Designation of the concept
Stray currents are charged electrical particles with a specific trajectory of movement that appear in the ground, which is a conductor. The term wandering appeared due to the fact that it is impossible to predict the localization of particles and the beginning of the process. The impact of stray electrical particles is very bad on iron products present above and below the ground.
The same processes appear due to the growing number of electrified objects that are the basis of modern countries. And since the soil is a conductor for electricity, there is a mutual action between the elements.
Wandering particles akin to electric ones appear, the mutual action of which requires a comparison of the potential difference at 2 arbitrary points; exclusively for the wandering version, the conductor is the ground. As a result, the iron material located near the process collapses faster due to corrosion.
What are stray currents?
Stray currents are currents that arise in the ground, which is used as a conductive medium. But this is too general a definition. In the case of heated towel rails, stray currents appear as a result of electricity leakage from the wiring as a result of a wire breakdown. The lost current tends to places with low potential, that is, to any metal structures.
Stray currents are dangerous because they cause metal corrosion, which leads to leaks and wear of the heated towel rail. Another dangerous factor is that a device with stray currents is unsafe for humans. Because there is a high risk of getting an electric shock.
To protect yourself from these two factors, you need to do the following:
- Grounding, that is, to ensure a strong connection between the water supply or heating pipes with the heated towel rail. Then the stray currents will disappear and the corrosion process will stop.
- Create a system that will balance the potentials of all pipes.
Grounding can protect the heated towel rail from corrosion.
Stray currents are a common phenomenon, and also dangerous for humans. Therefore, as soon as you notice this feature in your heated towel rail, you need to fix it: by calling a specialist or yourself
How to remove them
Stray currents can be removed using the methods listed above. The most radical way to protect the water supply is to replace it with plastic. Then the lines serve for many years, and there is no need to change the pipes due to their resistance to aggressive external environments. In addition, they are excellent dielectrics. Craftsmen will also help remove stray currents by using modern materials to protect pipes.

Replacing pipes with plastic models
Stray currents are those that lead to thinning of the walls of water supply pipes and interfere with the normal operation of the water supply system. They appear when the ground and the conductor come into contact. You can get rid of them by acting passively, actively and radically.
You may be interested in 1 sq. - how many watts is it?
Description of the phenomenon
Stray currents are those that appear in the ground when it is used as a conductive medium. They create corrosion of metal, which is entirely or partially located under the surface of the earth, and sometimes only comes into contact with land plots. Observed on tram and railway tracks, electrified roads. Sometimes they cause a short circuit and an emergency.
Destructive phenomenon
They differ from ordinary stationary electric currents in that they appear suddenly and in the most unpredictable area. The process taking place on the object through which the electric current begins to flow depends on the direction they have. If an object has a positive potential relative to another object, upon contact with it, an electric current appears with corrosion and oxidation of the wires. If an object has a negative potential, then the parameters of the substance that is in the liquid composition of the medium where the electric current flows are restored.
Note! Since the chemical reactivity of elements that come into contact with a liquid medium or electrolyte is not understood, it is difficult to predict the time and location of the appearance of a stray type of electric current. Currently, its presence leads to corrosion of an object with a positive potential.
Full Definition
Causes
Foucault's currents - concept and application in practice
The main reason for the appearance of BT is the direct contact of electrical elements with the ground. This is due to technical solutions for power supply schemes in the following transport sectors:
- electrified railway;
- mining or quarry;
- tram
Where the rails on which carriages or trolleys move are electrical conductors and form part of a circuit.

Ground contact electric transport
Sources in the water supply
The main sources of stray ground electric current are electrified main and suburban railways, trams, industrial with quarry and ore transport.
Their level depends on the electrochemical potential of the object where the electric current flows. It also depends on what kind of electrolyte the object has, whether there is an electromagnetic field that would penetrate the object and its electrolyte. In addition, stray current in a water supply system depends on distance, changes in the electromagnetic field and radian energy.

Stray currents in soils
We save your money. Regular customers receive discounts.
High-quality execution and competent design.
We treat every client very carefully.
Price is negotiable
When laying utility lines, specialists lay down a certain resource for their operation. The service period is designed for operation under normal conditions. The real situation is that metal pipes, structures, and insulation are destroyed many times earlier than expected. After a detailed study, the cause of premature corrosion was found - stray currents in the soil. In addition, experts have identified the main sources of their occurrence and identified the relationships between the magnitude of flowing currents and the rate of corrosion processes.
At the request of enterprises and individuals in Moscow and the Moscow region, our qualified specialists measure the intensity of stray currents in soils using certified equipment and prepare a detailed report on the work performed in accordance with current GOSTs.
Types of Stainless Steel Corrosion
Owners of stainless steel dryers often complain that the device has become covered with rust. Gradually, more and more spots with a diameter of a couple of match heads appear on the surface of the heated towel rail. If you wipe the area of rust, a barely noticeable mark will remain, which over time covers an increasingly larger surface.
Being affected by corrosion, the water heated towel rail begins to leak. The root cause of the destructive process is stray currents. Metal structures that are constantly in contact with water are subject to two types of corrosion: electrochemical and galvanic.
Electrocorrosion occurs when metal through which electricity passes comes into contact with water. Due to high load, so-called metal breakdowns occur, which leads to the development of corrosion processes.
Galvanic corrosion occurs due to the interaction of dissimilar metals, one of which is characterized by higher chemical activity. In this case, the electrolyte is water along with the minerals and salts it contains. Hot water especially enhances electrical conductivity. In this case, the metal deteriorates much faster.

Impact on metal objects
The formation of anodic areas on metal structures lying in the zone of influence of stray direct currents leads to corrosion of the metal in these places. At the same time, all metals, even non-ferrous ones, are subject to electrochemical destruction. The economic damage in terms of the service life allotted by the manufacturer for a metal product installed in the ground is enormous. For example, a high-quality steel pipe that has undergone all anti-corrosion treatments, as a result of exposure to BT, can last only two to three years instead of 50 years and rust.
For your information. It is not only underground structures laid in parallel that suffer. Rail soles, sleeper dies and crutches are subject to corrosive decomposition. This is due to the fact that each cathode zone corresponds to an anode zone of railway structural elements.

An example of corrosion of rails and pipes from BT
Relationship between currents and corrosion processes
Any water supply system located in the soil is damaged by corrosion due to exposure to moisture and salts, but if current activity is also connected here, an electrolytic process occurs. In this case, the rate of the electrochemical reaction is affected by the charge flowing between the anode and cathode. It follows that the activity of damage to metal products will be influenced by the resistance of the soil to the movement of charges, as well as the complexity of the flows located in the anodic and cathodic zones.
In such an environment, the water supply system is susceptible to normal corrosion under the influence of leakage currents. The impact forms a galvanic couple, accelerating the development of corrosion. There are many moments in history when the pipeline being laid was supposed to last 20 years, but in fact destruction occurred after 2 years.
What kind of power leaks are we talking about?
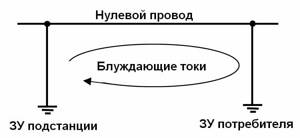
Power supply networks use phase and neutral wires. The latter is considered by many to be grounding, but in fact it is more complex. This wire is not connected to the ground, but to the power substation. This is where it is ultimately connected to ground. The neutral wires of all consumers of the substation are connected to it.
Such grounding has a non-zero potential and is directly connected to the ground. It can become one of the sources of stray currents.
Another widespread option is electric vehicles. When it moves, the phase wire is located at the top. A potential difference is created between it and the rails in direct contact with the ground. This soil is another source of electricity for stray currents.

The result of the destructive impact Source profazu.ru
If the potential of the neutral conductor is the same along the entire path, then a potential difference will not arise. When this is not the case, stray current occurs. Anodic and cathodic sections are formed on the rails. In the first of them, the rails are actively destroyed due to electrolytic reactions. If left unchecked, such situations can lead to disasters.
Power cables run underground. They have powerful insulation. However, over time it may begin to deteriorate. As a result, energy will begin to flow into the soil through bare areas. Sometimes such cables contain very high voltages, which can reach several thousand volts.
Here we talk about the most important types of leaks. However, there are also other options.
Mechanism of formation of stray currents
In the table we have given several sources as examples; now we will consider in detail how the process of interest to us is formed in them. As mentioned above, for it to appear, a potential difference must occur between two points on the ground. Such conditions are created by the circuits of the charger systems with a solidly insulated neutral.
The neutral wire (PEN) is connected at one end to the electrical substation charger, and at the other end it is connected to the consumer’s PEN bus, which is connected to the facility’s grounding device. Accordingly, the difference in electrical potential between the terminals of the neutral conductor will be transferred to the memory, which will create conditions for the formation of a circuit. The amount of leakage will be insignificant, since the main load will follow the path of least resistance (neutral conductor), but, nevertheless, part of it will go along the ground.
Formation of stray currents between the neutral wire charger
Almost similar conditions arise when problems arise with the insulation of wires (destruction of the sheaths) of cable mains or overhead lines. When a short circuit to ground occurs, at this point the potential is equal or close to phase. This causes the formation of a leakage current to the nearest charger at the potential of the PEN wire.
In the above example, we are not talking about a constant leakage of alternating currents, since according to current standards, two hours are allocated for searching and eliminating damage. In this case, in most cases, disconnecting a damaged line or localizing a section with a short circuit is carried out automatically. The process can be significantly delayed if the short-circuit current is below the emergency threshold.
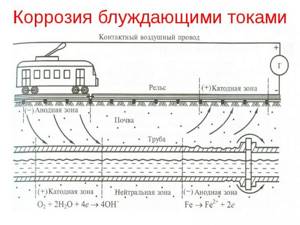
As practice shows, the largest share of sources of constant leakage currents comes from urban and suburban rail electric transport. The mechanism of their formation is demonstrated below.
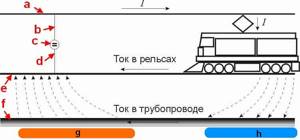
Electric rail transport as a source of stray currents
Designations:
- The contact wire from which the power plant of an electric vehicle receives power.
- Power feeder (connected to the contact wire).
- One of the traction substations that supplies the tram network.
- Drainage feeder (connected to rails).
- Rails.
- Pipeline in the path of stray currents.
- Anode zone (positive potentials).
- Cathode zone (negative potentials).
As can be seen from the figure, constant voltage enters the traction network from the substation and returns along the rails. If the resistance of the rail tracks relative to the ground is insufficient, electric stray currents arise in the ground. If there is a pipeline or other metal structure in the path of the leakage of stray currents, then it becomes a conductor of electricity.
This is due to the fact that current travels along the path of least resistance. Accordingly, as soon as a conductor appears, the current will spread through the metal, since its electrical resistance is less than that of the ground. As a result, the section of the pipeline through which the electric current passes will be more susceptible to metal corrosion. The reasons for this are discussed below.
Stray current protection
The best way would be to ground all metal pipes and gas pipelines, as well as all electrical products located in the house or apartment.
The essence of the method is simple: stray current flows from a place with a high potential to a place with a lower one. The use, in this case, of grounding equalizes the potential difference, thereby eliminating the possibility of stray currents. There is one more subtlety in using water supply. Water (except distilled water) is an excellent conductor, and even replacing metal pipes with plastic ones does not always protect against stray currents. Where the mixer, even slightly, comes into contact with a conductive surface (which can be a wall), stray currents can also arise. Of course, in most cases this does not happen; in this article we are talking about places where stray currents have become an everyday thing. By the way, the water itself, due to friction against the walls of the pipes, can also generate electric static voltage (although this cannot be called stray current and is unlikely to lead to rapid breakdown of the mixer, but it can give an unpleasant electric shock when touching the mixer). As can be understood from the above, in order to protect yourself from stray currents, you need to not only ground all metal conductors, but also taps, mixers and other metal parts of pipelines, if part of the pipeline has been replaced with plastic pipes. As for stray currents from the TV and radio tower, simple grounding will not help. The fact is that we receive a high-frequency stray current from the television and radio tower, which can only be removed using a television antenna cable. Therefore, if this is your case, then instead of a regular grounding wire you will have to use an antenna. As for the more global protection of main water pipelines, they can use equipment that can detect a stray current and start a kind of countercurrent, that is, this equipment is capable of electrically creating at certain points in the pipeline the same potential as at the source of the stray current. According to the laws of physics, this will create a very large resistance for the stray current, and it will begin to look, as I already said, for the path with the least resistance. No one can say where it will emerge after such measures, but the task of protecting the main pipelines will be completed. In fact, it is possible to minimize the manifestation of stray currents, but to do this you need to determine where they appear and make more thorough insulation there.
Another way to protect pipelines and cables is to use dielectric insulation (for cables and pipes) or make plumbing routes using plastic pipes.
Relationship between currents and corrosion processes
Any water-measuring unit located in the soil is damaged by corrosion due to the influence of moisture and salts on it, but if current activity is also added here, an electrolytic process appears. In this case, the rate of electrochemical reaction is affected by the charge flowing between the anode and cathode. It follows that the activity of damage to metal products will be influenced by the resistance of the soil to the movement of charges, as well as the complexity of the flows present in the anodic and cathodic zones.
In this environment, the water supply system is prone to ordinary corrosion under the influence of leakage currents. The influence forms a galvanic couple, accelerating the development of corrosion. There are a large number of factors in history when the pipeline being laid was supposed to last 20 years, but in reality the destruction occurred after 2 years.
Relationship between BT and corrosion on metal
Selectivity
This destruction of metal is called electrocorrosion. It is not associated with the impact of atmospheric or soil factors on the metal. The electrochemical reaction occurs as a result of the fact that the BTs try to move in the direction of least resistance. In the anodic zone, BT “flows” into the metal. The area of metal at this location is the cathode. Having encountered a favorable section of transition into the rails along the way, direct current “flows” from the metal into the soil. In this case, the metal area in this area becomes the anode, and the metal molecules from this anode follow. This is the cause of corrosion.
Impact on the water supply system
When constructing heating and water supply systems on a mass scale, steel pipes are used. Due to the noticeably higher conductivity of steel compared to soil, such pipes begin to “attract” electrical charges, and intense corrosion occurs at the points of current entry and exit (cathode and anodic zones, respectively).
The physics of the occurrence of a phenomenon immediately determines ways to protect against it. You can suppress stray currents in water pipes:
- improving and maintaining insulation;
- the use of plastic inserts subject to mandatory additional potential equalization;
- installation of cathodic protection.
Electrochemical corrosion in the home
The effects of electrochemical corrosion in everyday life most often occur in heating systems. The fact that the coolant in such systems is hot water, the conductivity of which quickly increases as the temperature rises, plays a role here. Stray currents in the heated towel rail lead to the accumulation of charge on its surface. With intensive pumping of water, the potential difference and drainage current reach large values, which is accompanied by intense rusting.
Similar processes occur in water heating radiators with improperly designed or defective grounding. However, due to the heated towel rail being in plain sight and its constant contact with damp fabric, its rusting begins faster and, moreover, is immediately noticeable.
It is not practical to equip the bathrooms of apartments and individual houses with a cathodic protection station. Therefore, the main means of protection against corrosion by stray currents in this situation is the equalization of potentials between metal surfaces and their grounding, implemented according to all the rules. When performing such grounding, it is advisable, if possible, to connect the grounding wire directly to the electrical panel bus.
In the residential sector, wiring with plastic pipes is beginning to gain great popularity. In this situation, you can avoid grounding and limit yourself to potential equalization. To implement this procedure, a connection to the riser of individual elements of plumbing and heating fittings (towel rail, mixer, etc.) is used. For this connection, a regular ground wire is used.
Rules for taking measurements
To assess the full extent of the resulting situation with leakage of electrical charges, a number of measures need to be taken:
- voltage measurement and current flow through the sheaths of main cables;
- designation of the potential difference between the contact rails and pipelines located in the soil;
- checking the level of insulation of rails from the ground covering, using a section of the track for the experiment;
- assessment of the density of energy leakage from the cable sheath into the soil.
To take measurements, a specialized device is used; if activities are carried out on railway tracks, the peak hour of transport traffic should be selected.
Measuring tools
To check, they use electrical energy converters and substations near the traffic line - the electrode connected to the device is combined with a charger and plugged in 10 meters from the substation. Any difference that appears is recorded by the device.
If a line of pipes for water supply is to be laid, it is important to detect the location of stray currents; for this purpose, the potential difference between 2 sample points on the earth's surface, located perpendicular to each other at an equal distance, is determined. It is important to carry out this designation systematically at intervals of a kilometer.
In this case, the devices used must certainly have an accuracy class of at least 1.5, and the equipment resistance must be from 1 MOhm. Use of measuring electrodes with potential differences above 10 mV. The time for one measurement primarily lasts within 10 minutes, and the gap between processes is 10 seconds.
Stray currents in soils. Causes
Electric current occurs in a network between two points when they have a potential difference. Stray currents arise in the ground for the same reason, only the ground acts as a conductor in such a situation. The source of voltage is devices operating on electrical energy. Most often this is electric rail transport (trains, trams) running on direct current.
Due to weak contact between the joints and insufficient insulation of the rails from the ground, electric current leaks into the ground (the rails act as a neutral conductor).
There are other possible reasons. In the practice of our specialists we have encountered:
- insulation failure of the existing power supply system;
- incorrect connection of electrical devices;
- deliberate grounding of electrical appliances to a metal pipeline (water supply, heating, sewerage), which is a criminal act that can lead to very serious consequences.
Remedies
The only way to prevent the appearance of stray currents is to remove the possibility of leakage from the conductors, which are the same rails, into the ground. For this purpose, they build embankments of crushed stone and install wooden sleepers, which are needed not only to obtain a solid foundation for the rail track, but also increase the resistance between it and the ground.
Additionally, installation of gaskets made of dielectric materials is practiced. But all these methods are more suitable for railway lines; it is difficult to isolate tram tracks in this way, since this leads to an increase in the level of the rails, which is undesirable in urban conditions.
In the case of distribution points and substations, power lines, the situation can be corrected by using more advanced automatic shutdown systems. But the capabilities of such equipment are limited, and constant power outages, especially in industrial settings, are undesirable.
Therefore, in most cases, they resort to protecting pipelines, armored cables and metal structures located in the area of stray currents.
Active and passive protection
There are two main methods of protection:
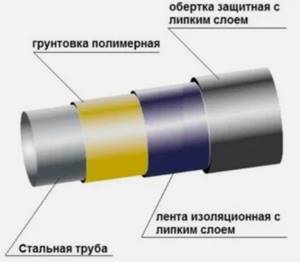
- Passive - prevents metal contact through the use of coatings made of dielectric materials. It is for this purpose that coating with bitumen mastics, winding with dielectric insulating tapes, and a combination of these methods are used. But such pipes are more expensive, and the problem is not completely solved, because if such coatings are deeply damaged, the protection practically does not work.
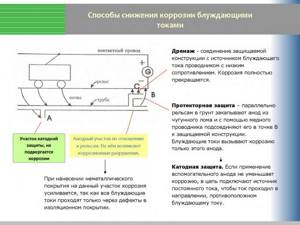
Passive protection - Active - based on the removal of stray currents from protected highways. Can be done in several ways. It is considered the most effective solution.
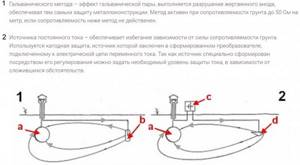
Active protection
In different conditions, different methods of protection against electrochemical corrosion are used. Let's look at a few basic examples.
Protection of heated towel rails
The main difference is that they are located in the open air, so insulation will not help, and there is nowhere to divert stray currents. Therefore, the only acceptable option is potential equalization.
To solve this problem, simple grounding is used. That is, they restore the conditions that existed before the chain was broken using polymer pipes. This requires grounding of each heated towel rail or heating radiator.
Water pipe protection
In this case, sacrificial protection using an additional anode is more suitable. This method is also used to prevent scale formation in electric water heating tanks.
An anode, most often magnesium, is connected to the metal surface of the pipe, forming a galvanic couple. In this case, stray currents do not exit through the steel, but through such a sacrificial anode, gradually destroying it. The metal pipe remains intact. It should be understood that the protective anode needs to be replaced from time to time.
Gas pipeline protection
To protect these objects, two methods are used:
- Cathodic protection, in which the pipe is given a negative potential through the use of an additional power source.
- Electrical drainage protection involves connecting the gas pipeline to the source of the problem with a conductor. This prevents the formation of a galvanic couple with the soil surrounding the main line.
Please note that significant damage caused to metal structures requires the use of comprehensive measures. These include protection and prevention of hazards.
What are stray currents?
People use electricity for various purposes:
- To create comfort (heating, use of air conditioning).
- To work with information (computer, smartphone, TV).
- Use of household appliances (dishwasher, washing machine, vacuum cleaner).
- Carrying out housekeeping work (electric motors).
The widespread use of electricity creates additional problems for humans. One of them is the appearance of stray currents. Every time electricity enters the soil, it creates the opportunity for their occurrence and destructive effects.
Usually the soil contains moisture with substances dissolved in it. She is a good guide. As soon as a potential difference is formed on a piece of land for one reason or another, current begins to flow through the ground. Its strength and direction are difficult to predict, since it is random.
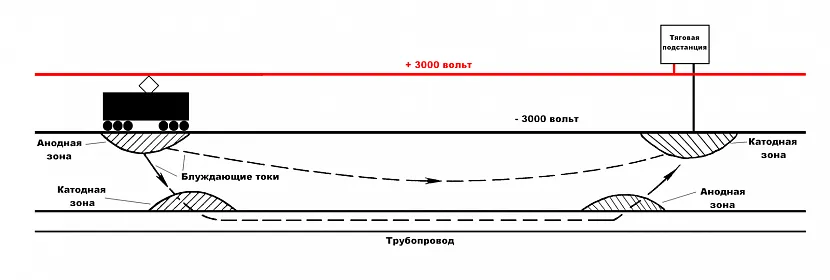
Scheme of formation of stray currents Source wikiwand.com
As you know from physics courses, current flows where resistance is minimal. Since there are a large number of metal pipes for various purposes in the ground, current often flows through their various sections. This can lead to significant destruction of pipelines. For example, over the course of a year, a hole the size of a palm may unexpectedly appear even in a strong and high-quality pipe.
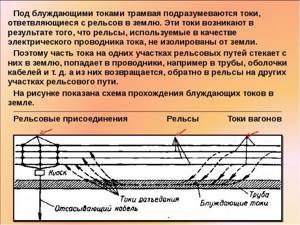
Stray currents are so called because they flow through random areas of the ground. It is difficult to predict in advance exactly where their path will take them. The flow chart looks like this:
There are various types of sources of electrical energy that are in direct contact with the ground. If there is a pipeline in the immediate vicinity, the current will first pass through the soil, then through the pipe, and then exit it at a certain point. Further along the soil he will go to an object with less potential installed on the ground.
Selecting components for bath grounding
Typically, in apartments and private houses, a stranded wire with a cross-sectional area of at least 6 square meters is used for grounding and grounding. mm. This cross-sectional area of the grounding conductor is quite sufficient to provide protection against electric shock to a person in residential premises. It is better to choose a copper cable, but in extreme cases you can use aluminum wire or copper-sheathed steel wire. The grounding conductor should be masked. This is necessary not only from an aesthetic point of view, but also to protect the grounding from accidental damage. Usually the cable is hidden in bathroom furnishings, behind screens and plastic panels. To connect the grounding of all items in the bathroom to a common bus, use a special distributor.

How to measure the magnitude of stray current
The presence of potential hazards must be checked when designing new pipelines in the area of their intended installation. For this, high-precision multimeters are used, the internal resistance of which must be at least 1 MOhm, and special electrodes with a minimum certified potential difference.
Also read: Why is the transformer humming?
Measurements are carried out according to the following scheme:
- Along the entire future route, installing electrodes every 1000 m.

- In two perpendicular directions, with the electrode installed at a distance of 100 m from the point of intersection of the lines.
The main task is to determine the existing potential difference between points. If this indicator exceeds 0.04 V, stray currents are operating in the area.
In the area where the existing rail tracks of the electric transport system are located, control is carried out through the following measurements:
- Insulation resistance between rails and ground.
- Potential differences between the rail bed and metal structures located in the ground.
- Leakage densities through cable conductor sheaths.
The entire range of measurements is performed using special equipment.
You can read more about measurements in the instructions (will open in a new tab): Read instructions
DIY grounding instructions
When everything fell into place with theory, it’s time to start practicing. The issue of grounding in an apartment can become a serious problem if the house does not have a grounding loop. But this can be easily fixed if you have the desire and opportunity. Select the right materials and tools, and then start installing the wire.
Step 1 - choosing materials before starting work
First you need to decide what materials to purchase for electrical work. After all, you definitely need to choose the right cross-sectional area of the wire, its type, and not make a mistake with the amount of consumables.

In addition to this basic element, you will need:
- potential equalization box;
- RCD for the required number of Amperes;
- terminals;
- pipe clamps.
The potential equalization box is a plastic compartment in which all branches of the ground wire are connected.
Since it is prohibited to ground objects in series, a separate cable must go from each device or pipe to the potential equalization box (PEC).

The residual current device completely cuts off the power to the circuit. Typically, each room is connected to a separate machine. In the event of an accident in the bathroom, only the corresponding area will be knocked out, and not the entire apartment
The RCD (residual current device) is not installed in the bathroom. Its place is in the corridor or other dry, safe place. It is advisable to familiarize yourself in advance with the possible diagrams and rules for connecting an RCD.
For apartments, a 10 or 16 A RCD is most often chosen, but if you have high-consumption electrical appliances, such as an electric oven or a high-performance instantaneous water heater, such protection may not be enough. We advise you to look at practical recommendations on choosing an RCD.

A couple of turns of copper stranded wire, twisted a couple of times around a pre-cleaned water supply, heating, or sewage pipe, are perfectly fixed with a clamp - the rubber prevents the oxidation of the surface
The above-mentioned terminals are special connections that allow you to carefully and “civilly” connect the wire to the bath petal. This type of connector comes in a variety of shapes.
Clamps are needed for those cases when, in addition to the bathtub, you want to separately ground the pipeline.
Step 2 - preparing tools for electrical work
The set of necessary tools for laying grounding in the bathroom is not very different from the standard set of an electrician.
You don’t have to buy anything new or specific, just take care of:
- screwdriver;
- wrench;
- drills and drill bits for metal;
- flashlight;
- tester or multimeter;
- welding machine (optional);
- protective equipment (extremely necessary).
The most common tool in a home craftsman's toolbox is a screwdriver. It is better to perform electrical work with an indicator screwdriver. It has a hidden light in the handle that lights up if you touch a live element with a screwdriver.

You can make a hole in the influx of a cast iron bathtub using a metal drill and a drill. Do not forget about the increased fragility of this metal, so you need to work with great care
A wrench is needed to tighten the bolts when connecting the ground wire to the metal plates.
A drill will be needed if the manufacturer does not provide a special hole for connecting the cable or the bathtub model is too old.

The bathroom is a poorly lit place. Since work with electricity is carried out only when the power is turned off, working without a flashlight in a dark room will be extremely inconvenient
A tester or multimeter is a device that allows you to measure the voltage in a circuit. It is especially important to have one of these devices when you do not know for sure whether your outlet is grounded or not.
You will need a welding machine when you decide to install a grounding loop outdoors. You need to weld a steel structure reliably; if you do not have experience and appropriate skills, a welding machine may not be enough; you will also need a qualified welder.

All sorts of instructions, posters and documents on electrical installation work never tire of reminding us about protective equipment. But nevertheless, cases of electric shock during the repair of a simple socket or installation of an RCD occur with enviable regularity
Before grounding the bathtub in your apartment, prepare tools only with handles made of dielectric materials, additionally check the presence of voltage in the circuit even when the power is turned off, hang a notice on the electrical panel warning about the work, so that someone does not accidentally turn on the machine.
Step 3 - laying a grounding bus for the apartment
Ideally, an apartment building should have a common grounding bus to which any resident can connect and ground. In practice, general house grounding is a huge success; it is very rare.
If you are lucky and the management company of your home, the developer or active residents who are aware of the dangers and responsibility of using electrical appliances in the bathroom have installed a grounding loop, you can connect all your dangerous electrical appliances, metal pipes and the bathtub directly to it through the electrical panel on the floor.

The main grounding bus has the form of a plate to which all grounding cables are connected at the terminals. This simplifies wiring and reduces the chance of unplugging the wrong wire and causing other confusion. Since all the cables are the same color, it is quite easy to mix things up
If no one has taken care of your home yet, you will have to do it yourself.
And there are several options:
- ask the management company or city authorities to do the grounding;
- convince other residents and pay for installation from your own pocket;
- take care of your safety and make an individual grounding loop on your own.
In the last two cases, you will need to run a copper wire at least 6 mm2 thick along the entire riser all the way to the basement.
Then, near the house, in an open, preferably fenced and deserted area, a pit is made about 1.5 m deep. Three thick electrodes are placed vertically in this pit - most often rolled steel or fittings are used.
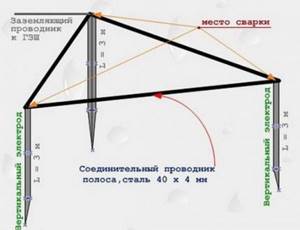
In fact, it is not necessary to make the ground electrode in the shape of a triangle. Three strip-shaped electrodes will do the job perfectly. Traditional triangular shape takes up little space, simplifies excavation and ensures good contact
The three racks are connected at the top with a steel strip using a welding machine or a thick wire to form a closed triangular contour.
Then the grounding wire is removed and laid underground in a special protective sleeve. The wire is connected to the metal structure. This creates a common, fairly reliable and durable grounding circuit that can be used by all residents of apartments along the riser.
The stages of installing a grounding loop next to a high-rise building are similar to installing such a loop in a private house. If you decide to make it yourself, we recommend that you familiarize yourself with useful tips on designing and installing a circuit.
Step 4 - Grounding all appliances in the bathroom
Once you have verified that your home has a ground and found how to connect to it, the further process will not be difficult.
- Select a location for the potential equalization box. It should be located on a dry wall, at a distance from the bath.
- If the bathtub is new, it should be turned over for convenience. Often people think about grounding when the bathtub is not only installed, but also covered with facing tiles, hidden behind a screen or decorative panel. Then it will be a little more difficult to do the job.
- Decide exactly where the cable will be connected. Find the location provided by the manufacturer. As a rule, this is a plate with a hole, welded or screwed to the body.
- If there is no special grounding point, you need to use a drill. Drill a small hole in the metal part. If it is cast iron, most likely there are ridges at the bottom of the bowl, which should ensure the stability of the structure on the legs. These sagging can be used for grounding.
- Lay the wire along the wall from the connection point to the control panel.
- Using a terminal, connect one end to the plate in the potential equalization box, and the other to the bath body through the drilled hole.
- Connect the PMC to the grounding bus in the electrical panel with a copper wire of sufficient thickness.
- Then you need to check the correct connection and hide the wire. This is done not only for aesthetic purposes, but also to avoid accidentally damaging the cable.
After installation is complete, you need to check the grounding operation using a tester. To do this, connect the phase and the grounded bath. If the tester light is bright, it means that current will flow through this circuit in the event of an accident and will not affect a person.
Determination of corrosion hazards for underground structures
To determine the corrosion hazard for underground structures, the following geophysical work is carried out:
- determination of soil resistance;
- determining the presence of stray currents in the ground;
- determining the presence of stray currents in underground structures;
Determination of soil resistance is necessary for various engineering works, including the laying of pipelines and gas pipelines, steel underground tanks and structures, power cables and metal-clad communication cables to assess the corrosiveness of the soil.
The work methodology is implemented in accordance with GOST 9.602-89 and GOST 9.602-2005. The work is carried out using the electrical profiling method using a Venus installation, with a distance between the electrodes (a) equal to the depth (for communication cables - double the depth) of laying the underground structure. The electrodes are placed on the surface of the earth in line with the axis of the route for the structure being designed, and for a structure already laid in the ground - on a line running perpendicular or parallel, at a distance ranging from 2 to 4 m from the axis of the structure (Fig. 1.) . The distance between observation points is 100 – 200 m.
Rice. 1. Venus installation for determining the apparent resistivity of the soil
Based on the results of the work, the apparent resistivity is calculated, which in its values is close to the electrical resistivity (SER) of the soil. , where k=2pa is the Venus installation coefficient, dU is the potential difference at the receiving electrodes, I is the current in the supply line. After calculations according to Table 1, the corrosive activity of the soil is determined.
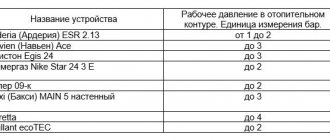
Table 1. Corrosive aggressiveness of soil in relation to carbon and low-alloy steel
Soil resistivity , Ohm * m
Average cathode current density, A/m^2
Determining the presence of stray currents in the ground. Stray currents are dangerous, first of all, due to their electrochemical activity, which leads to accelerated corrosion of underground metal structures, including pipelines and gas pipelines.
The presence of stray currents is determined in the field using the natural field method. The work methodology is implemented in accordance with GOST 9.602-89 and GOST 9.602-2005. The work uses non-polarizing electrodes, which are a porous ceramic vessel into which a saturated solution of copper sulfate is poured, and a rod is immersed in the solution (Fig. 2.). Contact in such an electrode is carried out by filtering a solution of copper sulfate into the ground through the porous surface of the electrode.
Fig.2. Non-polarizing electrode. 1 – porous part of the electrode, 2 – glazed part of the electrode, 3 – copper rod, 4 – plug, 5 – terminal, 6 – saturated solution of copper sulfate (CuSO4).
For the structure being designed, the potential difference along the route of the structure being designed is measured between two points on the ground every 1000 m in two mutually perpendicular directions (Fig. 3.) with the measuring electrodes separated by 100 m. The value of the potential difference at each point is recorded every 10 seconds for 10 minutes.
Electrochemical corrosion: how to protect a heated towel rail?
Every owner knows that renovations in a house or apartment are continuous. Not everyone is able to immediately take into account all the details and nuances, and during the repair process everyone tries to do everything as quickly as possible, while at the same time making it more durable and of better quality. Moreover, the criterion “inexpensive” is also a frequent choice for those who have begun repair work. However, those who have already encountered its consequences know that cheap and durable are antonymous concepts. Therefore, it is better to immediately give preference to the best materials. This applies to everything, including the heated towel rail.
Why is it important to use a heated towel rail correctly?
Everyone knows that a heated towel rail is responsible for maintaining a comfortable temperature, as well as for high-quality drying of laundry. The significance of this device is noticed only in those moments when it begins to fail. Unfortunately, such situations are not uncommon. At the same time, heated towel rails can easily undergo electrocorrosion and leakage.

Why is it important to use a heated towel rail correctly?
What are the dangers of leaks and electrocorrosion?
First of all, these diseases are dangerous for your neighbors. This means that they can aggravate pressure drops, which can lead to failure of the device. We think there is no need to explain how much this breakdown will cost you.
How to protect your heated towel rail from all damage?
There are universal methods on how to protect a heated towel rail from electrical corrosion and damage. First, you need to choose a heated towel rail that is made of high quality materials that are reliable and durable.
The most popular among such materials is AISI 304 stainless steel. Any product using it will serve its owner for decades. However, there is a nuance - it cannot be done without stray currents, which trigger the process of electrochemical corrosion and provoke the formation of corrosion points that increase over time. At the same time, they cause the formation of unfortunate leaks.

How to protect your heated towel rail from all damage
Why are stray currents formed?
Electric current is generated in the aquatic environment due to its friction against the metal walls of the pipes or due to grounding by a neighbor of a malfunctioning electrical appliance, for example, an old-made washing machine.
These factors allow currents to spread through the pipes and into the water, which leads to internal rust of the heated towel rail.
Increased water hardness is also the cause of an unfavorable environment for the formation of currents due to the contact of metals with different potentials. In addition, even tram tracks that pass close to pipes can cause current to form in the water.
How to fix this phenomenon?
Manufacturers know how to partially solve this problem. Output is grounded. But it must also be done correctly: the metal insert, which is located in front of the heated towel rail, is grounded, but in no case does it ground the body.
How to protect a heated towel rail from corrosion?
It is recommended to buy a heated towel rail that is made of high quality materials that are considered high quality. You can also choose the design that suits you exclusively.
In order to save money, it is not recommended to install a heated towel rail yourself - there is a high risk that you will harm yourself and your household. It is better to entrust the installation to specialists and be sure to require a guarantee of work from them.
Methods for detecting stray currents
Special equipment allows you to detect the presence of stray currents in the soil. We use reliable modern devices designed for electrochemical protection.
The set of instruments for determining stray currents includes:

Photo 2. Universal multimeter AMM-1009.
Using such a set, you can determine the presence of direct currents in the ground, the dangerous influence of alternating and stray current.
If the installation of communications is just planned, then at the design stage along the route, the potential difference between points is measured every 1000 m. When inspecting operating objects, the resistance of the metal is measured under the influence of stationary and stray currents.

Photo 3. Copper-sulfate portable reference electrode EMC - 0.4 and a connecting insulated flexible wire with a length of at least 100 m.
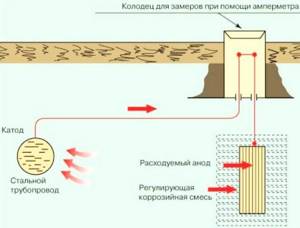
Cathodic protection
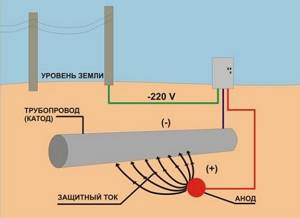
The cathodic method of protecting pipelines from stray currents is considered the most effective in industry and in the main sections of residential buildings. The essence of this technique is to create a direct current, due to which the formation of the anode zone on the protected object is compensated. To do this, the negative pole of the protective station is connected to the metal structure, and the positive pole to an additional electrode. As a result, the anodic zone of the resulting system moves to this electrode, and the remaining cathodic zone corrodes noticeably less.
As the additional electrode is destroyed, it is simply replaced with a new one.
The effect of “overprotection” when constructing such systems is compensated by selecting the voltage generated by the station based on measurement results using a special technique.
Water supply protection
Passive and active methods are used to protect the water supply. Active consists of installing a device that generates a counter electrical signal. The passive method is to use an insulator. In addition, prevention and comprehensive pipeline protection are used as a method of protecting water pipes from stray electric current. Specialists coat the pipes with a polymer composition. As a result, metal corrosion does not occur.
You may be interested in: Features of tantalum capacitors
Water supply protection
Passive option
The passive option is the main measure to rid any installation of stray electric current. It is called cathodic protection. Thanks to it, corrosion in long pipelines is eliminated. To perform cathodic protection, a high negative potential is applied to the pipeline. It guarantees the maintenance of a negative pipe potential, regardless of the parameter values caused by stray electric currents in pipeline systems. As a rule, a potential of 6 kilowatts is supplied.
Note! It is believed that in this case, regardless of the medium and electrolyte, there is no positive charge. This protects the pipeline.
This method is effective, but has one significant drawback: the elements that are in the medium are deposited on its inner surface. These are elements in the form of paraffins, which significantly reduce the diameter of the pipe and increase the energy required to pump the contents of the pipes. To restore the original internal pipe diameter and remove wax deposits, mechanical cleaning with a brush is usually used.
Passive option
Active protection
The only effective way to protect a pipeline from corrosion caused by stray energy is to reduce the current flowing in different areas to zero. To do this, the master divides the pipe into sections. He applies voltage to them. Thanks to this equalizing method, electricity does not cause corrosion. In this case, the resulting zero from the equation is supported automatically by analog electronics.
Disadvantages of cathodic protection systems
The technique is by no means universal; it is necessary to build each object for specific operating conditions. If the strength of the protective current is incorrectly calculated, the so-called “overprotection” occurs, and the cathode station becomes a source of stray currents. Therefore, even after installation and commissioning, cathode systems are constantly monitored. To do this, special wells are installed at different points to measure the protection current.
Control can be manual or automatic. In the latter case, a parameter monitoring system is installed, connected to the cathode station control equipment.
Stray currents. Why is their size determined?
A one-time passage of current through metal structures does not cause much harm. Electrolytic corrosion is caused by constantly acting stray currents of certain parameters.
If the appearance of stray currents is caused by insulation failure in the power system or incorrect connection of electrical installations, then the most competent solution would be a detailed examination of the entire electrical circuit and elimination of the source of the leak. If stresses are detected in the soil near electric transport mains, it is necessary to take measures to protect metal structures (pipelines) from their influence (installation of drainage, insulation of metal with special protective coatings).
Source