Characteristics of basalt wool
First of all, let's find out what this material consists of. It includes a base (fibers obtained from molten basalt). This rock is an absolutely safe raw material, which has found application not only in construction, but also in medicine. Binding components, which are resins, and special impregnations are added to the base, improving the following qualities of the material:
- durability;
- low thermal conductivity;
- fire resistance;
- safety of use;
- sound insulation and others.
However, among all types of basalt wool, there are also those that are produced without following technology. As a rule, these are cheap materials that do not meet quality standards. They can be dangerous for the consumer.
What does mineral wool consist of?
Many say that mineral wool causes serious harm to health. How true this statement is can only be said after studying the composition of the basalt-based material. It consists of several components:
- bases - fibers obtained by melting rocks;
- binder resins capable of forming the required shape of the material - roll or slab;
- impregnations that make mineral wool impervious to external influences.
Glass wool, which is based on a mixture of broken glass, limestone, and quartz glass, also belongs to the category of mineral wool. The mixture is melted and inflated with steam to obtain the finest air threads, allowing the insulation to recover after compression.
The material has a number of advantages that make it one of the industry leaders, namely:
- low thermal conductivity - from 0.035 to 0.042 W/mK;
- reduced moisture saturation coefficient (up to 1%);
- no shrinkage during long-term use;
- durability.
The stone base is environmentally friendly and does not have any harmful effects on the human body. Basalt, most often used in the manufacture of insulation, is even used in the medical field, which indicates its safety. Resins and impregnations, if the manufacturing and installation technology is not followed, can negatively affect health, but how serious will this impact be?

How does mineral wool affect the health of household members and insulation workers?
Common myths about stone wool
Fibers enter the lungs and harm health
Basalt fibers should not be confused with glass wool, which has a lower density - its fibers are easily separated and can penetrate into the human lungs. Basalt wool is denser and stronger, so its fibers cannot enter the respiratory system.
Harmful substances enter the atmosphere
Production is carried out using resins, so many are confident that they release formaldehyde into the environment. However, the resin undergoes special processing, and its amount in cotton wool is no more than 2-3 percent. Accordingly, it practically does not get into the air. And some manufacturers have completely abandoned the use of resins and produce absolutely environmentally friendly materials based on basalt fibers (Basfiber is one of them).
The material is dangerous during installation
It is believed that this material can cause allergic skin reactions and a negative reaction if it comes into contact with the eyes or mouth. This myth is again associated with the well-known glass wool and with those who continue to confuse these two materials. Glass wool can cause severe irritation and allergies, unlike high-quality basalt wool. Moreover, when laying wool, builders follow safety regulations, working in respirators, gloves and goggles.
The cotton wool becomes damp and mold grows in it
According to the latest myth, basalt fibers quickly accumulate moisture and serve as a breeding ground for fungus and mold. In fact, many manufacturers treat their products with water-repellent impregnations. And even at high humidity, their moisture absorption level is only a few percent of the total volume. In addition, an antiseptic is added to the composition of a high-quality product, which prevents the appearance of microorganisms.
Types of mineral wool
Glass wool
It is obtained from broken glass and small crystalline materials. Fiberglass has a good thermal conductivity coefficient - 0.030-0.052 W/m K. The length of its fibers is from 15 to 55 mm, thickness - 5-15 microns. Working with glass wool requires extreme caution. Due to its properties, it is prickly; broken threads can penetrate the eyes and damage the skin. Therefore, gloves, goggles, and a respirator are required to work with the material. It is optimal to heat glass wool to 450 degrees, do not cool it below 60 degrees. The positive properties of glass wool are good strength and elasticity, easy installation, and the ability to trim.
Slag
The fibers of this product from blast furnace slag are about 16 mm long. The high hygroscopicity of this raw material does not allow the use of slag wool in the insulation of facades and heating mains. Most often it is used for insulation of non-residential structures. Heating temperature 250-300 degrees. In these and other properties, it is inferior to other types of mineral wool. Its main advantage is its low price, easy installation, and reliable sound insulation.
Stone wool
This is the highest quality type of mineral wool. The size of its sheets is not inferior to slag fiber. But it is not prickly, very easy to use. It has a fairly high thermal conductivity coefficient; this fiber can be heated to 1000-1500 degrees. When heated above permissible degrees, it will not burn, but only melt. When we talk about modern material for insulating houses, we mean exactly this type of wool - it is also called basalt.

Internal wall insulation
How to protect yourself from purchasing a low-quality product?
Although myths about basalt wool do not correspond to reality, health risks when using it are still possible. We are talking about low-quality materials made handicraft. Therefore, it is better to purchase products from responsible manufacturers.
An example of a high-quality product is Basfiber basalt wool, which has excellent thermal insulation and fire-resistant characteristics. This environmentally friendly material has already proven itself on the positive side and is completely safe for work and use. Basfiber wool has a strong structure and retains its original properties during long-term use.
Content
- What is mineral wool
- Scope of application
- Types of mineral wool
- Production and properties of basalt wool
- Stamps
- Facade mineral wool
- Mineral wool and harm to health
Wall insulation means economical heating, the absence of fungi, and salvation from mold and dampness. During the summer months, good insulation prevents the walls from overheating and maintains a comfortable room temperature.
What is basalt insulation and how is it made?
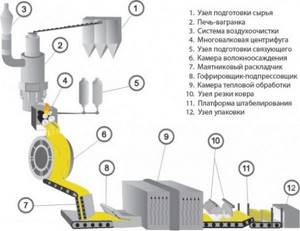
Modern basalt thermal insulation is the same as “hair”, only made in a much more modern way. Here is a simplified production diagram:
- Preparation of raw materials . Raw materials from rocks of the gabbro-basalt group are delivered to production and sifted so that large pieces remain. Then the mixture (called “charge”) is weighed in order to feed a strictly defined amount to the second stage.
- Melting . The charge is placed in a special vertical furnace - a cupola. There, the rock melts at a temperature of about 1500 ° C. At this stage, the raw materials are cleaned of impurities - for example, metals, which are poured through a hole into a cart with a cast-iron bath.
- Structuring . The molten rock is sent to a special centrifuge with nozzles. It pulls the droplets into a fiber, similar to the process of making cotton candy. When fiber is formed, additives are added to it - a binder, hydrophobic substances and others.
- Creating a "carpet" . The raw materials are cooled, fed onto a conveyor belt and into a pendulum spreader. He walks back and forth and evenly spreads the resulting cotton wool onto the next tape.
- Molding . It is too early to use the resulting “carpet” as insulation - it needs to be shaped. Therefore, it is fed into a special machine - a corrugator-prepressor. It gives the future insulation the required dimensions.
- Heat treatment . Now the even carpet of basalt insulation is fed into the heat treatment chamber. It is set at a temperature of about 250° C. It is at this temperature that the binding materials harden, and the product acquires the necessary physical properties.
- Cutting and packaging . The carpet is fed onto a belt for cutting into even slabs, after which they are packaged by a special machine.
This is what modern basalt insulation is made of: raw gabbro-basalt rock, binding material and additives to impart the desired properties.
By the way, basalt fiber as insulation is cut into slabs, since it turns out to be much stiffer than fiberglass.
Is it harmful during installation?
The harm of mineral wool during installation work is often mentioned. If you handle this material with bare hands, the tiny sharp fibers can dig into the skin and cause irritation. Therefore, you should only work with it while wearing gloves.
However, if stone wool gets on your hands without gloves, nothing bad will happen. You just need to thoroughly wash your palms with cool water (so as not to enlarge the pores), and then collect all the fibers from the skin by hand. Experienced installers use masking tape to remove these particles, applying it with the adhesive side to those areas of the skin that came into contact with the mineral wool.
Mineral insulation with acrylic in its composition does not cause harm. In addition, it has increased elasticity. When installed inside buildings, a “spring effect” occurs and the insulation fills the entire allocated space, leaving no cracks or gaps. No additional protection against dust flying is required.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of all types of fire-resistant, fire-resistant mineral wool include:
- High thermal resistance even with prolonged, constant fire and thermal contact without decomposition or destruction of the internal structure.
- Low density, which is a priority when choosing thermal insulation and fire retardant coatings for load-bearing structures and interfloor ceilings of construction projects.
- Low thermal conductivity and low heat capacity, which form excellent thermal insulation and energy-saving characteristics of this product.
- Dielectric properties, important when used at thermal power facilities, even when operating temperatures increase to 700–800℃.
- Excellent chemical resistance to strong acids and alkalis.
- Resistance to seismic vibrations and vibration influences.
- Soundproofing qualities.
- Oil/moisture resistant.
- Not wetting with melts of non-ferrous metals.
- Long period of operation without loss of thermal insulation and fire retardant parameters of the product.
- Safety of use due to the absence of release of toxic volatile compounds both during normal operation of heating and technological equipment, and during severe overheating of housing surfaces; as well as in the event of a fire, contact with an open flame inside a construction site, where mineral fire-resistant (fire-retardant) wool, or rolled, slab products based on it, are used as fire-resistant, heat-insulating coatings.
- Low cost of products, which is important both for customers of construction and reconstruction of large production facilities, and for the construction of multi-storey and private houses.
- A significant reduction in the volume of more expensive ceramic refractory products as part of the structures of casings, linings of heating and technological equipment, a reduction in material consumption, in situations where replacement with fire-resistant mineral wool is possible.
Due to its structure, softness, and elasticity, lump wool is easily stuffed into thermal insulating casings of equipment, but more often such products are used in the form of rolled, slab insulating materials, including in the form of finished products; for example, half-cylinders for thermal insulation of pipelines of engineering and technological communications.
The disadvantages include the need for extreme caution, the mandatory use of thick protective clothing, respiratory tract and eye protection devices when carrying out any work with fire-resistant mineral wool, due to the fact that the smallest ultra-fine fibers of such products can harm human health.
Application
Due to its excellent fire-resistant characteristics and heat-saving properties, mineral wools are used in construction for the construction of objects for almost any purpose, for laying/installing utility networks/systems, and assembling technological equipment; as well as in the manufacture of various products where the technical parameters of these products are in demand.
On this topic ▼
Fire safety during construction
Buildings, private houses, baths

Application area:
- For the production of fire-resistant insulation materials.
- For insulation, and often at the same time fire protection of ceilings, floors, roofs, technical, attic floors; facades, basements, attics of buildings.
- As a heat-insulating filling of cavities in brickwork; joints, gaps, cracks between reinforced concrete structures.
- For thermal insulation, preventing freezing of pipeline networks, technological communications of populated areas, industrial and warehouse facilities.
- As carriers of catalysts, filters for the purification of high-temperature gases, including acting as fire arresters for flammable gas mixtures.
- In the production of various products - from pipe products to vehicle brake pads as a reinforcing, heat-insulating base.
- For reinforcing refractory (fire-resistant) concrete.
- For constructive fire protection of load-bearing and enclosing building structures made of wood, metal, reinforced concrete; ducts of transit air ducts of ventilation units; exhaust chimneys, shafts of smoke removal systems.
- For thermal insulation, fire protection of pipes, fireplace chimneys, stoves.
- As a fire-resistant, heat-impervious protective coating, lining for combustible waste disposal furnaces; steam boilers, gas turbines of thermal power engineering facilities.
- For thermal protection of metallurgical furnaces, technological installations for oil refining, gas condensate.
- As a binder in the production of fire-resistant coatings, pastes, fire-retardant plasters.
- For thermal insulation of containers and tanks with compressed and liquefied gases.
- For filling the internal space of fire gates, partitions, hatches, doors.
- In heat/sound insulation of engine compartments, engine rooms, generator rooms of automobile, railway transport, sea and river vessels.











