kitchen is forcibly removed when the stove is turned on, the remaining 271 cubic meters goes through two identical shafts naturally. The flow rate through 1 air duct will be 271 / 2 = 135.5 m³/h. The cross-sectional area of the pipe is determined by the formula:
- F – cross-sectional area of the ventilation duct, m²;
- L – exhaust flow through the shaft, m³/h;
- ʋ—flow speed, m/s.
Reference. The air speed in the natural ventilation channels is in the range of 0.5–1.5 m/s. We take the average value as the calculated value - 1 m/s.
How to calculate the cross-section and diameter of one pipe in the example:
- We find the diameter size in square meters F = 135.5 / 3600 x 1 = 0.0378 m².
- From the school formula for the area of a circle, we determine the diameter of the duct D = 0.22 m. We select the nearest larger air duct from the standard range - Ø225 mm.
- If we are talking about a brick shaft embedded inside the wall, then the size of the ventilation duct 140 x 270 mm will fit the found cross-section (good coincidence, F = 0.0378 sq. m.).

The diameter of the outlet pipe for a household hood is calculated in the same way, only the flow speed forced by the fan is assumed to be greater - 3 m/s. F = 100 / 3600 x 3 = 0.009 m² or Ø110 mm.
Air exchange rate in healthcare institutions
| № | Name of premises | T, °C | Air exchange rate | Category by frequency of premises | Exhaust ratio with natural air exchange | ||
| influx | hood | ||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | |
| I. | Hospitals, clinics, emergency and ambulance stations | ||||||
| 1. | Manipulation-toilet rooms for newborns | 25 | 2 | H | 2 | ||
| 2. | Manipulation with the use of chlorpromazine | 22 | 8 | 10 | G | not allowed | |
| 3. | Doctors' offices, staff rooms, rest rooms for patients using hydrotherapy and mud therapy procedures, acupuncture rooms, discharge rooms, audiometry rooms, anthropometry rooms, dispatch rooms for receiving calls and sending teams, room for filling out documents, rest room for dispatchers, doctors, paramedics, orderlies, drivers , mobile teams, medical statistics | 20 | influx from the corridor | 11 | H | 1 | |
| 4. | Angiography rooms, X-ray diagnostic rooms, treatment rooms and dressing rooms, fluorography rooms, electrolight therapy rooms, massage room | 20 | 3 | 4 | G | not allowed | |
| 5. | Undressing rooms in X-ray rooms | 20 | 3 | — | H | » | |
| 6. | Procedural for X-ray. dental images, washing laboratory glassware, pathology departments, control room of X-ray rooms and radiology departments, photo laboratory | 18 | 3 | 4 | G | » | |
| 7. | Sterilization in operating rooms | 18 | — | 3 septic departments | G | 2 | |
| 3 | aseptic departments | H | 2 | ||||
| 8. | Laboratories and rooms for analysis, rooms (rooms) for radiotelemetry, endocrinology and other studies, rooms for receiving, sorting and taking samples for laboratory tests, installation and washing rooms for an artificial kidney and rooms for a heart-lung machine, solution-demineralization, preparation laboratories, rooms for staining smears, weighing, colorimetric, media preparation, material and hardware laboratories, fixation, prescription, rooms for the preparation of dressings and surgical materials and linen, control, acquisition and packaging of instruments, reception, disassembly, washing and drying of surgical instruments, syringes, needles , catheter, treatment rooms for antipsychotic treatment, radio post, voice recording center, current sterilization rooms, hardware room | 18 | — | 3 | see table 3 | 2 | |
| 9. | Halls of therapeutic physical culture | 18 | 50 m3/hour per student in the gym 80% | 100 % | G | ||
| 10. | Functional diagnostic rooms, sigmoidoscopy rooms | 22 | — | 3 | G | 2 | |
| 11. | Rooms for physical therapy, mechanotherapy, dental rooms, probing rooms, rooms for deworming | 20 | 2 | 3 | G | 2 | |
| 12. | Premises (rooms) for sanitary treatment of patients, showers, personal hygiene cabins, premises for subaqueous, hydrogen sulfide and other baths (except radon), premises for heating paraffin and ozokerite, therapeutic swimming pools | 25 | 3 | 5 | G | 2 | |
| 13. | Premises for storing plaster bandages, plaster, museums and preparatory rooms in pathology departments, compressor inhalation rooms, central linen rooms, storerooms for infected linen and bedding, storerooms for household equipment, storerooms for patients' things and ironing, instrumental materials, storerooms for reagents and equipment in pathology departments departments, rooms for routine repairs of physiotherapy equipment, storage of boxes for visiting teams, a current supply of medicines, a pharmacy room, a pantry for a month's supply of medicines, a pantry for non-sterile materials and linen | 18 | — | 1 | G | 1 | |
| 14. | Sterilization-autoclave central sterilization rooms: | 18 | by calculation | is allowed | |||
| a) clean compartment | 100 % | — | H | ||||
| b) dirty compartment | — | 100 % | G | ||||
| 15. | Rooms for washing, sterilization and storage of vessels, pots, washing and drying oilcloths, sorting and temporary storage of dirty linen, storage of cleaning items, rooms for temporary storage of linen and solid waste contaminated with radioactive substances, storage rooms for acids and disinfectants, stretcher washing rooms and oilcloths, a room for drying clothes and shoes of visiting teams | 18 | — | 5 | G | 3 | |
| 16. | Registration offices, information lobbies, dressing rooms, rooms for receiving packages for patients, a waiting room, storerooms for warm clothes on the verandas, pantries, dining rooms for patients, distribution rooms with utility rooms in milk distribution points, storerooms for patients’ clothes and clothes, medical archives | 18 | — | 1 | G | 1 | |
| 17. | Rooms for processing rubber gloves, for washing and sterilizing tableware and kitchen utensils in the buffet and dining rooms, hairdressing salons for serving patients, dummy rooms | 18 | 2 | 3 | G | 2 | |
| 18. | Storage facilities for radioactive substances, packaging and washing in radiological departments, washing in laboratories | 18 | 5 | 6 | G | not allowed | |
| 19. | Treatment rooms in rooms for static and mobile tele-gamma therapy, rooms for centralization in rooms for mobile tele-gamma therapy, treatment rooms for X-ray therapy, microwave therapy rooms, ultra-high frequency therapy rooms, thermotherapy rooms, wrap rooms, rooms for preparing solutions for radon vayans, ultrasound treatment rooms | 20 | 4 | 5 | G | » | |
| 20. | Changing rooms and undressing rooms in hydrotherapy departments | 23 | influx according to the balance of exhaust from the halls with baths, mud procedures | H | 2 | ||
| 21. | Corpse storage rooms | 2 | — | 3 | G | 3 | |
| 22. | Premises for radon baths, mud therapy rooms. shower room with a lectern, mud therapy rooms for gynecological procedures | 25 | 4 | 5 | G | doesn't go down | |
| 23. | Premises for storing and regenerating dirt | 12 | 2 | 10 | G | » | |
| 24. | Rooms for dressing corpses, issuing corpses, storage rooms for funeral supplies, for processing and preparing for burial of infected corpses, rooms for storing bleach | 14 | — | 3 | G | » | |
| 25. | Disinfection chamber premises: | ||||||
| a) reception rooms; | 16 | from a clean compartment | 3 | G | » | ||
| b) dirty compartments: | from a clean compartment | 5 | G | » | |||
| c) unloading (clean) compartments | 5 | Through dirty compartments | |||||
| 26. | Sluices for hydrogen sulfide baths | 25 | 3 | 4 | H | not allowed | |
| 27. | Undressing rooms for hydrogen sulfide baths | 25 | 3 | 3 | H | » | |
| 28. | Room for preparing a solution of hydrogen sulfide baths and storing reagents | 20 | 5 | 6 | G | » | |
| 29. | Room for washing and drying sheets, canvases, tarpaulins, mud kitchens | 16 | 6 | 10 | G | » | |
| 30. | Inhalations (procedural) | 20 | 8 | 10 | G | ||
| 31. | Sectional | 16 | — | 4 | G | 4 | |
| 32. | Airlocks in front of neonatal wards | 22 | by calculation, but not less than 5 times the exchange | H | not allowed | ||
| 33. | Rooms for the discharge of postpartum women and irradiation of children with a quartz lamp | 22 | — | 1 | H | 1 | |
| 34. | Bathrooms | 20 | — | 50 m3 for 1 toilet and 20 m3 for 1 urinal | G | 3 | |
| 35. | Washrooms | 20 | — | 3 | G | 3 | |
| 36. | Enema | 20 | — | 5 | G | 2 | |
| 37. | Airlocks in boxes and semi-boxes of infectious diseases departments | 22 | by calculation, but not less than 5 times the exchange | H | not allowed | ||
| 38. | Small operating rooms | 22 | 10 | 5 | H | 1 | |
| 39. | Premises of hospital pharmacies (see section General self-supporting pharmacies) | ||||||
| Vivariums5) | |||||||
| 40. | Quarantine section for entry of vehicles with animals. Reception room with a warm vestibule | 16 | 1 | 1 | G | 1 | |
| 41. | Sink for dogs, cats, miniature pigs with bathtub and circular shower | 22 | 3 | 5 | G | 2 | |
| 42. | Hot air drying for dogs and miniature pigs | 25 | 3 | 5 | G | 2 | |
| 43. | Room for keeping laboratory animals:6) | ||||||
| a) mice | 20:22 | 10 | 12 | G | 2 | ||
| b) hamsters | 20 | 10 | 12 | G | 2 | ||
| c) guinea pigs | 14:16 | 8 | 10 | G | 2 | ||
| d) rabbits7) | 5 | 8 | 10 | G | 2 | ||
| e) dogs (with access to walking) | 14 | 8 | 10 | G | 2 | ||
| e) cats | 18 | 10 | 12 | G | 2 | ||
| g) sheep (with access to walking) | 5 | 10 | 12 | G | 2 | ||
| h) dwarf pigs | 18 | 10 | 12 | G | 2 | ||
| i) roosters | 18 | 10 | 12 | G | 2 | ||
| 44. | Staff quarters | 18 | 1 | 1 | H | 1 | |
| 45. | Warehouse of cages and equipment | 10 | — | 1 | G | 1 | |
| 46. | Inspection of sick animals and disinfection | 20 | 8 | 10 | G | 2 | |
| 47. | Isolator for large animals | 15 | 8 | 10 | G | 2 | |
| 48. | Premises for storing and preparing disinfectants (with a fume hood) | 18 | according to technologists | G | 3 | ||
| 49. | Storage of feed and bedding | 10 | — | 1 | G | 1 | |
| Disinfection and washing department | |||||||
| 50. | Cleaning and washing equipment: | ||||||
| a) during manual washing; | 16 | 3 | 5 | G | 2 | ||
| b) when washing by machine: | |||||||
| rough cleaning room | 16 | 3 | 5 | G | 2 | ||
| washing | 16 | 5 | 6 | G | 2 | ||
| 51. | Sterilization and drying of equipment | 18 | by calculation | H | not allowed | ||
| 52. | Storage of clean cages, racks, containers, feeders, stretchers, bedding | 10 | — | 1 | G | 1 | |
| 53. | Loading food, water, and bedding into cages | 18 | — | 3 | G | 1 | |
| 54. | Temporary storage of animal carcasses | 2:4 | — | 3 | G | 3 | |
| Department for keeping experimental animals | |||||||
| Block for keeping small laboratory rodents (mice, rats, guinea pigs) in conditions that exclude the penetration of pathogenic flora8) Premises of the barrier zone. | |||||||
| 55. | Forced sanitary inspection | 25 | 3 | 5 | G | not allowed | |
| 56. | Dressing in sterile clothing: | 1 | |||||
| - clean zone | 25 | by calculation | H | » | |||
| - dirty area | 25 | » | G | » | |||
| 57. | Sterilization room with steam autoclave | 18 | » | G | » | ||
| 58. | Bactericidal hydrolock: | 18 | 3 | H | » | ||
| - clean zone | 18 | 3 | H | » | |||
| - dirty area | 18 | 3 | G | » | |||
| 59. | Germicidal airlock | 18 | by calculation | H | » | ||
| Premises of the barrier zone3) | |||||||
| 60. | Room for keeping SV&B animals and conducting experiments: | ||||||
| a) for mice | 20:22 | 15 | 10 | VERY | » | ||
| b) for rats | 18 | 15 | 10 | VERY | not allowed | ||
| c) for guinea pigs | 14:16 | 15 | 10 | VERY | » | ||
| 61. | Experiment room | 20 | VERY | » | |||
| 62. | Staff | 18 | 1 | 1 | VERY | » | |
| 63. | Warehouse for sterile equipment, feed, bedding | 18 | 1 | 1 | VERY | » | |
| 64. | Distribution and distribution of feed | 18 | 1 | 1 | VERY | » | |
| 65. | Water sterilization | 18 | 1 | 1 | VERY | » | |
| Block for keeping laboratory animals under normal conditions | |||||||
| 66. | Premises for keeping laboratory animals (except rams) | according to points 50a: 50i | |||||
| 67. | Experimentation rooms | 18 | 1 | 3 | G | 2 | |
| 68. | Surgical section premises: | ||||||
| a) preoperative with sterilization | 18 | 1 | 2,5 | H | not allowed | ||
| b) operating room, postoperative room, room for intensive care of convalescent animals | 20:22 | by calculation | VERY | — | |||
| 69. | Premises for infecting animals and working with them: | ||||||
| a) premises for toxicological studies | 18 | ||||||
| b) premises for infecting animals (handling room, boxes for control animals) | 18 | 5 | 6 | G | not allowed | ||
| c) personnel and specialists | 18 | — | 1,.5 | H | » | ||
| d) storage of clean: equipment, feed, bedding | 18 | — | 1 | G | » | ||
| e) waste collection | 10 | — | 10 | G | » | ||
| Veterinary Services Department | |||||||
| 70. | Doctor's office | 18 | 1 | 1 | H | » | |
| 71. | Sectional | 16 | 3 | 3 | G | » | |
| 72. | Laboratory diagnostics with animal autopsy box | 18 | 1 | 3 | G | » | |
| 78. | Storage of medicines | 18 | 1 | 3 | G | not allowed | |
| 74. | Isolation unit for sick animals: | ||||||
| a) patient room with airlock | according to points 50a-50i | ||||||
| b) storage of feeders, cages, equipment, storage of bedding and feed | 10 | — | 1 | G | » | ||
| c) staff | 18 | 1 | 1 | H | » | ||
| d) cleaning items with tap, drain and drying | 10 | — | 10 | G | » | ||
| Feed preparation department | |||||||
| 75. | Preparation of vegetables from the washing machine, preparation of grain mixtures | 16 | 3 | 4 | G | » | |
| 76. | Digestion hall | 16 | by calculation | » | |||
| 77. | Washing - kitchen utensils | 18 | 4 | 6 | G | » | |
| 78. | Feed sterilization | 18 | 1 | 3 | G | » | |
| 79. | Refrigerated chamber for food products | 2-4 | — | — | G | » | |
| II. General self-supporting pharmacies | |||||||
| 80. | Public service halls | 16 | 3 | 4 | G | 3 | |
| 81. | Work rooms or isolated work areas in the service hall, forwarding rooms for receiving and processing orders of an attached institution, prescription | 18 | 2 | 1 | H | 1 | |
| 82. | Assistant, aseptic, defector, walk-through gateway; blanking and filling with a sluice, sealing and control-marking sterilization-autoclave, sterilization distillation | 18 | 4 | 2 | H | 1 | |
| 83. | Packaging room, control and analytical room, washing room, sterilization solution room, distillation and sterilization room, coctorium, unpacking room | 18 | 2 | 3 | G | 1 | |
| 84. | Premises for the preparation of dosage forms under aseptic conditions | 18 | 4 | 2 | VERY | not allowed | |
| 85. | Main stock storage premises: | ||||||
| a) medicinal substances, finished medicinal products, including thermolabile and medical supplies; dressings | 18 | 2 | 3 | G | 1 | ||
| b) medicinal plant materials | 18 | 3 | 4 | G | 3 | ||
| c) mineral waters, medical glass and returnable transport containers, glasses and other optical items, auxiliary materials, clean dishes | 18 | — | 1 | G | 1 | ||
| d) poisonous drugs and drugs | 18 | — | 3 | G | 3 | ||
| 86. | Flammable and combustible liquids | 18 | — | 10 | G | 5 | |
| 87. | Disinfectants and acids, disinfection with airlock | 18 | — | 5 | G | 3 | |
| 88. | Administrative premises | according to paragraphs 13, 19, 20, 25, 26, 44 of this table | |||||
| 89. | Refrigeration machine room | 4 | — | 3 | G | 3 | |
| 90. | Electrical control room | 15 | — | 1 | |||
| SANITARY-EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STATIONS (SES) | |||||||
| Radiology group | |||||||
| 91. | Laboratory room | 18 | 3 | 5 | G | not allowed | |
| 92. | Bacteriological group Accommodation for doctors and laboratory technicians, study rooms | 18 | — | 1,5 | H | » | |
| 93. | Room for serological studies, culture, rooms for express diagnostics | 18 | 5 | 6 | G | » | |
| 94. | Boxes | 18 | 6 | 5 | H | » | |
| 95. | Preboxes | 18 | — | 10 | G | » | |
| 96. | Entomology premises for helminthological research, environmental | 18 | 5 | 6 | G | » | |
| 97. | Washing | ||||||
| a) without washing machine | 18 | 5 | 6 | G | » | ||
| b) with a washing machine | 18 | 3 | 5 | G | » | ||
| 98. | Sterilization autoclaves | 18 | — | 3 | G | not allowed | |
| 99. | Thermal rooms | As required by technology Internal air temperature is provided by technological equipment | |||||
| 100. | Rooms for registration, sorting and delivery of test results | 18 | — | 3 | G | » | |
| Virology Department and Laboratory of the Department of Particularly Dangerous Infections | |||||||
| 101. | Facilities for identification of respiratory and enteric viruses, for tissue culture preparation | ||||||
| a) working rooms of doctors and laboratory assistants | 18 | 5 | 6 | G | » | ||
| b) boxes | 18 | 5 | 6 | G | » | ||
| c) preboxes | 18 | 6 | 5 | H | » | ||
| d) boxes | 18 | 6 | 5 | H | » | ||
| e) preboxes for preparing tissue culture | 18 | — | 10 | G | » | ||
| 102. | Arbovirus identification room: | ||||||
| a) working rooms of doctors and laboratory assistants | 18 | 5 | 6 | G | not allowed | ||
| b) boxes | 18 | 5 | 6 | G | » | ||
| c) preboxes | 18 | — | 10 | G | » | ||
| 103. | Rooms for conducting bacteriological research, rooms for processing traps and preparing baits, dissection rooms | 18 | 3 | 6 | G | » | |
| 104. | Rooms for rodent infestation (bioassay) | 18 | 8 | 10 | G | » | |
| 105. | Corridors | 18 | According to the department's balance | H | » | ||
| Dairy kitchens | |||||||
| 106. | Brewhouse | 5 | By calculation | G | » | ||
| 107. | Puree making shop | 16 | 3 | H | » | ||
| 108. | Packing milk and juices | 16 | 2 | 3 | G | » | |
| 109. | Sterilization of finished products | ||||||
| a) “clean zone” | 16 | 6 | — | H | not allowed | ||
| b) “dirty zone” | 16 | — | 4 | G | » | ||
| 110. | Washing flask | 20 | 4 | 6 | G | » | |
| 111. | Taking milk | 16 | — | 1 | G | » | |
| 112. | Preparation of biolact | 16 | 12 | 12 | H | » | |
| 113. | Milk filtration and bottling room | 16 | 19 | 19 | H | » | |
| 114. | Room for heat treatment of milk and preparation of milk mixtures | 16 | 3 | 4 | G | » | |
| 115. | Cooling room | 16 | 3 | 4 | G | » | |
| 116. | Premises for the preparation of lactic acid products and lactic acid mixtures: | ||||||
| a) room for preparing sourdough starters | 16 | 3 | 4 | H | » | ||
| b) kefir workshop | 16 | 20 | 20 | H | » | ||
| c) acidophilus milk workshop | 16 | 20 | 20 | H | » | ||
| d) thermostatic | 16 | 12 | 12 | H | » | ||
| 117. | Premises for preparing and packaging cottage cheese | 16 | 3 | 4 | G | » | |
| 118. | Premises for the preparation of fruits, fruits, vegetables | 16 | 3 | 4 | G | » | |
| 119. | Premises for preparing fruit and vegetable mixtures | 16 | 12 | 12 | H | » | |
| 120. | Room for preparing fish, meat, preparing fish and meat dishes | 16 | 3 | 4 | G | » | |
| 121. | Laboratory | 18 | 2 | 3 | G | » | |
| 122. | Reception room for containers for finished products | 16 | 4 | 6 | G | » | |
| 123. | Raw materials reception room | 16 | 3 | — | G | » | |
| 124. | Washing and sterilization room | 20 | 4 inflow into the “clean” zone | 6 hood - through the “dirty” zone | G | » | |
| 125. | Kitchenware washing station | 20 | 4 | 6 | G | » | |
| 126. | Washing room: | ||||||
| a) milk pipelines | 20 | 4 | 6 | G | » | ||
| b) inventory | 20 | 4 | 6 | ||||
| 127. | Expedition, loading | 16 | 3 | — | H | » | |
| 128. | Refrigeration machine room | 16 | — | 3 | G | » | |
| 129. | Temporary storage room | 12 | — | 1 | G | » | |
| milk | periodic ventilation | ||||||
| 130. | Dry food pantry | 12 | — | 2 | H | » | |
| 131. | Pantry of vegetables and fruits | 4 | 4 (per day) | 4 (per day) | G | » | |
| 132. | Storage and reception room for containers | 12 | 4 | 6 | G | 1 | |
| 133. | Storage room for household equipment | 12 | 2 | 2 | G | » | |
| 134. | Linen room | 16 | 2 | 1 | G | » | |
| 135. | Material Pantry | 12 | — | 1 | G | » | |
| 136. | Refrigerated food waste chamber with vestibule | 2 | — | 10 | G | not allowed | |
| 137. | Service and household premises | according to section I of this table | |||||
| Donor point | |||||||
| 138. | Breast milk expressing room | 22 | — | 2 | H | » | |
| 139. | Sterilization room | 18 | — | 3 | H | » | |
| 140. | Filtration and bottling of milk | 16 | 19 | 19 | H | » | |
| 141. | Heat treatment | 16 | 3 | 4 | G | » | |
| 142. | Cooling room | 16 | 3 | 4 | H | » | |
| Milk distribution points | |||||||
| 143. | Handout | 16 | 2 | 2 | H | 1 | |
| 144. | Refrigeration chamber (for finished products) | 2 | Periodic ventilation | ||||
| 145. | Room for receiving and storing dishes from the public | 12 | — | 1 | G | 1 | |
| 146. | Cash register | 18 | — | 1 | H | » | |
| 147. | Storage room for disinfectant solutions and cleaning equipment | 16 | — | 5 | G | 3 | |
| Sauna | |||||||
| 148. | Expected | 18 | — | 3 | H | ||
| 149. | Corridor | 18 | — | 2 | H | ||
| 150. | Locker room | 22 | — | 3 | H | ||
| 151. | Shower room | 22 | — | 8 | G | ||
| 152. | Steam room10) | 100/80 (85/80) | — | 5 | G | ||
| 153. | Cooling room inside the sauna | 1 | — | 4 | G | ||
| 154. | Restroom | 26 | — | 3 | H | ||
| 155. | Massage room | 25 | — | 4 | G | ||
| 156. | Solarium | 23 | — | 3 | H | ||
| 157. | Restroom | 22 | — | 50 m3 for 1 toilet | G | ||
Source: Manual on the design of healthcare facilities (to SNiP 2.08.02-89)
Air exchange rate in preschool premises
| Premises | t° (C) - not lower | Air exchange rate per hour | |||
| In IA, B, D climatic regions | In other climatic regions | ||||
| influx | hood | influx | hood | ||
| Reception rooms, play nursery group cells | 22-24 | 2,5 | 1,5 | — | 1,5 |
| Reception, gaming junior, middle, senior group cells | 21-23 | 2,5 | 1,5 | — | 1,5 |
| Bedrooms of all group cells | 19-20 | 2,5 | 1,5 | — | 1,5 |
| Nursery toilets | 22-24 | — | 1,5 | — | 1,5 |
| Toilet facilities for preschool groups | 19-20 | 2,5 | 1,5 | — | 1,5 |
| Medical premises | 22-24 | 2,5 | 1,5 | — | 1,5 |
| Halls for music. and gymnastics classes | 19-20 | 2,5 | 1,5 | — | 1,5 |
| Walking verandas | at least 12 | according to calculation, but not less than 20 m3 per 1 child | |||
| Hall with swimming pool bath | at least 29 | ||||
| Changing room with shower pool | 25-26 | ||||
| Heated passages | at least 15 | ||||
Source: Sanitary and epidemiological rules and regulations SanPiN 2.4.1.3049-13. Appendix 3
How to simplify the task - tips
You could see that calculations and organization of air exchange in a building are quite complex issues. We tried to explain the methodology in the most accessible form, but the calculations still look cumbersome for the average user. Let's give some recommendations for a simplified solution to the problem:
- The first 3 stages will have to be completed in any case - find out the volume of emitted air, develop a flow pattern and calculate the diameters of the exhaust air ducts.
- Take the flow velocity to be no more than 1 m/s and use it to determine the channel cross-section. It is not necessary to master aerodynamics - calculate the diameters correctly and simply bring the air ducts to a height of at least 3 meters above the intake grilles.
- Inside the building, try to use plastic pipes - thanks to their smooth walls, they practically do not resist the movement of gases.
- Ventilation ducts laid in a cold attic must be insulated.
- Do not block the mine exits with fans, as is customary to do in apartment toilets. The impeller will not allow the natural hood to function normally.
To increase the flow, install adjustable wall valves in the rooms, get rid of all the cracks from where cold air can enter the house uncontrollably.