Add to bookmarks
One of the skills required for high-quality and quick replacement of pipes at home is accurately determining their diameter using available tools.
Before making measurements, you should understand in what units they are made. It is generally accepted that the diameter of pipes is always measured in inches (1 inch = 2.54 cm).
Whether it's problems with the plumbing or plumbing in the bathroom or problems with the water supply in the kitchen, knowing how to determine the diameter of a pipe using available tools will come in handy.
Of course, there are special tools for measuring, such as a ruler-circometer, laser meter, etc. But everything can be much simpler.
Before making measurements, you should understand in what units they are made. It is generally accepted that such values are always measured in inches (1 inch = 2.54 cm), and the standard size, for example, of steel products is most often 1 or 0.5 inches. By the way, the diameters of plastic, steel and metal-plastic parts vary.
The next step is to select the measured value. External - more important, because It is on it that threads and threaded connections are installed. This diameter directly depends on the thickness of the pipe walls. The dimensions of the wall thickness are determined by the difference between the external and internal diameters of a given pipe.
Taking words to action
In order to correctly measure both diameters, you should take into account the features of all measurement methods, because each of them is suitable for different conditions.
In order to correctly measure both diameters, you should take into account the features of all measurement methods, because each of them is suitable for different conditions.
One method is to measure the circumference of the piece by wrapping it with a measuring tape or tape measure. Then the resulting value must be divided by Pi (3.14).
We will need:
- ruler;
- calipers;
- tape measure (measurement tape).
If access to an area of the part is not difficult and you can measure it before installation, then the easiest way is to use a ruler or tape measure. The outer diameter is determined by placing a ruler over the widest part of the pipe and counting from the first outer point on the scale to the last.
There may be cases where measurements are already indicated in inches (imported deliveries). To convert to centimeters, the size is multiplied by 2.54, and to convert back to inches - by 0.398.
There is another way to determine the internal diameter if the pipe is directly accessible. The walls are measured along the cut using a caliper or ruler, and then the resulting reading is subtracted from the measurements of the outer diameter and multiplied by 2.
What if there is no direct access to the required area? One method is to measure the circumference of the piece by wrapping it with a measuring tape or tape measure. Then the resulting value must be divided by Pi (3.14). This way we can find out the outer diameter of the pipe. This method is also suitable if the length of the caliper or ruler is not enough.
There is a method for determining the outer diameter that excludes all sorts of calculations, but only for those parts for which it is no more than 15 cm. To do this, you will need to measure the readings using only a caliper, on the scale of which the correct results are measured.
One of the most extraordinary ways is to compare the values of a pipe with some object, take photographs and further recognize the measurements. Take a ruler or any object whose length is already known in advance (a coin) and bring it to the area to be measured, then take a picture. Further scaling on the computer will help determine the exact dimensions of the outer diameter. This method is ideal if it is impossible or extremely difficult to get close to the area being measured.
Imagine that you are going to paint the gas pipes connected to your house. How much paint will be needed? One or two cans? As a rule, on paint containers it is written what area this amount of paint is designed to cover. This means that in order to accurately determine how many cans of paint to take, you need to calculate the area of the gas pipes.
Imagine that you are going to paint the gas pipes connected to your house. How much paint will be needed? One or two cans? As a rule, on paint containers it is written what area this amount of paint is designed to cover.
You will need
- - roulette;
- - caliper;
- - strong thread;
- - calculator.
Instructions
To calculate the area of a round pipe, find out the length of this pipe in linear meters. Also for the calculation you will need the outer diameter of the pipe.
Calculate the outer diameter of the gas pipe. There are two ways to do this. The first method is to measure the outer diameter of the gas pipe using a caliper. To do this, spread the jaws of this measuring tool and attach it to the pipe so that the pipe is between the jaws of the caliper. Then move the jaws of the measuring tool: they should tightly grip the gas pipe. Looking at the measuring scale, determine the outer diameter of the pipe. The second way is to wrap a thick thread around the pipe. Then use a tape measure to measure the circumference of the pipe. Substituting the value into the formula D = L / Pi, where L is the circumference of the pipe, Pi = 3.14 (the number “pi”), calculate the outer diameter of the gas pipe. Convert the resulting indicator to
Water supply, heating, sewer, chimney, casing, copper, steel, plastic, metal-plastic, narrow, wide - pipes for various purposes from various materials surround us everywhere. The need to lay new communications or replace old ones arises both during the construction of a house and during ongoing repairs. When drawing up a project for the upcoming work, it would not hurt to arm yourself with a calculator to calculate the weight of the pipe, its mass, volume and other parameters.
Why do you need to calculate pipe parameters?
Preliminary calculation of pipe parameters is necessary in many cases. For example, for proper communication of the pipeline with other elements of the system. When working with pipes, designers and installers use indicators such as:
- pipeline permeability;
- heat loss;
- amount of insulation;
- amount of material for corrosion protection;
- roughness of the inner surface of the pipe, etc.
As a result, it is possible to determine the exact number of pipes required for a particular system, as well as their optimal characteristics. Correct calculations eliminate unnecessary costs for purchasing and transporting material and allow the substances in the pipeline to move at a given speed for the most efficient use of the system.
This table provides some useful information about the characteristics of different types of pipes that will help you select the appropriate designs needed to create a pipeline
In heating systems, the diameter of the pipes significantly depends on the permissible speed. An example of this kind of calculation is presented in the video:
Application of polypropylene pipes
If polypropylene heating pipes are used for the heating circuit, how to choose the diameter according to the above formulas? Yes, exactly the same. But polypropylene pipes have a huge service life, up to 100 years, so a heating system, correctly calculated and carefully installed, will last a very long time. To the question - how to choose the size of pipes for heating, the answer can be found in the tables that can be downloaded on the Internet.
The popularity of polypropylene pipes for creating heating systems is quite high, because they are much cheaper than metal ones, are environmentally friendly and have a good appearance. And the installation of system circuits when using such pipes is greatly facilitated. Special devices for welding pipes, various adapters, fittings, taps and other necessary components have been developed. The installation process itself is similar to assembling a system from a construction kit.
Calculations of various pipe parameters
- the material from which the pipe is made;
- type of pipe section;
- internal and external diameter;
- Wall thickness;
- pipe length, etc.
Some of the data can be obtained simply by measuring the structure. A lot of useful information is contained in certification documents, as well as in various reference books and GOSTs.
How to find out the diameter and volume of a pipe?
Some calculation formulas are familiar to every schoolchild. For example, if you need to determine the diameter of a specific pipe, you should measure its circumference. To do this, you can use a measuring tape that seamstresses use. Alternatively, wrap the pipe with another suitable tape and then measure the resulting length using a ruler.
- L is the circumference of a circle;
- π is a constant number “pi”, equal to approximately 3.14;
- D is the diameter of the circle's circumference.
It is enough to carry out a simple transformation to calculate the outer diameter of the pipe using this formula:
Calculation of pipe cross-section

This figure clearly shows indicators such as the outer diameter of the pipe and the thickness of its wall. The difference between the outer diameter and thickness allows you to calculate the inner diameter of the pipe
The formula for the area of a circle looks like this:
S=πR², where:
- S is the area of the circle;
- π—pi number;
- R is the radius of the circle, calculated as half the diameter.
If information about the outer diameter and wall thickness of the pipe is used, the formula may look like this:
S=π(D/2-T)², where:
- S—sectional area;
- π—pi number;
- D is the outer diameter of the pipe;
- T is the thickness of the pipe walls.
Let's say there is a pipe whose outer diameter is 1 meter and the wall thickness is 10 mm. First, you need to agree on all units of measurement. The wall thickness will be 0.01 meters. According to the above formula, we calculate the cross-section of such a pipe:
S=3.14Х(1m/2-0.01m)²=0.75m²
Thus, the cross-section of the pipe with the specified parameters will be equal to 0.75 square meters. m.
As you know, the accuracy of calculations with the number “pi” depends on the number of decimal places that are used when applying this constant. However, in construction there is usually no need for ultra-precise calculations, and the number “pi” is taken equal to 3.14. It also makes sense to round the final result to two decimal places.
How to calculate the volume of a pipe?

This diagram clearly shows the use of data such as the cross-sectional radius of the pipe and its length to determine the volume of the pipe
Calculating the volume of a specific pipe section is also not difficult. To do this, you must first find the circumference of the pipe based on its outer diameter using the formula given above:
S=π(D/2)² or S=πR²
In this case, D is the outer diameter of the pipe, and R is the outer radius, i.e. half the diameter. After this, the resulting value must be multiplied by the length of the pipe section, obtaining the volume, which is expressed in cubic meters. The formula for calculating pipe volume may look like this:
- V—pipe volume, cubic meters. m.
- S—external section area, sq.m.;
- H is the length of the pipe section, m.
Let's say there is a pipe with an outer diameter of 50 cm and a length of 2 meters. First, all units of measurement must be agreed upon. D=50 cm=0.5 m. Substitute this value into the formula for the area of a circle:
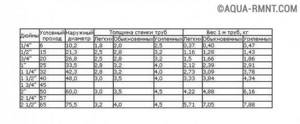
This table provides reference weight data
of various types, taking into account their sizes and features of production technology
Middle school students are well aware that the mass of an object can be found by multiplying its volume by the density of the substance from which the object consists. Builders are spared from tedious calculations of the mass of a specific pipe section, since various construction reference books contain information on the weight of a linear meter of a wide variety of types of pipes. The easiest way is to calculate the mass of the pipe using the relevant GOSTs, using information about:
- the material from which the pipe is made;
- its outer diameter;
- wall thickness;
- internal diameter, etc.
Having found out the weight of one linear meter of pipe, you should multiply the resulting value by the total number of linear meters. The complexity of the task corresponds to the level of the fourth-fifth grade of a general education school.
The occurrence of problems in the water, gas or sewer system often involves pipe installation - replacing a fragment of an old pipe or installing a new one. When performing such work, you will need the skills to determine the diameter of the pipes of your system using improvised means. When installing a new water supply system, it is also necessary to accurately determine the dimensions of old pipes in order to determine the choice of new plastic or metal-plastic pipes.
Of course, there are special tools for carrying out such measurements, for example, a laser meter, a ruler-circometer and others. But what if you are not a professional specialist, and your home tool kit does not include such high-precision instruments? How to measure the diameter of a pipe in another way?
Before answering this question, it is useful to know in what units these indicators are measured. Pipe diameter is usually measured in inches. One inch is equal to 2.54 centimeters.
When working with a pipe, both its internal and external diameter will be measured. The external diameter of the pipe is important due to the fact that it is its value that is taken into account when applying threads and creating threaded connections. The outer diameter is directly dependent on the thickness of the pipe walls. The wall thickness size is the difference between the outer and inner diameters of the pipe.
How to calculate the volume of water in a pipeline
When organizing a heating system, you may need a parameter such as the volume of water that will fit in the pipe. This is necessary when calculating the amount of coolant in the system. For this case, we need a formula for the volume of a cylinder.
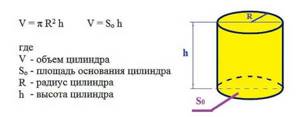
Formula for calculating the volume of water in a pipe
There are two ways: first calculate the cross-sectional area (described above) and multiply it by the length of the pipeline. If we calculate everything according to the formula, we will need the internal radius and the total length of the pipeline. Let's calculate how much water will fit in a system of 32 mm pipes 30 meters long.
First, let's convert millimeters to meters: 32 mm = 0.032 m, find the radius (divide in half) - 0.016 m. Substitute into the formula V = 3.14 * 0.0162 * 30 m = 0.0241 m3. It turned out = a little more than two hundredths of a cubic meter. But we are used to measuring the volume of the system in liters. To convert cubic meters into liters, you need to multiply the resulting figure by 1000. It turns out 24.1 liters.
From words to deeds
There are several ways to measure pipe diameters, differing in their characteristics depending on the conditions that are important to consider in order to avoid mistakes. The choice of a specific measurement method often depends on accessibility to the measurement object. Let's look at some of them.

Most often, the well-known caliper is used to measure the diameter of a pipe. But you may not have it, or if you do have it, it may not be possible to measure a large pipe diameter with it. In this case, the simplest set of tools and knowledge is used:
- flexible ruler (similar to the type of measuring tape used in sewing);
- roulette;
- school knowledge of the number Pi (it is equal to 3.14).
Using a similar set of tools, you can measure the diameter of not only a pipe, but also any other round object - a rod, column or garden bed.
We only need to make one measurement - determine the circumference of the pipe using a tape measure or flexible ruler. To do this, a measuring tape or tape measure is placed on the surface of the pipe in its widest part. The resulting circumference value should be divided by 3.14. For more accurate dimensions, use the value 3.1416.
It should be noted that imported supplies of pipes are accompanied by documentation that already indicates the pipe diameters in inches. To convert these values to centimeters, they are multiplied by 2.54. Similarly, to convert centimeters back to inches, multiply by 0.398.

Measurements are taken using a caliper without any mathematical calculations. The condition is complete accessibility to the pipe. This method is suitable for measuring accessible pipes of small diameter (no more than 15 cm). To take measurements, the legs of the caliper are applied to the end of the pipe and clamped tightly on the outer walls. The resulting value on the caliper scale, accurate to tenths of a millimeter, will be the outer diameter of the pipe.

If the end part of the pipe is inaccessible for measurement, that is, when the pipe is a mounted element of an already existing water or gas supply circuit, then for measurements a caliper is applied to the side surface of the pipe. In this case, an important condition for taking measurements is that the length of the caliper legs must exceed half the diameter of the pipe.
How to calculate cross-sectional area
Formula for finding the cross-sectional area of a round pipe
If the pipe is round, the cross-sectional area should be calculated using the formula for the area of a circle: S = π*R2. Where R is the radius (internal), π is 3.14. In total, you need to square the radius and multiply it by 3.14.
For example, the cross-sectional area of a pipe with a diameter of 90 mm. We find the radius - 90 mm / 2 = 45 mm. In centimeters this is 4.5 cm. We square it: 4.5 * 4.5 = 2.025 cm2, substitute it into the formula S = 2 * 20.25 cm2 = 40.5 cm2.
The cross-sectional area of a profiled pipe is calculated using the formula for the area of a rectangle: S = a * b, where a and b are the lengths of the sides of the rectangle. If we consider the cross-section of the profile to be 40 x 50 mm, we get S = 40 mm * 50 mm = 2000 mm2 or 20 cm2 or 0.002 m2.
Related article: How to make a table from a stool?
Large diameter pipe measurement

We have already mentioned a formula with a value above. The circumference of a large pipe can be measured using a cord or tape measure, and then its diameter is determined using the formula D = L: 3.14, where: D is the diameter of the pipe;
L – pipe circumference.
For example, if the length of the pipe circumference you measured was 31.4 cm, then the diameter of the pipe will be D = 31.4:3.14 = 10 cm (or 100 mm).
Measuring pipes using photography (copy method)

This non-standard method is used when there is complete inaccessibility to a pipe of any size. A ruler or any other object is applied to the pipe being measured, the dimensions of which are known in advance to any master (often in this case they use a matchbox, the length of which is 5 cm, or a coin). Next, this section of the pipe with the attached object is photographed (in addition to a camera, in modern conditions it is also possible to use a mobile phone). The following size calculations are made from photographs: the visual thickness in mm is measured in the photograph, and then converted into real values, taking into account the scale of the photographs.
What can experts advise?
Sergey Voronenkov, master installer: As a rule, pipes made of steel intended for installation of water supply systems are characterized by their inner diameter. You can often hear from professionals about half-inch or inch pipes. This means that their internal diameter is 12.7 mm or 25.4 mm. But the outer diameter is the province of the plumber and plumber. Simply because most plumbing systems today are installed using a threaded connection. In turn, the thread is cut on the outside of the pipe.
Viktor Ivanovich Petrov, plumber: The use of a metal measuring tape during measurements is less preferable. Metal cannot ensure a tight fit of the tape measure to the pipe, which is why the error will be too large. The result will be much more accurate if you use the so-called flexible tailor's meter.
Monitoring pipe parameters in production conditions

The outer diameter of water or sewer pipes in large production conditions is controlled and checked using a more complicated formula: D = L: 3.14 - 2∆p - 0.2 mm.
In this formula, in addition to the already known values, the symbols ∆p mean the thickness of the tape measure in mm, which you use to measure the diameter, and “0.2 mm” from the formula are the permissible deviations that take into account the fit of the tape measure to the pipe. The permissible deviation value for pipes with a cross-section of 200 mm is ±1.5 mm.
When measuring large diameter pipes, permissible deviations are measured as percentages. Example, for products ranging in size from 820 to 1020 mm, permissible deviation = 0.7%. For such measurements, an ultrasound-based measuring system is used.
In large production conditions, the wall thickness of pipes is measured with a caliper with a scale division of 0.01 mm. The permissible deviation from the nominal thickness towards reduction should not exceed 5%.
The values of pipe curvature are also subject to control, which should not be higher than 1.5 mm per linear meter of pipe length. The total curvature of products in relation to its length should not be more than 0.15%. The ovality of the pipe ends is determined by the ratio of the difference between the largest and smallest diameters to the nominal diameter of the pipe.
The value of this parameter should not exceed 1% for pipes with a wall thickness of up to 20 mm and not higher than 0.8% for walls above 20 mm.
The ovality of the pipe can be determined by measuring the diameter of the pipe end using an indicator clamp or bore gauge in two mutually perpendicular planes.
Simple school knowledge and careful use of simple tools will significantly simplify your task - how to measure the diameter of a pipe using improvised means.
What diameters are measured?
The main dimensions of any pipe are its internal and external diameters (D) and wall thickness (S); in the future, for the first two parameters we will use the abbreviated designations Dinternal. and Dnar.
The most common terms for the name of the internal pipe diameter: nominal (this is a generally accepted name with markings according to GOST 28338-89 - DN), conventional (an outdated name with symbolic markings Du, Dy). DN is often called conditional or light pass.
It is important for any specialist or user to know that the nominal DN shown in the table in Fig. 2 is not a fixed value and is approximately determined by the internal D in mm.
On technical drawings, DN is indicated by the symbols of a crossed out circle Ø or the same letters with a numerical value in mm next to it.
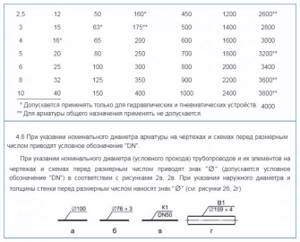
Rice. 2 Row DN according to GOST 28338-89 and its designation on the drawings (GOST 21.601-2011)
The designation of the outer diameter is not regulated in GOST for rolled metal products, therefore, various symbols from the series D, Dн, DE, Дн and others can be placed in the technical documentation, depending on the choice of their compilers.
In the drawings Dout. without a special designation, they are shown by a crossed out circle Ø with its digital denomination and a symbol with a number indicating the wall thickness S.
Another pipe size in terms of outer diameter that an installer may encounter is a threaded notch, often designated by the symbol G. The main types of threads used in technology are metric and inch, respectively, next to the symbol its nominal value in millimeters or inches is indicated.
For pipes made of thermoplastics (polymers that change their linear dimensions when exposed to temperature), GOST ISO 161-1-2004 establishes the following types of dimensions:
- nominal outer diameter dn, the designation applies to all polymer pipelines with the exception of flanged and threaded ones, is represented as an integer. The normalized indicators dn correspond to those given in the table in Fig. 3;
- external, external average and average minimum diameters with designations de, dem, and dem.min, respectively.

Rice. 3 Typical range of dn values according to GOST ISO 161-1-2004 and its description










