Gas valve adjustment
The useful thermal power can be reduced by reducing the fuel supply to the burner as a result of changing the valve setting.
It is important to remember that the burner power is controlled by a complex electronics algorithm that takes into account several basic indicators, represented by the start time, temperature indicators, the temperature difference in the direct pipe and the “return”
Adjusting the power indicators of the gas boiler burner is carried out by rotating special adjusting screws located on the valve body counterclockwise. More modern models are equipped with special automation that easily blocks clocking and changes power indicators. For this purpose, hold down the button with the wrench (5 seconds), and use special buttons to select the optimal duration of the intervals (0-15 minutes).
Boilers used in private homes
In private households, the main heat generator can be boilers that differ not only in power indicators, but also in other technical parameters, including type of fuel and functionality. The equipment produced operates on solid (wood, special pellets, coal), liquid, gaseous (main and bottled gas) fuels, as well as from a traditional electrical network.
Design features:
- according to the material of execution - cast iron or steel models;
- by installation method - floor or wall models;
- according to the number of circuits - single- or double-circuit models.
Non-volatile devices are able to function without being connected to the electrical network, and when installing volatile boilers, you must remember that systems with forced circulation of the coolant are not able to operate without the presence of electricity.
When purchasing a heat-generating device, you need to take into account a large number of criteria
In this regard, special attention is paid to the cost of the boiler, the features of the installation and installation of the heating system, the power of the device and the number of circuits, the type of fuel used, as well as the option of removing all exhaust gases
The most affordable boilers in terms of price include domestic models, and you need to choose a device based on the type of fuel, taking into account the climatic conditions and existing capabilities inherent in the locality in which the house is supposed to be operated. If desired, it is quite possible to significantly increase the performance of the system and the uniformity of heating of the premises using a special heat accumulator attached to the installed heating boiler.
How much energy does a home heating system consume?
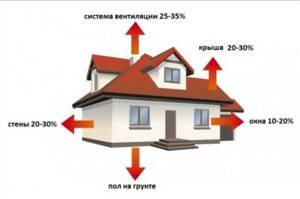
Heat losses include conditions and factors that lower the temperature in the house. It’s impossible to take into account everything, but let’s highlight a few:
- geographical point;
- heated area;
- if the apartment is heated - where is it located;
- external wall material;
- ventilation;
- heat consumption for additional needs.
The first point relates to the climate zone; the further north, the greater the losses. Location of the house in the area. For example, a house located separately, on a hill, is subject to greater influence of wind loads than one protected by other buildings in a lowland.
The second point is more correctly called the heated volume; raising the ceiling increases the area of the external walls that introduce losses. An exception is that a basement room of the same volume loses significantly less heat than an upper room.
The apartment in the center of the house has losses only through one external wall, the upper corner has two street walls plus a ceiling connected to the attic and roof. The southern rooms receive additional heating from the sun, which cannot be said about the northern location.
Thermal insulation of walls is the most important point in saving heat. Most come into contact with the outside air, even a slight reduction in heat loss can produce results. During construction and design, it is worth thinking about the building material. If the building is built, it is necessary to evaluate the thermal conductivity of the walls and insulate them. The expenses will be recouped by reducing gas consumption.
Heat loss diagram
Ventilation is a weak point. Correctly adjusted and in good working order will provide the necessary oxygen and save generated heat. Some use window and door slits as ventilation, however, this approach is not justified by common sense. Gaps may appear in the wall of a home that has not been renovated.
The last item on the list includes gas stoves and hot water supply. Heating occurs indirectly, through an additional heat exchanger. The higher the DHW consumption, the more gas will be consumed.
After determining the heat loss, the energy for replenishment can be calculated. There are formulas and tables, but they are difficult to understand. You can use the simplified diagram shown in the table:
| External surfaces | Losses, W/m2 |
| wall, wall with window | 100 |
| corner two walls, window | 120 |
| two walls, two windows | 130 |
The losses for external walls and windows are shown; you need to select a line and measure the area of the room. For example, we have a wall with one window, the losses will be 100 W/m2. The length of the room is 4 m, the width is 2.75 m, the product is 11 m2. Multiply by 100 W/m2, we get 1100 W or 1.1 kW. Calculations are carried out in all rooms, the result is summed up.
How to save on payments
Laying heating communications or installing a gas tank has a set price, and some discounts are one-time in nature. Significant savings can be achieved only by reducing fuel consumption using energy-saving technologies, for example:
- improve the thermal insulation of not only walls and roofs, but also basements, foundations, and floors with preliminary drawing up of a heat map;
- replace standard double-glazed windows with multi-chamber and frost-proof ones;
- exchange the boiler for the latest model with maximum efficiency and electronic control of operating modes;
- instead of ventilating rooms through windows and vents, create a computerized ventilation and air conditioning system;
- lay “warm floors” in all or individual rooms;
- equip all heating radiators with sensors that regulate temperature.
The listed measures will not only reduce heat losses in the house, but will also allow you to maintain a comfortable temperature in it with less energy consumption, which will lead to significant financial savings over time.
How to reduce gas consumption?
If suddenly your gas costs do not suit you, then the following recommendations will help you optimize them:
- Start insulating your home. The better you insulate your house, the less heat you will lose to the street.
- Check windows and doors for possible cracks. A lot of heat is lost through such structures
- If you use an open heating system with a tank on the roof, then convert the heating system to a closed one. A significant amount of heat is also lost through the roof.
- If you have a simple floor-standing boiler, then replace it with a wall-mounted one. Costs can also be reduced by 10-30%.
- Have your heating system serviced. Sometimes this can also have a positive effect on gas consumption. This is especially true for the boiler itself.
The bitter truth about gas consumption in your home
Now you may be surprised, but not a single person will be able to tell you the gas consumption of the boiler in the case of your home. When performing calculations, an experienced specialist will be able to give average values that will be close to the truth, but in any case they will not reflect the exact essence.
This is due to several factors:
- Winter is different from winter every year. Accordingly, the warmer it is, the less will be spent and vice versa.
- 100 square meters in your house and 100 square meters in your neighbor’s house are two completely different houses. Below we will talk about why
- Different boilers have different flow rates
Pay attention to heat losses
The following calculation method assumes that the level of heat loss of the building is known - and this statement is true in most cases.
The calculation process is simple:
- The total heat loss is divided in half, and 10% is added to the resulting value for hot water supply and ventilation heat outflow;
- The result of the previous action (measured in kilowatts per hour) allows you to find out the gas consumption for a day, a month or the entire heating period;
- The total gas consumption is converted into cubic meters (for this you will need to find out the specific heat of combustion of the gas) and multiplied by the cost of one cubic meter, as a result of which you can get the cost of heating for the desired period of time.

Using a similar method, you can calculate the consumption of any fuel - you just need to know the heat capacity of a particular energy resource. In addition, it is worth remembering the efficiency of heating equipment, which in the case of gas boilers fluctuates around 90%, i.e. It is worth adding another 10% to the total expense.
Of course, the described technique cannot give an exact answer to the question of how much a gas boiler consumes per month. On cold days, consumption will increase, and on warm days it will decrease, and this is completely logical. However, even a rough calculation allows you to understand how much gas a gas boiler consumes per month and how profitable its installation will be.
What determines the price of heating?
The cost of heating a home is determined by the price of fuel and the volume of its consumption. The product of these two quantities, as well as the length of the time period for which the calculation is required, gives the amount of money invested in heating alone. Gas consumption from main networks is measured in liters or m³, and from bottled gas - in kg. The cost of methane is 4 times less than that of a mixture of butane and propane.
Due to the lower calorific value, the consumption of the first type of gas consumed by the unit will be 3 times higher to produce the same amount of energy. As a result, payments for any type of gas become approximately the same.
Connection diagram for gas cylinders to a heating boiler
To connect the cylinder to the boiler, a special reducer is used, which converts liquefied fuel into a gaseous state. It is in this form that it is supplied to the heating equipment. If several containers are used at once, then the same number of reducers will be needed to connect to each cylinder. This is much safer than connecting several containers at once through one common gearbox.
To assemble the entire structure, a two-arm collector is used. This is a special ramp that divides all containers into two groups. One group is the main one. From it, gas enters the boiler first. The second group is the reserve group. It is used after the main group runs out of gas. Switching from one group to another occurs automatically. At the same time, a characteristic signal is heard. After refueling and connecting the tanks of the main group, the collector begins to consume fuel from these cylinders.
Gas equipment for home heating - burners for stoves and boilers

All containers with fuel are installed from the boiler at a distance of no closer than 200 cm. It is best to allocate a separate room for these purposes or fence off a compartment in the furnace room. It is prohibited to install cylinders in an uncovered place exposed to sunlight.
To connect containers, metal pipelines with a wall thickness of less than 2 mm are used. In the place where the pipes pass through the walls, protective cases are installed, and all openings are filled with foam. A durite hose is used to connect the pipeline to the heater.
Features of liquefied fuel
Liquefied gas is produced by converting natural fuels into a liquid state. To do this, it is cleaned of impurities, and then cooled until condensation. This technology allows you to reduce gas volume up to 600 times. Liquefied fuel is stored in cylinders that are connected to the boiler. This heating system is suitable for private homes if there is no centralized gas supply.
Consumption of liquefied fuel depends on the same factors as for conventional natural gas. On average, a 10 kW unit consumes 0.86 l3/hour of bottled fuel. A gas boiler with a capacity of 30 kW consumes approximately 2.58 l3/hour.

How to reduce heating costs in a private home
There are 5 options:
Insulation of walls using polystyrene or mineral wool. Both substances are usually located outside the building, covered with decorative material on top.

- Placing various substances in roof slopes to retain heat. They use the same as for walls, as well as shavings or cheaper materials, such as polystyrene foam.
- Additional floor heating, including using convectors or pipes.
- Replacement windows with new ones with double or triple glazing. If they are of good quality, you should check the joints and the presence of various cracks. If necessary, they are covered.
- Installation of additional heat sources in the room. They can be standard combinations of boilers with radiators or convectors.
Consumption of liquefied propane-butane mixture
Not all owners of country houses have the opportunity to connect to a centralized gas pipeline. Then they get out of the situation using liquefied gas. It is stored in gas holders installed in pits, and replenished using the services of certified companies that supply fuel.

Liquefied gas used for domestic purposes is stored in sealed containers and reservoirs - propane-butane cylinders with a volume of 50 liters, or gas holders
If liquefied gas is used to heat a country house, the calculation formula is taken as the basis. The only thing you need to take into account is that the bottled gas is a G30 mixture. In addition, the fuel is in an aggregate state. Therefore, its consumption is calculated in liters or kilograms.
Formula for calculating fuel mixture consumption
A simple calculation will help you estimate the cost of a liquefied propane-butane mixture. The initial construction data is the same: a cottage with an area of 100 square meters, and the efficiency of the installed boiler is 95%.

When calculating, it should be taken into account that fifty-liter propane-butane cylinders, for safety reasons, are filled to no more than 85%, which is about 42.5 liters
When performing calculations, we focus on two significant physical characteristics of the liquefied mixture:
- The density of bottled gas is 0.524 kg/l;
- The heat released during the combustion of one kilogram of such a mixture is equal to 45.2 MJ/kg.
To facilitate calculations, the values of heat released, measured in kilograms, are converted into another unit of measurement - liters: 45.2 x 0.524 = 23.68 MJ/l.
After which joules are converted to kilowatts: 23.68/3.6 = 6.58 kW/l. To obtain correct calculations, the same 50% of the recommended power of the unit is taken as a basis, which is 5 kW.
The obtained values are substituted into the formula: V = 5/(6.58 x 0.95). It turns out that the consumption of the G 30 fuel mixture is 0.8 l/h.
An example of calculating liquefied gas consumption
Knowing that on average 0.8 liters of fuel are consumed per one hour of operation of a boiler generator, it will not be difficult to calculate that one standard cylinder with a 42-liter refill will be enough for approximately 52 hours. This is a little more than two days.
For the entire heating period, the consumption of the combustible mixture will be:
- For a day 0.8 x 24 = 19.2 liters;
- For a month 19.2 x 30 = 576 liters;
- For a heating season lasting 7 months, 576 x 7 = 4032 liters.
To heat a cottage with an area of 100 square meters you will need: 576/42.5 = 13 or 14 cylinders. For the entire seven-month heating season, you will need 4032/42.5 = from 95 to 100 cylinders.
A large volume of fuel, taking into account transportation costs and the creation of conditions for its storage, will not be cheap. But still, in comparison with the same electric heating, such a solution to the issue will still be more economical, and therefore preferable.
Gas consumption for heating a house: calculator and calculations for a month, season, year
Autonomous gasification has two significant columns in the estimate: installation of a gas tank and annual fuel consumption. We will tell you how much you will spend on liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) when living in an area of 50 to 800 m2.
Popular house sizes
Gas consumption per month
Gas consumption during the heating season (7 months)
Gas consumption per year
| 100 m2 | 316 l | 2,212 l | 3,802 l |
| RUB 5,624 | RUB 39,368 | 67,000 rub. | |
| 150 m2 | 475 l | 3,325 l | 5,703 l |
| RUB 8,455 | RUB 59,185 | 101,000 rub. | |
| 200 m2 | 633 l | 4,431 l | 7,603 l |
| RUB 11,267 | RUR 78,869 | 135,000 rub. |
LPG at a price of 17.80 rubles/l as of 01/29/2019.
Gas consumption calculator for home heating
LPG consumption can be calculated in 3 ways: by boiler power, house area and the Soviet formula (27 liters per m2 per year). All options give an average result, because they are divorced from real living conditions.
We made a calculator based on heat loss at home. The room warms up correctly if the heating compensates for the thermal energy that the building loses through the roof, doors, walls, windows per unit of time.
The calculations include the height of the ceilings, the presence of an attic or basement, and building materials with different heat losses:
- foam blocks - 32.7 kW/m2;
- brick - 27.6 kW/m2;
- wood - 26.1 kW/m2.
How exactly does the calculation take place?
The final indicator of LPG consumption per year is derived using several formulas:
- We calculate the gas consumption without hot water (kW/h): house area × ceiling height × heat loss of the material × attic and basement coefficient.
- We find the gas consumption with DHW (kW/h): consumption without DHW × coefficient for DHW.
- We convert the kW/h indicator to Kcal/h, then to m3/h, then to l/h.
- We calculate the annual consumption: l/h × boiler operating hours per year.
In the calculation process, we take into account a number of indicators:
- The coefficient for DHW accounting is 1.15.
- The coefficient of the attic and heated basement is 0.95.
- The coefficient of the attic and unheated basement is 1.
- Coefficient without attic + heated basement - 1.
- Coefficient without attic + unheated basement - 1.05.
- The coefficient without an attic and without a basement is 1.1.
- The coefficient for converting energy (kW) into calories (Kcal) is 1.163.
- The conversion factor from m3 to liters of LPG is 2.37.
- Boiler operating hours per year - 2,265.
- Boiler efficiency is 0.92.
Unaccounted variables for gas consumption in a private home
The calculator still produces an average result. For accurate forecasting, much more data is needed:
- Required room temperature.
- Average temperature of the coldest week of the year.
- The number of windows, their height and width.
- Ratio of window to floor area: 10–50%.
- Window type: regular double glazed, double glazed, double glazed.
- Number of floors, upper and lower floors.
- Characteristics of external walls:
- masonry of 1-3 bricks with a thickness of 25–76 cm;
- log house made of logs with a diameter of 20–25 cm;
- log house made of timber 10–20 cm thick;
- frame wall 20 cm thick (board, mineral wool, board);
- foam concrete 20–30 cm thick.
Important adjustments are made by in-house gas equipment:
- number of burners on the stove;
- presence of an oven;
- real (not nameplate!) power of the gas boiler;
- device type: standard or condensing boiler.
A condensing boiler uses the potential of water vapor from gas combustion products. The equipment uses the generated heat as efficiently as possible and reduces fuel consumption by 15%.
By the way
If you want to determine the gas consumption for your home taking into account all the data, contact an engineer.
Heating a house with a gas holder
It is better to calculate the required amount of gas in relation to the barrel. That is, how long will each container last for different room sizes?
The gas tank is selected according to the number of refills. The optimal rate is 1-2 times a year. At a minimum, the tank should last for 7–8 months—the heating season.
Liquefied gas consumption per season
According to SP 131.13330.2012 Construction Climatology (updated edition of SNiP 23-01-99), the heating season in Russia is 207 days. This is approximately 7 months.
Also important information: the boiler does not operate around the clock. On average, heating operates 10 hours a day.
We carried out calculations based on the initial data:
- brick house without attic and basement;
- floor height 3.2 m;
- The efficiency of the gas boiler is 92%.
Indicators for refueling frequency are averaged. We assumed the same fuel costs for each month. In reality, residence may be seasonal or temporary, and consumption differs depending on the season.
The ratio of the area of the house and the volume of the gas tank (GG)
| GG volume (m3) | Full gas charge (l) | How long will gas last (months) | |||||||
| 50–100 m2 | 150 m2 | 200 m2 | 250 m2 | 300 m2 | 350–450 m2 | 500–600 m2 | 800 m2 | ||
| 3,802 l/year | 5,703 l/year | 7,603 l/year | 9,504 l/year | 11,405 l/year | 17,107 l/year | 22,809 l/year | 30,412 l/year | ||
| 2.5 | 2 125 | 6.7 | 4.5 | 3 | 2.7 | 2 | 1.5 | 1.1 | 0.8 |
| 2.7 | 2 295 | 7 | 5 | 3.6 | 3 | 2.4 | 1.6 | 1.2 | 0.9 |
| 4.6 | 3 910 | 12 | 8 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 2.7 | 2 | 1.5 |
| 4.8 | 4 080 | 12.8 | 8.5 | 6.4 | 5.1 | 4.2 | 2.8 | 2.1 | 1.6 |
| 4.85 | 4 112 | 13 | 8.6 | 6.5 | 5.2 | 4.3 | 2.9 | 2.2 | 1.6 |
| 5 | 4 250 | 13.4 | 9 | 7 | 5.4 | 4.5 | 3 | 2.2 | 1.7 |
| 6.4 | 5 440 | 17 | 11.4 | 8.5 | 6.8 | 5.7 | 3.8 | 2.8 | 2.1 |
| 6.5 | 5 525 | 17.4 | 11.6 | 8.7 | 6.9 | 5.8 | 3.9 | 2.9 | 2.2 |
| 6.6 | 5 610 | 17.6 | 12 | 9 | 7 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 2.2 |
| 8.6 | 7 310 | 23 | 15 | 11.5 | 9 | 7.7 | 5 | 3.8 | 2.9 |
| 9.1 | 7 735 | 24.4 | 16 | 12 | 9.7 | 8 | 5.4 | 4 | 3 |
| 9.15 | 7 777 | 24.5 | 16.4 | 12.3 | 9.8 | 8.2 | 5.5 | 4.1 | 3.1 |
| 9.6 | 8 160 | 25.7 | 17 | 13 | 10 | 8.6 | 5.7 | 4.3 | 3.2 |
| 10 | 8 500 | 27 | 18 | 13.4 | 10.7 | 9 | 6 | 4.5 | 3.4 |
Interpretation of colors in the table:
| irrational | Capacity supply is too large or too small |
| optimal | For seasonal or permanent residence with 2 refills per year |
| perfect | It is best to install for the heating season |
| with reserve | One-time refill is enough for a year |
Houses with an area of 800–1000 m2 are served by:
- gas tanks with industrial volumes of more than 10 m3 (installation is more complicated);
- two containers located side by side (8.6, 9.1 or 9.15 m3).
Liquefied gas consumption per month and year
Let's go over the costs of refilling a gas tank for houses of different sizes. We use the LPG price current at the beginning of 2021 - 17.80 rubles/liter. This is the cost of refueling in our company.
House area (m2)
Gas consumption per month (l)
Gas price per month (RUB)
Gas consumption per year (l)
Gas price per year (RUB)
| 50–100 | 316 | 5 624 | 3 802 | 67 675 |
| 150 | 475 | 8 455 | 5 703 | 101 153 |
| 200 | 633 | 11 267 | 7 603 | 135 533 |
| 250 | 792 | 14 097 | 9 504 | 169 171 |
| 300 | 950 | 16 910 | 11 405 | 203 009 |
| 350–450 | 1 425 | 15 365 | 17 107 | 304 504 |
| 500–600 | 1 900 | 33 820 | 22 809 | 406 000 |
| 800 | 2 534 | 45 105 | 30 412 | 541 334 |
Thus:
- gas consumption for heating a house of 100 m2 is 68 thousand rubles per year;
- gas consumption for heating a house of 150 m2 is 101 thousand rubles per year;
- gas consumption for heating a house of 200 m2 is 136 thousand rubles per year.
Real gas consumption: reviews from gas tank owners
We have selected examples of using autonomous heating on the ForumHouse forum. Owners have different experiences. In the project, the insulation of the house, the climate, the needs of the residents and the quality of the boiler are important.
Case 1. The user actively spends LPG - permanent residence with regular showers. A 2,300 liter refill lasts for almost 2 years at a room temperature of at least 21°C. Costs are reduced by using the fireplace 6 times a month - 3 hours of burning and 9 hours of smoldering.
Consumption per year: 20,700 rubles (1150 l at 18 rubles/l). House 125 m2.
Quote from user +Egoza from the ForumHouse forum
Case 2. The user has well insulated the house and installed a low-temperature boiler. In winter I did not take away the hot water supply. Daytime temperature in the rooms is 23°C, night temperature is 20°C. Daily gas consumption is from 6 to 12 liters.
Consumption per year: 15,000 rubles (1000 l at 15 rubles/l). House 120 m2.
Quote from user Khozain2000 from the ForumHouse forum
Case 3. The user heats the house and garage. There are problems with insulation: heat loss through the door, floor and ceiling. Gas consumption is about 15 liters per day. Daytime temperature in the rooms is 22°C, night temperature is 19°C.
Consumption per year: 81,000 rubles (5,475 liters at 15 rubles/l). House and garage 165 m2.
Quote from user AntonVT from the ForumHouse forum Quote from user AntonVT from the ForumHouse forum
Case 4. The user lives at his dacha on weekends. Only the first floor of the two is heated. On weekdays, if there are no residents, the temperature is automatically maintained at 7°C. The hot water supply has not yet been started. Uses remote heating control via a ZONT room thermostat with its own SIM card.
Consumption per year: 33,900 rubles (2,275 liters for 14.90 rubles/l). House 190 m2.
Quote from user Dimabol from the ForumHouse forum
Safety Recommendations
Converting the boiler and reconfiguring it to consume liquefied gas dictates the need to “reconfigure” your attitude towards the device for supplying and storing blue fuel.
You must remember that:
- Cylinders or gas tanks, which are gas storage tanks that supply fuel to household appliances as needed, need to be refilled periodically.
- To fill a group of cylinders or a gas holder with gas, you need to contact certified organizations that have equipment to record the weight of the gas in the cylinder and its actual volume in the gas holder.
- Filling closed gas tanks is carried out to 85% of the useful volume of the vessel. This reserve is necessary in case of thermal expansion of the fuel to avoid an explosion.
A non-hazardous situation that requires special attention when replenishing liquefied blue fuel reserves is the filling of liquid with a density different from the density of the previous liquid. Because of this difference, the remaining liquefied gas may not mix with the newly filled portion.
In the tank, due to the difference in density, a kind of two non-connecting sectors are formed, in each of which liquefied gas circulates. However, convective heat exchange will occur at the sector boundary after a short period. After the temperatures are equalized, the densities will be equal and the liquids will be able to mix.

Liquefied gas, like main gas, is a highly flammable, combustible liquid with a high flame propagation speed. To avoid catastrophic situations, you should strictly follow the operating rules and fill the cylinders no more than 85%
Usually this process, meaning direct mixing, is accompanied by intense evaporation of liquefied gas. To avoid associated losses, mixing devices should be used during the filling process. But it is better to choose a method that eliminates the above-described phenomenon.
Replenishing cylinders and gas tanks with blue fuel in general is a process that requires increased attention, otherwise problems can be very serious and even catastrophic. The rapid spread and evaporation of the liquefied gas mixture is recognized as a significant problem.
If the rules for the safe operation of gas-consuming equipment are not violated, main methane rarely explodes. This only happens with significant leaks, if the technical state of the gas in the surrounding space changes dramatically. For example, in a kitchen with obvious signs of a leak, instead of mandatory ventilation, they turn on the light.
When liquefied gas expands in a closed container due to external heating, it will necessarily explode if there is not enough space left in the container for its expansion. Blue fuel burns extremely intensely. Since the gas is quickly absorbed by the atmosphere, the combustion zone expands at high speed.
Autonomous heating with liquefied gas mixture
If natural gas is not supplied to the building via a pipeline, then the boiler is connected to a cylinder or gas holder with a propane-butane mixture. Liquefied gas is recorded in kilograms. Therefore, the value “C” from the calculation formula is equal to 12.8 kW/kg.
The weight of one liter of the mixture is 0.54 kg. Let's calculate the weight of the hourly volume of the mixture.
H = 5 / (12.8 * 0.92) = 0.4246 kg/h, liquefied mixture.
Now it remains to calculate the gas consumption for heating a house of 100 m2 in liters.
Volume L = 0.4246 * 5808 = 2466 liters.
How many refilled cylinders will be needed for one heating season? One cylinder holds 42 liters of fuel. All you need is
2466 / 42 = 59 cylinders.
Calculation of gas consumption for a certain period
To calculate the gas consumption of boilers of different capacities, you need to take into account that in cold weather there is 10 sq.m. for heating. a living area requires 10 kW of energy, and in severe frosts this figure increases to 1.2 kilowatts. To calculate consumption, you need to do the following:
- Calculate the area of all rooms of a house or apartment using the technical plan of the structure.
- Divide the sum by 10 and multiply by 1.2. The result obtained is the maximum consumption indicator of the heating circuit.
This parameter just needs to be rounded up. If you need to calculate how much gas a boiler consumes per day, you need to take into account that the burner does not work 24 hours. To carry out the calculation, this time must be halved. The consumption rate of a 10 kW unit is 14.4 cubic meters. per day (10*0.12*12).
Beretta CIAO 16 CSI
This Italian-made model is equipped with a copper bithermal heat exchanger, a closed combustion chamber, a modulating burner and weather-compensating automation. Power changes are allowed in the range of 7-17.7 kW.
DHW heats up to 37-60°C. The boiler is equipped with a standard safety and control system.

Main characteristics of the unit:
- Efficiency=90.4%;
- gas consumption – 1.87 m3/hour;
- DHW productivity at Δt=35°C – 8.3 l/min;
- warranty period – 1 year;
- price – 42,000 rub.
Using economical condensing gas boilers
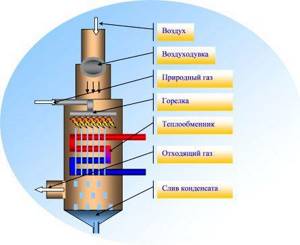
Operating principle of a condensing gas boiler
Modern modernization of gas heating boilers has significantly increased their operating efficiency. The latest innovation in gas heating equipment is condensing boilers. They use the higher calorific value of the energy carrier and consume approximately 17 percent less gas. In some cases, gas savings when using condensing boilers can reach 33 percent.
The “higher heat” of combustion products when using modern gas boilers is achieved by summing the combustion energy of the gas itself and the energy of steam condensation in heat exchange devices.
In a conventional gas boiler, after passing through the heat exchange unit, heated water vapor escapes, and therefore its thermal energy is not fully used.
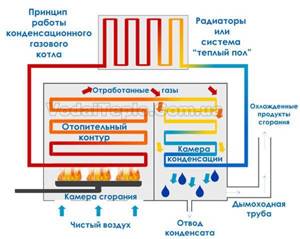
condensing gas boiler
However, a condensing boiler also uses latent thermal energy, which condensing steam can release. Water vapor turns into a liquid state, releasing some of the thermal energy.
Despite the fact that the effect of releasing energy during steam condensation has been known for quite some time, it was possible to implement it in serial devices only after the industry learned to use materials that are resistant to corrosion. A gas boiler with condensation shows significantly lower gas consumption compared to conventional devices.
How to calculate how much gas a gas boiler consumes
Gas is still the cheapest fuel, so if you have a gas main, you should choose a gas boiler without hesitation.
According to surveys and practice, the top three most important selection criteria for most buyers include gas consumption.
Despite the fact that it is indicated in the characteristics of almost every modern boiler, this does not allow you to quickly imagine the approximate cost of gas consumed per day, month or for the entire heating season.
To make heating budget planning easier, it is enough to once understand the principles of calculating gas consumption by boilers.
We calculate how much gas a gas boiler consumes per hour, day and month
When designing individual heating systems for private houses, 2 main indicators are used: the total area of the house and the power of the heating equipment.
With simple average calculations, it is generally accepted that for heating every 10 m2 of area, 1 kW of thermal power + 15-20% of the power reserve is sufficient. However, for planning expenses it is more convenient to measure the work of gas boilers directly per cubic meter.
m/hour (cubic meters) – if natural gas from the pipeline is used; or in kg/hour (kilograms) - if liquefied gas is used (which is much more expensive).
It is known that the calorific value of natural gas is 9.3-10 kW per m3, which means that for 1 kW of thermal power of a gas boiler, about 0.1-0.108 m3 of natural gas is needed. At the time of writing, the cost of 1 m3 of main gas in the Moscow region is 5.6 rubles/m3 or 0.52-0.56 rubles for each kW of boiler thermal power.
But this method can be used if the boiler’s passport data is unknown, because the characteristics of almost any boiler indicate the gas consumption during its continuous operation at maximum power.
For example, the well-known floor-standing single-circuit gas boiler Protherm Volk 16 KSO (power 16 kW), operating on natural gas, consumes 1.9 m3/hour.
- Per day – 24 (hours) * 1.9 (m3/hour) = 45.6 m3. In value terms – 45.5 (m3) * 5.6 (tariff for Moscow region, rub.) = 254.8 rub/day.
- Per month – 30 (days) * 45.6 (daily consumption, m3) = 1,368 m3. In value terms – 1,368 (cubic meters) * 5.6 (tariff, rub.) = 7,660.8 rubles/month.
- For the heating season (suppose from October 15 to March 31) - 136 (days) * 45.6 (m3) = 6,201.6 cubic meters. In value terms – 6,201.6 * 5.6 = 34,728.9 rubles/season.
However, these are only approximate theoretical calculations, since in practice the boiler does not operate 24/7 at full capacity: in this case, the wear of its elements accelerates many times over.
A gas boiler correctly selected in terms of power (taking into account the area, heat loss of the house and a small power reserve of 10-20%) consumes only 50-70% of the values calculated above for the maximum possible operating mode of the boiler.
That is, in practice, depending on the conditions and heating mode, the same Protherm Wolf 16 KSO consumes 700-950 cubic meters of gas per month, which is about 3,920-5,320 rubles/month. It is impossible to accurately determine gas consumption by calculation!
To obtain accurate values, metering devices (gas meters) are used, because gas consumption in gas heating boilers depends on the correctly selected power of the heating equipment and model technology, the owner’s preferred temperature, the arrangement of the heating system, the average temperature in the region during the heating season and many other factors , individual for each private home.
Consumption table for well-known boiler models, according to their passport data
| Model | power, kWt | Max natural gas consumption, cubic meters m/hour |
| Lemax Premium-10 | 10 | 0,6 |
| ATON Atmo 10ЕВМ | 10 | 1,2 |
| Baxi SLIM 1.150i 3E | 15 | 1,74 |
| Protherm Bear 20 PLO | 17 | 2 |
| De Dietrich DTG X 23 N | 23 | 3,15 |
| Bosch Gaz 2500 F 30 | 26 | 2,85 |
| Viessmann Vitogas 100-F 29 | 29 | 3,39 |
| Navien GST 35KN | 35 | 4 |
| Vaillant ecoVIT K INT 366/4 | 34 | 3,7 |
| Buderus Logano G234-60 | 60 | 6,57 |
Calculator for quick calculations
Let us remind you that the calculator uses the same principles as in the example above; real flow data depend on the model and operating conditions of the heating equipment and can only be 50-80% of the data calculated under the condition that the boiler operates continuously and at full capacity .
Based on heat loss at home
A visual representation of heat loss in a private home.
The exact heat loss of a house is calculated based on the area + adjustments related to the glazing area, the degree of insulation of the house, climate zone and temperature in the coldest ten-day period of the heating season.
To put it simply, it is generally accepted that for every 10 m2 of an average house with 2-brick masonry and a ceiling height of up to 2.7 m, there is 1-1.2 kW/hour of heat loss.
Accordingly, to maintain a comfortable temperature, it is necessary to establish a balance between the heat received from the heating system and heat loss.
Let's calculate using the example of an average house with an area of 100 m2, located in the Moscow region, which does not involve adjustments related to the climate zone.
The heat loss of such a house will be about 11 kW/hour, the same amount will be produced by a gas boiler. Let us remember that the specific heat capacity of natural gas combustion is 9.3 kW.
However, most gas boilers are 90% efficient, so adjustments must be made accordingly for efficiency.
Total gas consumption = 11 (kW/hour) / (9.3 (kW) * 0.9 (90% efficiency)) = 1.31 m3/hour, which is equal to 31.44 cubic meters per day. According to the tariff at the time of writing for the Moscow region, this is 176.1 rubles/day.
But, like other methods, calculation based on heat loss shows an approximate picture with deviations of 10-30% in each direction. In the warmest month of the season, consumption may be minimal, while in the coldest ten days, due to large heat losses, the boiler will operate at maximum capacity with the burners constantly running.
Consumption of a certain power by the boiler
Some calculate gas consumption based on the boiler power; this is appropriate if, for example, the boiler unit is quite old and the nominal consumption is unknown. Let's say you have a 10 kW boiler, for calculations you will also need efficiency, which is probably also unknown, but in practice the efficiency of old Soviet and post-Soviet gas boilers barely reached 70%.
We calculate the boiler consumption according to the principle already clear from the previous examples: 10 kW / (9.3 kW * 0.7 (estimated efficiency 70%)) = 1.54 cubic meters. m/hour or 36.96 cubic meters. m/day with continuous operation of the main burners. Gas consumption by the boiler is 24 kW = 24 / (9.3 * 0.7) = 3.69 cubic meters per hour.
Consumption of a gas boiler using liquefied gas
For ease of replacement and for safety reasons, cylinders are placed outdoors.
Many not only modern, but also quite early gas boilers operate on both natural and liquefied (cylindered) gas; to change the fuel used, it is usually enough to change the burner included in the kit and connect the gas cylinder. The consumption is calculated according to any of the previously mentioned principles: according to passport data on consumption when operating on liquefied gas, according to heat losses or boiler power.
It is a mistake to take into account the consumption of liquefied gas in m3 or liters; in the context of boiler equipment, it is more convenient and logical to indicate its volume in kg.
For example, the Rinnai BR-K12 gas wall-mounted boiler, when continuously operating at maximum power, consumes 1.0 kg/hour of liquefied gas. The average cost of liquefied gas at the time of writing is 33 rubles/kg.
- Per day – 24 (hours) * 1.0 (kg/hour) = 24 kg. In value terms – 24 (kg) * 33 (cost of 1 kg, rub.) = 792 rubles/day.
- Burns per month – 30 (days) * 24 (daily consumption, kg) = 720 kg. In value terms – 720 (kg) * 33 (price, rub.) = 23,760 rubles/month.
- For the heating season (suppose from October 15 to March 31) - 136 (days) * 24 (kg) = 3,264 kg. In value terms – 3,264 * 33 = 107,712 rubles/season.
Despite the lower consumption, the cost of heating when using liquefied gas becomes simply “golden”, without taking into account the additional concerns of purchasing, transporting and connecting the fuel supply.
What affects consumption in practice?
The greatest influence on consumption is the boiler power and its efficiency - how efficiently the fuel is used. However, these factors cannot be significantly changed with existing and functioning heating equipment; they must be planned at the selection and purchase stage. The more powerful the boiler, the more fuel it will need when operating in extreme conditions.
The efficiency of most modern gas boilers is in the range of 90-94%; the most efficient are condensing gas boilers with an efficiency of 105-109%. You probably understand that efficiency cannot exceed 100%, since additional energy simply cannot come from nowhere, and this is quite true.
The fact is that condensing boilers use not only the thermal energy from gas combustion, but also the thermal energy of moisture condensates - one of the combustion products. When conventional convection boilers emit this energy into the chimney, condensing boilers direct it to heat the return.
In fact, the efficiency of such boilers tends to 100%, and the additional 7-10% obtained from condensate is only the next stage of conversion. For an ordinary buyer, all these processes do not matter, but in order to objectively compare efficiency with conventional boilers and explain the difference in price to the buyer, manufacturers designate efficiency in this way.
Gas consumption is also affected by the air temperature in the region ; in severe frosts, the boiler tries to maintain a stable temperature set by the owner, however, heat loss due to frost is higher, and accordingly, gas consumption is higher.
The standard calorific value of natural gas is 9.3-10 kW per m3, but it is no secret that domestic main gas is sometimes not of the best quality and has a lower calorie content.
In this case, the equipment must be provided with the same amount of heat as before: the boiler consumes a lot of gas.
A common reason for increased gas consumption is improper and irregular boiler maintenance . First of all, attention is required to the heat exchanger, which becomes clogged with scale or as a result of using a less than ideally clean coolant. You can reduce consumption simply by cleaning not only the heat exchanger, but also the burners.
The last criterion on which higher flow rates may depend is the presence of a second circuit for DHW. If the consumption of a double-circuit boiler has become noticeably higher, the reason may be more intensive use of hot water.
The boiler works and does not turn off
The next reason for the high gas consumption is the fact that the boiler simply does not turn off, or turns off, but extremely rarely. The most common reason for this phenomenon is that the gas boiler simply does not understand that it needs to be turned off somehow. Why is this happening?
Gas boilers are configured in such a way that they respond to shutdown based on return temperature. When the return temperature (the sensor most often stands on the supply, but due to circulation, until the temperature is reached, it will not turn off) reaches the required degrees, the boiler turns off. In other cases, it continues to work, and it does not matter what your supply temperature is set to. Until the boiler reaches the desired temperature, which is set in its software, it will continue to operate continuously. Continuous operation is associated with increased gas consumption and most likely at some point you will feel stuffy. Most often, this problem is due to the fact that boilers are installed in old heating systems, which, as a rule:
- unregulated;
- made on metal;
- Cast iron batteries with a large volume of water are installed.
Consequently, the boiler completely distills the coolant through a large circle, and the coolant has time to cool down during this time. In any case, the boiler copes with its task, but due to problems with circulation, the speed of movement of the coolant, as well as high heat removal, the return temperature is low.
At some point, the household really gets hot because the boiler is working non-stop. The boiler consumption at this moment is prohibitive.
Only installing a room thermostat will help cope with this problem. When you install a room thermostat, the boiler will be forced to turn off, no matter what the return temperature is. For example, if the thermostat is set to 20°C and the room temperature reaches the same level, the boiler is forced to turn off.
If you have high gas consumption, check whether the gas boiler turns off at all. If this does not happen, installing a room thermostat will solve the problem.
Low supply temperature

Another problem associated with a constantly running gas boiler is setting the boiler to a low temperature. Because of this, the boiler also constantly works and does not turn off.
It is a mistake to believe that if you are hot and you set the temperature to 40°C, but there are cast iron radiators or aluminum or other radiators in the house, then the boiler will work normally and turn off normally. Usually, under such conditions, on the contrary, a problem arises from the fact that the return flow has cooled down. The fact is that this kind of radiators does not accumulate heat, the heat transfer process occurs quickly, and the return also cools down quickly.
When you set a higher operating temperature for such radiators (It’s not for nothing that it is indicated in the passports when purchasing such radiators. The operating temperature range ranges from 60°C and above), the problem is leveled out, and the boiler returns to normal operation. Therefore, when you set a low temperature in the boiler in the hope that it will save money, this is not always the case. If the house has ordinary radiators, then the boiler, on the contrary, is required to operate at a higher temperature. And if at some point you feel hot and you want to lower the temperature, but the boiler won’t turn off, then the solution is simple - install a room thermostat.
Calculation of gas volume for home heating
Let's carry out calculations for the climatic conditions of the Southern Urals. According to the rules, the heating interval for housing is set from September 15 to May 15. The reasonableness of the norm is confirmed by the fact that in the Urals it still snows in the first half of May, and in the second half of September. The duration of the heating season is 242 days. The consumer will regulate the start and end of heating independently.
Heat is supplied to living rooms 24 hours. In total, the gas will have to be burned for 5808 hours. This is the maximum required operating time for gas equipment.
Axiom of heating calculations: heating 10 square meters of housing requires 1 kilowatt of energy. Then the house considered in the example needs 10 kilowatts. In reality, this standard is half as much due to a sudden early and warm spring, or a long and hot autumn, or the winter frosts will not be the Ural cold, but the weak Crimean cold snap. Let’s agree that the energy consumption for heating one hundred square meters of living space will be 5 kilowatts.
Let's calculate the gas volume consumption per hour. Let be:
0.92 - maximum efficiency of the heating unit;
H – volume of gas consumption for heating a house 100 m2 per m3;
T – power for heating 100 m2, kilowatt;
C – the lowest calorific value of main fuel is 10.175 kW/m3.
Then H = T / (C * 0.92) = 0.5341 m3/h.
Consequently, the gas consumption for heating a house of 100 m2 in cubic meters will be 3102 m3.
What volume of gas needs to be burned to generate 1 kW
Depends on the calorific value of the fuel; the higher the value, the less fuel is needed. Heat is usually measured in J/kg, J/m2, J/l. The task is to determine the calorific value and bring it to the required value. For heating use:
- methane;
- propane;
- butane;
- propane-butane.
Propane, butane, and their mixtures have different purifications and calorie content varies. The volume and weight of gas are very variable. Temperature and pressure greatly affect the performance. This is explained by the large expansion coefficient compared to water, 16 times greater. To compare indicators, the test substance must be under the same conditions (temperature, pressure, product purity).
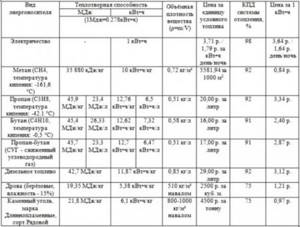
Fuel calorie content
Another indicator that affects the amount of heat received is the efficiency of the boiler. Depending on the design, the average productivity is determined:
- gas convector 86%;
- open type boiler 88%;
- closed combustion chamber 92%;
- condensing gas boiler 96%.
The figures given are averaged; performance is influenced by many factors, for example, heat exchanger material. May be:
- steel;
- cast iron;
- aluminum;
- copper.
Efficiency may deteriorate, the heat exchanger plates burn and become clogged with soot.

Gas heat exchanger
What power reserve should be
The power for selecting a heating source with an indirect heating boiler with simultaneous operation of heating and hot water supply is determined by the formula:
M k= (Mo+Mgvs)*Kz,
Where:
- Mk-combined power, kW;
- Mo - source power sufficient to provide the heating load of the house, kW;
- Mgvs - source power required to compensate for the load on hot water supply, kW;
- Кз - safety factor.
In the case of alternating operation of heating and hot water systems:
Mk= Mgvs *Kz Very important! When calculating the performance of heating and hot water equipment, it is necessary to take into account that the power of the BKN does not in any way exceed the same indicator in the boiler. For this reason, it must be selected with a heating capacity in kW so that it can cover the load of both heating and domestic hot water with a margin. The performance reserve is calculated depending on the design of the heating equipment
For single-circuit modifications, the margin is 20.0%; for dual-circuit - 20.0%+20.0%.
For the above examples, the heating output of the boiler will be equal.
When heating and hot water systems operate simultaneously:
Mo = 24 kW. Mgvs = 24 kW. Kz= 1.4.
Mk= (24+24)* 1.4= 67.2 kW.
When operating heating and hot water systems alternately:
Mk=24*1.4= 33.6 kW.
Thus, performing an initial calculation of the power of a gas thermal energy source is not a difficult process. It may be used for preliminary selection of boiler equipment. If the subscriber lacks an approximate calculation of the efficiency of gas boilers, and it is necessary that the heat loss of the building, the DHW load and the boiler performance be determined more accurately, he will need to contact qualified specialists to carry out a comprehensive home heating project with the development of a diagram and selection of equipment .
Average gas consumption per month, day, hour
How to calculate how much gas is consumed? It can be done approximately; it is impossible to take into account all factors. Data:
- calorific value of gas;
- Heater efficiency;
- heat loss of the building;
- additional costs (for example, hot water supply system).
A simplified version, you can get an idea of upcoming expenses. Explanation of symbols:
- V – calculated volume of gas;
- Q – required heat;
- q – calorific value of gas.
The volume of gas strongly depends on temperature and pressure; the volume of gas vapor at normal atmospheric pressure is taken into account. From 1 kg of the liquid phase of gas, approximately 450 liters of vapor are obtained. To calculate how much heat is needed for heating, the heat loss of walls, doors, windows, floors, and ceilings is calculated. If there is ventilation, an indicator is added. When using DHW, the V indicator is multiplied by a factor of 1.15. The calorific value of gas is determined from tables and converted to kW.
As an example, you can calculate for a house with an area of 100 m2. Based on the table, we determine the average loss value of 120 W/m2h, convert it to kilowatts, it turns out 0.12 kW/m2h. We multiply by the total area of the house, we get 12 kW/h - the Q indicator.
A liquefied mixture of propane-butane gas is used, with a calorific value of 11.5 kW/kg. Boiler with a closed chamber, productivity 92%. All that remains is to insert the indicators into the formula. V = 12: (11.5 x 92: 100) = 12: 10.58 = 1.13 m3/h. Per day it will be 1.13 x 24 = 27.12, per month 813 m3.
Gas consumption of Proterm Medved boilers 20, 30, 40, 50, 60
The manufacturer provides the following information in the operating instructions for boiler equipment:
| Model name | Power, kW (1 stage) | Gas consumption, m3/hour at 1 power stage | Power, kW (2nd stage) | Gas consumption, m3/hour at 2 power levels |
| Bear 20 KLOM/PLO | 17 | 2 | 12 | 1.4 |
| Bear 30 KLOM/PLO | 26 | 3 | 18 | 2.1 |
| Bear 40 KLOM/PLO | 35 | 4.1 | 24.5 | 2.9 |
| Bear 50 KLOM/PLO | 44.5 | 5.2 | 31 | 3.7 |
| Bear 60 KLOM/PLO | 49.5 | 5.8 | — | — |
| Bear 20 KLZ | 11.9 | 1.4 | 17 | 2 |
| Bear 30 KLZ | 18.2 | 2.1 | 26 | 3 |
| Bear 40 KLZ | 24.5 | 2.9 | 35 | 4 |
| Bear 50 KLZ | 31.5 | 3.3 | 44 | 5.2 |
| Bear 20 TLO | 17 | 1.9 | — | — |
| Bear 30 TLO | 26 | 3 | — | — |
| Bear 40 TLO | 35 | 4 | — | — |
| Bear 50 TLO | 44.5 | 5.2 | — | — |
After studying this table and comparing the models, you can make an approximate conclusion about how economical and cost-effective Protherm Bear boilers are to operate. However, these data provide only a rough idea of future heating costs.
Types of gas boilers
Heating boilers according to their design are divided into single-circuit and double-circuit. Single-circuit devices are used exclusively for heating rooms. Double-circuit models also provide hot water supply.
Single-circuit boilers
Single-circuit gas boilers are structurally designed for heating, however, by connecting an additional indirect heating boiler, it is possible to obtain hot water supply in the house.
It should be borne in mind that such a connection creates instability in the operation of the heating network, since in the event of a peak withdrawal of hot water for domestic purposes, the temperature of the coolant in the heating system will inevitably fall.
Double-circuit boilers
By their design, double-circuit boilers provide both space heating and hot water supply, thanks to the presence of an additional heat exchanger designed specifically for these purposes. This design scheme is more beneficial from the point of view of comfort, and consumer reviews for devices such as double-circuit gas heating boilers are always positive.
The market offers a wide range of boilers of all types, capacities and technical equipment in the form of timers and thermostats from manufacturers in different countries.
How to save gas on the stove and gas water heater
The easiest way to save gas are small “tricks” in the kitchen, which, with constant use, turn into a useful habit:
Do not allow liquid to boil excessively
When cooking with gas, pay attention to the size of the burner flame and do not allow it to heat the walls of the pan. The highest temperature is at the flames, therefore, to quickly heat the dishes, the fire should be located directly under the bottom of the container
During the cooking process, it is necessary to adjust the flame depending on the stages of cooking.
So, to boil water, the fire can be large, but after that you can reduce the burning intensity by at least half.
Helpful tip: cover the dishes with a lid: the food will cook faster and use less gas!
This bottom design quickly heats up over the entire surface from the center to the edges, while consuming a minimal amount of gas. To save fuel on heating water, it is advisable to use special dishes for gas stoves:
- pans with special grooves on the bottom that maintain the temperature for some time after the stove is turned off;
- kettles with a whistle, which will warn you in time that the water has boiled and will not allow you to use excess gas.
If blue energy is used to heat the column, then installing economical shower heads will help save it. Filling the bathroom also increases the consumption of hot water: it is enough to replace this procedure with taking a shower and you can get significant gas savings.
How to calculate fuel consumption
To heat a private house or apartment, calculations are used that are based on two parameters: the power of the heating equipment and the area of the room. The average calculation is taken - 1 kW per 10 m².
Many articles have been written on this topic, but few clarify that the kilowatt unit of measurement is thermal power, not electrical power. This misleads many users.
It would be more logical to measure work on natural gas in cubic meters (m³ per hour), and on liquefied gas in kilograms (kg/hour).
On average, 1 kilowatt of thermal power consumes 0.112 cubic meters per hour of main gas.
For example, let’s take the AOGV unit with a power of 17.4 kW. The passport data indicates the consumption of main fuel is 1.87 cubic meters, liquefied gas - 1.3 kg/hour. These values are valid for continuous operation, but if the device is constantly running under wear and tear, then the parts will quickly fail. When choosing, add plus 20% to the indicated power.
“AOGV” in our example will be installed in a room of 140 m². Now take a look at the rates (approximately):
- Natural fuel: 3.9 rubles per cubic meter.
- For bottled gas, the calculation is based on the volume of the container. For 50 liters - 600 rubles. The cylinder is not completely filled with propane, approximately 80% (21 kg). This means: 600/21= 28.6 rubles. You can add shipping costs here.
The daily calculation for the main connection will be as follows::
Day (24 hours) x 1.87 (cubic meters/hour)/2 = 22.4 cubic meters. To find out the cost: 22.4 x 3.9 (tariff) = 87.5 rubles.
Per month:
22.4 (daily consumption) x 30 (number of days) = 672 m³.
Per year (seven months - heating season):
7 x 672 (monthly norm) = 4,704 m³.
When working on propane per day:
24 (hours) x 1.3 (kg/h) /2 = 15.6 kg. To find out the minimum costs: 15.6 x 28.6 (tariff) = 446 rubles.
For a month (30 days):
15.6 (per day) x 30 = 468 kg. That means you use 22.3 propane tanks per month.
For a year (seven months):
7 x 468 (per month) = 3,276 kg or 156 cylinders.
Please remember that these calculations are for one model only. The meanings vary for each brand; you need to look them up in the documentation. See tables below:
| Brand / Power | Consumption cu. m/h |
| "Proterm" 24 | 2,677 |
| "Navien" 24 | 2,06 |
| Buderus ("Buderus") 24 | 2,72 |
| "Ariston" 20 | 2,73 |
| "Baksi" 10 | 1,2 |
| "Bosch" 24 | 2,52 |
| "Vailant" 24 | 2,3 |
| "Visman" 26 | 2,6 |
And also for bottled gas:
| Manufacturer | Consumption kg/h |
| "Baksi" 10 | 0,86 |
| "Proterm" 24 | 1,96 |
| "Buderus" 24 | 1,93 |
| "Vailant" 24 | 1,8 |
| Beretta 24 | 2,0 |
Consumption is affected by the location of the device: floor or wall. Material of manufacture of the heat exchanger, type of gas burner, number of working days.
Natural gas consumption at home
The owners of all apartments and houses and many enterprises need to calculate the volume of gas consumed. Data on the need for fuel resources is included in the designs of individual houses and their parts. To pay according to actual figures, gas meters are used.
The level of consumption depends on the equipment, the thermal insulation of the building, and the time of year. In apartments without centralized heating and hot water supply, the load goes to the water heating boiler. The device consumes up to 3-8 times more gas than a stove.
Gas water heaters (boilers, boilers) are wall-mounted and floor-mounted: they are used simultaneously for heating and water heating, and less functional models are mainly used only for heating
The maximum consumption of the stove depends on the number of burners and the power of each of them:
- reduced - less than 0.6 kW;
- regular - about 1.7 kW;
- increased - more than 2.6 kW.
According to another classification, low power burners correspond to 0.21-1.05 kW, normal - 1.05-2.09, high - 2.09-3.14, and high - more than 3.14 kW.
A typical modern stove uses at least 40 liters of gas per hour when switched on. Typically, a stove consumes about 4 m³ per month per resident, and the consumer will see approximately the same figure if they use a meter. In terms of volume, much less compressed gas in cylinders is required. For a family of 3 people, a 50 liter container will last about 3 months.
In an apartment with a 4-burner stove and no water heater, you can install a counter marked G1.6. A device with standard size G2.5 is used if there is also a boiler. To measure gas flow, large gas meters are also installed, on G4, G6, G10 and G16. A meter with parameter G4 can handle the calculation of gas consumption by 2 stoves.
Water heaters are 1- and 2-circuit. For a boiler with 2 branches and a powerful gas stove, it makes sense to install 2 meters. One reason is that household gas meters do not cope well with large differences between the power of the equipment. A weak stove at minimum speed uses many times less fuel than a water heater at maximum.
A classic stove has 1 large burner, 2 medium and 1 small; using the largest one is the most economical.
Subscribers without meters pay for volume based on consumption per 1 inhabitant multiplied by their number, and consumption per 1 m² multiplied by the heated area. The standards are valid all year round - they contain an average indicator for different periods.
Norm for 1 person:
- Gas consumption for cooking and heating water using a stove in the presence of a centralized hot water supply (DHW) and central heating is about 10 m³/month per person.
- Using a stove alone without a boiler, centralized hot water supply and heating is approximately 11 m³/month per person.
- Using a stove and water heater without central heating and hot water supply is about 23 m³/month per person.
- Heating water with a water heater is about 13 m³/month per person.
In different regions, the exact flow parameters do not coincide. Individual heating using a water heater costs approximately 7 m³/m² for heated residential premises and about 26 m³/m² for technical ones.
On the notice from the meter installation company you can see how different the consumption indicators are with and without a gas meter
The dependence on gas consumption is indicated in SNiP 2.04.08-87. The proportions and indicators are different there:
- stove, central hot water supply - 660 thousand kcal per person per year;
- there is a stove, no hot water supply - 1100 thousand kcal per person per year;
- there is a stove, a water heater and no hot water - 1900 thousand kcal per person per year.
Consumption according to the standards is influenced by the area, the number of residents, the level of amenities with household communications, the presence of livestock and its number.
The parameters are differentiated based on the year of construction (before 1985 and after), the use of energy-saving measures, including insulation of facades and other external walls.
You can read more about gas consumption standards per person in this material.
Calculation of gas boiler power depending on area
In most cases, an approximate calculation of the thermal power of the boiler unit by heating area is used, for example, for a private house:
- 10 kW per 100 sq.m;
- 15 kW per 150 sq.m;
- 20 kW per 200 sq.m.
Such calculations may be suitable for a not very large building with an insulated attic floor, low ceilings, good thermal insulation, double-glazed windows, but nothing more.
According to old calculations, it is better not to do this. Photo source: porjati.ru
Unfortunately, only a few buildings meet these conditions. In order to carry out the most thorough calculation of the boiler power indicator, it is necessary to take into account the full package of interrelated quantities, including:
- atmospheric conditions in the area;
- size of residential building;
- wall thermal conductivity coefficient;
- actual thermal insulation of the building;
- gas boiler power control system;
- the amount of heat required for DHW.
Calculation of a single-circuit heating boiler
Calculating the power of a single-circuit boiler unit for a wall-mounted or floor-mounted boiler modification using the ratio: 10 kW per 100 m2 must be increased by 15-20%.
For example, you need to heat a building with an area of 80 m2.
Calculation of the power of a gas heating boiler:
10*80/100*1.2 = 9.60 kW.
In the case where the required type of device does not exist in the retail network, a modification with a larger kW size is purchased. A similar method is suitable for single-circuit heating sources, without a load on the hot water supply, and can be used as the basis for calculating gas consumption for the season. Sometimes, instead of living space, calculations are made taking into account the volume of the residential building of the apartment and the degree of insulation.
For individual premises built according to a standard design, with a ceiling height of 3 m, the calculation formula is quite simple.
Another way to calculate boiler OK
In this option, the built-up area (P) and the specific power coefficient of the boiler unit (SPC), depending on the climatic location of the facility, are taken into account.
It varies in kW:
- 0.7 to 0.9 southern territories of the Russian Federation;
- 1.0 to 1.2 central regions of the Russian Federation;
- 1.2 to 1.5 Moscow region;
- 1.5 to 2.0 northern regions of the Russian Federation.
Therefore, the formula for calculation looks like this: Mo=P*UMK/10
For example, the required power of a heating source for a building of 80 m2, located in the northern region:
Mo = 80*2/10 = 16 kW
If the owner installs a double-circuit boiler unit for heating and hot water supply, professionals advise adding another 20% of the power for water heating to the result obtained.
How to calculate the power of a double-circuit boiler
Calculation of the heating capacity of a double-circuit boiler unit is carried out based on the following proportion:
10 m2 = 1,000 W + 20% (heat loss) + 20% (DHW heating).
If the building has an area of 200 m2, then the required size will be: 20.0 kW + 40.0% = 28.0 kW
This is an approximate calculation, it is better to clarify it based on the rate of water use for hot water supply per person. The following data is provided in SNIP:
- bathroom - 8.0-9.0 l/min;
- shower installation - 9 l/min;
- toilet - 4.0 l/min;
- mixer in the sink - 4 l/min.
The technical documentation for the water heater indicates what heating output of the boiler is required to ensure high-quality water heating.
For a 200 l heat exchanger, a heater with a load of approximately 30.0 kW will be sufficient. Afterwards, the productivity sufficient for heating is calculated, and at the end the results are summed up.
Calculation of indirect heating boiler power
In order to balance the required power of a single-circuit unit running on gas fuel with an indirect heating boiler, you need to determine how much heat exchanger volume is required to provide hot water to the residents of the house. Using data on hot water consumption standards, you can easily establish that the consumption per day for a family of 4 people will be 500 liters.
The performance of an indirect heating water heater directly depends on the area of the internal heat exchanger; the larger the coil, the more thermal energy it transfers to the water per hour. You can detail such information by studying the characteristics according to the equipment passport.
Photo source: coolandtheguide.com
There are optimal ratios of these values for the average power range of indirect heating boilers and the time to obtain a given temperature:
- 100 l, Mo - 24 kW, 14 min;
- 120 l, Mo - 24 kW, 17 min;
- 200 l, Mo - 24 kW, 28 min.
When choosing a water heater, it is recommended that it heats the water in about half an hour. Based on these requirements, the 3rd option of BKN is preferable.
Weather-compensated automation
You can adjust the power level of a gas boiler using weather-dependent automation. A special feature of the delivery set is the presence of external and internal temperature sensors. Thanks to the automatic mode, you can make changes to the power without overheating the indoor air.
The most popular manufacturers today produce high-precision and modern weather-dependent automation kits for most models of gas boilers. However, the basic supply of equipment, as a rule, does not include such systems, so they must be purchased separately.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Video instruction: how to calculate heat loss at home and boiler power using the Valtec program.
Competent calculation of heat loss and power of a gas boiler using formulas or software methods allows you to determine with high accuracy the necessary equipment parameters, which makes it possible to eliminate unreasonable fuel costs.
Please write comments in the block form below. Tell us how you calculated heat losses before purchasing heating equipment for your own dacha or country house. Ask questions, share information and photographs on the topic.